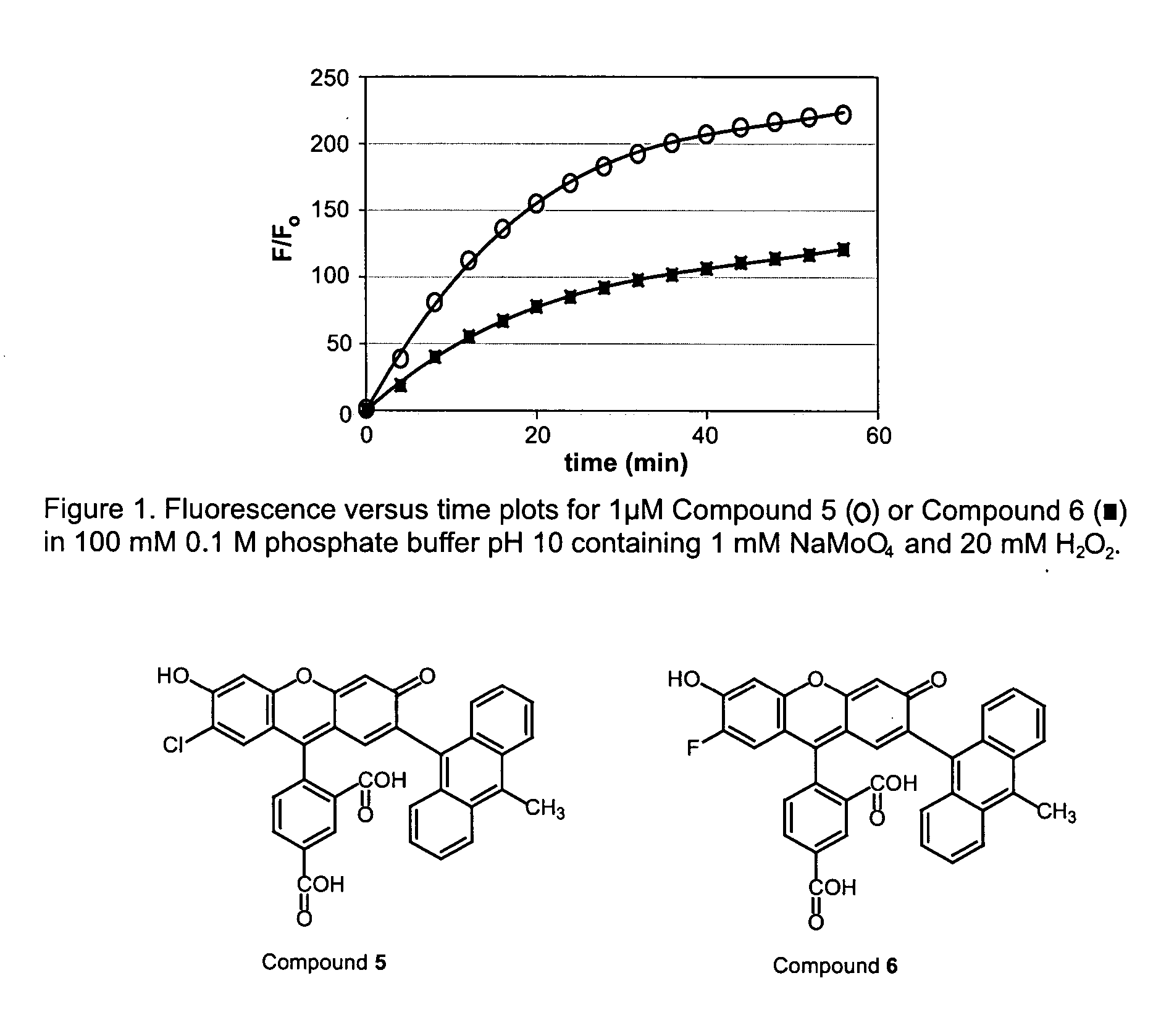
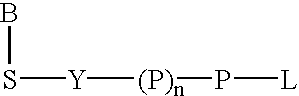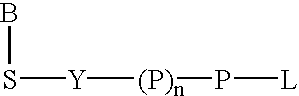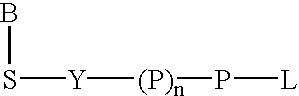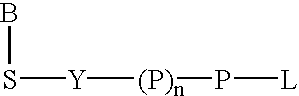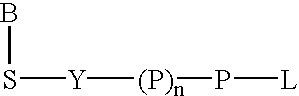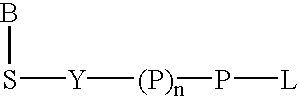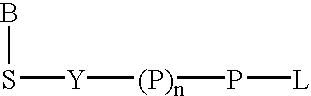Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
278results about "Coumarine dyes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
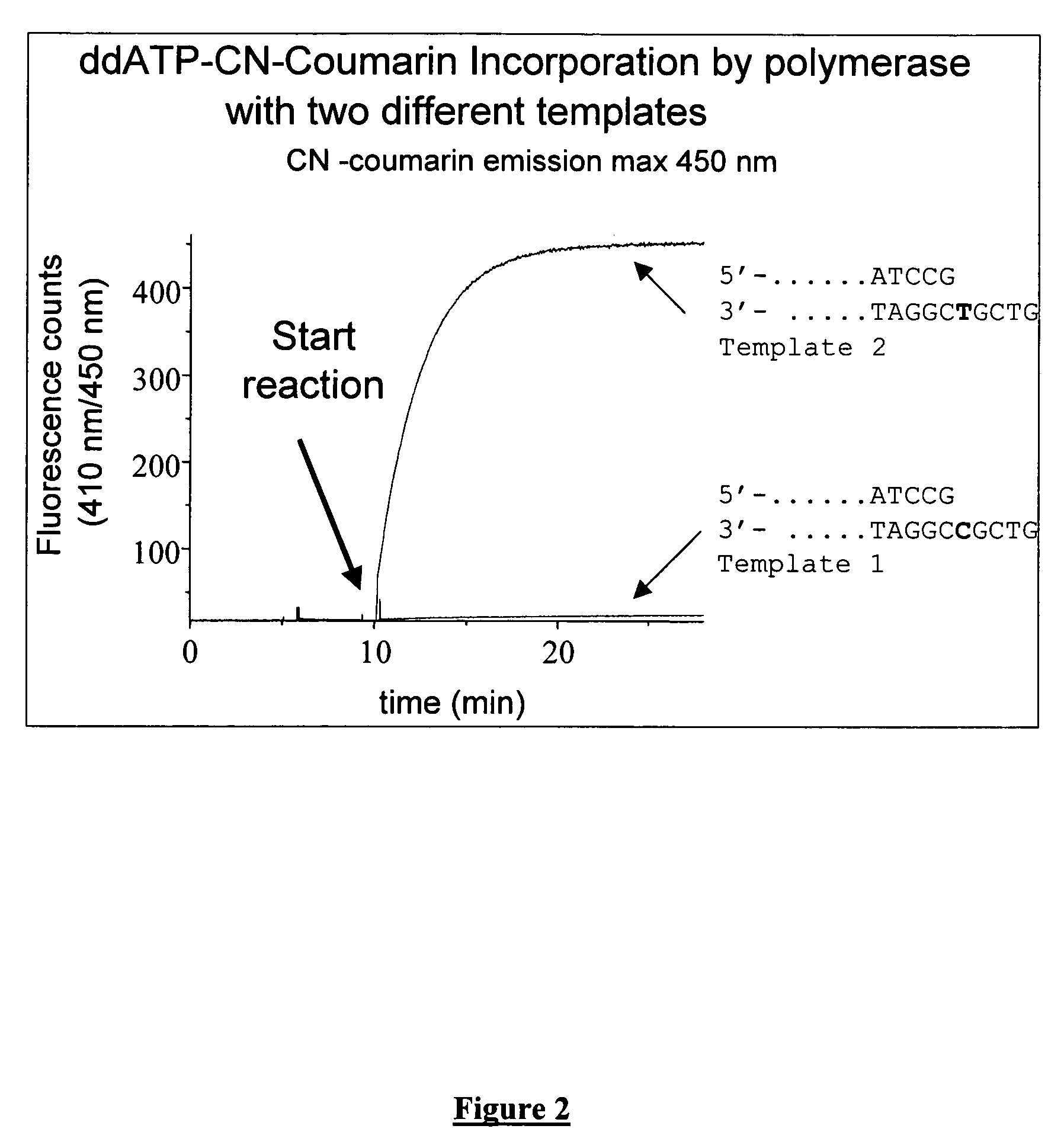
Labeled nucleoside polyphosphates
InactiveUS7041812B2Sugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorNucleic acid detectionFluorescence
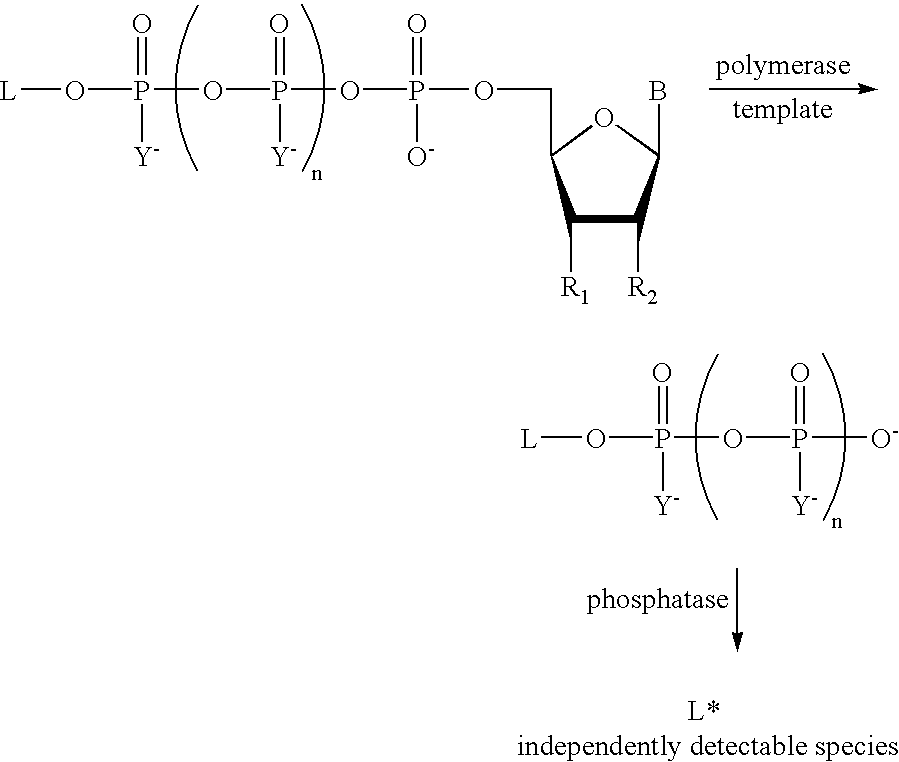
The present invention describes new compositions of matter in the form of labeled nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates. In addition compositions of nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates that are substrates for nucleic acid polymerases with enhanced substrate properties and methods of using these nucleoside polyphosphates for nucleic acid detection, characterization and quantification are described. The compositions provided by this invention include nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogues which have colorimetric, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moieties, mass tags or an electrochemical tags attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Removal of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphate or polyphosphate transferring enzyme leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Labeled nucleoside polyphosphates
InactiveUS20030124576A1Sugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorNucleic acid detectionFluorescence
The present invention describes new compositions of matter in the form of labeled nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates. In addition compositions of nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates that are substrates for nucleic acid polymerases with enhanced substrate properties and methods of using these nucleoside polyphosphates for nucleic acid detection, charcterization and quantification are described. The compositions provided by this invention include nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogues which have calorimetric, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moieties, mass tags or an electrochemical tags attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Cleavage of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphatase leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides and methods of use
