Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Occipital lobe" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The occipital lobe is the visual processing center of the mammalian brain containing most of the anatomical region of the visual cortex. The primary visual cortex is Brodmann area 17, commonly called V1 (visual one). Human V1 is located on the medial side of the occipital lobe within the calcarine sulcus; the full extent of V1 often continues onto the occipital pole. V1 is often also called striate cortex because it can be identified by a large stripe of myelin, the Stria of Gennari. Visually driven regions outside V1 are called extrastriate cortex. There are many extrastriate regions, and these are specialized for different visual tasks, such as visuospatial processing, color differentiation, and motion perception. The name derives from the overlying occipital bone, which is named from the Latin ob, behind, and caput, the head. Bilateral lesions of the occipital lobe can lead to cortical blindness (See Anton's syndrome).
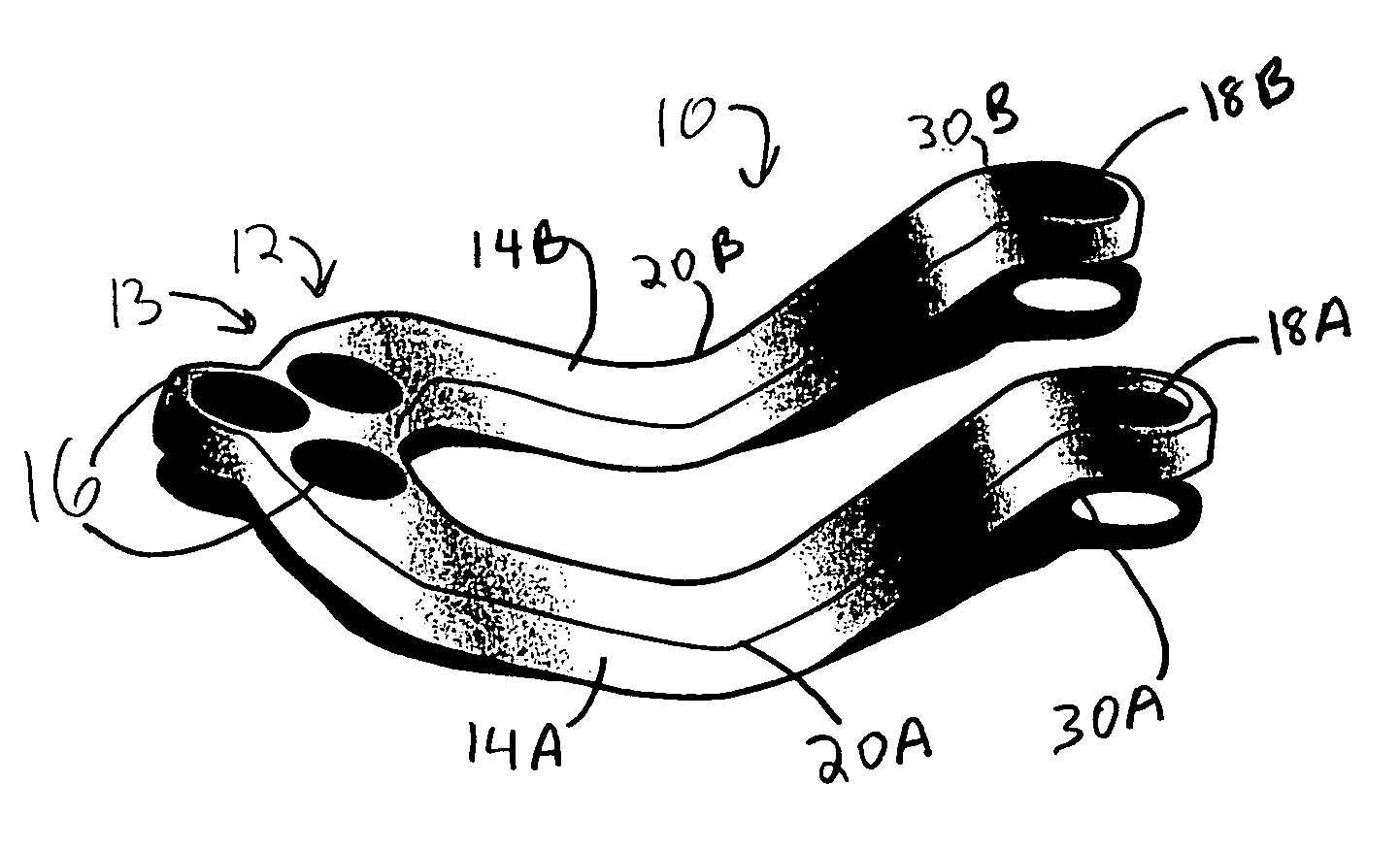
