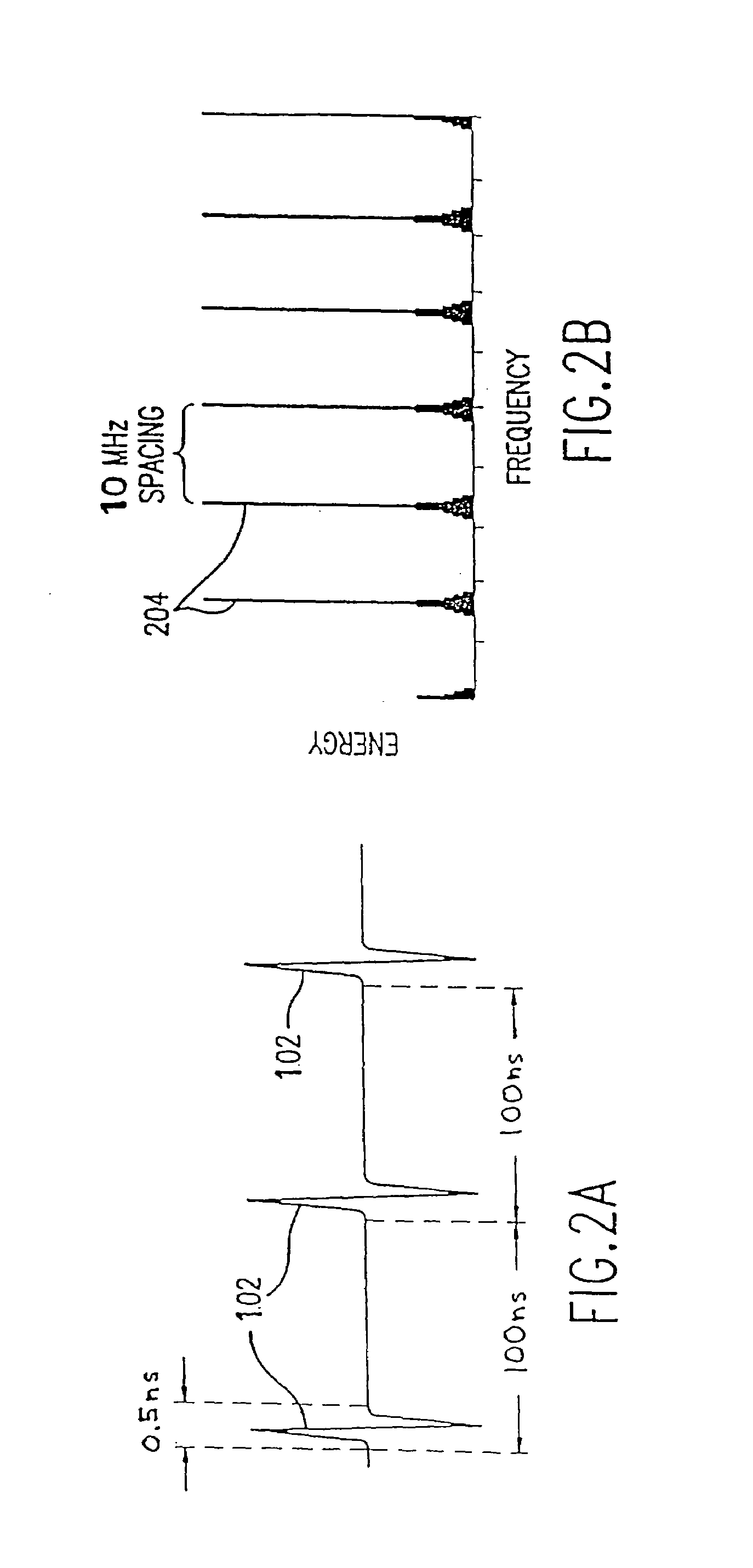
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
146 results about "Radio propagation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves as they travel, or are propagated, from one point to another, or into various parts of the atmosphere. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, like light waves, radio waves are affected by the phenomena of reflection, refraction, diffraction, absorption, polarization, and scattering. Understanding the effects of varying conditions on radio propagation has many practical applications, from choosing frequencies for international shortwave broadcasters, to designing reliable mobile telephone systems, to radio navigation, to operation of radar systems.
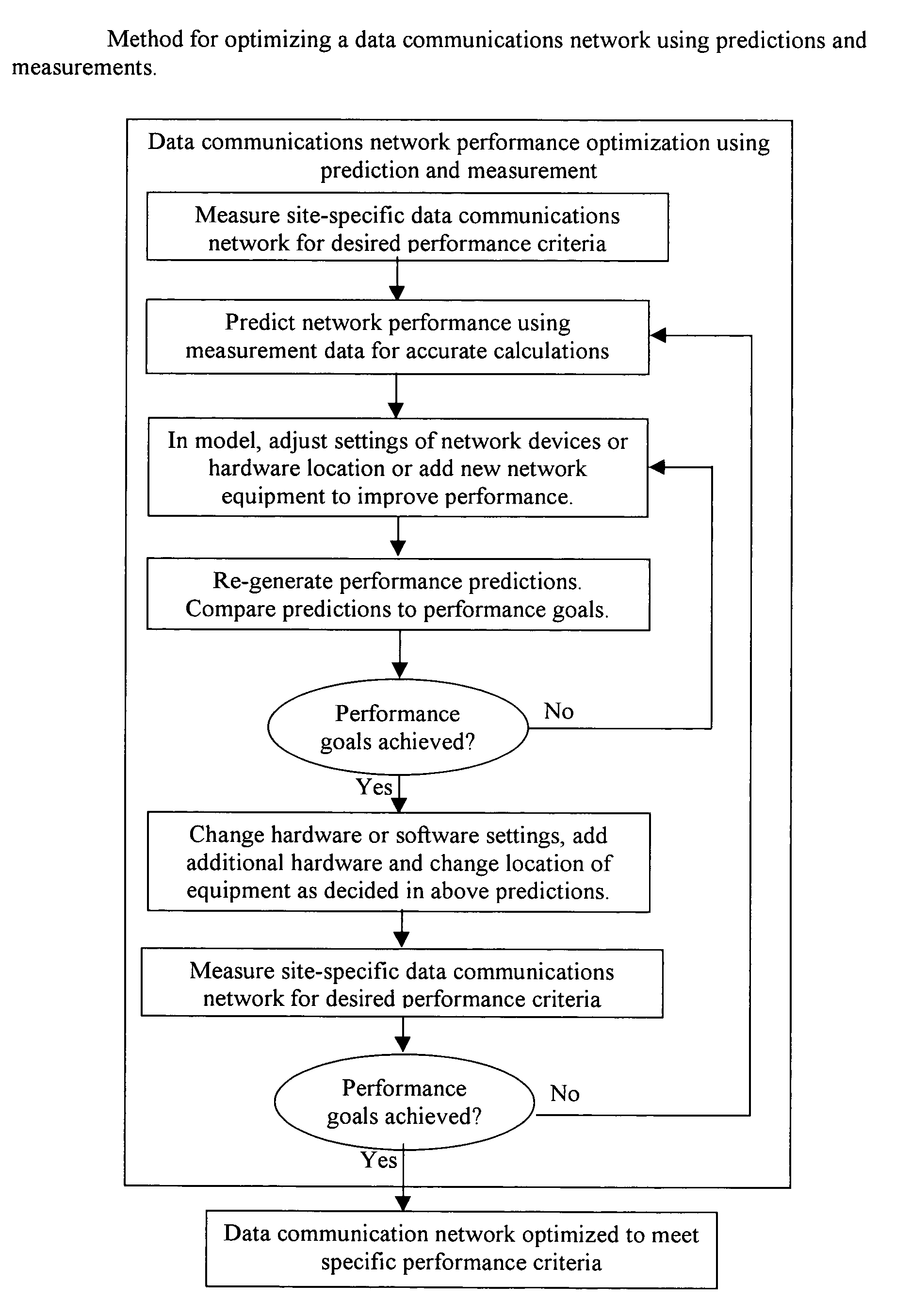
System and method for design, tracking, measurement, prediction and optimization of data communication networks
InactiveUS6973622B1MeasuringImprove performanceAnalogue computers for electric apparatusData switching by path configurationRadio propagationSpecific model
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
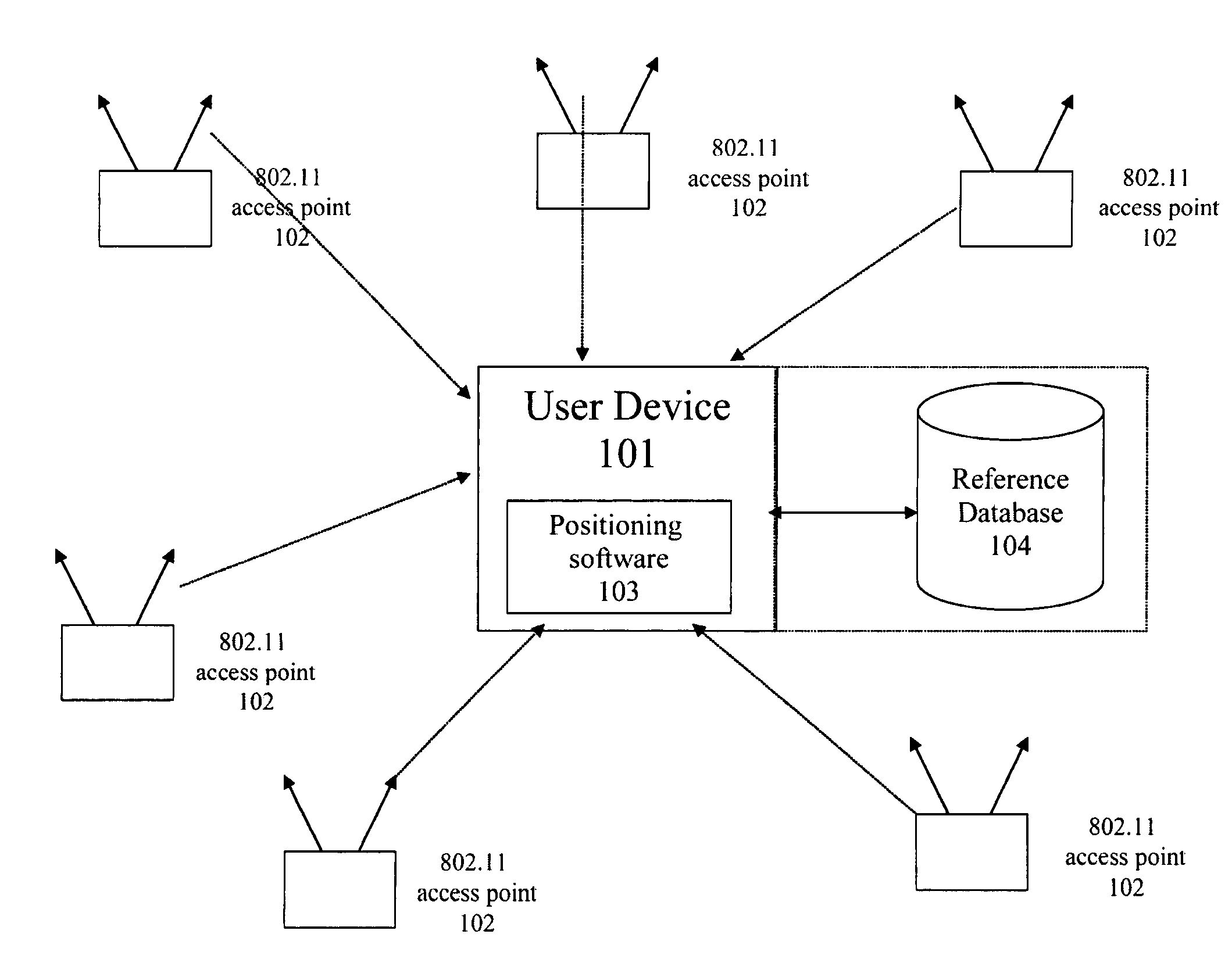
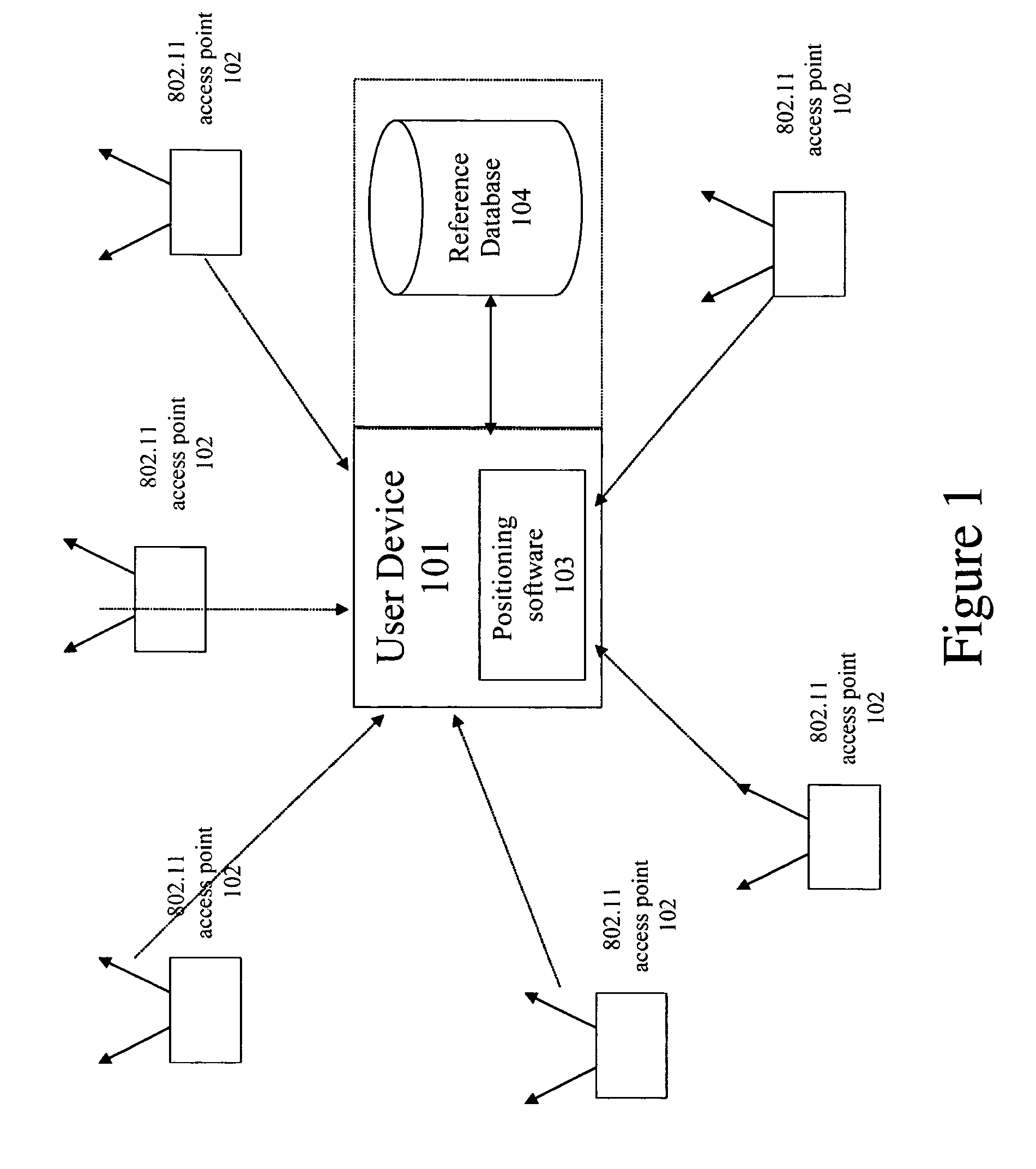
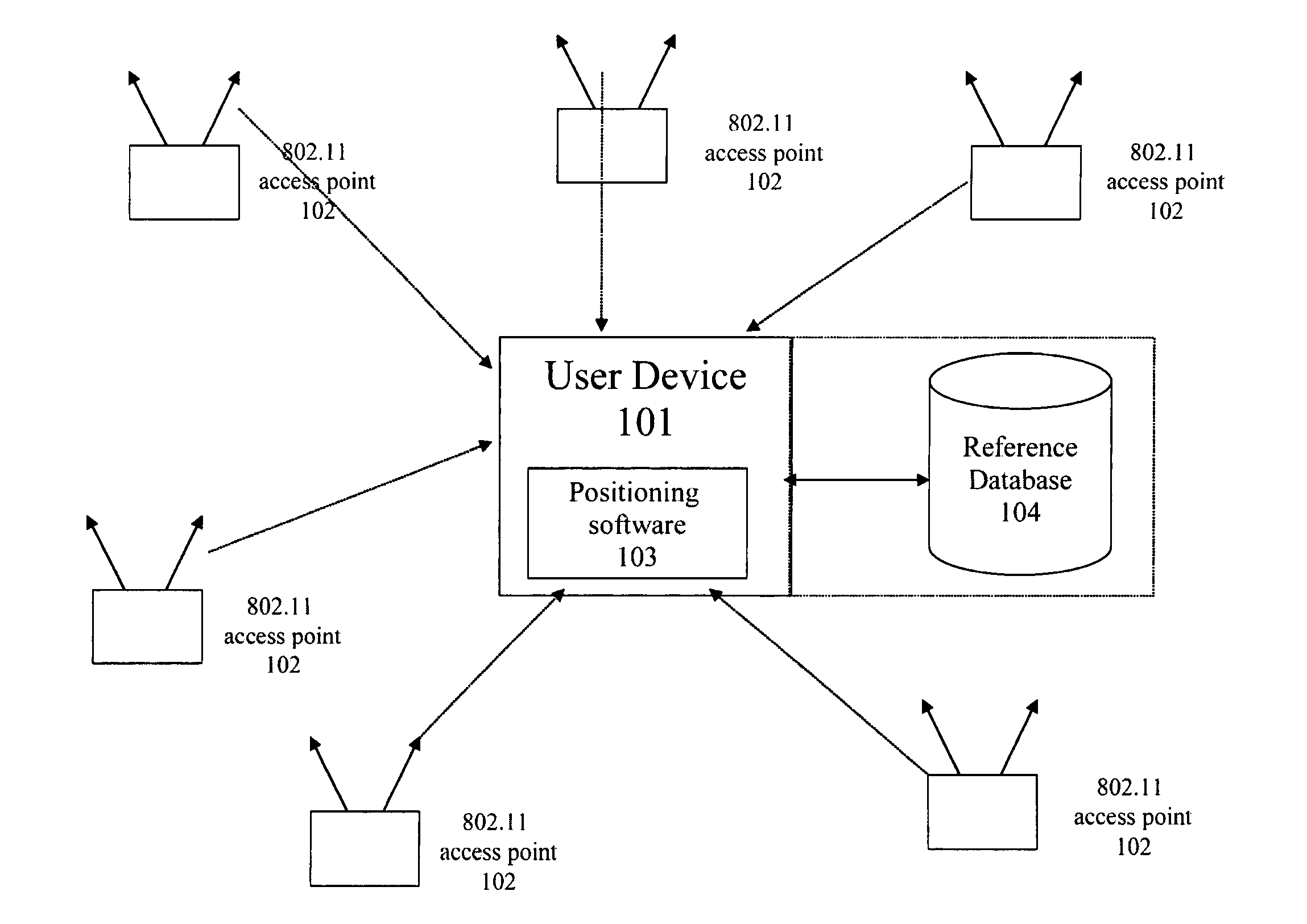
Estimation of position using WLAN access point radio propagation characteristics in a WLAN positioning system
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
System and method for design, tracking, measurement, prediction and optimization of data communication networks
InactiveUS20050265321A1Quickly and easily designQuick and easy measurementError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRadio propagationSpecific model
A system and method for design, tracking, measurement, prediction and optimization of data communications networks includes a site specific model of the physical environment, and performs a wide variety of different calculations for predicting network performance using a combination of prediction modes and measurement data based on the components used in the communications networks, the physical environment, and radio propagation characteristics.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Estimation of position using WLAN access point radio propagation characteristics in a WLAN positioning system
A method for estimating position using WLAN access point radio propagation characteristics in a WLAN location based service is provided. A location-based services system has a plurality of Wi-Fi access points in a target area. The Wi-Fi access points are positioned at geographic locations and have signal coverage areas. A method of characterizing at least one of the Wi-Fi access points comprises determining the geographic location of the Wi-Fi access point, dividing the signal coverage area of the Wi-Fi access point into at least one section, and determining radio propagation characteristics for each section. The radio propagation characteristics of each section characterize a radio channel of the Wi-Fi access point, and the characterization can be used in a location algorithm.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
