Novel recombinant human blood coagulation factor VIII and production method thereof
A blood coagulation factor and gene recombination technology, applied in the direction of blood coagulation/fibrinolytic factor, VII factor, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty, FVIII difficulty, FVIII expression level can not meet the needs of treatment, etc., to improve screening efficiency, The effect of simplifying the screening process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1 Obtaining of coagulation factor VIII gene sequence
[0020] (1) Preparation of DNA and RNA
[0021] High molecular weight DNA is extracted from the peripheral blood cells of a normal person according to conventional methods. Total RNA was extracted from fresh embryonic tissue using a guanidine isothiocyanate-cesium chloride gradient method, and mRNA was isolated using an oligodeoxyadenylate (Oligo-dT) cellulose column.
[0022] (2) Design of oligonucleotide primers and polymerase chain reaction
[0023] Seven pairs of primers were designed and synthesized. In order to facilitate the cloning of the whole molecule, the fragments amplified by each pair of primers contained corresponding restriction endonuclease sites on both sides. The primers are amplified by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT / PCR), wherein the second primer of each pair of primers is used as a primer for the reverse transcription reaction. Reverse transcription reaction syst...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2 Construction of coagulation factor VIII B domain deletion cDNA (FVIII(ΔB))
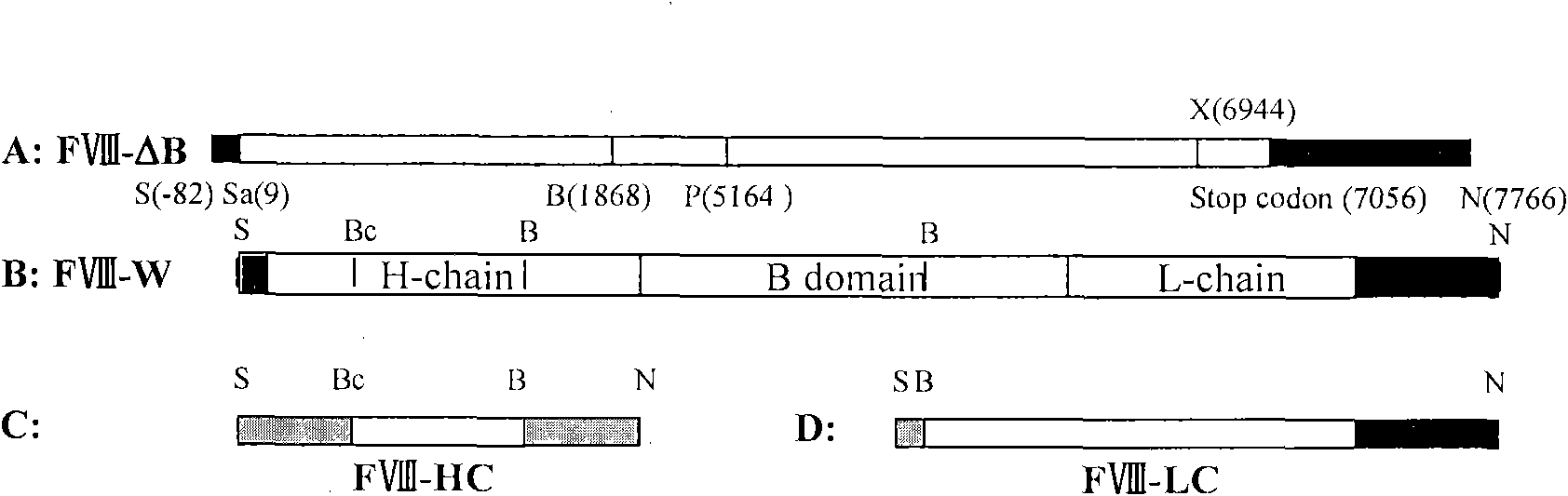
[0030] Four oligonucleotide primers were designed, and most of the B domains of FVIII were deleted and mutated by PCR (polymerase chain reaction). The obtained PCR products A and B respectively correspond to 1868-2334bp and 4974-5164bp of FVIII. After the products A and B are denatured and re-annealed, 16 bp of nucleic acid sequences can be hybridized. This hybridization product can be used as a template to amplify to obtain product C (658 bp), corresponding to 1868-2334 bp and 4974-5164 bp of the FVIII gene. PCR product C and FVIII gold long cDNA were restricted with BamHI and PstI, and PCR product C was used to replace the corresponding fragment of FVIII full-length cDNA, thus producing FVIII cDNA with B domain deletion (see figure 2 ), named as FVIII(ΔB). Compared with the full-length FVIII cDNA, this FVIII (ΔB) lacks the base sequence of 2334-4974 bp in the FVIII cDNA. ( fig...