The present invention describes methods of detecting a nucleic acid in a sample, based on the use of terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides as substrates for nucleic acid polymerases. The methods provided by this invention utilize a nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogue which has a colorimetric dye, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moiety, a mass tag or an electrochemical tag attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Cleavage of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphatase leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides and methods of use
The present invention relates to improved methods of detecting a target using a labeled substrate or substrate analog. The methods comprise reacting the substrate or substrate analog in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction which produces a labeled moiety with independently detectable signal only when such substrate or substrate analog reacts. The present invention, in particular, describes methods of detecting a nucleic acid in a sample, based on the use of terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides as substrates for nucleic acid polymerases. The methods provided by this invention utilize a nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogue which has a colorimetric dye, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moiety, a mass tag or an electrochemical tag attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Cleavage of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphatase leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
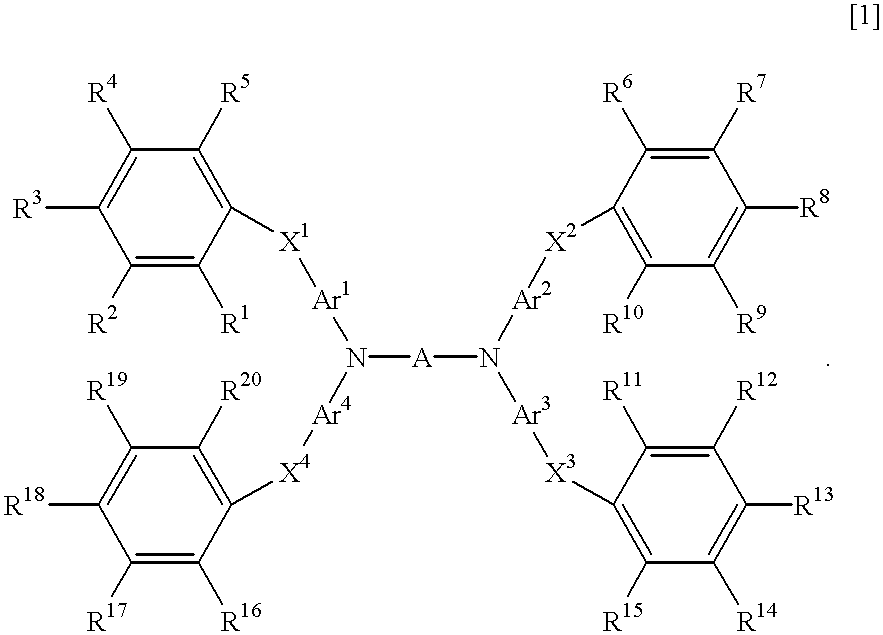
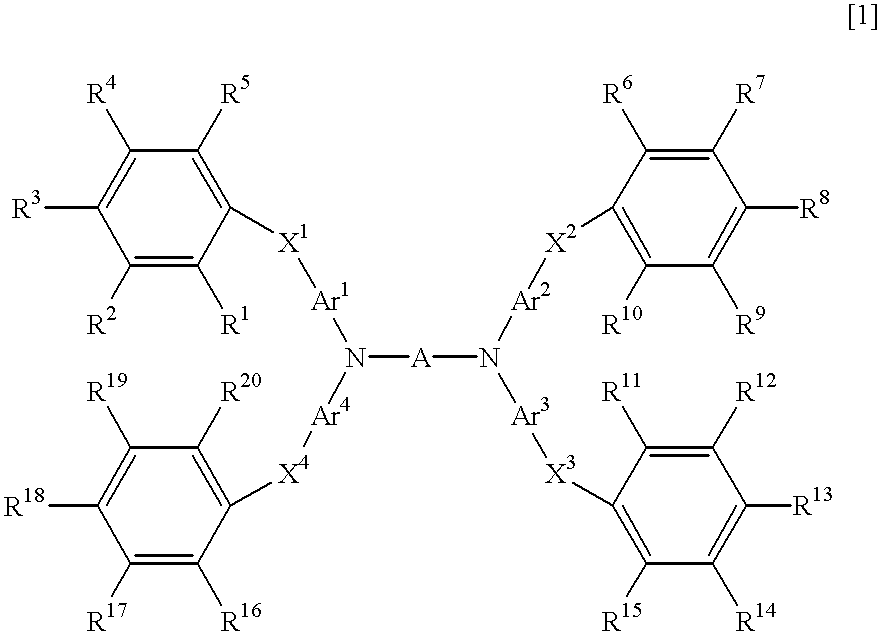
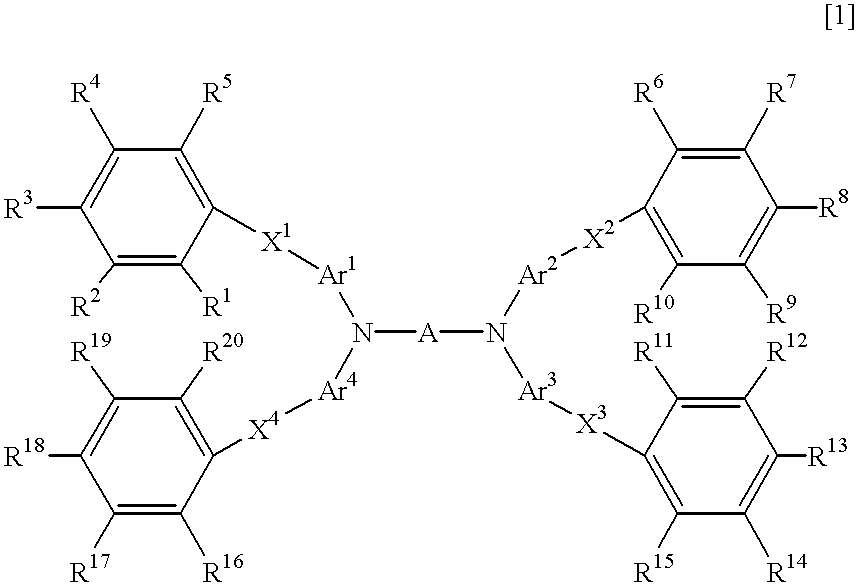
Light-emitting material for organo-electroluminescence device and for organic electroluminescence device which the material is applied
InactiveUS6280859B1Methine/polymethine dyesOrganic chemistryOrganic electroluminescenceLight emission