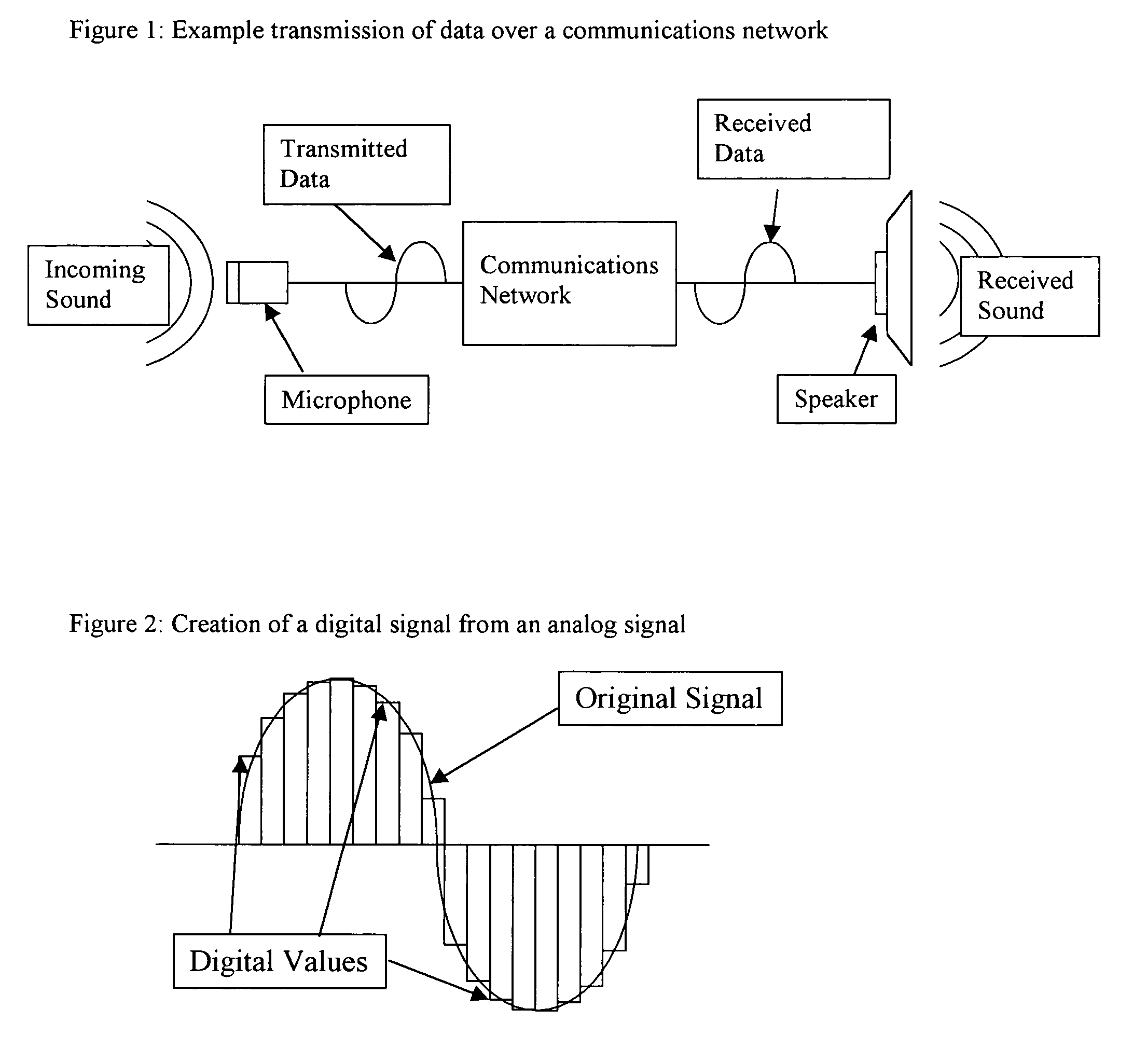
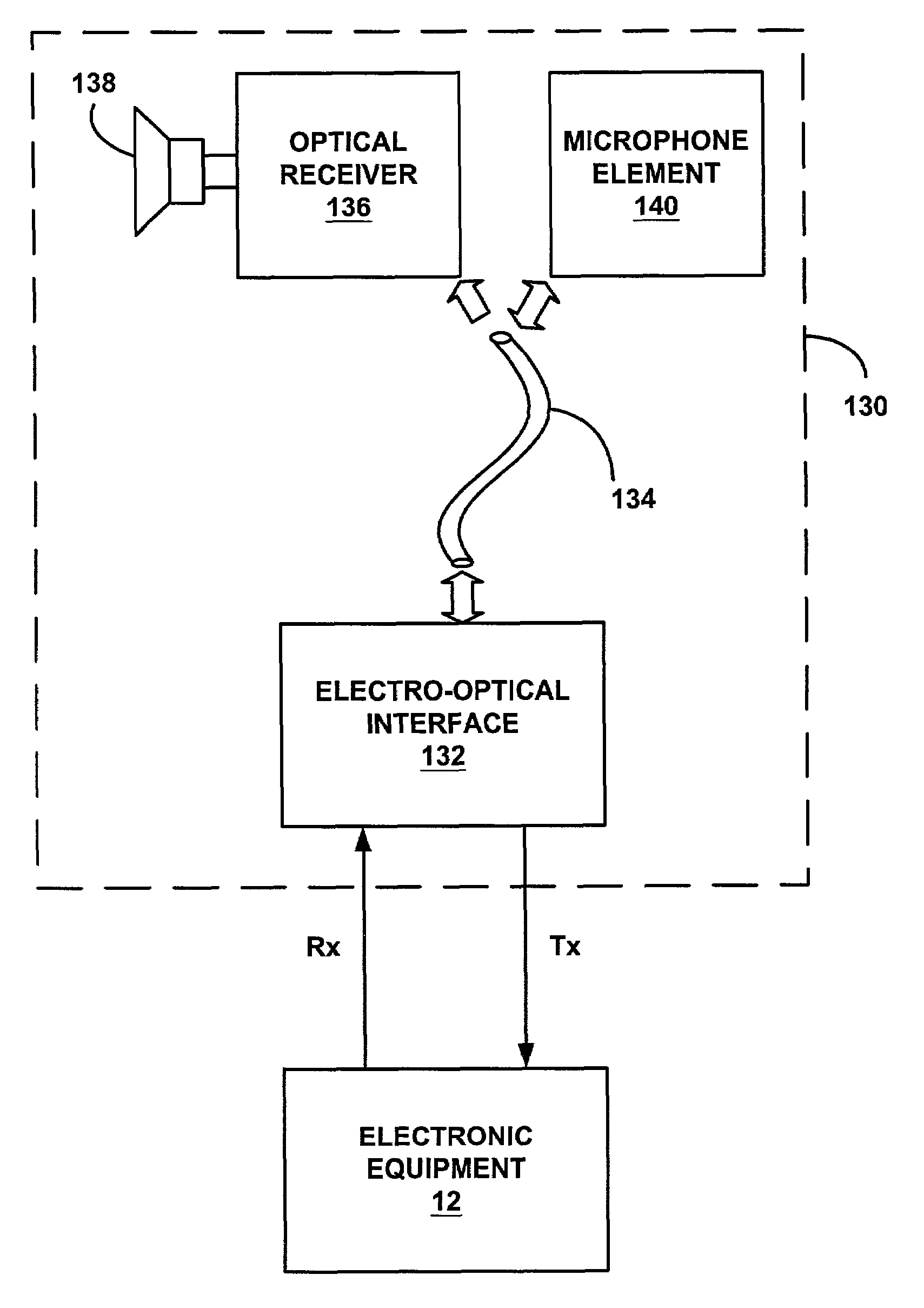
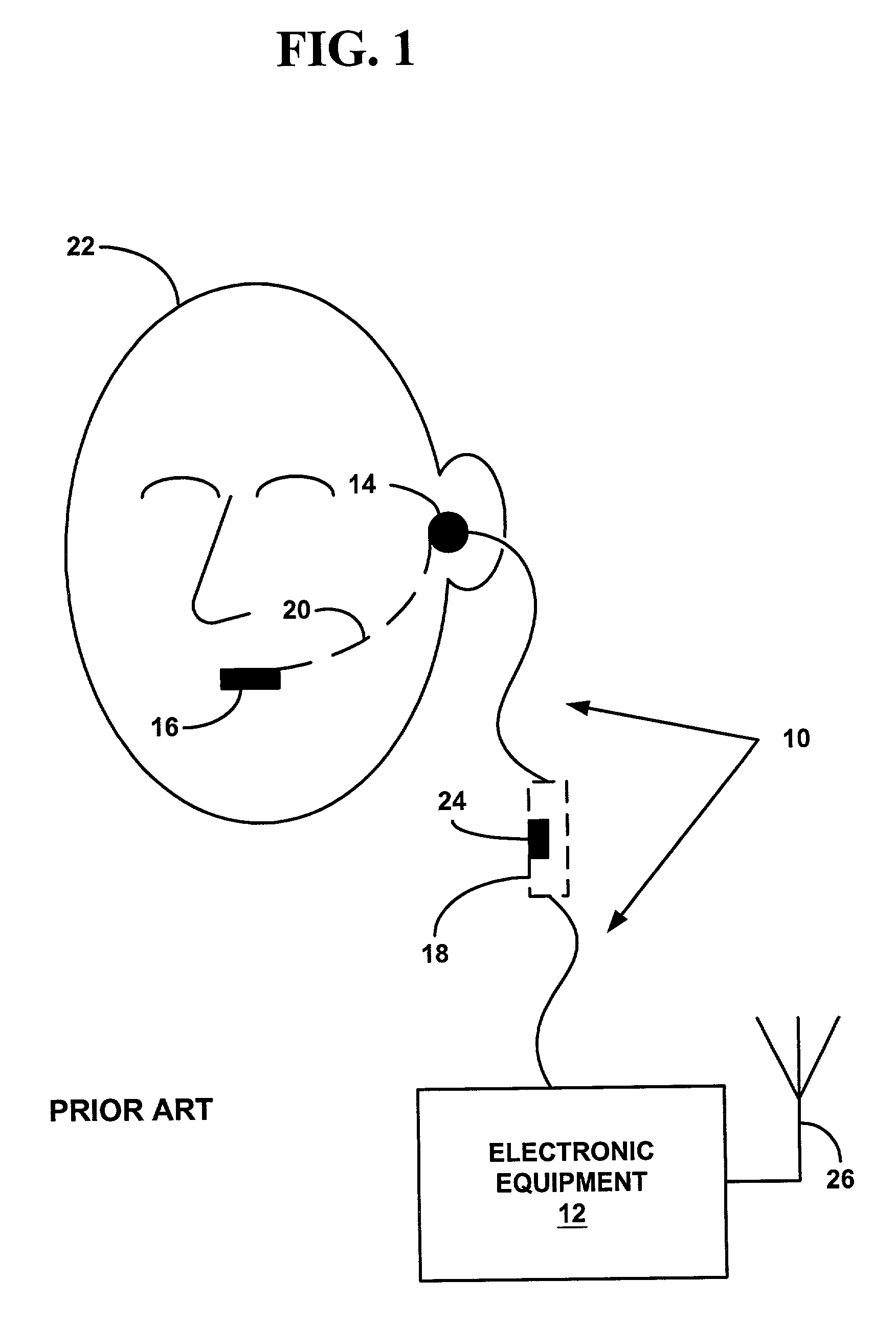
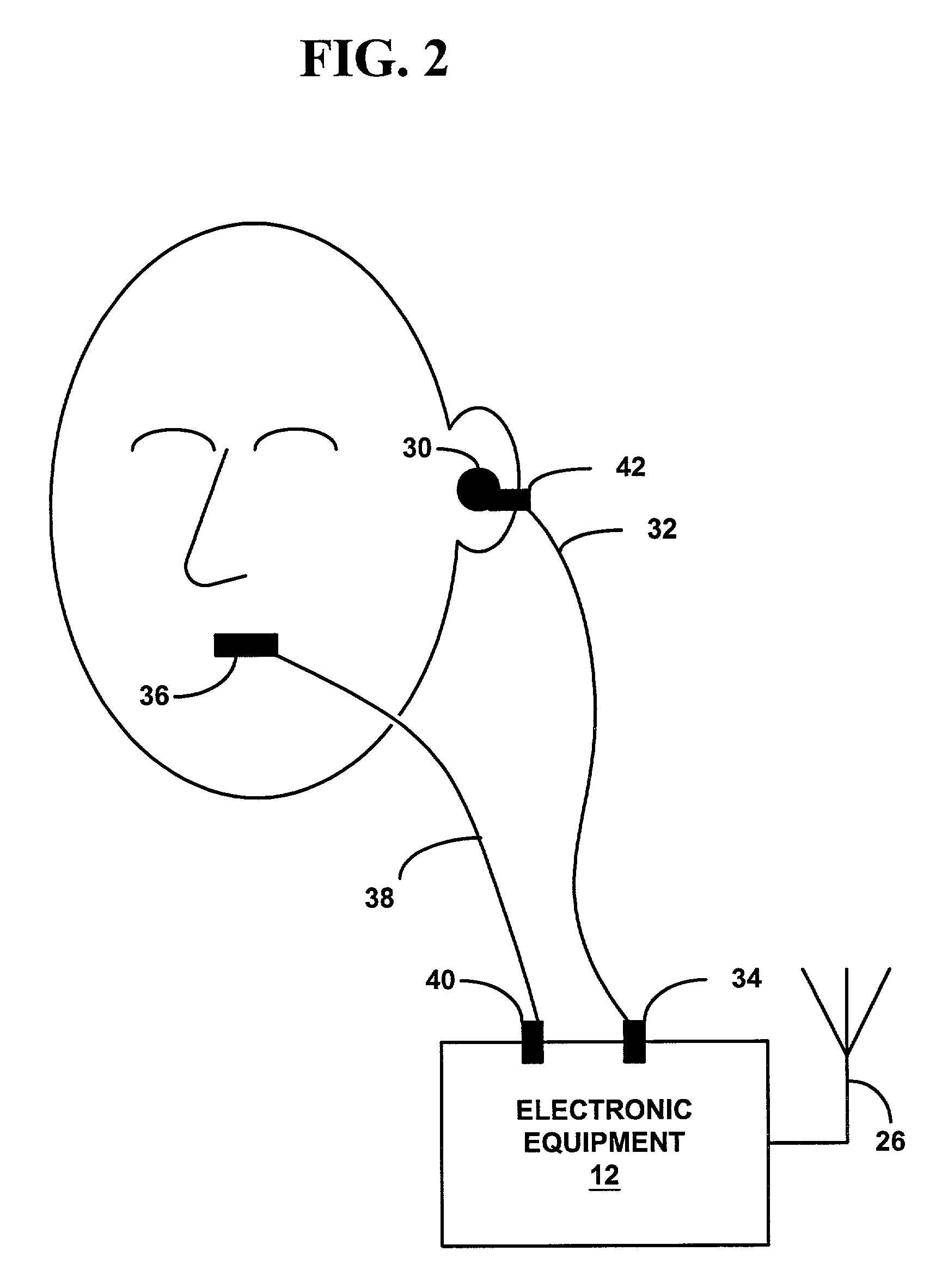
Optically coupled headset and microphone
InactiveUS7072475B1Total current dropReduce voltageMicrophonesLoudspeakersRadio propagationEngineering
Apparatus and methods for transferring audio between a headset and electronic equipment over an optical link. The apparatus includes an electro-optical interface for electrically connecting to the electronic equipment, an optical link, and an electro-optical headset. Audio from the electronic equipment modulates a light source in the electro-optical interface. A modulated light signal is transmitted through the optical link to the electro-optical headset where it is demodulated and reproduced as the original audio in the ear of a user wearing the headset. Also, another audio from the user's mouth produces another modulated light signal in the electro-optical headset. The other modulated light signal is transmitted through the optical link to the electro-optical interface where it is demodulated to provide the other audio to the electronic equipment. The non-electrical optical link may improve audible communications between the electronic equipment and the headset in radio-frequency noisy environments. Also, the non-electrical optical link may prevent coupling with an aerial of the electronic equipment and improve radio propagation.
Owner:SPRING SPECTRUM LP
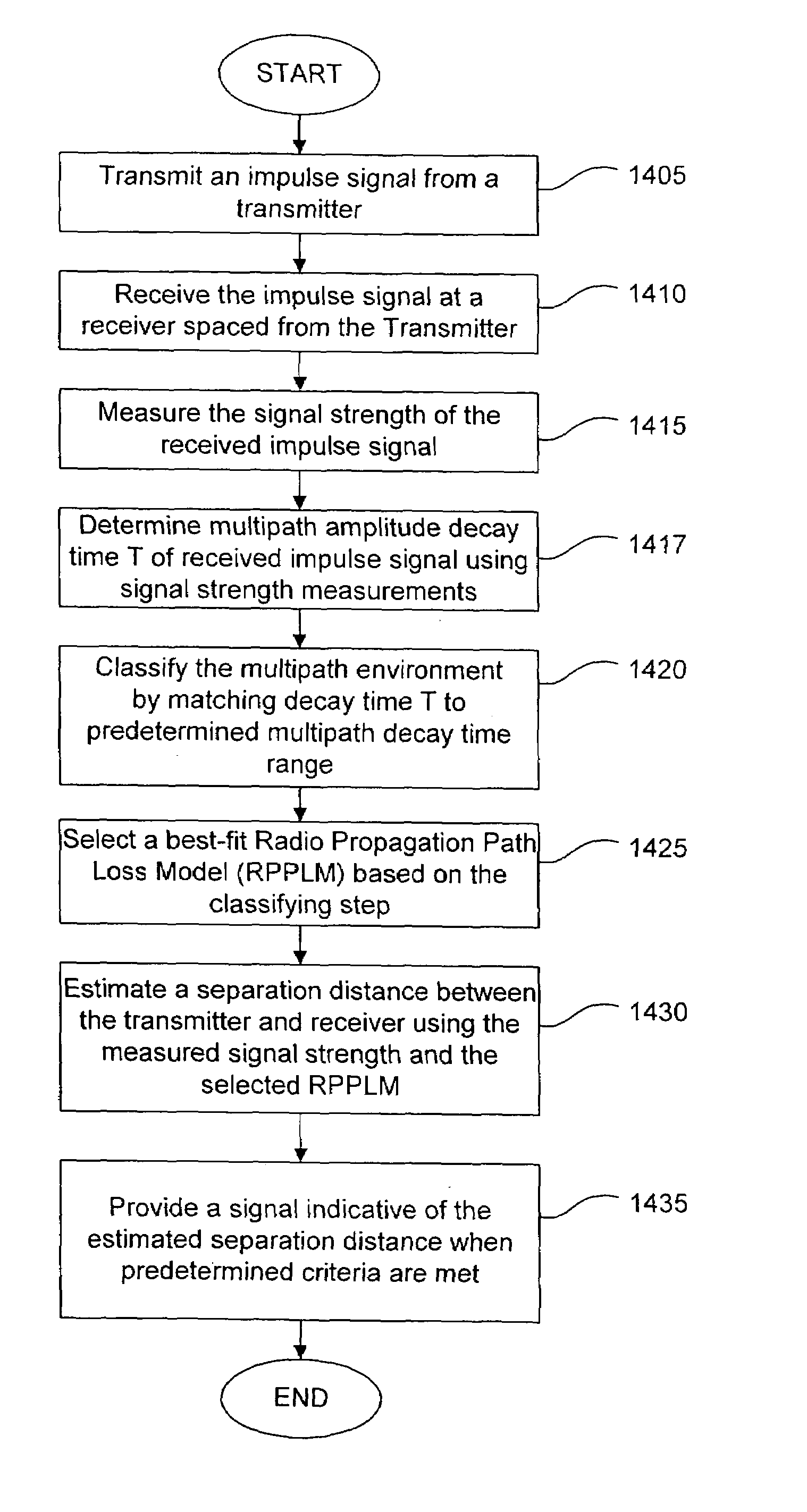
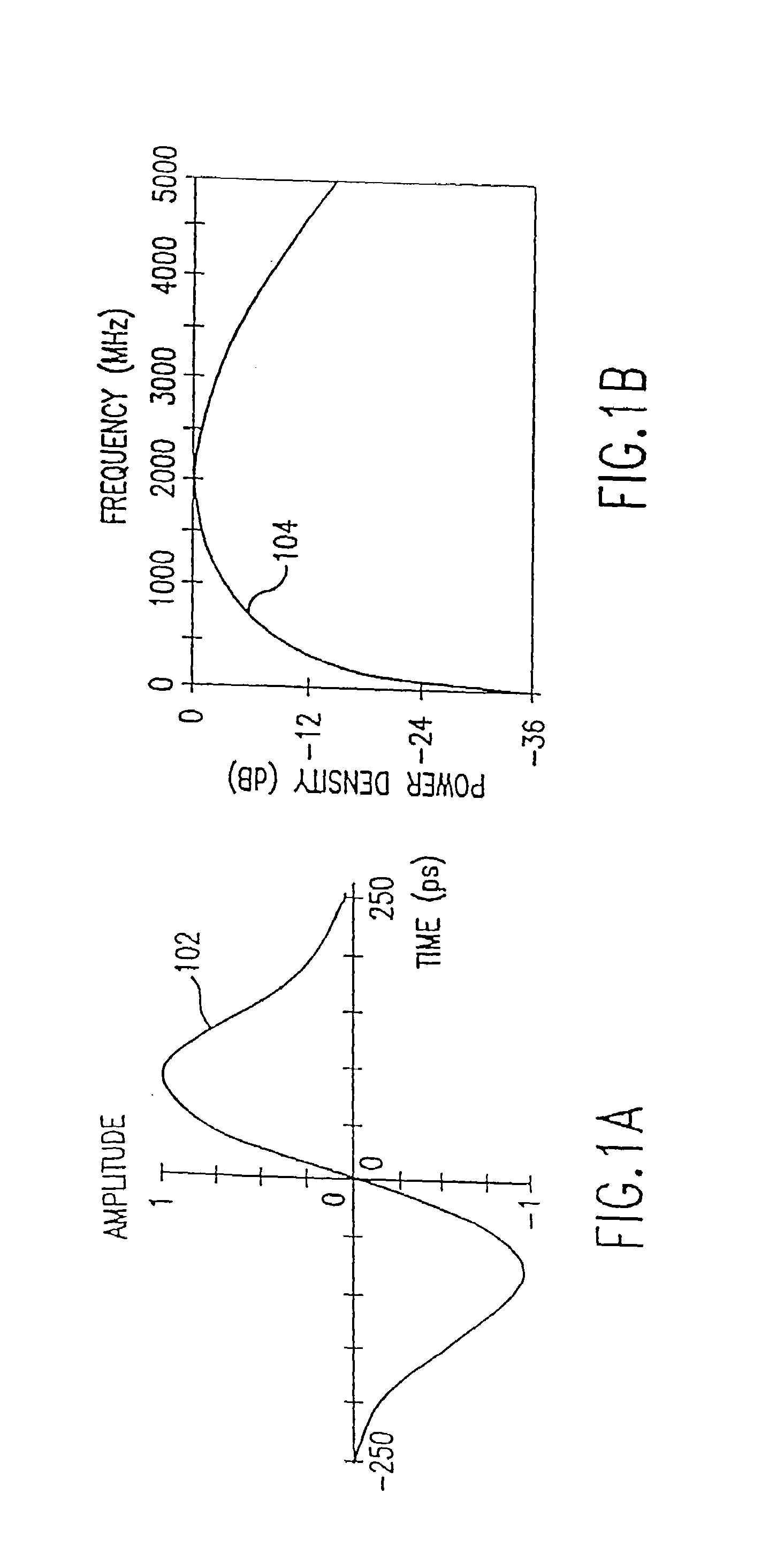
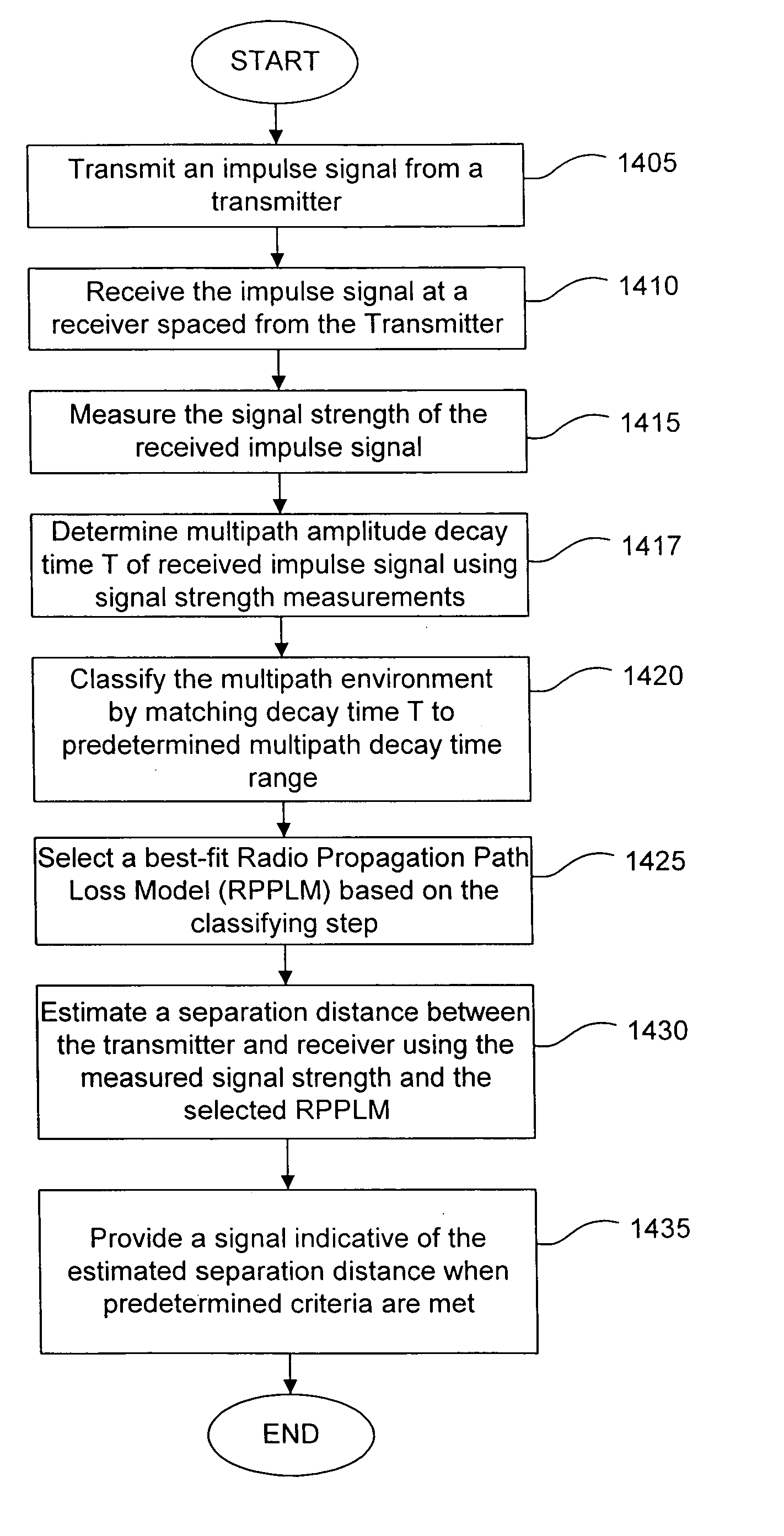
System and method for estimating separation distance between impulse radios using impulse signal amplitude
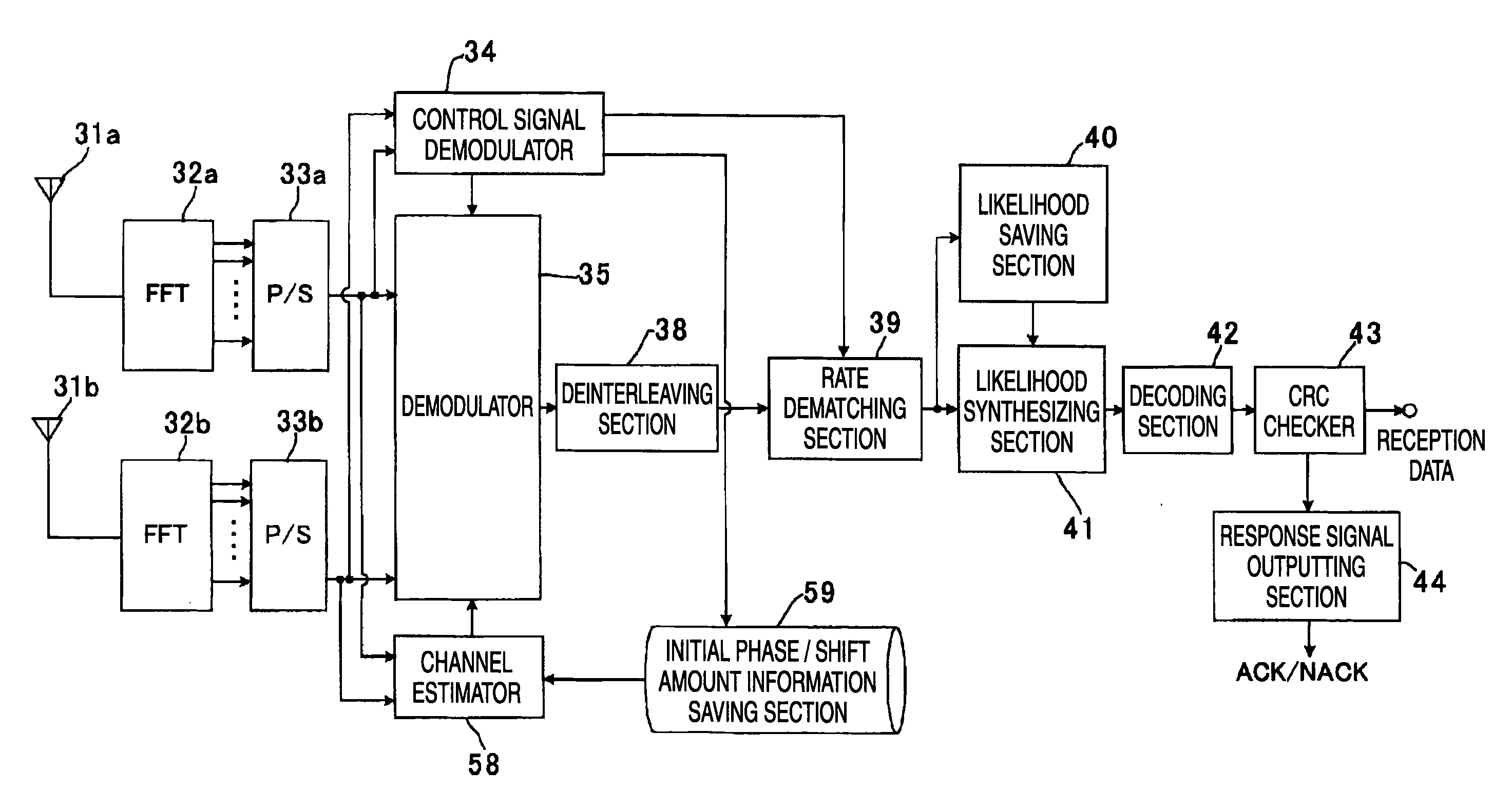
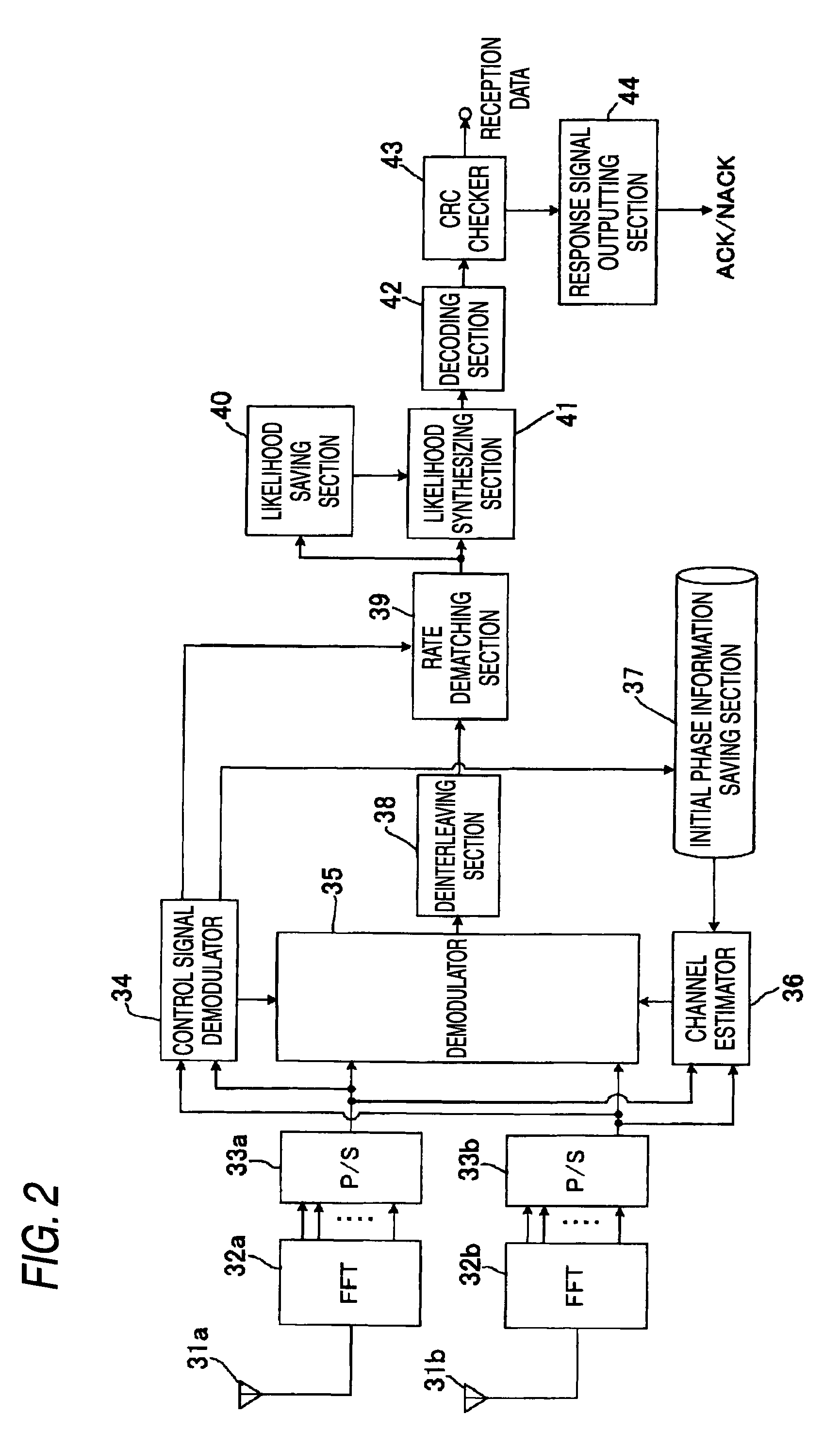
InactiveUS7151490B2Resists fading effectImprove accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesUsing reradiationRadio propagationImpulse radio
A method and system are provided for locating an impulse radio. Impulse radio signals are communicated between a first impulse radio and a plurality of second impulse radios. A received signal strength measurement is determined for each of the impulse radio signals. One of a plurality of radio propagation path models is selected and used to estimate a plurality of separation distances between the first impulse radio and the plurality of second impulse radios. The plurality of separation distances is used to determine a location relating to the first impulse radio.