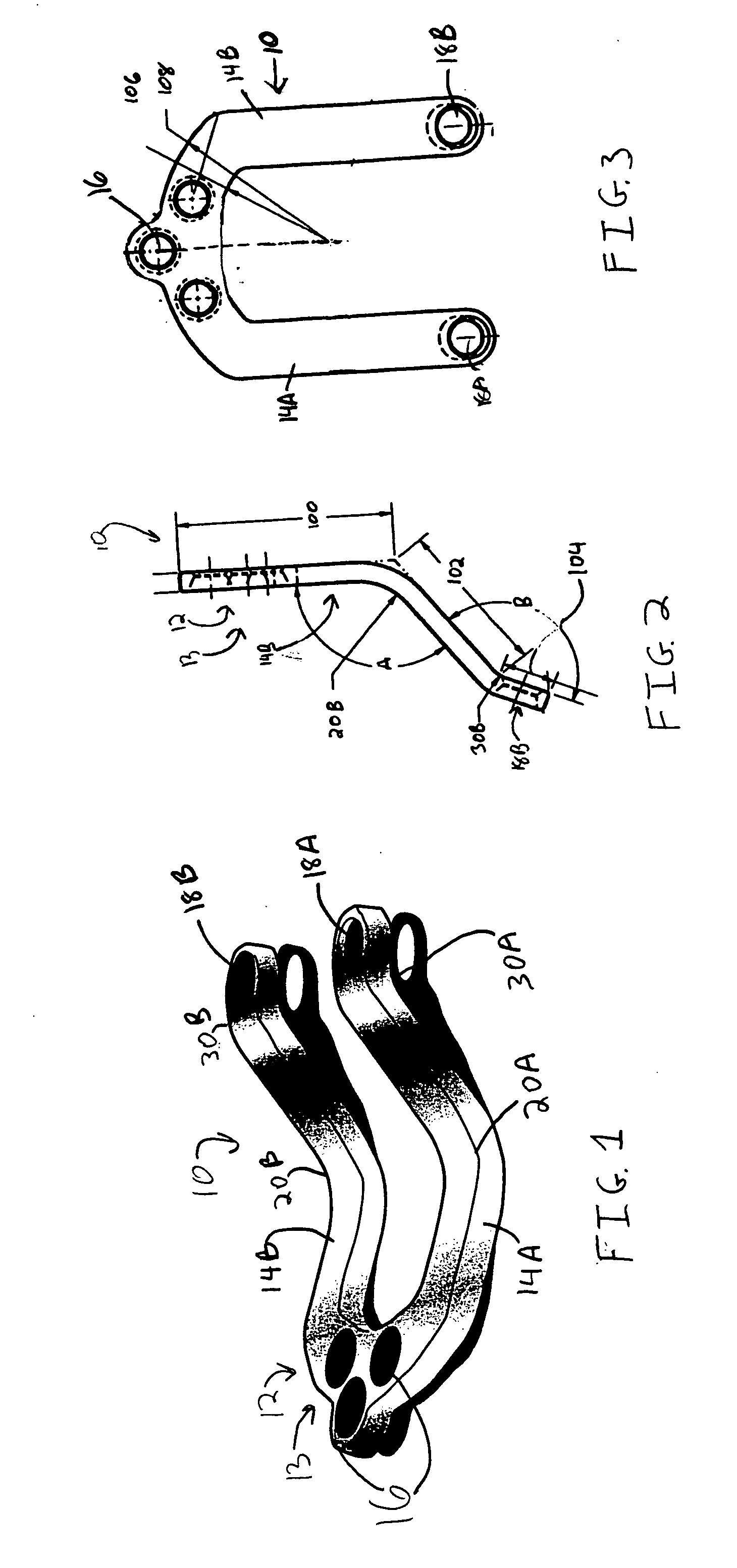
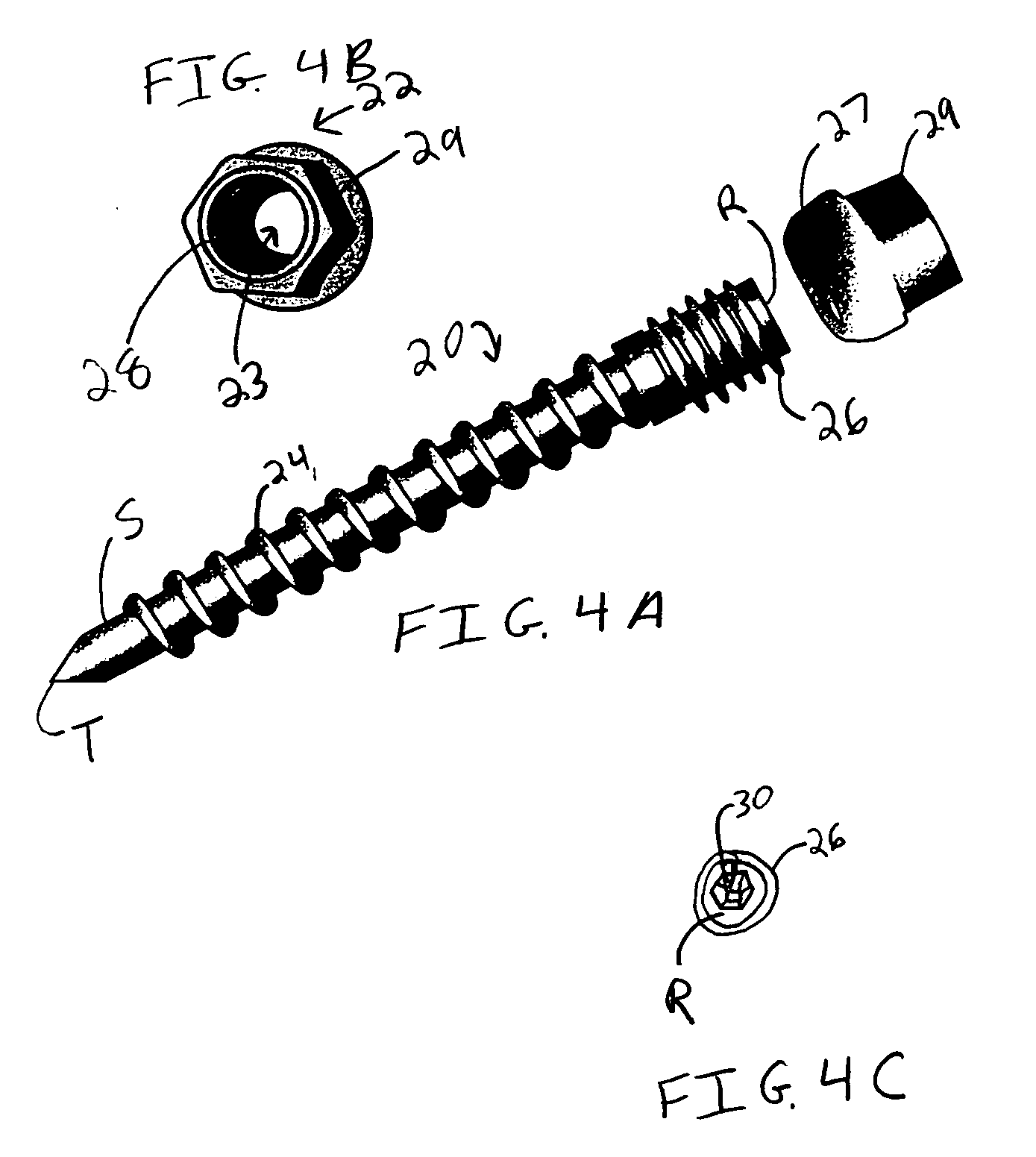
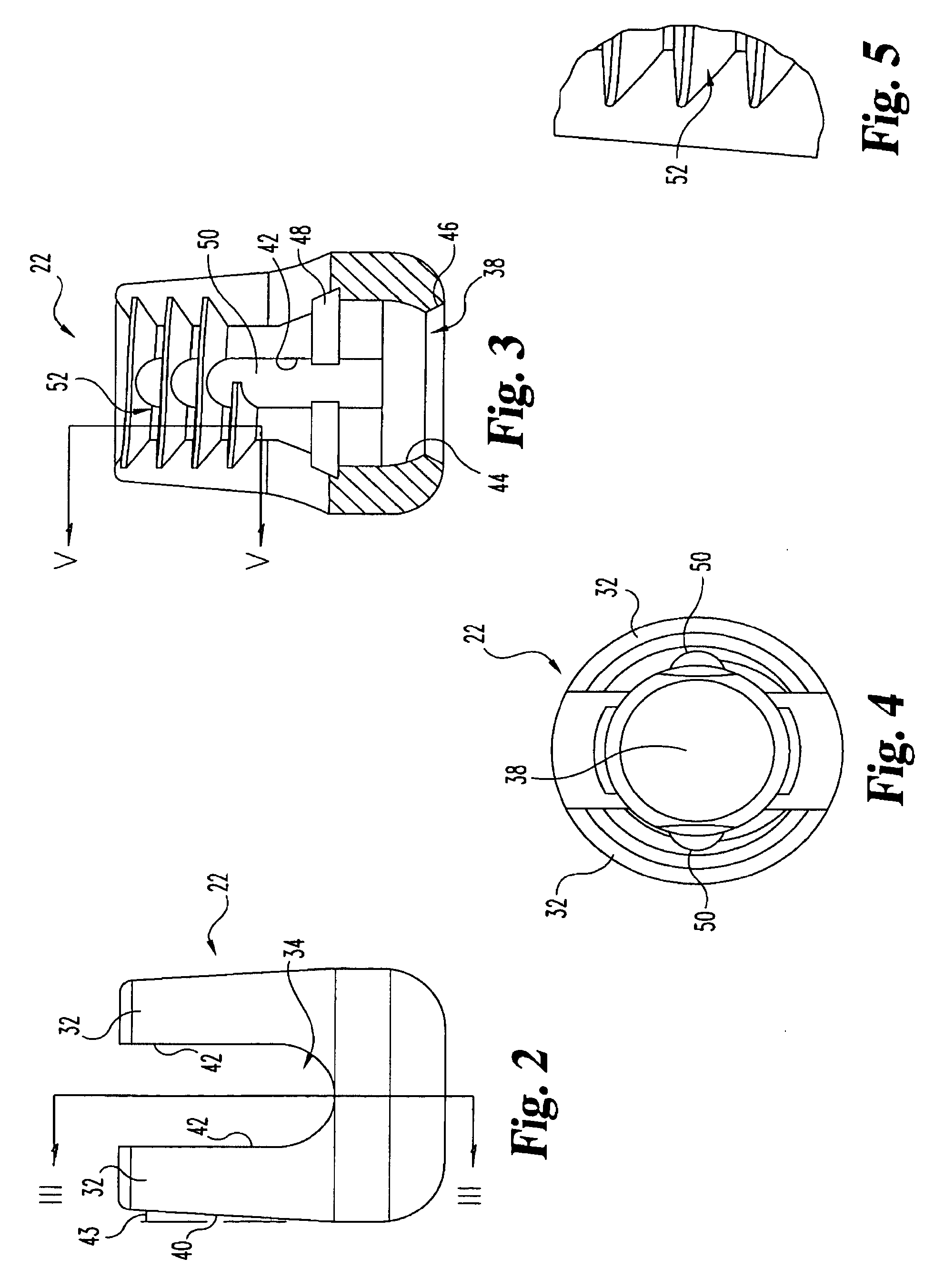
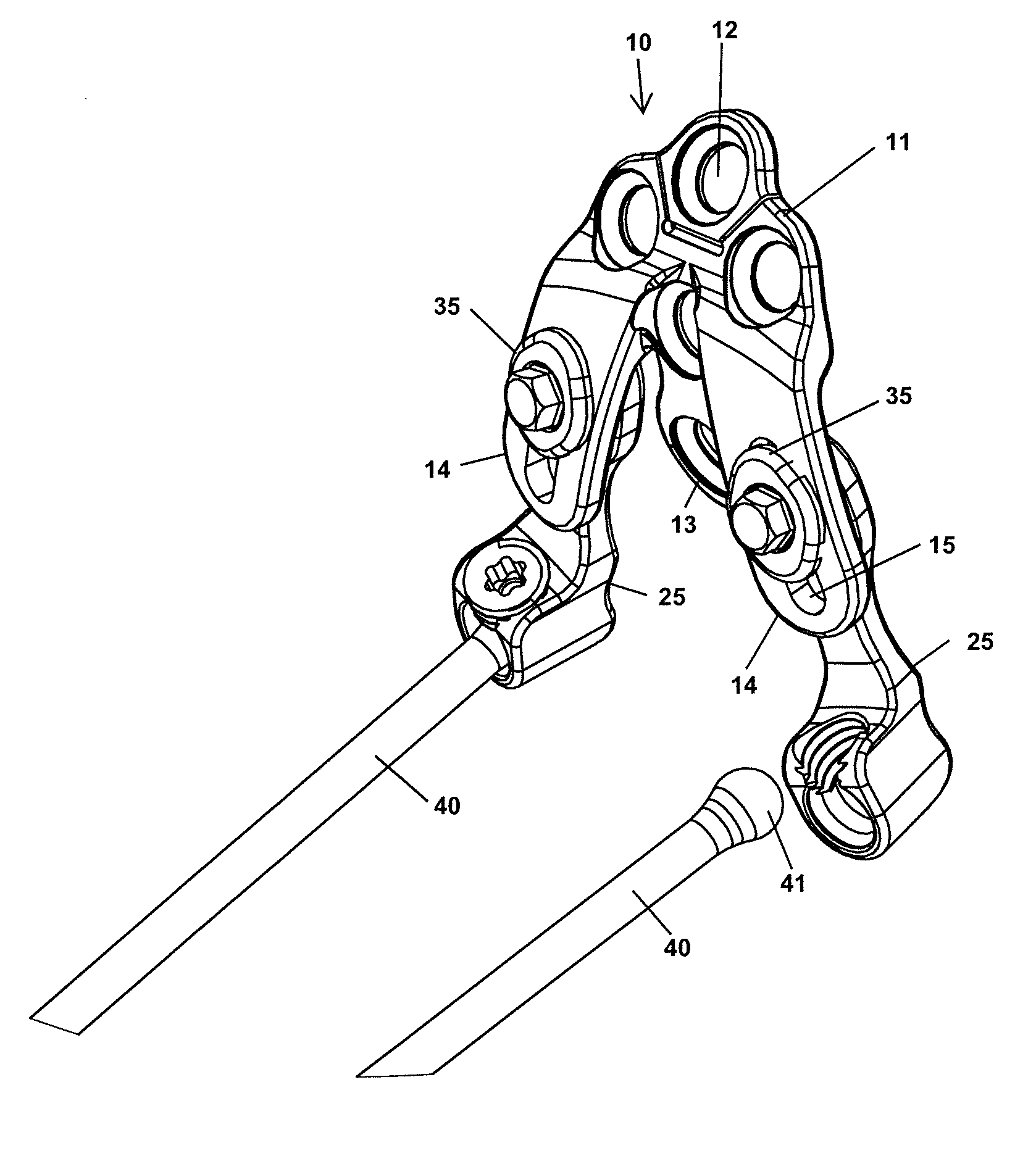
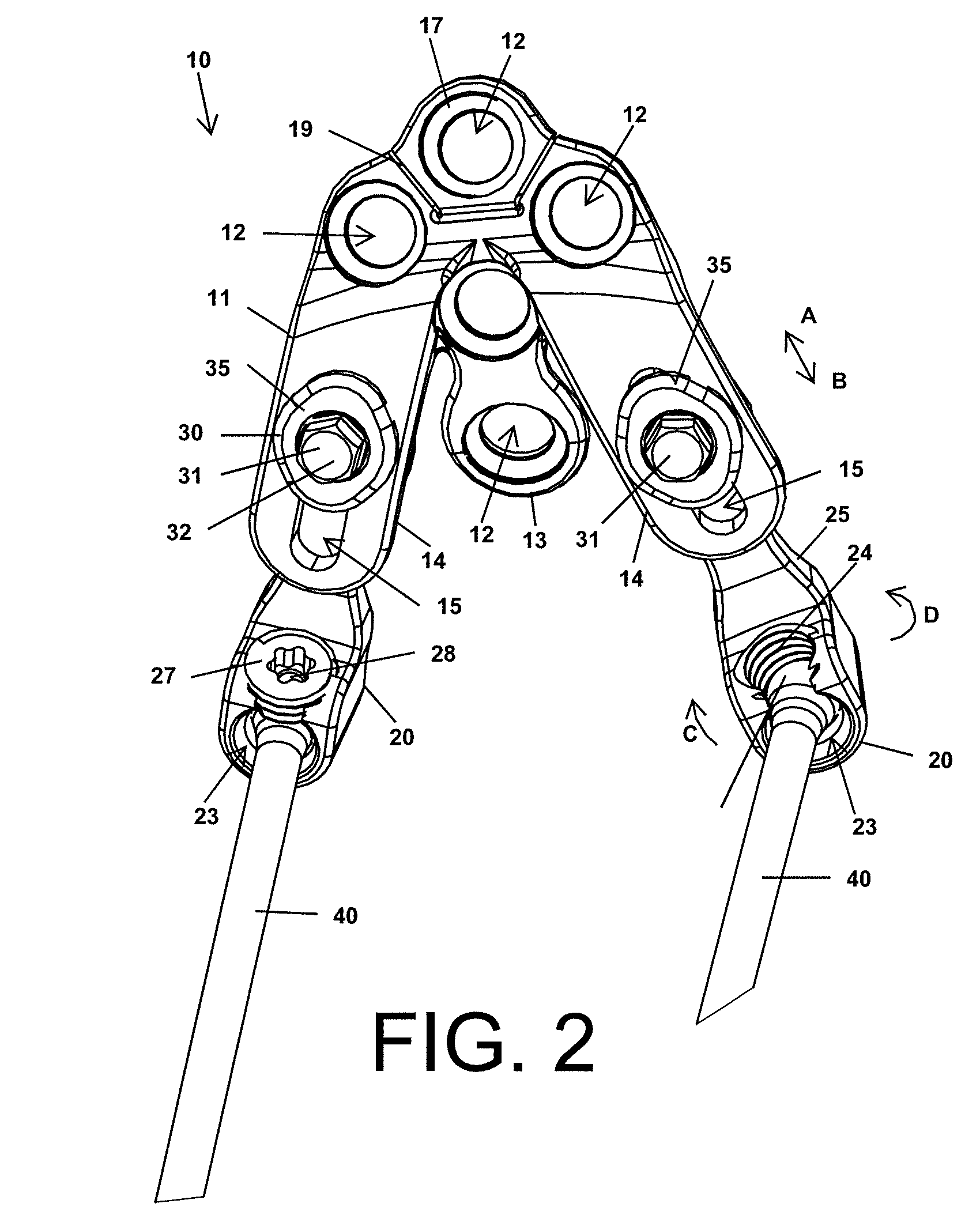
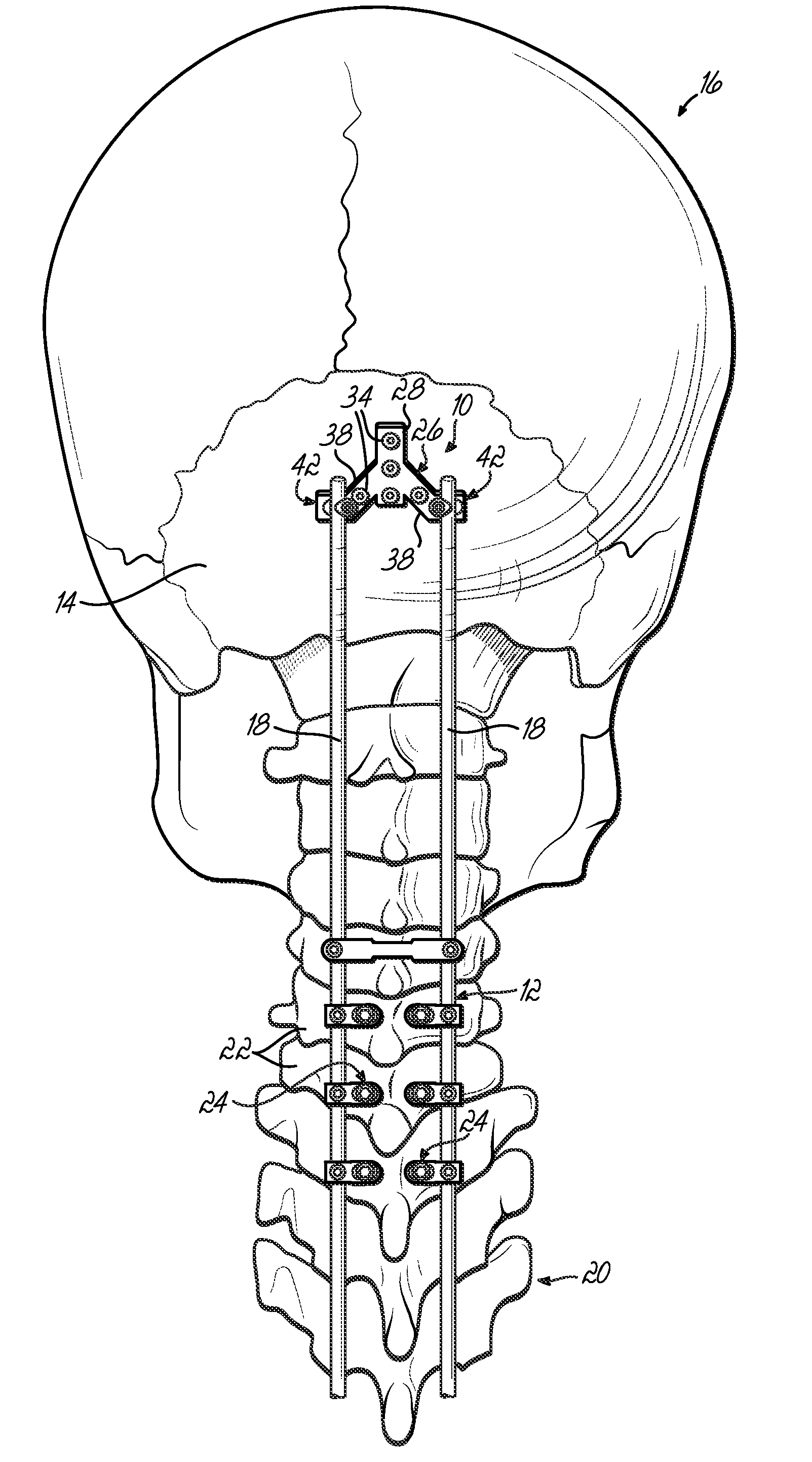
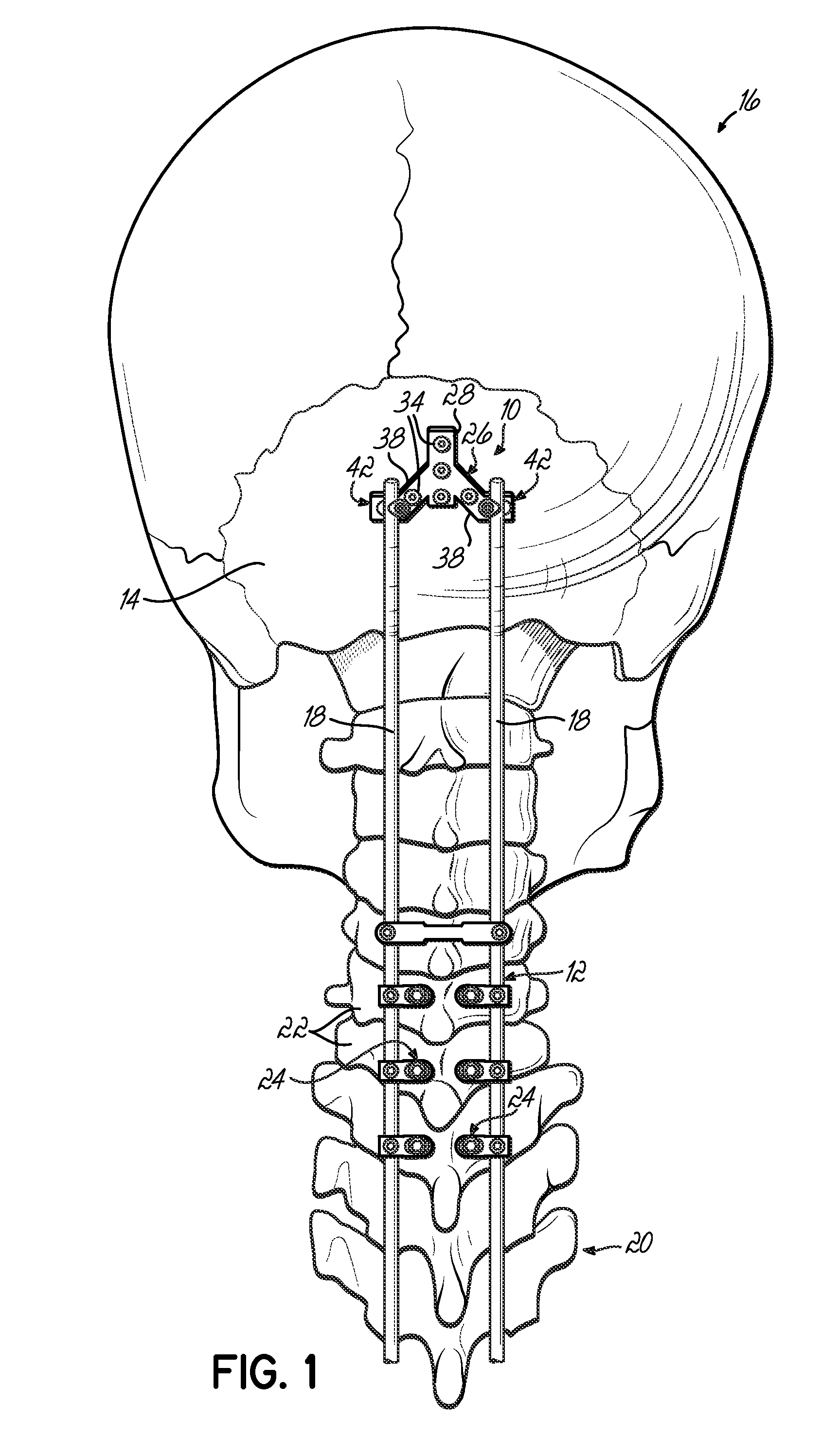
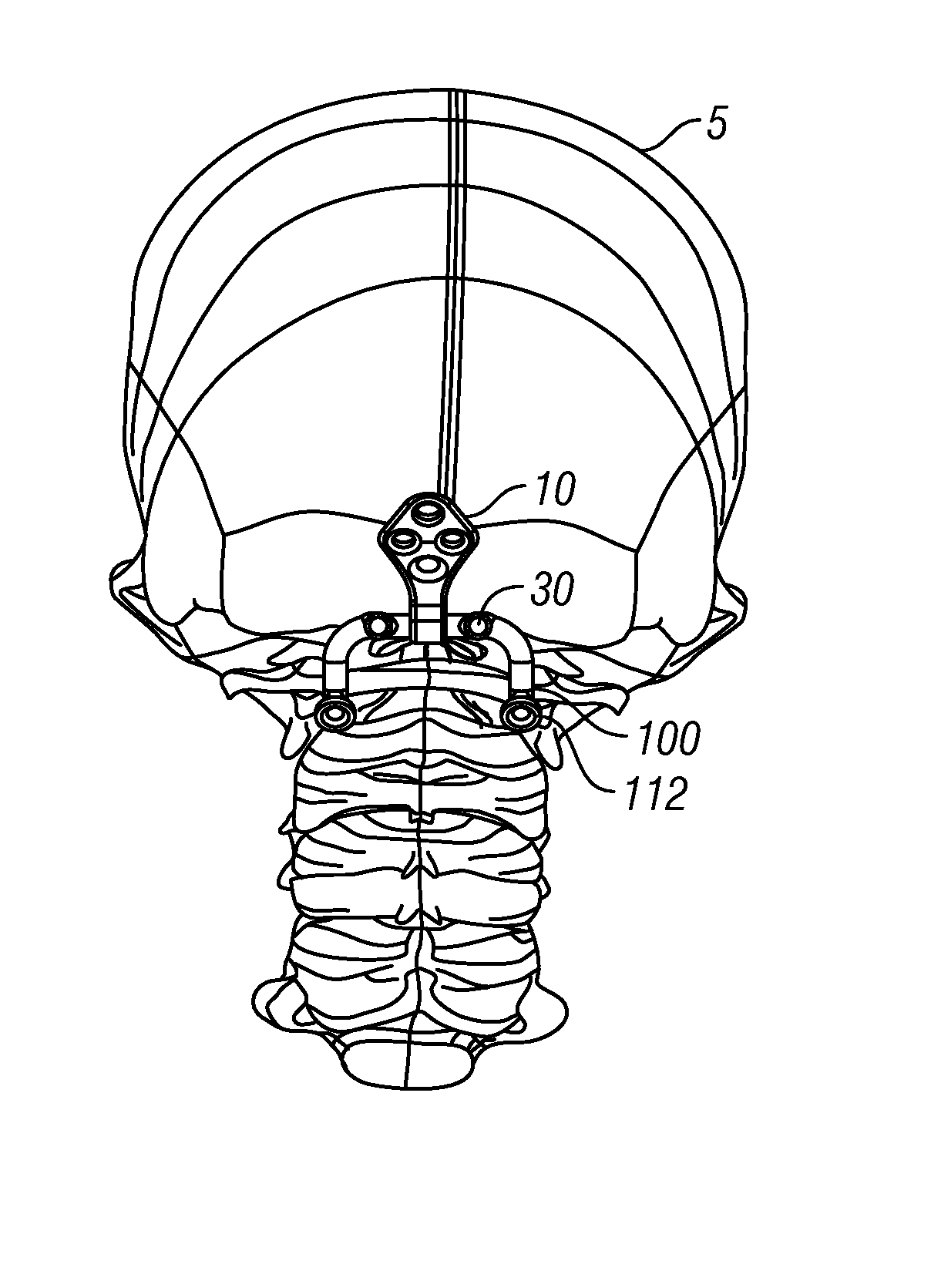
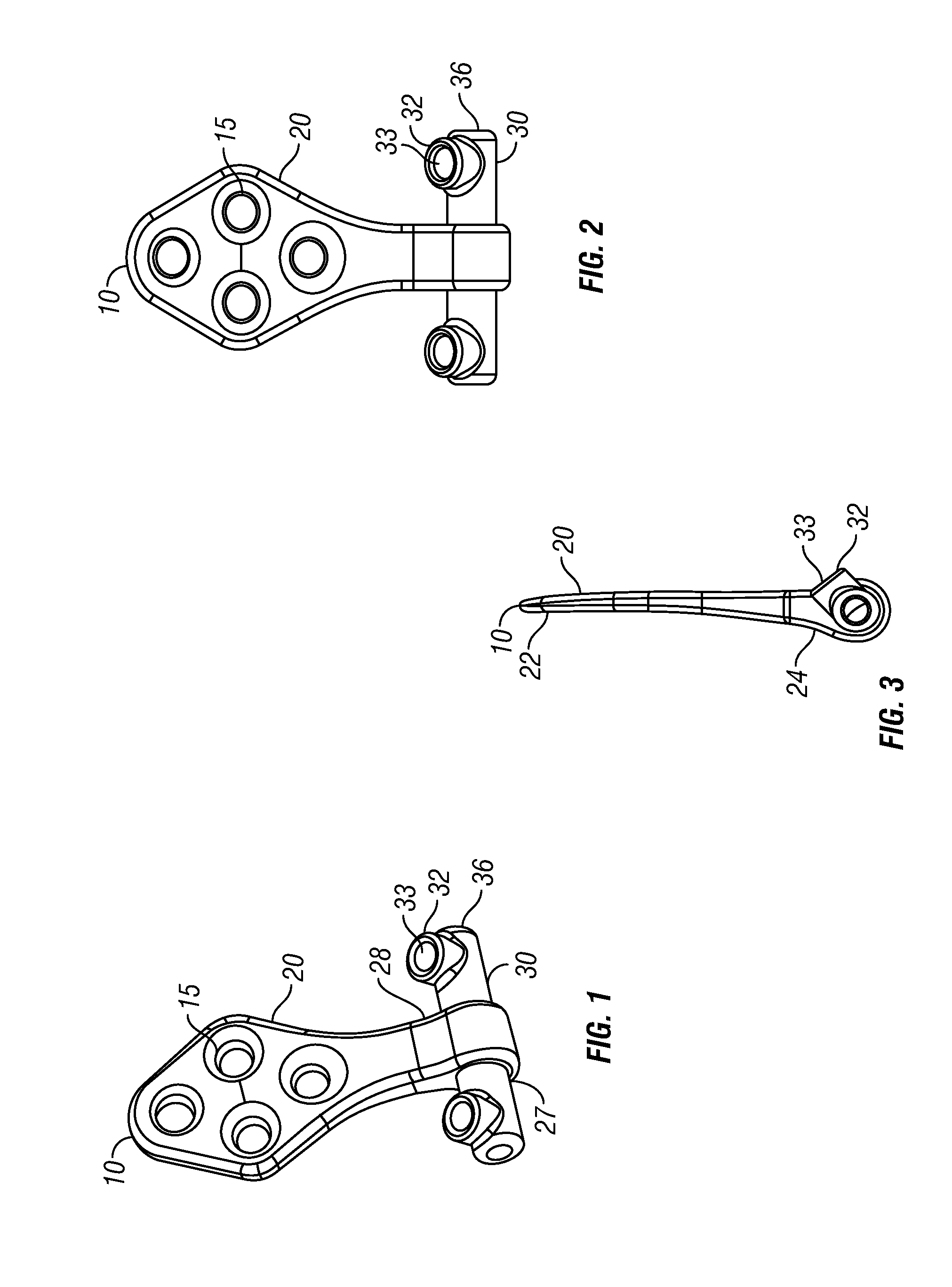
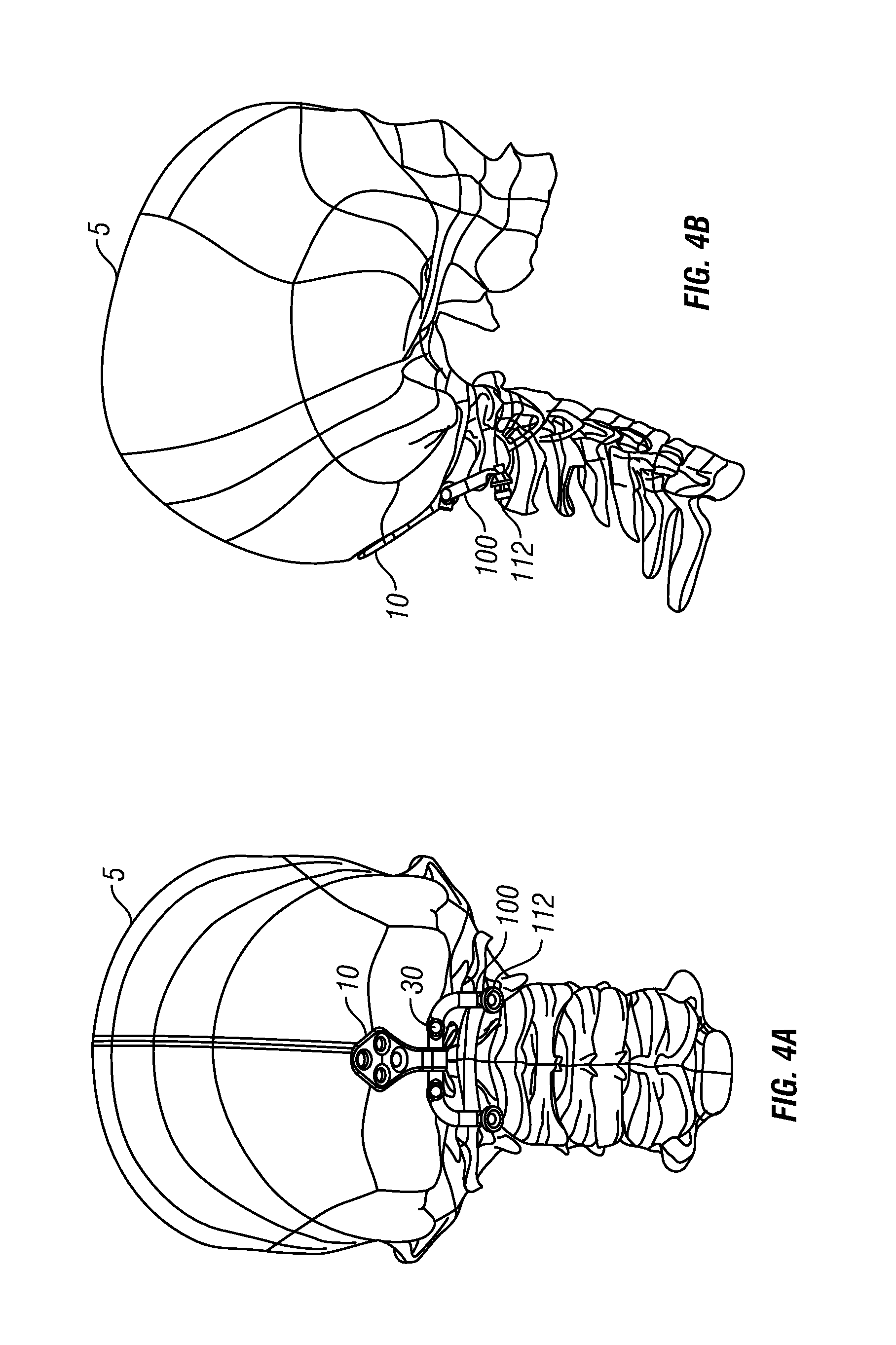
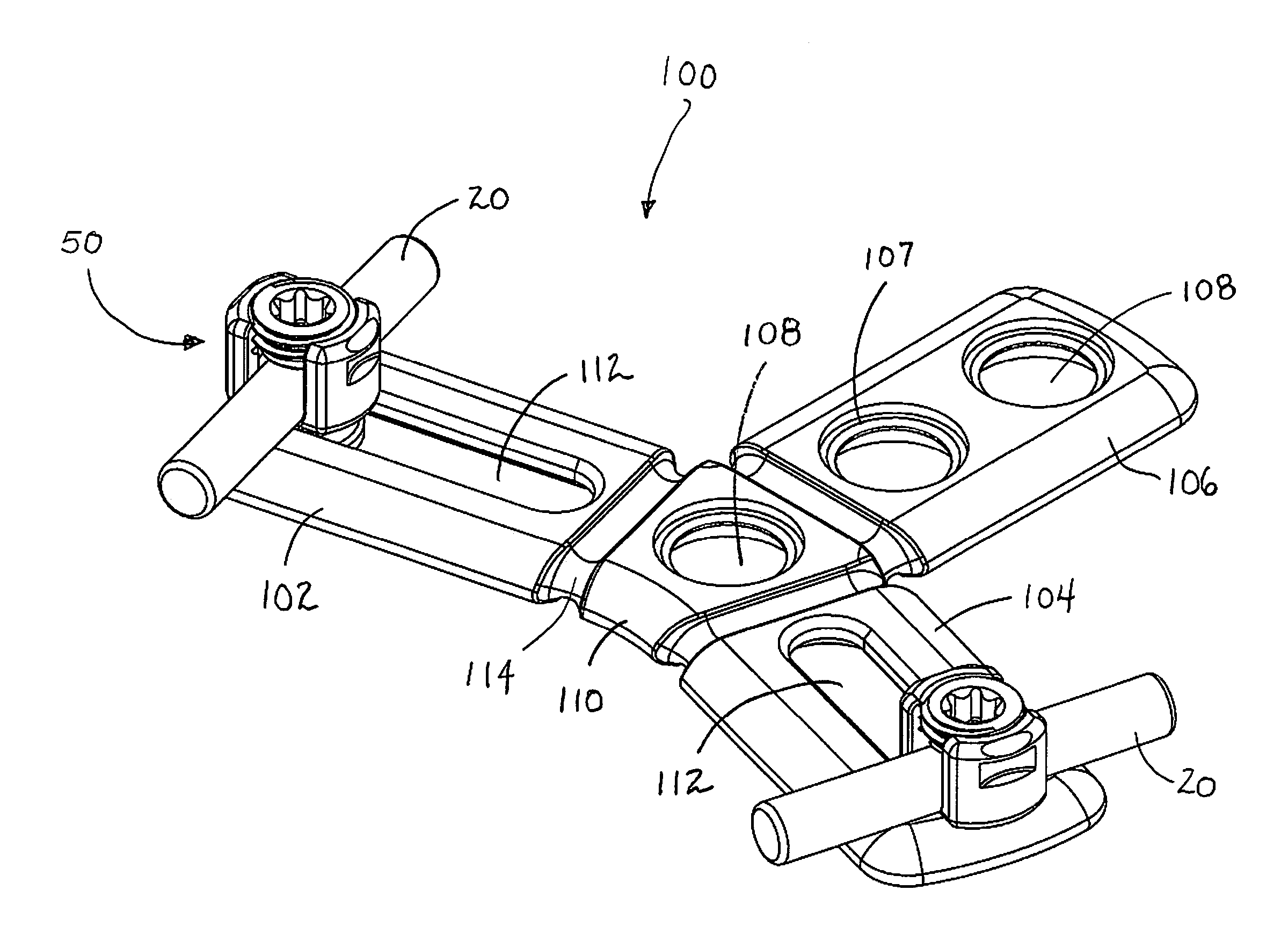
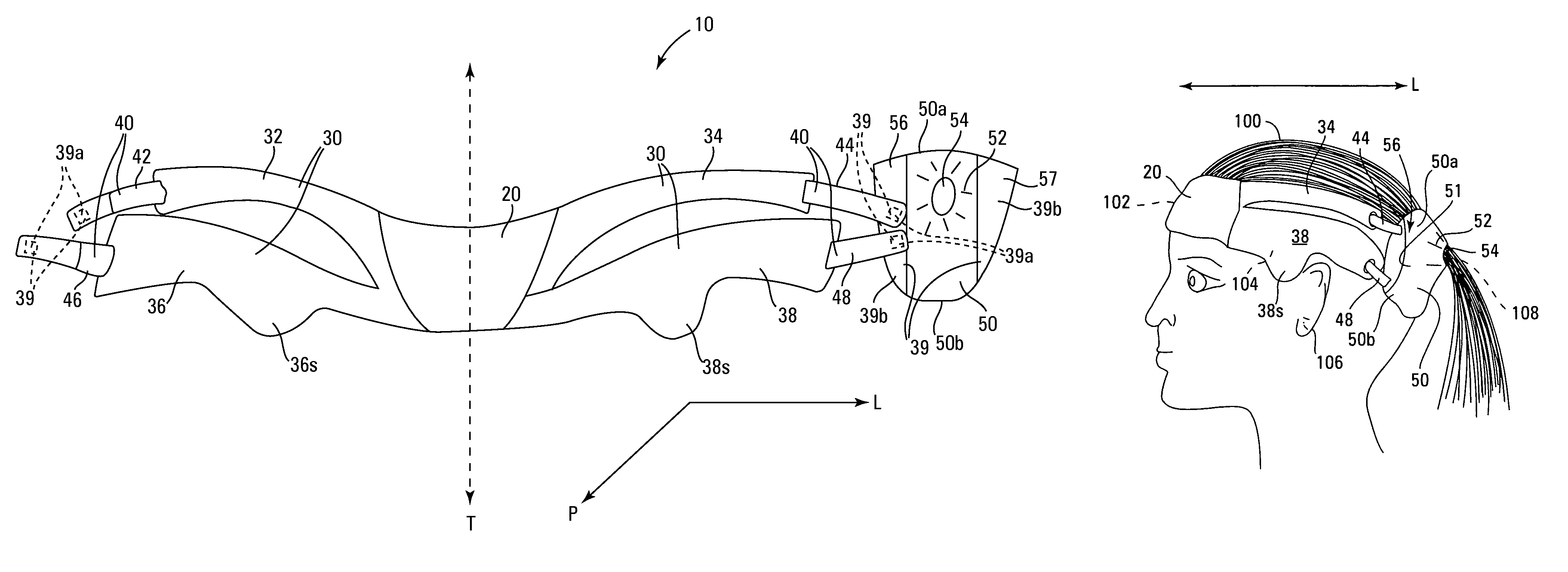
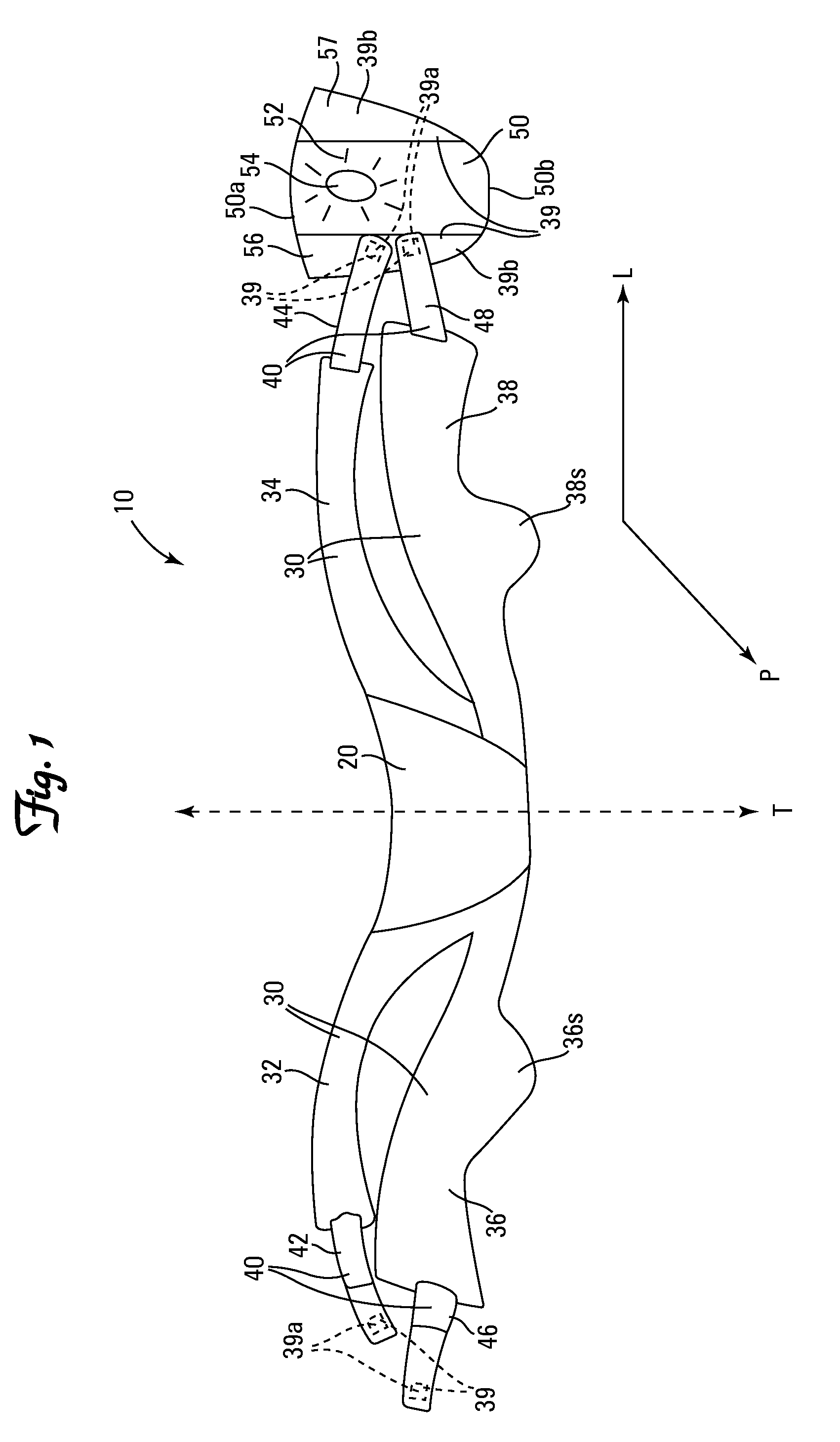
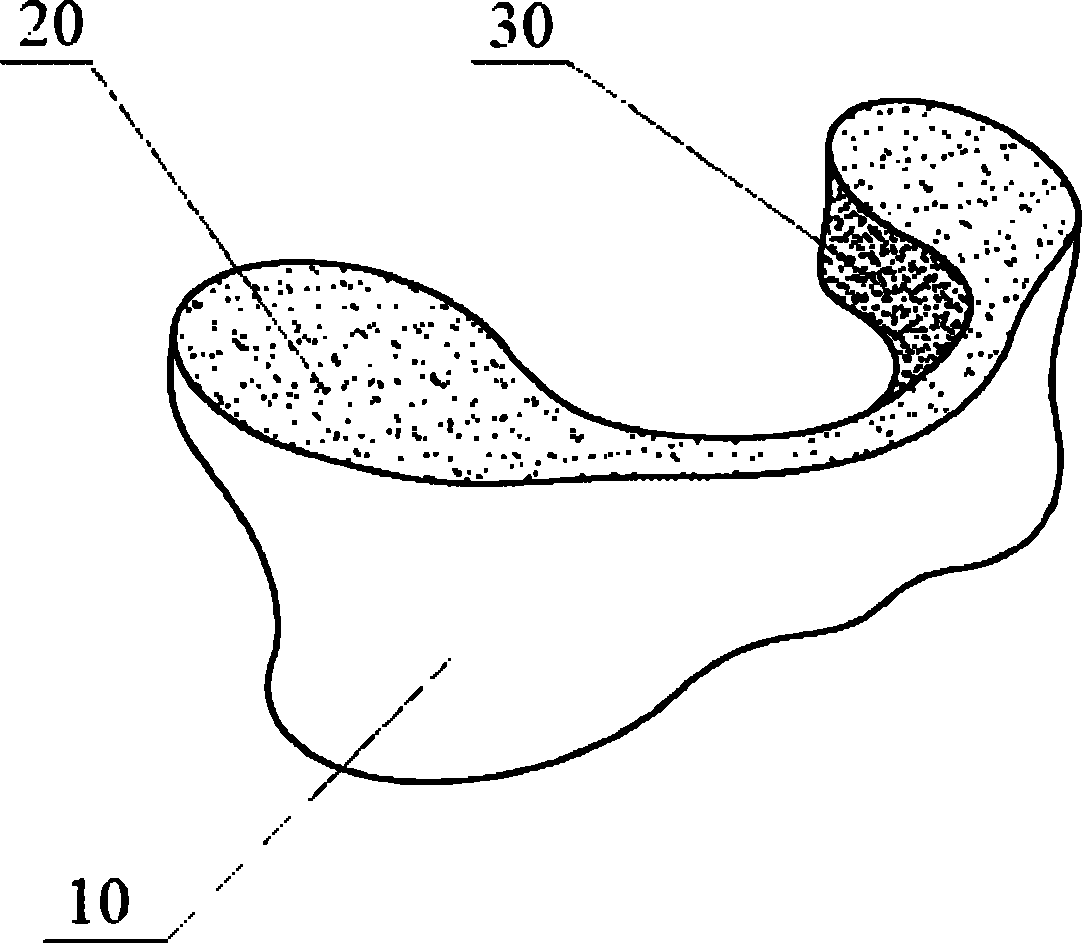
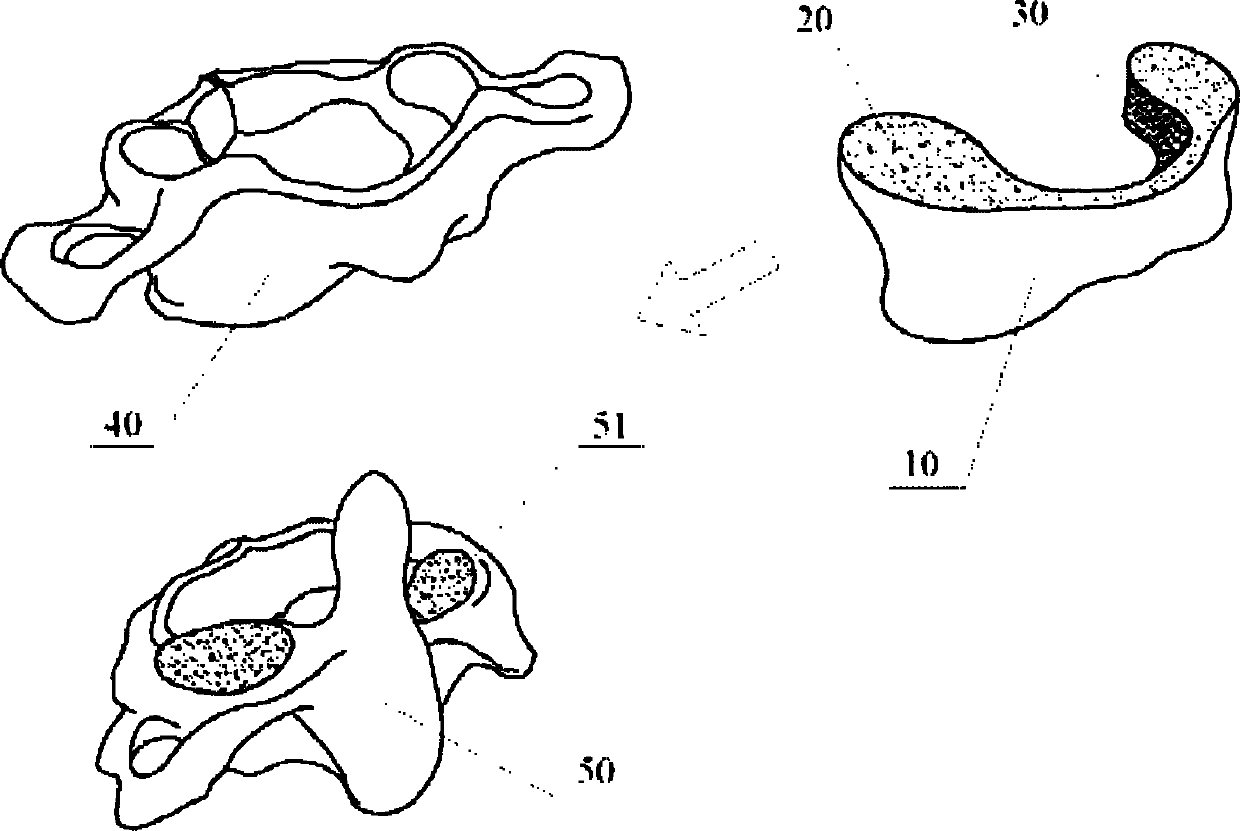
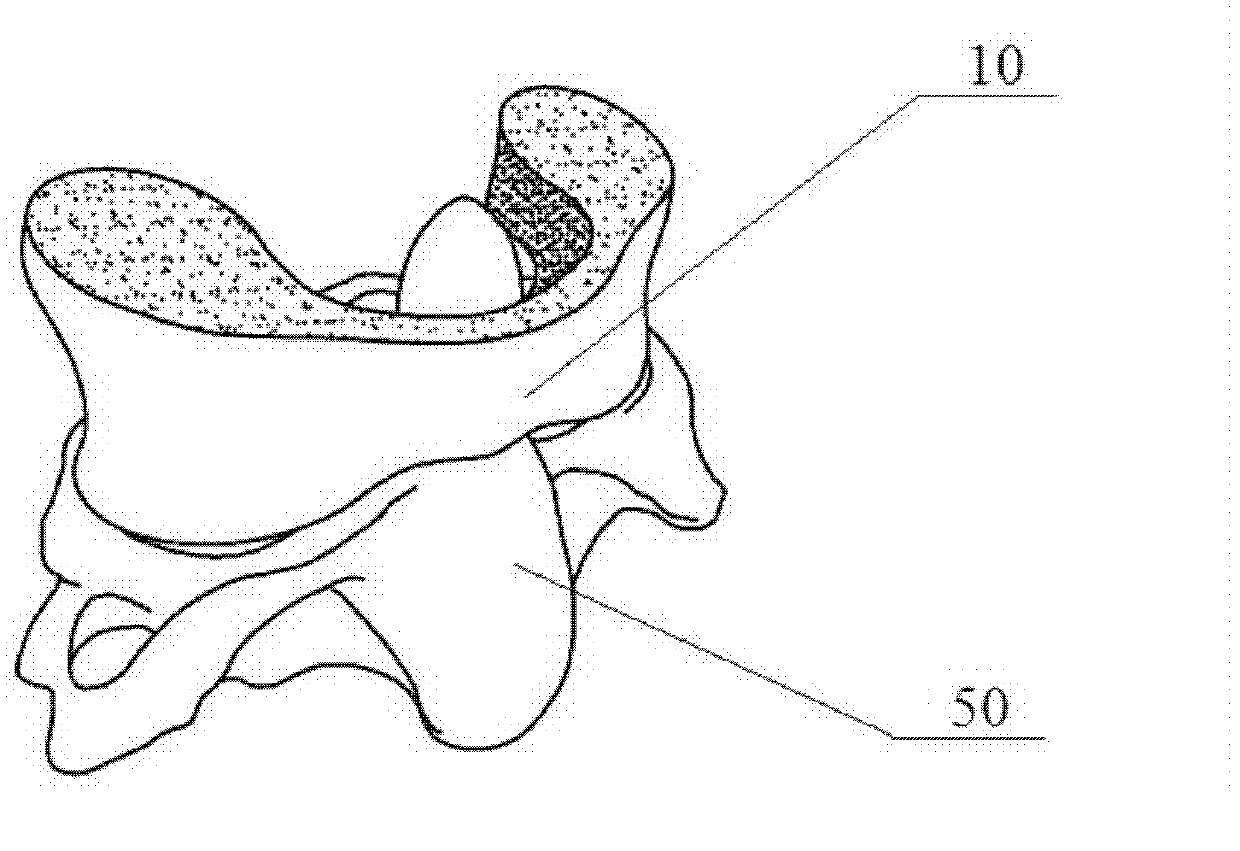
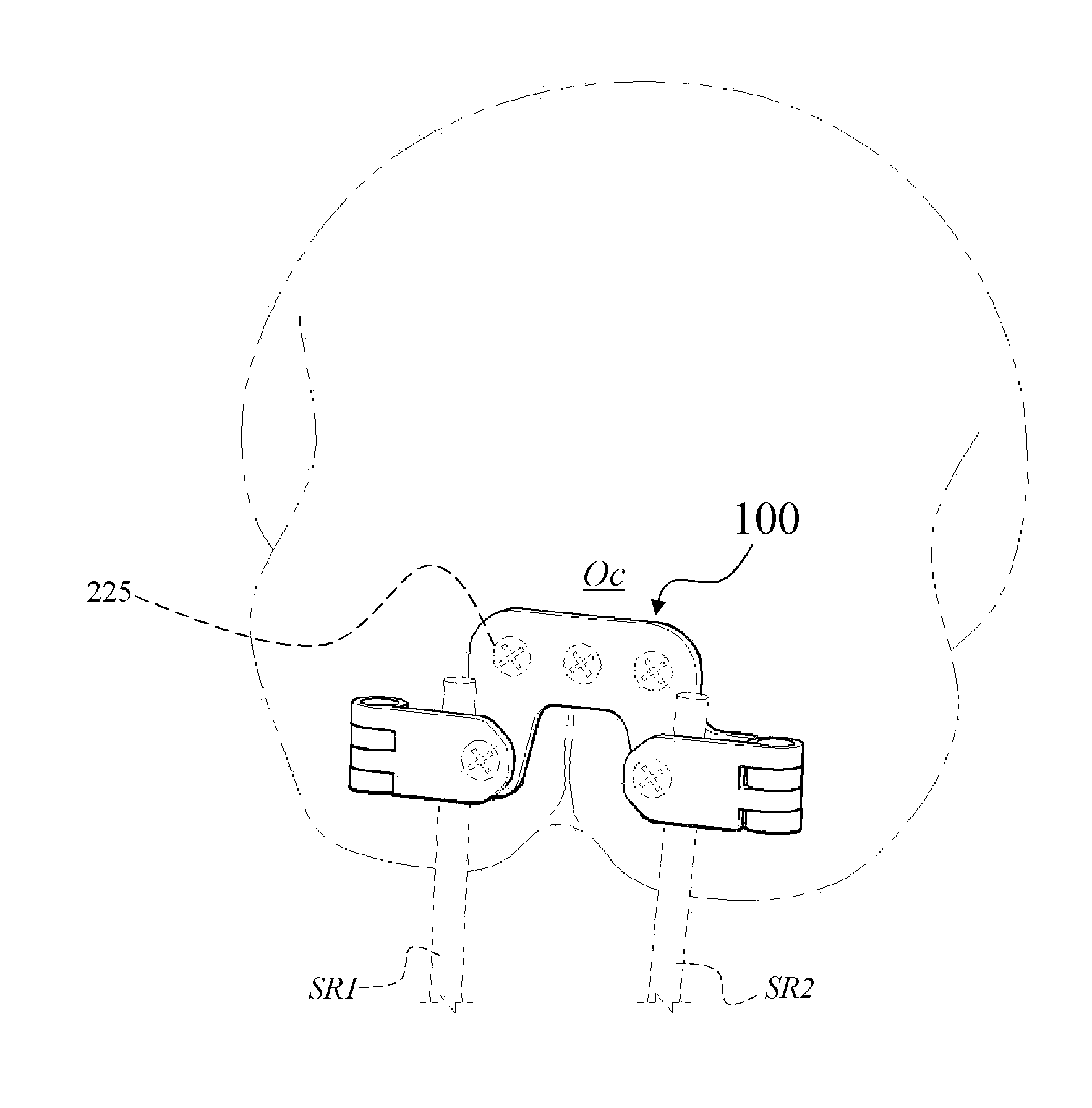
Occipitocervical plate
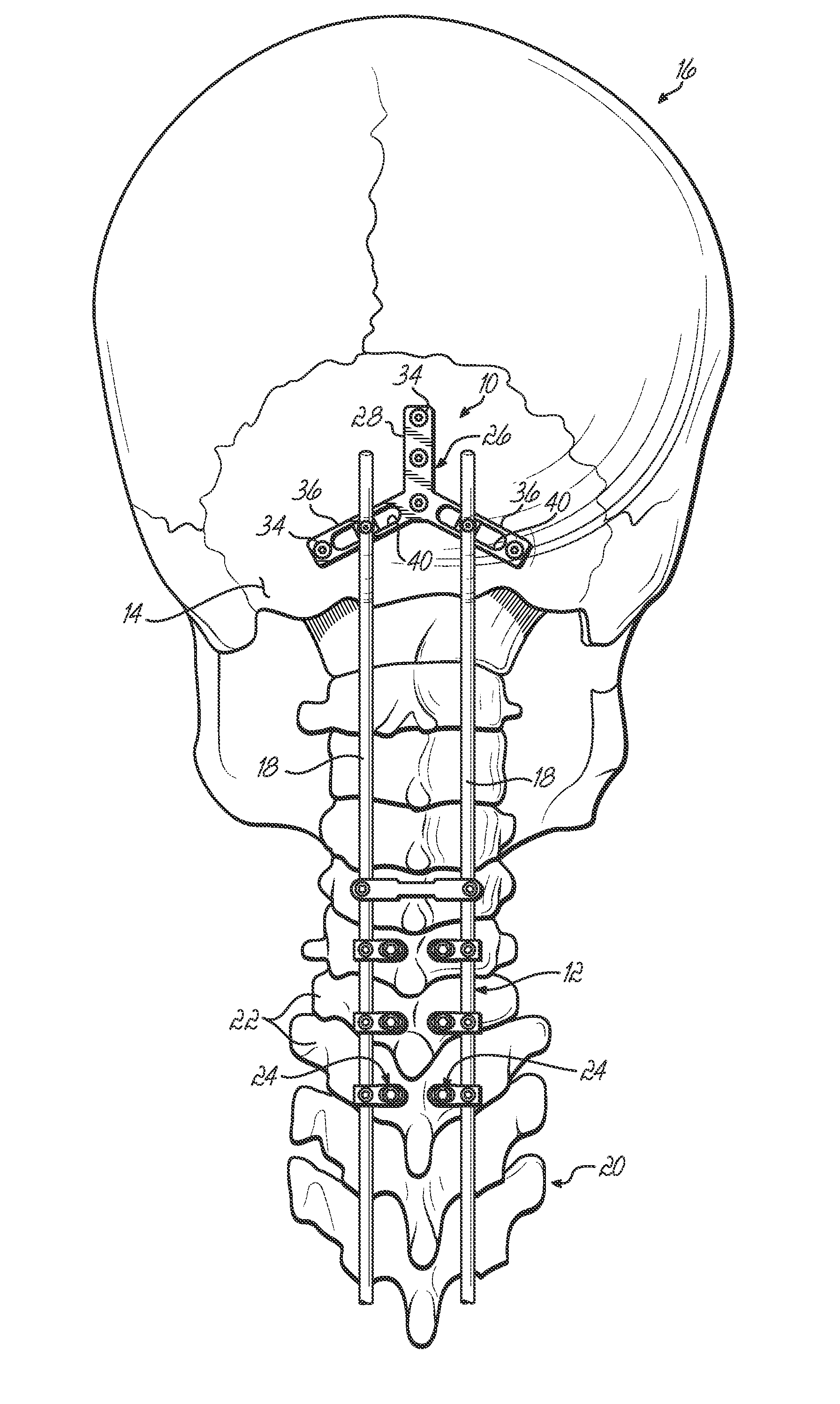
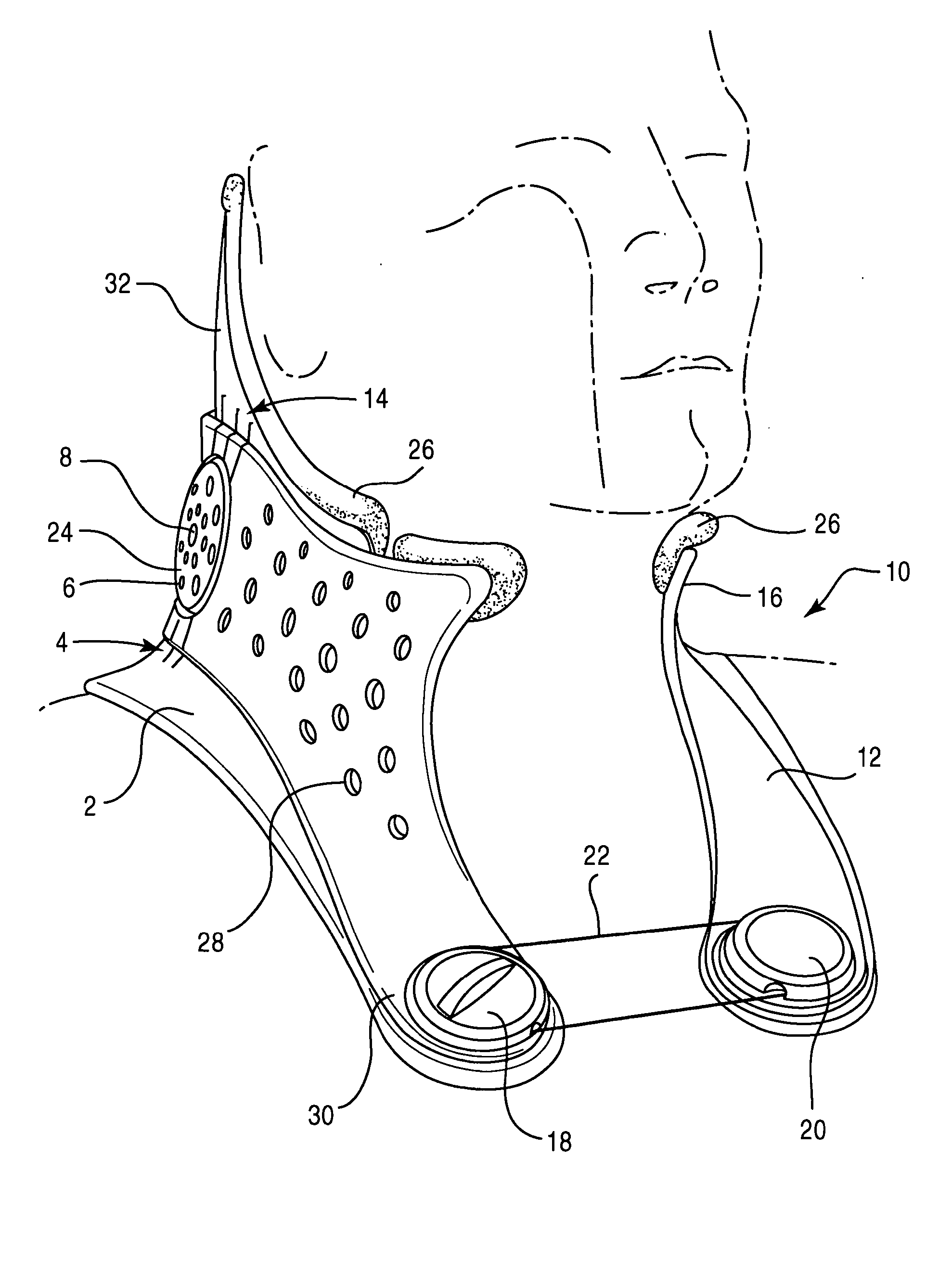
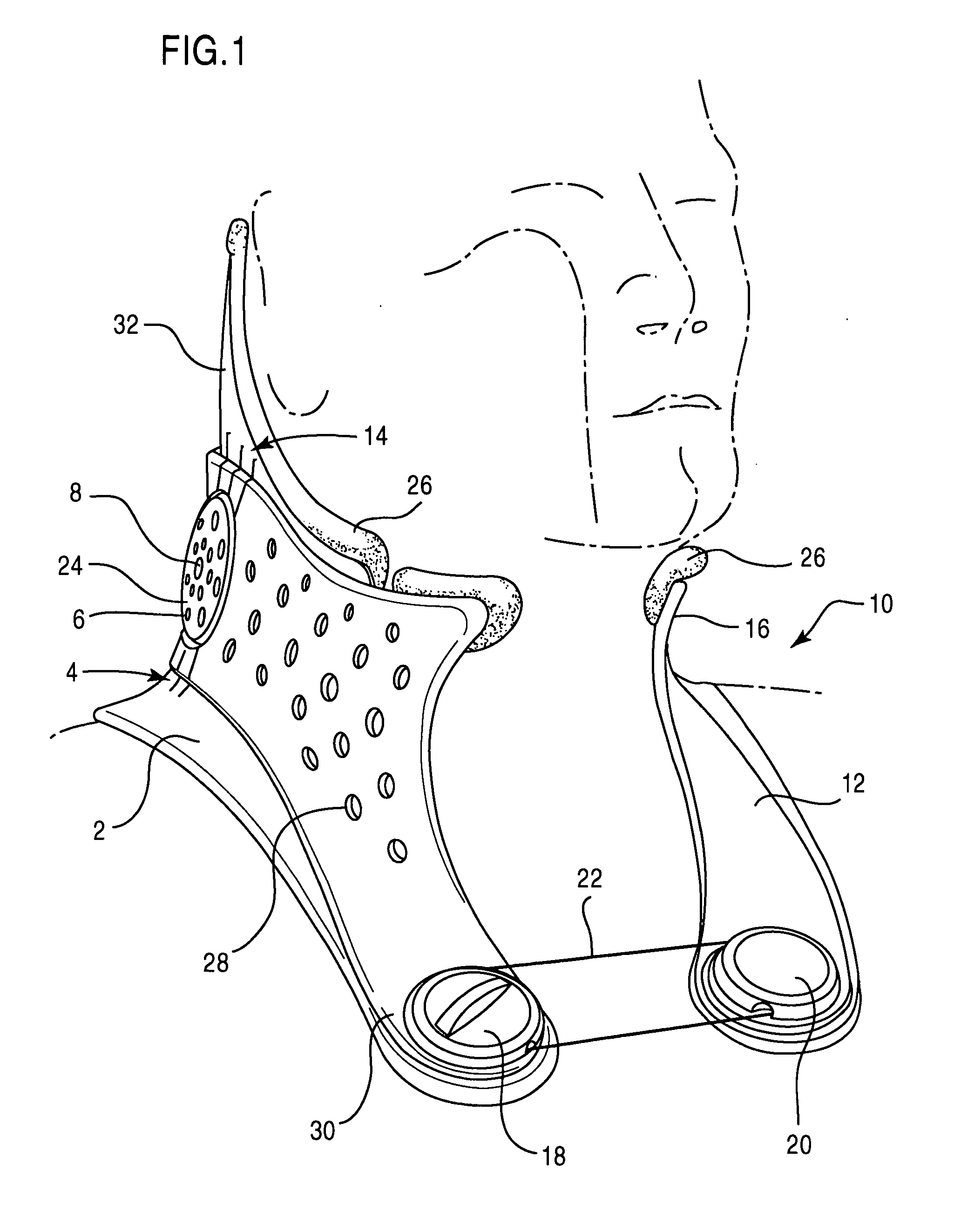
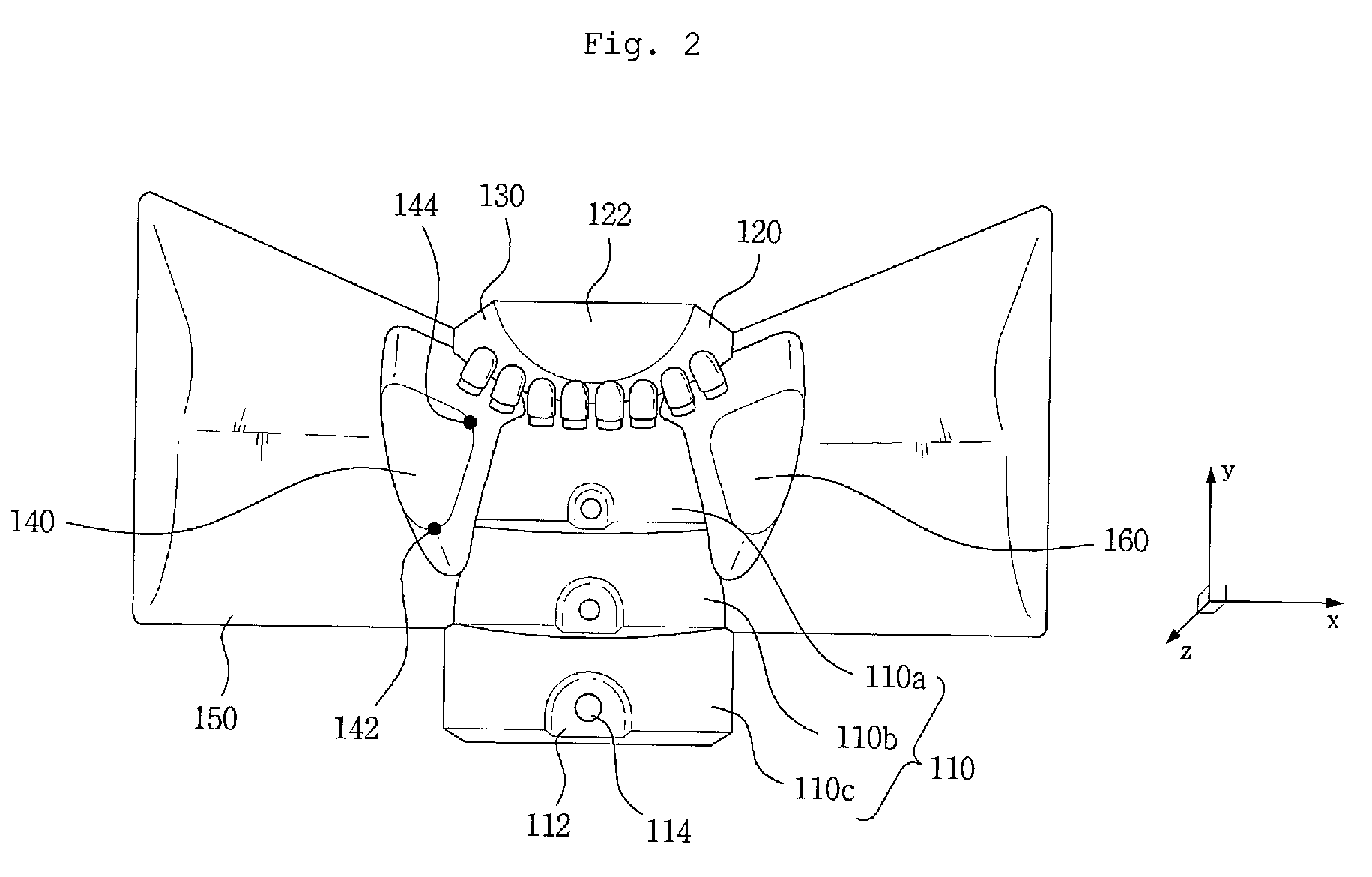
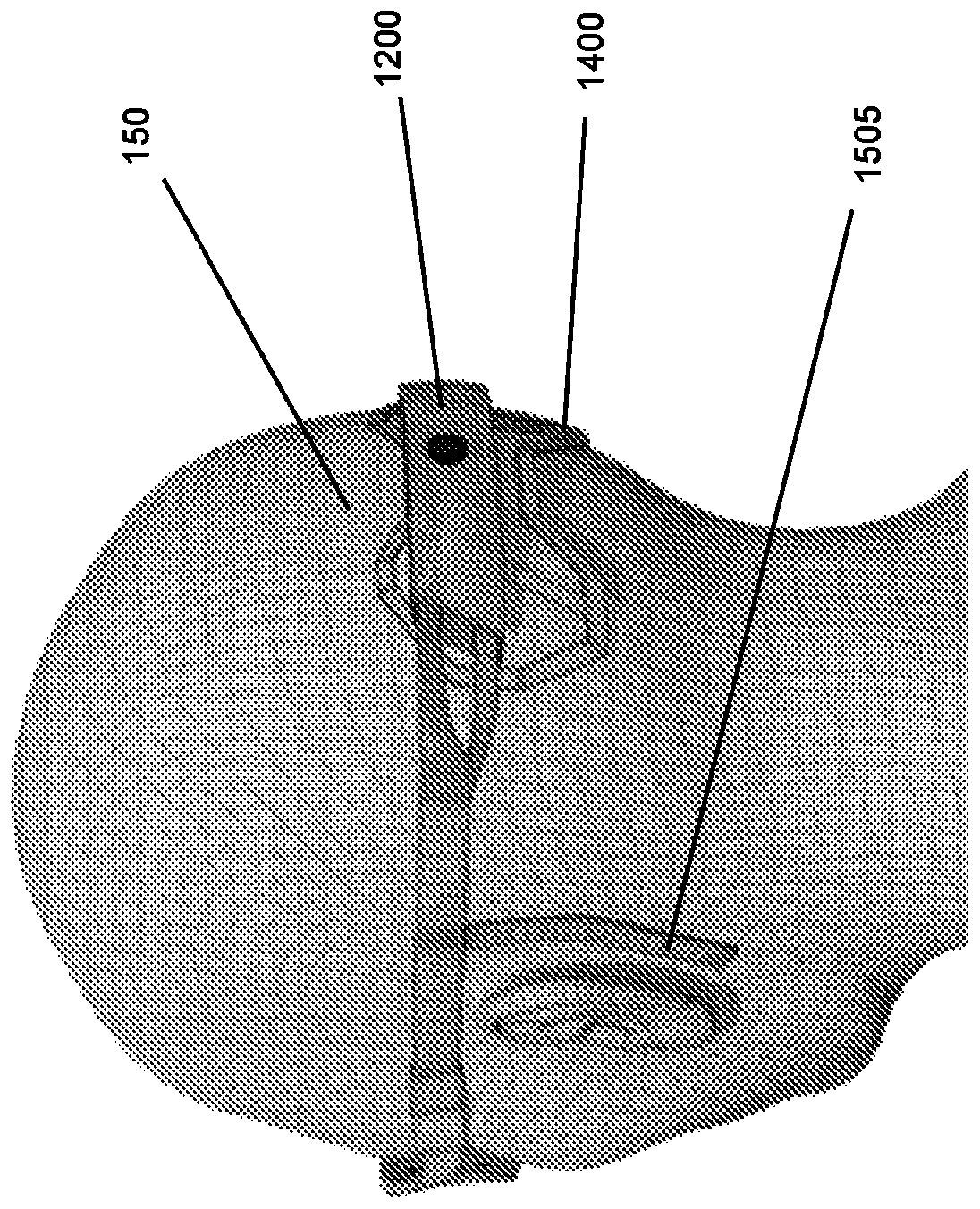
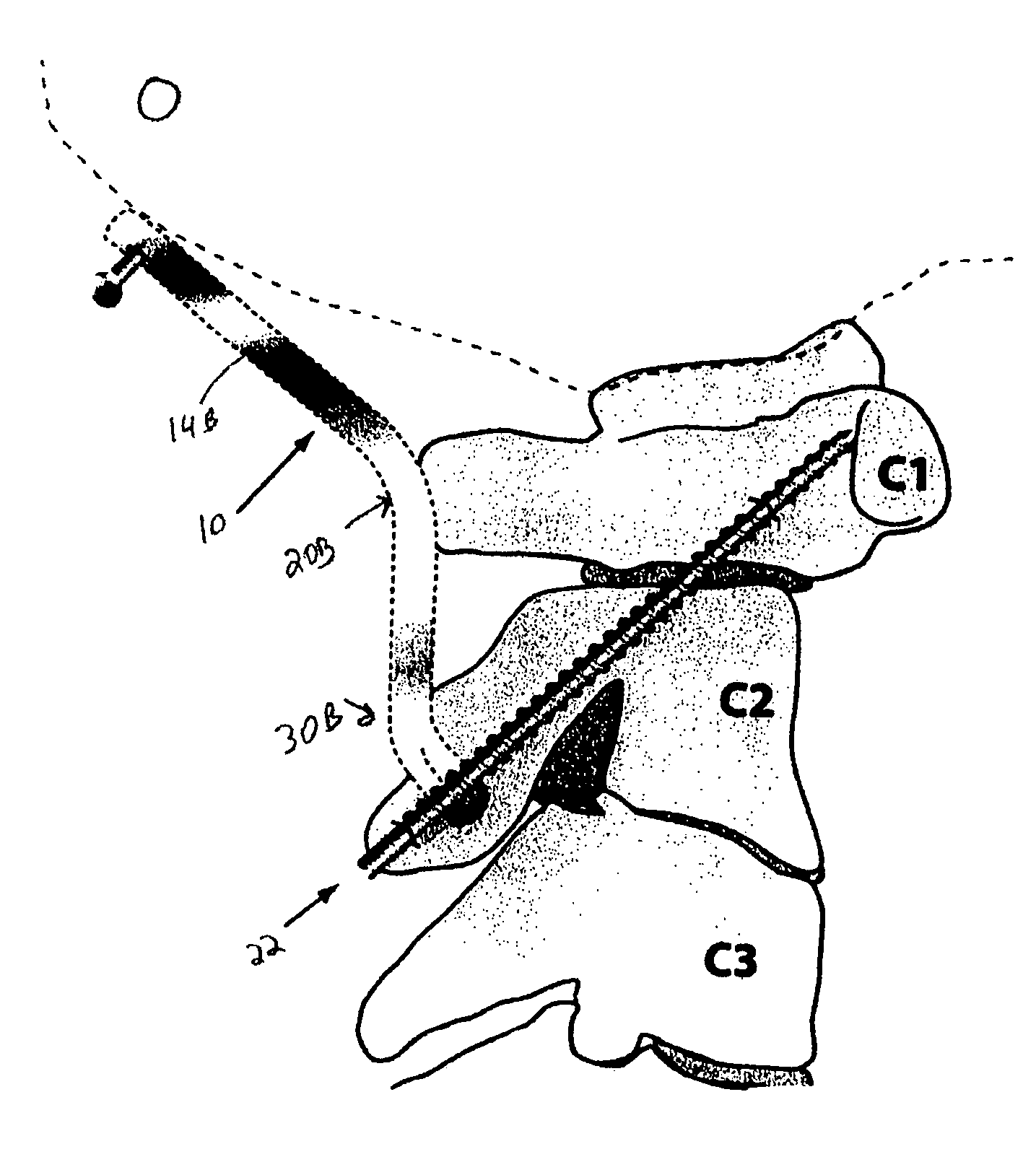
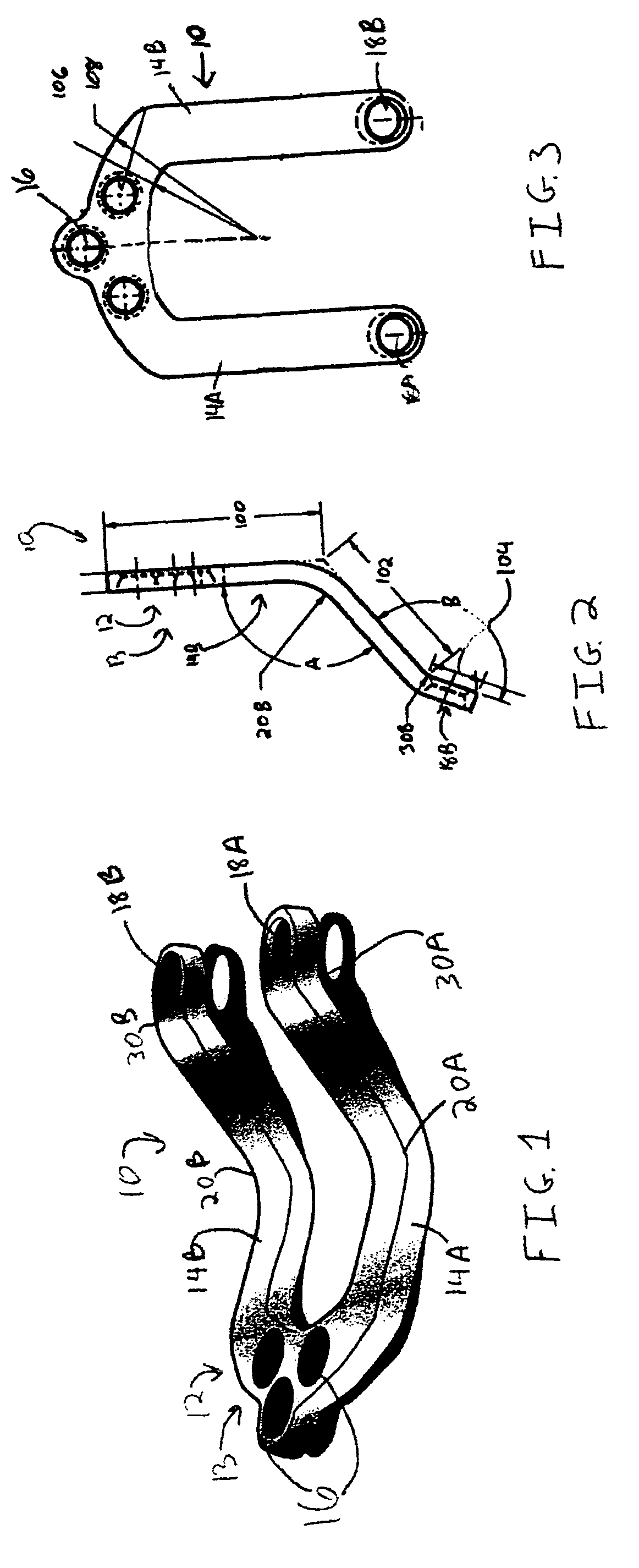
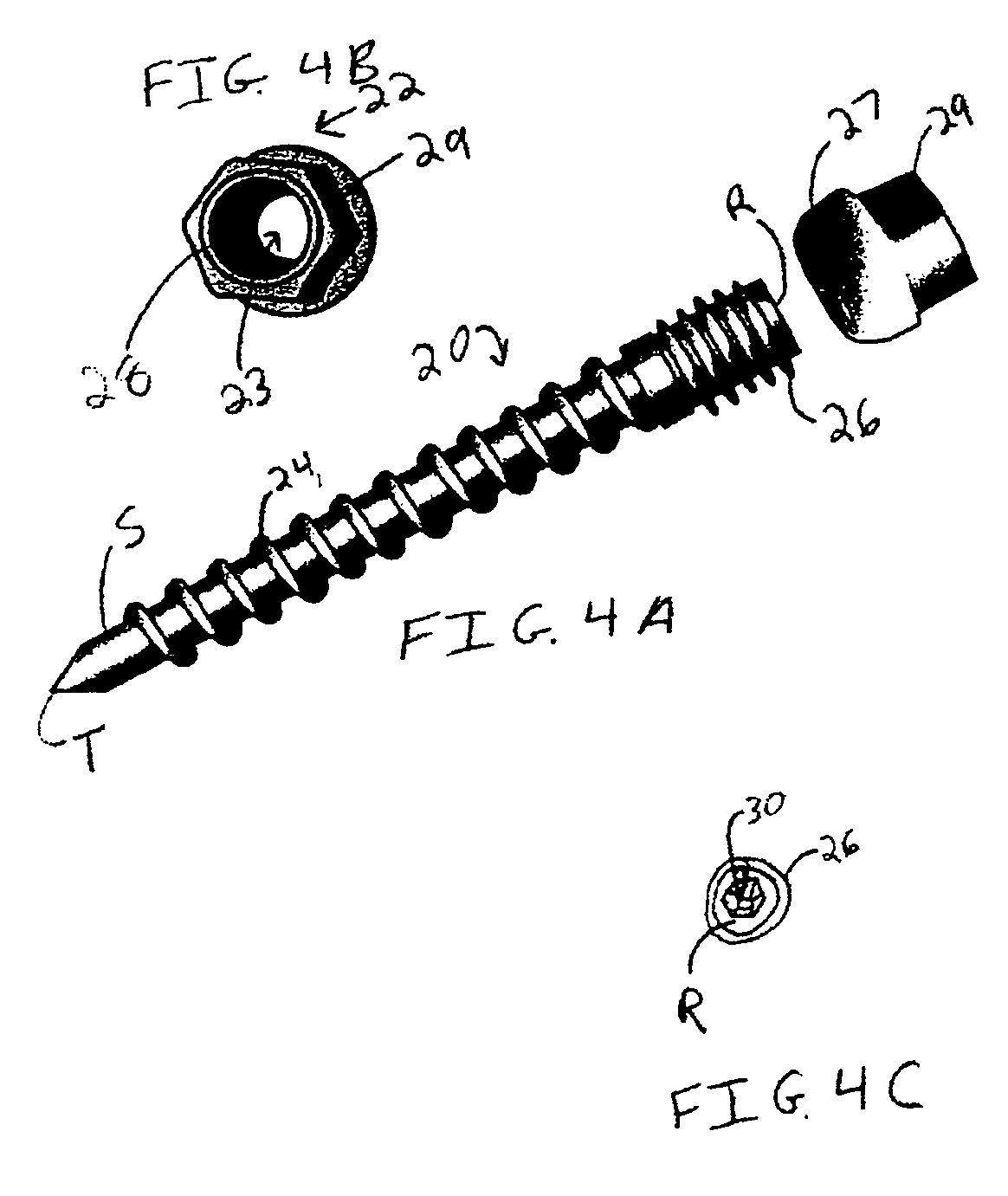