A light-emitting material which serves to emit light having a high brightness and is almost free of deterioration in light emission, and an organic EL device for which the light-emitting material is adapted, the material having the formula [1],
Owner:TOYO INK SC HOLD CO LTD
Terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides with new linkers
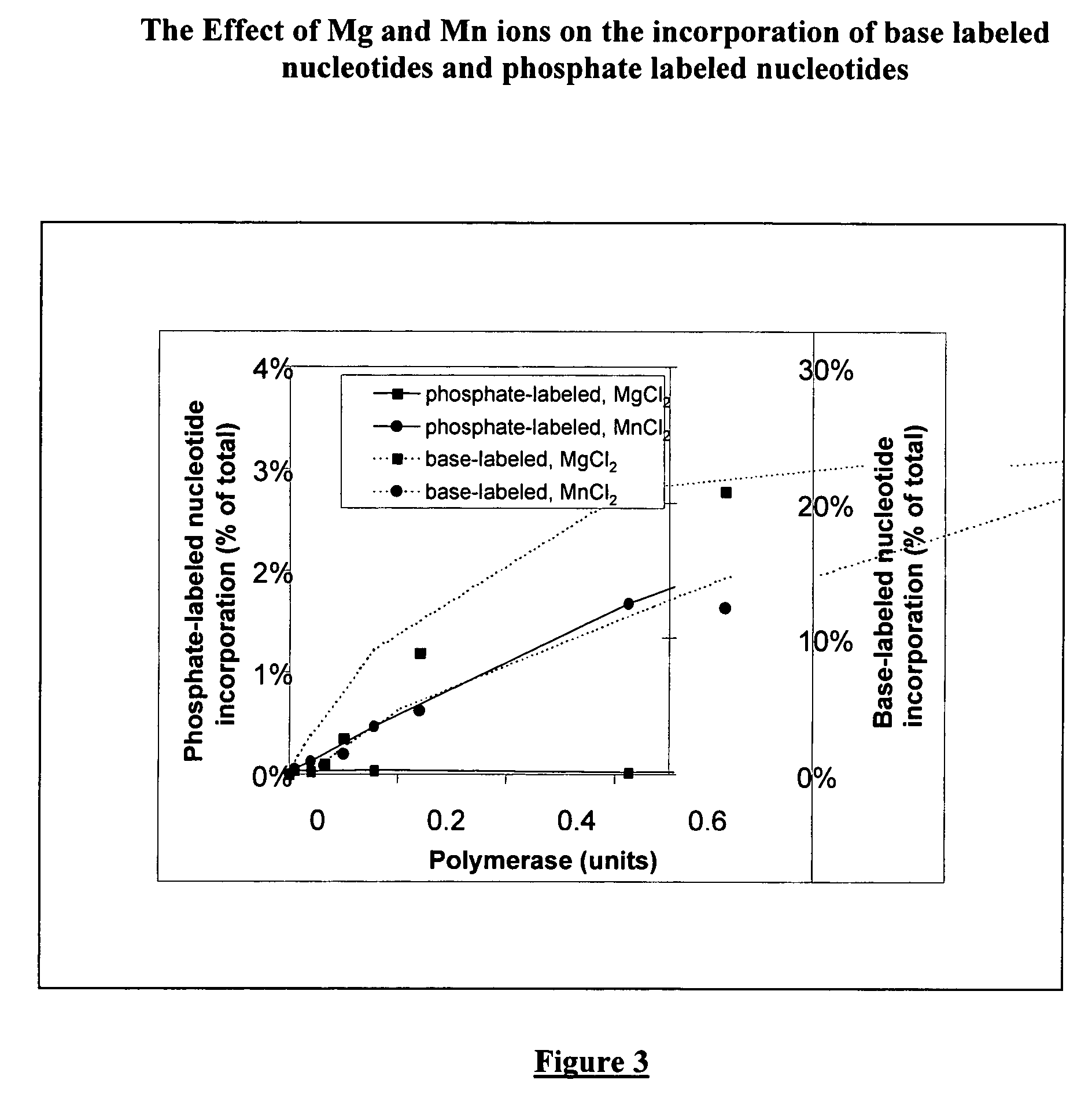
The present invention describes methods of using terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides in the presence of a manganese salt to enhance their substrate properties towards various enzymes. Particularly described are methods of detecting a nucleic acid in a sample, based on the use of terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides as substrates for nucleic acid polymerases, in the presence of a manganese salt. Further provided are manganese complexes of terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides as well as terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides with new linkers with enhanced substrate properties.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
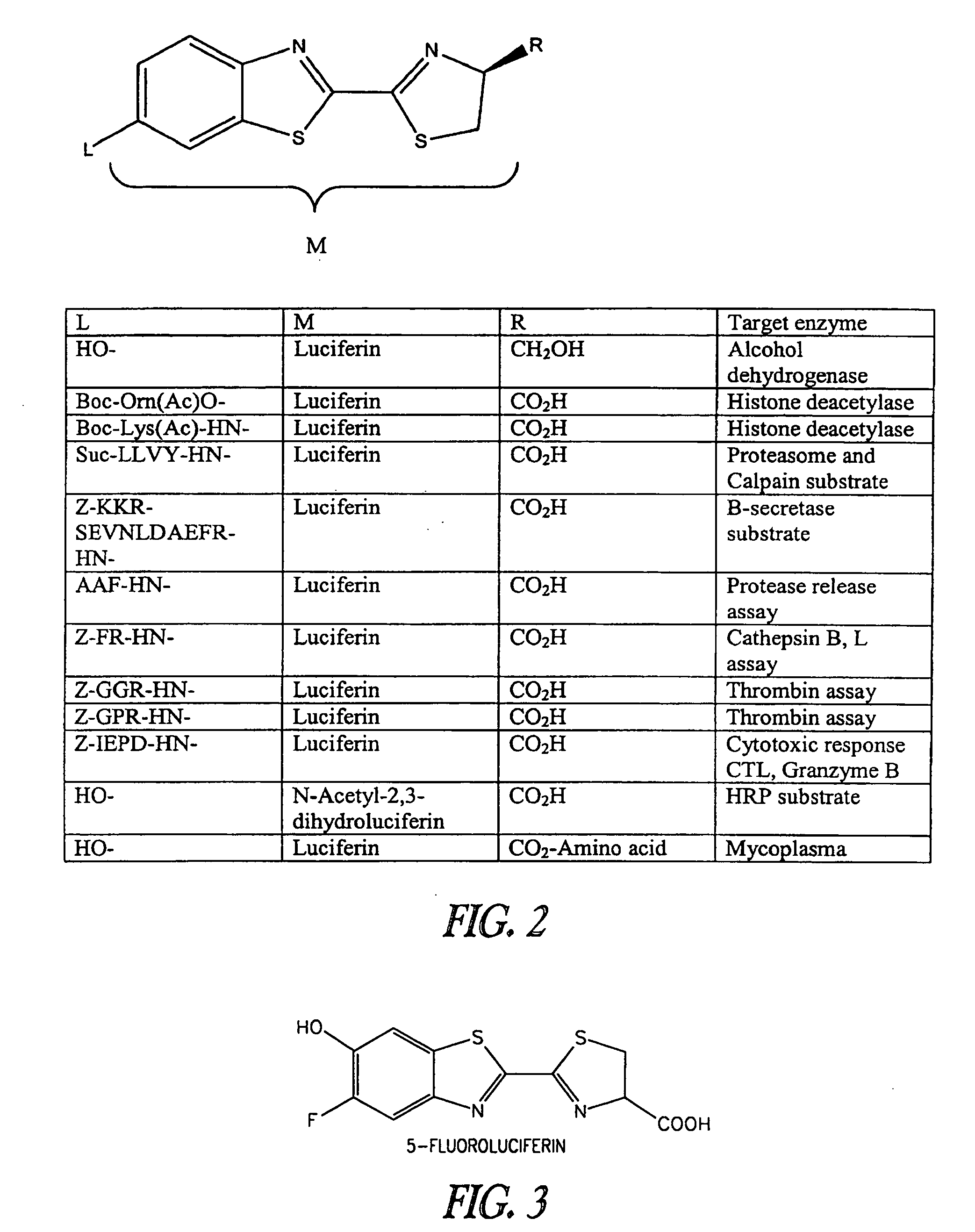
Luminogenic and fluorogenic compounds and methods to detect molecules or conditions
A method to detect the presence or amount of at least one molecule in a sample which employs a derivative of luciferin or a derivative of a fluorophore is provided.
Owner:PROMEGA
Compound, especially marker-dye on the basis of polymethines
InactiveUS20040260093A1Improve light resistanceLong storage periodMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic chemistryQuantum yieldFluorophore
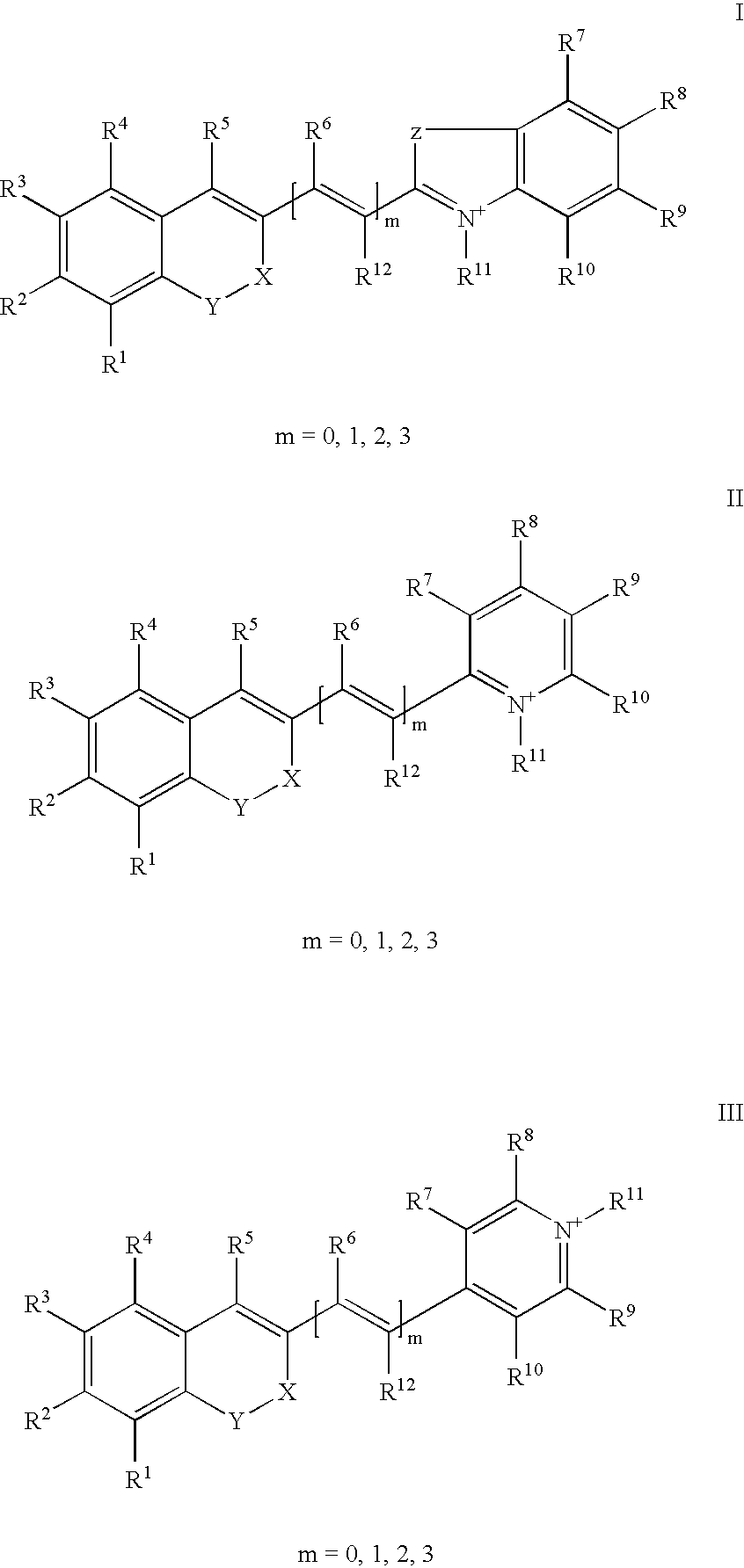
The invention relates to fluorescent dyes (fluorophores) based on polymethines for use in optical measurement and detection procedures, in particular those employing fluorescence, for example in medicine, in pharmacology and in the biological, materials and environmental sciences. The objective was to create fluorophores based on polymethines that have a large Stokes shift, high photostability, long storage life and a high fluorescent quantum yield, and that can be excited in the simplest possible manner by white-light sources or laser radiation in the UV, visible or NIR spectral region. According to the invention dyes on the basis of polymethines having the general formulas I, II or III are employed.