Owner:HUMATICS CORP
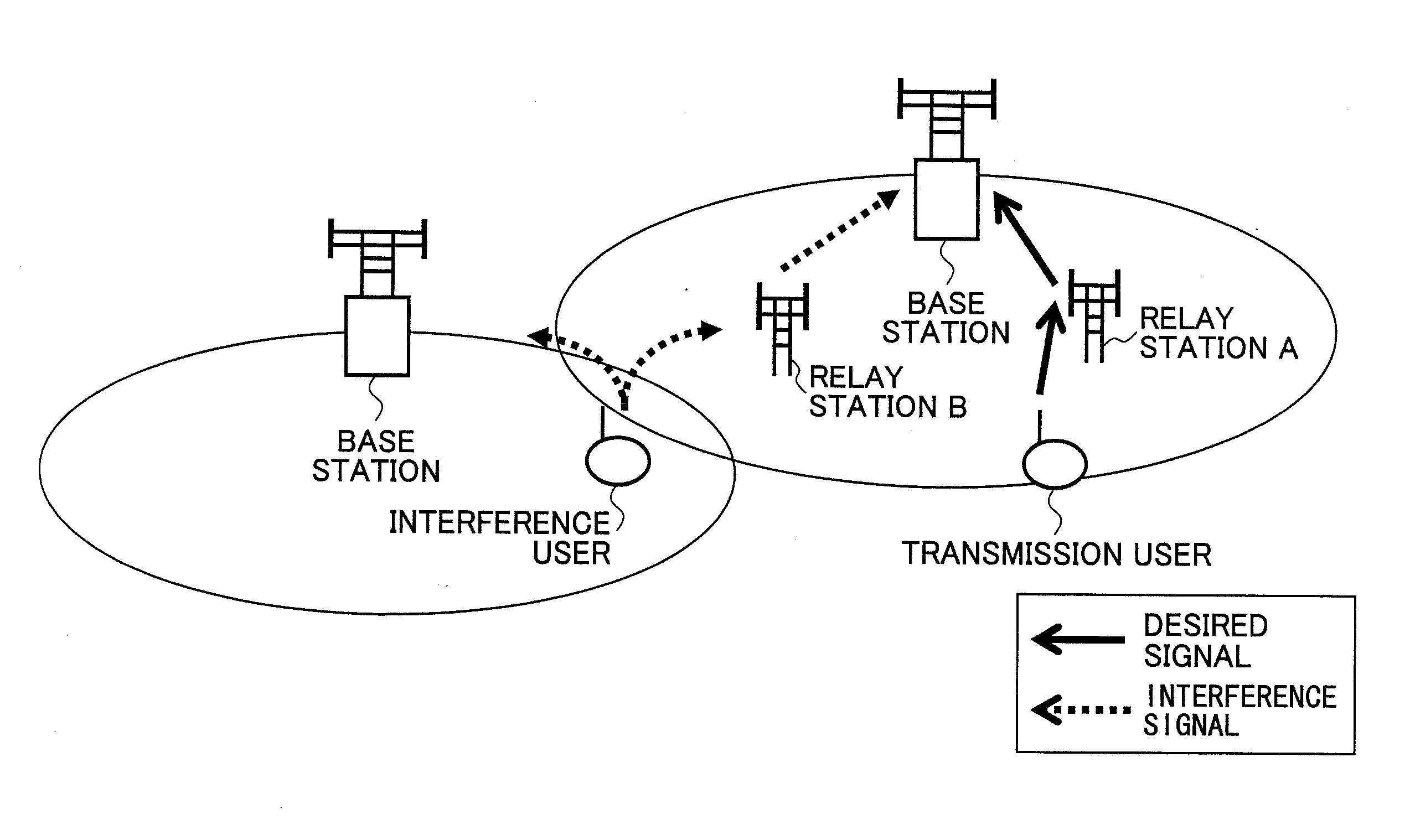
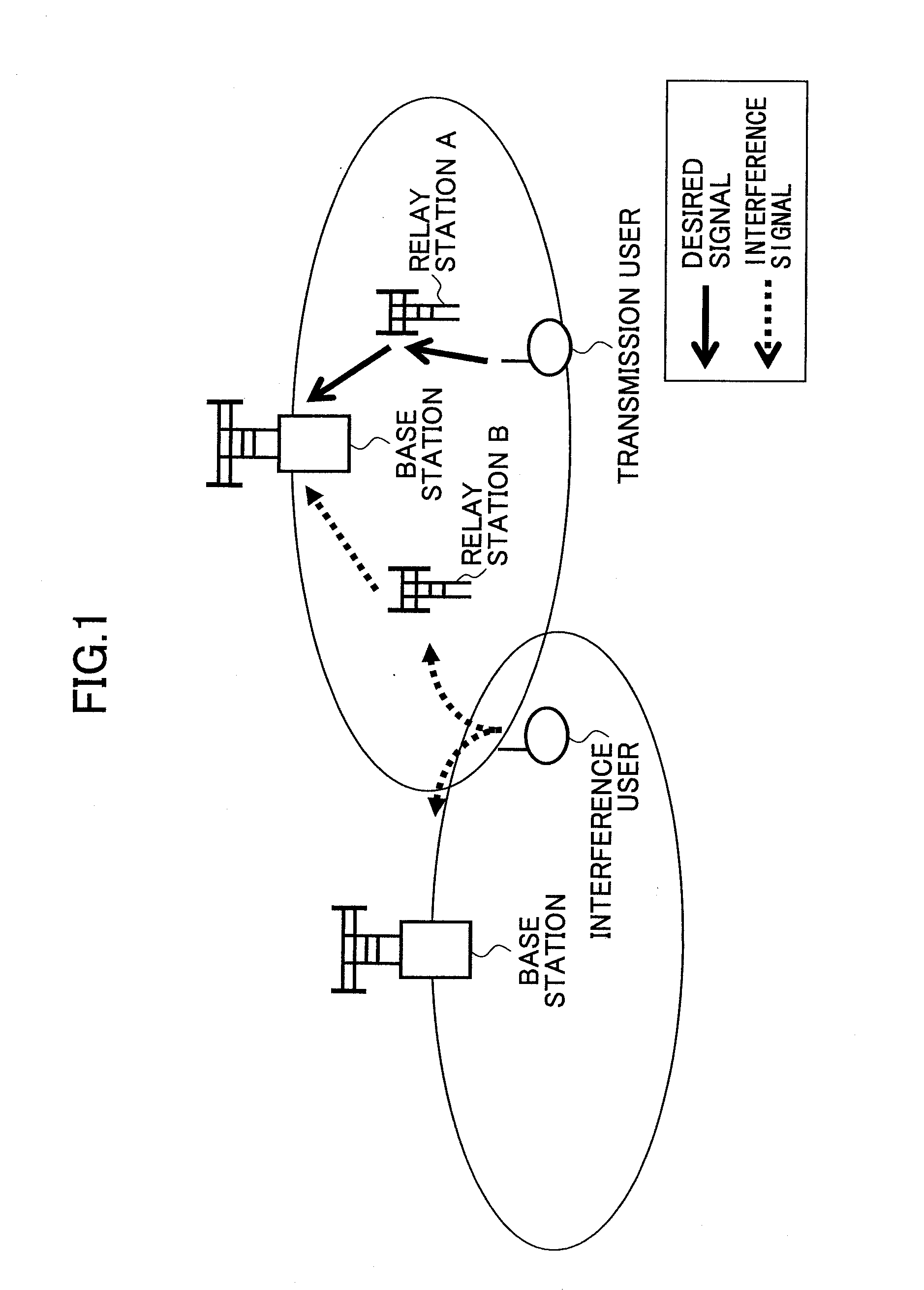
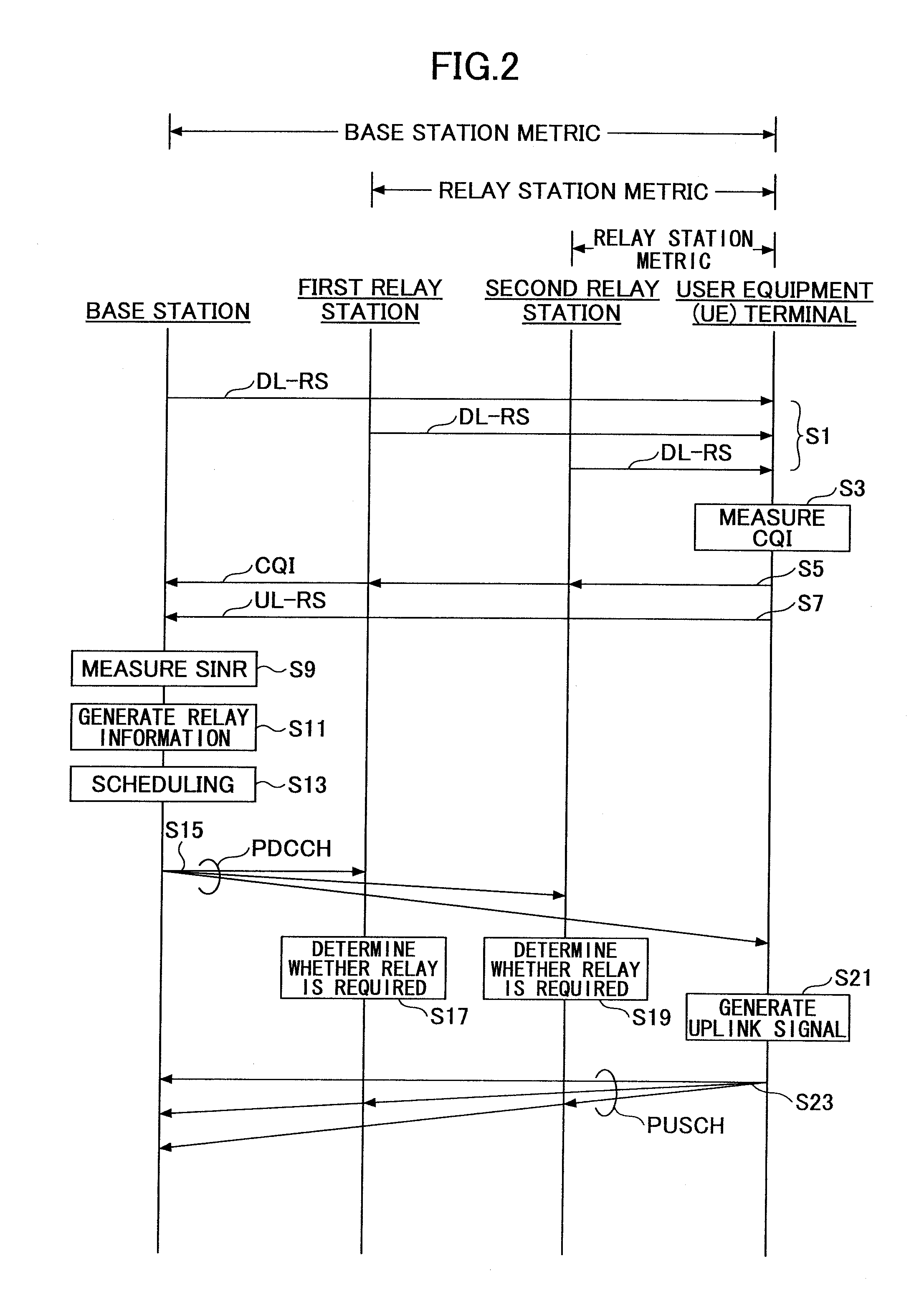
Relay transmission system, base station, relay station, and method
InactiveUS20100304665A1Improve signal qualityEasy to useNetwork topologiesRepeater circuitsControl signalRadio propagation
A base station used in a relay transmission system is disclosed. The base station includes a metric provision unit providing a metric indicating radio propagation conditions of a user equipment terminal; a relay information generation unit generating a relay information for the user equipment terminal based on the metric, the relay information indicating whether an uplink signal is to be transmitted via one or more relay stations; a scheduling unit generating an allocation plan of radio resources based on the relay information; and a control signal transmission unit transmitting a control signal including a scheduling information indicating the allocation plan.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
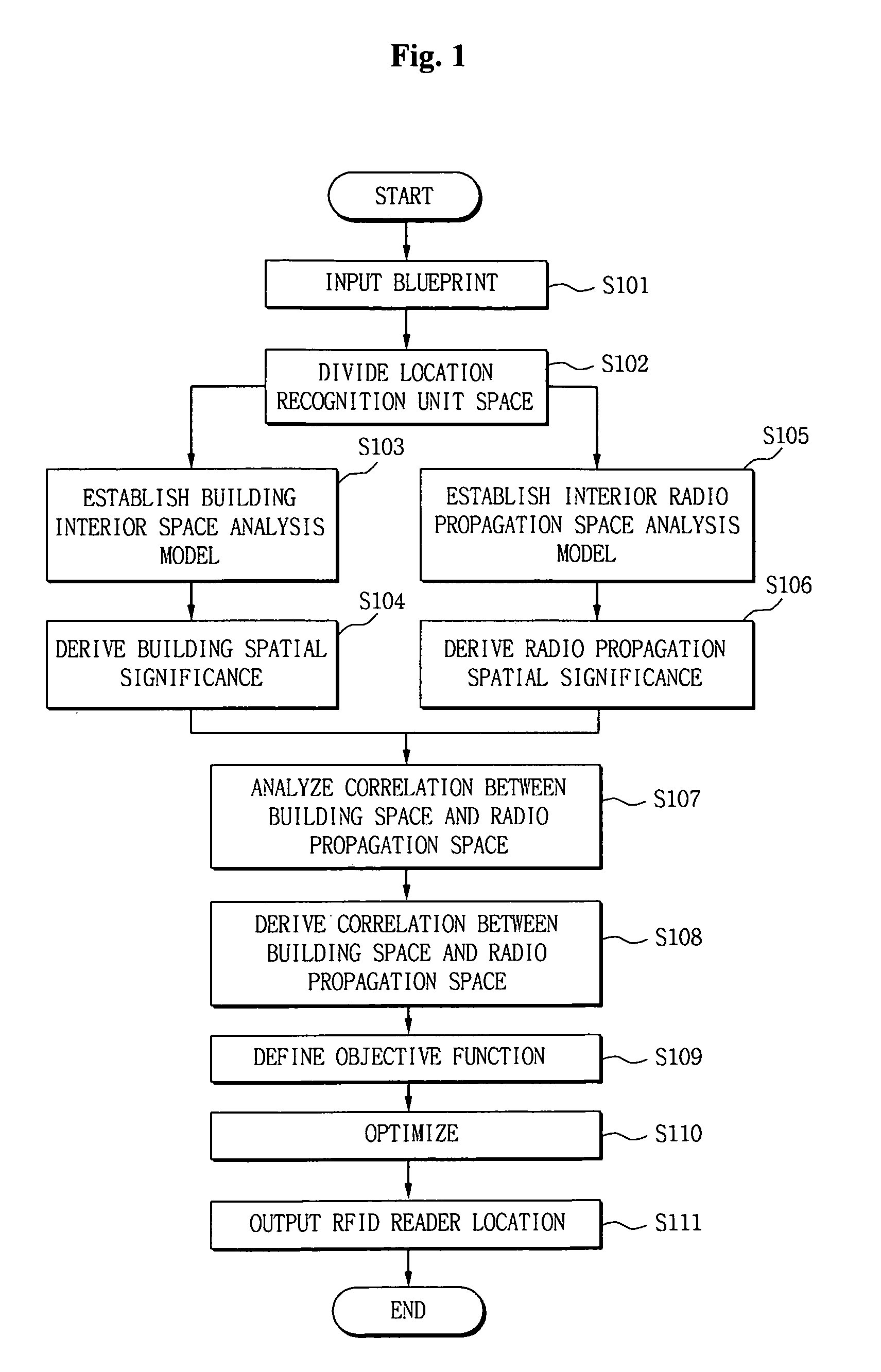
Method for optimization in RFID location recognition system using blueprint
InactiveUS20100045439A1Easy to identifyTransmission systemsWireless architecture usageCorrelation coefficientRadio propagation
A method for optimization in an RFID location recognition system is developed to use in a blueprint in which an optimum location for installing an RFID reader is determined for using a blueprint so as to improve location recognition. The method includes the steps of inputting a blueprint and dividing a location recognition unit space from the blueprint; establishing a building interior space analysis model and an interior radio propagation space analysis model and deriving a building spatial significance and a radio propagation spatial significance; analyzing correlation between a building space and a radio propagation space and deriving a correlation coefficient; and defining an objective function for determining a location of a RFID reader based on the building spatial significance, the radio propagation spatial significance, and the correlation coefficient between the building space and the radio propagation space and performing optimization.
Owner:PUSAN NAT UNIV IND UNIV COOPERATION FOUND
Protocol using forward error correction to improve handover
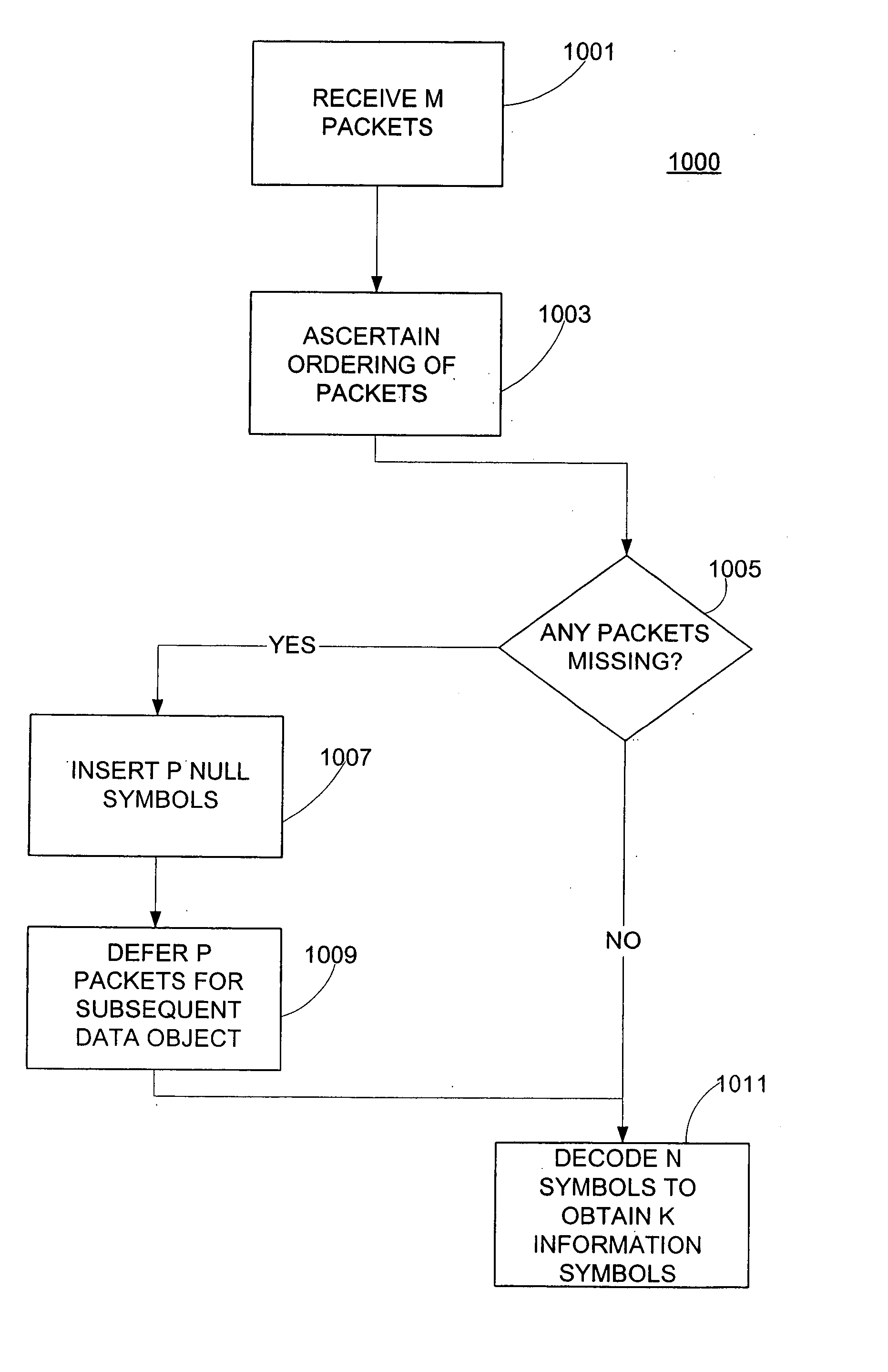
InactiveUS20050009523A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionData packRadio propagation
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for a wireless system broadcasting a plurality of data packets to a wireless terminal as the wireless terminal performs a handover in order to support a service. Corresponding data packets are sent in bursts from base stations to the wireless terminal. The data packets are encoded with a forward error correcting (FEC) code, thus generating encoded symbols. When the wireless terminal executes a handover from the first base station to the second base station, some of the encoded symbols (that are contained in the bursts of data packets) may be lost or may be corrupted, as result of practical network considerations and radio propagation characteristics. Consequently, the wireless terminal decodes the received data packets in accordance with the FEC code so that missing or corrupted encoded symbols may be determined.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
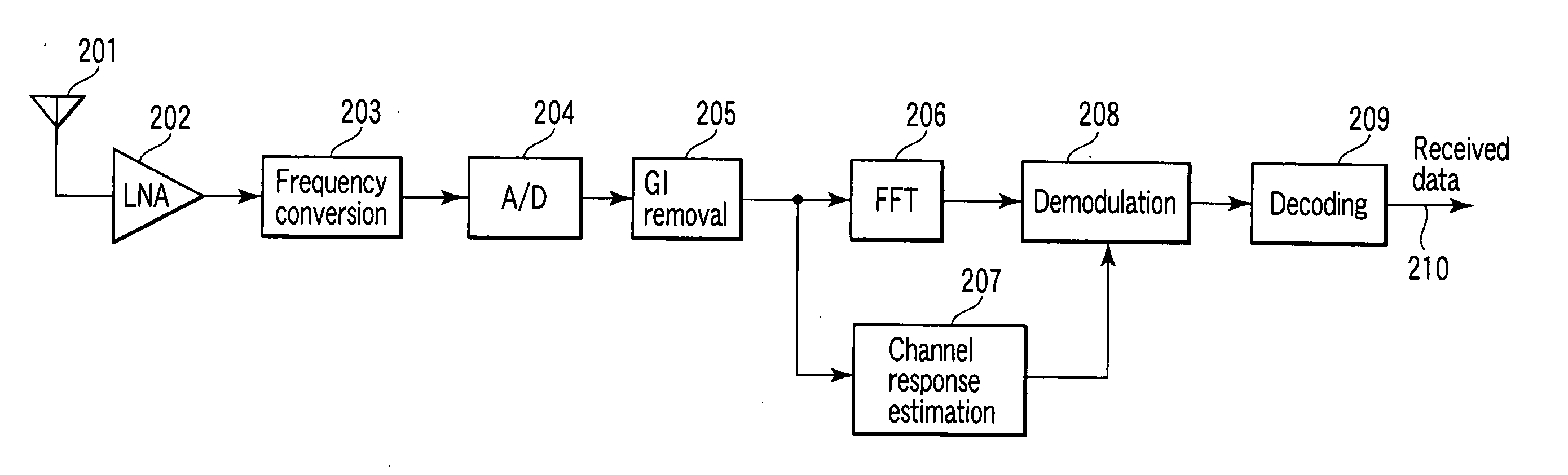
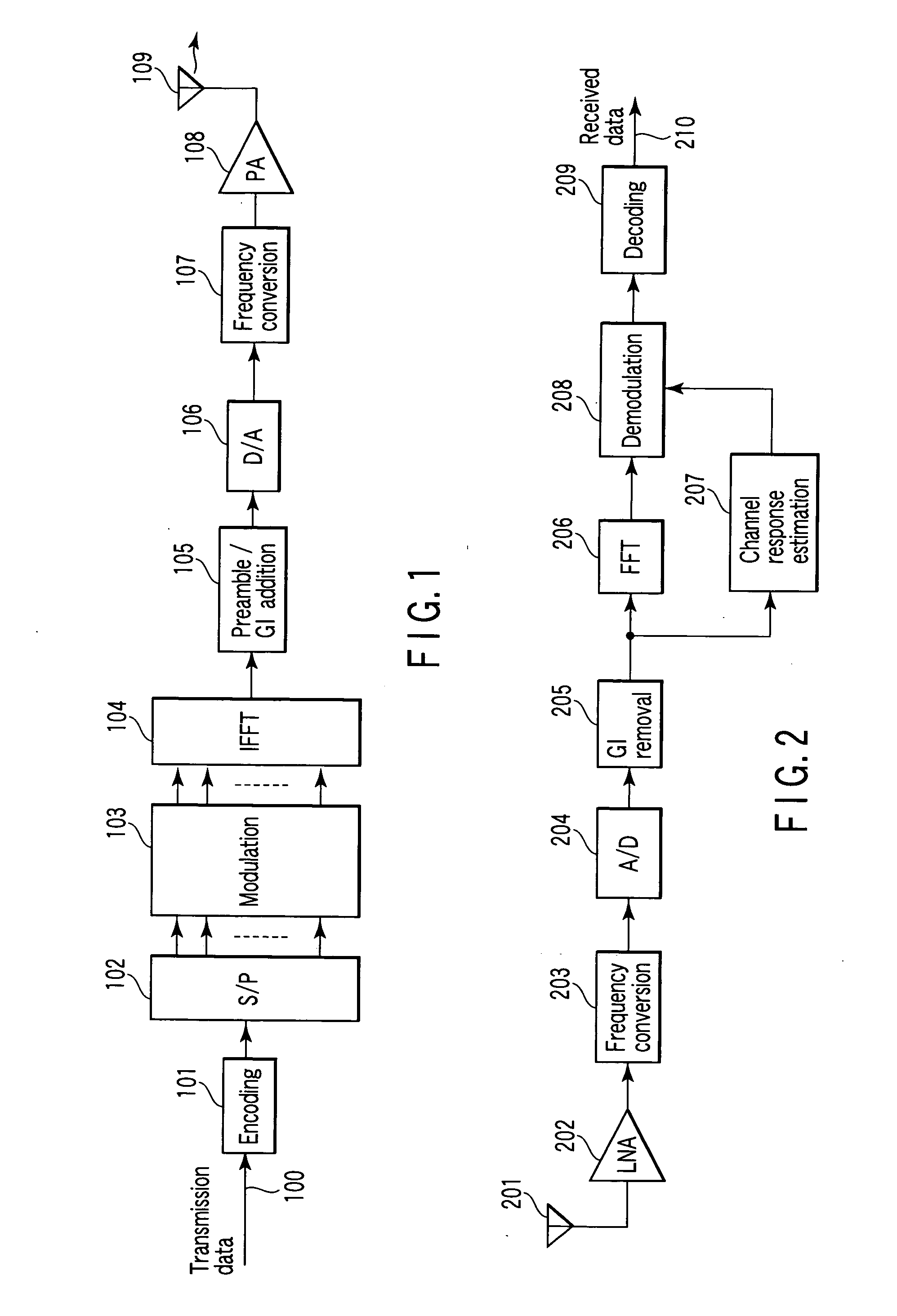
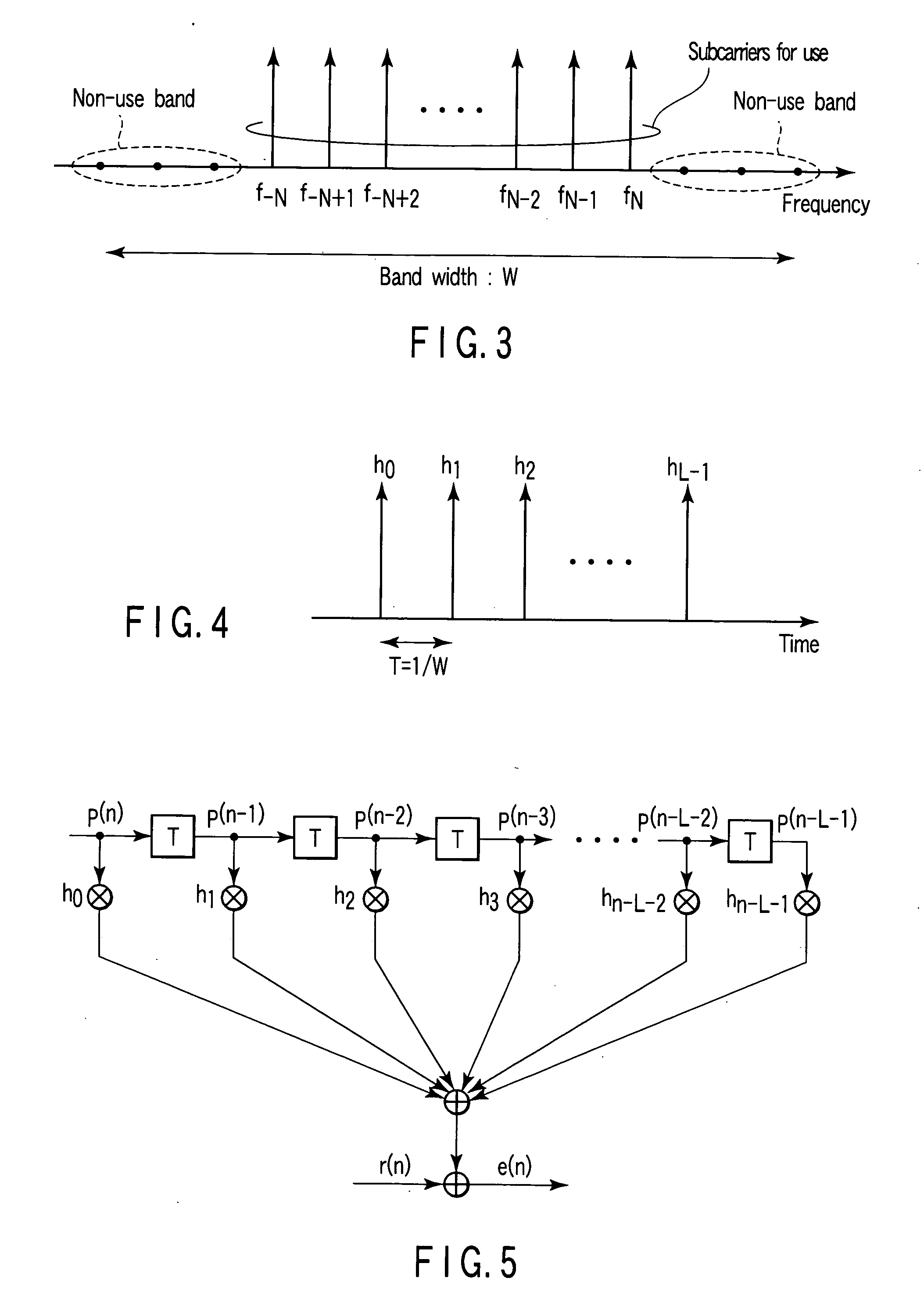
Method and apparatus for estimating channel response and receiver apparatus using the estimated channel response for OFDM radio communication systems
InactiveUS20050141649A1Improve accuracyHigh precision estimationSpecial service provision for substationData representation error detection/correctionCommunications systemRadio propagation