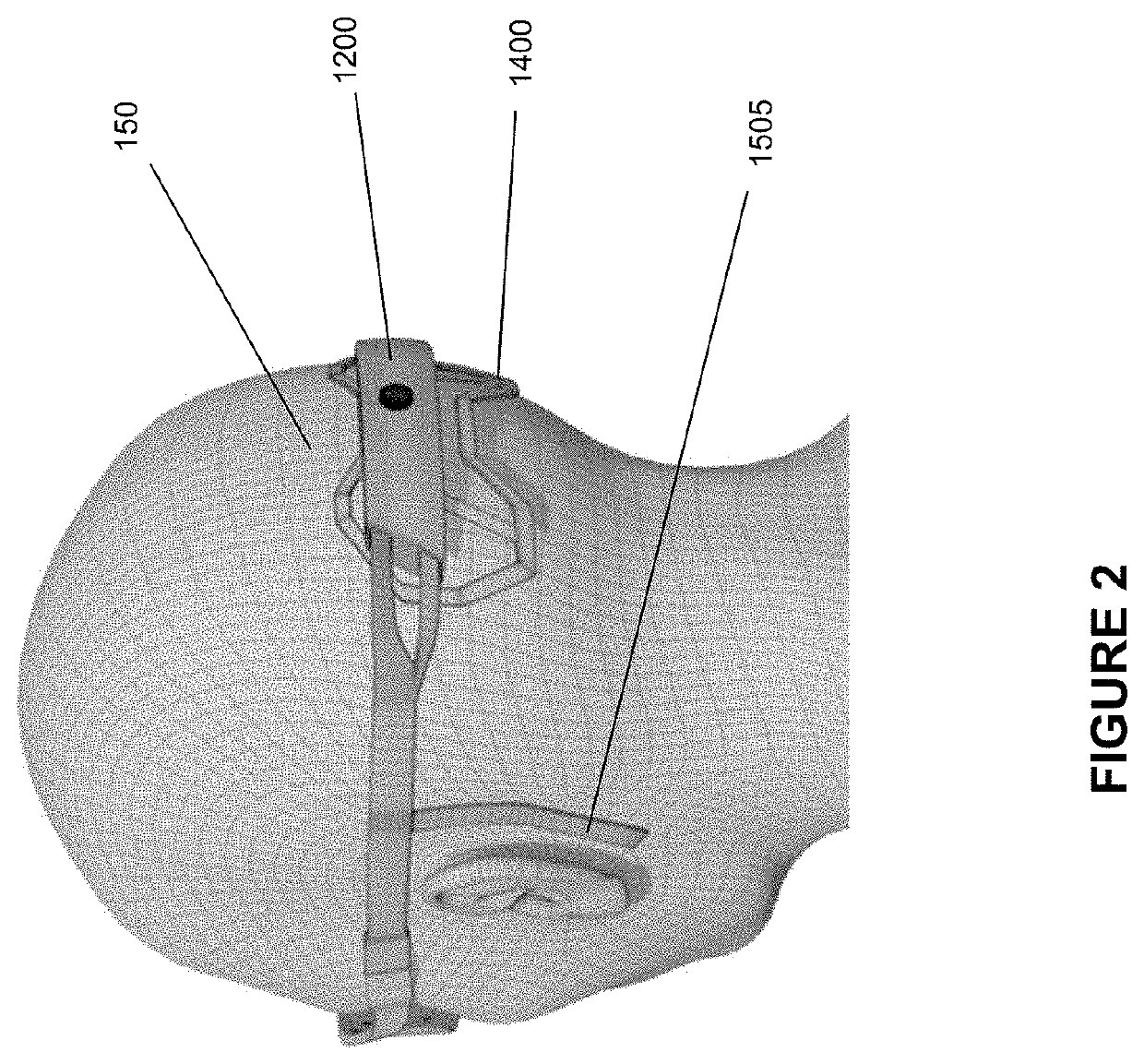
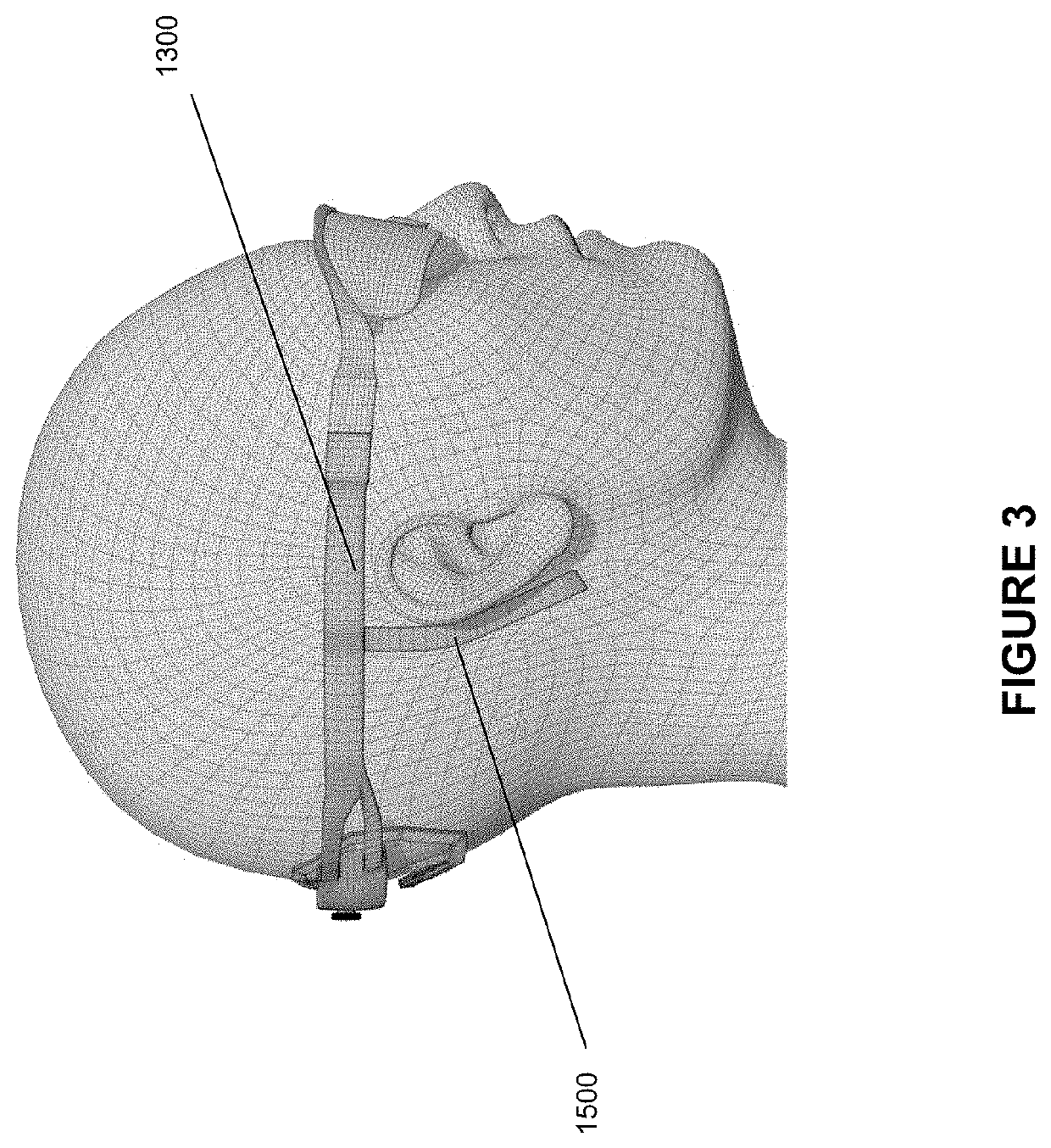
Methods and systems for occipital-cervical spinal fixation. A plate configured for attachment to the occipital bone has two arms extending out from either side, which turn downwards parallel to one another. A first bend is disposed in the arms, such that the arms extend down from the occipital bone behind the spinous process of the C1 and C2 vertebrae, upon installation. A second bend in the arms allows attachment to the C2 vertebra. The system may be dimensioned for pediatric installation. A bone graft material may be held in place between the cervical vertebrae and the skull by installing a cable to the installed system to retain the bone graft material in place. Methods and kits for occipital-cervical spinal fixation are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
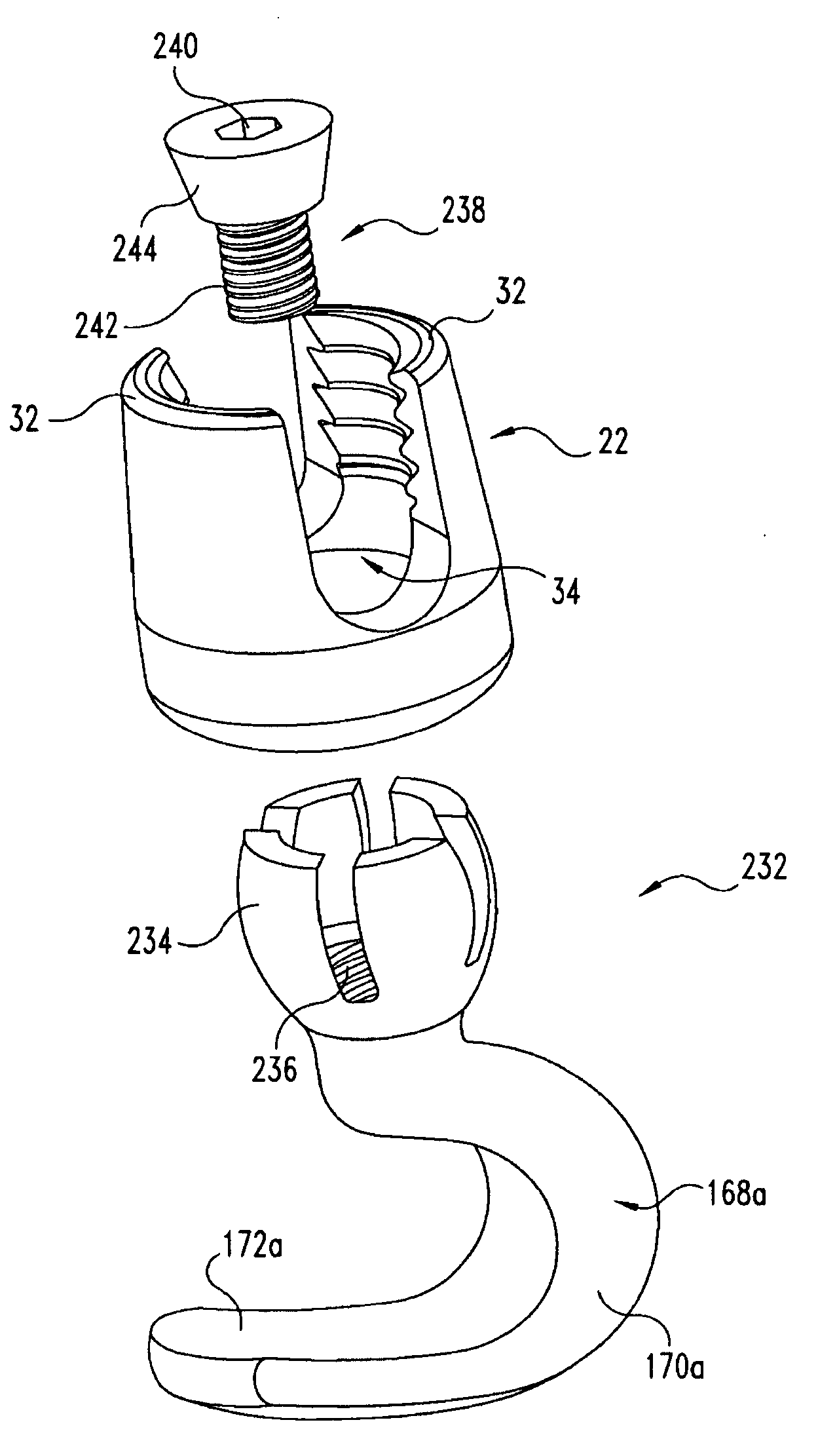
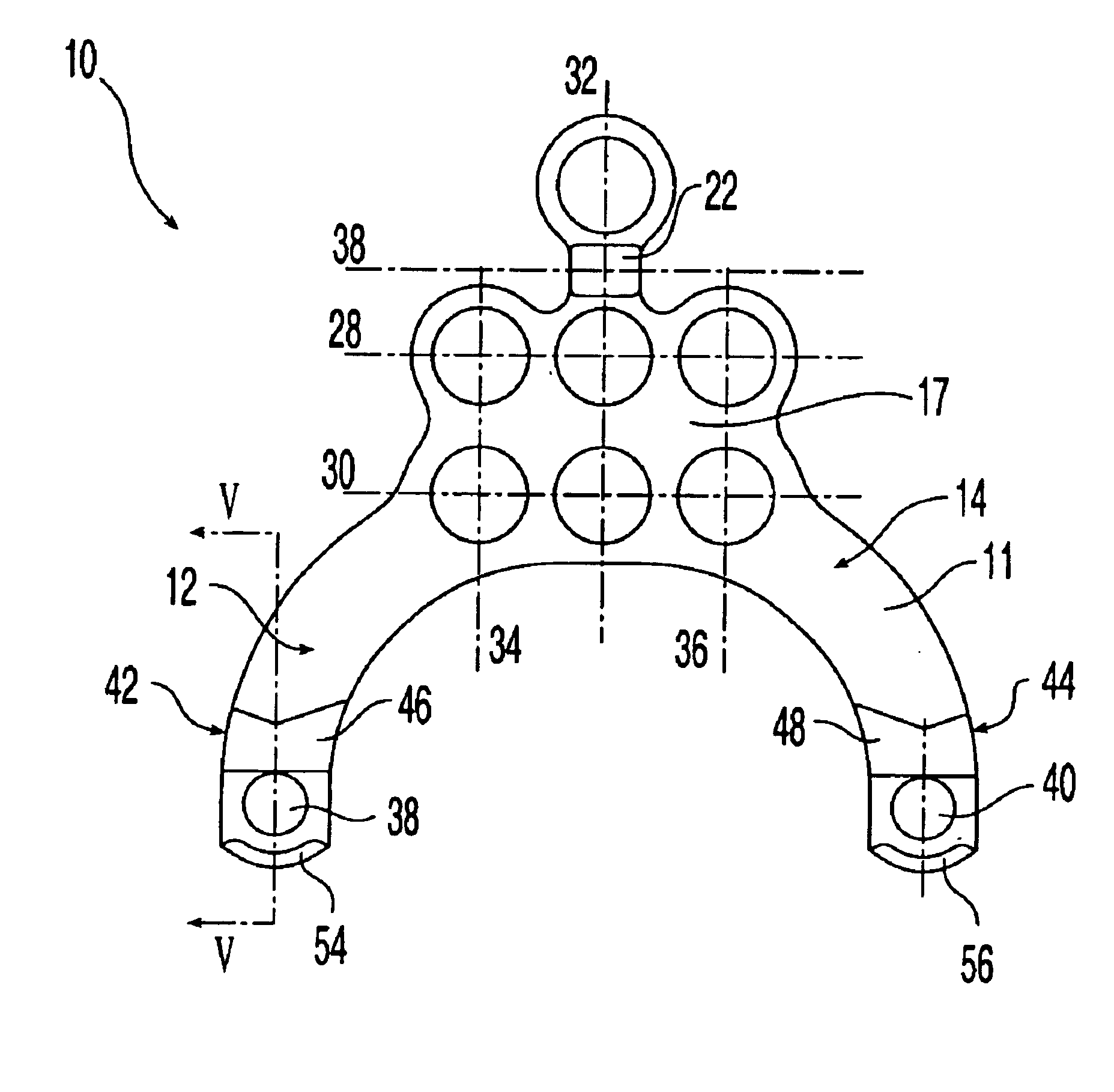
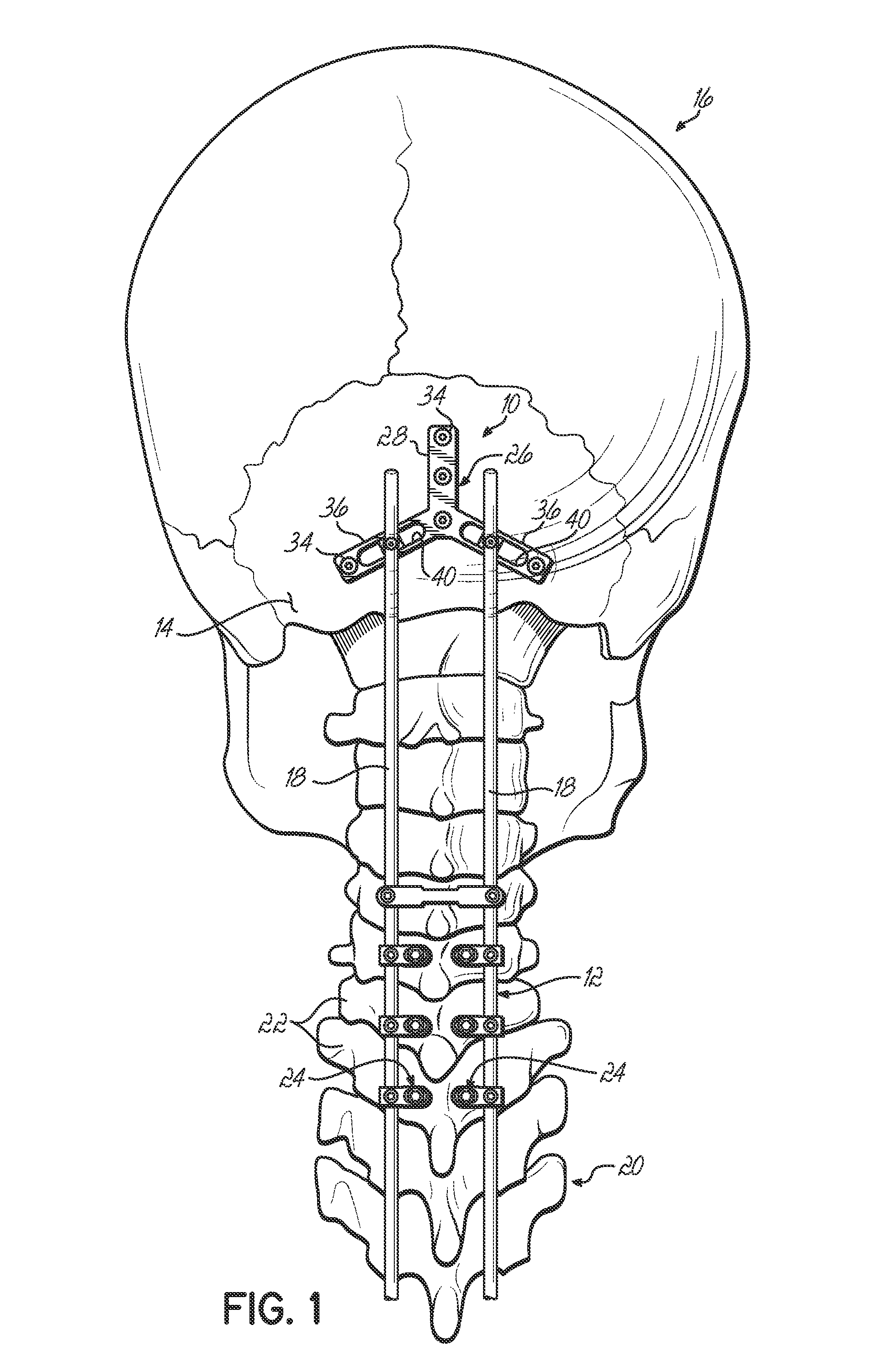
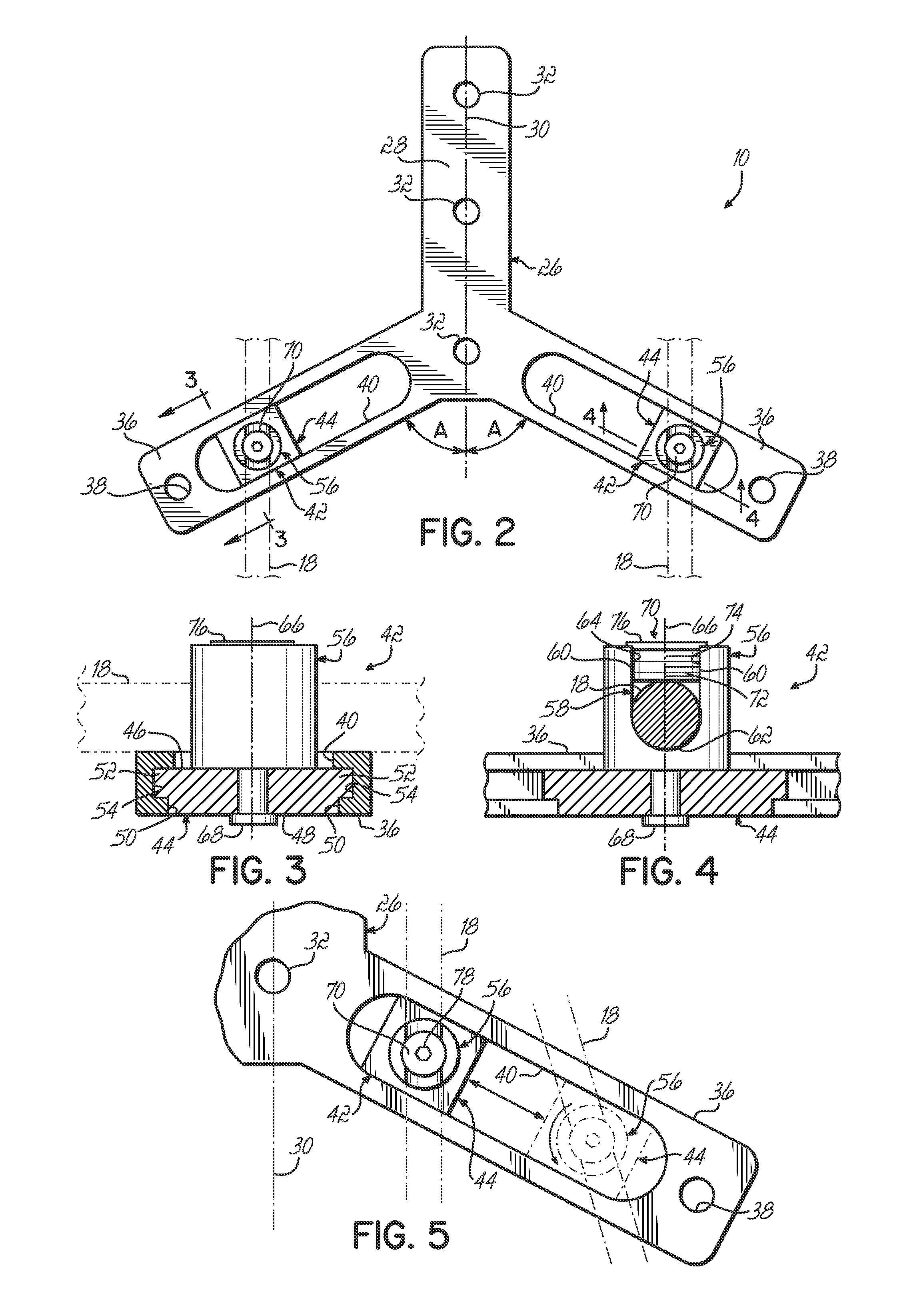
Posterior Fixation System