Owner:DYOMICS
Fluorescent compounds
ActiveUS20090305410A1Convenient and effective labelingMethine/polymethine dyesPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyDisease
Owner:BIOTIUM INC
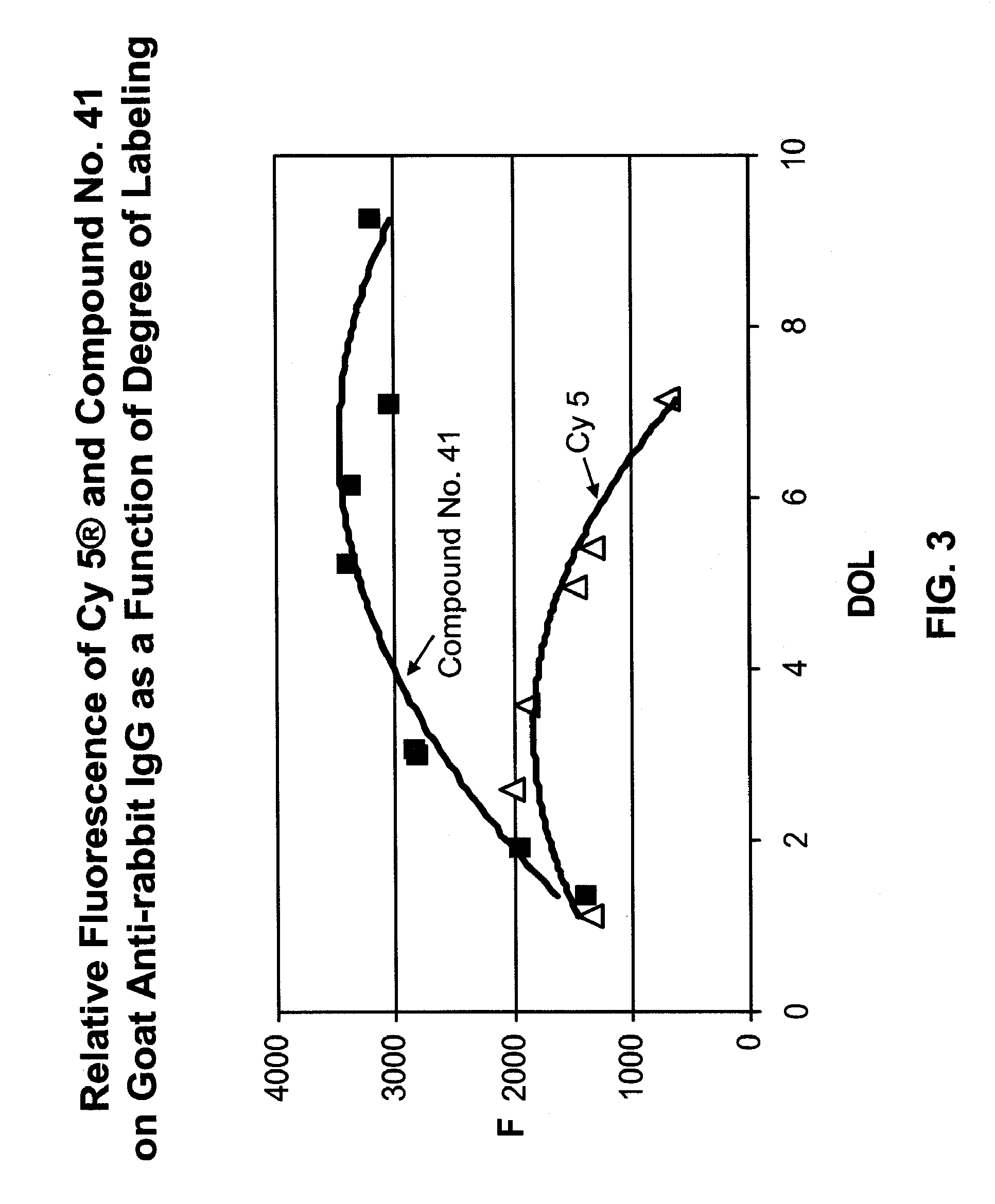
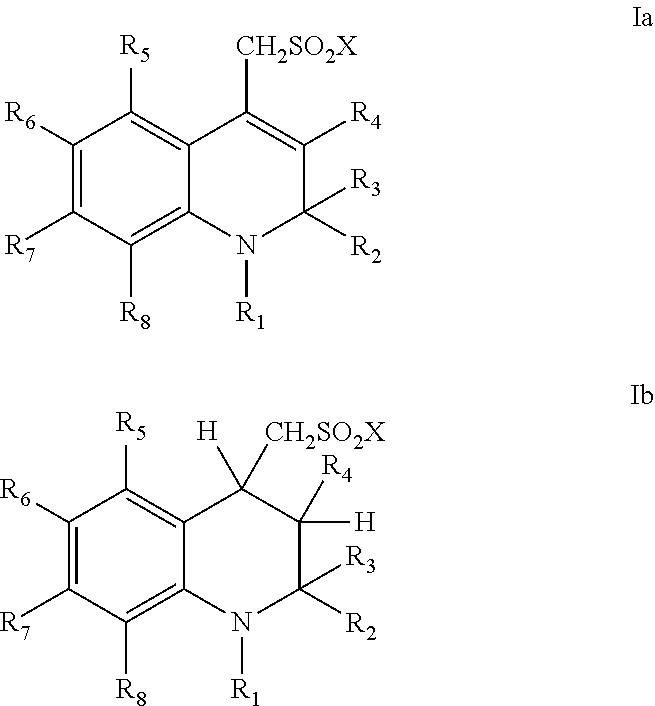
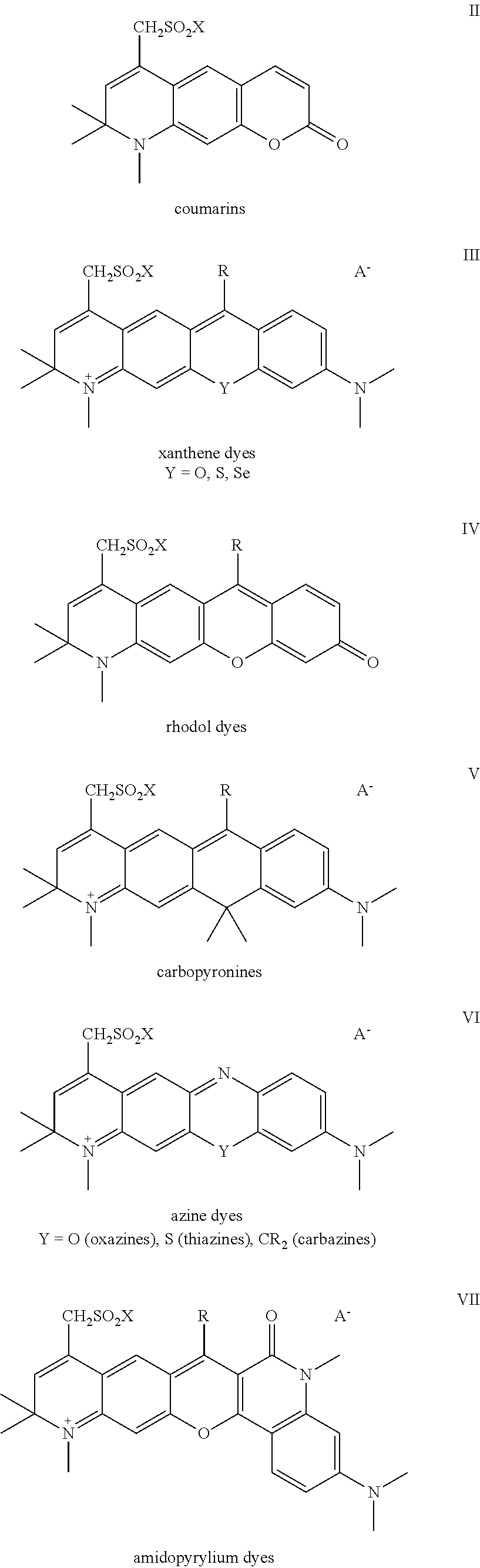
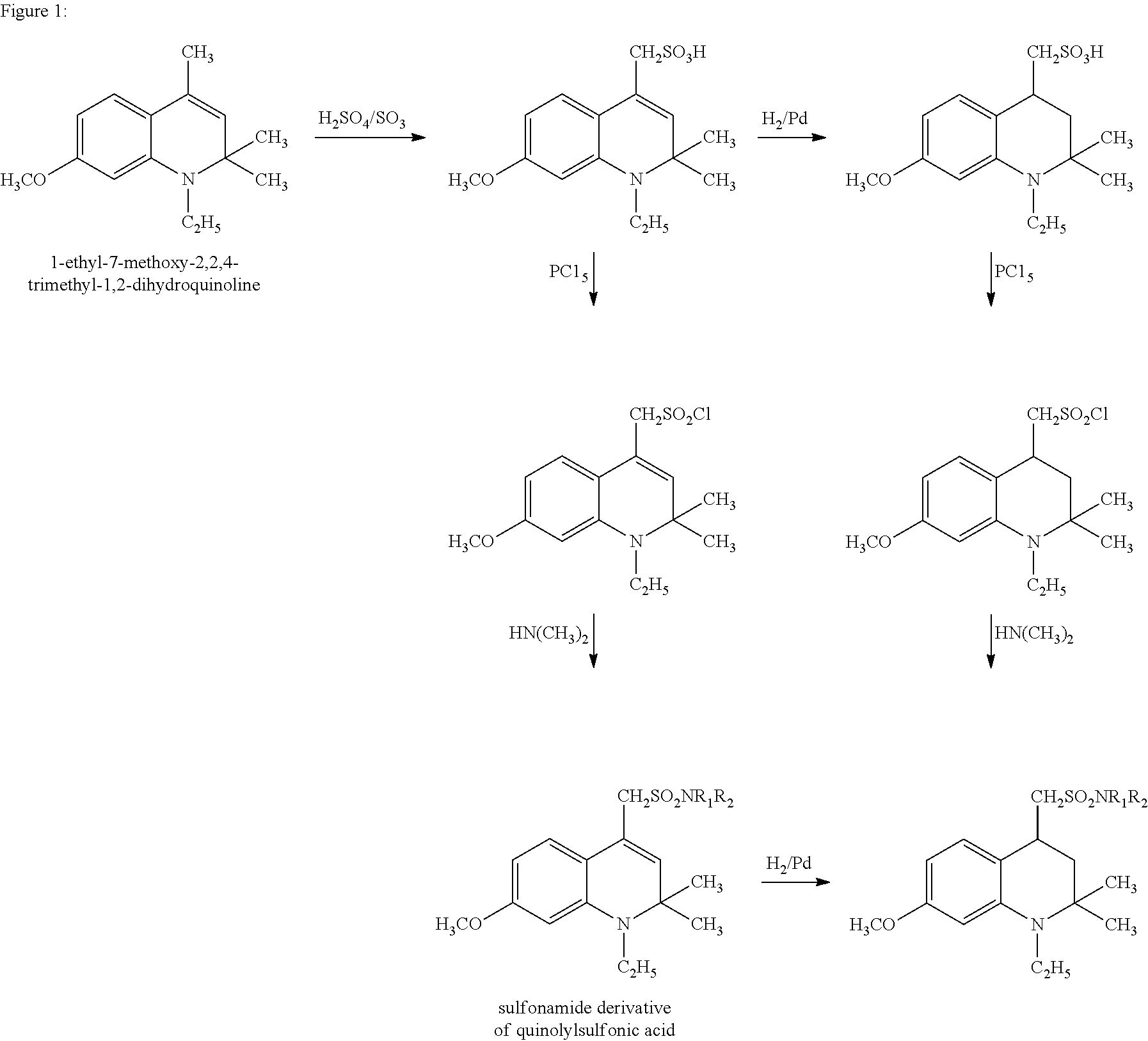
Sulfonamide derivatives of polycyclic dyes used for analytical applications
ActiveUS20110190486A1Simple waySimple and cost-effectiveSugar derivativesPyronine/xanthon/thioxanthon/selenoxanthan/telluroxanthan dyesQuinolinePhotochemistry
The invention concerns the production of quinoline compounds containing sulfonic acid groups, the said quinoline compounds and their conversion into dyes containing sulfonic acid groups. The dyes according to the invention are used especially to label analytes, for example to label biomolecules.
Owner:ATTO TEC
Sulfonamide derivatives of polycyclic dyes used for analytical applications
ActiveUS20110172420A1Unrestricted applicabilitySimple wayOrganic chemistryPyronine/xanthon/thioxanthon/selenoxanthan/telluroxanthan dyesAnalyteQuinoline
The invention concerns the production of quinoline compounds containing sulfonic acid groups, the said quinoline compounds and their conversion into dyes containing sulfonic acid groups. The dyes according to the invention are used especially to label analytes, for example to label biomolecules.
