Novel microelectronic device radiator
A technology for microelectronic devices and heat sinks, applied in the field of heat dissipation of microelectronic devices, can solve the problems of large equivalent thermal resistance, small contact area of heating surfaces, damage to microelectronic devices, etc. Small area and the effect of enhancing heat transfer capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The present invention will be described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
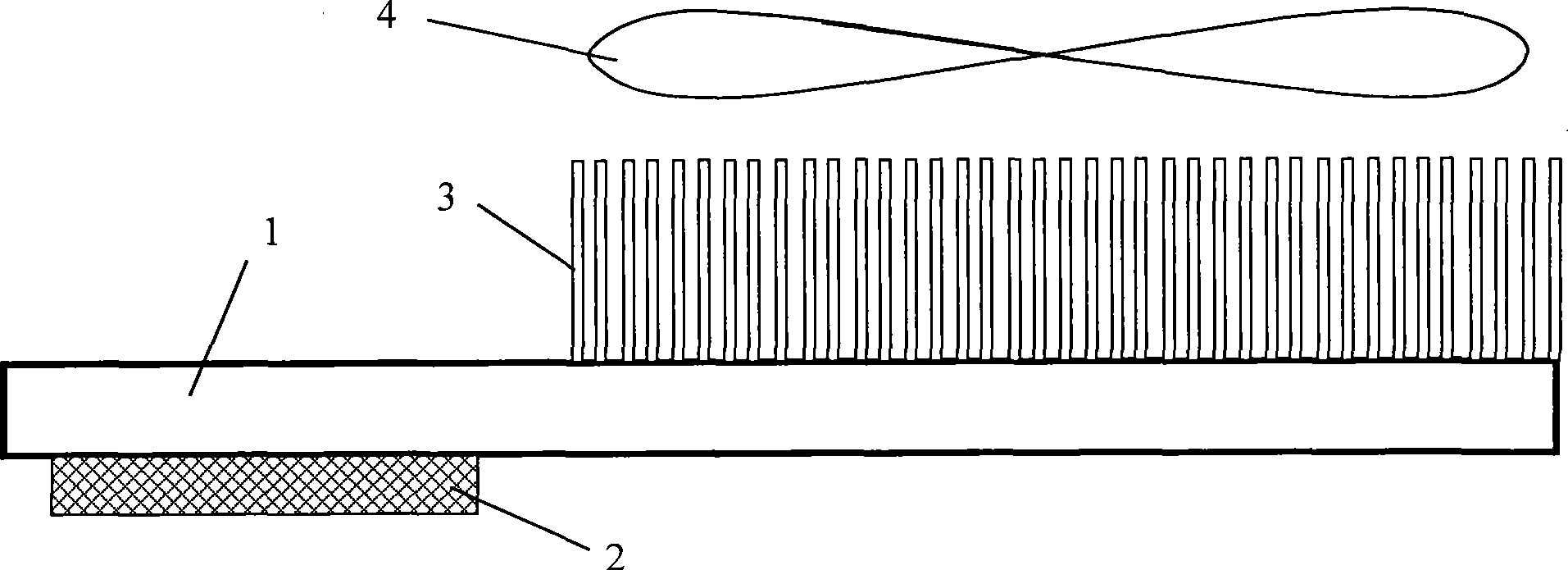
