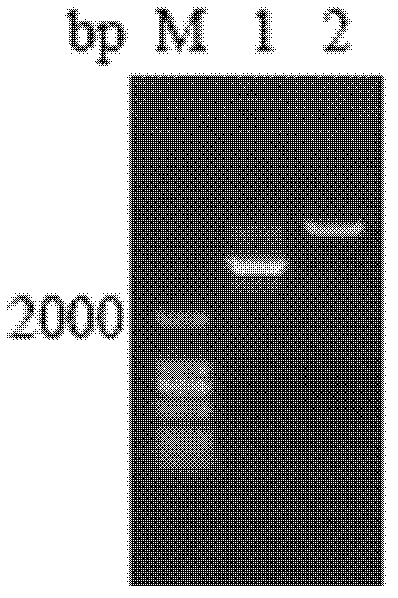Scylla paramamosain anti-lipopolysaccharide factor, and preparation method and application thereof
A technology for resisting lipopolysaccharide factor and pseudocynids, which is applied in the field of gene engineering of pseudocymbids, and can solve problems such as loss of crab breeding industry
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Construction of Eukaryotic Recombinant Expression Vector for Anti-lipopolysaccharide Factor Sp-ALF of Scylla pseudomaculata
[0041] According to the multiple cloning site of the pPIC9k vector, a specific upstream primer F1 and a downstream primer R1 for amplifying the ORF of the gene coding for Scylla sclerophyllus Sp-ALF (cDNA) were designed. Add a SnaB I restriction site and a base encoding His-tag at the 5' end of the upstream primer F1; add a stop codon and an Avr II restriction site at the 5' end of the downstream primer R1:
[0042] Upstream primer F1: 5′-CGTACGTACACCATCATCATCATCATCAGTATGAAACTCTGATAG-3′,
[0043] Downstream primer R1: 5'-AA CCTAGGTTAATTATTCACCCACACCGTAG-3'.
[0044] A fragment of the coding region of Sp-ALF was amplified. The PCR reaction conditions were: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 min; denaturation at 94°C for 30 s, annealing at 60°C for 30 s, extension at 72°C for 30 s, repeating 30 cycles; extension at 72°C for 10 min.
[0045...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2 Induced expression of pPIC9k / Sp-ALF recombinant plasmid in Pichia pastoris GS 115
[0047] The sequenced correct plasmid pPIC9k / Sp-ALF was digested and linearized with Sal I (see figure 2 ), and then transformed into Pichia pastoris GS115 competent cells by electric shock method, and induced expression.
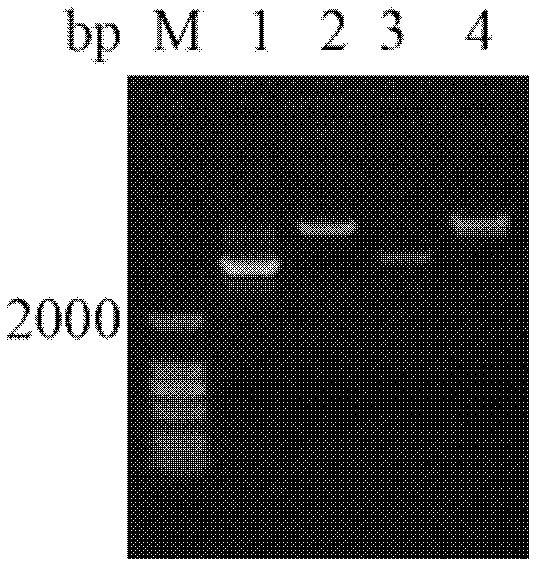
[0048] Pichia pastoris GS115 transformed with pPIC9k empty plasmid was used as the control, and Pichia pastoris GS115 transformed with pPIC9k / Sp-ALF recombinant plasmid was used as the experimental group. The protein expression was detected by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE).
[0049] The results showed that Pichia pastoris GS115 transformed with the pPIC9k / Sp-ALF recombinant plasmid had obvious protein induction expression after induction compared with before induction, and the protein band was around 14kDa (see image 3 ), which is similar to the calculated theoretical molecular weight. In addition, there is a band of about 18kDa in the indu...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3 Purification and antibacterial activity identification of pPIC9k / Sp-ALF recombinant plasmid induced expression product in Pichia pastoris GS115
[0051] 1. Purification of target protein by affinity chromatography
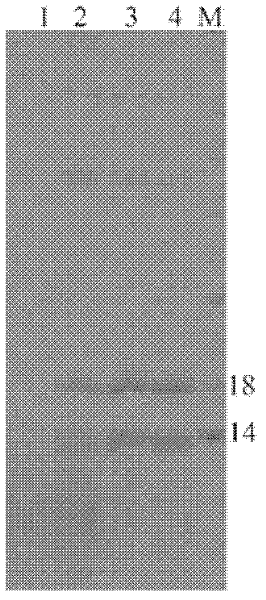
[0052] After a large amount of recombinant positive Pichia pastoris GS115 strain was induced and expressed, 1 L of the supernatant of the culture medium was collected by centrifugation to remove the bacterial cells, dialyzed twice with PBS (new dialysate was changed every 12 hours), centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 35 minutes at 4°C, and the supernatant was obtained. Load the sample on the column. Then, the dialyzed protein was subjected to affinity chromatography using a metal chromatographic column. Collect the elution peak, identify as Sp-ALF recombinant protein through SDS-PAGE electrophoresis analysis and mass spectrometry (see Figure 4 ).
[0053] 2. Antibacterial activity identification of Sp-ALF recombinant protein
[0054] The standard c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com