Polypeptide with brain targeted medicine delivery characteristic and preparation method thereof
A brain-targeting and characteristic technology, applied in the field of protein polypeptides, can solve problems such as the research and reports of targeting functional groups that have not yet been seen, and achieve good brain-targeting effects, small molecular weight, and strong specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 In vivo screening of phage display random cyclic heptapeptide library
[0032] The present invention uses a phage display random peptide library to screen polypeptides with blood-brain barrier affinity, which includes the following steps:
[0033] Ph.D-C7C of NEW ENGLAND Biolabs TM Peptide library diluted to 1 x 10 10 pfu titer, the diluent is TBS buffer (tris, Tris) (50 mM Tris, 150 mM sodium chloride), injected into the rat body through the tail vein, and the rat was sacrificed after 60 min. Cardiac perfusion with saline to remove nonspecific phages from the systemic circulation. Remove the rat brain tissue in the ultra-clean bench, homogenize it under sterile conditions, and add 1 mM phenylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), 20 μg / mL protease inhibitor (Aprotin) and 1 μg / mL leupeptin at the same time (Leupeptin) in TBS; wash three times with washing solution TBST (0.1% Tween-20); add glycine elution buffer (0.2M Glycine-HCl, pH 2.2) to elute and recover the speci...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2 In vivo screening of phage display random dodecapeptide library
[0039] Choose Ph.D-12 from NEW ENGLAND Biolabs TM peptide library. The first round of screening method is as follows: the Ph.D-C7C of NEW ENGLAND Biolabs TM Peptide library diluted to 1 x 10 10 pfu titer, the diluent is TBS buffer (tris, Tris; 50 mM Tris, 150 mM sodium chloride), and the tail vein of rats is injected. After 60 min, the rats were anesthetized, and 100 μL of cerebrospinal fluid was extracted under sterile conditions. Take an appropriate amount of cerebrospinal fluid and use ER2738 Escherichia coli in logarithmic growth phase to determine the titer of phage by titration method, and the rest will be used for the next round of screening after amplification. In this way, four rounds of screening were carried out, and the titer of phage obtained in each round of screening was determined, and a single phage clone was randomly selected from the results of the last round for use.
...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3 Determination of phage titer
[0042] The phages obtained in each round of screening in Example 1 and Example 2 were diluted 10-fold with LB medium, and 10 μL of the diluted phage was mixed with 200 μL of E. coli ER2738 in logarithmic growth phase, and added to LB top layer agar (top layer agar: each liter contains 10 g tryptone, 5 g yeast extract, 5 g sodium chloride, 1 g magnesium chloride and 7 g agar powder, which is preheated at 50 °C, and is ready for use after autoclaving) quickly Pour into LB plates containing isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside and 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolegalactopyranoside (IPTG / Xgal), overnight, and count phage coeruleus .
[0043] Titer calculation formula: phage titer (pfu) = 100 × number of plaques × dilution factor, that is, phage forming units per 1 mL.
[0044] Enrichment of phages displaying brain-targeting peptides: As shown in Table 1 and Table 2, after four rounds of screening, the brain recovery rates of phages obtained...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
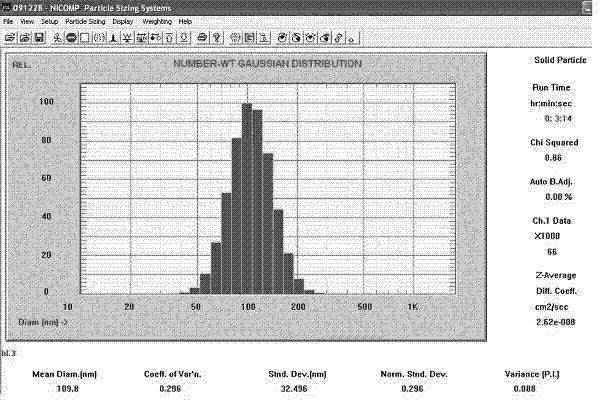
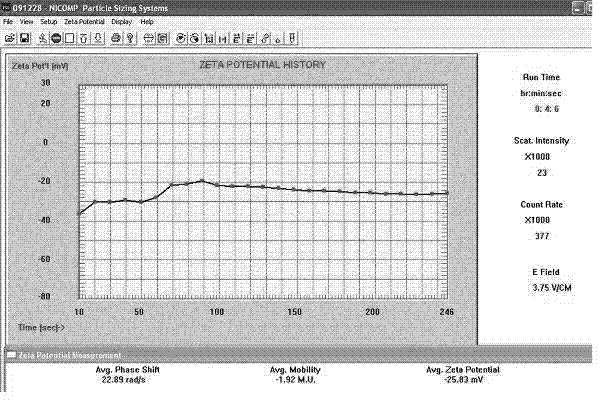
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com