Owner:ATTO TEC
Limited play optical storage medium, method for making the same
InactiveUS20050013232A1Timely controlEnhance limited playabilityLayered productsPhotomechanical apparatusExtinctionFiltration
In one embodiment, a limited play optical storage medium for data comprises: a reflective layer, a control portion comprising an optically transparent polymeric resin and a light absorbing material, wherein the control portion has a light transmission of greater than or equal to about 70% at 650 nm, a curing index of greater than or equal to about 0.1 and a filtration index of greater than or equal to about 2.5, and wherein the light absorbing material has a minimum extinction coefficient (measured in CH2Cl2 solution) at 600 nm of greater than or equal to 1,500 mol−1·cm−1·L, a maximum extinction coefficient (measured in CH2Cl2 solution) at 650 nm of less than about 1,000 mol1·cm−1·L, a ratio of extinction coefficient at 650 nm to 600 nm less than about 0.1, and a reactive layer disposed between the reflective layer and the control portion, wherein the reactive layer is designed to limit the time during which data on the medium (disposed on a side of the reactive layer opposite the control portion), can be accessed after exposure to oxygen.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ophthalmic devices comprising photochromic materials having extended PI-conjugated systems
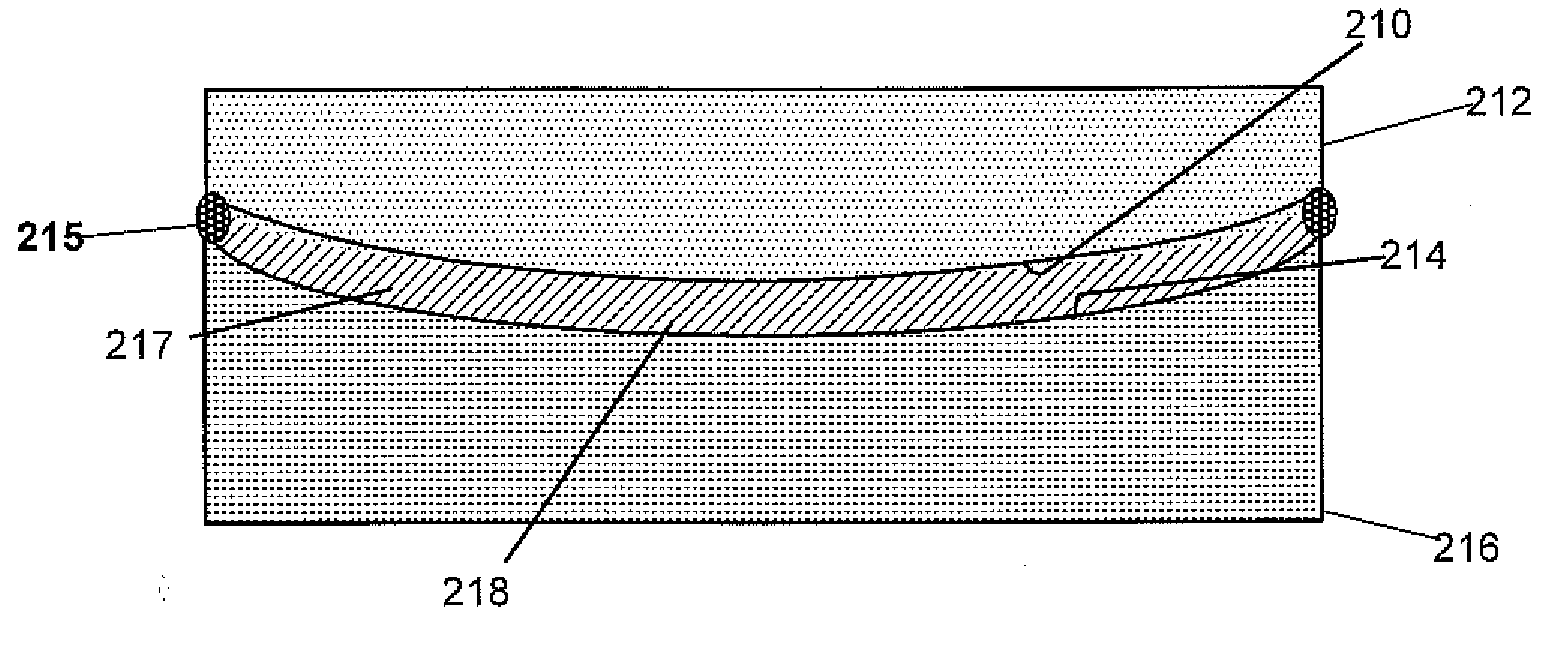
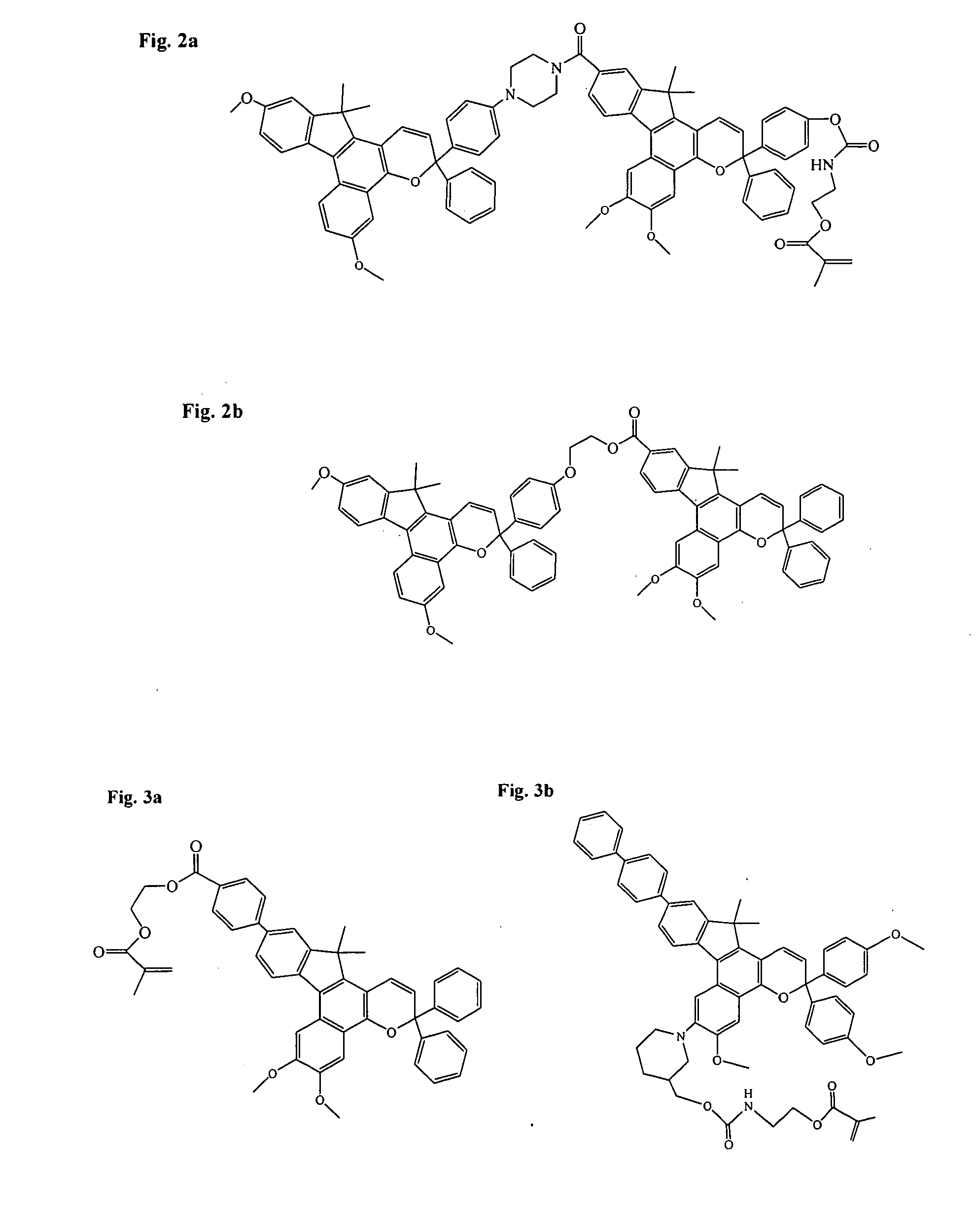
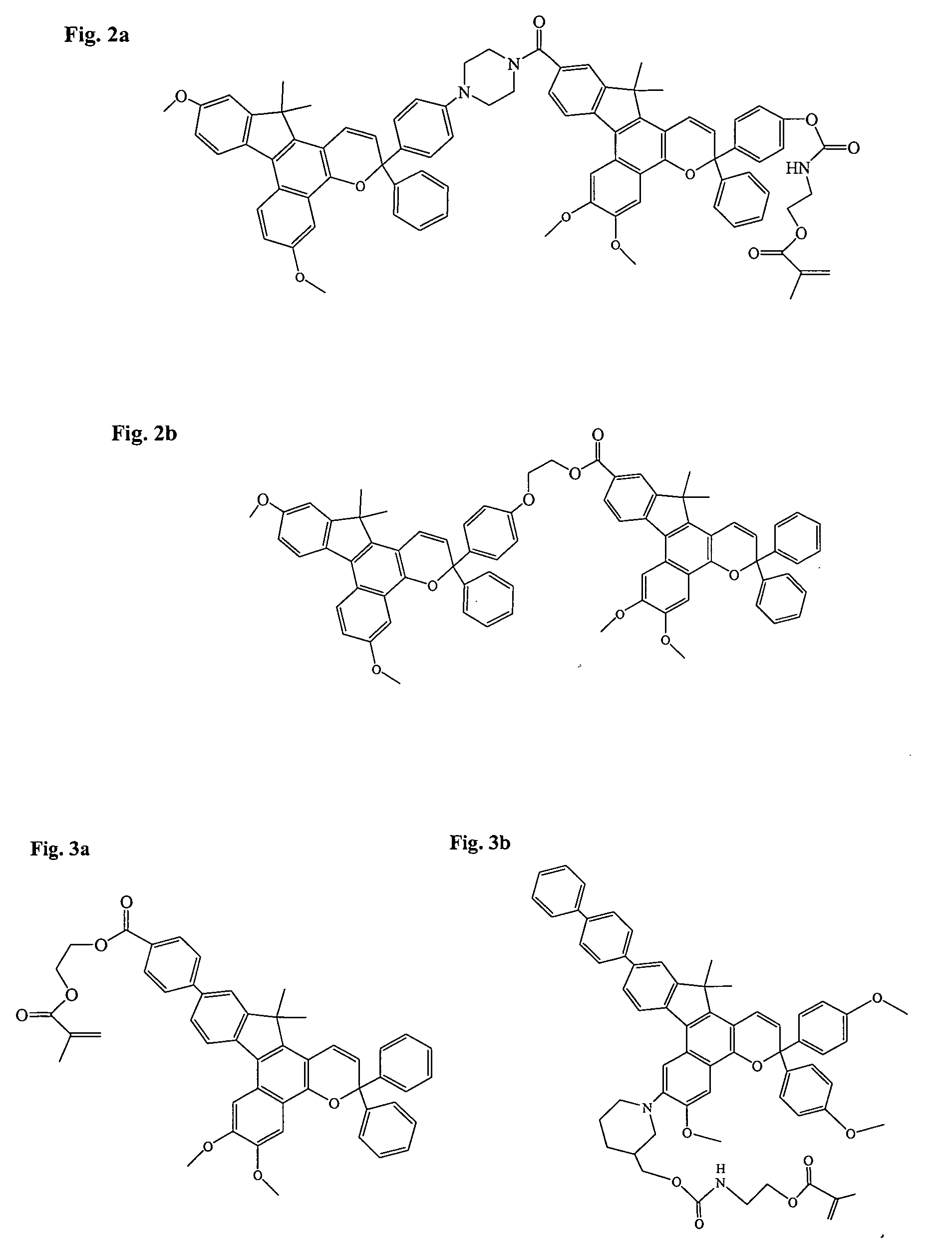
Various non-limiting embodiments disclosed herein relate to ophthalmic devices comprising photochromic materials having extended pi-conjugated systems. For example, various non-limiting embodiments disclosed herein provide a photochromic material, such as an indeno-fused naphthopyran, which comprises a group that extends the pi-conjugated system of the indeno-fused naphthopyran bonded at the 11-position of thereof. Further, the photochromic materials according to certain non-limiting embodiments disclosed herein may display hyperchromic absorption of electromagnetic radiation as compared to conventional photochromic materials and / or may have a closed-form absorption spectrum that is bathochromically shifted as compared to conventional photochromic materials. Other non-limiting embodiments relate to methods of making the ophthalmic devices comprising photochromic materials.