An estimation apparatus for estimating a channel response of a radio propagation path using a received signal including a first known signal, comprises a generator which generates a reference signal matrix, a calculator which calculates a generalized inverse matrix of the reference signal matrix including singular values which exceed a preset threshold value, an estimation unit configured to estimate an impulse response of the radio channel modeled using a transversal filter based on the first known signal and the generalized inverse matrix, and a converter which converts the estimated impulse response into a frequency-domain signal to acquire a frequency transfer function of the channel.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
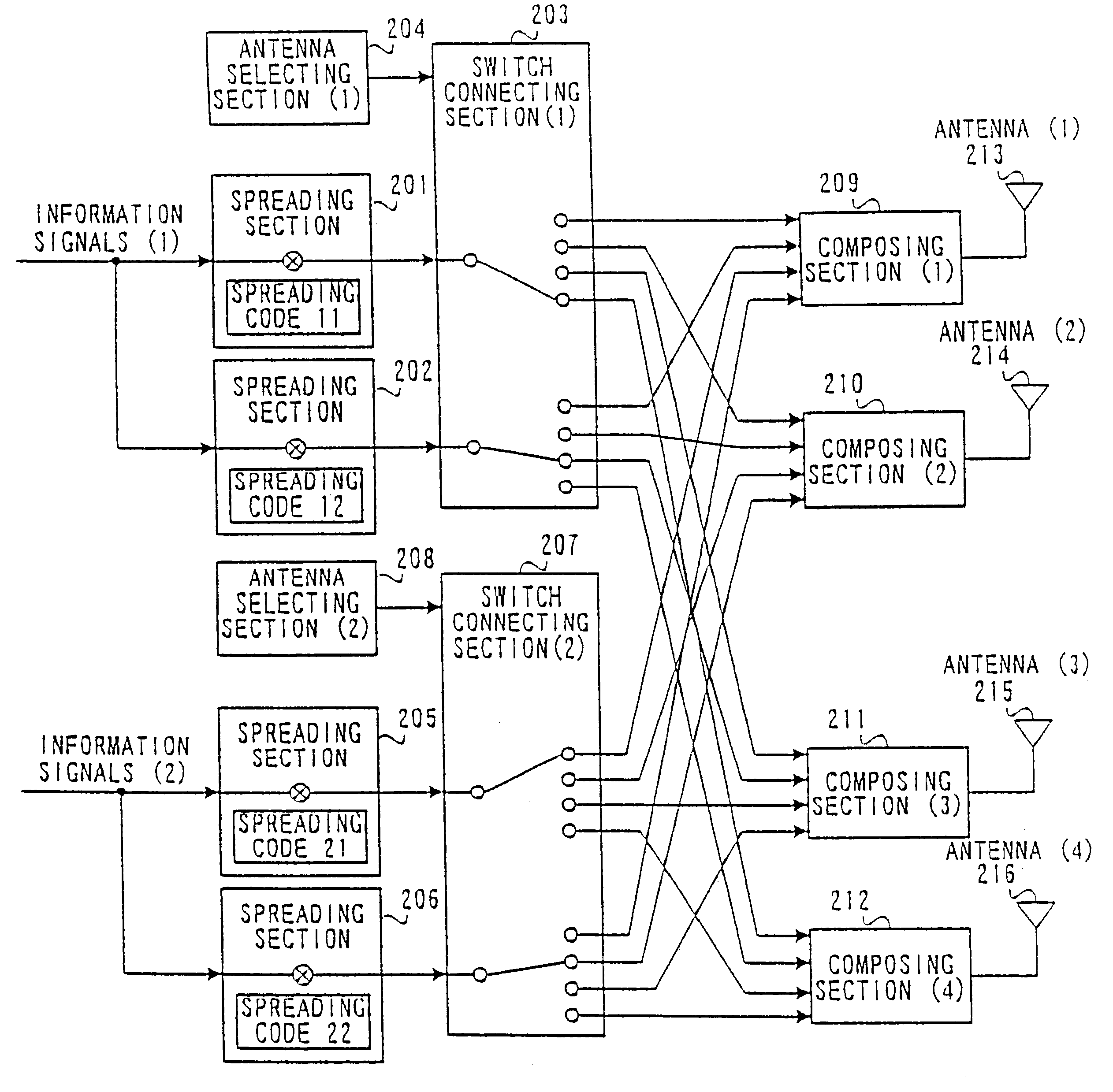
CDMA communication apparatus and CDMA communication method
InactiveUS6252864B1Drop in communication qualityChannel conditions vary fast is reducedSpatial transmit diversityCode division multiplexCommunication qualityRadio propagation
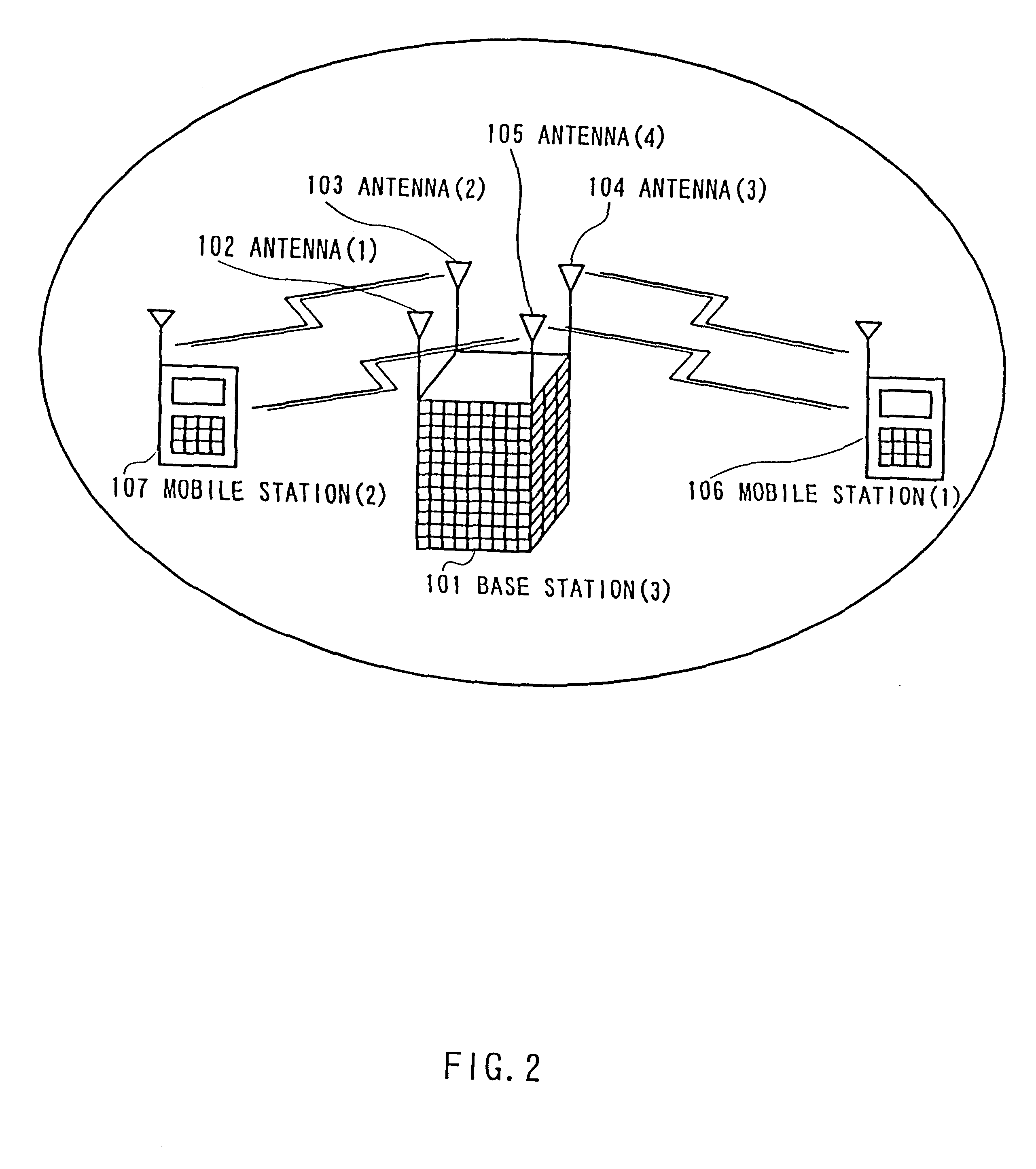
At base station 101, information signals for mobile station (1) are distributed, each spread with a different spreading code then transmitted from two antennas (3) and (4) assumed under good condition in radio propagation. In mobile station (1), composed waves of both signals are received and each is despread with respective spreading code, as well as in mobile station (2). According to it, it is possible to transmit the same information from a plurality of different antennas at the same time, which prevents the deterioration in communication quality in the case where a wrong antenna is selected or the radio propagation condition varies fast.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Method, apparatus and system of configuring a wireless device based on location
ActiveUS7421276B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationRadio propagationRadio unit
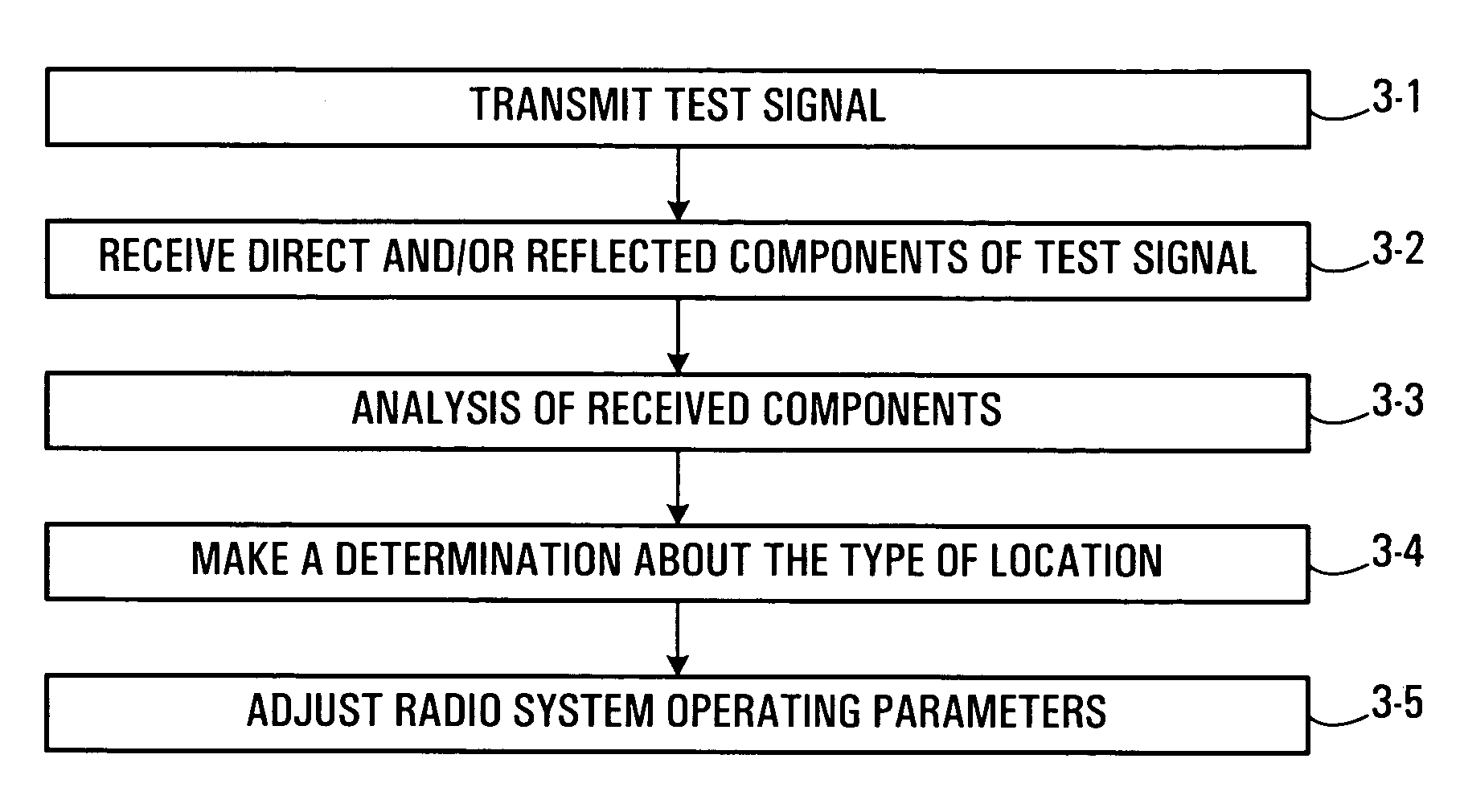
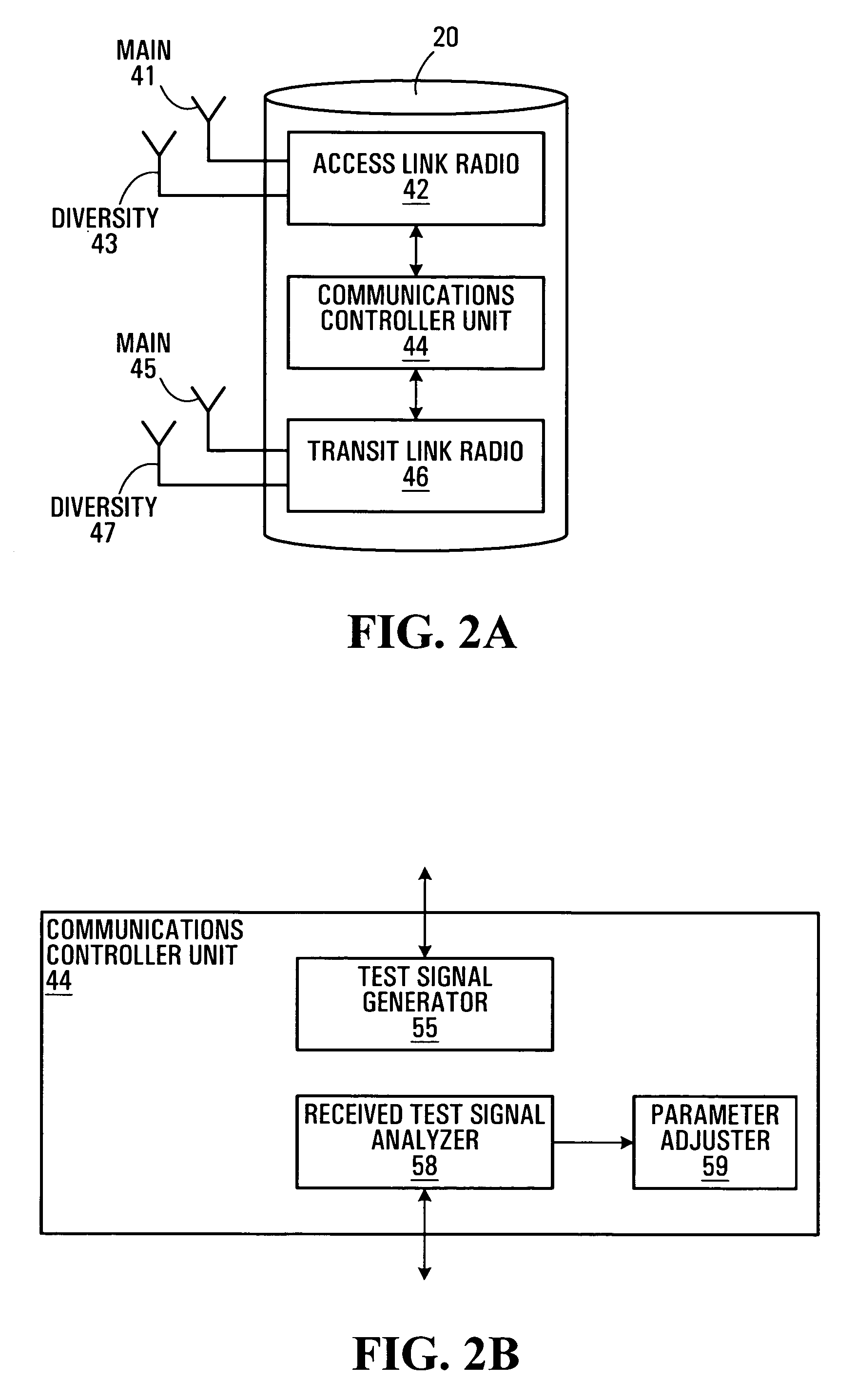
According to an aspect of the present invention one or more radio units of a wireless device are used to measure or detect clues about the radio propagation environment and type of space that surrounds a wireless device. From the measurements, the wireless device may determine the type of location that it is located within, whether that is simply a determination between inside and outside or a more complex determination of the type of building or space that the wireless device is located within. In either case, this determination can be used to automatically change / adjust the radio system operation parameters the wireless device operates in accordance with. With the type of location determined, a wireless device may then automatically select the appropriate radio system operation parameters for the type of location that it is in and the corresponding regulations that apply.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method of controlling a mode of reporting of measurements on a radio interface and radio network controller for the implementation of the method
ActiveUS7418260B2Quick changeAvoids unnecessary uploadsError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransceiverRadio networks
Parameters of radio propagation between a mobile terminal and at least one fixed transceiver are measured. Report messages indicating at least a part of the measured parameters, in accordance with a mode of reporting specified by the radio network controller are transmitted to the radio network controller. An estimate of speed of movement of the mobile terminal is obtained at the radio network controller. The report messages are processed at the radio network controller so as to determine, by taking account of the said estimate of speed, a mode of reporting to be specified for a part at least of the report messages.
