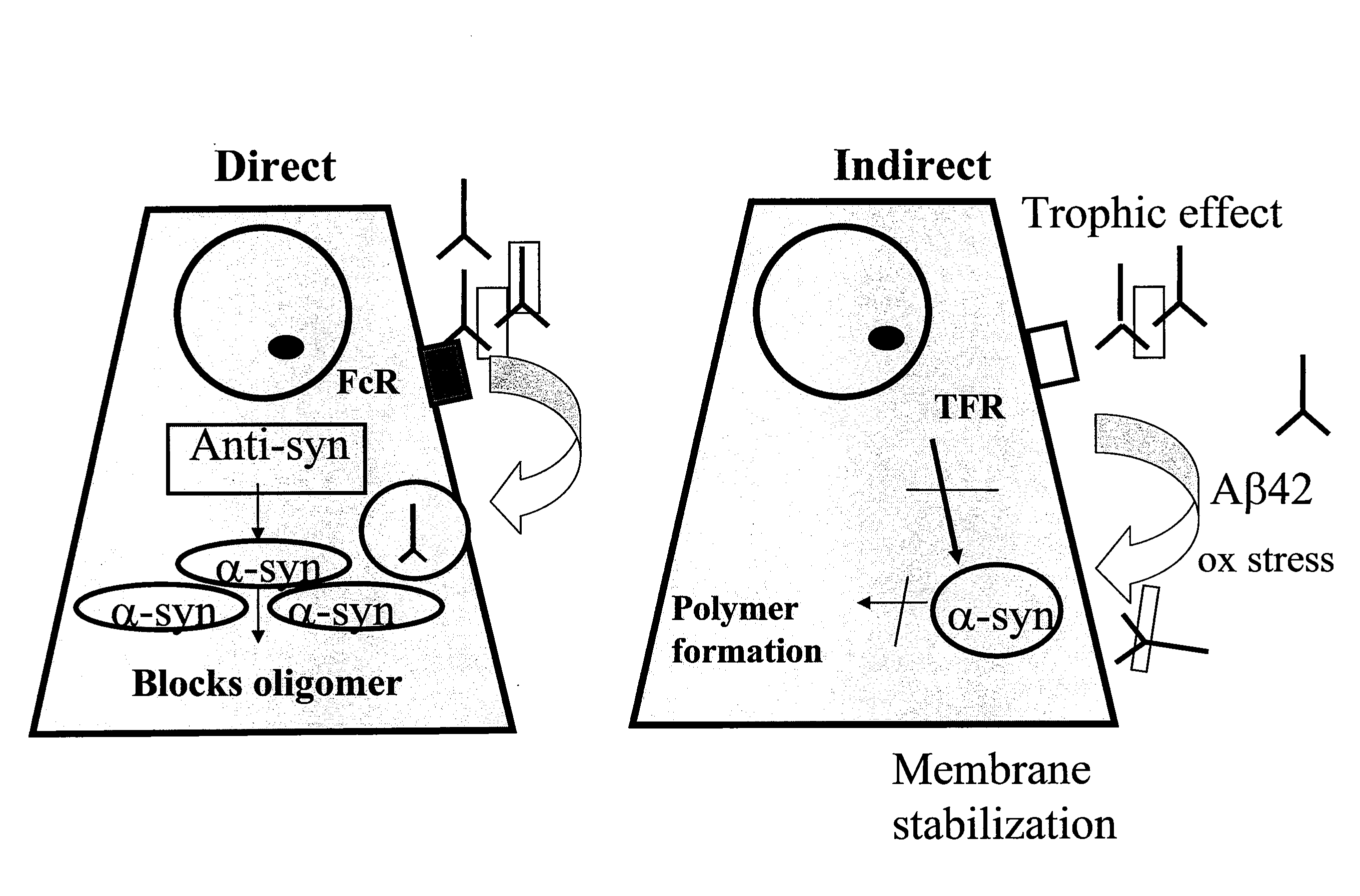
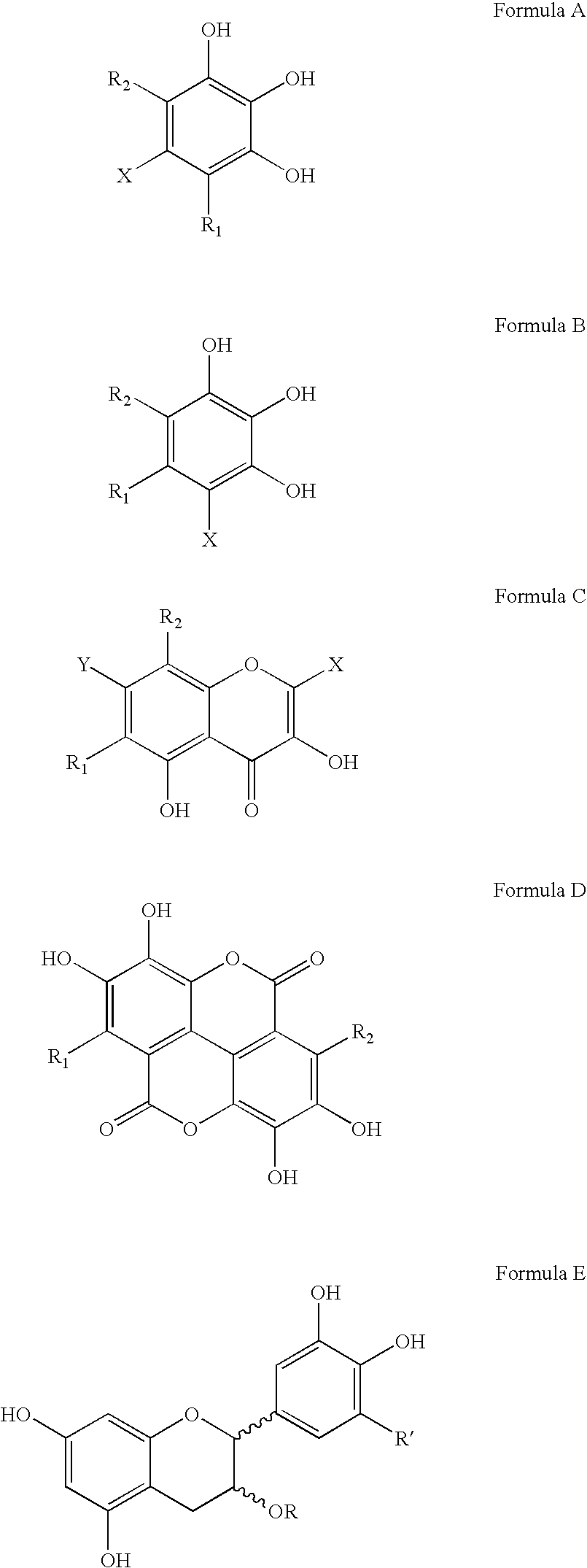
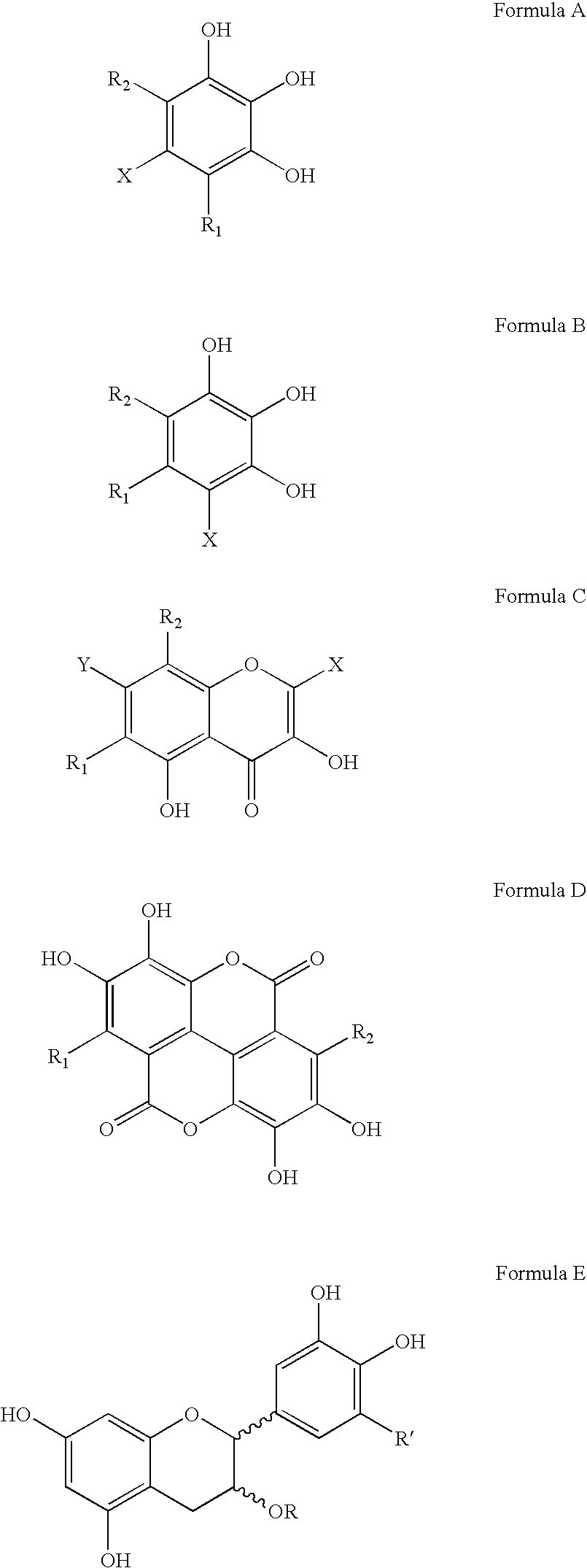
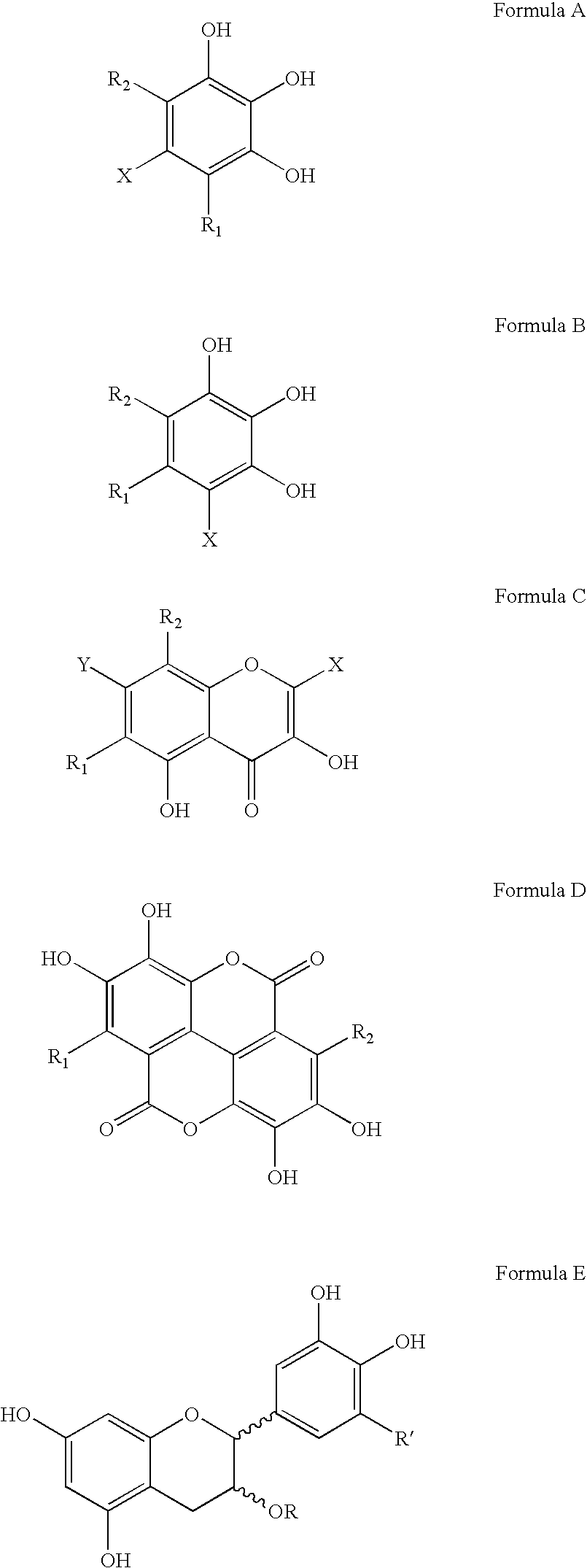
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
173 results about "Synuclein alpha" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
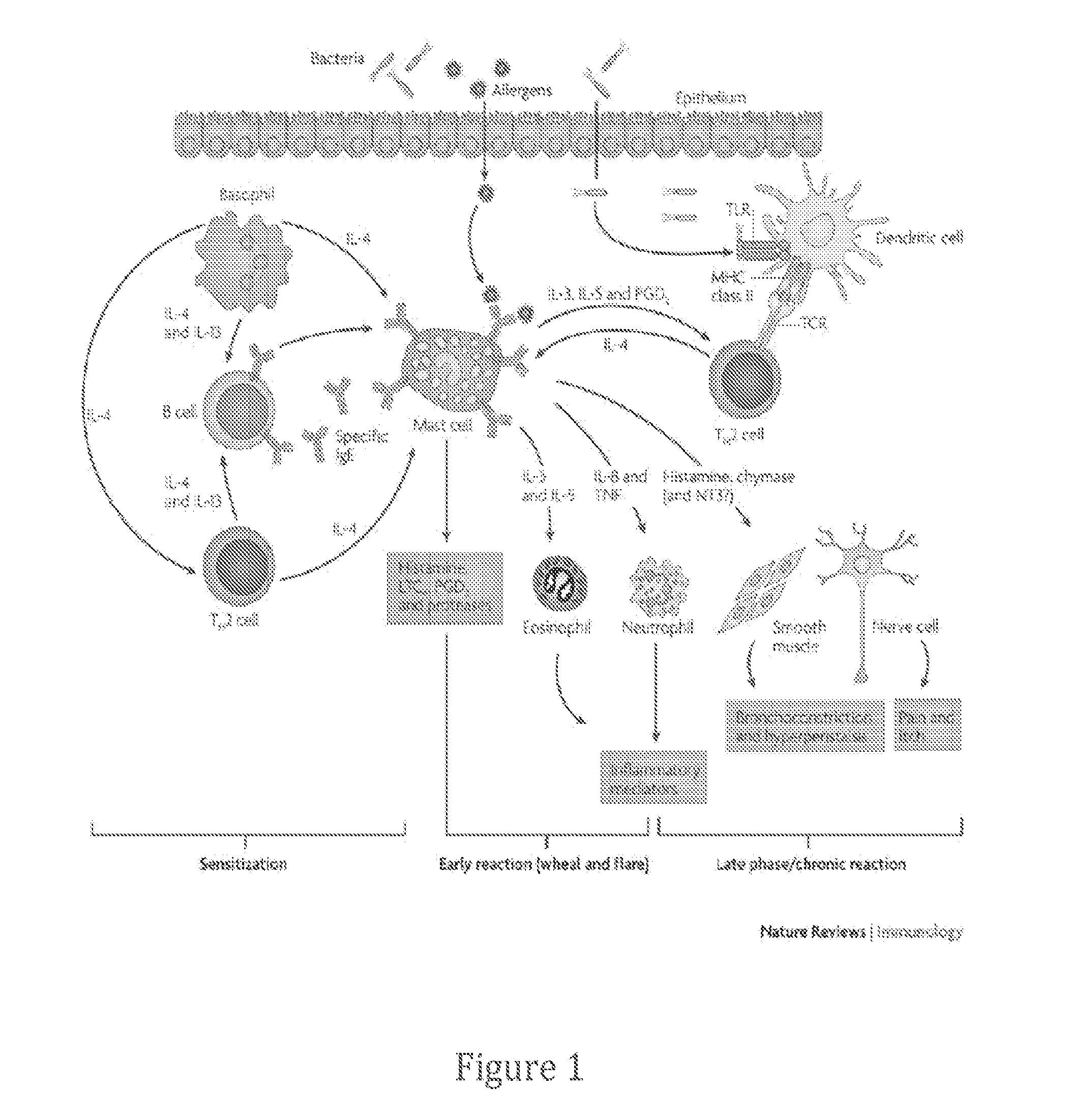
Alpha-synuclein is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the SNCA gene. It is abundant in the brain while smaller amounts are found in the heart, muscles, and other tissues. ... In the brain, alpha-synuclein is found mainly at the tips of nerve cells (neurons) in specialized structures called presynaptic terminals.