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Construction of embodiment 3FVIII cDNA expression vector and expression in mammalian cells
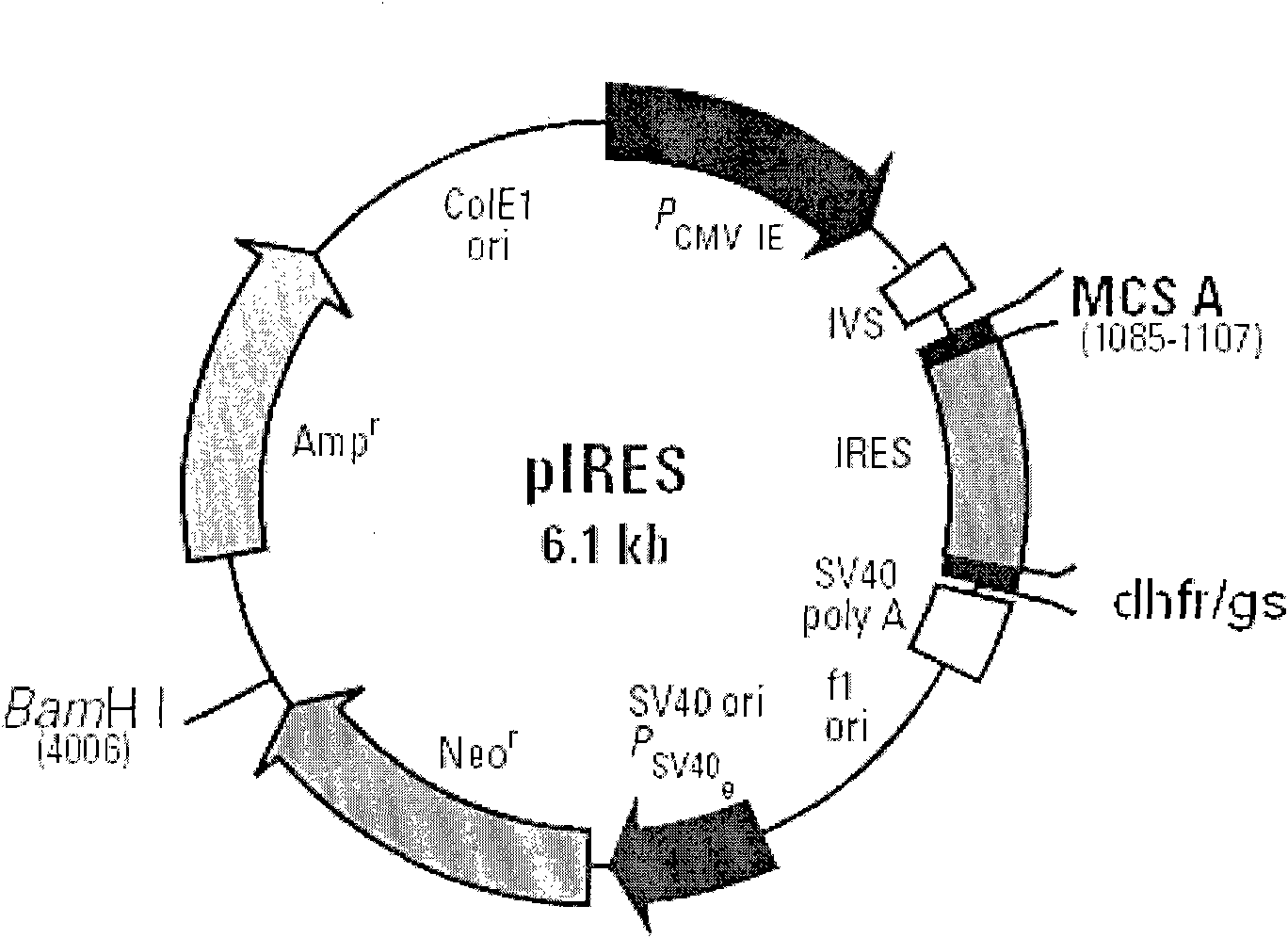
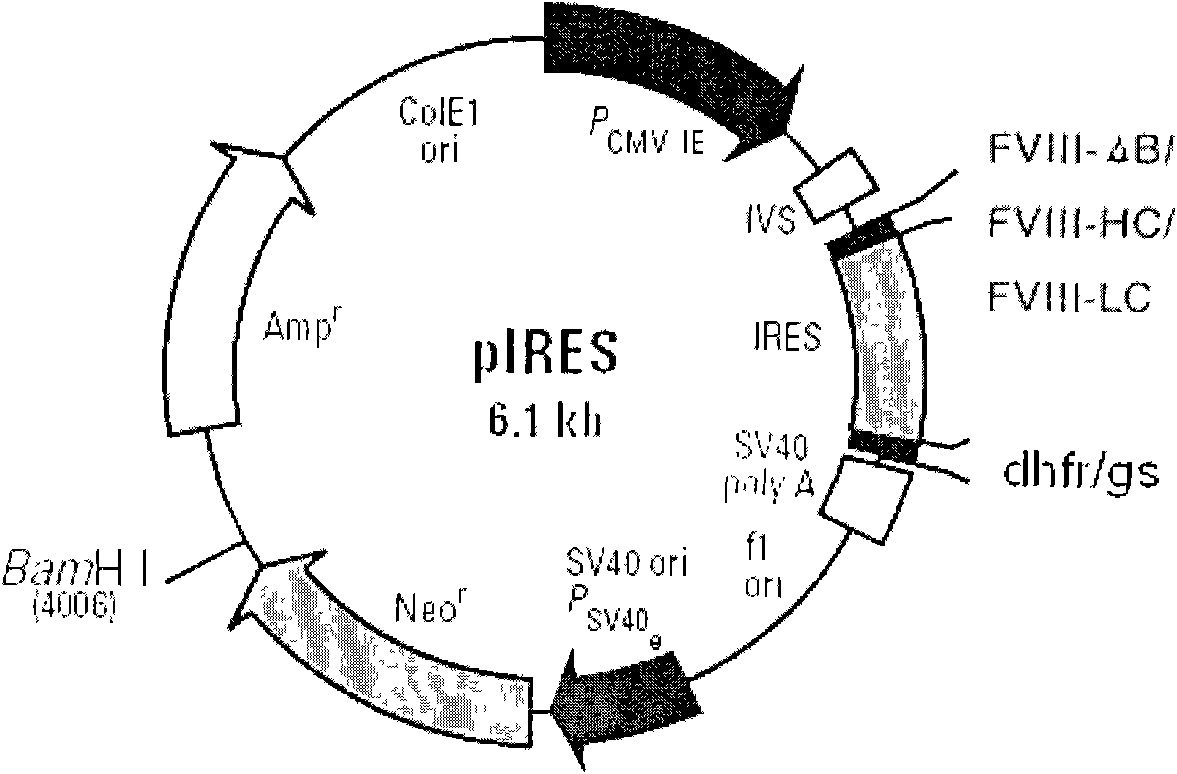
[0032] The above FVIII cDNAs (FVIII full-length cDNA, FVIII(ΔB) cDNA, FVIII-HL) were cloned into the expression vector pIRES-dhfr. figure 2 is a schematic diagram of the construction of different FVIII expression plasmids, image 3 It is a schematic diagram of cloning different FVIII expression plasmids into pIRES-DHFR / GS respectively, Figure 4 It is a schematic diagram of FVIII-HC / FVIII-LC double expression plasmid, such as figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4As shown, different FVIII expression plasmids were constructed, including B domain deletion and FVIII heavy and light chain co-expression plasmids, and FVIII full-length cDNA (FVIII-W) was cloned. On this basis, various molecular reconstructions were constructed, including B Domain-deleted FVIII (FVIII-ΔB), heavy chain portion of FVIII (FVIII-HC) and light chain portion of FVIII (FVIII-LC), and cloned into the A multiple...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com