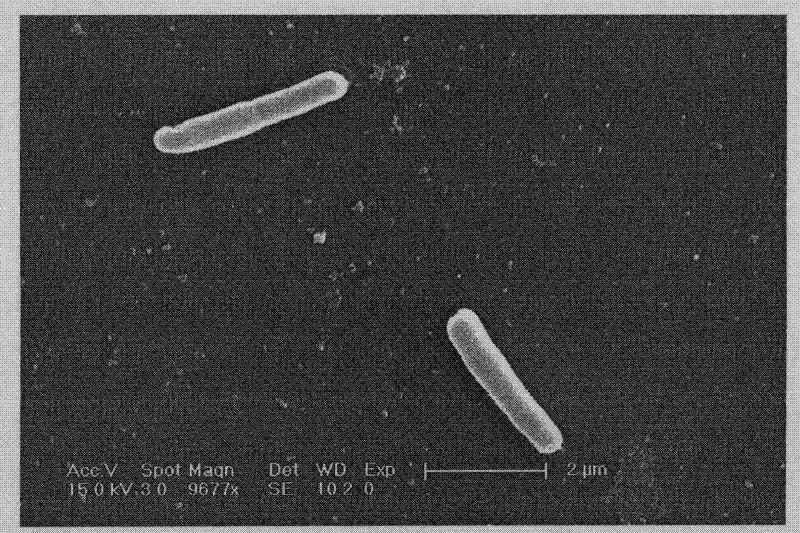
Pseudomonas and application thereof to degrading macromolecular synthetic plastics
A technology of Pseudomonas bacteria, colonies, used in the field of microbial biotechnology and environmental biology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1 Screening of degrading strains
[0027] According to literature reports, the number of microorganisms that degrade synthetic polyesters in nature has the following relationship: poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid-degrading bacteria > polycaprolactone-degrading bacteria > polylactic acid-degrading bacteria. Therefore, in order to obtain microorganisms that can degrade all three compounds, polylactic acid was first used as the sole carbon source for screening.
[0028] Place environmental samples in polylactic acid liquid medium for enrichment and spread them on emulsified plates, culture them upside down in a 30°C incubator, observe the growth of strains and the formation of transparent circles in 15-30 days, and screen for growth on plates And form the strains with obvious transparent hydrolysis circle. Screening media components and production methods are as follows:
[0029] Basic medium: 250mg yeast extract, 1g (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 100mg NaCl, 200mg MgSO 4 ·7H 2...
Embodiment 2
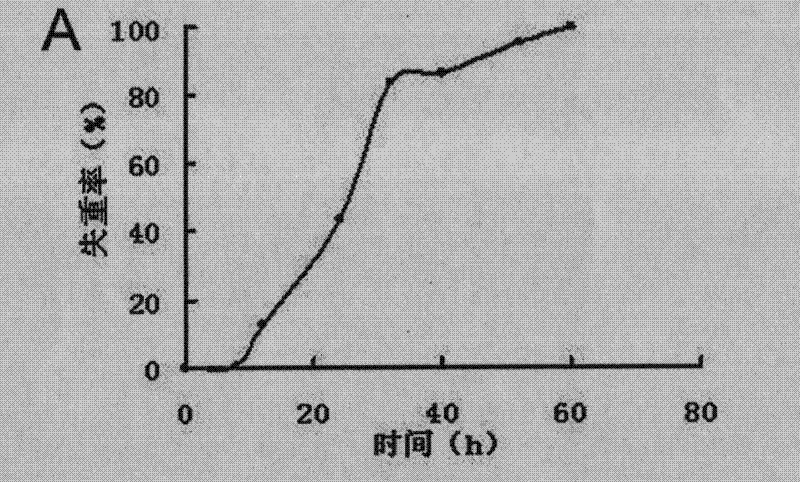
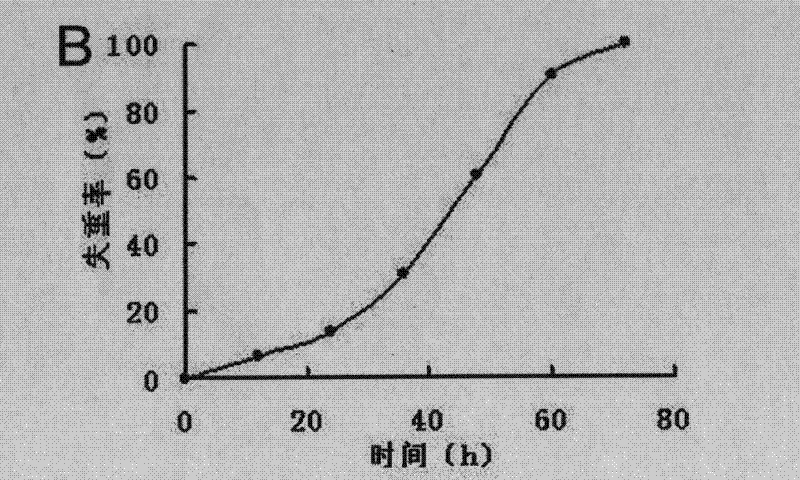
[0034] Example 2 Degradation of polymer film by Pseudomonas sp.DS1001
[0035] Cut the film of polylactic acid, poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid or polycaprolactone to a size of 2cm*2cm, weigh it with an analytical balance, wipe the surface with 75% ethanol, sterilize it with ultraviolet light, and then put it into a sterile basic medium as the only carbon source for bacterial culture. Pseudomonas sp.DS1001 was inoculated into the culture medium with 10% inoculum amount, and cultured in shake flasks at 37°C and 150 rpm. At the same time, a bottle of culture medium without bacteria was placed under the same conditions as a control for membrane degradation. Samples were taken regularly, and the film was dried to a constant weight and then weighed to calculate the weight loss rate.
[0036] In the experiment of degrading the polylactic acid film, after 15 days of cultivation, the weight loss rate of the polylactic acid film reached 55%, while the control film did not lose weight, indica...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3 Preparation of crude enzyme solution of Pseudomonas sp.DS1001 and analysis of its enzymatic hydrolysis product
[0039] Pseudomonas sp.DS1001 was cultured by shaking flask fermentation, and polylactic acid, poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid and polycaprolactone were used as inducers to induce their respective degrading enzymes. After 3 days, the supernatant was collected by centrifugation at 12000rpm, which was fermented crude enzyme liquid. Mix the induced fermented crude enzyme liquid with their respective substrates (polylactic acid, poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid, and polycaprolactone) emulsion, and incubate at 40°C for 15 minutes (polylactic acid reacts slowly, and the incubation time can be extended to 1-6 hours), centrifuge at 12000rpm to take the supernatant reaction solution, and use LDI-1700 laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometer to measure the degradation products therein. The working parameters of the instrument are: mass range: 0-800m / ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com