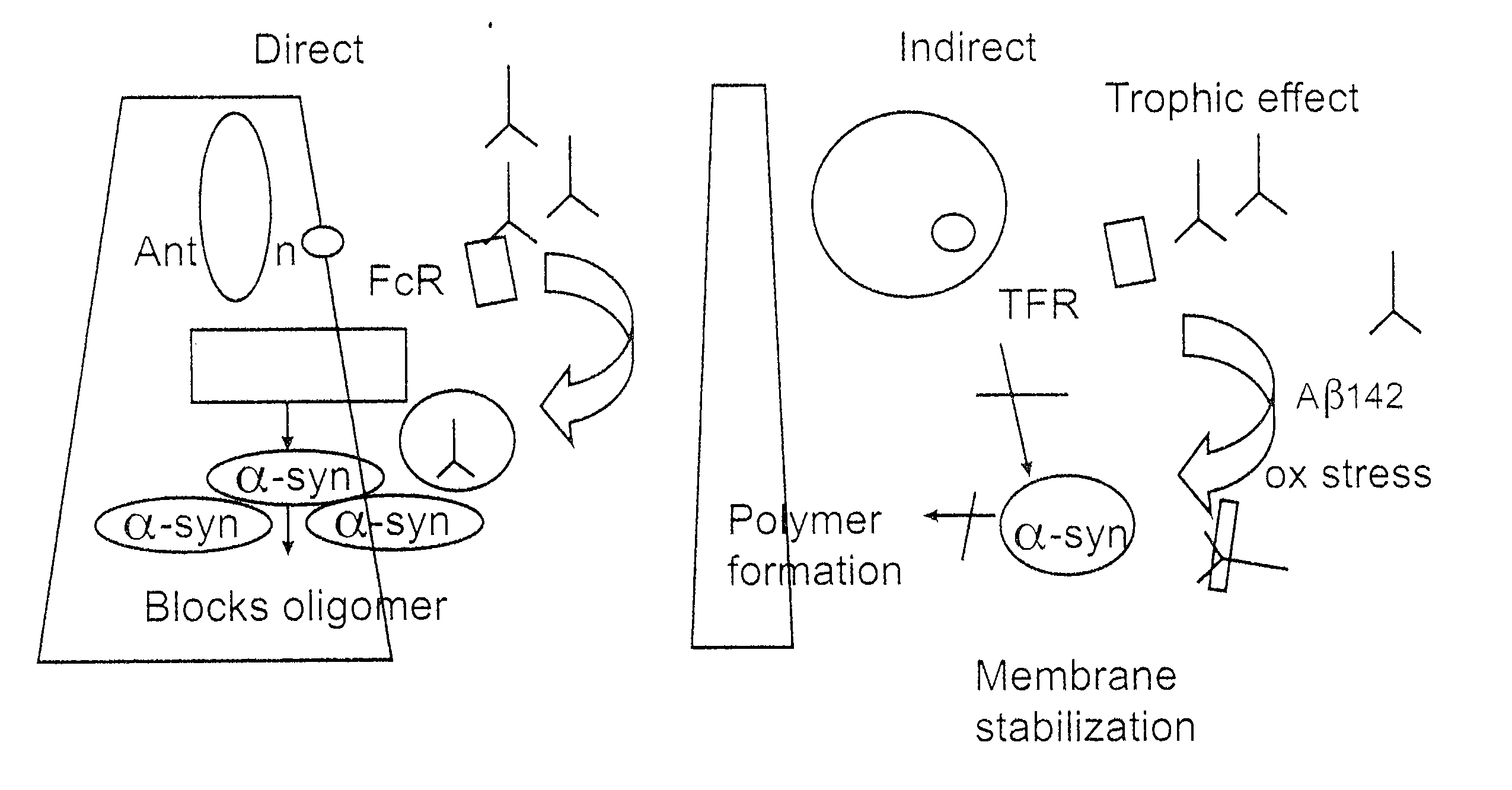
Prevention and treatment of synucleinopathic and amyloidogenic disease
ActiveUS20090208487A1Improves motor characteristicInhibit deteriorationAnimal cellsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansSynucleinLewy body
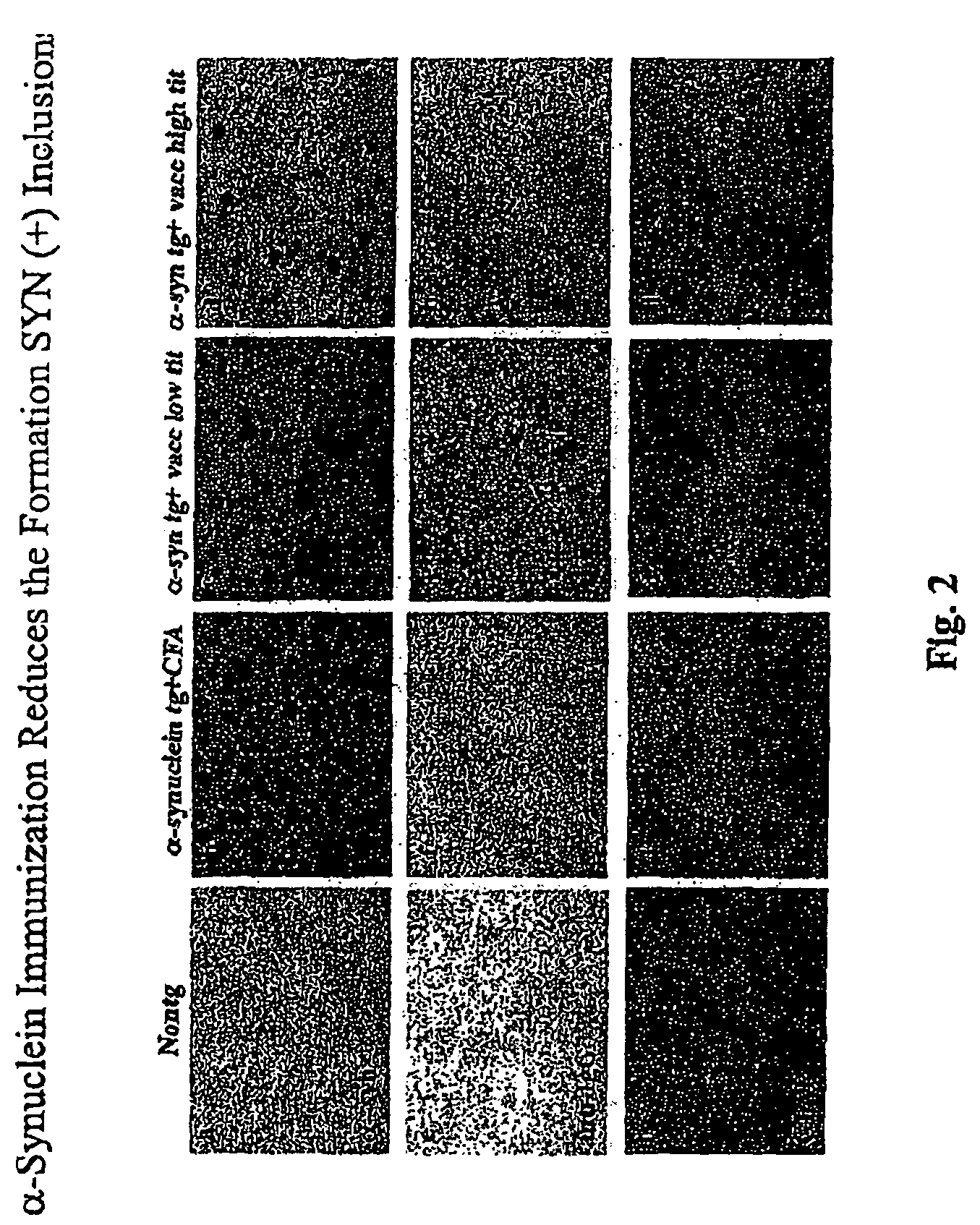
The invention provides improved agents and methods for treatment of diseases associated with synucleinopathic diseases, including Lewy bodies of alpha-synuclein in the brain of a patient. Such methods entail administering agents that induce a beneficial immunogenic response against the Lewy body. The methods are particularly useful for prophylactic and therapeutic treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Prevention and Treatment of Synucleinopathic and Amyloidogenic Disease
InactiveUS20080014194A1Improves motor characteristicInhibit deteriorationNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansTherapeutic treatmentAmyloid
The invention provides improved agents and methods for treatment of diseases associated with synucleinopathic diseases, including Lewy bodies of alpha-synuclein in the brain of a patient. Such methods entail administering agents that induce a beneficial immunogenic response against the Lewy body. The methods are particularly useful for prophylactic and therapeutic treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:JANSSEN ALZHEIMER IMMUNOTHERAPY +1