A posterior fixation system includes a saddle member, an anchoring member, an occipital plate, an occipital rod, and a cross-link connector. The anchoring member anchors the saddle member to bone. The saddle member includes a pair of upright portions that define a channel. The channel is adapted to receive an orthopedic rod, and the saddle member can include a hole to receive the anchoring member. The saddle member and the anchoring member can be coupled so as to allow multi-axial movement of the members. The anchoring member in one embodiment is a screw coupled to the hole of the saddle, and in another embodiment, the anchoring member is a hook. The offset member may be coupled to the saddle member to allow for offset connection of rods. Connection of individual rods can be accomplished by connecting the rods with the cross-link connector. The cross-link connector has an integrally formed cylindrical member that couples a pair of coupling portions together. The cylindrical member can be bent along multiple axes. The occipital plate secures the rods to the occipital bone of the skull. The occipital plate has a cross-shaped plate with a plurality of apertures defined in the plate and at least one saddle member coupled to the plate. Alternatively, the occipital rod can be secured to the occipital bone.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
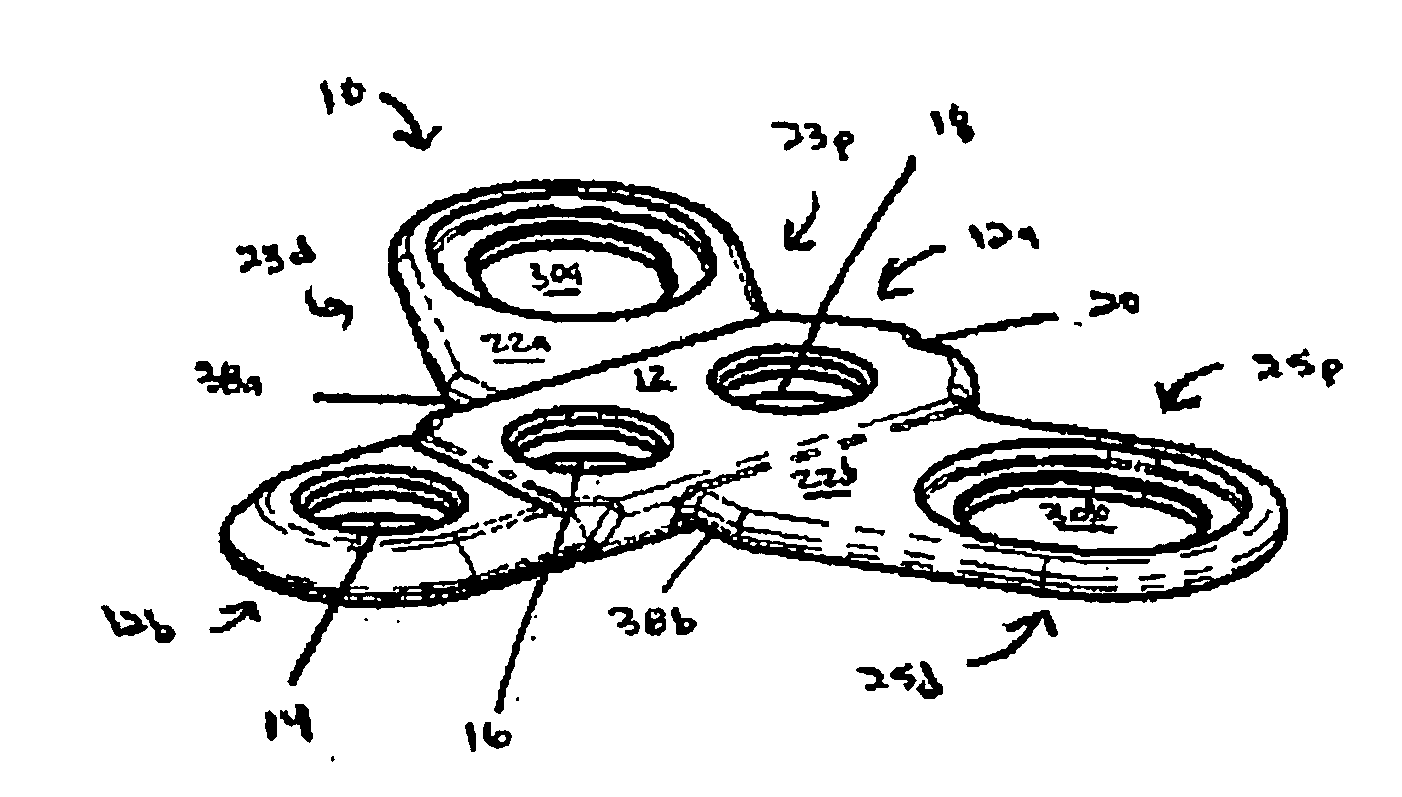
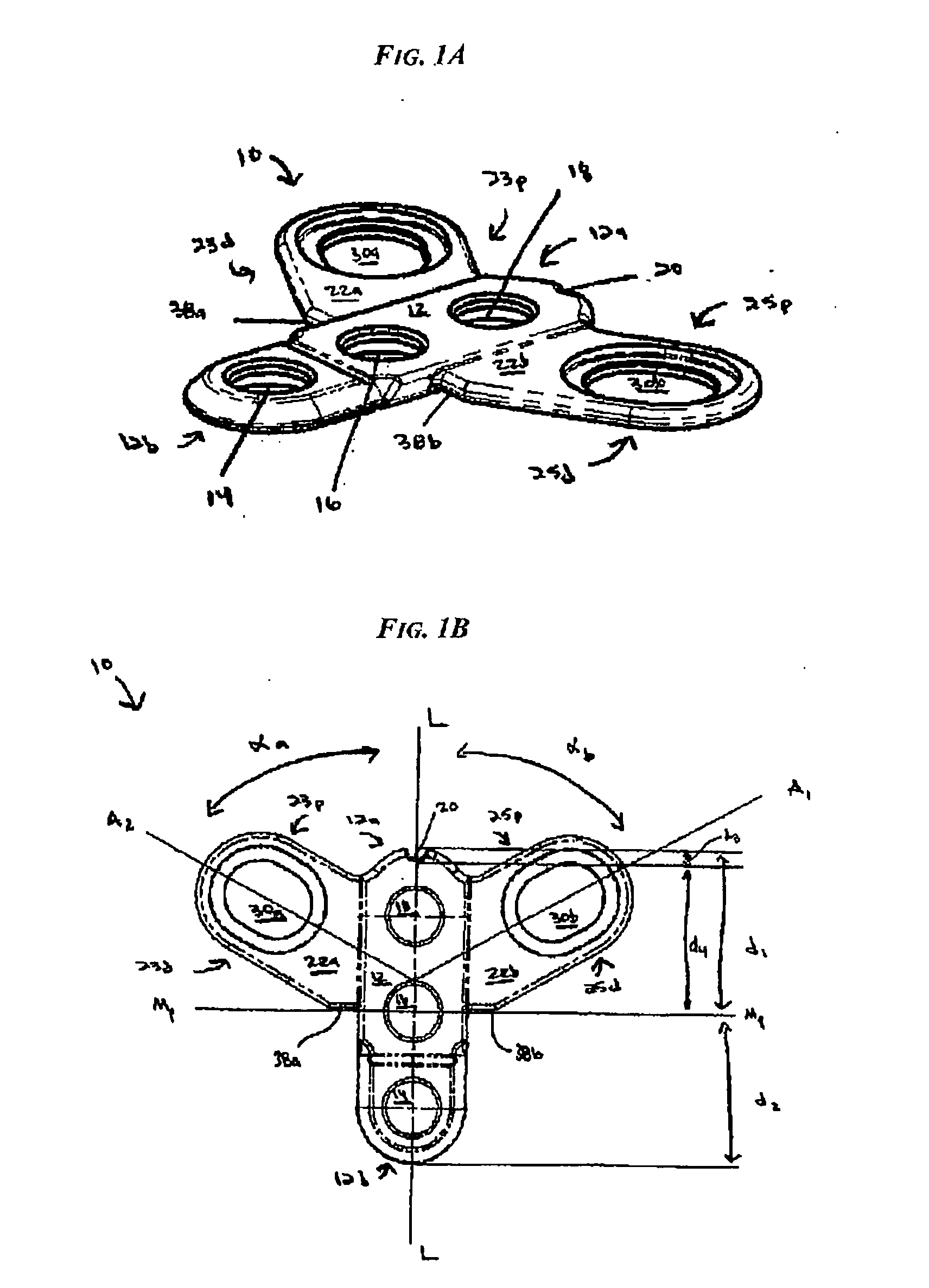
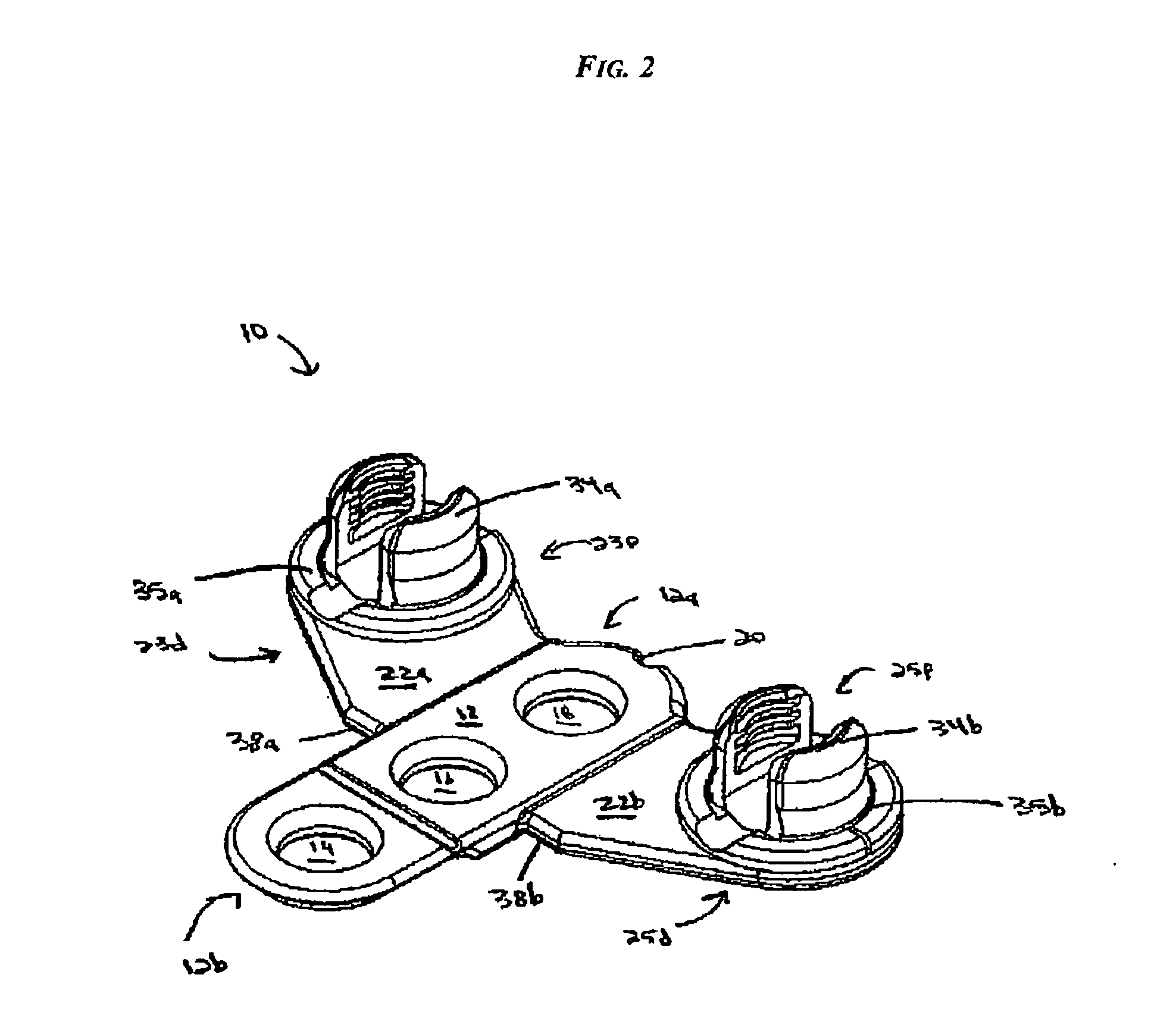
Occipital plate and system for spinal stabilization
An occipitocervical fixation system includes a plate for securing to the occiput and at least one pre-bent rod. The plate includes holes for receiving bone fasteners, and at least one clamping assembly for retaining a portion of a rod. The clamping assembly is selectively pivotable and lockable in place to fix the position of the rod.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
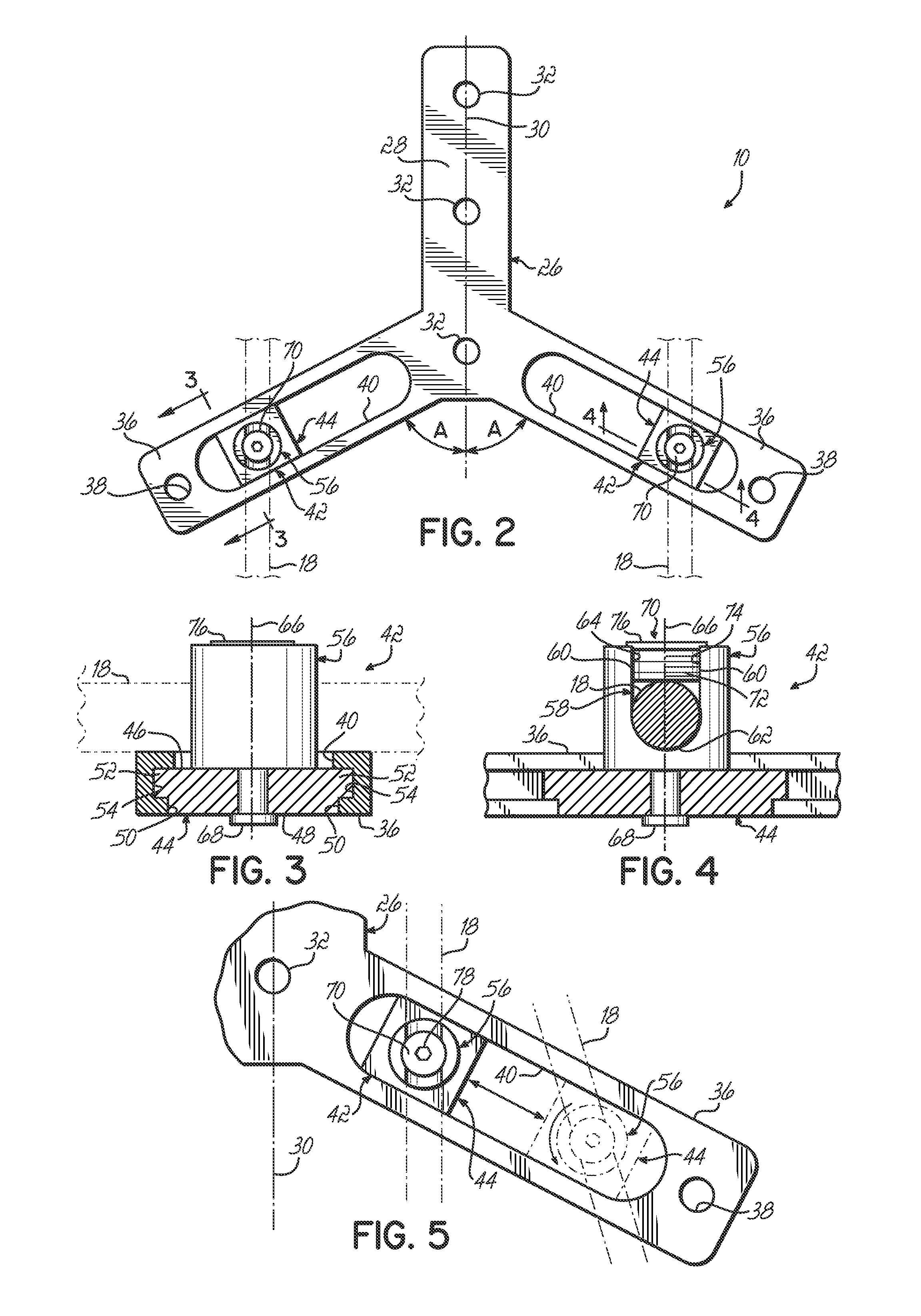
Occipital plate and guide systems
InactiveUS20060155284A1Facilitate matingInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsOccipital lobeBiomedical engineering
Owner:DEPUY SPINE SARL
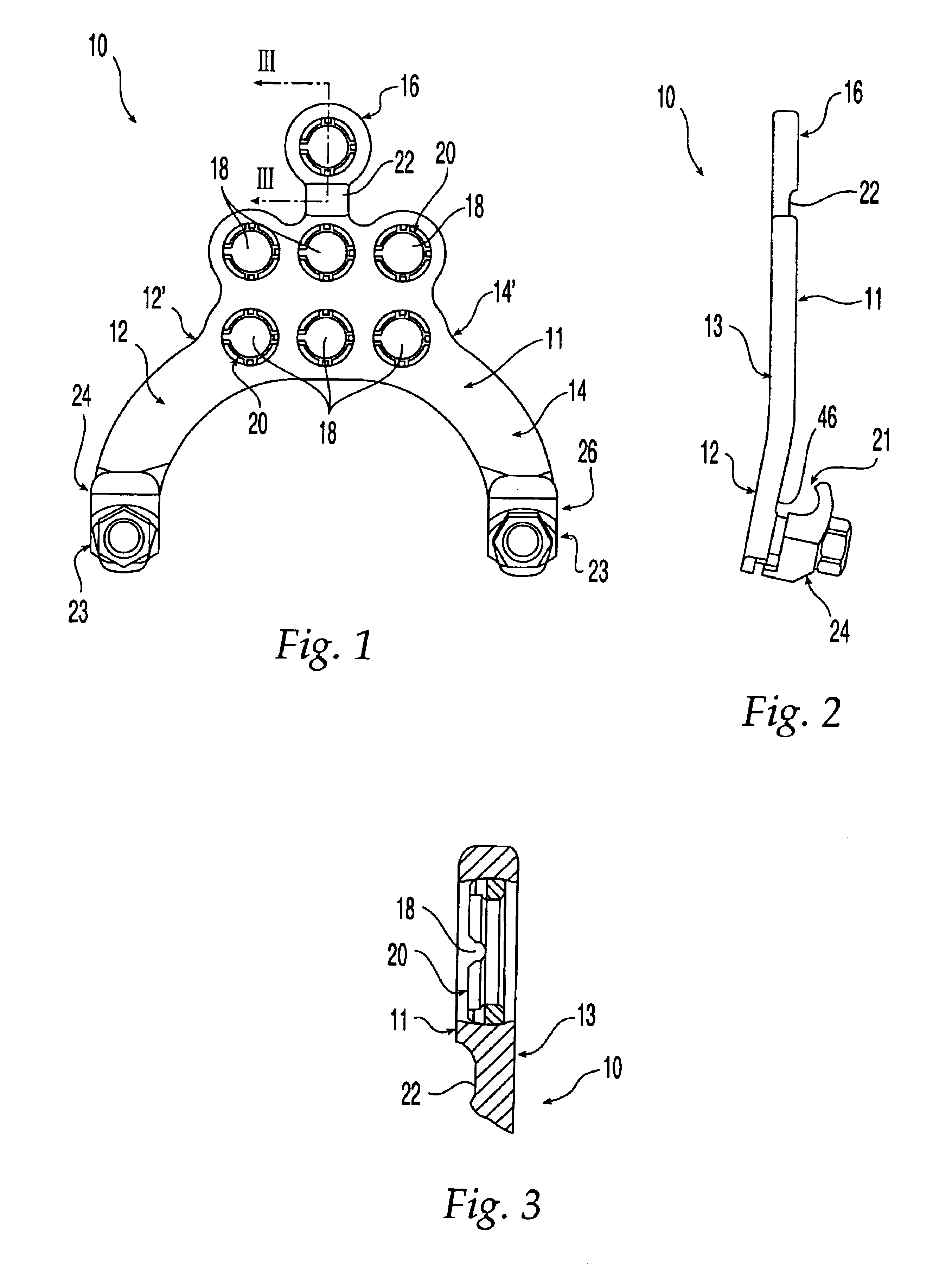