Owner:RPX CORP
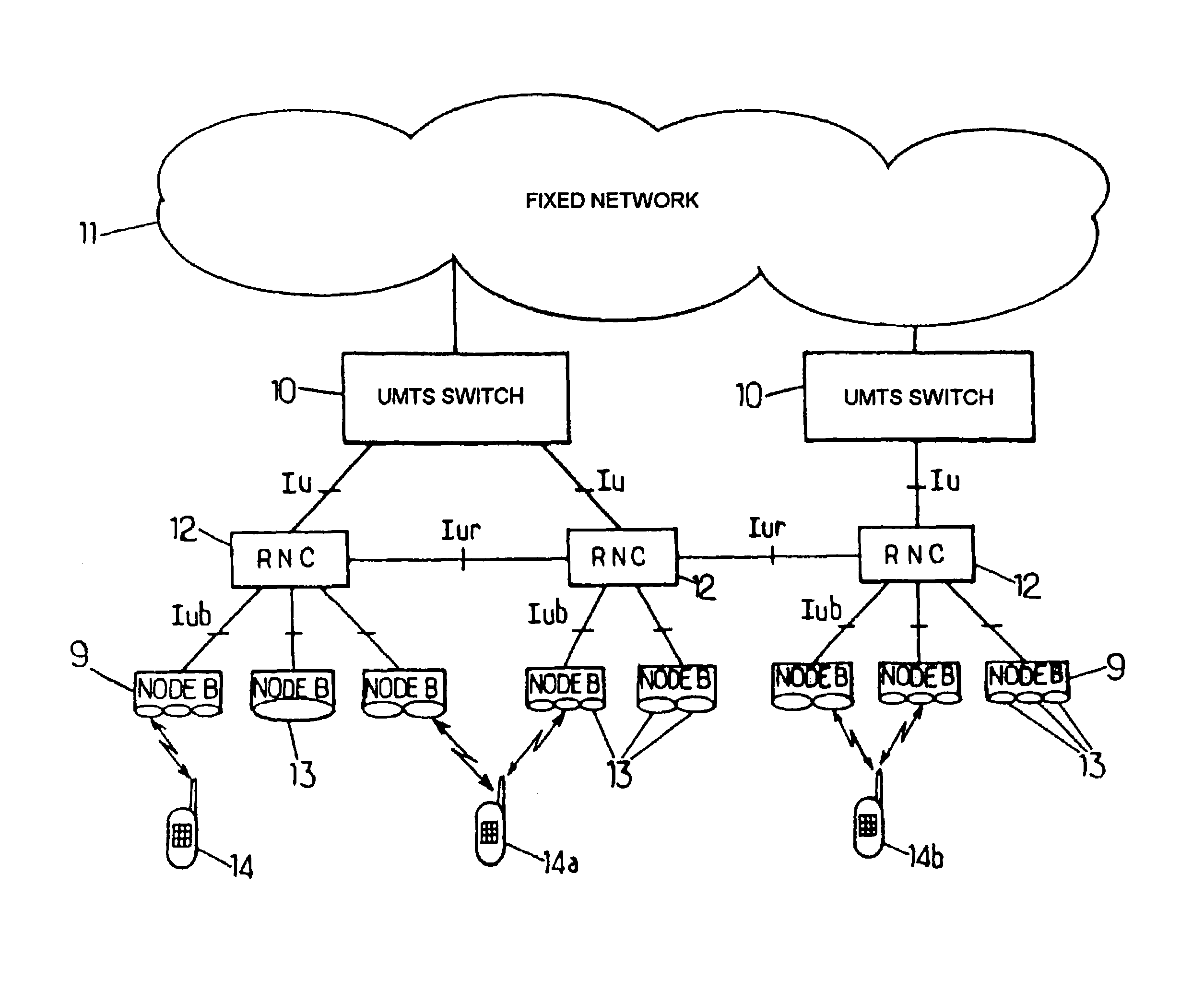
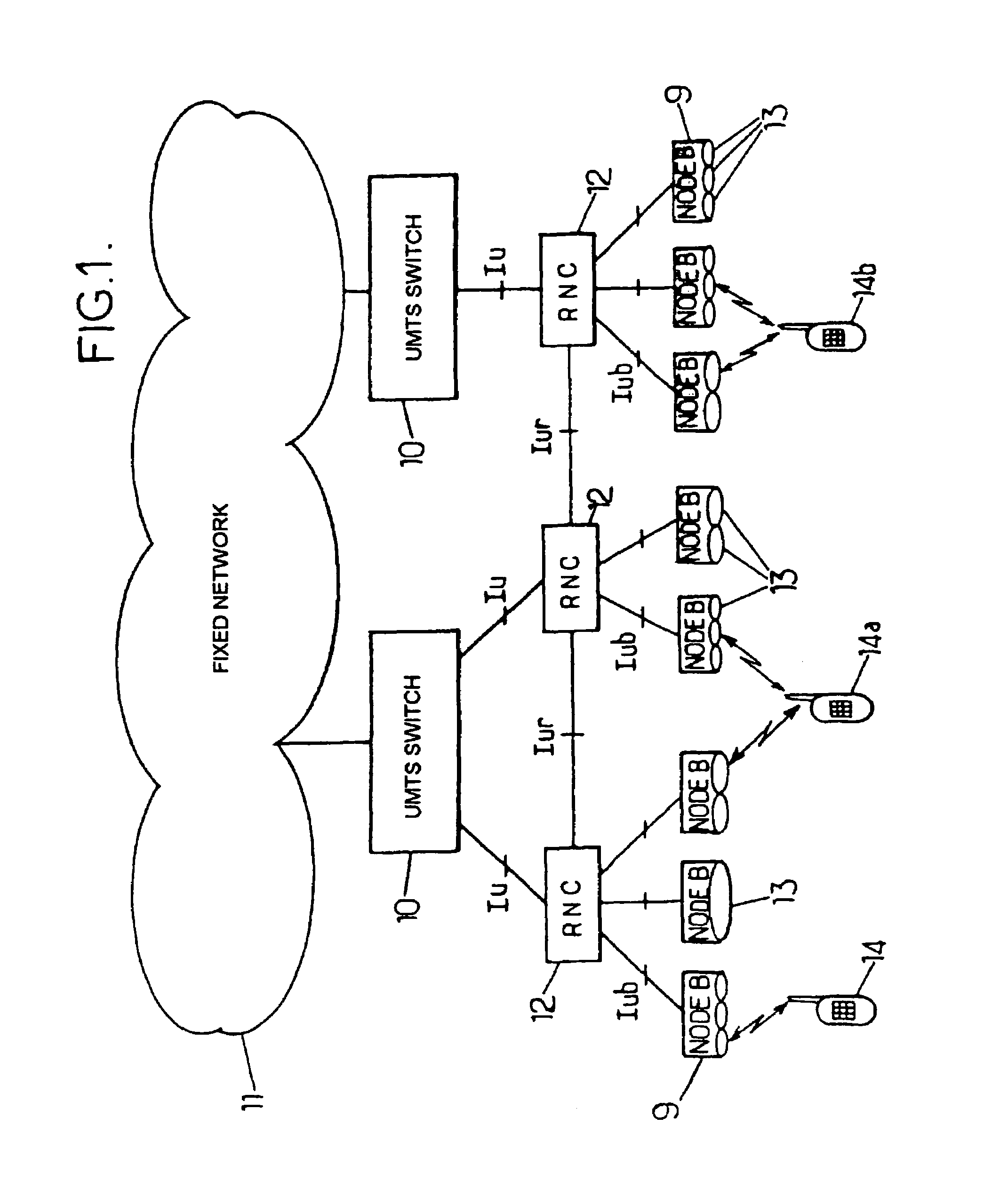
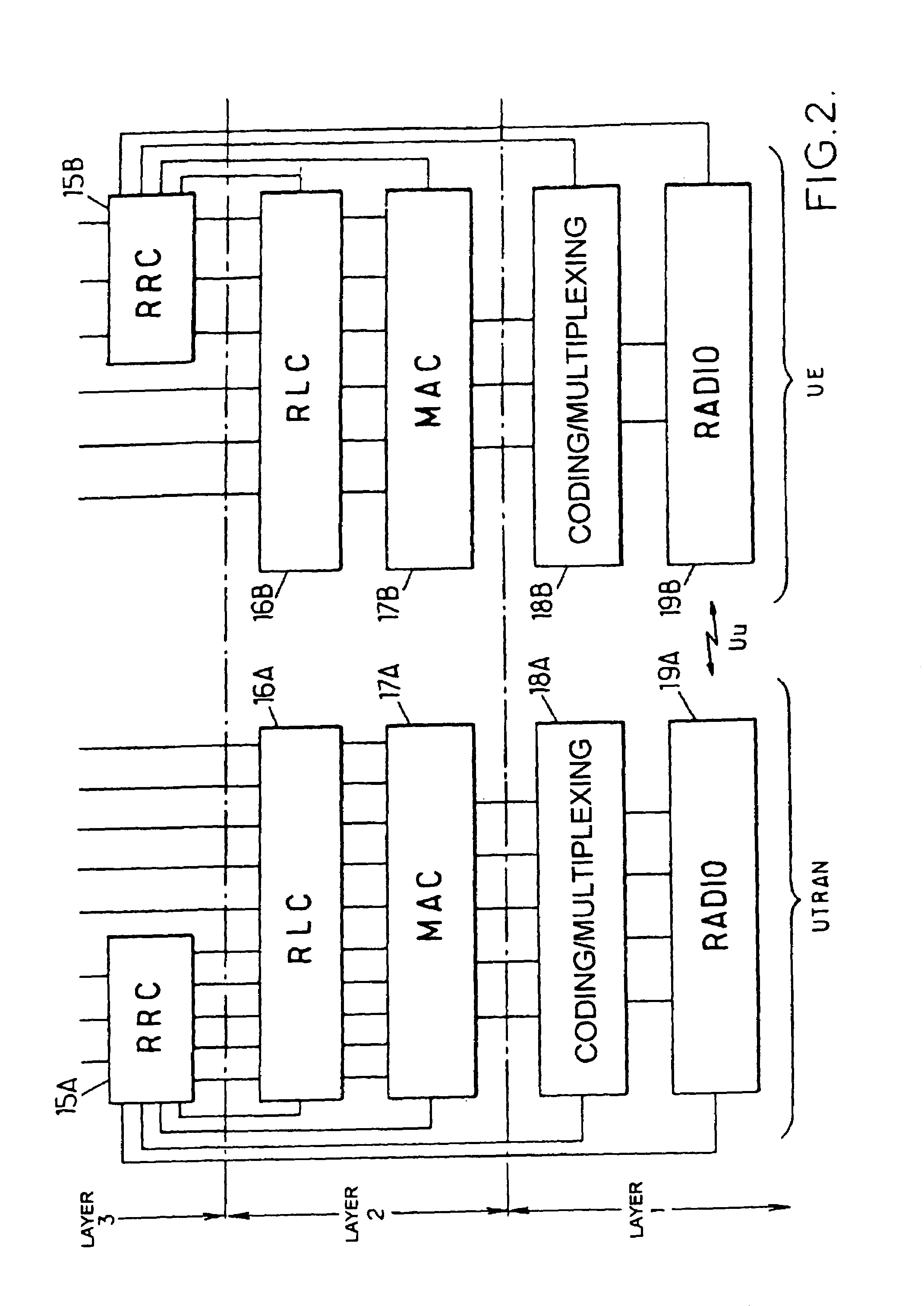
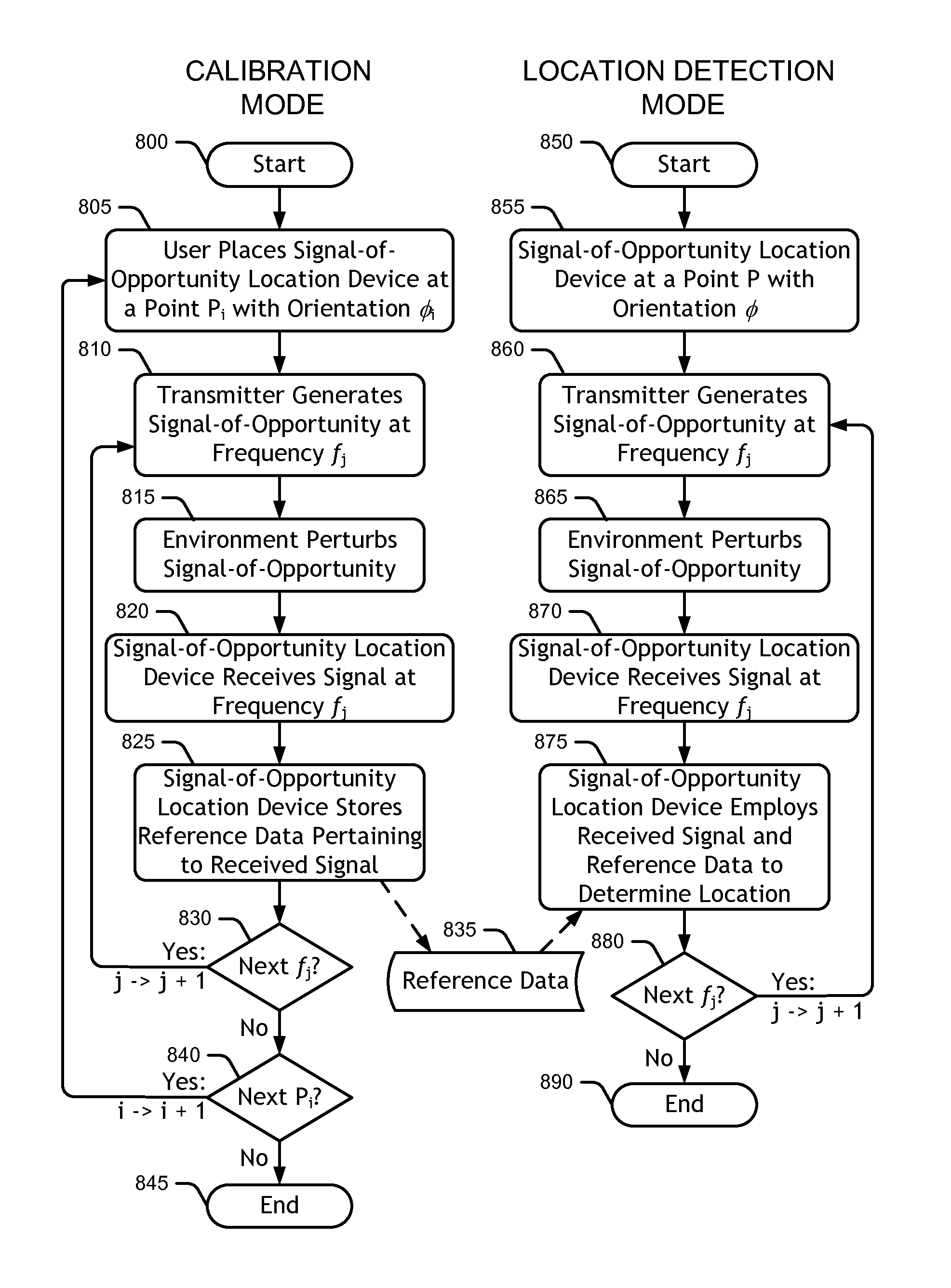
Method and apparatus for determining location using signals-of-opportunity
A signal-of-opportunity location device (SOLD) that may be situated in a complex radio propagation environment with multiple RF signal obstructions receives RF signals from a distant transmitter. The RF signals from the distant transmitter interact with obstructions in the propagation environment local to the SOLD. The local obstructions perturb the RF signals causing the RF signals to exhibit near field behavior in the complex radio propagation environment. The SOLD receives the locally perturbed signals. The SOLD detects signal characteristics of RF signal components of the received signals and compares these signal characteristics with reference data in a reference data store to determine the current location of the SOLD.
Owner:GAN CORP
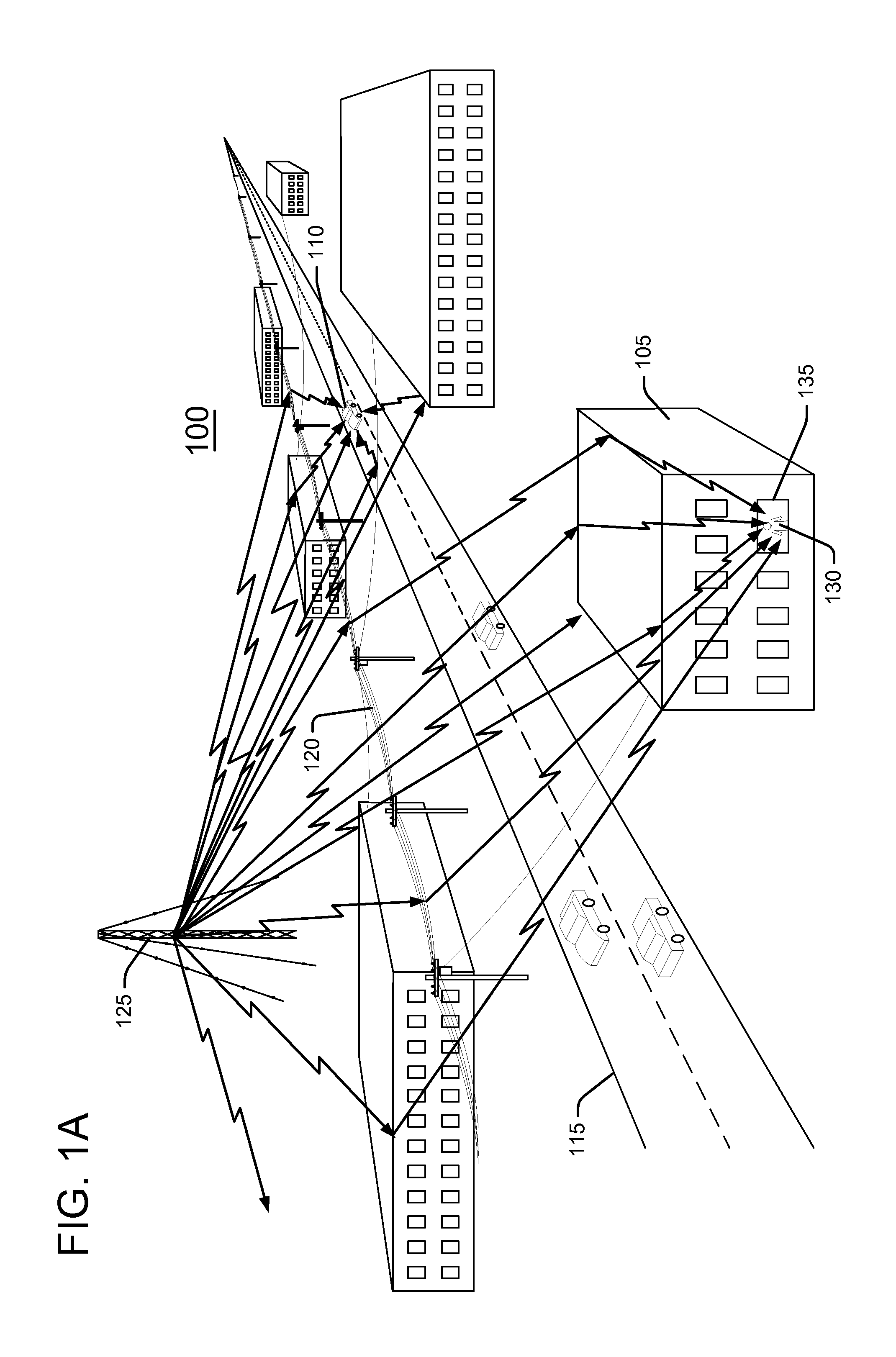
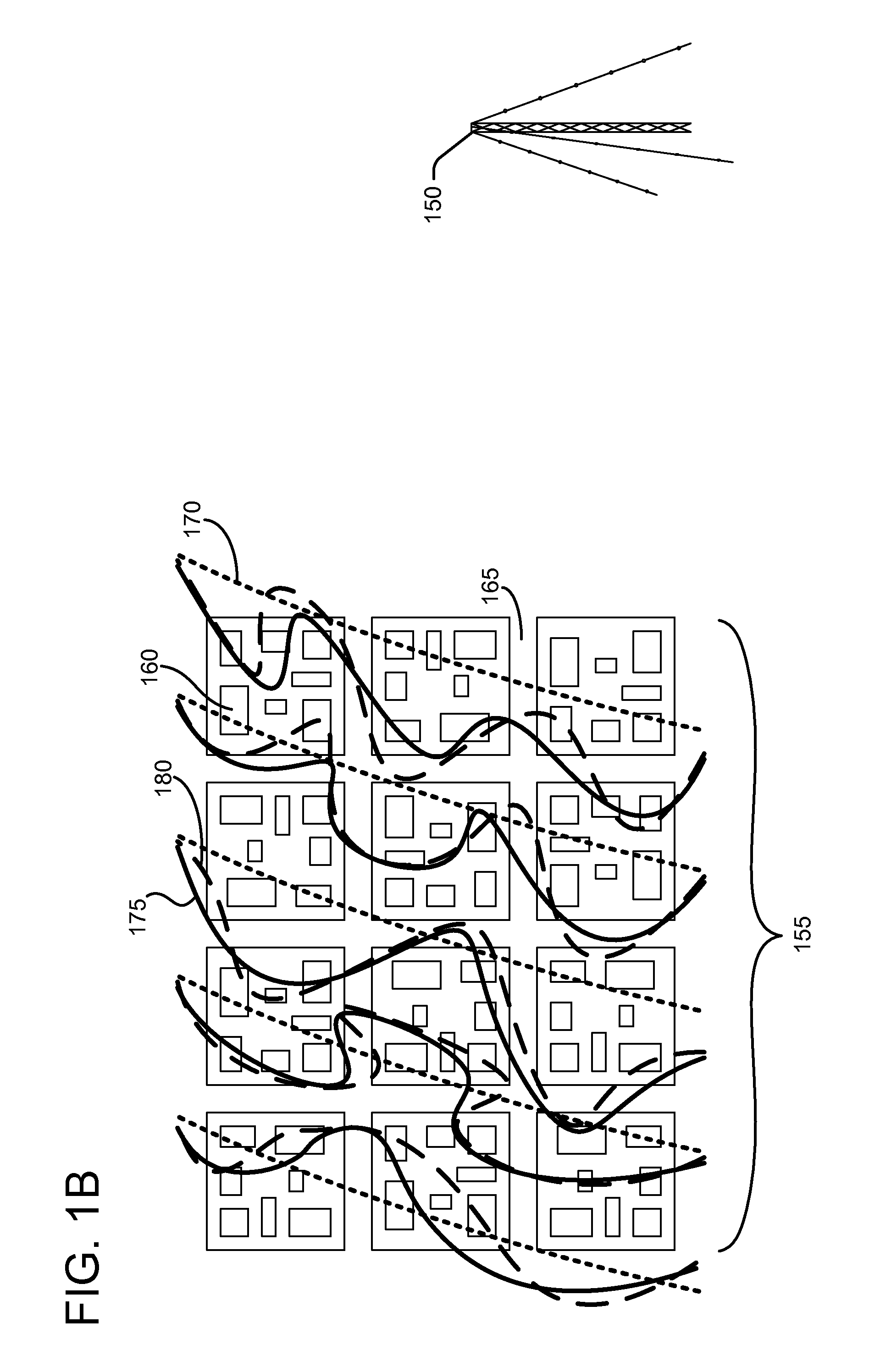
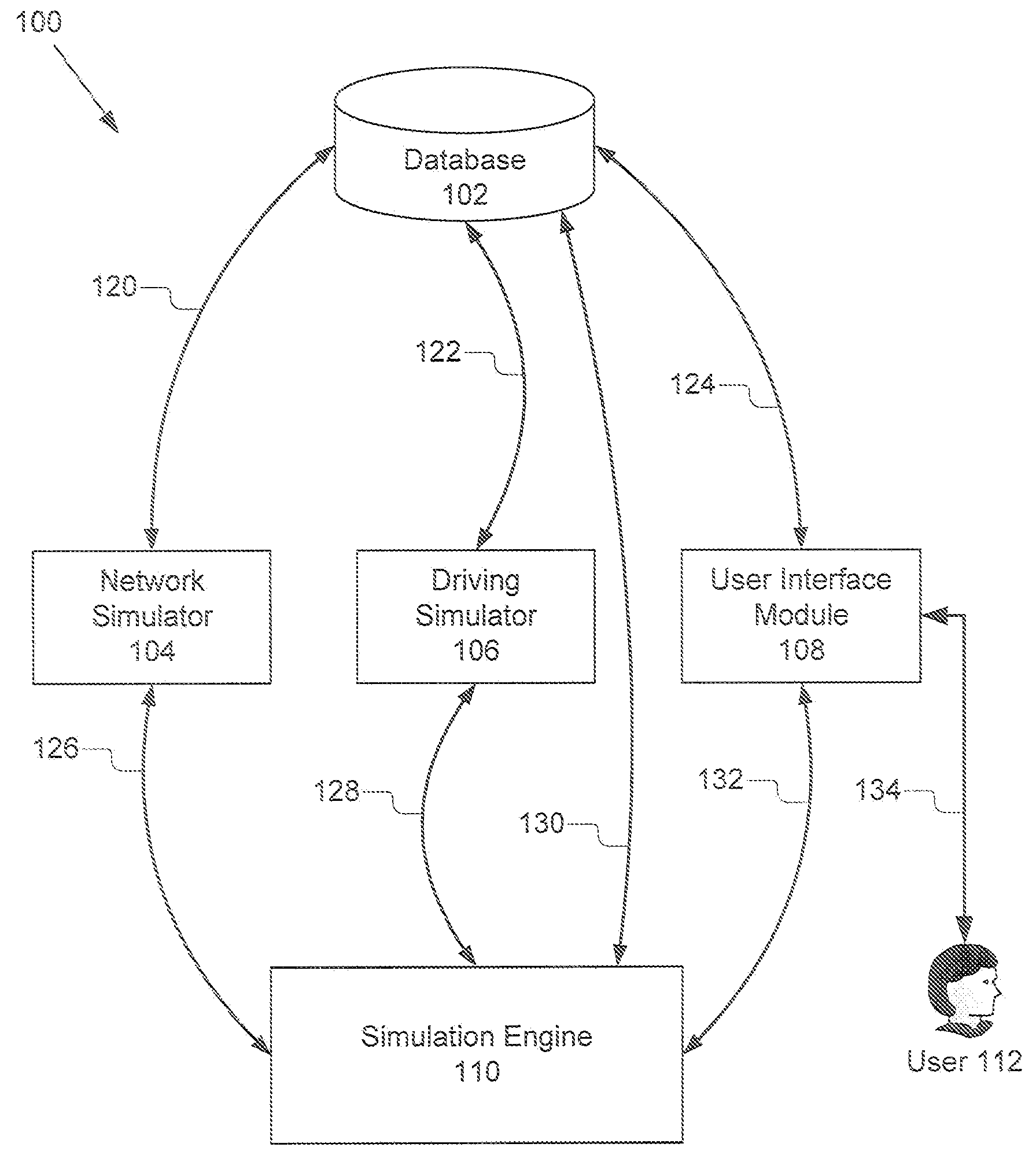
Simulator for Vehicle Radio Propagation Including Shadowing Effects
InactiveUS20070271079A1Transmission monitoringAnalogue processes for specific applicationsShadowingsTerrain
A simulator for inter-vehicle radio communication includes terrain and building data and can simulate the effects of buildings in terrain on radio propagation. The simulator also models other vehicles and the shadow effects of their presence. The system comprises a simulation engine, a network simulator, a driving simulator, a database and a user interface module adapted for communication. The simulation engine simulates the propagation of communication signals between vehicles including the effects of shadowing, and also receives data from the network simulator, the driving simulator and database to generate the propagation simulation. The simulation engine outputs the results of the propagation simulation to the user interface module which translates the information into various displays. The present invention is particularly advantageous because it provides a variety of different user interfaces to show the effective range / propagation of communication signals for different conditions including vehicle locations, terrain, vehicle movements, data traffic and networks configuration.
Owner:TOYOTA INFOTECHNOLOGY CENT CO LTD
Systems and methods for increased mobility among mobile nodes in a wireless network
InactiveUS7602747B2Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesComputer networkRadio propagation
An apparatus, comprising a first router to communicatively couple to a mobility anchor point and one or more further routers to n-cast data items to ones of a plurality of mobile nodes that are experiencing similar radio propagation conditions.
Owner:INTEL CORP
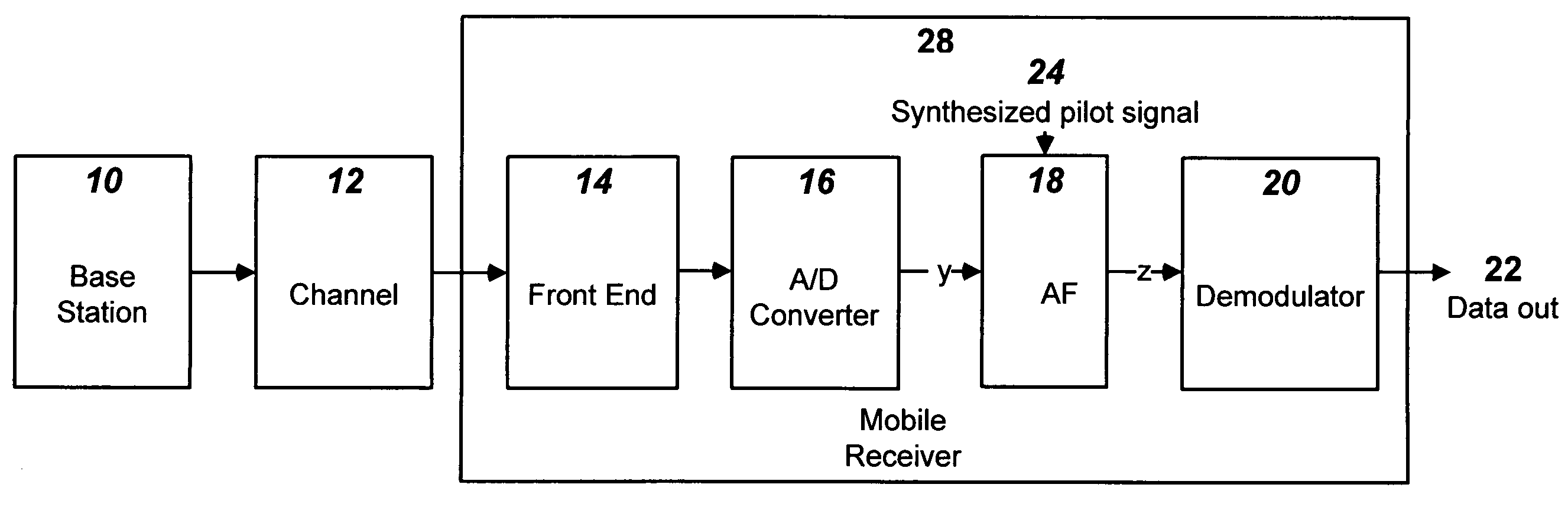
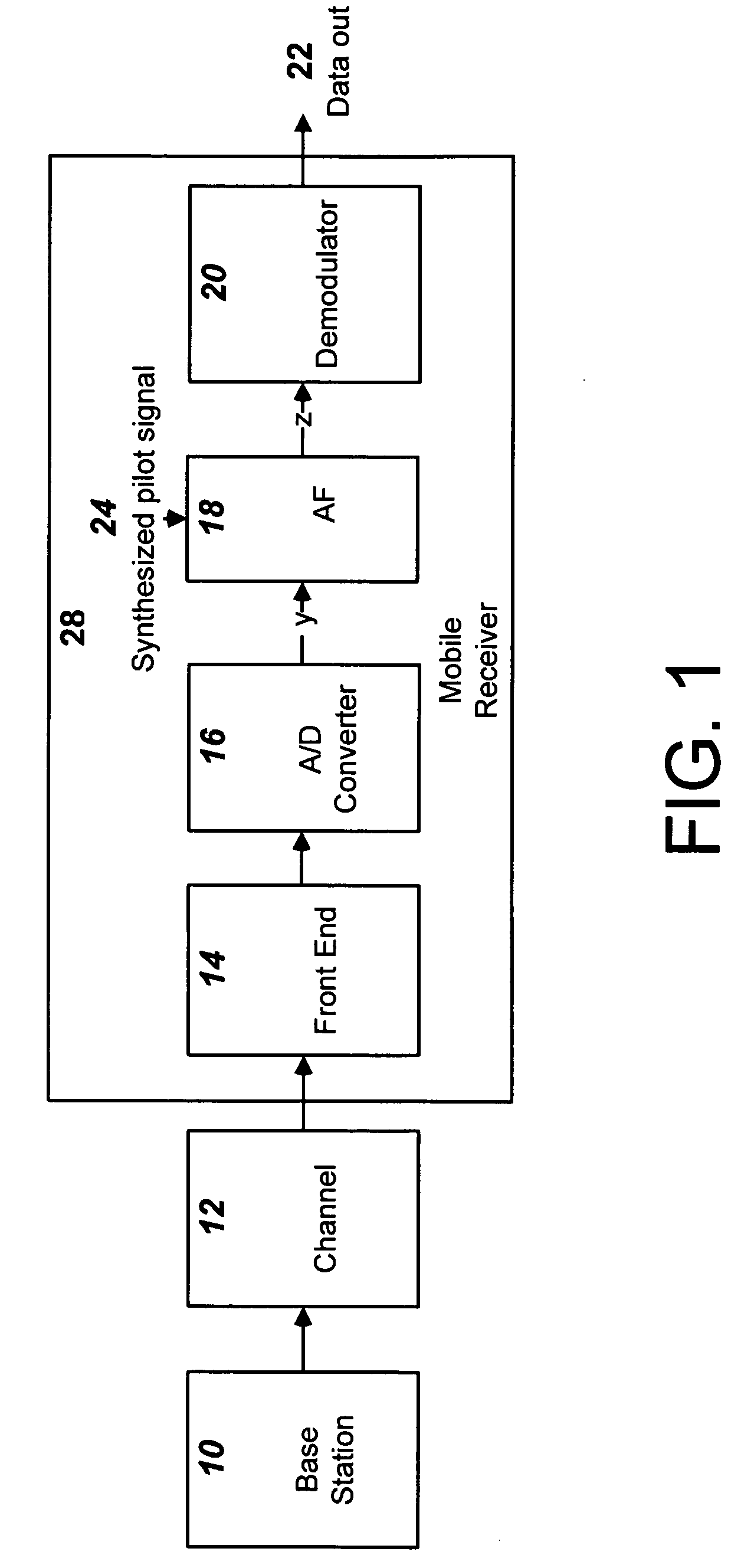
Use of adaptive filters in CDMA wireless systems employing pilot signals
A CDMA radio system uses an adaptive filter in a receiver to mitigate multipath radio propagation and to filter out interfering signals. Characteristics of an initial stage of the filter preferably are determined by cross correlation of a generated pilot signal and the input signal with the integration of the correlation performed over a time period selected to be an integral number of symbol periods. The integration causes the portions of the cross correlation corresponding to the user subchannels to average substantially to zero, so that the pilot channel signal correlation is the primary contribution to the signal used to characterize the channel to establish the coefficients of the adaptive filter for the receiver.