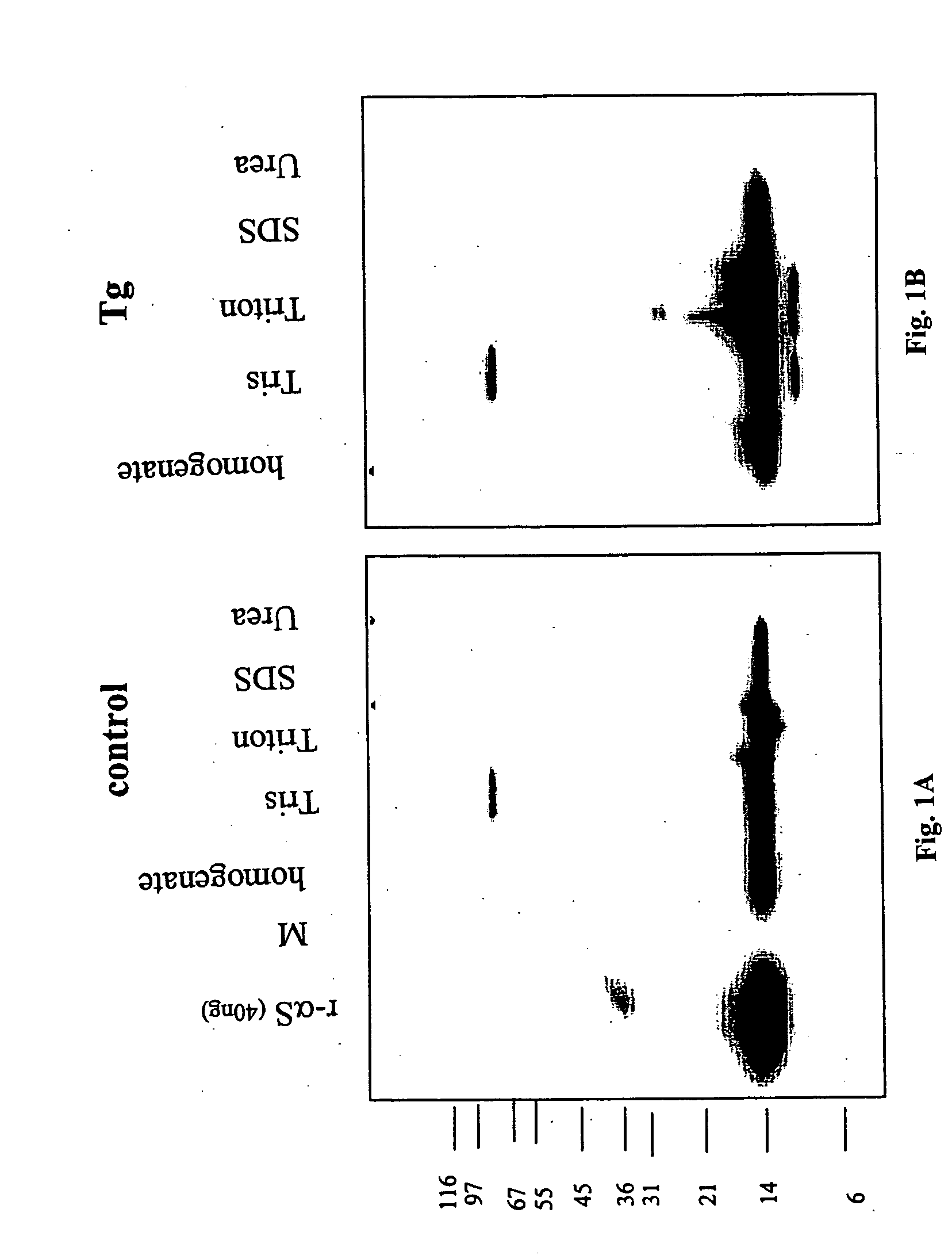
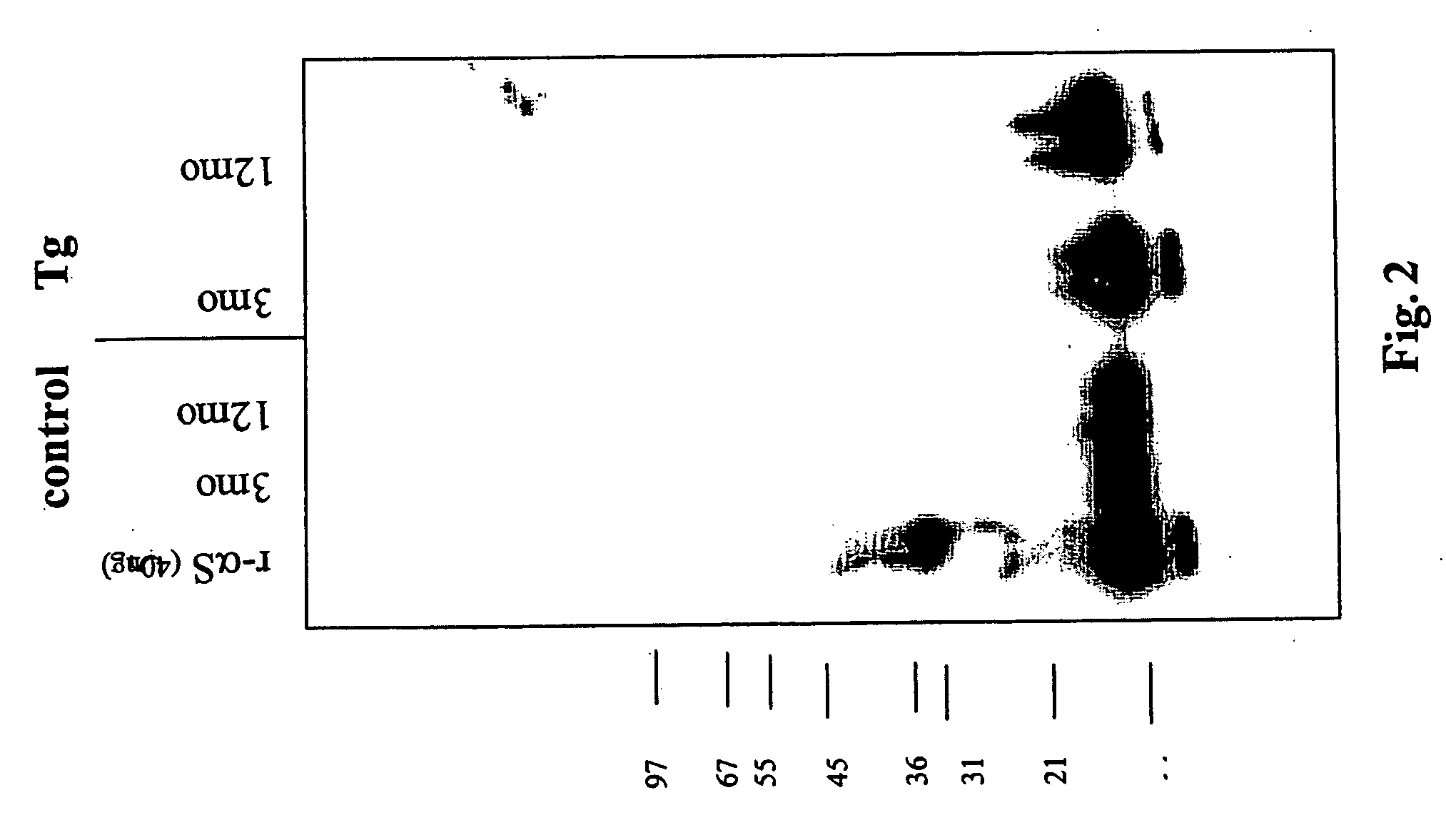
Truncated fragments of alpha-synuclein in Lewy body disease
ActiveUS20050198694A1Useful pharmacological activityBiocideNervous disorderGel electrophoresisC-terminus
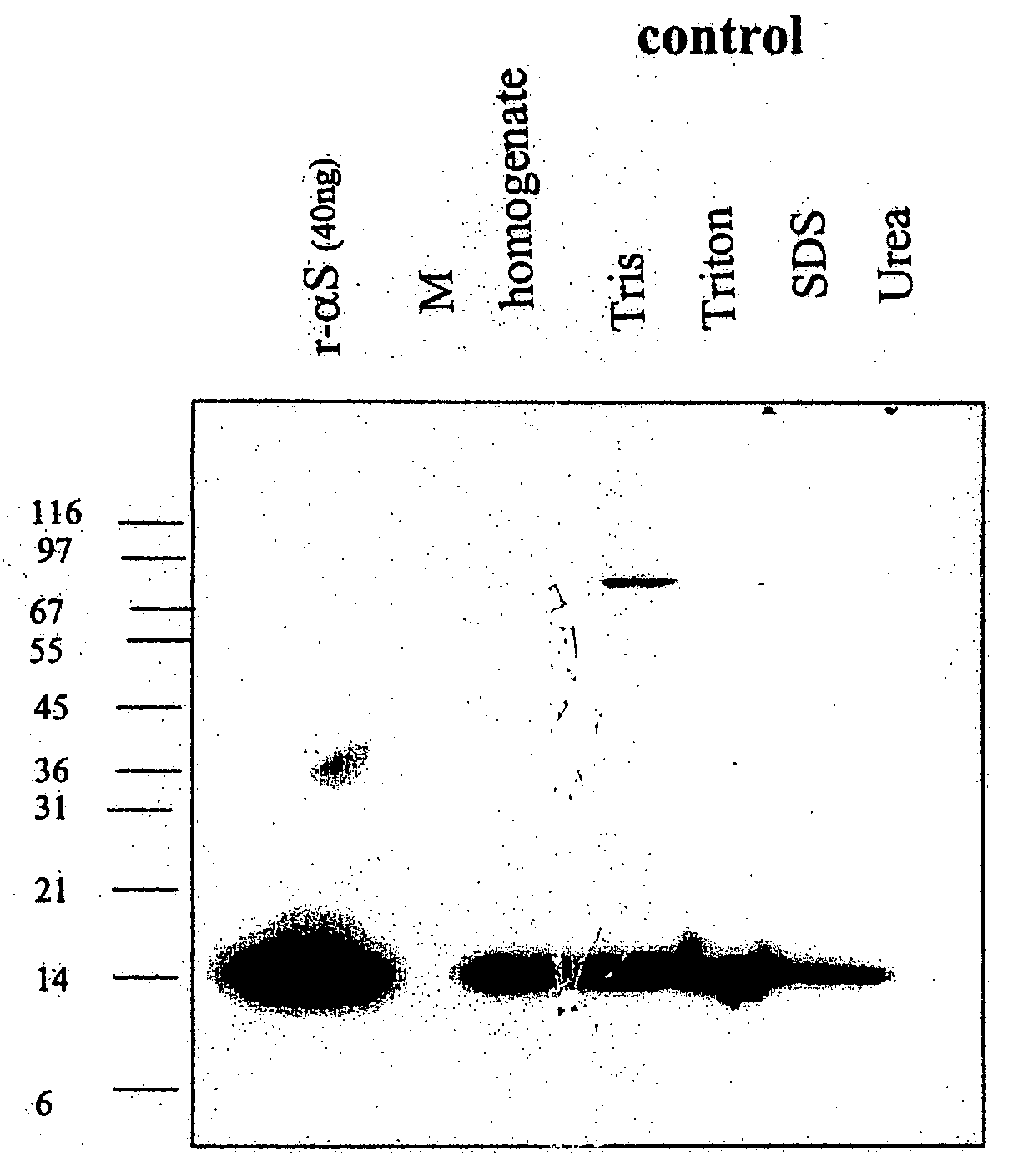
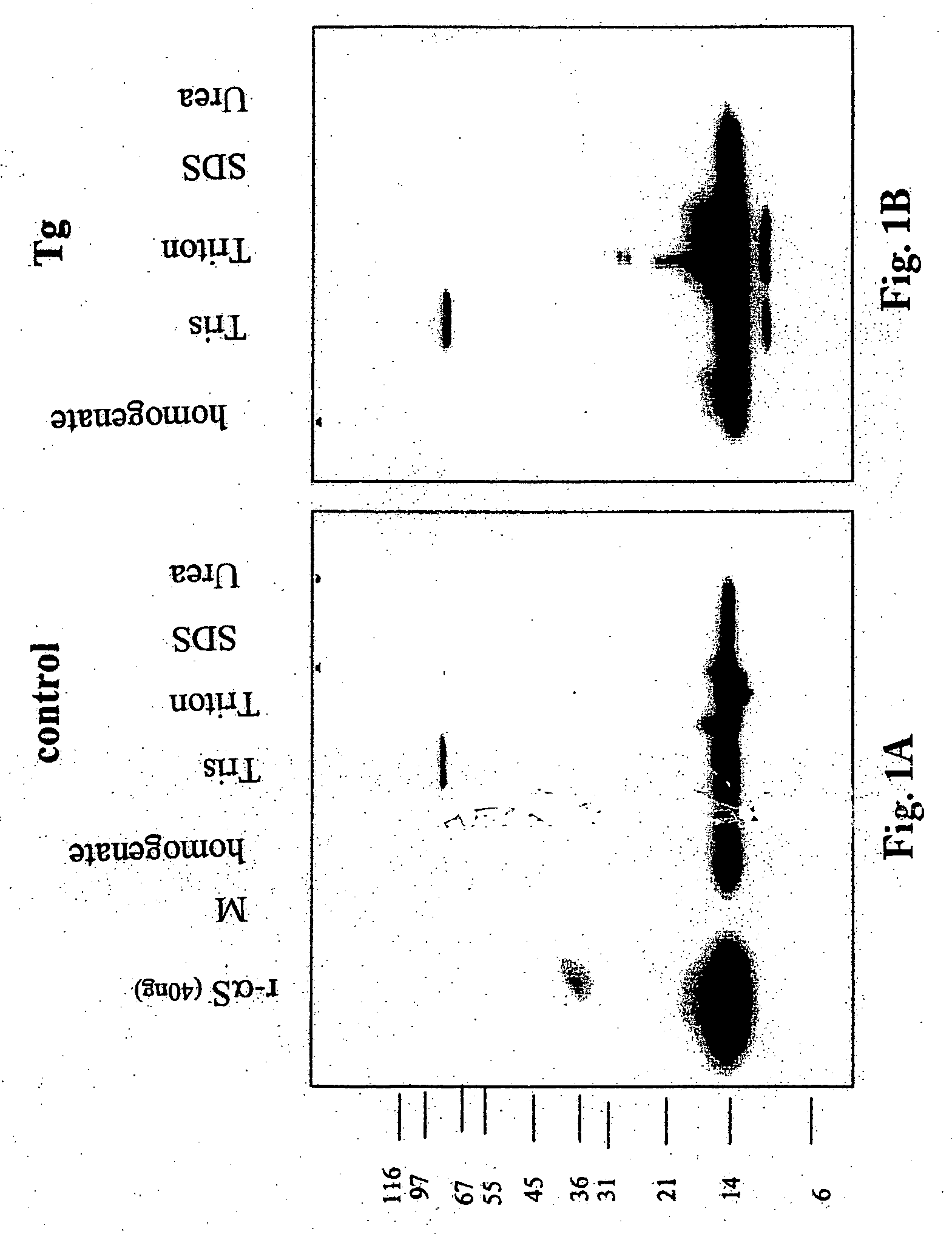
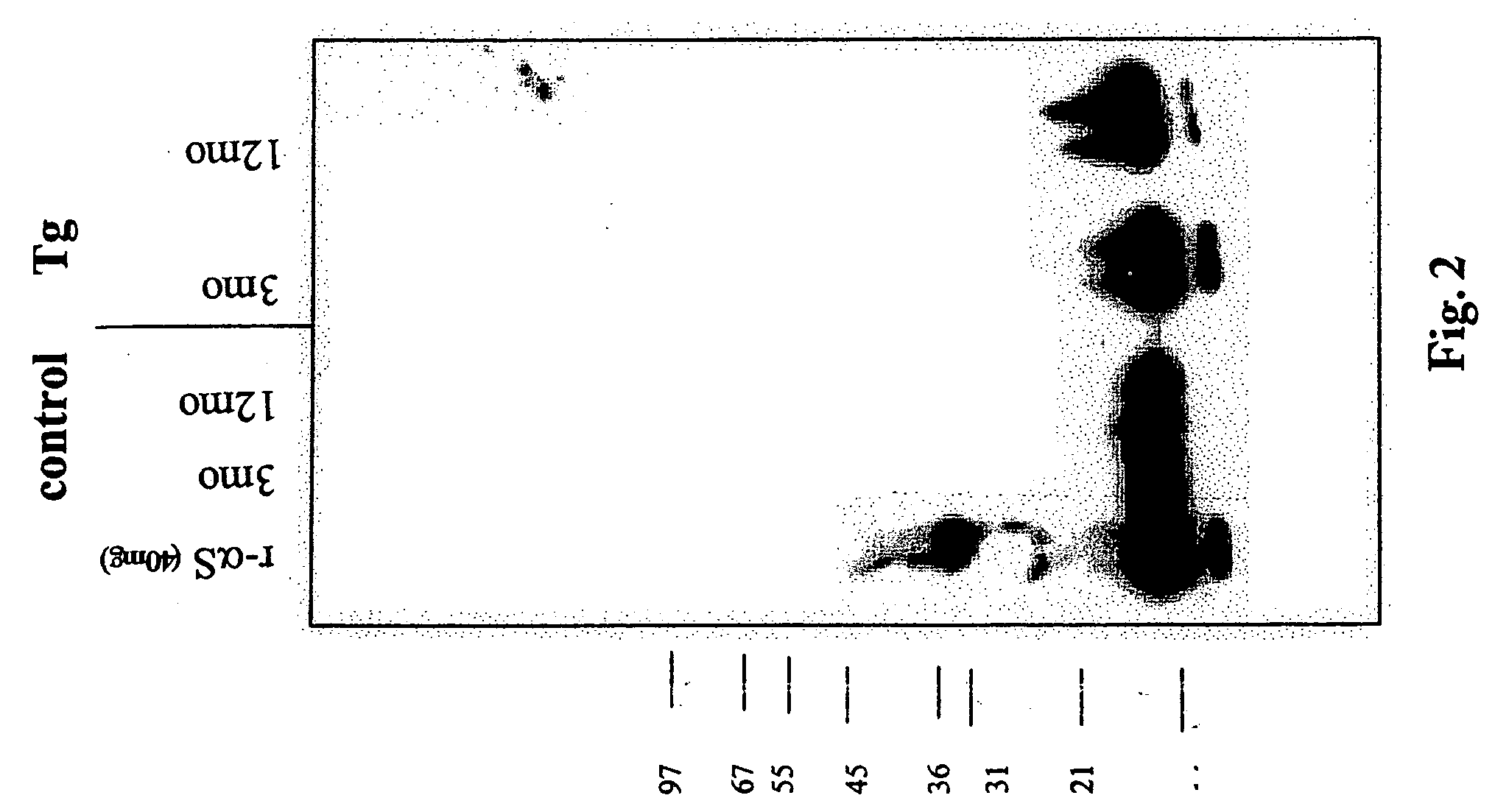
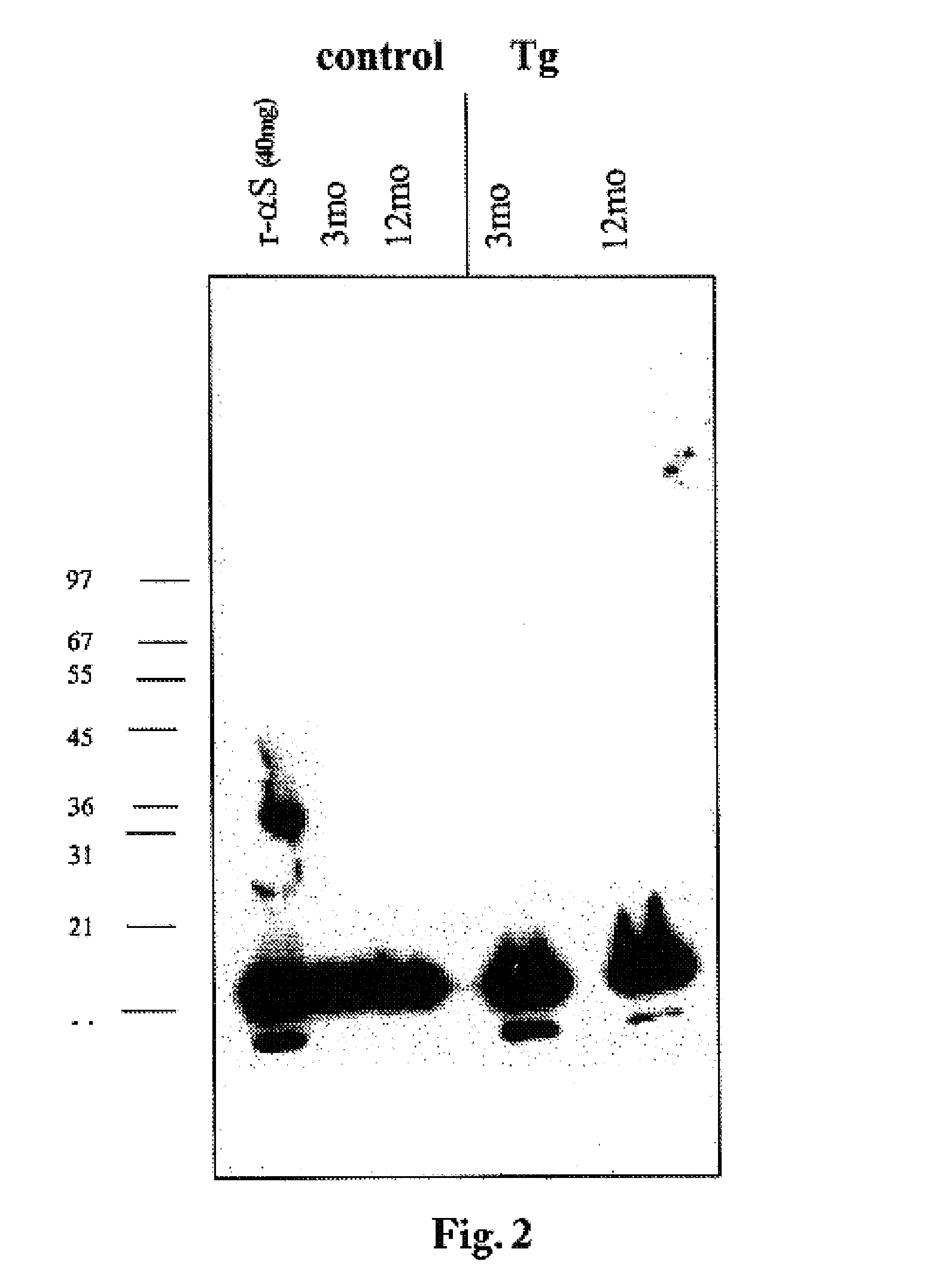
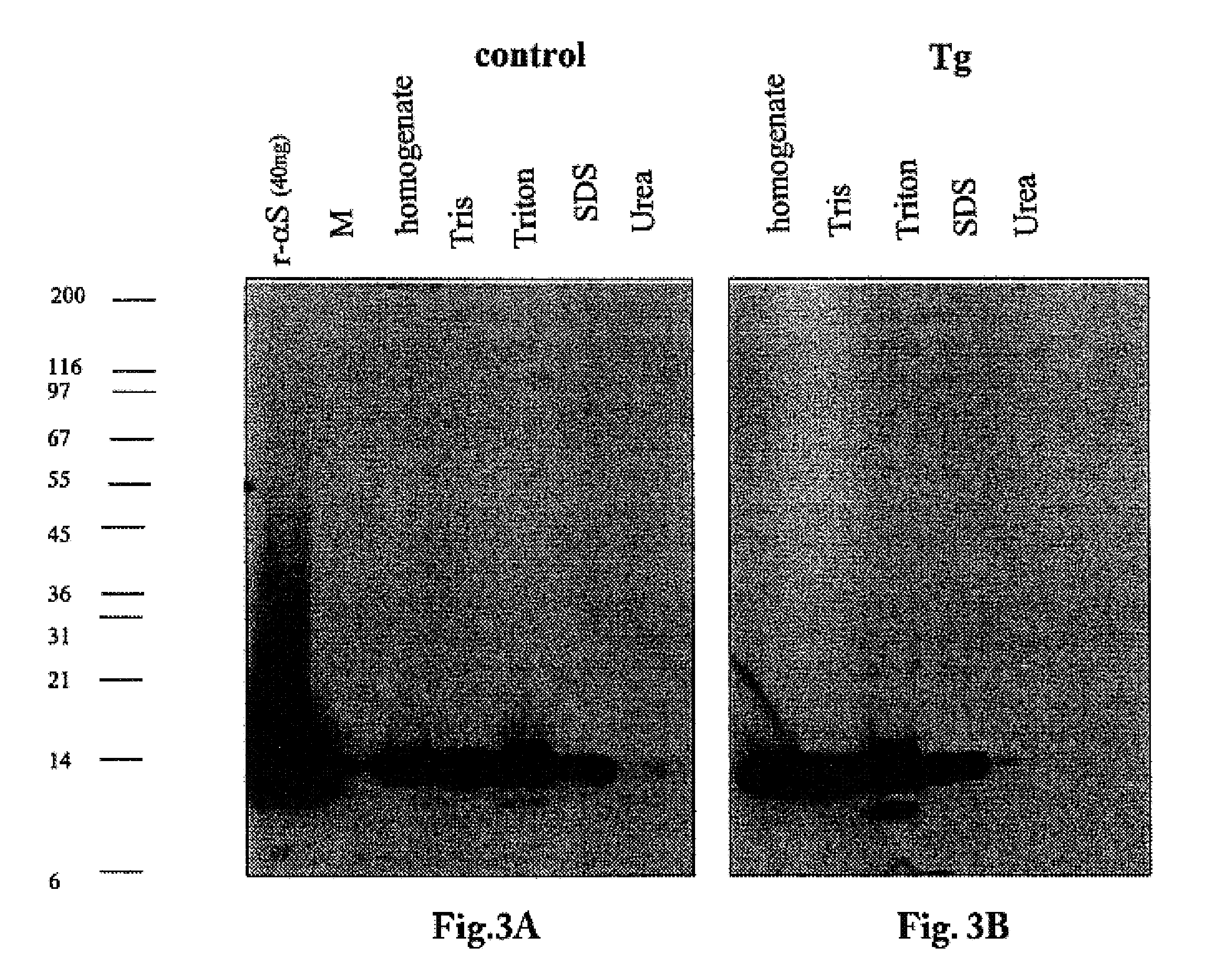
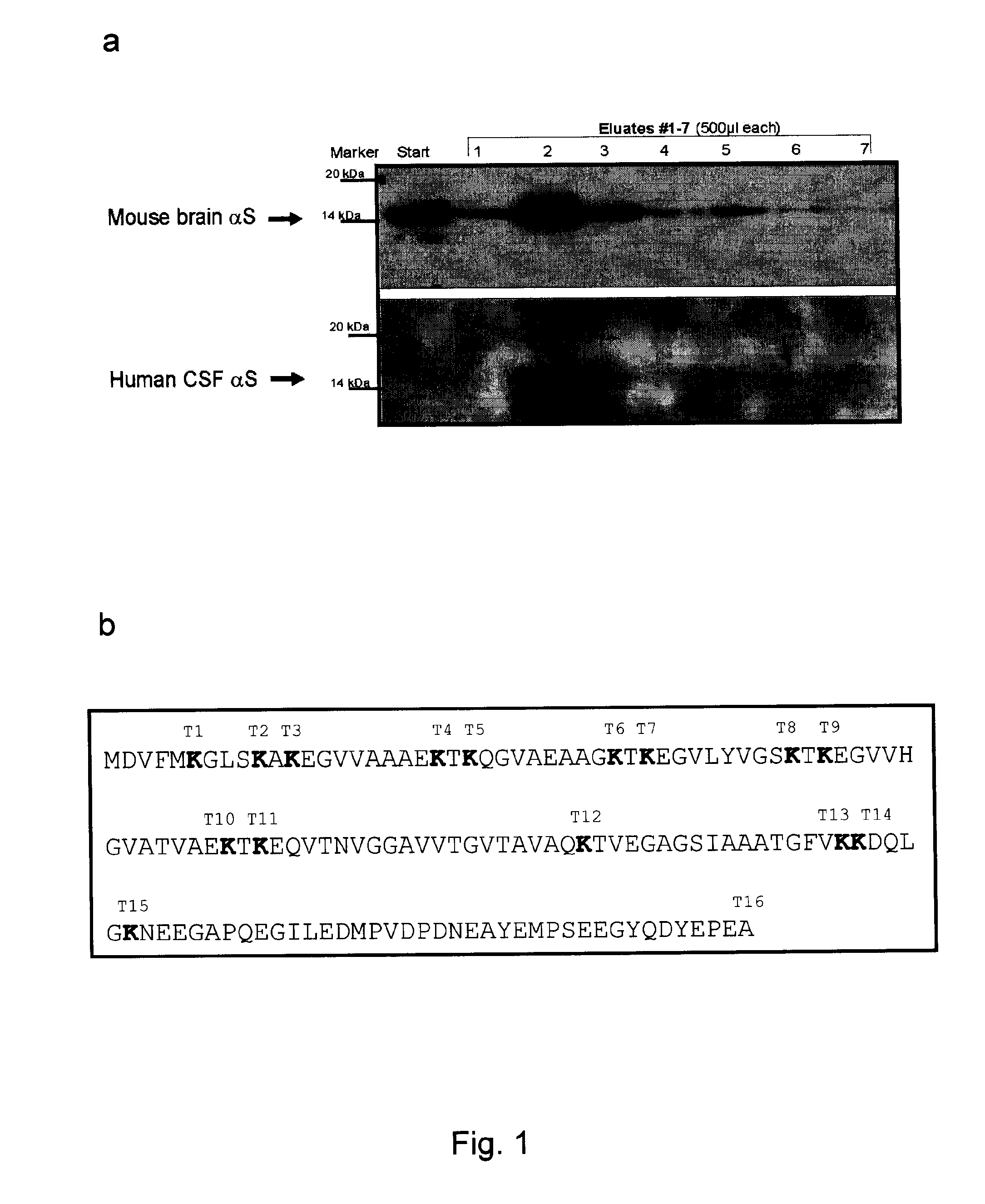
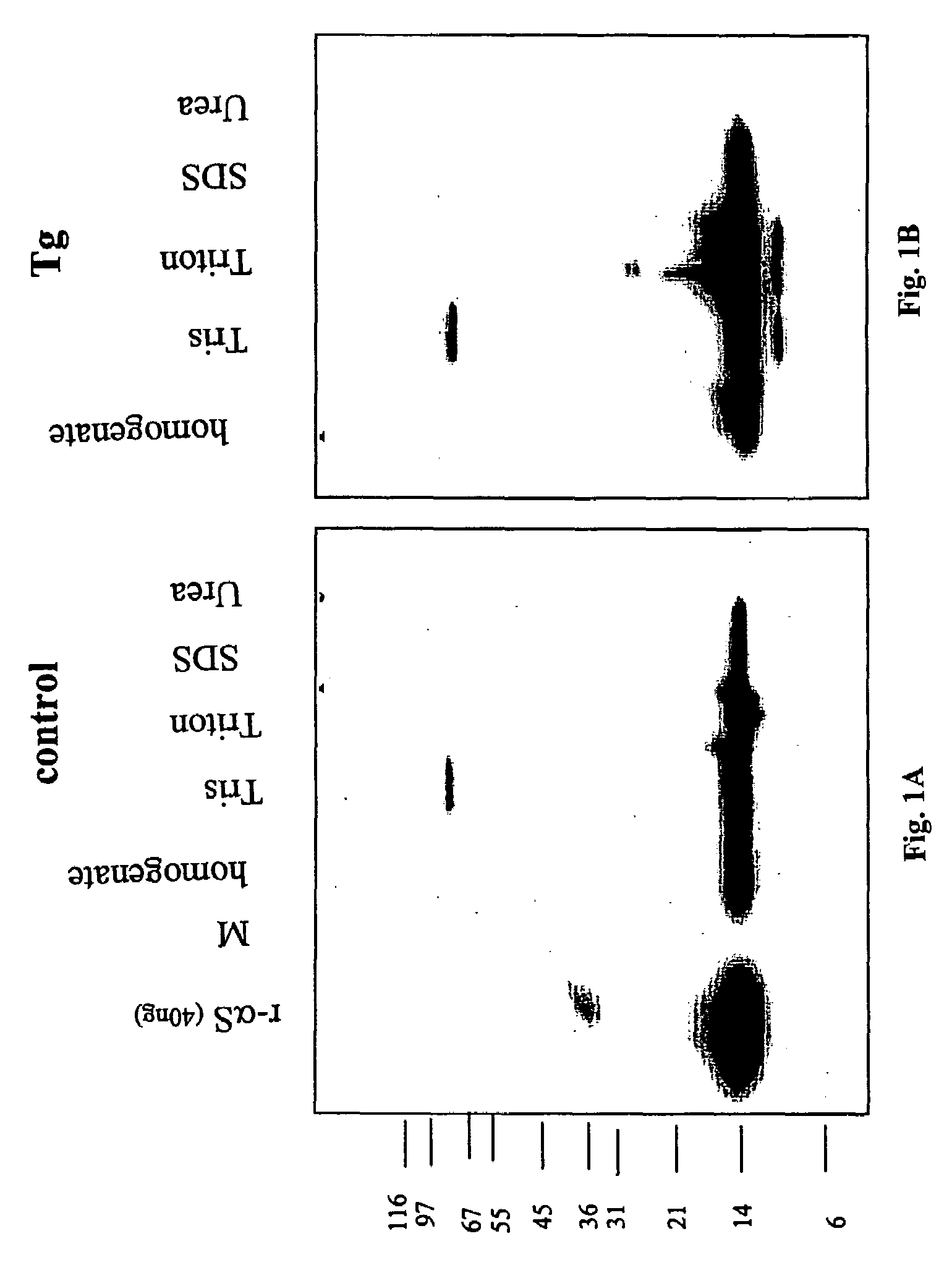
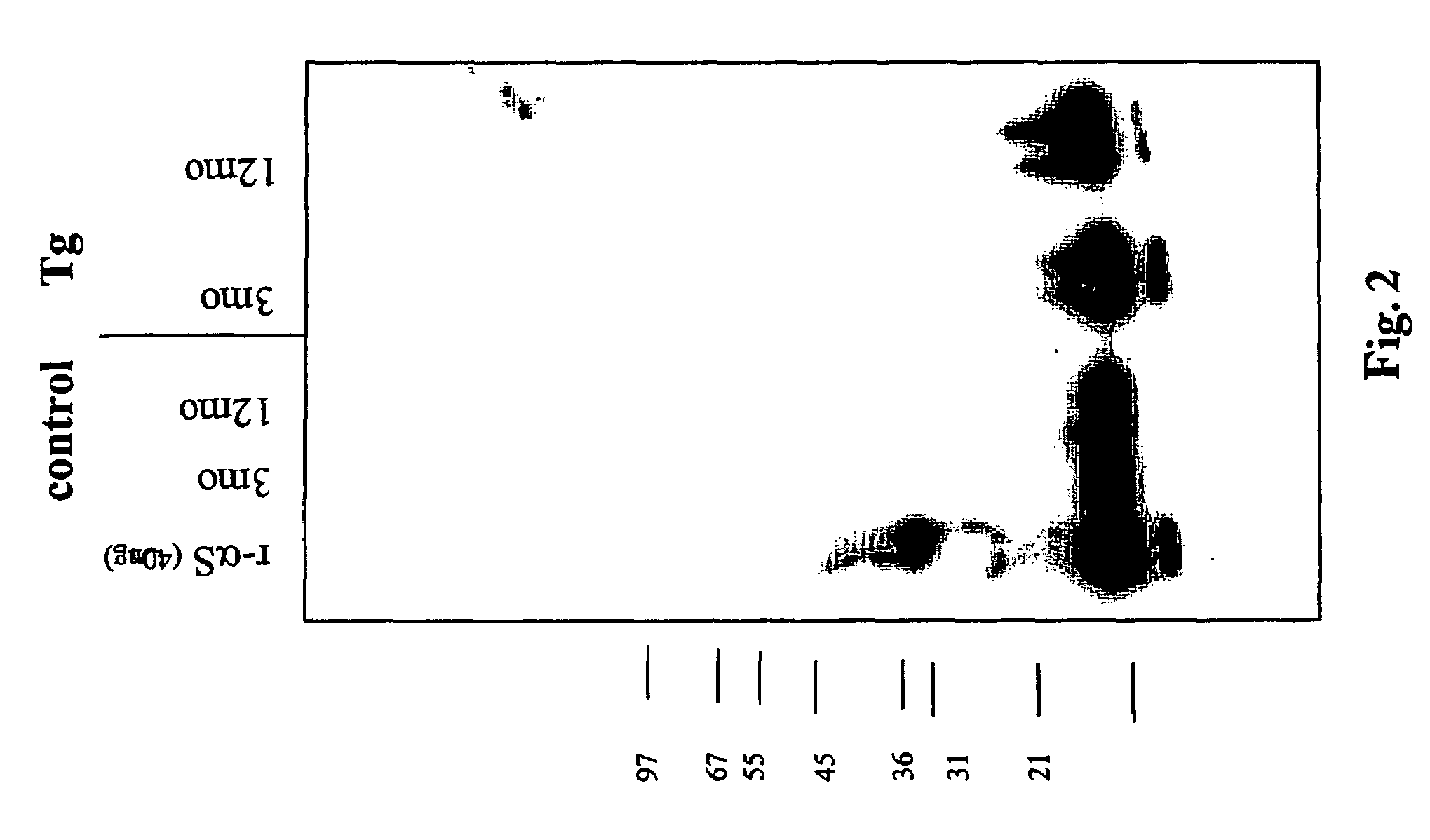
The application identifies novel fragments of alpha-synuclein in patients with Lewy Body Disease (LBD) and transgenic animal models thereof. These diseases are characterized by aggregations of alpha-synuclein. The fragments have a truncated C-terminus relative to fill-length alpha-synuclein. Some fragments are characterized by a molecular weight of about 12 kDa as determined by SDS gel electrophoresis in tricine buffer and a truncation of at least ten contiguous amino acids from the C-terminus of natural alpha-synuclein. The site of cleavage preferably occurs after residue 117 and before residue 126 of natural alpha-synuclein. The identification of these novel fragments of alpha-synuclein has a number of application in for example, drug discovery, diagnostics, therapeutics, and transgenic animals.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF FLINDERS UNIV +2
Truncated fragments of alpha-synuclein in Lewy Body Disease
The application identifies novel fragments of alpha-synuclein in patients with Lewy Body Disease (LBD) and transgenic animal models thereof. These diseases are characterized by aggregations of alpha-synuclein. The fragments have a truncated C-terminus relative to full-length alpha-synuclein. Some fragments are characterized by a molecular weight of about 12 kDa as determined by SDS gel electrophoresis in tricine buffer and a truncation of at least ten contiguous amino acids from the C-terminus of natural alpha-synuclein. The site of cleavage preferably occurs after residue 117 and before residue 126 of natural alpha-synuclein. The identification of these novel fragments of alpha-synuclein has a number of application in for example, drug discovery, diagnostics, therapeutics, and transgenic animals.
