Method for extracting valuable metals from electronic waste
An electronic waste and valuable metal technology, applied in the field of environmental engineering, can solve the problems of strong corrosiveness, strong oxidation, and long immersion time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] A waste circuit board is broken to 0.1mm~1.0mm, the main metal components are Cu26.8%, Ni0.47%, Zn1.5%, Sn1.0%, Fe5.3%, Al4.7%, Ag3300g / t , Au80g / t, non-metal components about 51.4%.
[0054] Using NH 4 Cl-NH 3 -H 2 O system leaching, leaching agent composition: [NH 4 + ]=4.5mol / L, [NH 3 ]=2.5mol / L, measure 2L of leaching agent, weigh 500g of the above-mentioned crushed material, leaching time for 2 hours, leaching temperature 50°C, slowly add 30% H 2 o 2 85ml into the leaching system, after 120min the reaction was terminated and left to stand for 30min. Afterwards, the organic components floating on top of the solution were separated by scraping. Dry to obtain polymer raw materials that can be used for further utilization. The remaining leaching solution is filtered and separated, and the leaching residue is further used as a raw material for extracting Sn, Fe, Al and other metals. Add about 5 g of sponge copper powder into the leach solution, stir for 30 mi...
Embodiment 2
[0056] A waste printing plate was broken to 0.05mm~1.0mm, the main metal components were Cu32.1%, Ni0.12%, Zn2.1%, Sn1.3%, Pb0.92%, Fe6.9%, Al6.7 %, Ag2800g / t, Au110g / t, Pd45g / t, non-metal components about 47.2%.
[0057] Using NH 3 -(NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 -H 2 O system leaching, leaching agent composition: [NH 4 + ]=6.0mol / L, [NH 3 ]=4.0mol / L, measure 2L of leaching agent, weigh 500g of the above-mentioned crushed material, leaching time for 3 hours, leaching temperature 40°C, slowly add 75gNaClO 3Into the leaching system, finish the reaction after 120min and let stand for 30min. Afterwards, the organic components floating on top of the solution are separated by the overturning method. Dry to obtain polymer raw materials that can be used for further utilization. The remaining leaching solution is filtered and separated, and the leaching residue is further used as a raw material for extracting Sn, Fe, Al, Pb and other metals. Add about 5 g of sponge copper powder into the l...
Embodiment 3
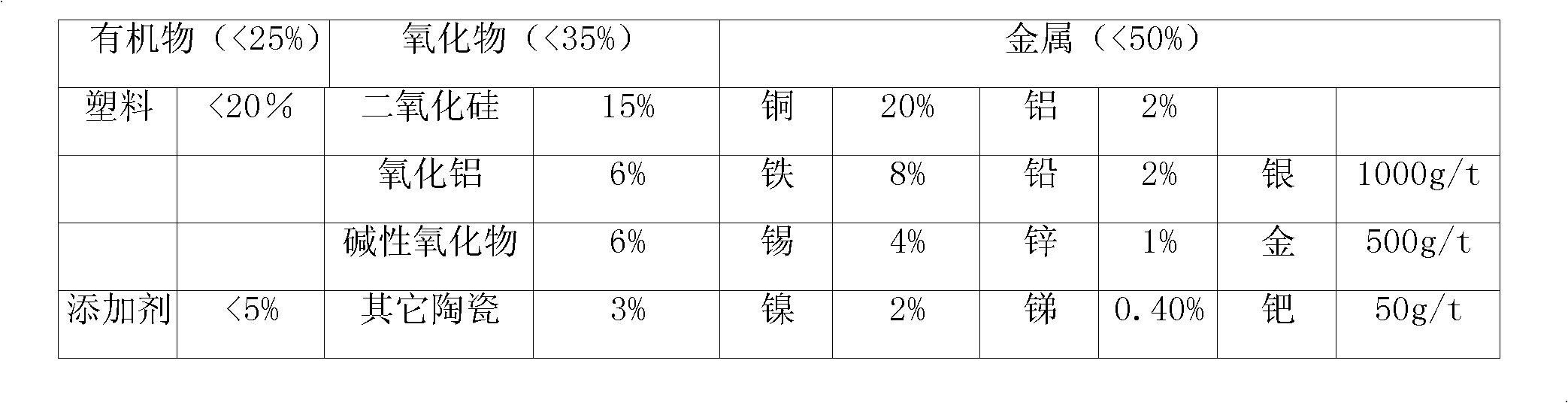
[0058] Example 3 A certain electronic waste is crushed to 0.04mm~1.0mm, the main metal components are Cu20%, Fe8%, Sn4%, Ni2%, Al2%, Pb2%, Zn1%, Sb0.4%, Ag1000g / t, Au500g / t, Pd50g / g, organic component about 30%.
[0059] Using NH 3 -(NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 -NH 4 Cl-H 2 O system leaching, leaching agent composition: [NH 4 + ]=4.0mol / L, [NH 3 ]=2.0mol / L, measure 10L of leaching agent, weigh 2kg of the above-mentioned crushed material, leaching time for 3 hours, leaching temperature 45°C, slowly add 550g of bleaching powder into the leaching system, finish the reaction after 180min and let stand for 50min. Afterwards, the organic components floating on the upper layer of the solution are separated by an overturning method, the overturned organic components are filtered and dried, and the filtrate is incorporated into the leaching solution. The filter residue is dried to obtain polymer raw materials that can be used for further utilization. The leaching solution is filtered and s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com