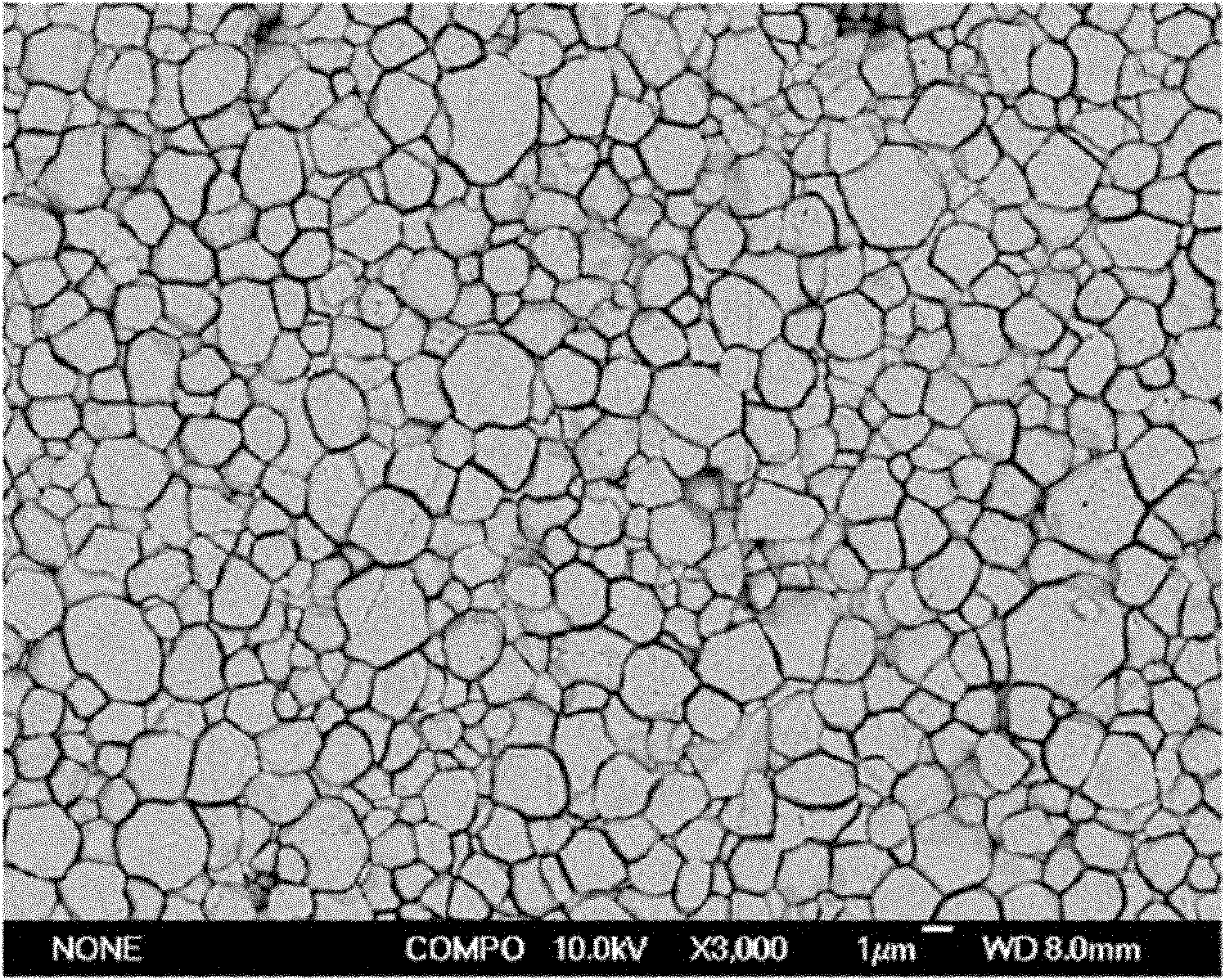
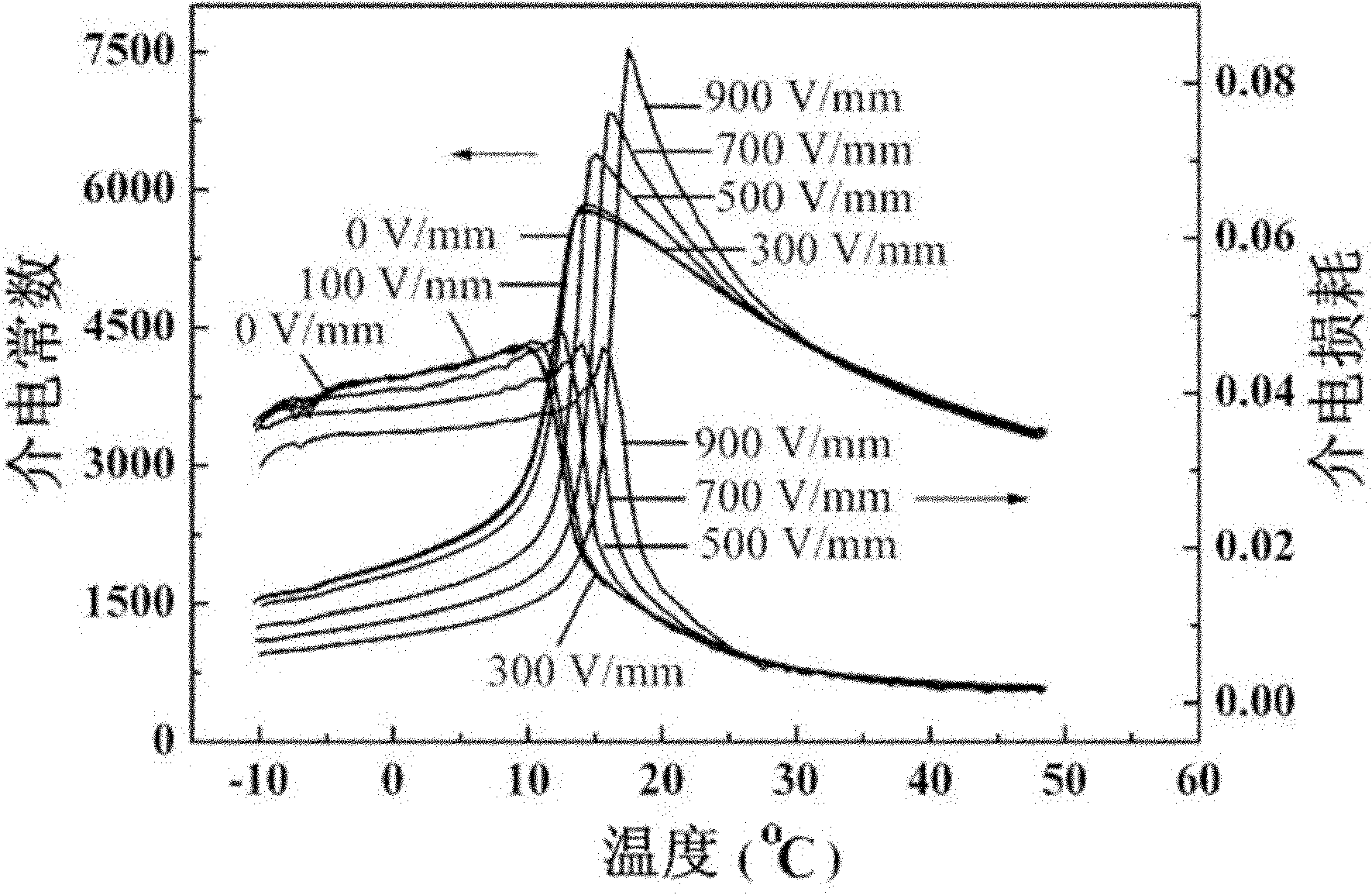
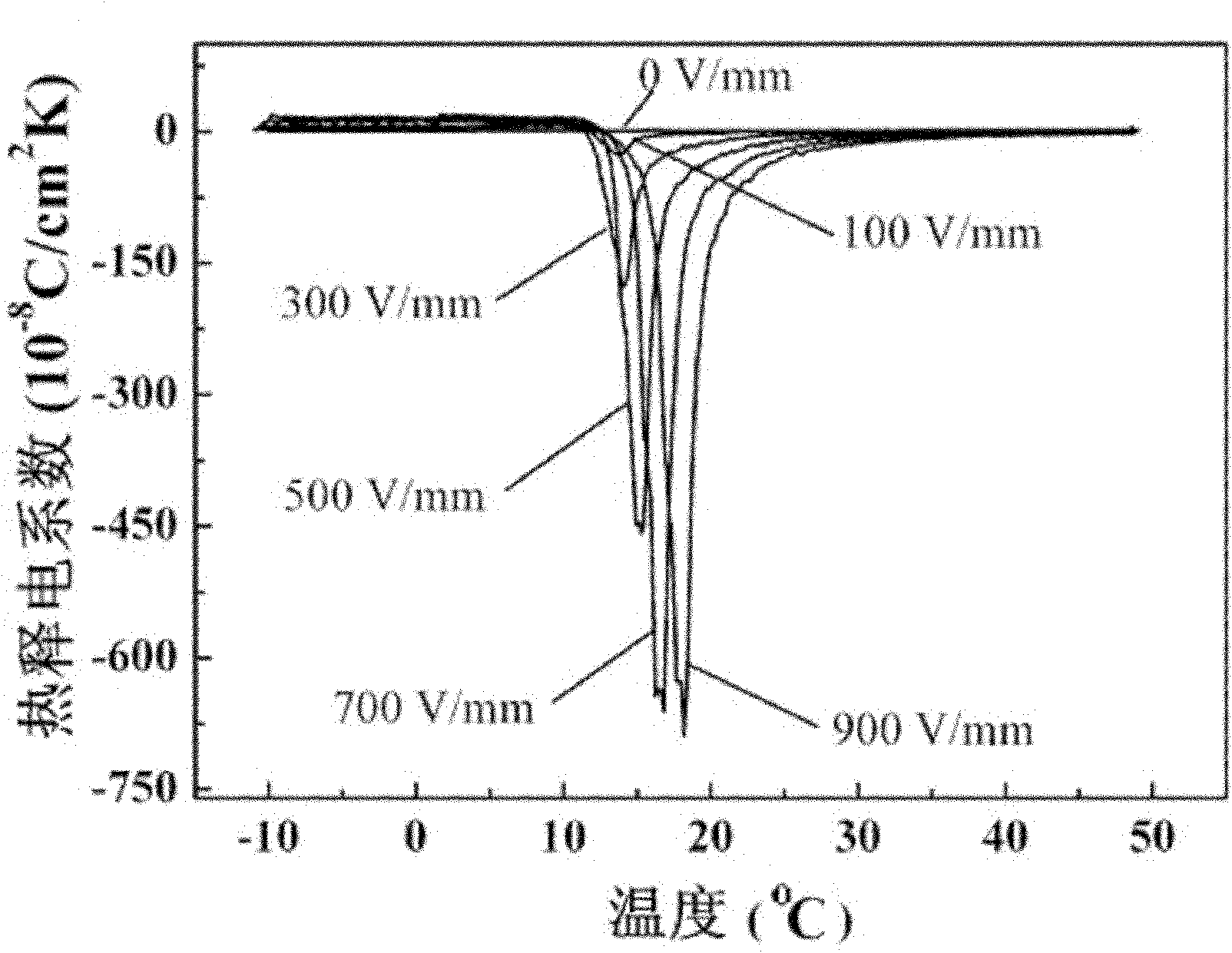
Method for preparing fine-grain lead scandium tantalate pyroelectric ceramic material
A technology of pyroelectric ceramics and lead tantalum scandate, which is applied in the field of pyroelectric ceramic material preparation to achieve the effects of small grain size, simple process and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] According to Pb(Sc 0.5 Ta 0.5 )O 3 The stoichiometric ratio and excess 0.3 ~ 3mol% take tantalum ethoxide, drop tantalum ethoxide into the mixed solvent formed by lactic acid and deionized water at a rate of 1 drop / 2 seconds, stir vigorously at room temperature for 24 hours, seal and stand still, Make the solution stable; wherein: the mass ratio of lactic acid to deionized water is 3:2, and the mass ratio of tantalum ethoxide to lactic acid is 1:1.