Owner:PROTHENA BIOSCI LTD
Alpha-Synuclein Antibodies and Methods Related Thereto
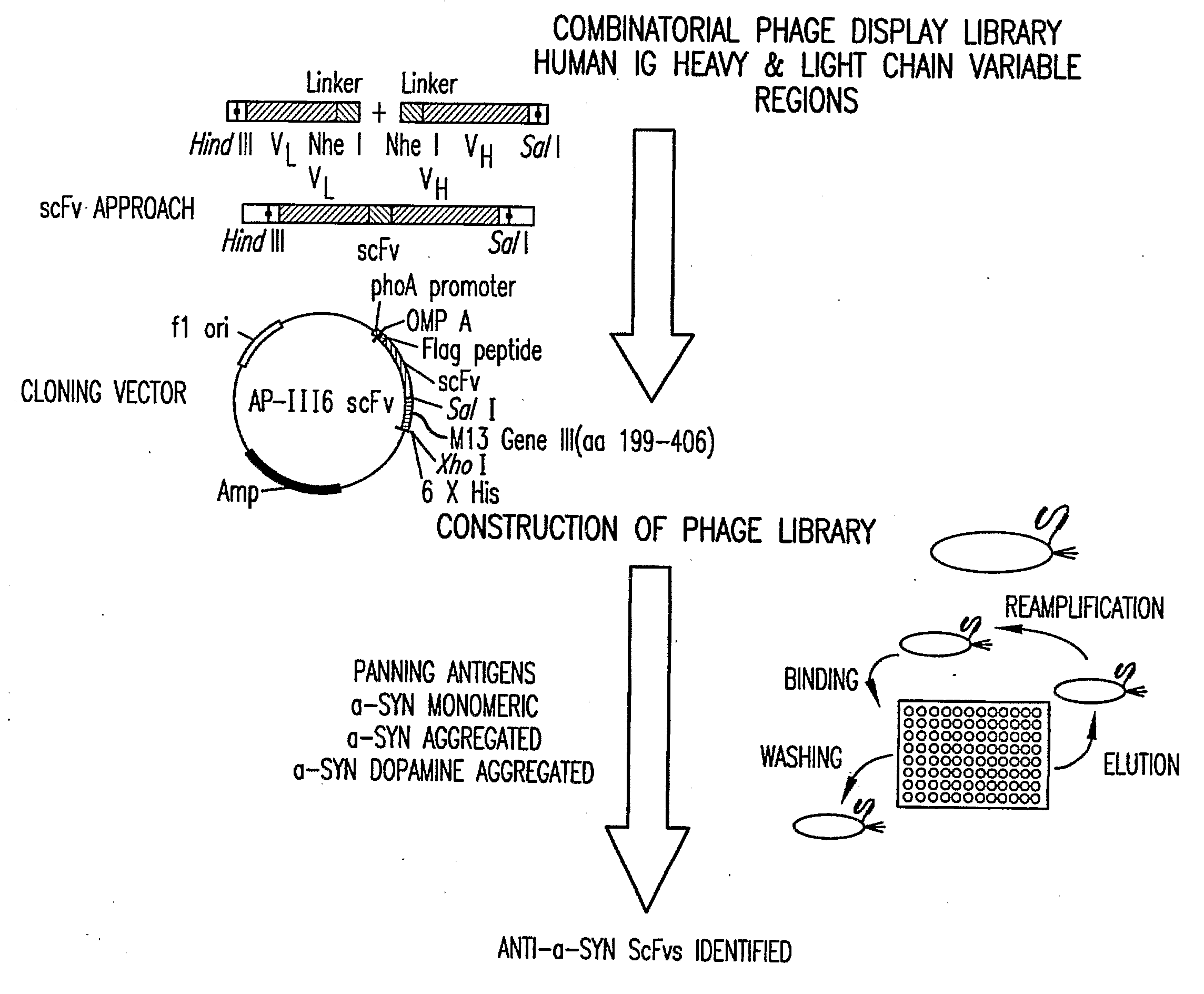
Disclosed are antibodies specific for alpha-synuclein conformers and methods related thereto. For example, disclosed are methods of diagnosing a neurodegenerative monitoring a neurodegenerative disease treatment using the disclosed antibodies. Assays, kits, and solid supports related to alpha-synuclein and antibodies specific for alpha-synuclein are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Treatment and delay of outset of Parkinson's disease
ActiveUS7727957B2Improves motor characteristicInhibit deteriorationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic treatmentSynuclein
The invention provides improved agents and methods for treatment of diseases associated with synucleinopathic diseases, including Lewy bodies of alpha-synuclein in the brain of a patient. Such methods entail administering agents that induce a beneficial immunogenic response against the Lewy body. The methods are particularly useful for prophylactic and therapeutic treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Antibodies and Vaccines for Use in Therapeutic and Diagnostic Methods for Alpha-Synuclein-Related Disorders
A vaccine for delaying an onset of or for treatment of an α-synuclein-related disorder in an individual comprises a therapeutically effective amount of isolated stabilized soluble α-synuclein oligomer having a lower formation rate to a non-soluble aggregated form than a non-stabilized oligomer of the α-synuclein. An antibody for delaying an onset of or for treatment of an α-synuclein-related disorder in an individual binds soluble α-synuclein. Methods for delaying an onset of for treatment or for prevention of an α-synuclein-related disorder employ the vaccine or antibody. Methods of detecting α-synuclein oligomers employ the antibody.
Owner:BIOARCTIC NEUROSCI AB
Truncated fragments of alpha-synuclein in Lewy body disease
The application identifies novel fragments of alpha-synuclein in patients with Lewy Body Disease (LBD) and transgenic animal models thereof. These diseases are characterized by aggregations of alpha-synuclein. The fragments have a truncated C-terminus relative to full-length alpha-synuclein. Some fragments are characterized by a molecular weight of about 12 kDa as determined by SDS gel electrophoresis in tricine buffer and a truncation of at least ten contiguous amino acids from the C-terminus of natural alpha-synuclein. The site of cleavage preferably occurs after residue 117 and before residue 126 of natural alpha-synuclein. The identification of these novel fragments of alpha-synuclein has a number of application in for example, drug discovery, diagnostics, therapeutics, and transgenic animals.
Owner:PROTHENA BIOSCI LTD
Synthetic immunogenic but non-deposit-forming polypeptides and peptides homologous to amyloid beta, prion protein, amylin, alpha-synuclein, or polyglutamine repeats for induction of an immune response thereto
InactiveUS7479482B2Reduce formationAvoid formingHormone peptidesNervous disorderPassive ImmunizationsAmyloid beta
The present invention relates to immunogenic but non-depositing-forming polypeptides or peptides homologous to amyloid β, prion, amylin or α-synuclein which can be used alone or conjugated to an immunostimulatory molecule in an immunizing composition for inducing an immune response to amyloid β peptides and amyloid deposits, to prion protein and prion deposits, to amylin and amylin deposits, to α-synuclein and deposits containing α-synuclein, or to polyglutamine repeats and deposits of proteins containing polyglutamine repeats. Described are also antibodies directed against such peptides, their generation, and their use in methods of passive immunization to such peptides and deposits.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Prevention and treatment of synucleinopathic and amyloidogenic disease
ActiveUS8092801B2Improves motor characteristicInhibit deteriorationNervous disorderNervous system antigen ingredientsSynucleinTherapeutic treatment
The invention provides improved agents and methods for treatment of diseases associated with synucleinopathic diseases, including Lewy bodies of alpha-synuclein in the brain of a patient. Such methods entail administering agents that induce a beneficial immunogenic response against the Lewy body. The methods are particularly useful for prophylactic and therapeutic treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
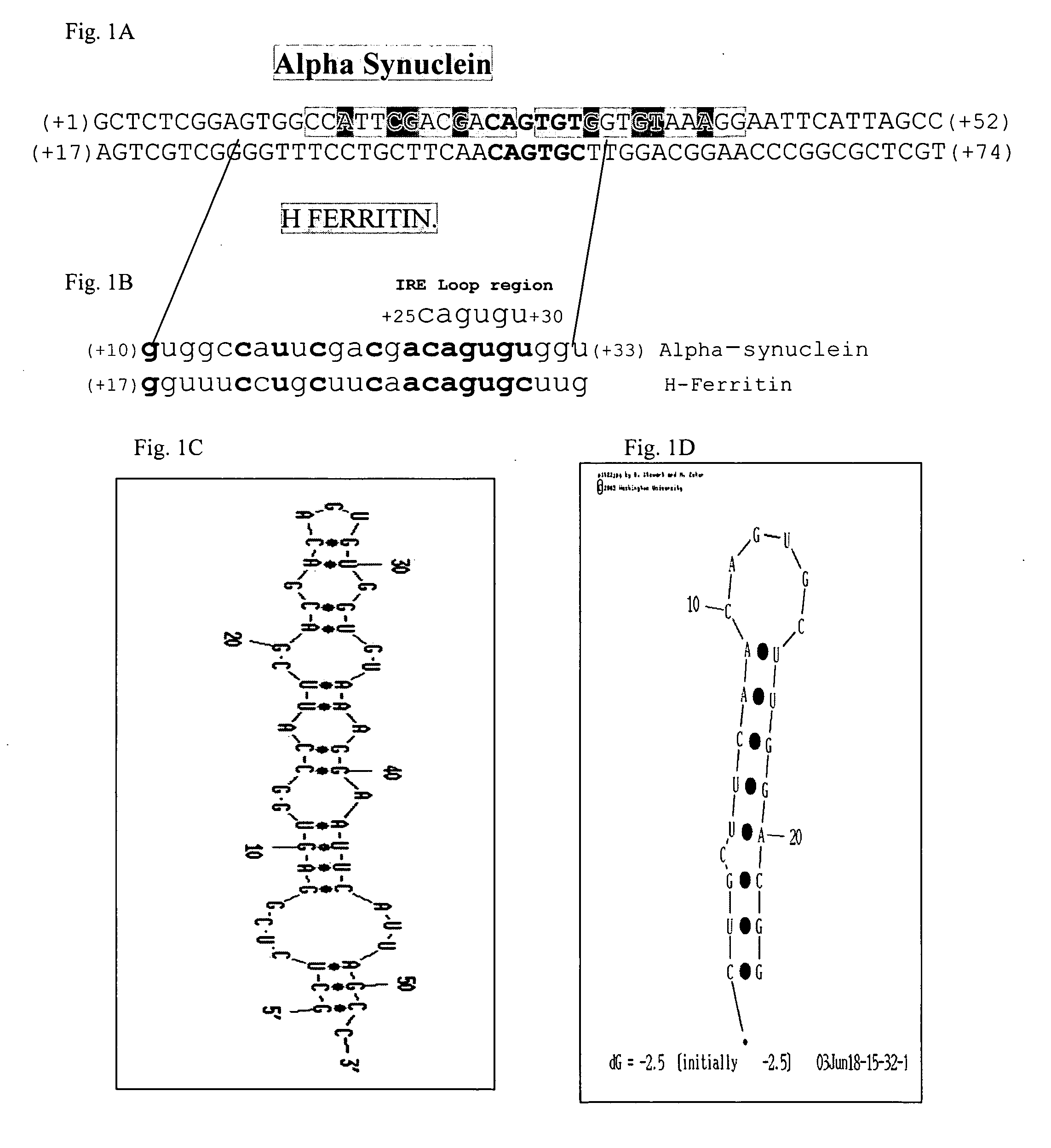
Translation enhancer elements of genes encoding human Tau protein and human alpha-synuclein protein
InactiveUS20080003570A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNeuro-degenerative diseaseEnhancer Elements
The invention relates to translation enhancer elements that enhance translation of the gene encoding the human microtubule-associated tau protein and nucleic acid molecules that enhance translation of the gene encoding the human α-synuclein protein. The translation enhancer elements of the invention are useful in compositions and methods for identifying compounds for the prevention and / or treatment of neurodegenerative disease. The invention also includes in some aspects, vectors that include a translation enhancer element of the invention. The invention also includes the use of enhancer element containing vectors in methods to produce recombinant protein and in assays to identify compounds that modulate expression of tau protein or α-synuclein protein.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Differential diagnosis of neurodegeneration
InactiveUS20040014142A1Specific detectionSpecific quantificationDisease diagnosisBiological testingSpecific detectionSynuclein
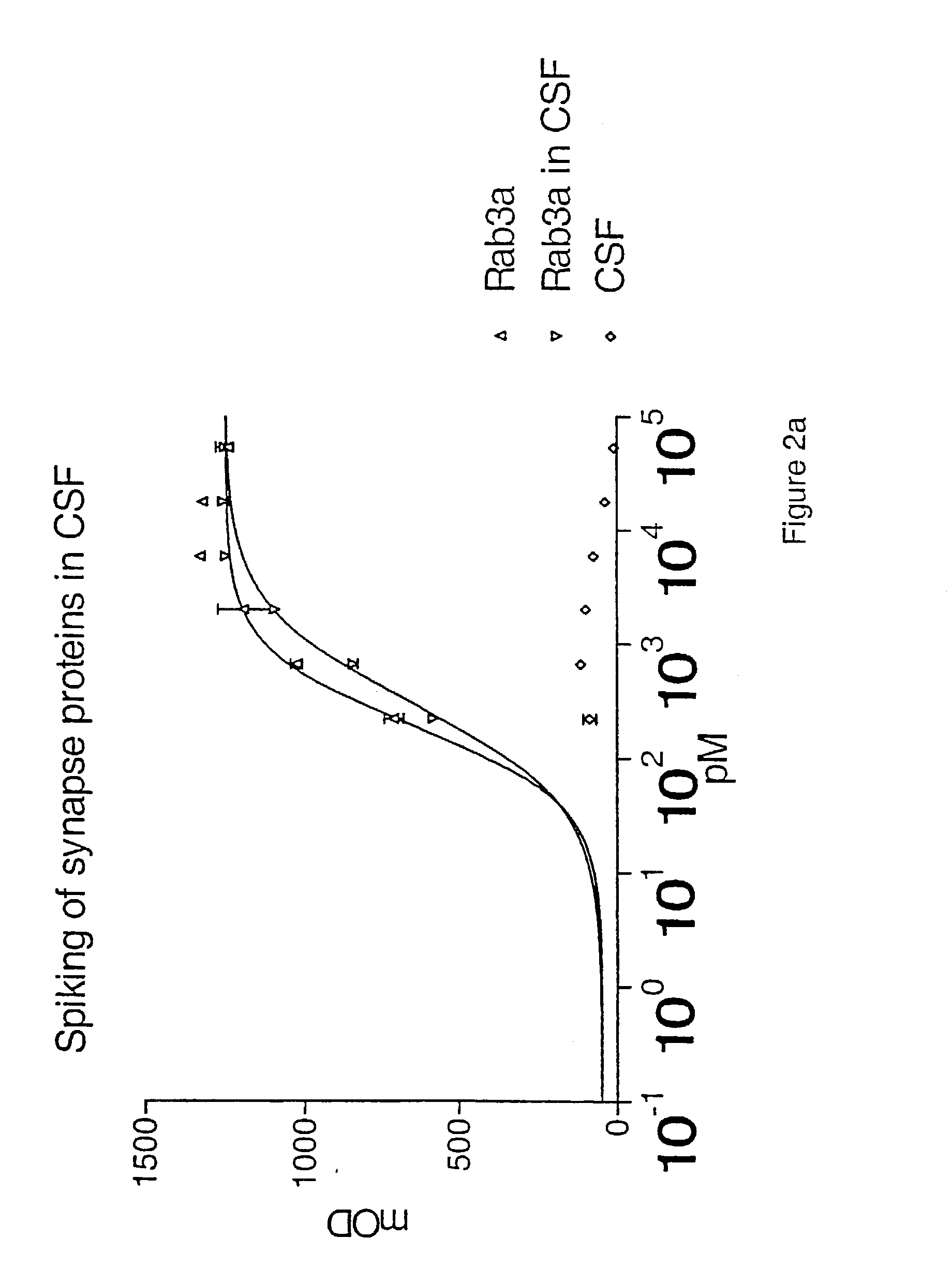
The present invention relates to new methods for the specific detection, quantification and / or differential diagnosis of neurodegeneration in an individual making use of a combination assay detecting at least three neurological markers in one or more body fluids of said individual, the type and degree of neurodegeneration being reflected in the quantitative changes in the level of all of said neurological markers compared to the control sample. The present invention also relates to methods for the detection of Rab3a, SNAP25 and alpha-synuclein in cerebrospinal fluid and to the use of these methods in a combination assay for specific detection, quantification and / or differential diagnosis of neurodegeneration.