Owner:ACORN TECH INC
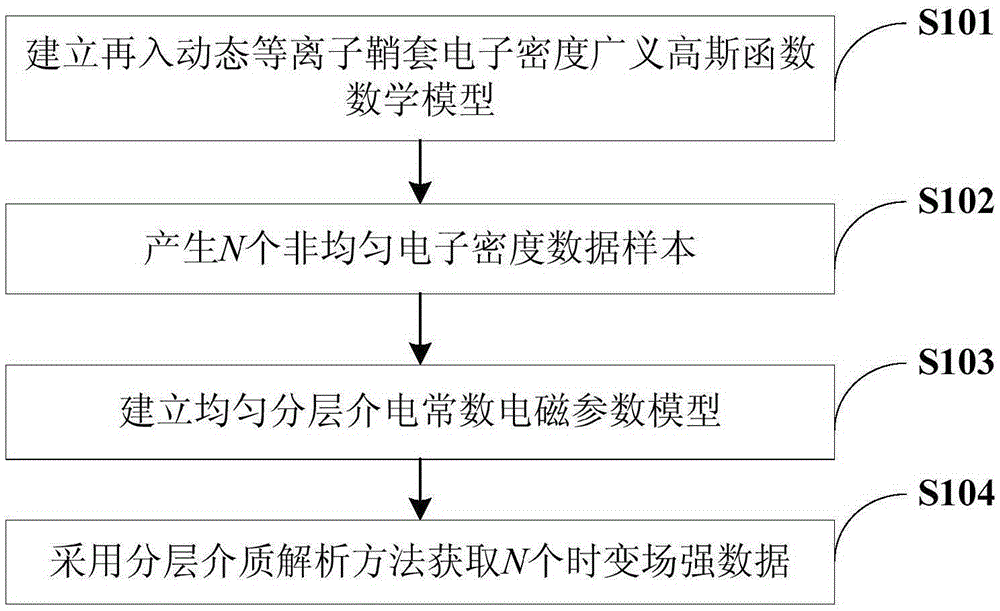
Fast calculation method for dynamic plasma sheath radio wave propagation
ActiveCN105260507AReduce difficultySpecial data processing applicationsRadio propagationMathematical model
The invention discloses a fast calculation method for dynamic plasma sheath radio wave propagation. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a mathematical model of a dynamic plasma sheath electron density based on a physical mechanism of the change speed of the electron density; then adopting a quasi-steady-state monte carlo method and a classical electromagnetic computing method on this basis to acquire a time-varying field intensity result of radio wave propagation of this complex random change medium. The invention is a simple, effective and fast radio wave calculation method, and can solve the radio wave propagation calculation of the dynamic plasma and avoid the high difficulty and high complexity by directly using a random medium modeling method to calculate.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Radio communication apparatus and resending controlling method
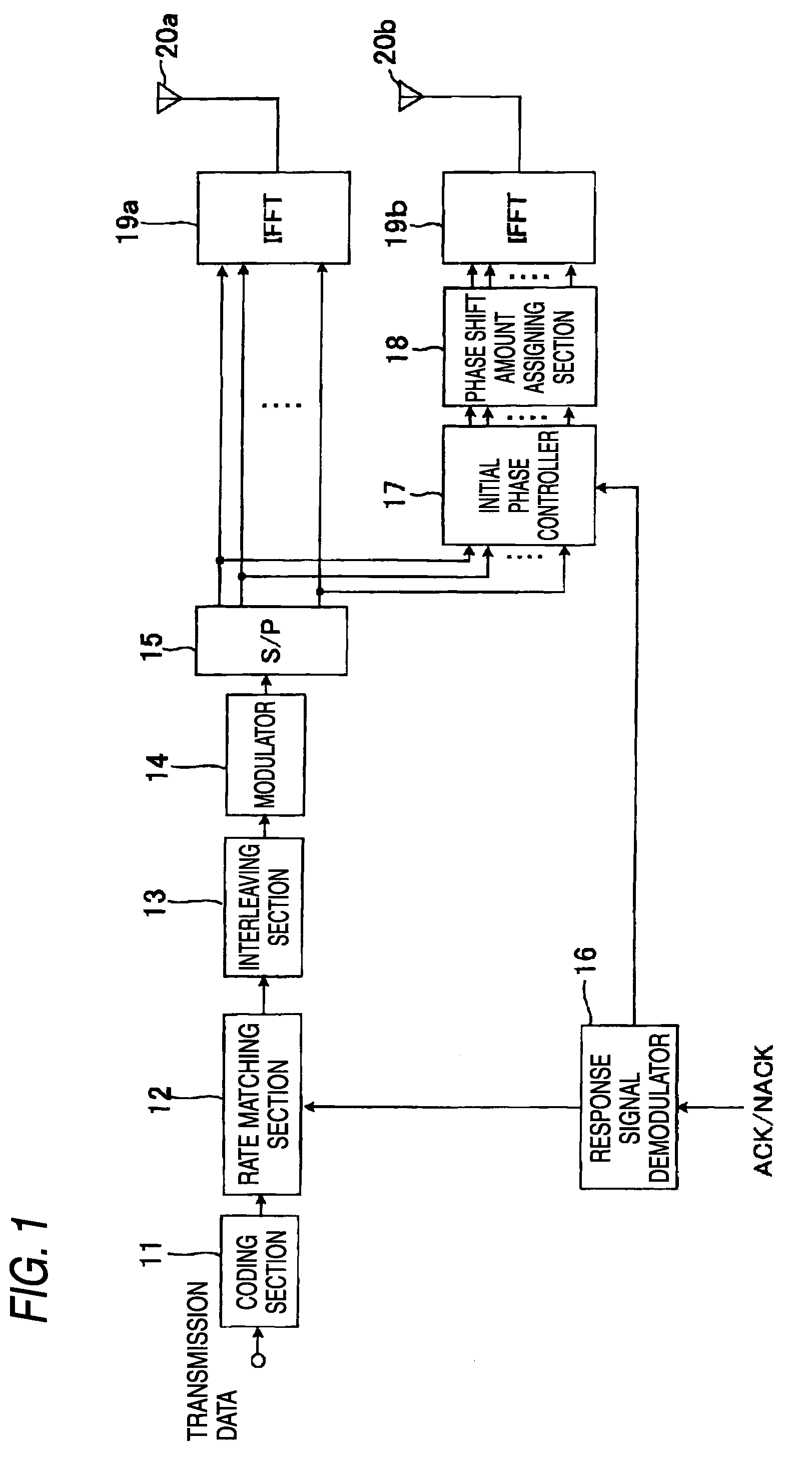
ActiveUS20100020893A1Easy to operateSpatial transmit diversityMultiplex communicationSignal onPhase difference
A synthesized gain in a resending operation can be improved significantly by relatively simple control when resending control is applied upon executing of a transmission diversity using CDD. A radio communication apparatus equipped with a plurality of antennas and for performing communication by MIMO, includes a phase shift amount assigning section 18 for executing a CDD process to assign a cyclic phase shift to a transmission signal on a frequency axis, a response signal demodulator 16 for demodulating ACK / NACK received from a destination station, and outputting control information about a resending operation when NACK is received and a reception is failed, and an initial phase controller 17 for setting an offset to a phase shift at a time of CDD process in response to a number of transmission times in resending control such that a predetermined offset, which is produced by adding a phase difference from a signal transmitted from other antenna to the phase shift, is assigned to a signal transmitted from the antenna over a full frequency band, wherein a frequency characteristic of a radio propagation path at a time of resending is changed every time of transmission times.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Mobile communication system, base station apparatus, user apparatus and method
InactiveUS20100177688A1Quality improvementNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementRadio propagationMobile communication systems
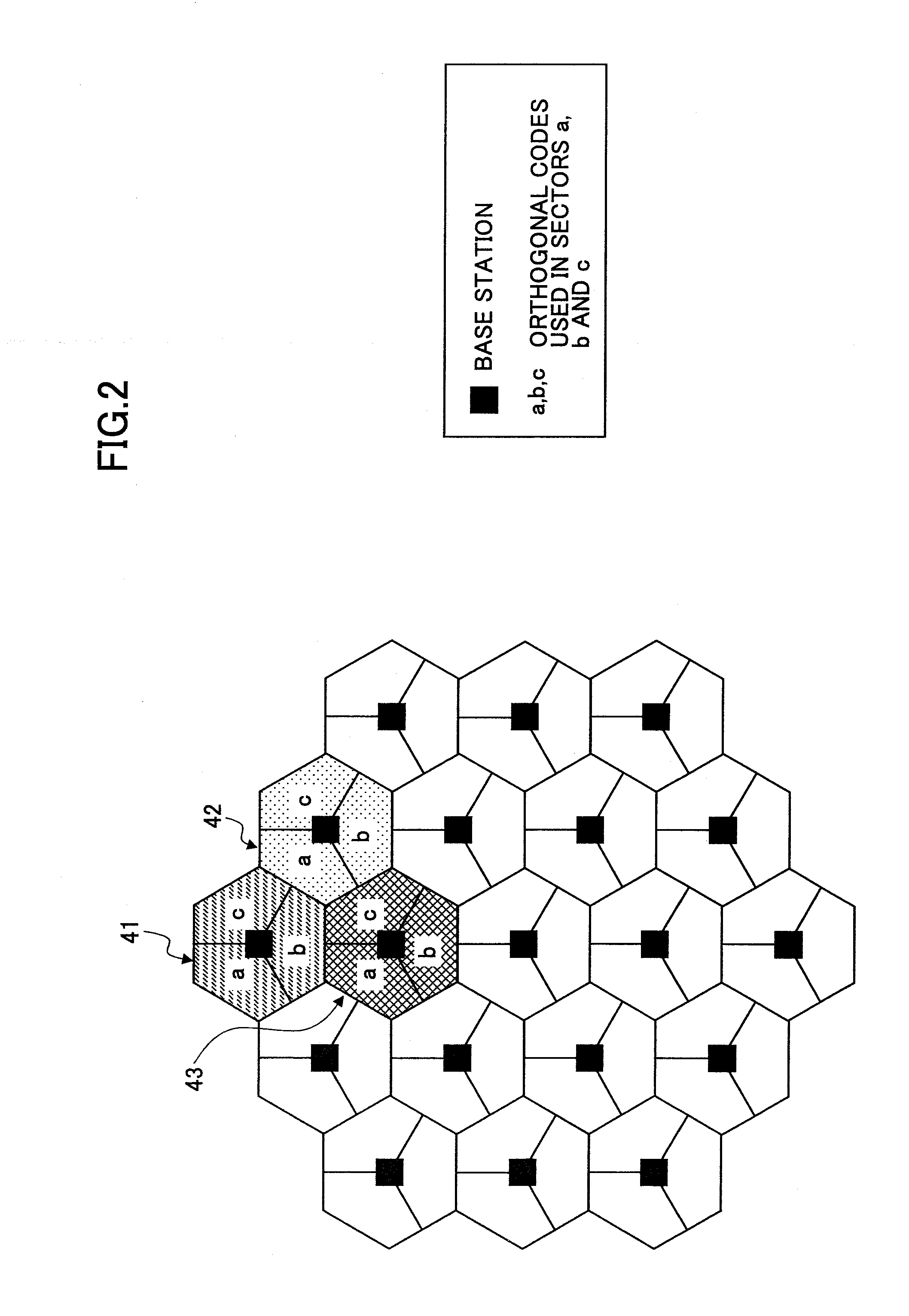
A base station apparatus for use in a mobile communication system includes: a unit configured to generate a reference signal; a unit configured to generate a transmission symbol including the reference signal; a unit configured to transmit the transmission symbol for each sector; and a unit configured to monitor a radio propagation state. The reference signal is generated by multiplying a first sequence formed by a non-orthogonal code sequence which is different at least between an adjacent cell and an own cell, by a second sequence. Whether to form the second sequence by using an orthogonal code sequence which is different among sectors or by using a non-orthogonal code sequence is determined according to the radio propagation state.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
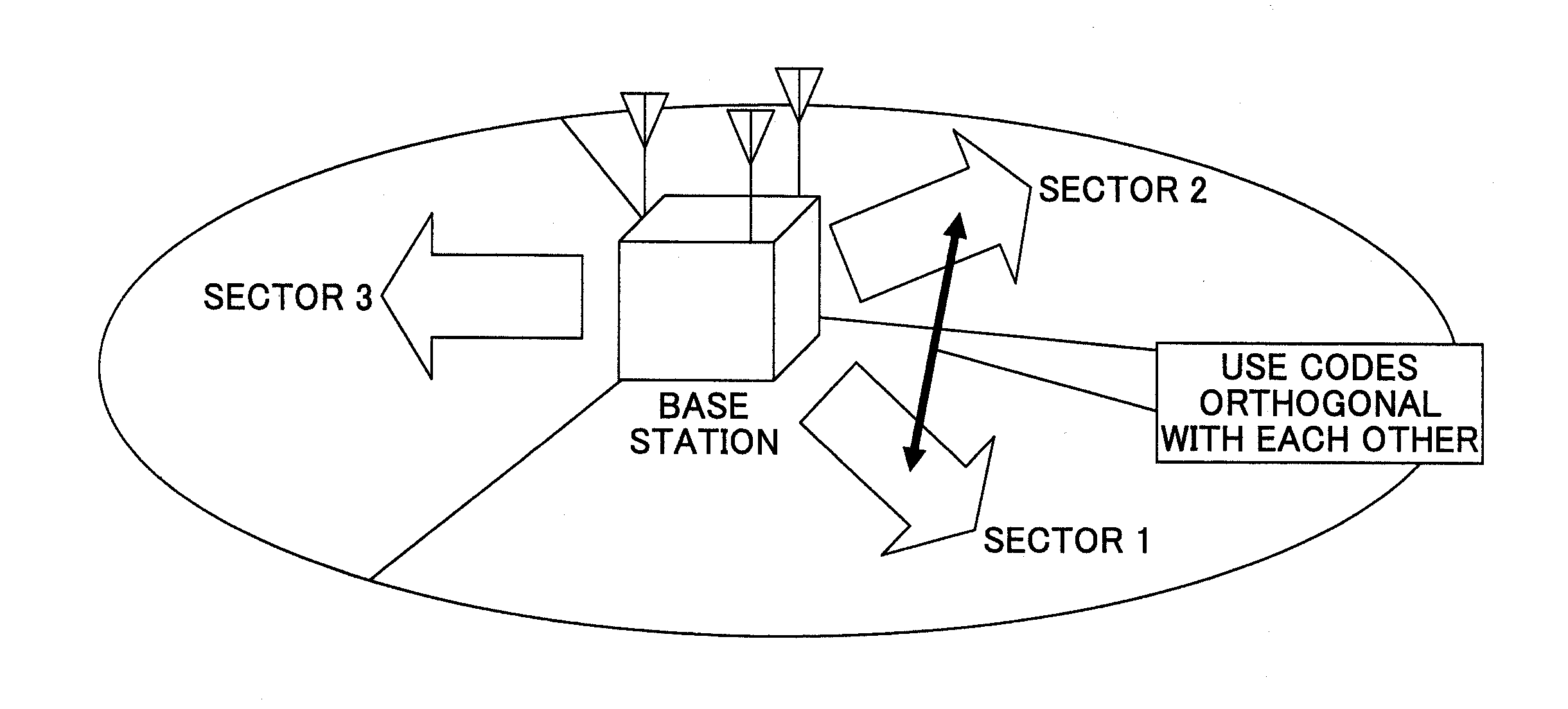
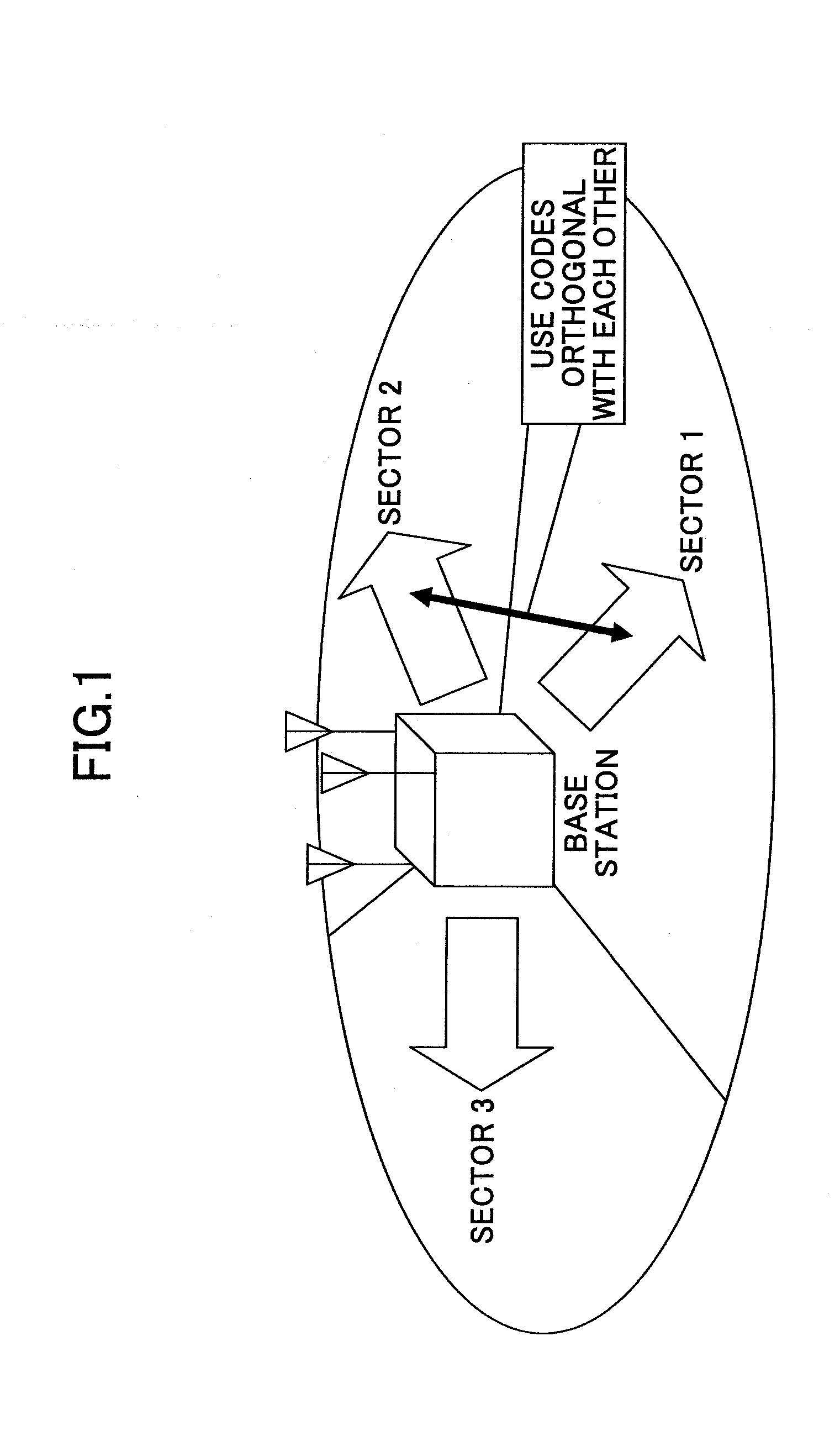
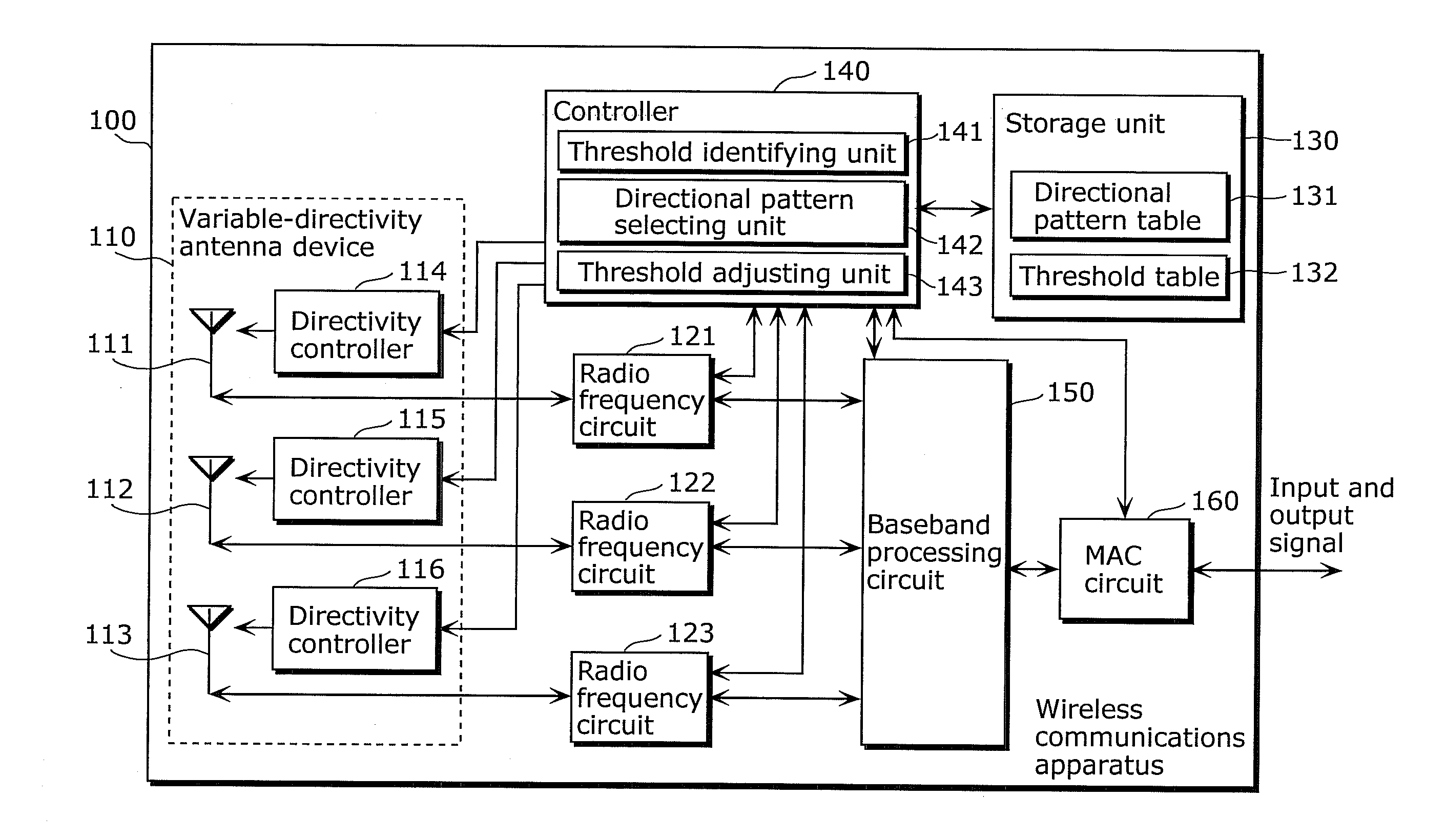
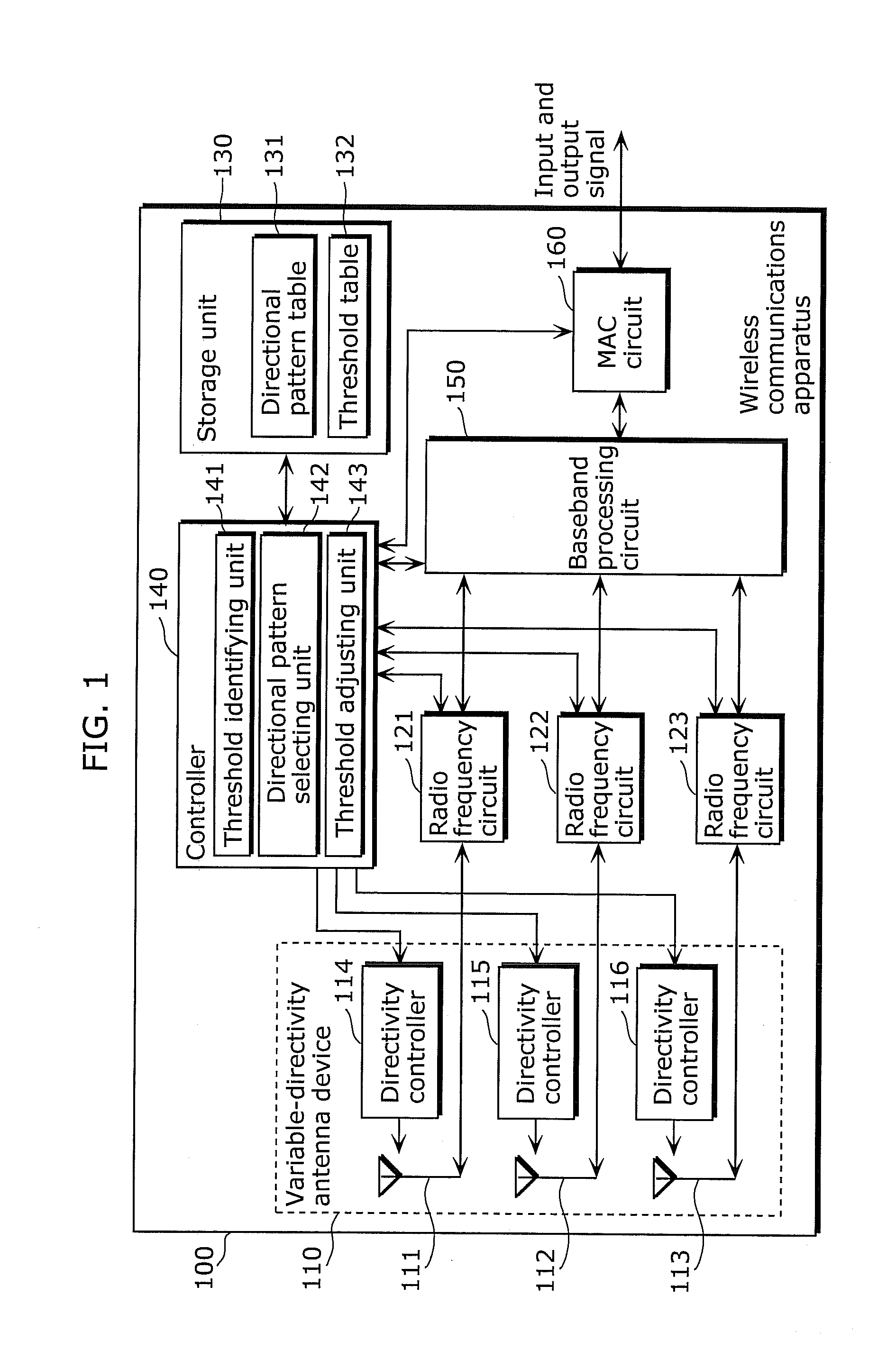
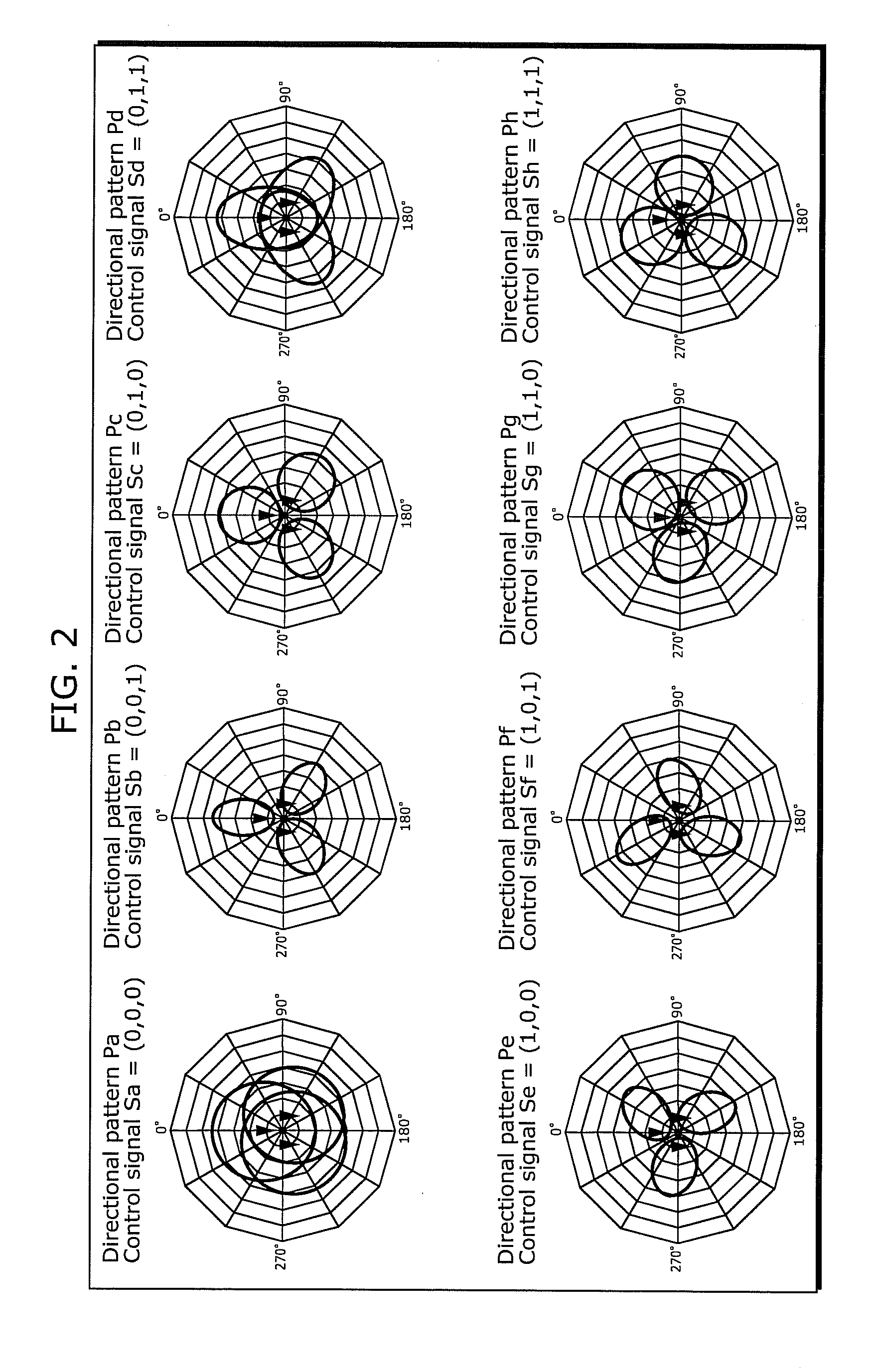
Wireless communications apparatus, wireless communications method, program, and integrated circuit
InactiveUS20110244808A1Improve communication performanceShorten the timeSubstation equipmentTransmission monitoringRadio propagationCommunicator device
A wireless communications apparatus (100) includes: antennas (111, 112, and 113); a threshold identifying unit (141) which measures a first radio propagation environment parameter by using a specific directional pattern, and identifies a threshold, from among thresholds, which corresponds to the measured first radio propagation environment parameter; a directional pattern selecting unit (142) which performs test communications by sequentially switching directional patterns, and selects a directional pattern having an actual throughput, calculated from a measurement value of a second radio propagation environment parameter, greater than the threshold; and a threshold adjusting unit (143) which changes the threshold identified by the threshold identifying unit (141), according to the number of test communications that is the number of the directional patterns used for the test communications performed by the directional pattern selecting unit (142).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System and method for estimating separation distance between impulse radios using impulse signal amplitude
InactiveUS20050184908A1Resists fading effectImprove accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRadio propagationRadiotransmitter
An impulse radio system estimates a separation distance between an impulse radio transmitter and an impulse radio receiver. The system includes an impulse transmitter that transmits an impulse signal having an ultra-wideband frequency characteristic. An impulse receiver spaced from the transmitter receives the transmitted impulse signal and measures a signal strength of the received impulse signal. The receiver estimates the separation distance based on the measured signal strength. The receiver classifies a signal propagational / multipath environment using the received impulse signal, and then selects a radio propagation path loss model corresponding to a classified multipath environment. The receiver translates the measured signal strength to a separation distance based on the selected radio propagation path loss model.