[0038] According to Pb(Sc 0.5 Ta 0.5 )O 3 The stoichiometric ratio and excess of 5 ~ 10mol% lead acetate was weighed and according to Pb (Sc 0.5 Ta 0.5 )O 3 Weigh scandium acetate, add deionized water to partially dissolve it, and form a suspension; add the obtained suspension to the tantalum ethoxide solution, add an appropriate amount of deionized water, and make the mass concentration of the formed mixed solution 15%; adjust the pH value of the mixed solution to 6.0 with ammonia water; fully stir to form Pb(Sc 0...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The difference between this example and Example 1 lies in the process conditions of the two-step sintering: heating up to 800°C at a heating rate of 3°C / min, and then stopping heating immediately after heating up to 1200°C at a heating rate of 10°C / min , and then cooled to 1050°C at a cooling rate of 30°C / min, kept for 20 hours, and finally cooled to room temperature with the furnace.
[0049] The remaining content of this embodiment is the same as that described in Example 1, and the performance test results of the prepared samples are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0051] The difference between this example and Example 1 lies in the process conditions of two-step sintering: heating up to 800°C at a heating rate of 3°C / min, and then stopping heating immediately after raising the temperature to 1100°C at a heating rate of 10°C / min , and then cooled to 950°C at a cooling rate of 30°C / min, kept for 20 hours, and finally cooled to room temperature with the furnace.
[0052] The remaining content of this embodiment is the same as that described in Example 1, and the performance test results of the prepared samples are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com