Owner:INNOGENETICS NV
Methods and kits for diagnosing neurodegenerative disease
InactiveUS20110159527A1Prevent slaughterRaise the ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDisease freeTotal protein
Methods and diagnostic kits for determining whether a subject may develop a or for diagnosing a neurodegenerative disease. The method includes quantitating the amount of alpha-synuclein and total protein in a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) sample obtained from the subject and calculating a ratio of alpha-synuclein to total protein content; comparing the ratio of alpha-synuclein to total protein content in the CSF sample with the alpha-synuclein to total protein content ratio in CSF samples obtained from healthy neurodegenerative disease-free subjects; and (c) determining from the comparison whether the subject has a likelihood to develop neurodegenerative disease or making a diagnosis of neurodegenerative disease in a subject. A difference in the ratio of alpha-synuclein to total protein content indicates that the subject has a likelihood to develop a neurodegenerative disease or has developed a neurodegenerative disease.
Owner:SCHLOSSMACHER MICHAEL GEBHARD +2
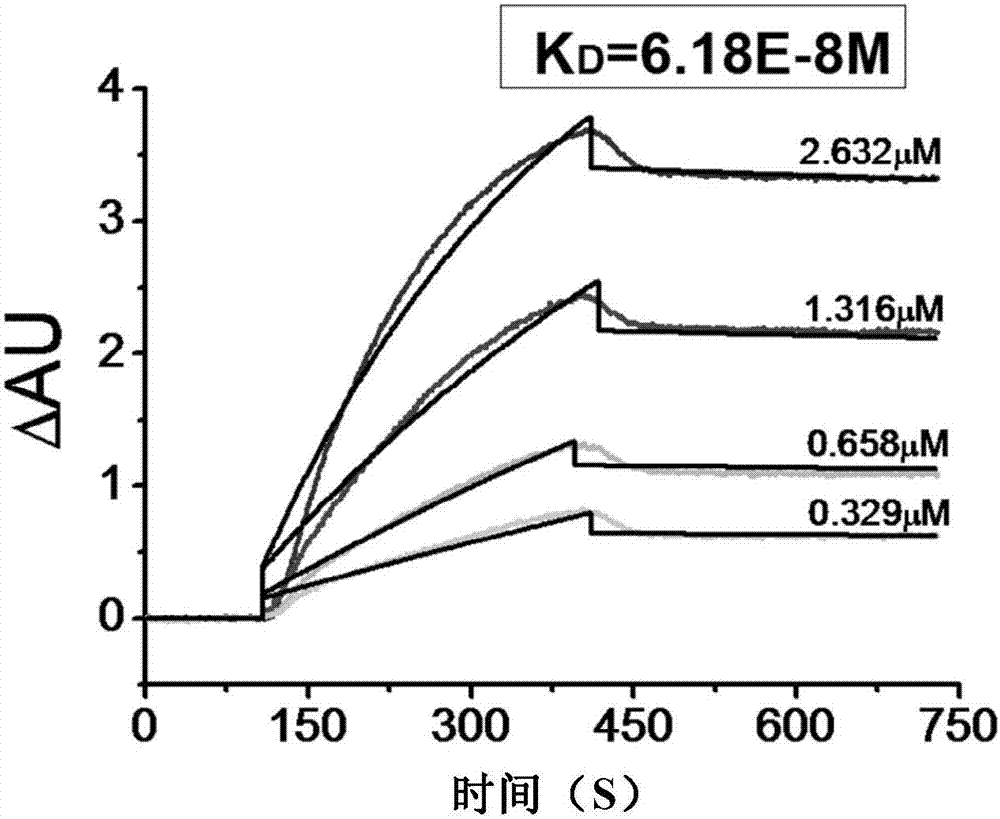
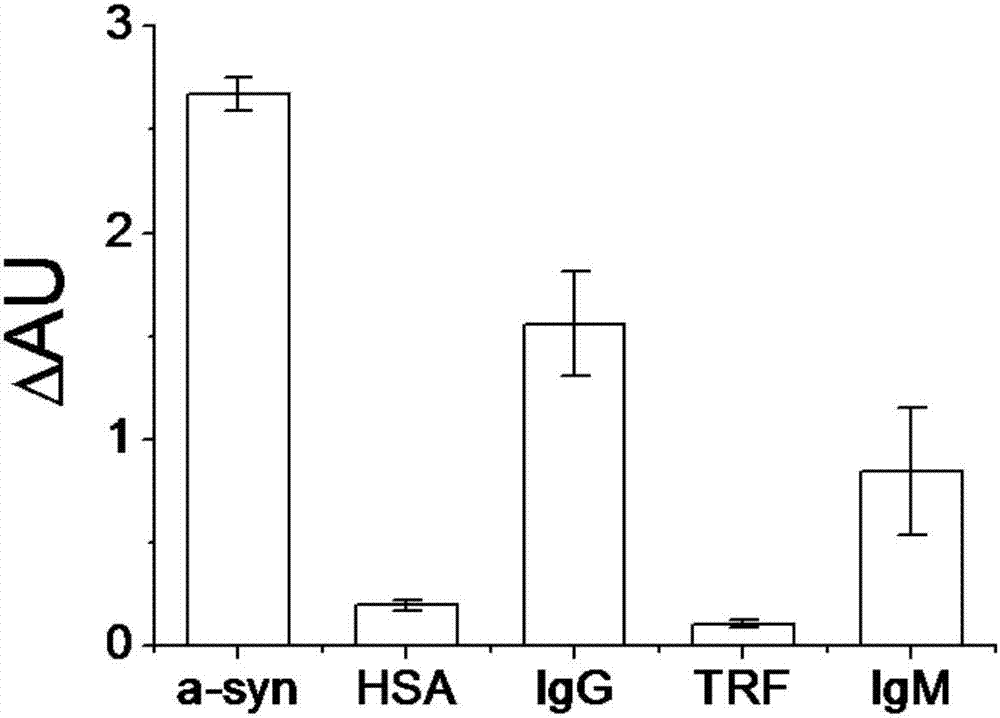
Alpha-synuclein antibodies and uses thereof
The invention describes antibodies having a high affinity for aggregated forms of α-synuclein and a low affinity for monomeric forms of α-synuclein. The antibodies are useful in the diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:UNITED ARAB EMIRATES UNIVERSITY
Prevention and treatment of synucleinopathic and amyloidogenic disease
ActiveUS20100278814A1Improves motor characteristicInhibit deteriorationNervous disorderNervous system antigen ingredientsLewy bodySynuclein
The invention provides improved agents and methods for treatment of diseases associated with synucleinopathic diseases, including Lewy bodies of alpha-synuclein in the brain of a patient. Such methods entail administering agents that induce a beneficial immunogenic response against the Lewy body. The methods are particularly useful for prophylactic and therapeutic treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Polyhydroxylated aromatic compounds for the treatment of amyloidosis and alpha-synuclein fibril diseases
Owner:COGNITIVE CLARITY INC
Truncated fragments of alpha-synuclein in Lewy body disease
The application identifies fragments of alpha-synuclein in patients with Lewy Body Disease (LBD) and transgenic animal models thereof. These diseases are characterized by aggregations of alpha-synuclein. The fragments have a truncated C-terminus relative to full-length alpha-synuclein. Some fragments are characterized by a molecular weight of about 12 kDa as determined by SDS gel electrophoresis in tricine buffer and a truncation of at least ten contiguous amino acids from the C-terminus of natural alpha-synuclein. The site of cleavage preferably occurs after residue 117 and before residue 126 of natural alpha-synuclein. The identification of these novel fragments of alpha-synuclein has a number of application in for example, drug discovery, diagnostics, therapeutics, and transgenic animals.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF FLINDERS UNIV +2
Combination therapies for the treatment of alzheimer's disease and related disorders
The present invention relates to combination therapies for treating Alzheimer's disease or an amyloidosis-associated pathological condition comprising co-administering a therapeutically effective amount of a first compound, and a therapeutically effective amount of a second compound. In certain embodiments, the first compound or the second compound inhibits AB peptide polymerization; is an anti-inflammatory; improves cognitive function, mood, or social behavior; is associated with Tau or alpha-synuclein; or regulates amyloid peptide washout.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Human anti-alpha-synuclein antibodies
Provided are human alpha-synuclein-specific autoantibodies as well as fragments, derivatives and variants thereof as well as methods related thereto. Assays, kits, and solid supports related to antibodies specific for α-synuclein are also disclosed. The antibody, immunoglobulin chain(s), as well as binding fragments, derivatives and variants thereof can be used in pharmaceutical and diagnostic compositions for α-synuclein targeted immunotherapy and diagnosis, respectively.
Owner:BIOGEN INT NEUROSCI +1
Agents, Uses and Methods for the Treatment of Synucleinopathy
The invention relates to novel monoclonal anti-alpha-synuclein antibodies. The antibodies can be used for treating a synucleinopathy such as Parkinson's disease (including idiopathic and inherited forms of Parkinson's disease), Diffuse Lewy Body Disease (DLBD), Lewy body variant of Alzheimer's disease (LBV), Combined Alzheimer's and Parkinson disease, pure autonomic failure and multiple system atrophy.