Owner:HUMATICS CORP
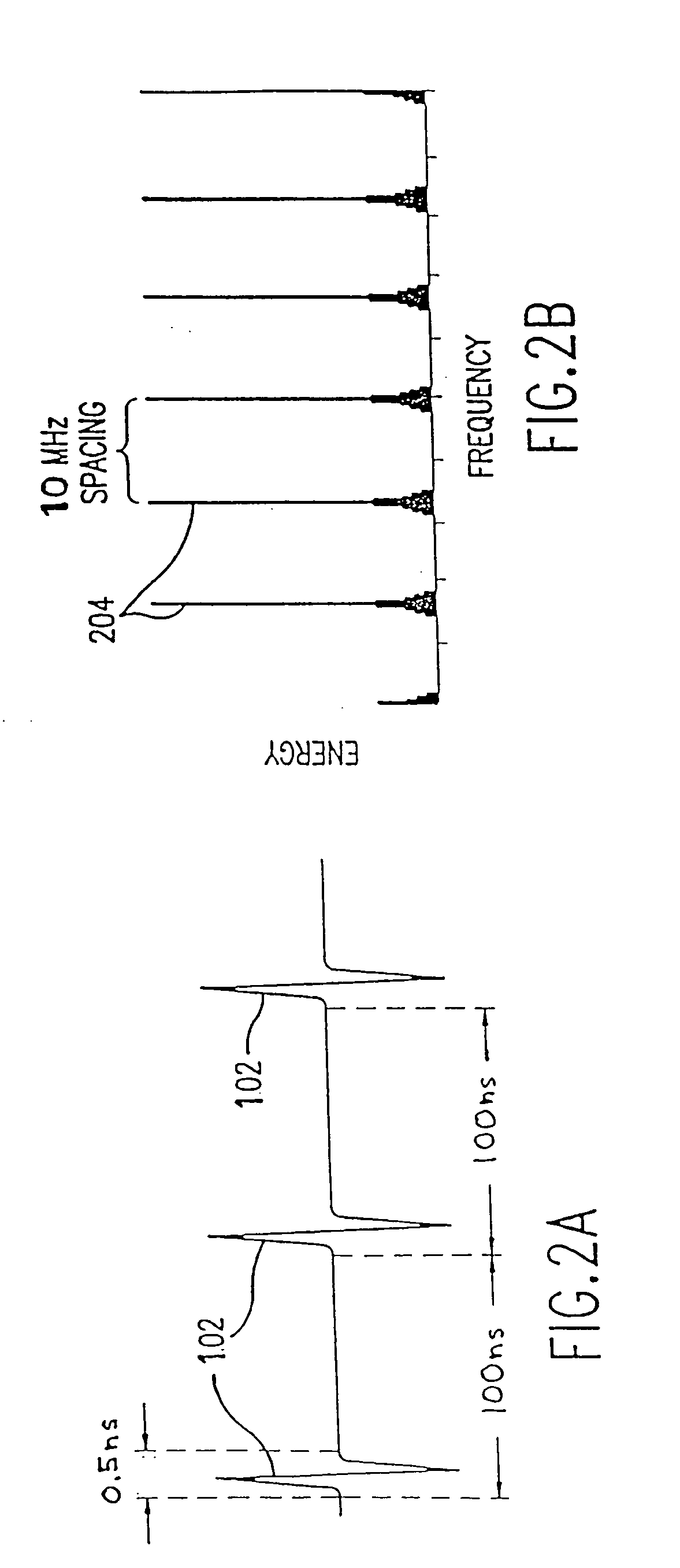
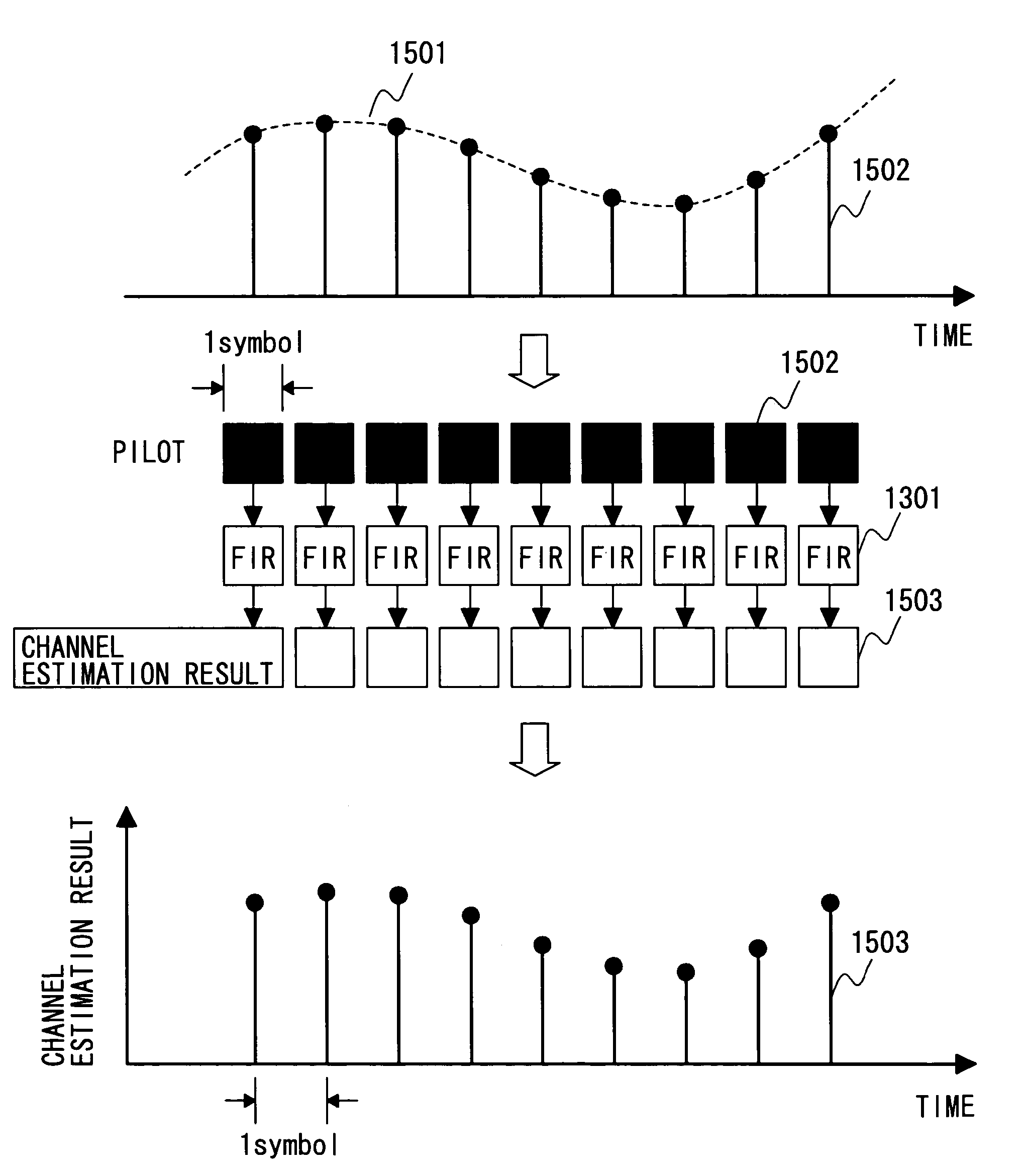
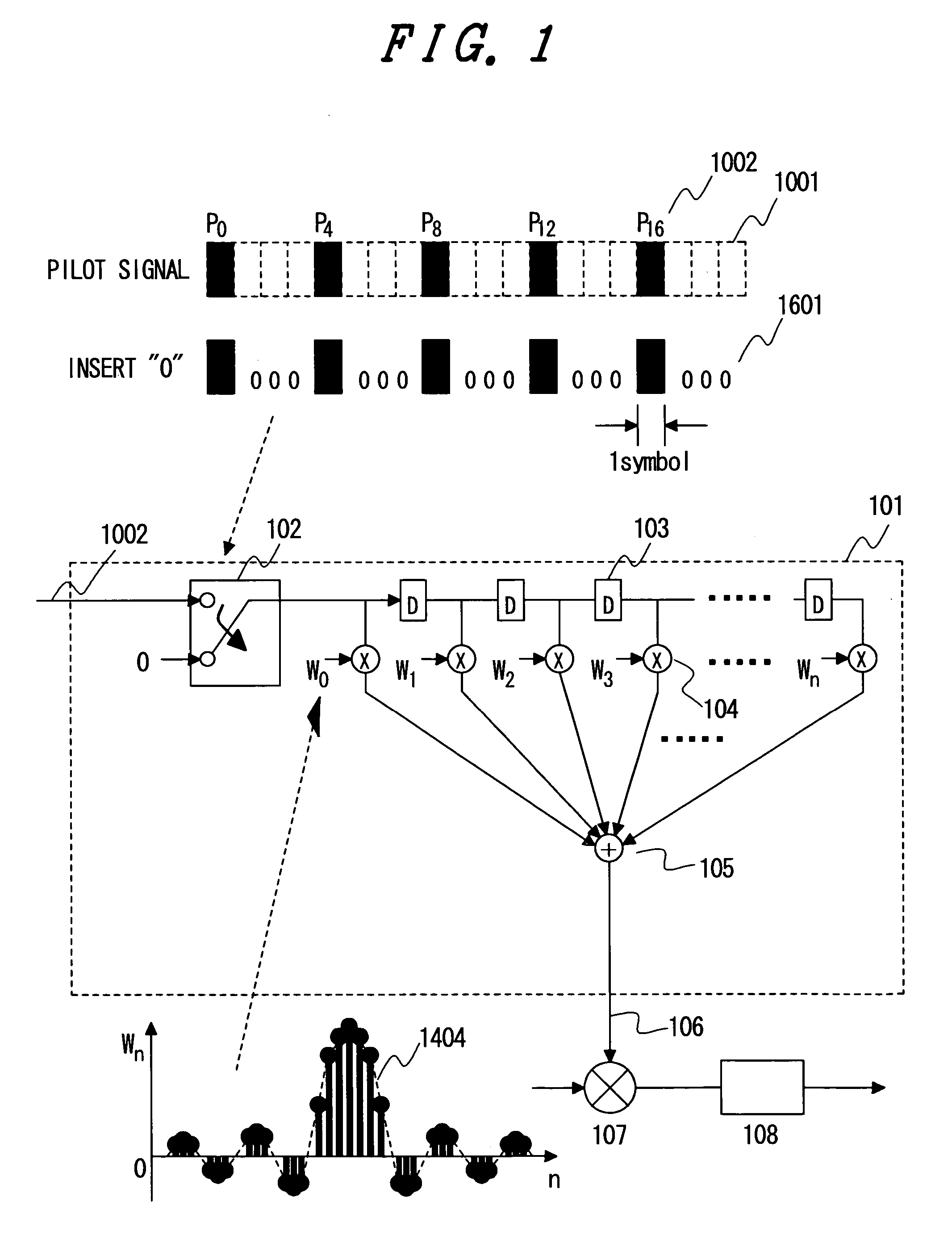
Channel estimation method for a mobile communication system
ActiveUS7158770B2Improve featuresImprove accuracyTransmission control/equlisationBaseband system detailsRadio propagationBand-pass filter
Under present circumstances, where an increasing number of wireless communication systems employ the QAM method as a modulation method for frequency use efficiency enhancement as the speed of information transmission in the wireless communication systems increases, it is an object of the present invention to provide a channel estimation method for estimating a channel efficiently and accurately and establishing communication at high quality, that is, providing communication with excellent error rate characteristics. To achieve the above object, the present invention improves characteristics by calculating the channel estimation results variously for all data signal symbols and using them for demodulation. To accomplish the object, the present invention also pays attention to the frequency characteristics of fading in a radio propagation path and enhances the accuracy in channel estimation result calculation by using a band pass filter for eliminating the thermal noise that would increase the estimation error.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
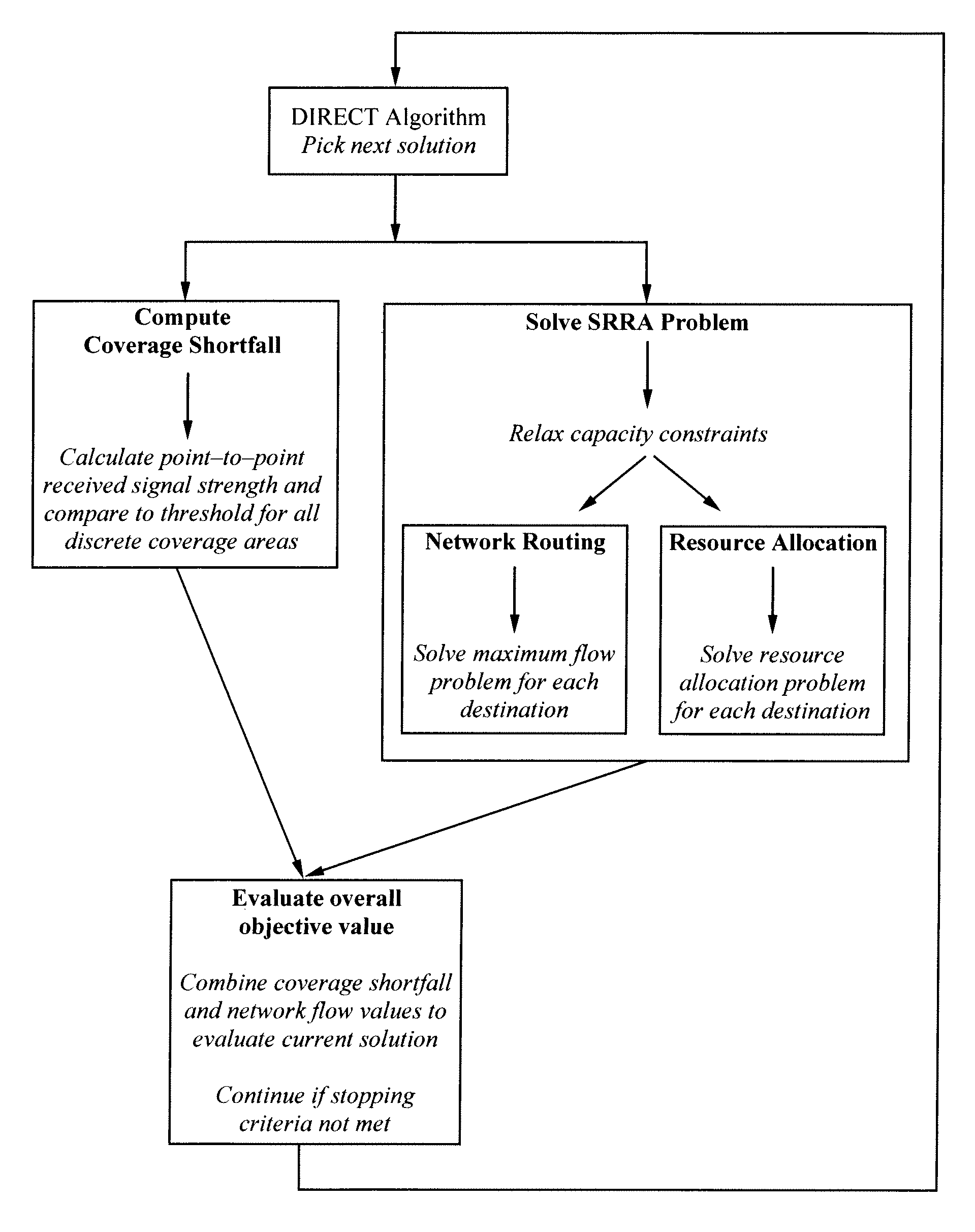
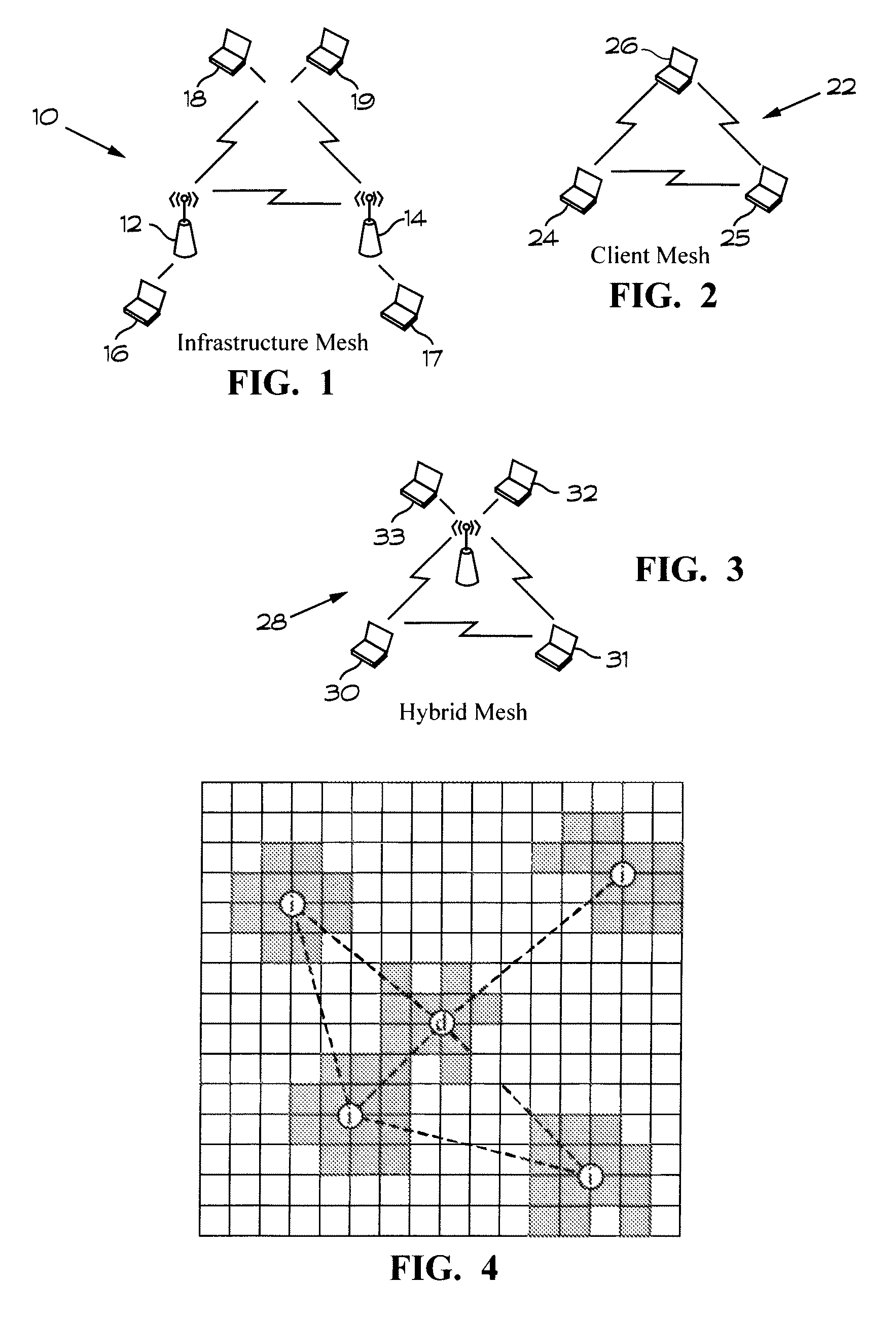
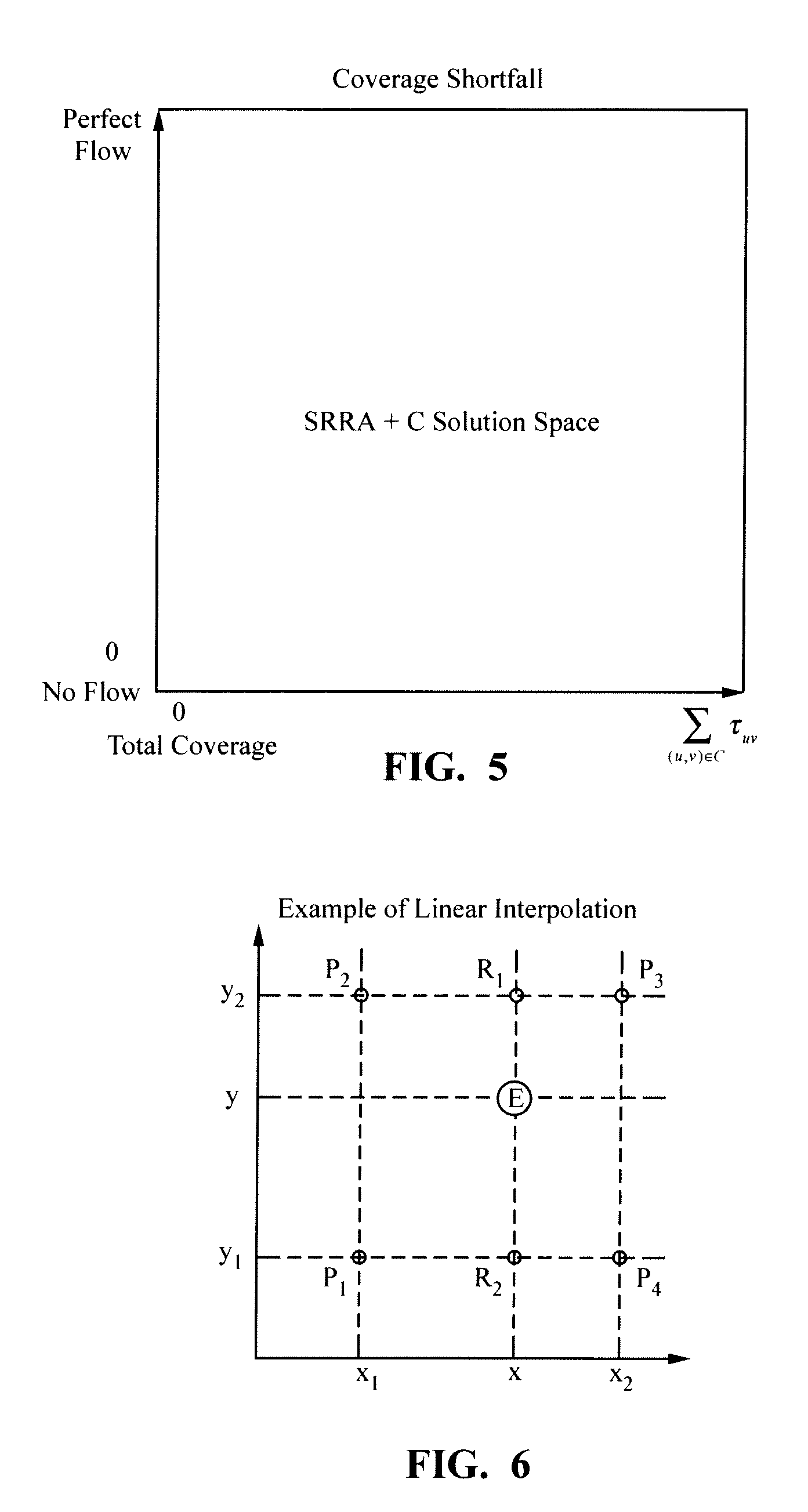
Method for optimal transmitter placement in wireless mesh networks
InactiveUS8654672B1Quickly and optimally designingMaximizes client coverage areaAnalogue computers for electric apparatusNetwork topologiesEnvironmental noiseTerrain
A process for forming a wireless mesh network (WMN) in which client coverage is calculated using a point-to-point propagation loss model and optimal routing and power allocation is determined to quantify the value of network flow. In one embodiment, the process calculates loss based on access point locations, operating characteristics and terrain and environment information. In one embodiment, the network flow and coverage subproblem values are combined via a penalty function. The process creates WMN topologies that maximize client coverage area by choice of access point locations, subject to constraints on network flow and power allocation, number and technical capabilities of access points, background and environmental noise, and radio propagation over terrain.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
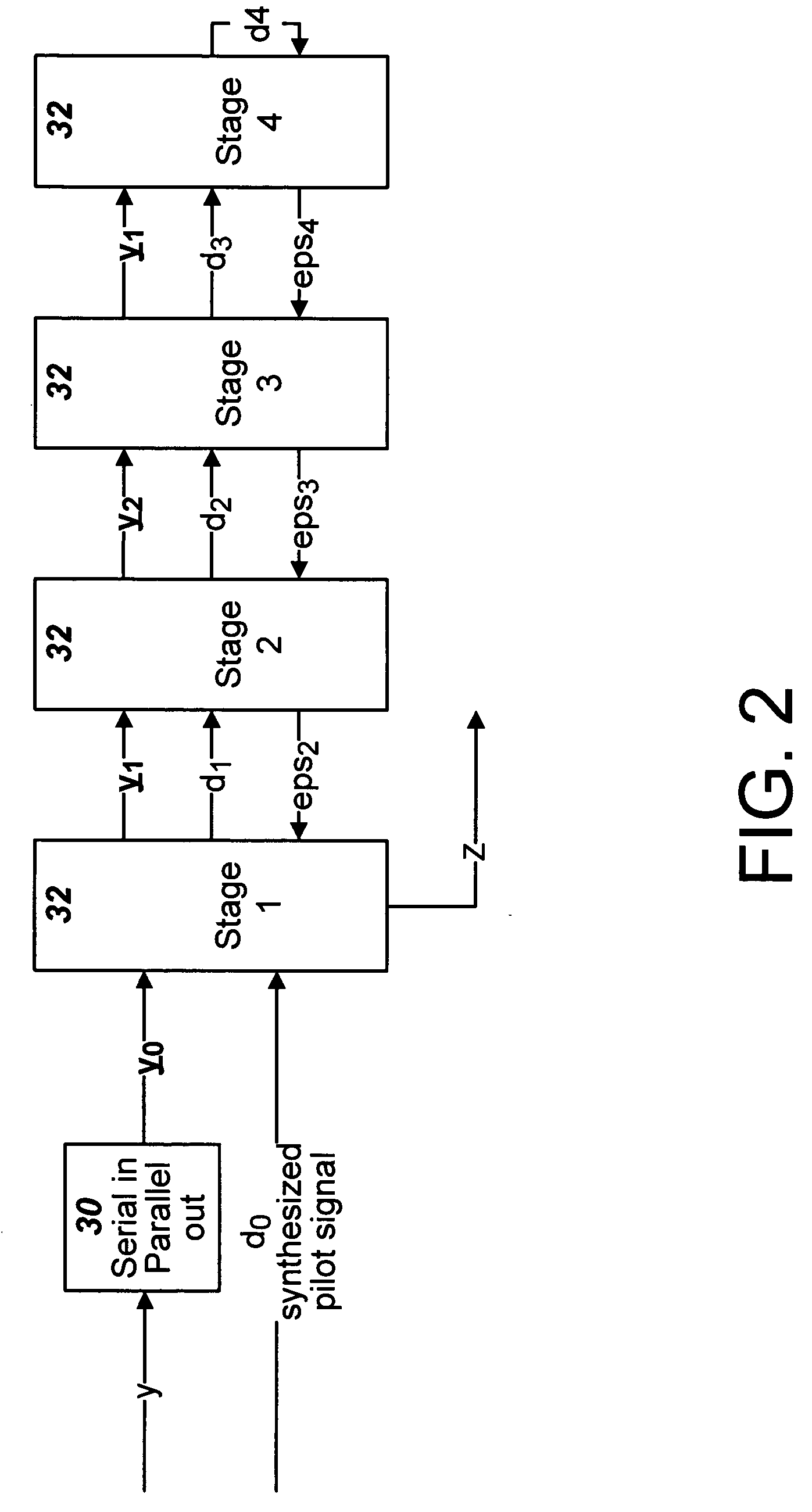
Efficient adaptive filters for CDMA wireless systems
ActiveUS7756196B1Precise cuttingError preventionModulated-carrier systemsAdaptive filterRadio propagation
A CDMA radio system uses an adaptive filter in a receiver to mitigate multipath radio propagation and to filter out interfering signals. Characteristics of an initial stage of the filter preferably are determined by cross correlation of a generated pilot signal and the input signal with the integration of the correlation performed over a time period selected to be an integral number of symbol periods. The integration causes the portions of the cross correlation corresponding to the user subchannels to average substantially to zero, so that the pilot channel signal correlation is the primary contribution to the signal used to characterize the channel to establish the coefficients of the adaptive filter for the receiver.