Owner:KIM BEON KYU +6
Environmental sensitive fluorogenic compounds and their application for singlet oxygen and protein detection
InactiveUS20050214807A1More sensitiveSensitive measurementOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein detectionFluorescence
Owner:JOHNSON IAIN +3
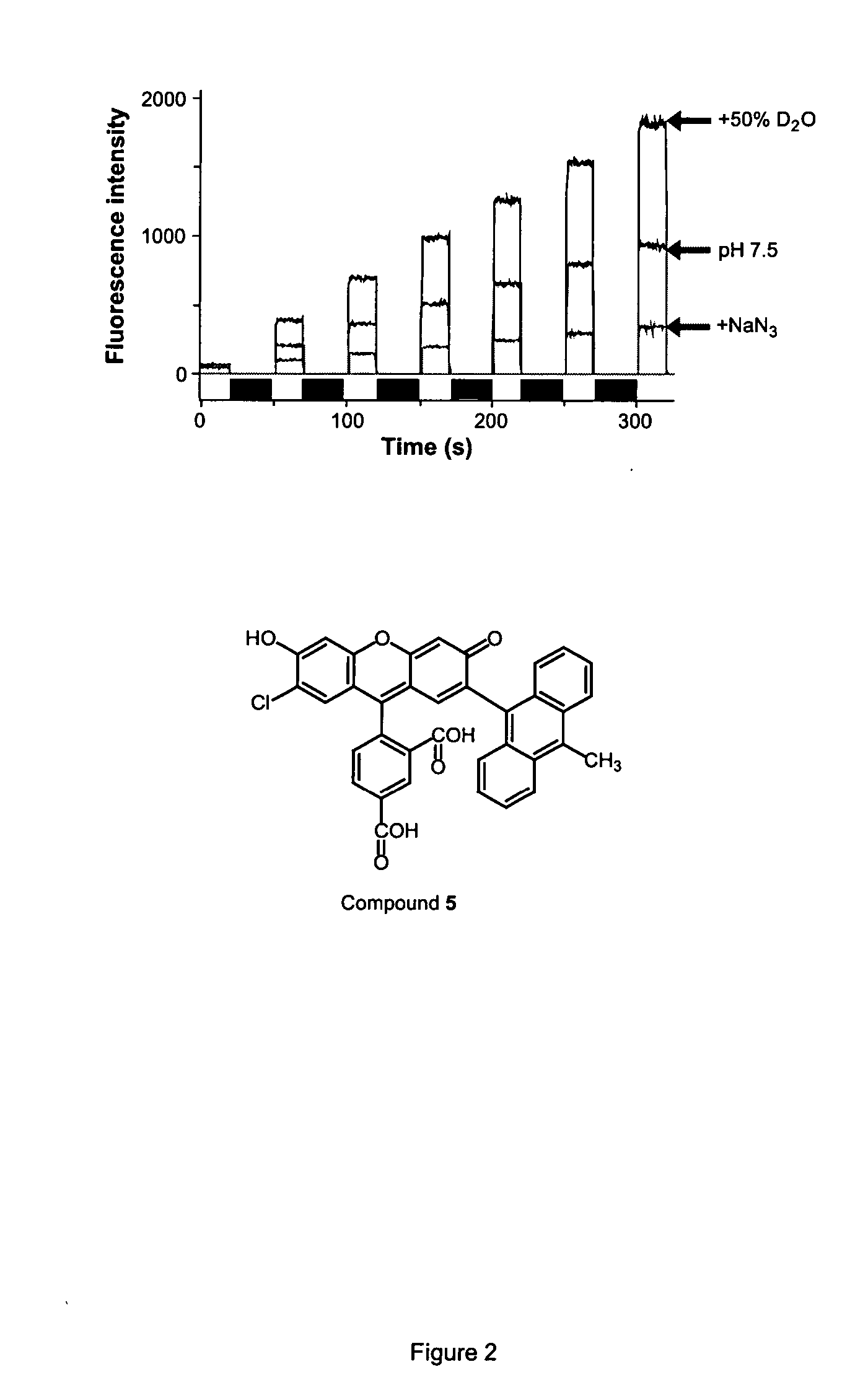
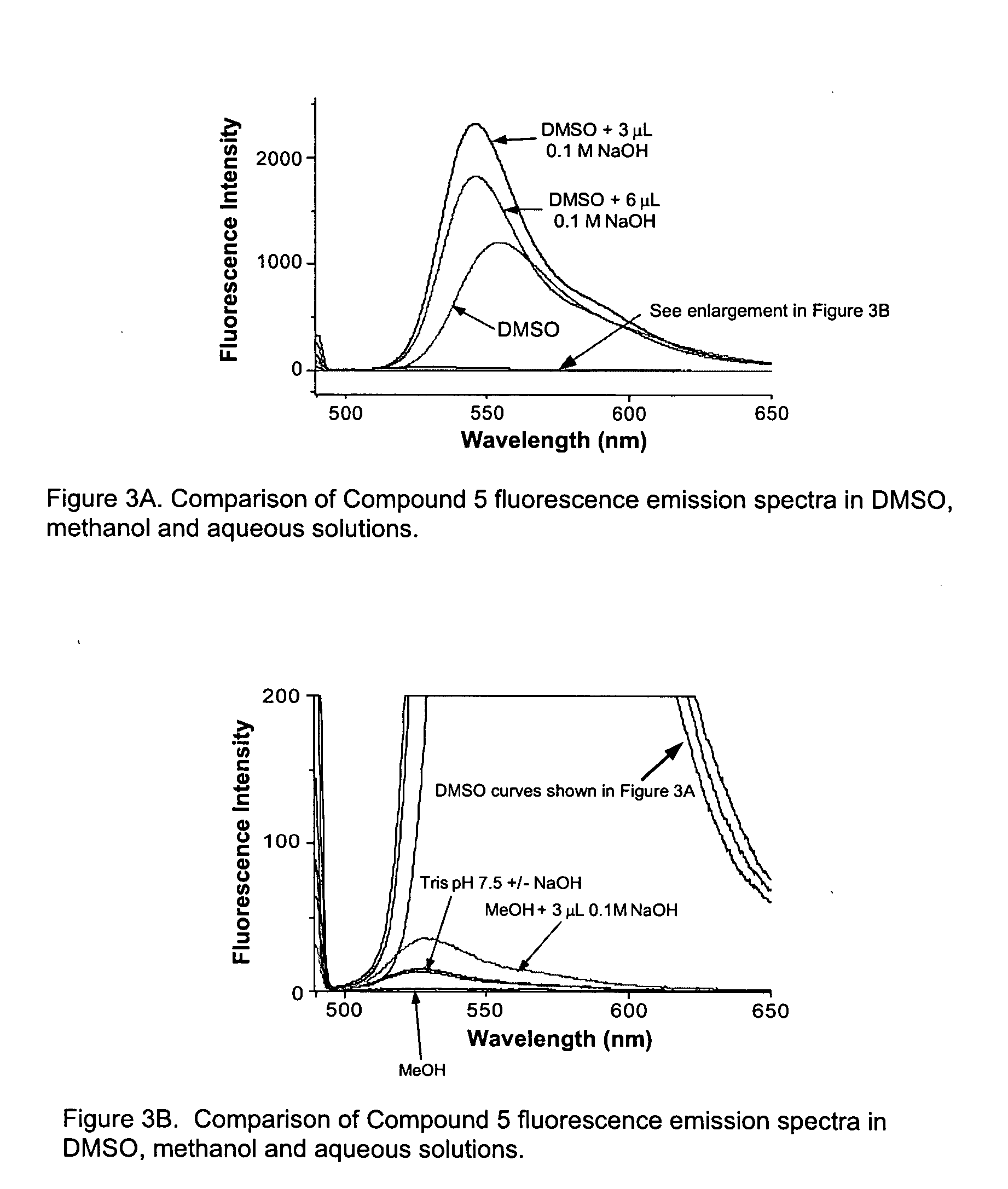
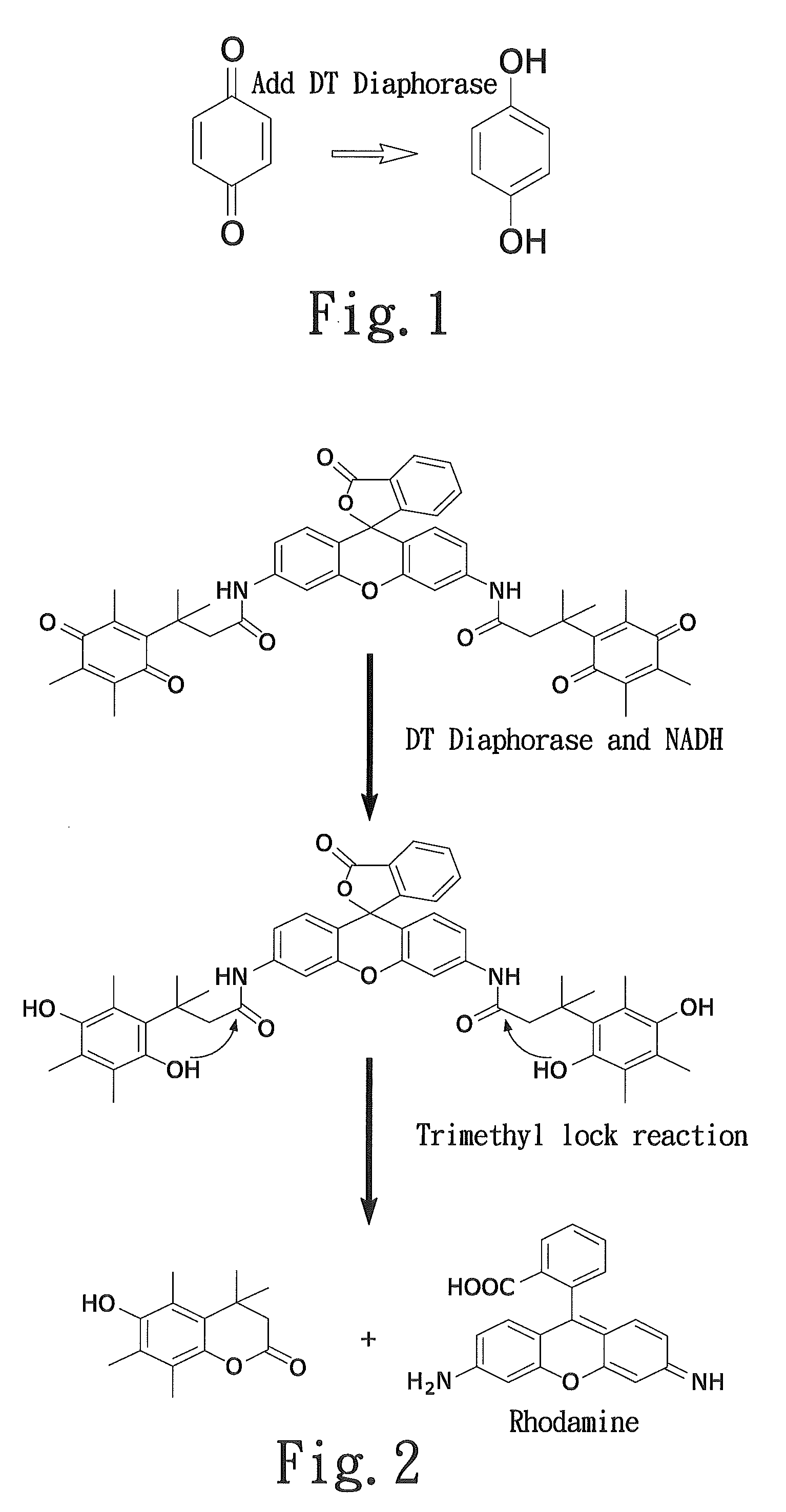
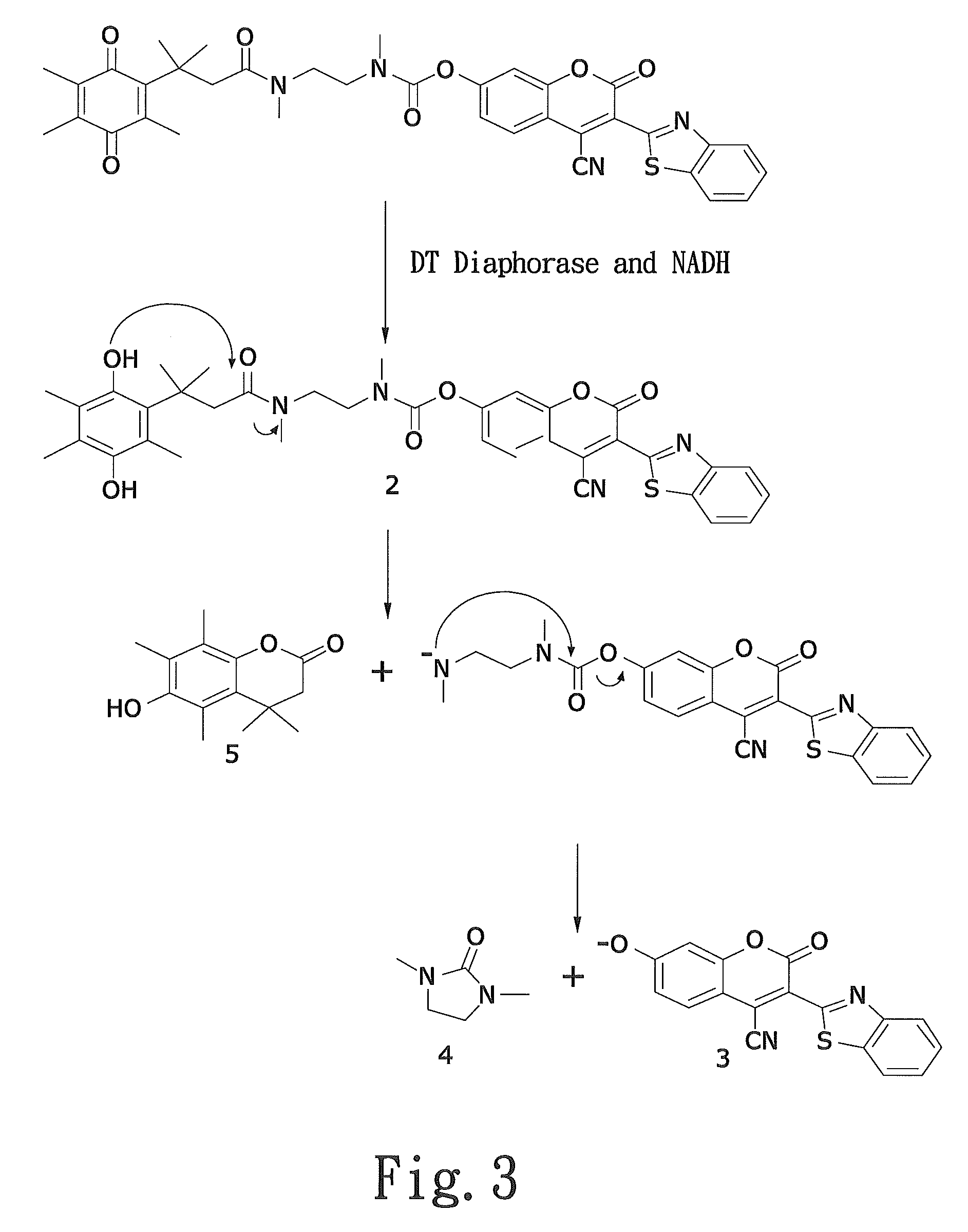
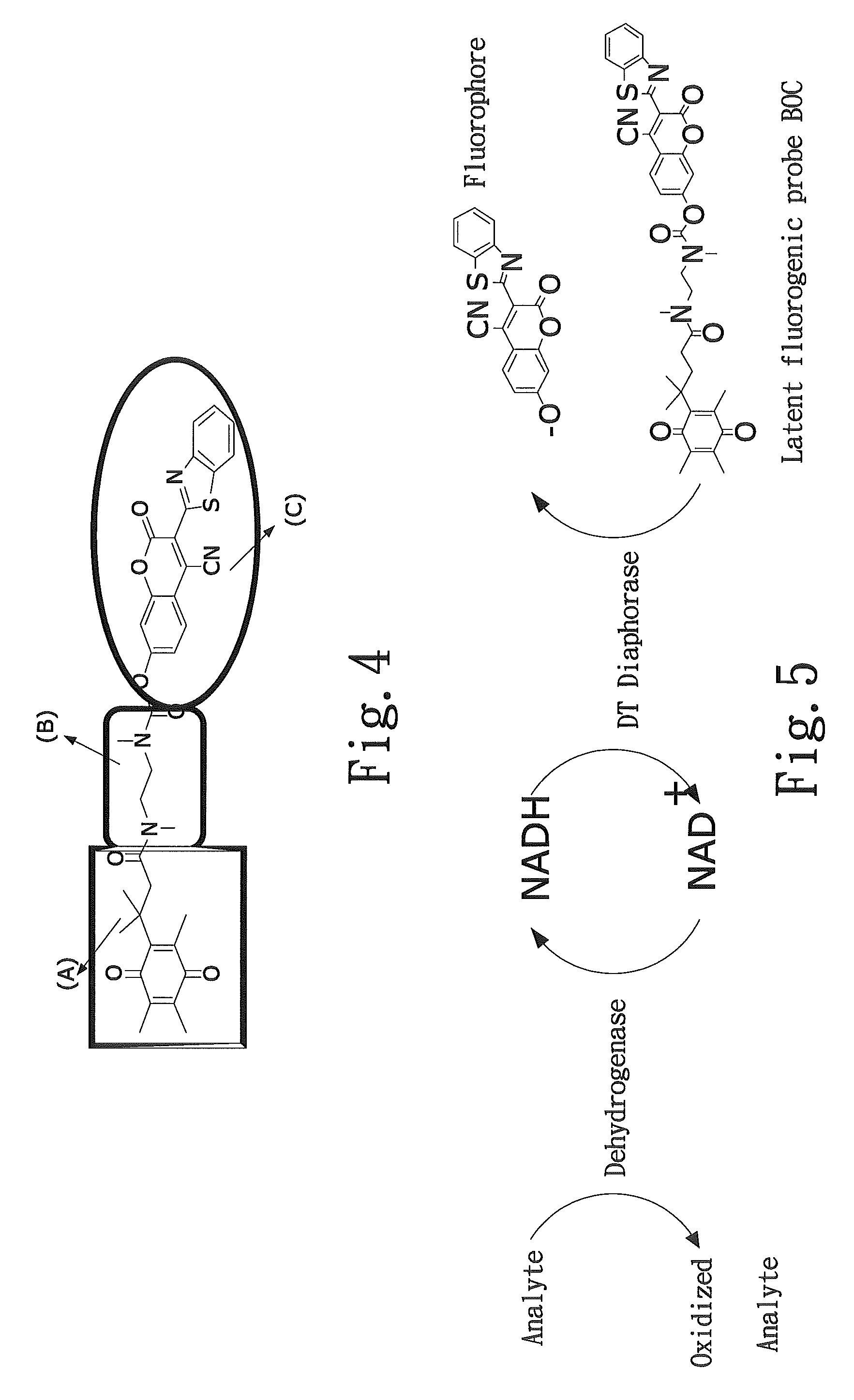
Latent fluorimetric indicator for biological analytes determination and the preparation method thereof
InactiveUS20100047839A1High sensitivityInterference minimizationOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteAssay
The present invention provides a sensitive fluorimetric indicator for analytes determination in the oxygen-insensitive DT-diaphorase-coupled dehydrogenases assay by omitting NADH, which is generated by reaction in the presence of analytes, which presents to the applicability as a biosensor for future clinical diagnostic. Furthermore, the novel long-wavelength latent fluorimetric indicator is also a user-friendly probe for monitoring DT-diaphorase activity. The fluorescence signal revealed by this process is specific and exhibited in the near red spectrum region.
Owner:NAT TAIPEI UNIV OF TECH
Light-emitting material for organo-electroluminescence device and for organic electroluminescence device which the material is applied
InactiveUS20010033944A1Organic chemistryMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic electroluminescenceLight emission
A light-emitting material which serves to emit light having a high brightness and is almost free of deterioration in light emission, and an organic EL device for which the light-emitting material is adapted, the material having the formula (1) disclosed in claim 1, 2 or 3.
Owner:TOYO INK SC HOLD CO LTD
Rapid fluorescence tagging of glycans and other biomolecules with enhanced ms signals
ActiveUS20140179011A1Strong fluorescent signalStrong signalOrganic chemistryNaphthalimide/phthalimide dyesGlycanFluorescence
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Two-photon absorption dye-containing material, three-dimensional refractive index modulation material, three-dimensional absorption index modulation material and three-dimensional optical recording material