Owner:H LUNDBECK AS
Compositions and methods for treatment of neurogenerative diseases
Medical compositions and methods of treating or preventing neurodegeneration in a human suffering from or that is at risk of or susceptible to neurodegeneration or cellular dysfunction associated with expression or impaired cellular function of a neuronal protein encoded by one or more genes that code for alpha-synuclein (SNCA), Parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin protein ligase, (PARK2), Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2), PTEN-induced putative kinase / (PINK1), Daisuke-Junko 1, (DJ-1) and ATPase type 13A2 (ATP13A2), are disclosed. Methods of treatment for these disorders is also provided, comprising administering a vector into a cell, wherein the vector facilitates expression of a molecular component that alters one of the aforementioned genes in the cell or expression of the gene in the cell, the gene being implicated in an etiology of the neurological deficit.
Owner:FLYNN ALEXANDER C
Method for detecting subject humoral disease related protein polymerizing power
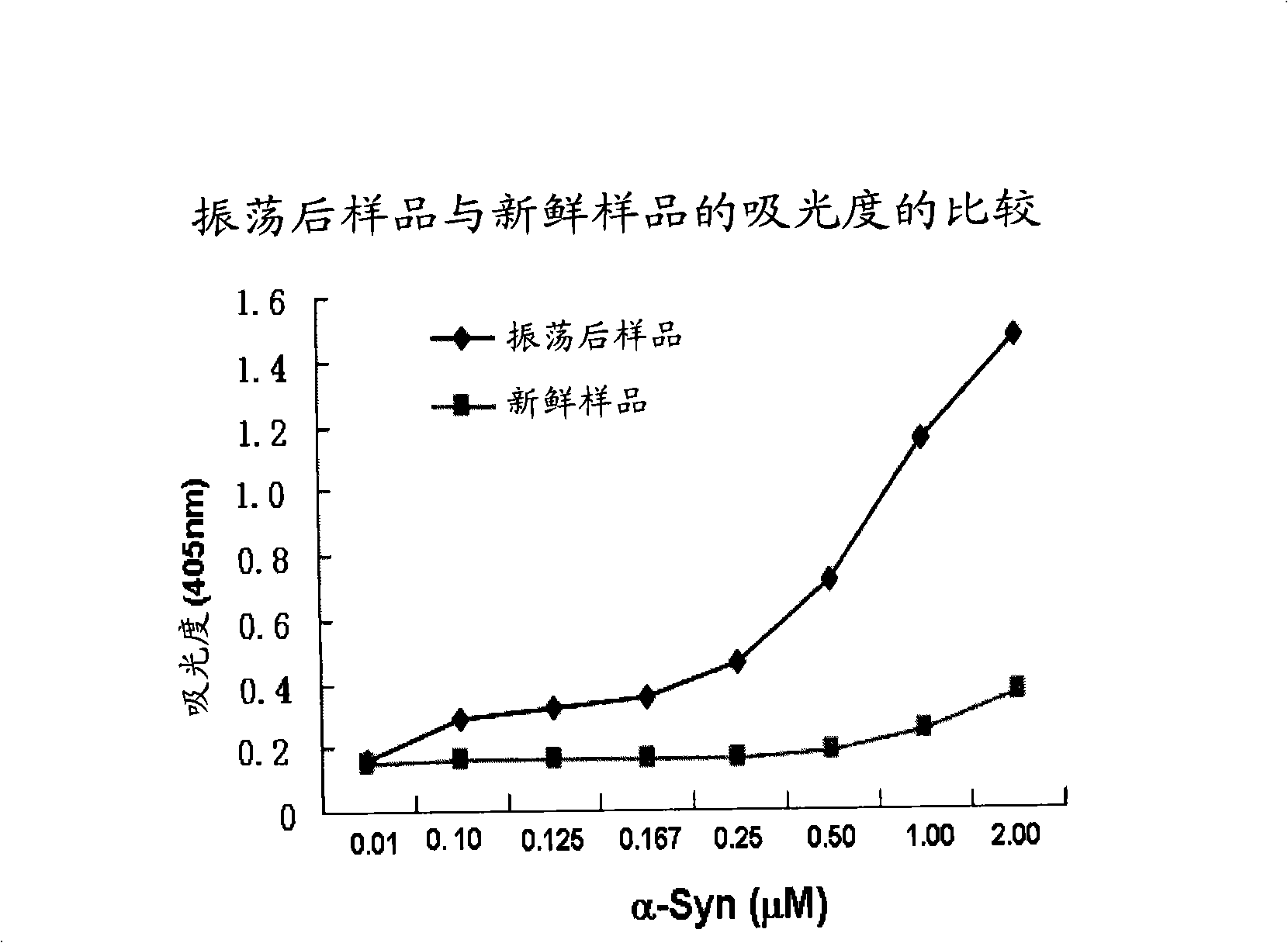
InactiveCN101308144AEasy to acceptDetermining comprehensive pathophysiological conditionsColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingProtein oligomerizationElisa method
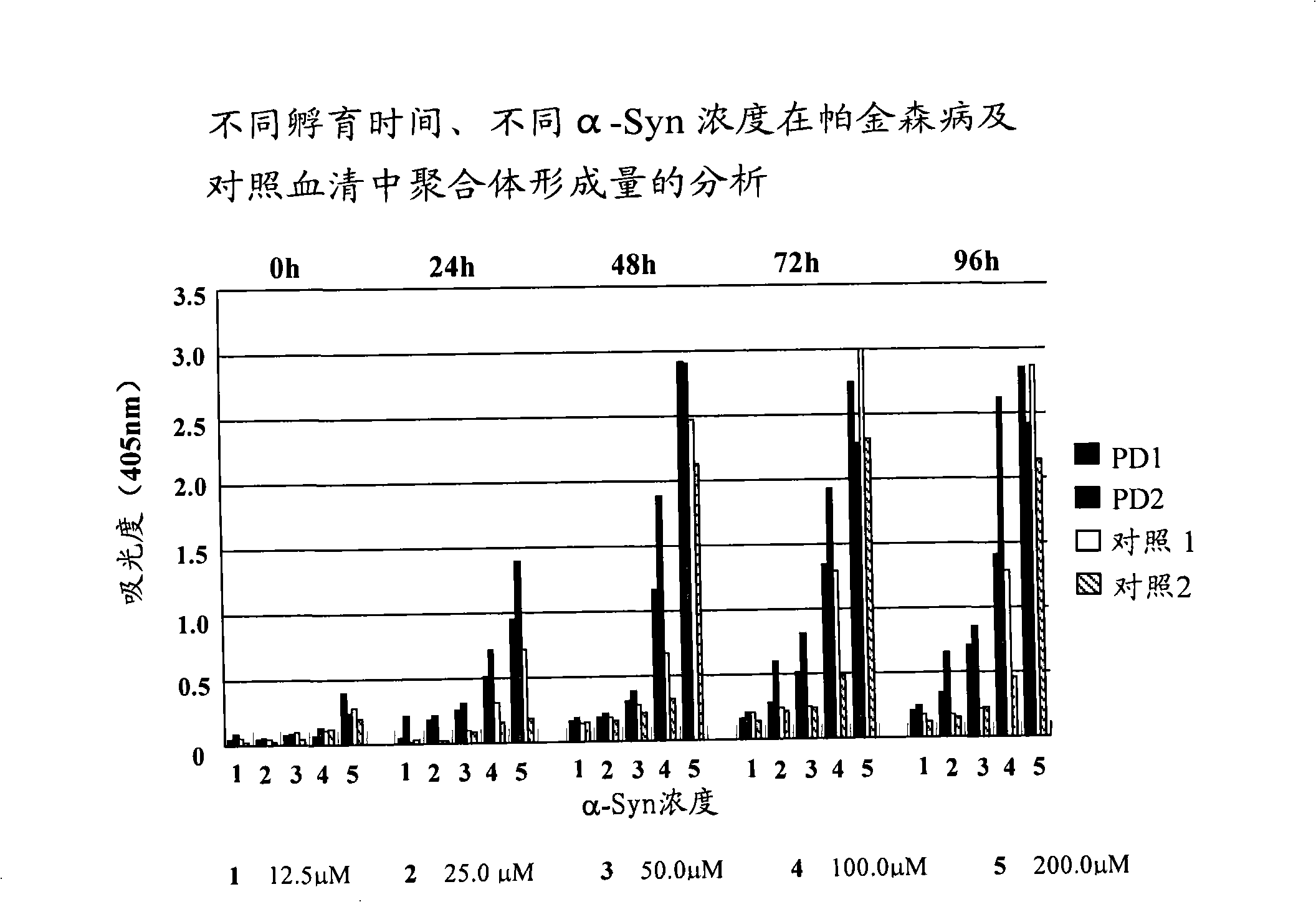
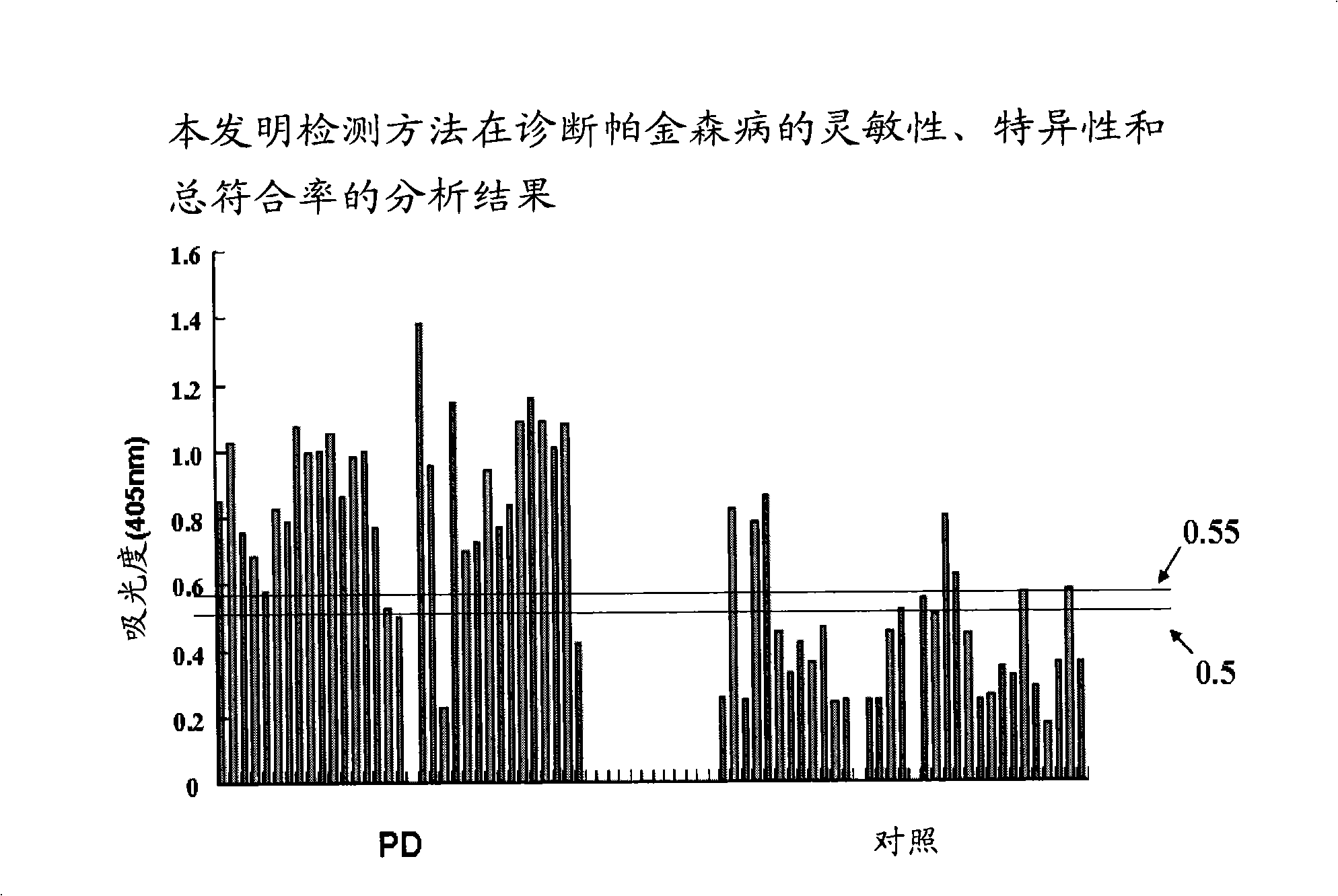
The invention relates to a method for external detection of polymerizing power of disease-related protein promoted by body fluids of subjects. More specifically, the invention concerns a method for detecting the oligomer formation power of disease-related protein such as alpha-synuclein promoted by body fluids of the subjects in vitro. The method comprises: incubating purified recombinant human disease-related protein and body fluids of the subjects by stirring at a certain temperature to make the two components be polymerized, and detecting the content of oligomers of disease-related protein such as alpha-synuclein in the incubated body fluids by utilizing a method that can detect protein oligomers. The method provided by the invention has advantages that: 1) the need for body fluid sample is less, so the subjects are easy to accept; 2) operations are simple; and 3) the result obtained from the detection method reflects the synthetic action of various factors of polymerization of disease-related protein to subjects, and the result is particularly more favorable for determining comprehensive pathophysiological situations of patients with Parkinson disease caused by complex factors.
Owner:XUANWU HOSPITAL OF CAPITAL UNIV OF MEDICAL SCI
Regulators of protein misfolding and aggregation and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20070204352A1Increase in protein misfoldingPromote aggregationCompound screeningNervous disorderCell AggregationsNucleotide
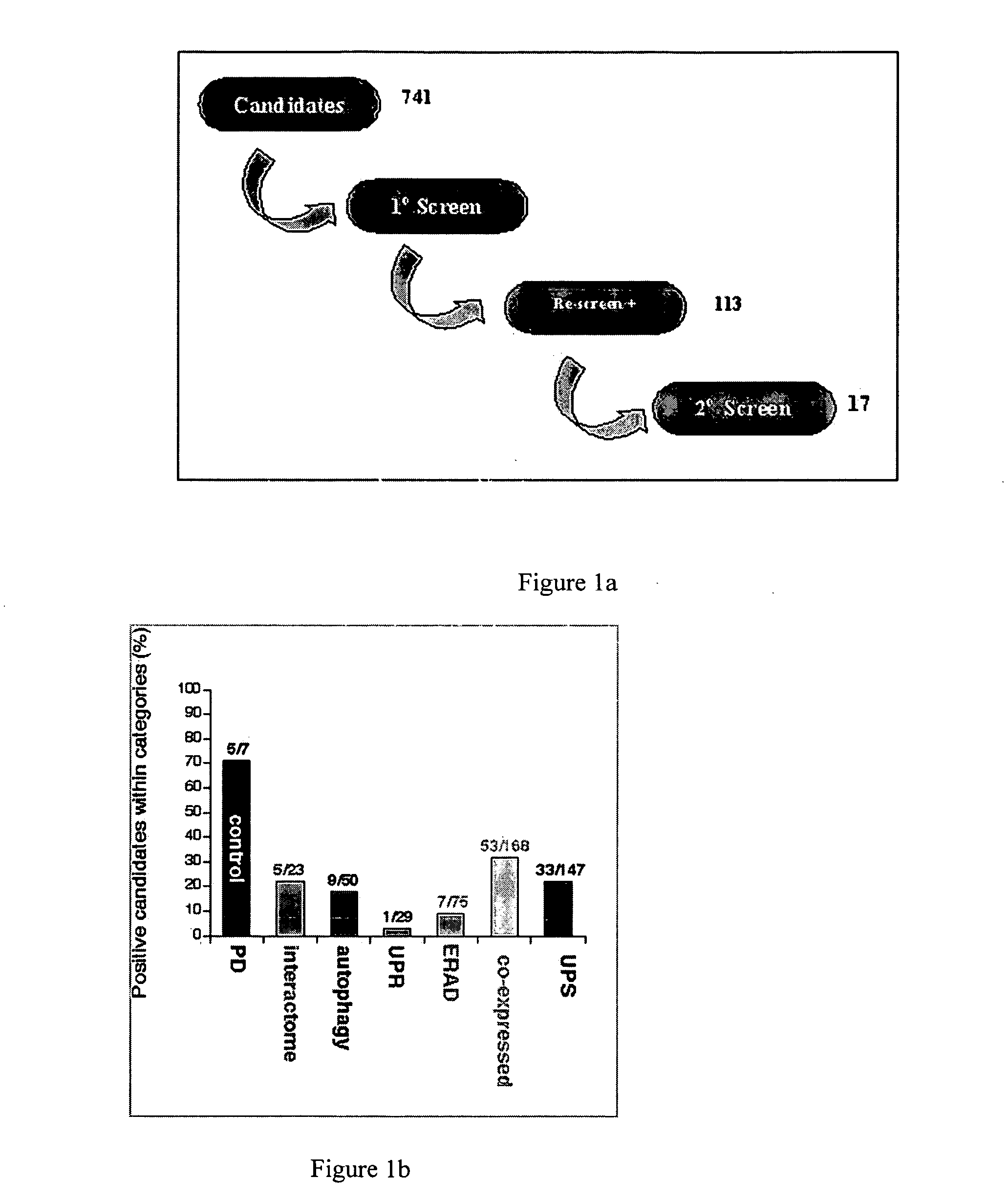
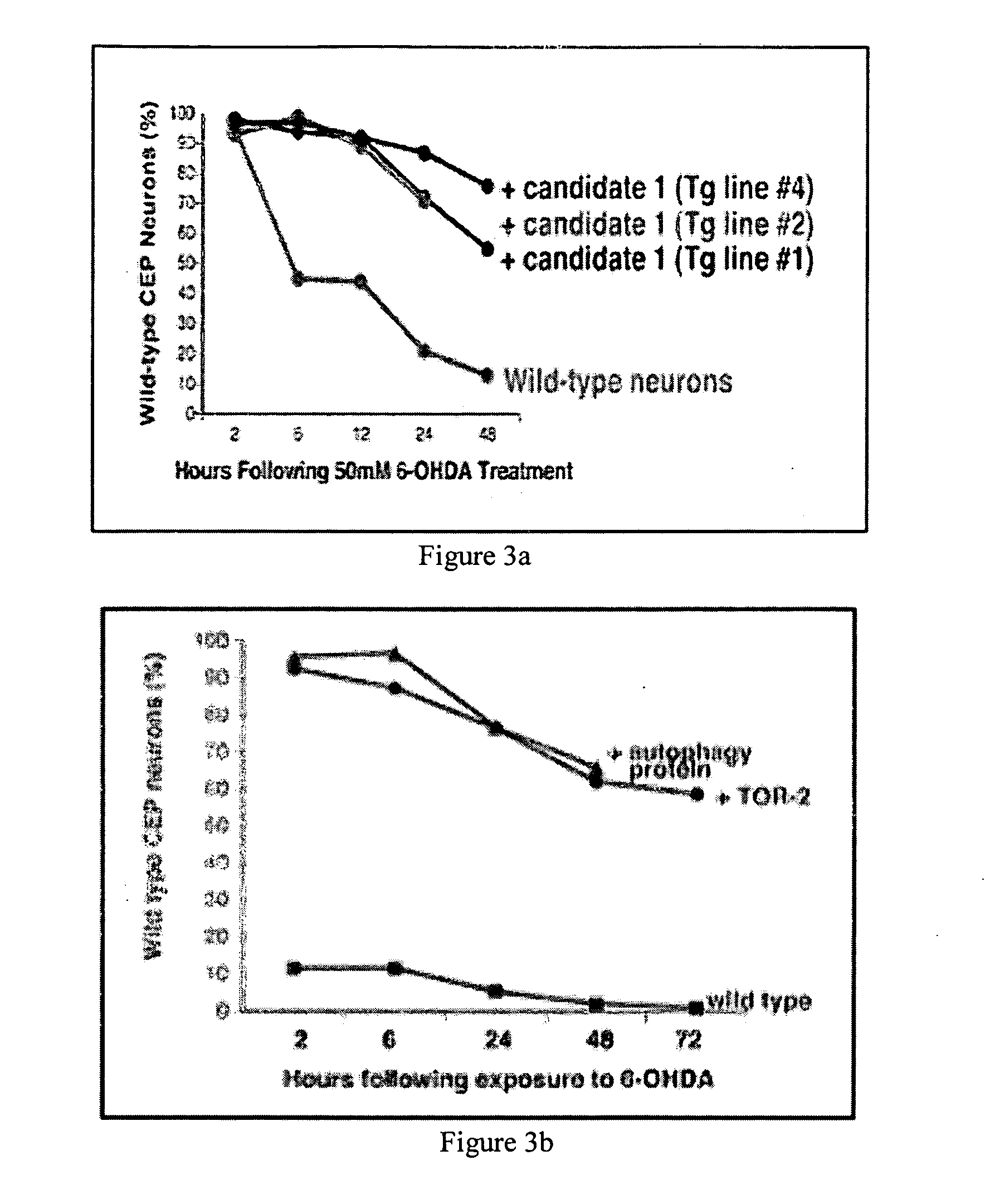
Polynucleotide molecules and the proteins encoded by the molecules, diagnostic and treatment methods for neurological disorders characterized by protein aggregation are provided. Genes are described herein that affect the misfolding of, and subsequent aggregation of, aggregation-prone proteins such as alpha-synuclein and have implications for the diagnosis and treatment of neurological diseases related to protein aggregation such as Parkinson's disease. Knockdown of expression of the genes described herein using RNAi results in alpha-synuclein protein aggregation in a C. elegans model of protein aggregation. Dopaminergic neuroprotection after exposure to the neurotoxin 6-OHDA or overexpression of alpha-synuclein may also be provided by overexpression of proteins. Knowledge of genes relating to protein misfolding and aggregation provides powerful means to develop diagnostic screening methods, mutation analysis and drug design information for the development of novel therapeutic and neuroprotective compounds to treat neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
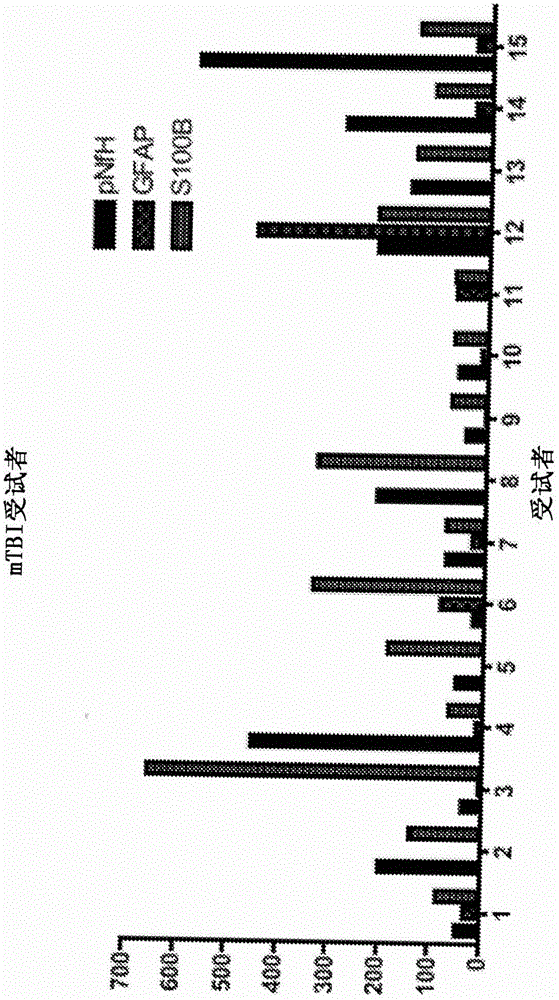
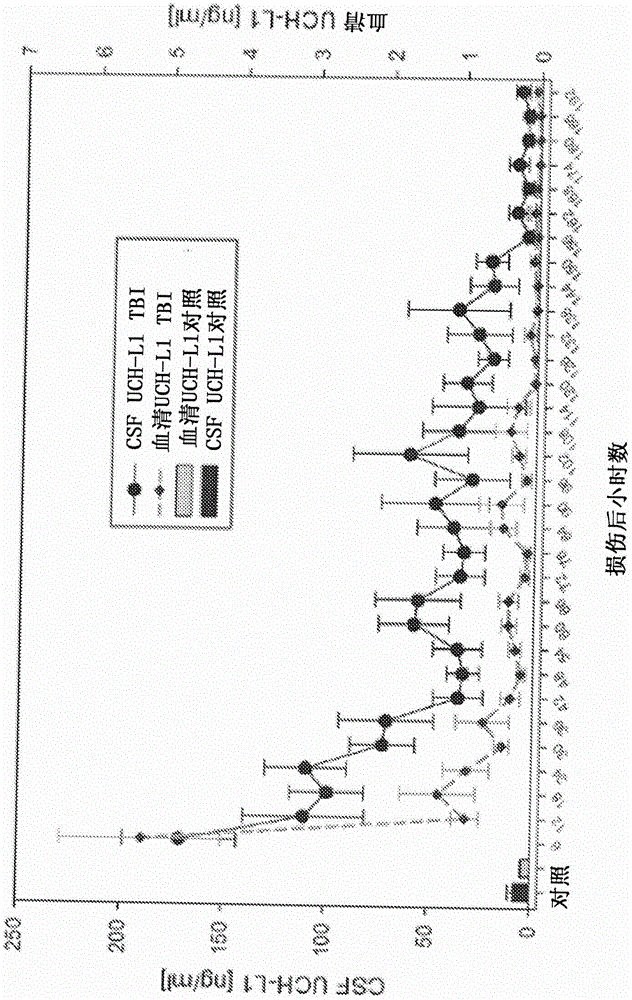
Traumatic brain injury and neurodegenerative biomarkers, methods, and systems
InactiveCN106461645ADisease diagnosisBiological testingGlial Fibrillary Acid ProteinVisinin Like Protein
Biomarkers, methods, and systems for assessment of traumatic brain injury of different severities, as well as treatment efficacy and blood brain barrier or blood cerebrospinal fluid integrity and assessment of neurodegenerative conditions. The methods include detecting in a patient sample one or more of ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase LI (UCH-L1), glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP), aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family member LI (ALDHILI), phosphorylated neurofilament heavy chain (pNFH), medium chain (NFM), or light chain (NFL), alpha-synuclein, visinin-like protein 1 (VILIP-1) and S100B.
