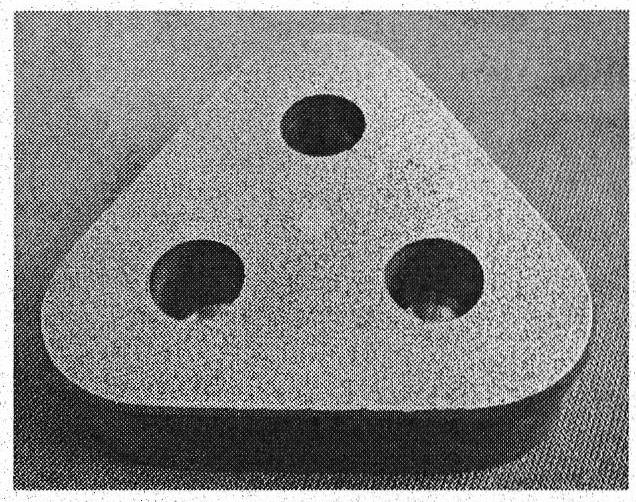
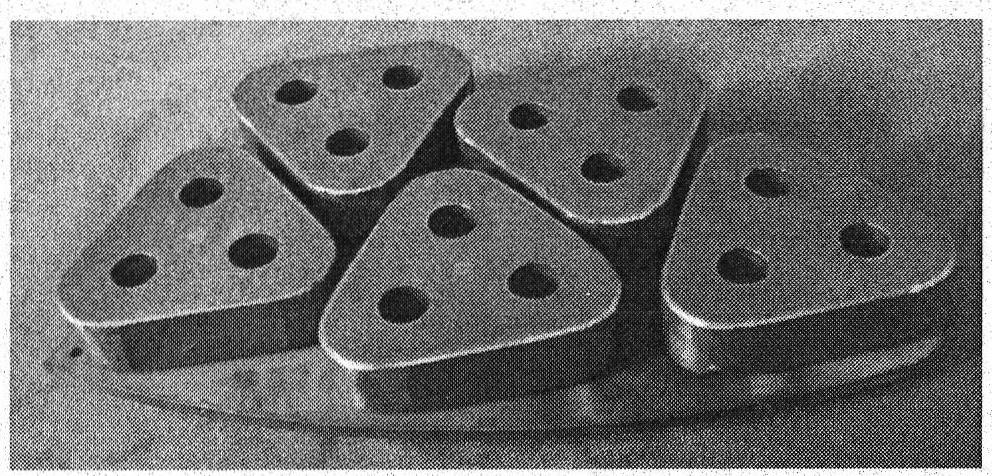
Ceramic/metallic double continuous phase composite material brake pad and preparation method thereof
A dual continuous phase and composite material technology, applied in friction linings, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve problems such as short life, high cost, and low performance of brake pads, and achieve considerable economic and social benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0043] (2) Preparation and filling of friction components
[0044] Fe powder (35~300 mesh, 30~10%wt); SiO 2 Powder (35-200 mesh, 45-10%wt); Cr powder (35-300 mesh, 10-20%wt); Ni powder (100-300 mesh, 5-20%wt); Mo powder (100-300 mesh, 5-15%wt); natural graphite powder (35-300 mesh, 0-25%wt) etc. are weighed in proportion and mixed, and 5-15%wt of binder (water glass, silica sol, etc.) is added ; Mix evenly and then dry; use mechanical means to pulverize and granulate through a 30-200 mesh sieve to obtain friction component particles; use mechanical vibration or suction to fill the friction component particles into the mesh of foam ceramics.
[0045] (3) Connection between silicon carbide foam ceramics and steel back
[0046] The silicon carbide foam ceramics filled with friction components in the mesh and the steel back are connected together by clamping or screw fixing.
[0047] (4) Preheating of silicon carbide foam ceramic skeleton steel back and melting of copper alloy ...
Embodiment 1
[0058] First prepare silicon carbide foam ceramics according to the method provided by the patent application number 03134039.3, wherein the size of the silicon carbide foam ceramic mesh is 0.8mm.
[0059] The composition of the friction components is shown in Table 1, and they were mixed evenly and then dried; mechanically pulverized and granulated through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain friction component particles. The oscillating method is used to fill the friction component particles into the meshes of the foam ceramics.
[0060] Table 1 Composition of surface wipe component mixed particles
[0061] make up
No
Mesh size
(mm)
(%)
silica
Micropowder g
(120~180 mesh)
Atomized iron powder g
(120~180 mesh)
Chromium powder g
300 mesh
Nickel powder g
300 mesh
Molybdenum powder g
300 mesh
Partial silicon
Sodium acid
ml
l...
Embodiment 2
[0065] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0066] Firstly, silicon carbide foam ceramics were prepared respectively according to the method provided by the patent application number 03134039.3, wherein the mesh size of the silicon carbide foam ceramics was 0.4mm.
[0067] The composition of the friction components is shown in Table 2. Mix them uniformly and then dry them; grind them mechanically, pass through a 120-mesh sieve and granulate to obtain the friction component particles. The oscillating method is used to fill the friction component particles into the meshes of the foam ceramics.
[0068] Table 2 Composition of friction components mixed particles
[0069] make up
No
Mesh size
(mm)
ceramic foam
(%)
silica
Micropowder g
(120~180 mesh)
Atomized iron powder g
(120~180 mesh)
Chromium powder g
300 mesh
Nickel powder g
300 mesh
Molybdenum powder ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com