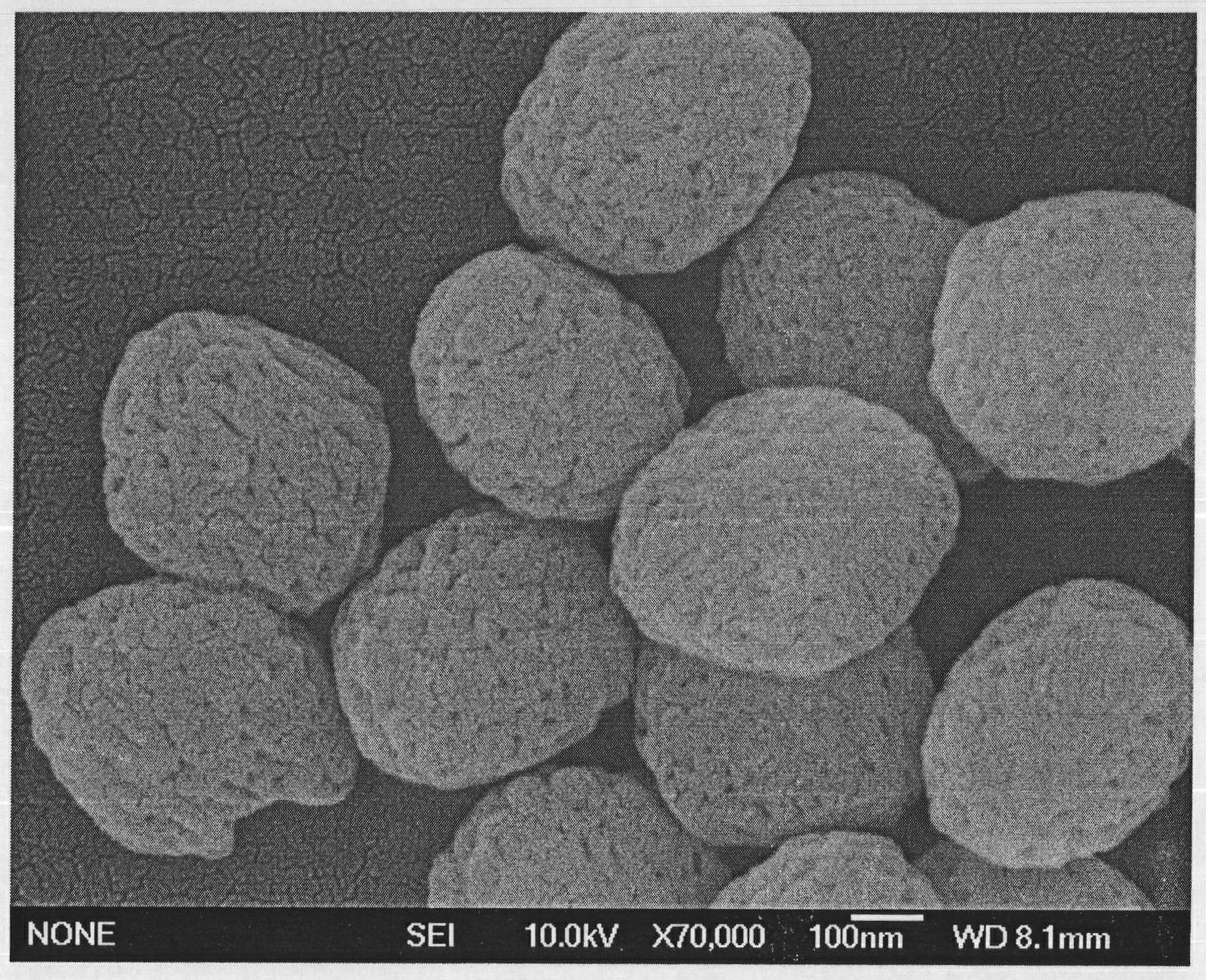
Porous cubic phase scandium oxide powder and preparation method thereof
A scandium oxide, cubic phase technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, rare earth metal compounds, etc., can solve the problems of poor dispersion and uneven size distribution, and achieve the effect of good performance and narrow particle size distribution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
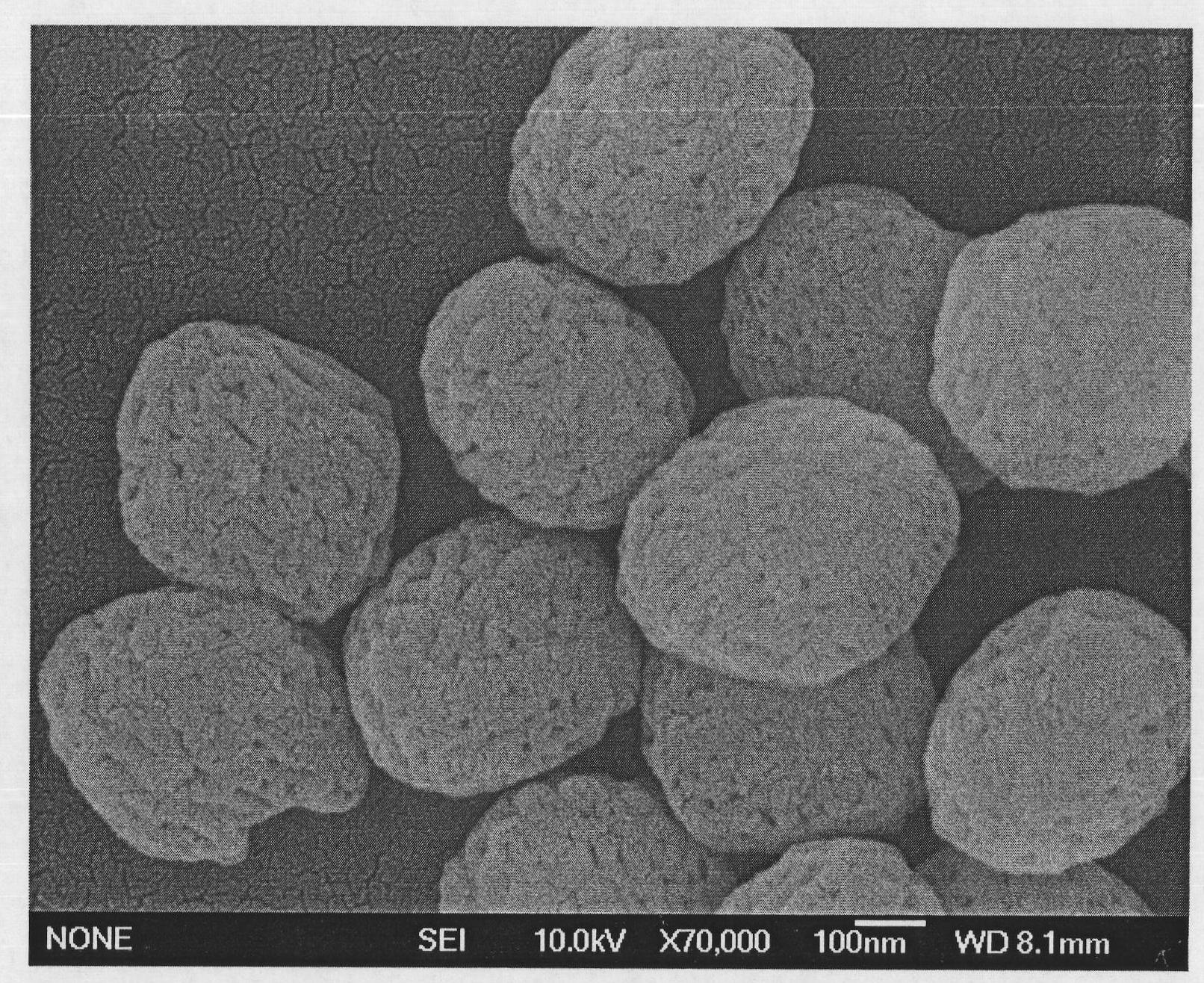
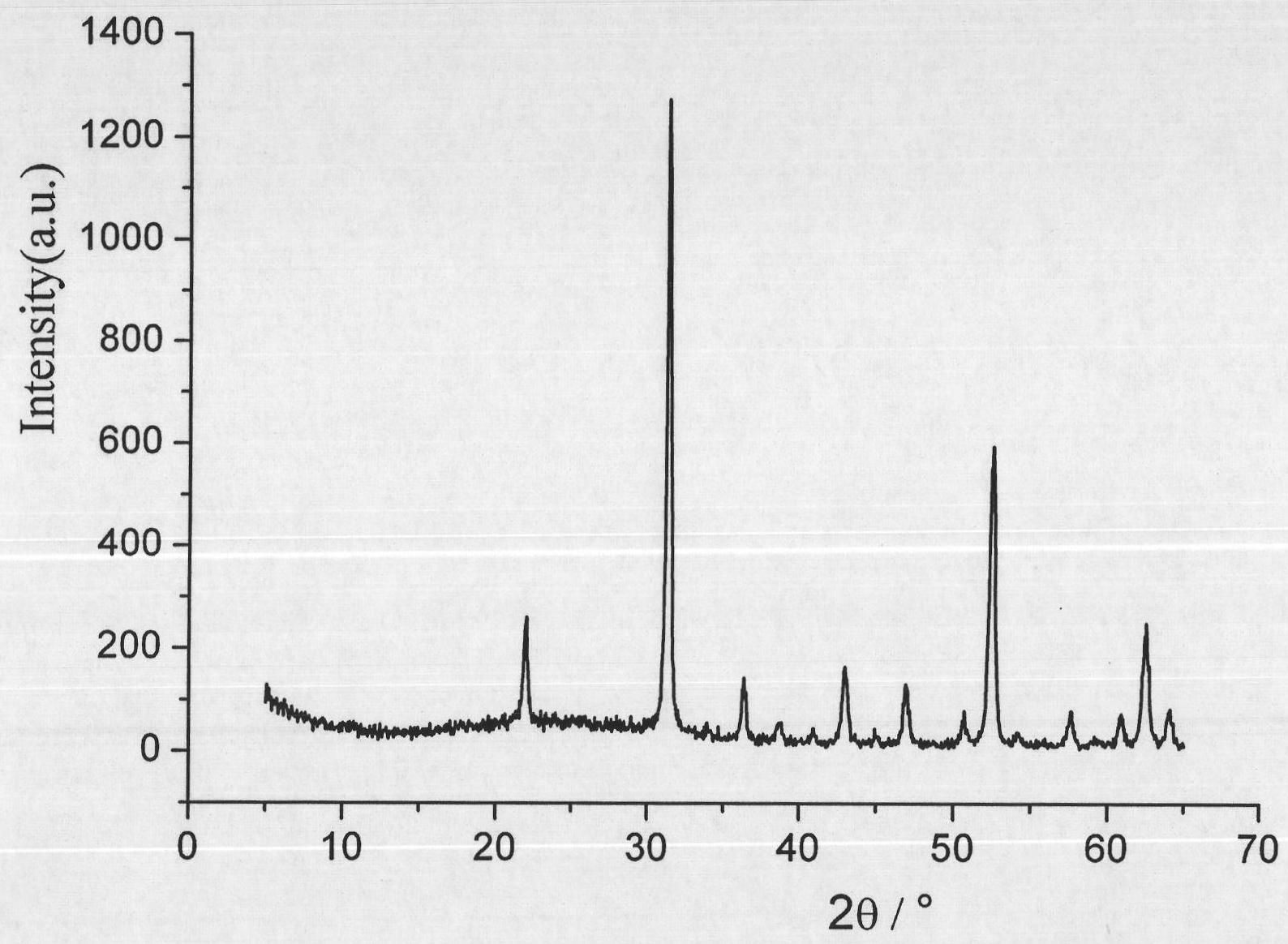
[0021] Add 0.138g of scandium oxide and 1ml of concentrated nitric acid into 10ml of distilled water, heat and stir to dissolve. After the dissolution is complete, the solution is evaporated to dryness to remove excess concentrated nitric acid to obtain dry white scandium nitrate. Then add 20ml of distilled water therein, stir at room temperature to dissolve, then add 0.410g of sodium acetate trihydrate, 0.500g of polyethylene glycol 1000 and 1.000g of hexamethylenetetramine into the scandium nitrate aqueous solution while stirring. After the dissolution is complete, pour it into a 30ml reaction kettle and keep the temperature