Owner:ACORN TECH INC
Spectrum detection strategy, base station and terminal device for cognitive radio system
InactiveCN101814962ARealize detectionImprove the performance of cooperative detectionTransmission monitoringOptimal decisionFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a spectrum detection strategy for a cognitive radio (CR) system, which is realized in a way that: by utilizing the differences among radio propagation channels and the theories of subset partition and linear programming, selecting the optimal strategy of the detected channel set, realizing the optimal detection on the authorized user among every CR users, reporting the detection result to a CR base station, and determining whether an authorized user signal exists by utilizing the CR base station, thereby determining whether the spectrum is idle. The invention also provides a cognitive radio system, a base station and a terminal device. By implementing the spectrum detection strategy, the base station and the terminal device for the cognitive radio system, the invention enhances the spectrum detection performance of the CR system, realizes the detection on the CR system within all bands, and enhances the overall detection performance of the system. In addition, the invention can be used in a centralized network structure, and is applicable to Standard IEEE802.22.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for establishing a radio coverage map
InactiveUS6876856B2Remove distortionImprove the level ofRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationRadio coverageCellular radio
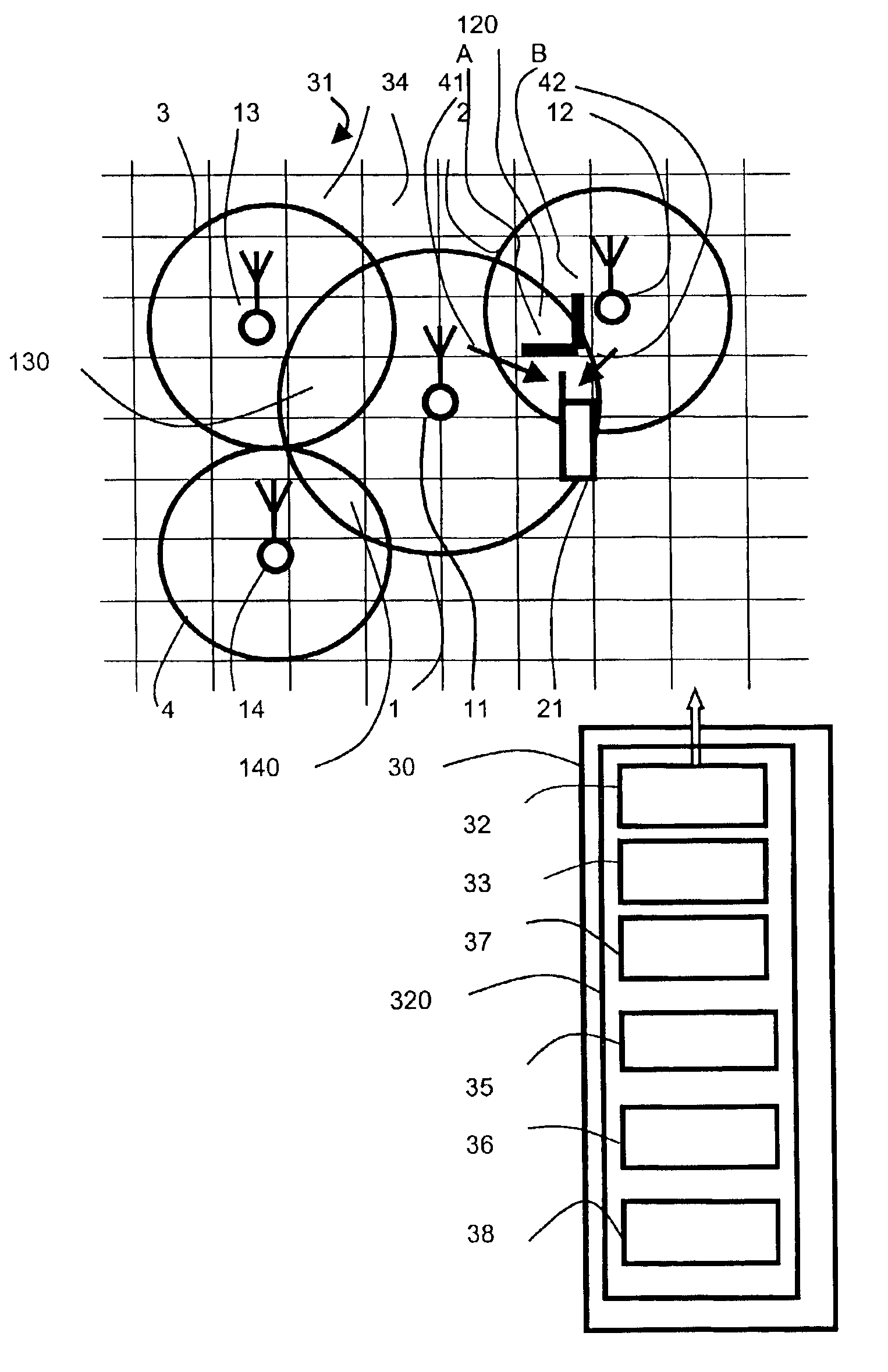
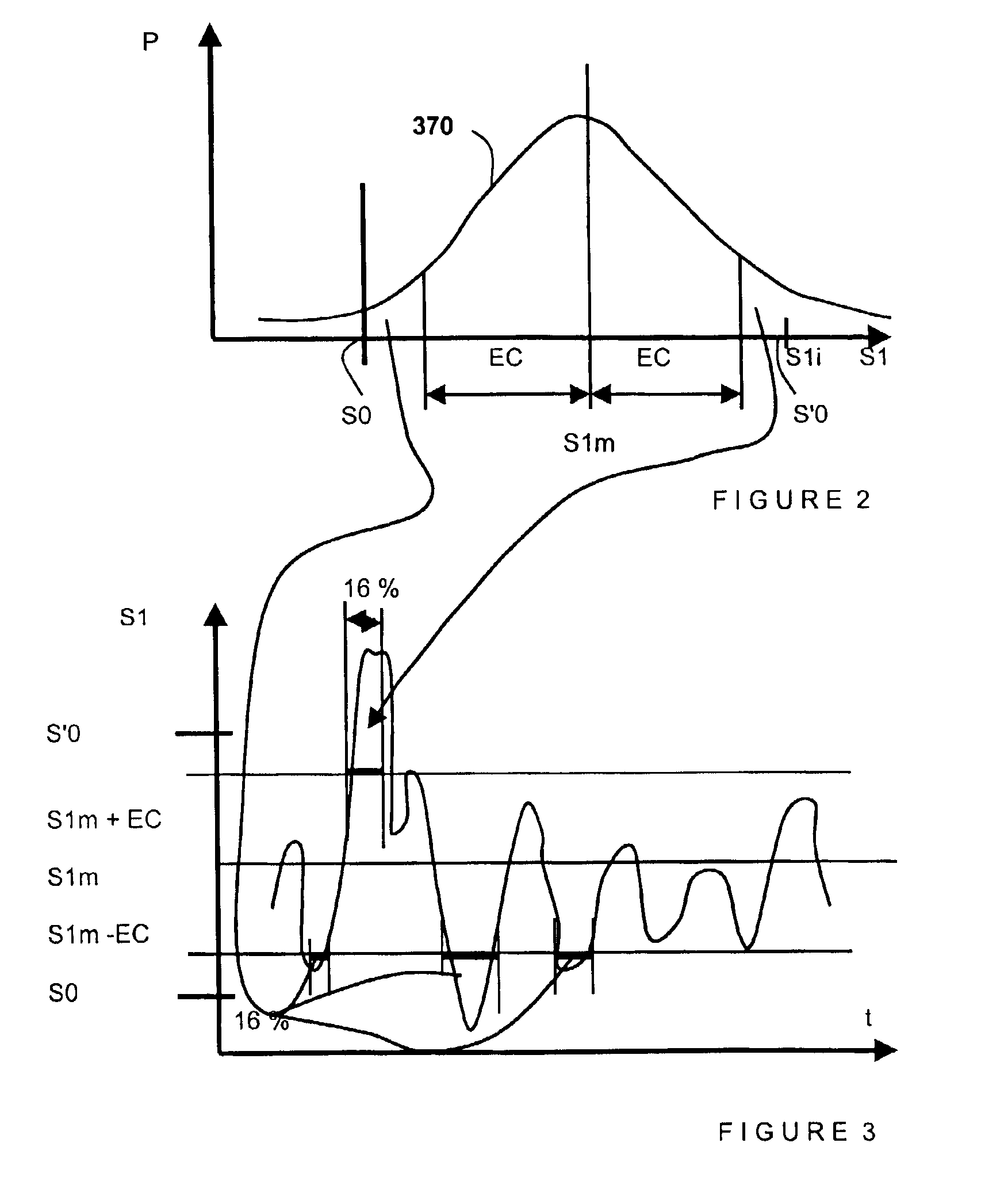
Method for establishing a radio coverage map of at least one cell for a cellular radio telephone network, by means of a calculation system using data memorized from a geographic map and the position of the cell and an associated radio base station, data memorized for a level of transmission for the station and a radio reception (S0) sensitivity threshold for handsets, and data memorized for a radio propagation attenuation law, a method in which the calculation system generates a grid of the cell map with a certain number (N1) of pixels on the map, calculates a number (N1) of attenuations of radio propagation for the level of transmission by the station for the respective pixels and a number of average reception levels (S1m), associated with respective pixels, which it memorizes, and compares them with the sensitivity threshold (S0) to determine a number of directions of disparity between the threshold value (S0) and the value of the average reception level (S1m) associated with each pixel, a method characterized by the fact that the data representing a temporal fluctuation law for the attenuation of radio propagation having been made available to the calculation system, the latter applies the fluctuation law to the number (N1) of average reception levels (S1m), it determines a corresponding number (N1) of probabilities (P, 311) so that the aforementioned respective disparities have a certain direction, and it establishes the radio coverage map by associating with each pixel the data representing the aforementioned probability (P, 311).
Owner:SOC FR DU RADIOTELEPHONE SFR
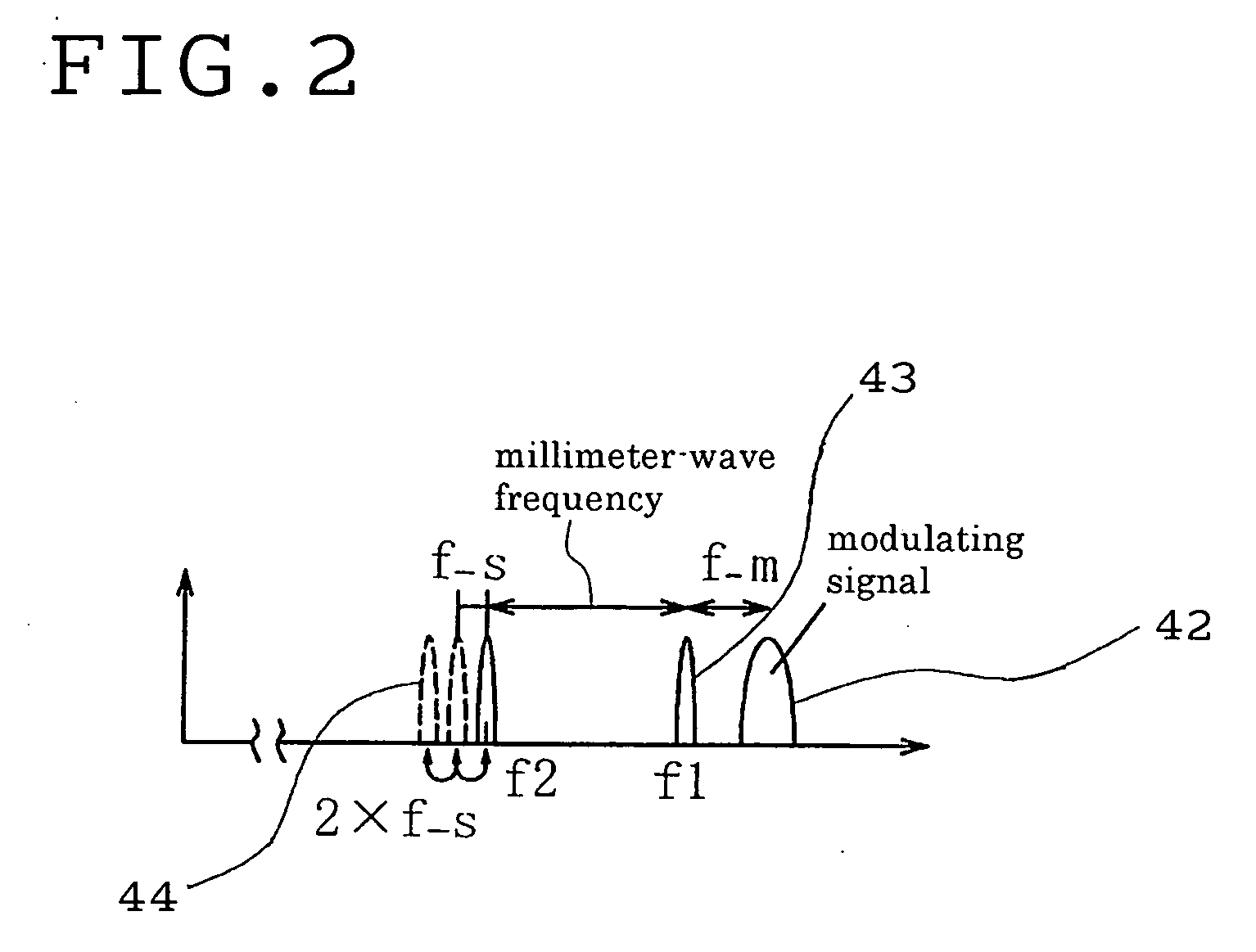
Method for Changing Frequency and Base Station in Radio Optical Fusion Communication System
InactiveUS20070206957A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationCommunications systemIntermediate frequency
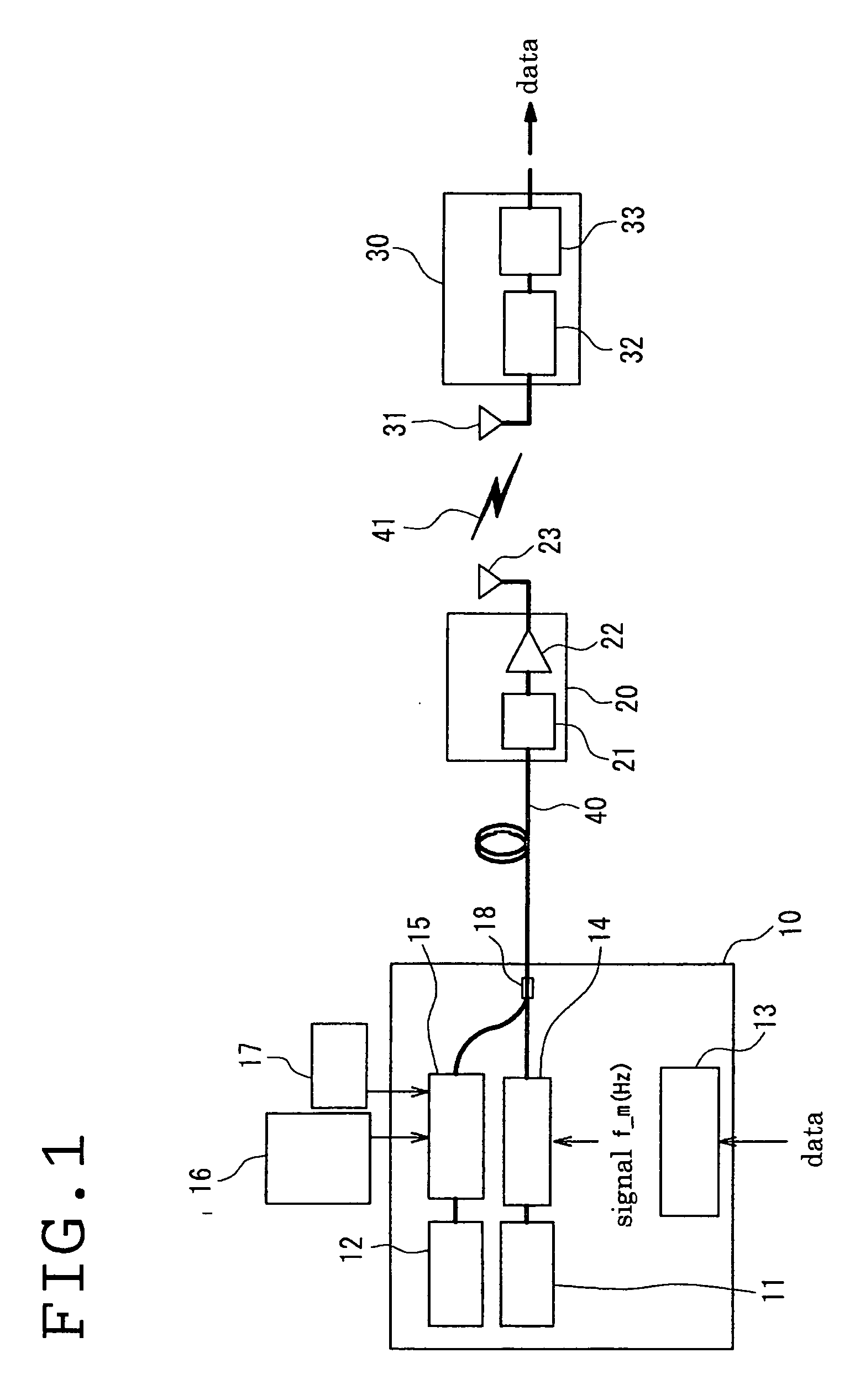
In a radio optical fusion communication system with the integration of an optical fiber transmission path and a radio propagation path, wherein by first and second light sources, an intermediate-frequency signal generating means for generating a modulating signal at an intermediate frequency band, a modulator for modulating an optical signal from the first light source into an SSB modulated optical signal using the intermediate-frequency signal, and an optical mixer for mixing the modulated optical signal with the optical signal from the second light source to obtain an optical transmission signal in a base station, the frequency of either of the optical signals is controlled such that the difference in frequency between the optical signals is a desired frequency of a modulated radio signal, thus switching the frequency channel of the modulated radio signal in the radio propagation path.
Owner:SUMITOMO OSAKA CEMENT CO LTD
Mobile Station and Mobile Communication System
InactiveUS20080014915A1Network traffic/resource managementSubstation equipmentRadio propagationMobile station
The present invention relates to a mobile station that controls a transmission rate of user data to be transmitted to a base station. The mobile station according to the present invention includes: a transmission rate control unit configured to decide an instantaneous transmission rate of the user data, based on a parameter notified from a network during establishment of a call, a radio propagation path quality of a radio propagation path between the mobile station and the base station, an average radio propagation path quality of the radio propagation path, and a factor related to a transmission rate, a transmission power or a transmission power ratio notified from the base station.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Radio wave propagation environment measurement device, wireless network construction system and radio wave propagation environment measurement method
The purpose of the present invention is to easily obtain three-dimensional shape data and material characteristics data that are necessary for estimating radio wave propagation between wireless stations, in order to construct a highly reliable wireless network. In the present invention, a wireless network system is provided with wireless signal transmission and reception equipment at a planned construction site. An electromagnetic wave measurement value for a wireless signal between the equipment is obtained. Three-dimensional structure information that includes the electrical characteristics and three-dimensional shape information of structures that comprise the site is used to estimate a propagation state of an electromagnetic wave for a wireless signal between the wireless signal transmission and reception equipment, and thereby an electromagnetic estimation value is obtained. An electromagnetic wave measurement value expressed as a signal intensity at each time point and an electromagnetic wave estimation value are compared for each time point to obtain a time zone in which such resultant error value is larger than a reference value. The path between the wireless signal transmission and reception equipment that is receiving in such time zone is calculated as the electromagnetic wave path. The three-dimensional structure information for the site positioned on the electromagnetic wave path is corrected and the electromagnetic wave estimation value is re-calculated. The electromagnetic wave measurement value and the re-calculated electromagnetic wave estimation value are compared to obtain corrected information for three-dimensional structure information with a smaller error value.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com