Owner:IRON HORSE DIAGNOSTICS
Human Anti-Alpha-Synuclein Antibodies
Provided are human alpha-synuclein-specific autoantibodies as well as fragments, derivatives and variants thereof as well as methods related thereto. Assays, kits, and solid supports related to antibodies specific for α-synuclein are also disclosed. The antibody, immunoglobulin chain(s), as well as binding fragments, derivatives and variants thereof can be used in pharmaceutical and diagnostic compositions for α-synuclein targeted immunotherapy and diagnosis, respectively.
Owner:BIOGEN INT NEUROSCI +1
Peptoid and preparation method as well as application thereof
ActiveCN106854233AImprove bindingRapid diagnosisNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsEthylenediamine1-Naphthylamine
The invention provides a peptoid as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The peptoid comprises the following subunits: ethylenediamine (I), piperonylamine (II), beta-alanine (III), 1-naphthylamine (IV) and cysteine (V). The peptoid is simple in synthesis, has strong combining capacity with alpha-synuclein, can effectively screen the serum of PD patients and able-bodied persons through alpha-synuclein in the serum, and provides a novel liquid biopsy method and concept for diagnosis and monitoring of the Parkinson's disease.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
New therapeutic approaches for treating parkinson's disease
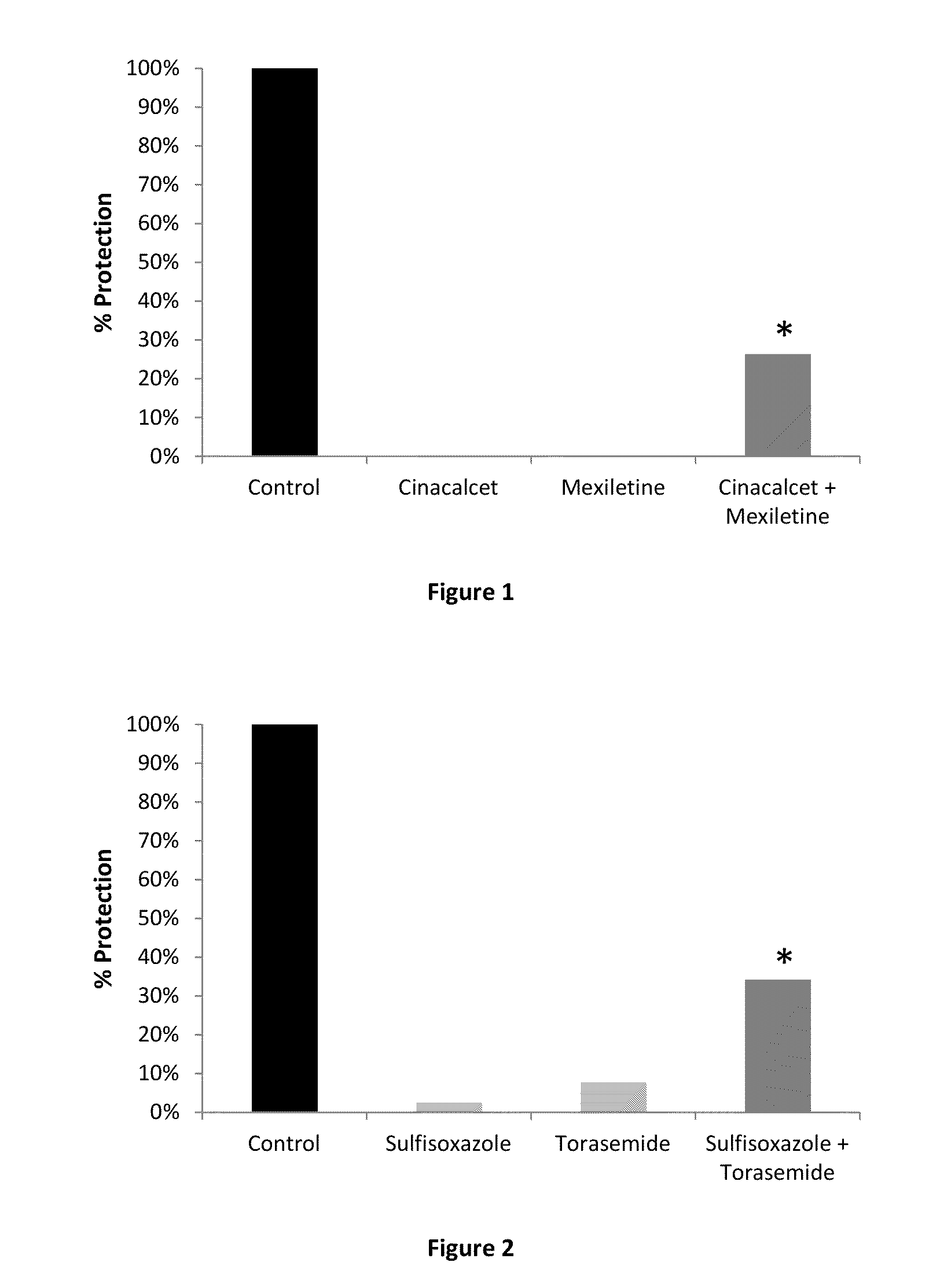
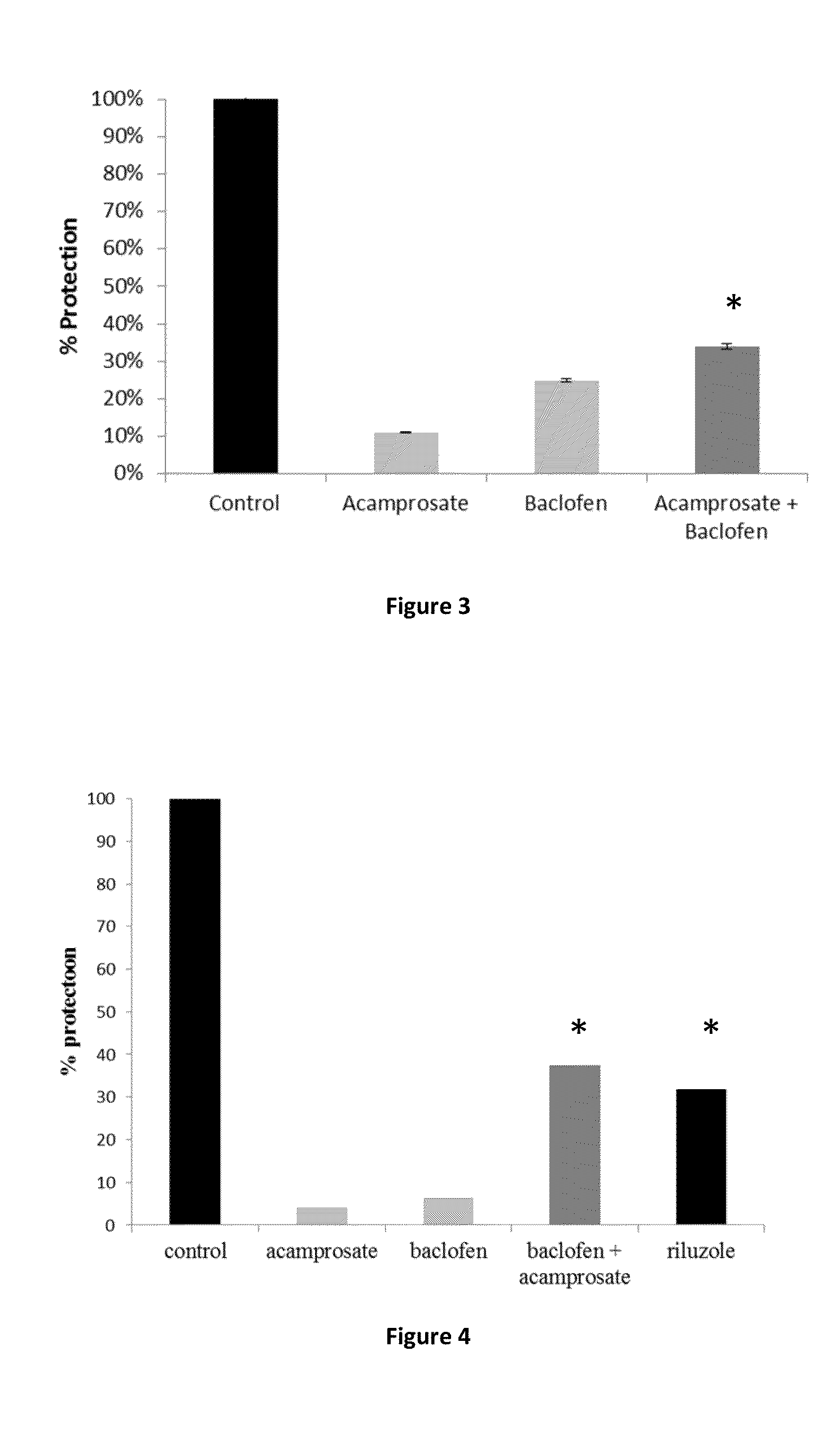
ActiveUS20140371229A1Delay disease progressionReduce and delay and prevent tremorBiocideNervous disorderJuvenile parkinson's diseaseSynuclein
Owner:PHARNEXT
Prevention and treatment of synucleinopathic and amyloidogenic disease
ActiveUS8147833B2Improves motor characteristicInhibit deteriorationAnimal cellsNervous disorderTherapeutic treatmentSynuclein
The invention provides improved agents and methods for treatment of diseases associated with synucleinopathic diseases, including Lewy bodies of alpha-synuclein in the brain of a patient. Such methods entail administering agents that induce a beneficial immunogenic response against the Lewy body. The methods are particularly useful for prophylactic and therapeutic treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Method for quantitatively detecting alpha-synuclein auto-antibodies in human sera
InactiveCN101692092AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMicroorganism based processesSerum igeAntigen-antibody reactions
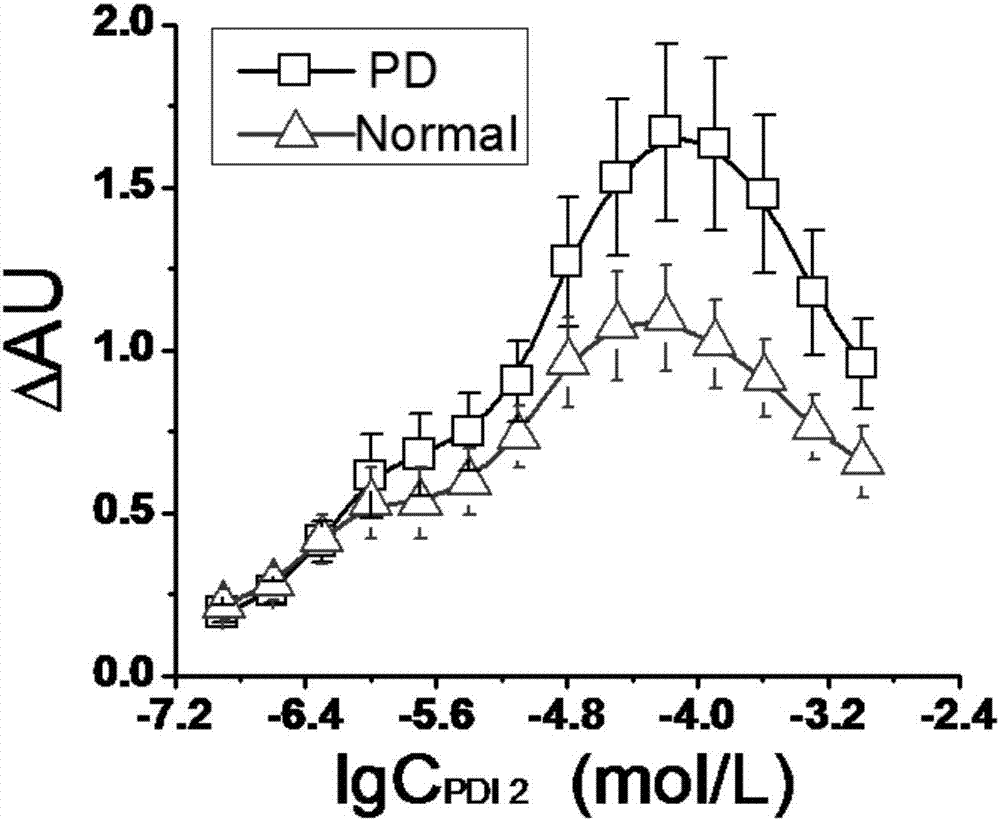
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively detecting alpha-synuclein auto-antibodies in human sera, and prepares recombinant human alpha-synuclein as antigens and rabbit anti-human alpha-synuclein polyclonal antibodies as antibodies into a kit, wherein, the quantities of alpha-synuclein auto-antibodies in the sera of patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) and in the sera of normal healthy persons are detected by utilizing the antigen-antibody reaction principle and are compared; and the presence and quantity of alpha-synuclein auto-antibodies in human sera are judged by the kit on the basis of color reaction.
Owner:XUANWU HOSPITAL OF CAPITAL UNIV OF MEDICAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com