InactiveUS20050019711A1Improve preservation qualityImprove spatial resolutionStyryl dyesMonoazo dyesTwo-photon absorptionOptical recording
To provide a two-photon absorption dye-containing material having a great off-resonant two-photon absorption cross section and comprising a two-photon absorption dye capable of decoloring itself through off-resonant two-photon absorption, useful for a three-dimensional refractive index or absorption index modulation material, a three-dimensional optical recording medium, three-dimensional refractive index modulation method and recording and reproducing method for a three-dimensional optical recording medium a two-photon absorption dye-containing material comprising at least a two-photon absorption dye capable of decoloring itself through two-photon absorption.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Dye for dye-sensitized solar cell, and solar cell prepared from same
The present embodiments relate to a dye for a dye-sensitized solar cell and a dye-sensitized solar cell prepared from the same. The dye includes a fluorenyl-containing compound. The dye according to the present embodiments is applied to a light absorption layer to improve photovoltaic efficiency and increase an open-circuit voltage.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Clear to circular polarizing photochromic devices and methods of making the same
The present invention provides optical elements comprising a photochromic linear polarizing element and a birefringent layer that circularly or elliptically polarizes transmitted radiation. The photochromic linear polarizing element comprises a substrate and either: (1) a coating comprising an aligned, thermally reversible photochromic-dichroic compound having an average absorption ratio of at least 1.5 in an activated state, and being operable for switching from a first absorption state to a second absorption state in response to actinic radiation, to revert back to the first absorption state in response to thermal energy, and to linearly polarize transmitted radiation in at least one of the two states; or (2) an at least partially ordered polymeric sheet connected to the substrate; and a thermally reversible photochromic-dichroic compound that is at least partially aligned with the polymeric sheet and has an average absorption ratio greater than 2.3 in the activated state.