at 100°C for 24h. The obtained white precipitate was collected by filtration and dried at 65° C., and finally the obtained white precipitate was calcined at 800° C. for 4 hours to obtain a white powder. The obtained white powder is confirmed to be cubic phase scandium oxide through X-ray diffraction analysis, such as figure 1 ; Scandium oxide powder is...
example 2
[0023] Add 0.138g of scandium oxide and 1ml of concentrated nitric acid into 10ml of distilled water, heat and stir to dissolve. After the dissolution is complete, the solution is evaporated to dryness to remove excess concentrated nitric acid to obtain dry white scandium nitrate. Then add 20ml of distilled water therein, stir at room temperature to dissolve, then add 0.410g of sodium acetate trihydrate, 0.500g of polyethylene glycol 1000 and 1.000g of hexamethylenetetramine into the scandium nitrate aqueous solution while stirring. After the dissolution is complete, pour it into a 30ml reaction kettle and keep the temperature at 100°C for 4h. The obtained white precipitate was collected by filtration and dried at 65° C., and finally the obtained white precipitate was calcined at 800° C. for 4 hours to obtain a white powder. The obtained white powder was confirmed to be cubic scandium oxide by X-ray diffraction analysis.
example 3
[0025] Add 0.138g of scandium oxide and 1ml of concentrated nitric acid into 10ml of distilled water, heat and stir to dissolve. After the dissolution is complete, the solution is evaporated to dryness to remove excess concentrated nitric acid to obtain dry white scandium nitrate. Then add 20ml of distilled water therein, stir at room temperature to dissolve, then add 0.410g of sodium acetate trihydrate, 0.500g of polyethylene glycol 1000 and 1.000g of hexamethylenetetramine into the scandium nitrate aqueous solution while stirring. After the dissolution is complete, pour it into a 30ml reaction kettle and keep the temperature at 100°C for 48h. The obtained white precipitate was collected by filtration and dried at 65° C., and finally the obtained white precipitate was calcined at 800° C. for 4 hours to obtain a white powder. The obtained white powder was confirmed to be cubic scandium oxide by X-ray diffraction analysis.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com