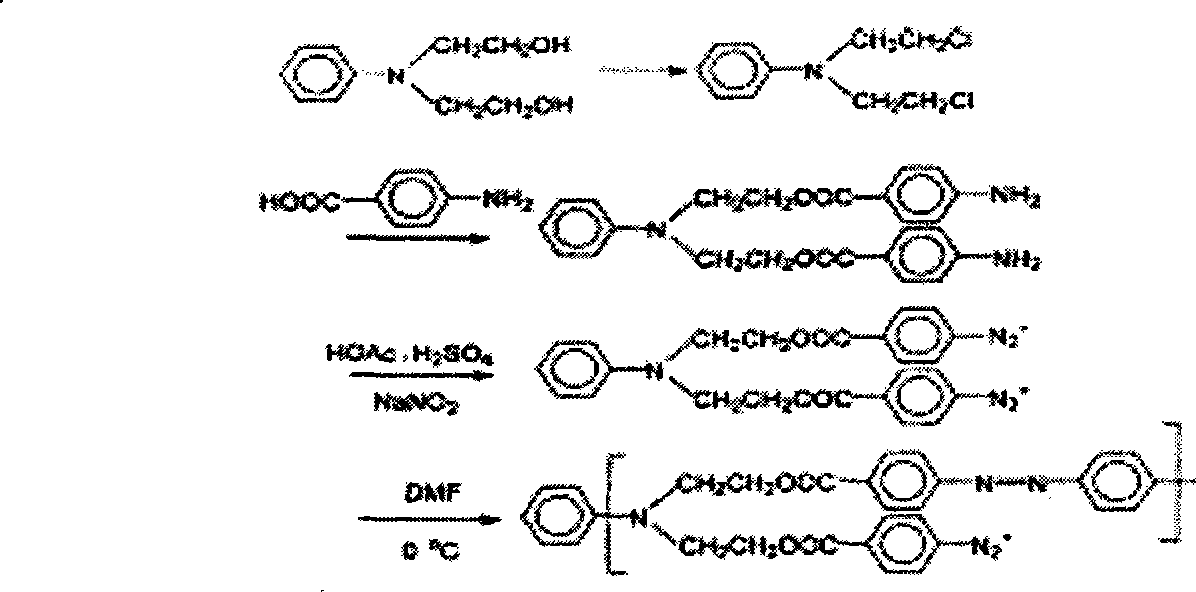
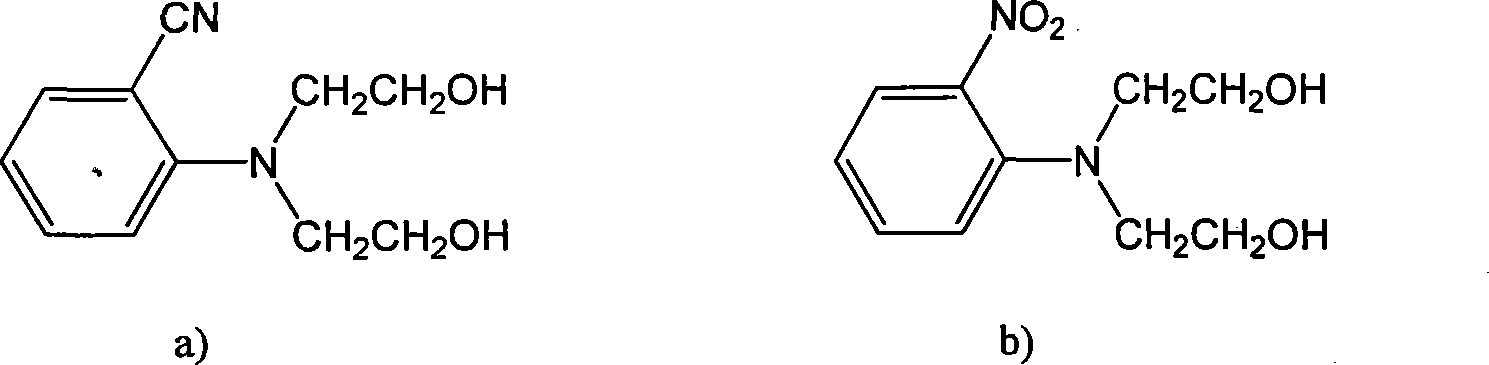
Enzyme immobilization method based on excessive expenditure polymer
A hyperbranched polymer and enzyme immobilization technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of easy shedding of immobilized enzymes, weak universality, special material requirements, etc., and achieves simple immobilization method, simplified operation steps, application wide range of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Cut the polyethylene film into a 2cm×2cm film, wash it with ultrapure water, dilute the synthesized DAS solution 10 times with water, then soak and absorb it in the diluted DAS solution at 4°C for 30min, and put the polyethylene film Take it out, wash it with water, add it to the phosphate buffer solution of beta-glucosidase at pH=7.0, let it stand at 4°C for 4 hours to make it saturated, take out the film, and wash it.
[0030] The material was immersed in the prepared substrate solution of a certain concentration, and the amount of immobilized enzyme was determined by measuring the ultraviolet absorption of the product. It was found that when the hyperbranched diazonium salt was used as the enzyme immobilization reagent, an obvious UV absorption; when the diazonium salt is not used as the enzyme immobilization reagent, the UV absorption of the product cannot be detected, indicating that the use of diazonium salt as the enzyme immobilization reagent can have a good immo...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Take a certain amount of polypropylene tubular material, wash it with ultrapure water, dilute the synthesized DAS-1 solution 20 times with DMF, then soak and absorb it in the DAS solution at 3°C for 40min, take out the polypropylene, and use ultrapure water Wash it with pure water, then add it to the citric acid-sodium citrate buffer solution of beta-glucosidase at pH=6.5, place it at 2°C for 6 hours to make it saturated, take out the material, wash it, and then put It is immersed in the prepared substrate solution of a certain concentration, and the amount of immobilized enzyme is determined by measuring the ultraviolet absorption of the product.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Cut the nylon 66 film into a 2cm×2cm film, wash it with water, dilute the synthesized DAS-2 solution 90 times with water, then soak and absorb it in the DAS solution at 1°C for 1 hour, take out the nylon 66 film, and use Wash it with ultrapure water, then add it to the beta-glucosidase disodium hydrogen phosphate-citric acid buffer solution at pH=6.0, place it at 4°C for 24 hours to make it saturated, take out the film, wash it, Then immerse it in the prepared substrate solution of a certain concentration, and determine the amount of immobilized enzyme by measuring the ultraviolet absorption of the product.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com