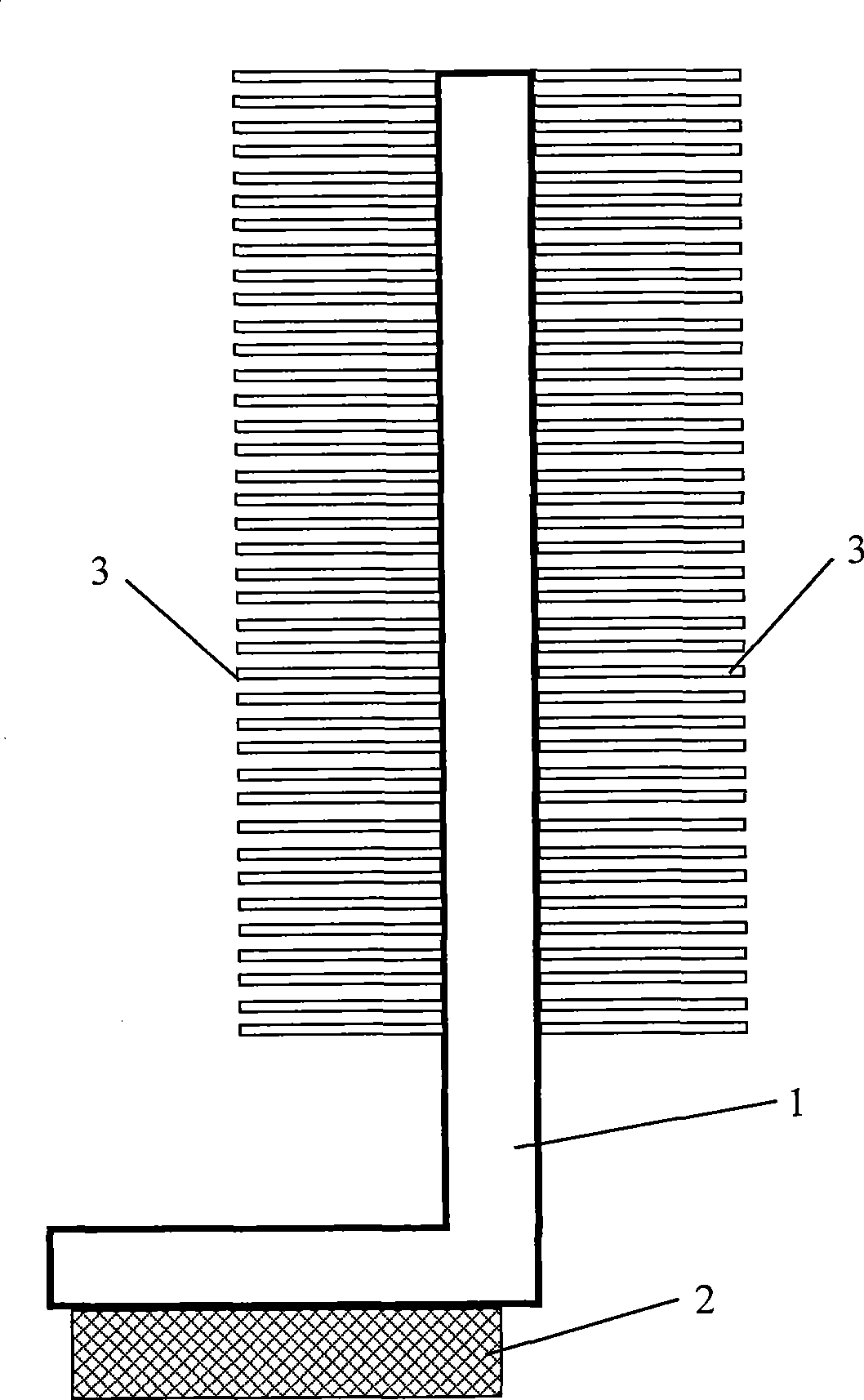
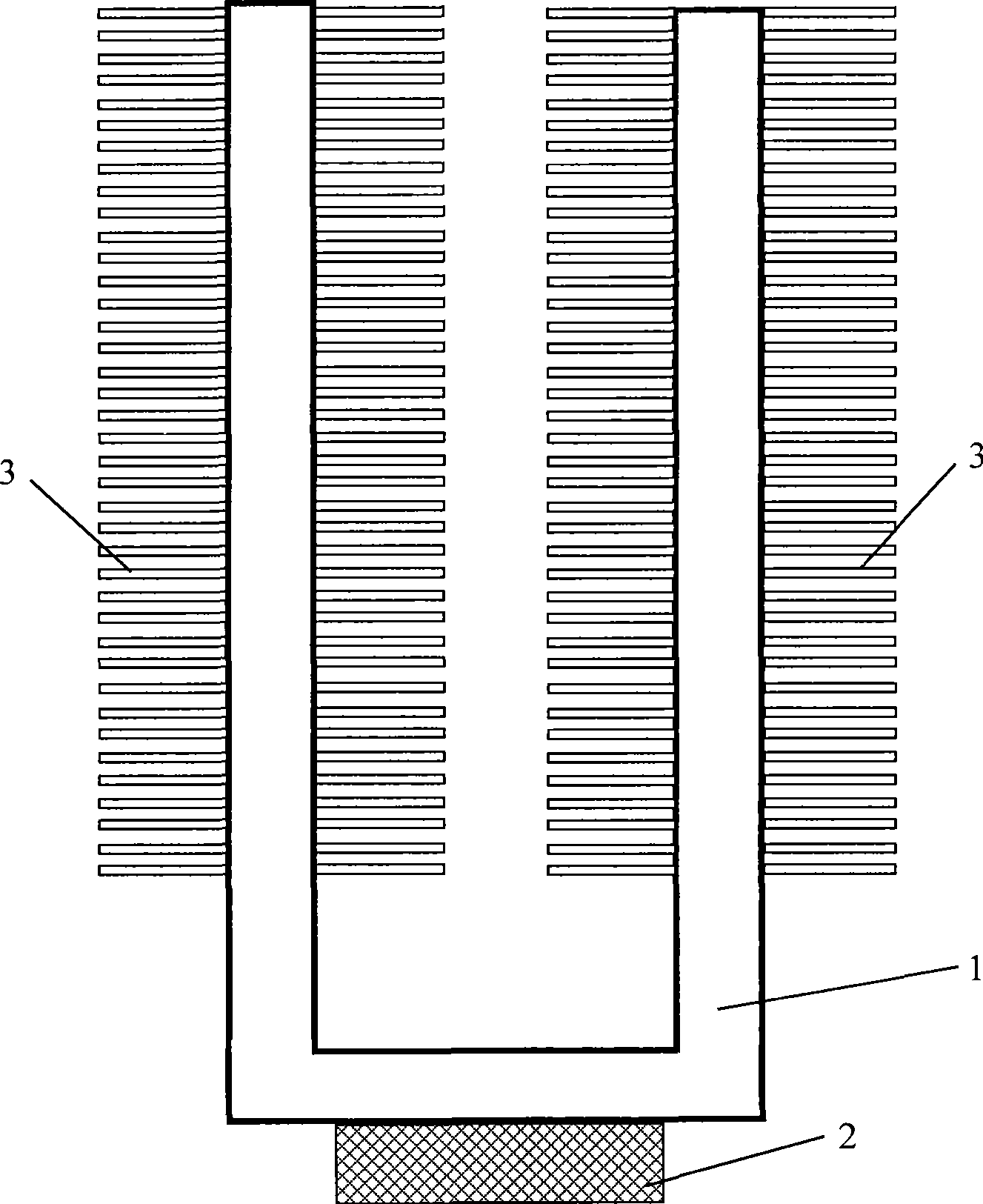
[0028] figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of the first preferred embodiment of the novel microelectronic device heat sink of the present invention. The novel microelectronic device heat sink includes a flat heat pipe 1, and the flat heat pipe is formed by extruding or stamping two or more metal materials. The through-hole array plate structure arranged side by side, considering the heat dissipation characteristics of the heating surface of the microelectronic device, the structural characteristics of the microelectronic device installation, and the influence of working environment factors, the equivalent diameter of the through hole of a specific size is set, such as a notebook computer The internal installation space is narrow, and the computer body is required to be relatively thin, while the installation space of the desktop computer is relatively large. The work...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Groove width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com