Owner:TRANSITIONS OPTICAL INC
Ophthalmic devices comprising photochromic materials having extended pi-conjugated systems
Various non-limiting embodiments disclosed herein relate to ophthalmic devices comprising photochromic materials having extended pi-conjugated systems. For example, various non-limiting embodiments disclosed herein provide a photochromic material, such as an indeno-fused naphthopyran, which comprises a group that extends the pi-conjugated system of the indeno-fused naphthopyran bonded at the 11-position of thereof. Further, the photochromic materials according to certain non-limiting embodiments disclosed herein may display hyperchromic absorption of electromagnetic radiation as compared to conventional photochromic materials and / or may have a closed-form absorption spectrum that is bathochromically shifted as compared to conventional photochromic materials. Other non-limiting embodiments relate to methods of making the ophthalmic devices comprising photochromic materials.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Luminogenic and fluorogenic compounds and methods to detect molecules or conditions
ActiveUS20080299593A1Low backgroundHigh sensitivityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionLuciferinFluorescein
A method to detect the presence or amount of at least one molecule in a sample which employs a derivative of luciferin or a derivative of a fluorophore is provided. Compounds and compositions for carrying out the methods of the invention are also provided.
Owner:PROMEGA CORP
Polarizing, photochromic devices and methods of making the same
Owner:TRANSITIONS OPTICAL INC
Rapid fluorescence tagging of glycans and other biomolecules with enhanced ms signals
ActiveUS20140242709A1Rapid fluorescence taggingQuick tagOrganic chemistryNaphthalimide/phthalimide dyesGlycanReagent
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Fluorescent retroreflective sheet
This invention provides encapsulated type fluorescent retroreflective sheeting which is excellent in appearance and weatherability, and which comprises a surface-protective layer disposed on the side on which light is to strike, a binder layer connected to the surface-protective layer through network bonding parts, an air layer which is sealed-up by the network bonding parts between the surface-protective layer and the binder layer, and a retroreflective element layer disposed between the surface-protective layer and the air layer, or between the binder layer and the air layer, wherein at least one layer located on the light-incident side of sealed-up air layer contains at least one fluorescent dye selected from the group consisting of benzimidazole coumarin type-fluorescent dyes of formula (1) as follows: and benzopyran type-fluorescent dyes of formula (2) as follows:
Owner:NIPPON CARBIDE KOGYO KK
Dye for dye-sensitized solar cell, and solar cell prepared from same
InactiveUS20070240756A1Improve photoelectric efficiencyMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic chemistrySolar cellPhotochemistry
The present embodiments relate to a dye for a dye-sensitized solar cell and a dye-sensitized solar cell prepared from the same. The dye includes a fluorenyl-containing compound. The dye according to the present embodiments is applied to a light absorption layer to improve photovoltaic efficiency and increase an open-circuit voltage.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Polarizing photochromic articles
Provided are photochromic articles that include a substrate, a primer layer that includes a first photochromic compound, and a photochromic-dichroic layer over the primer layer that includes a photochromic-dichroic compound. The first photochromic compound and the photochromic-dichroic compound each are selected such that the photochromic-dichroic compound has an absorbance of less than or equal to 0.1 at the wavelength of peak absorbance of the underlying first photochromic compound. The present invention also relates to such photochromic articles that further include a topcoat layer over the photochromic-dichroic layer. The topcoat layer can include a second photochromic compound that has an absorbance of less than 0.1 at the wavelength of peak absorbance of the underlying photochromic-dichroic compound. The photochromic articles provide, for example, a combination of linear polarizing properties, and reduced percent transmittance when in a colored or darkened state, such as when exposed to actinic light.
Owner:TRANSITIONS OPTICAL INC
Reactive labelling compounds and uses thereof
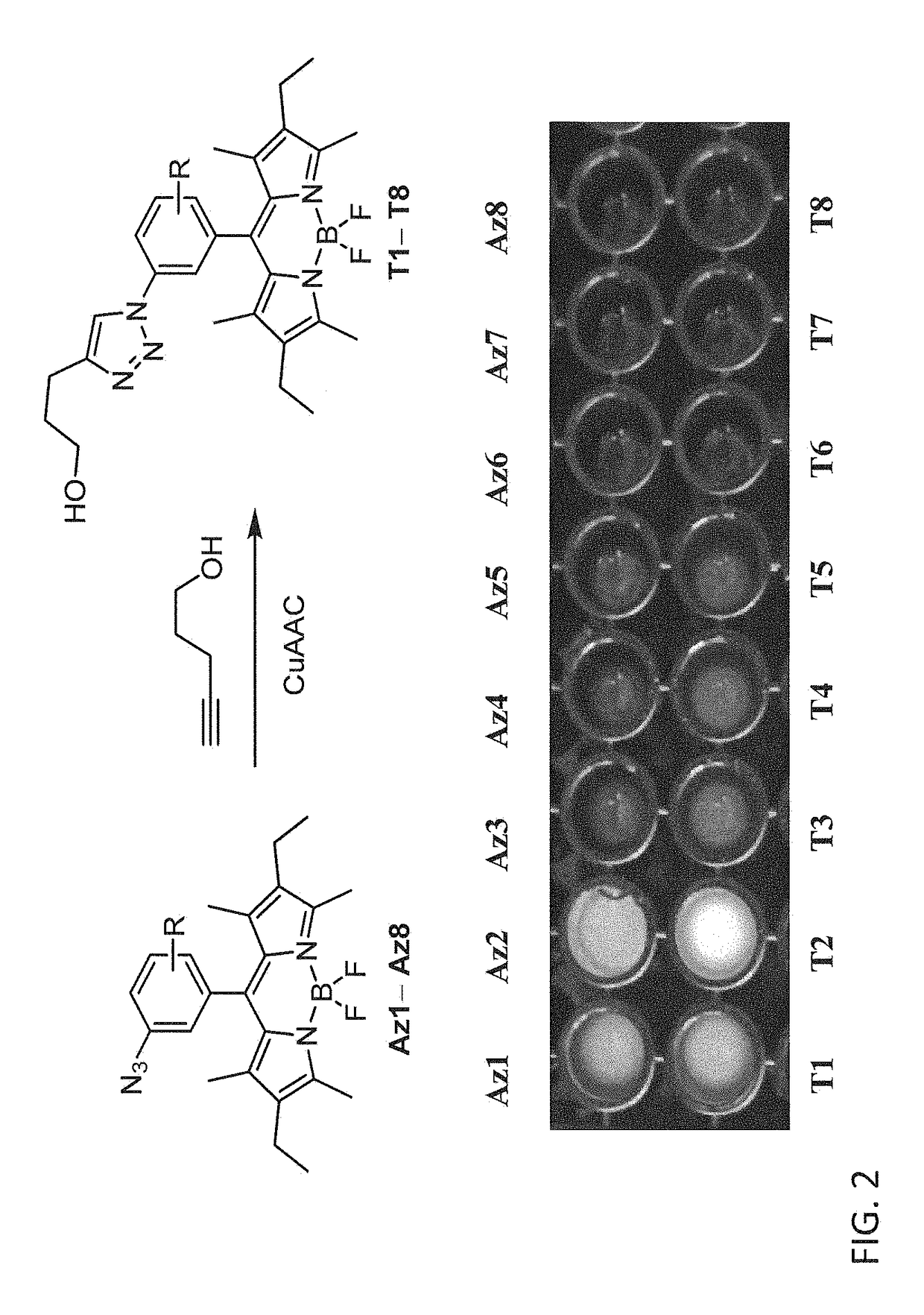
ActiveUS9759726B2Fluorescence enhancementEasy to detectPeptidesGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsAlkyneCombinatorial chemistry
Provided are azido-BODIPY compounds of formula (I), cyclooctyne-based fluorogenic probes of formula (IV), and activity-based probes of formula (VI). These compounds undergo azide-alkyne cycloadditions (AAC) with to form triazolyl products. The provided compounds are useful for detection and imaging of alkyne-, or azide-containing molecules. Methods for detection and imaging biomolecules using compounds of the present disclosure are disclosed.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Photochromic materials having extended pi-conjugated systems and compositions and articles including the same
InactiveUS20090032782A1Organic chemistrySpiro-condensed pyran compound compositionsElectromagnetic radiationPhotochromism
Various non-limiting embodiments disclosed herein relate to photochromic materials having extended pi-conjugated systems, such as an indeno-fused naphthopyran, which comprises a group that extends the pi-conjugated system of the indeno-fused naphthopyran bonded at the 11-position thereof. Further, the photochromic materials according to certain non-limiting embodiments disclosed herein may display hyperchromic absorption of electromagnetic radiation as compared to conventional photochromic materials and / or may have a closed-form absorption spectrum that is bathochromically shifted as compared to conventional photochromic materials. Other non-limiting embodiments relate to photochromic compositions and photochromic articles, such as optical elements, made using the disclosed photochromic materials, and methods of making the same.
Owner:TRANSITIONS OPTICAL INC
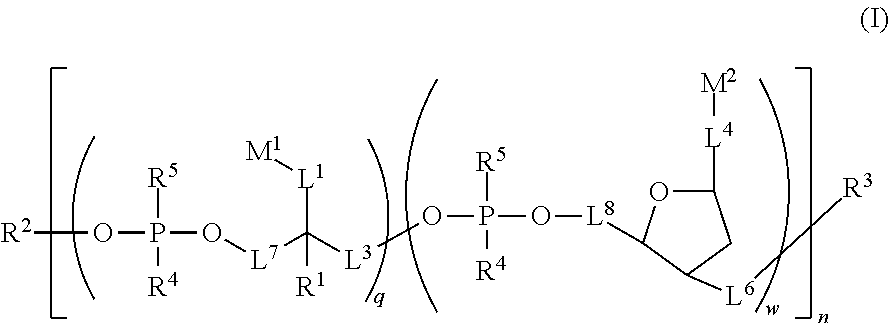
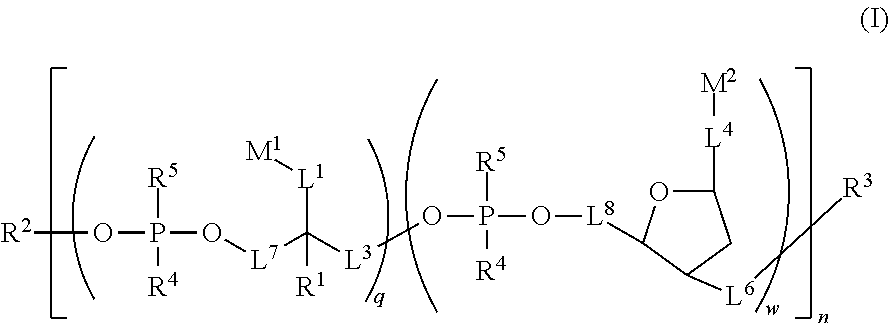
Water soluble fluorescent or colored dyes comprising conjugating groups
Compounds useful as fluorescent or colored dyes are disclosed. The compounds have the following structure (I): or a stereoisomer, tautomer or salt thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, L1, L3, L4, L6, L7, L8, M1, M2, q, w and n are as defined herein. Methods associated with preparation and use of such compounds are also provided.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com