Adjustable occipital plate
ActiveUS20080125781A1Efficient and secure multi-adjustabilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEngineeringOccipital bone
An occipital plate for use in an occipito-cervico-thoracic (OCT) construct is mounted to a patient's occipital bone. The occipital plate includes an elongate central section aligned with a midline of the base and a pair of angled sections that project away from the central section and include attachment assemblies for securing a rod to the occipital plate. The attachment assemblies have multi-adjustability features. At least a portion of the attachment assemblies is rotatable with respect to the base so that the rods may be coupled to the occipital plate at a variety of angles with respect to the midline. The angular adjustability may accommodate any misalignments in the rods. Additionally, the position of the attachment assemblies relative to the midline of the occipital plate is adjustable to thereby provide for medial-lateral adjustability when attaching the rods to the occipital plate as part of the OCT construct.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
Posterior fixation system
A posterior fixation system includes a saddle member, an anchoring member, an occipital plate, an occipital rod, and a cross-link connector. The anchoring member anchors the saddle member to bone. The saddle member includes a pair of upright portions that define a channel. The channel is adapted to receive an orthopedic rod, and the saddle member can include a hole to receive the anchoring member. The saddle member and the anchoring member can be coupled so as to allow multi-axial movement of the members. The anchoring member in one embodiment is a screw coupled to the hole of the saddle, and in another embodiment, the anchoring member is a hook. The offset member may be coupled to the saddle member to allow for offset connection of rods. Connection of individual rods can be accomplished by connecting the rods with the cross-link connector. The cross-link connector has an integrally formed cylindrical member that couples a pair of coupling portions together. The cylindrical member can be bent along multiple axes. The occipital plate secures the rods to the occipital bone of the skull. The occipital plate has a cross-shaped plate with a plurality of apertures defined in the plate and at least one saddle member coupled to the plate. Alternatively, the occipital rod can be secured to the occipital bone.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Occipital Plate for Spinal Fusion
ActiveUS20110190824A1Easy to catchPrevent slidingInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsMultiple pointEngineering
Plate devices are provided for mounting to bone and receiving one or more spinal rods. The devices may include coupling members or rod receiving members coupled to the plate member and configured to have multiple degrees of adjustability in order to accommodate elongate connecting members of various orientations. The plate devices may also include quick locking features or locking devices that secure multiple points of articulation simultaneously.
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
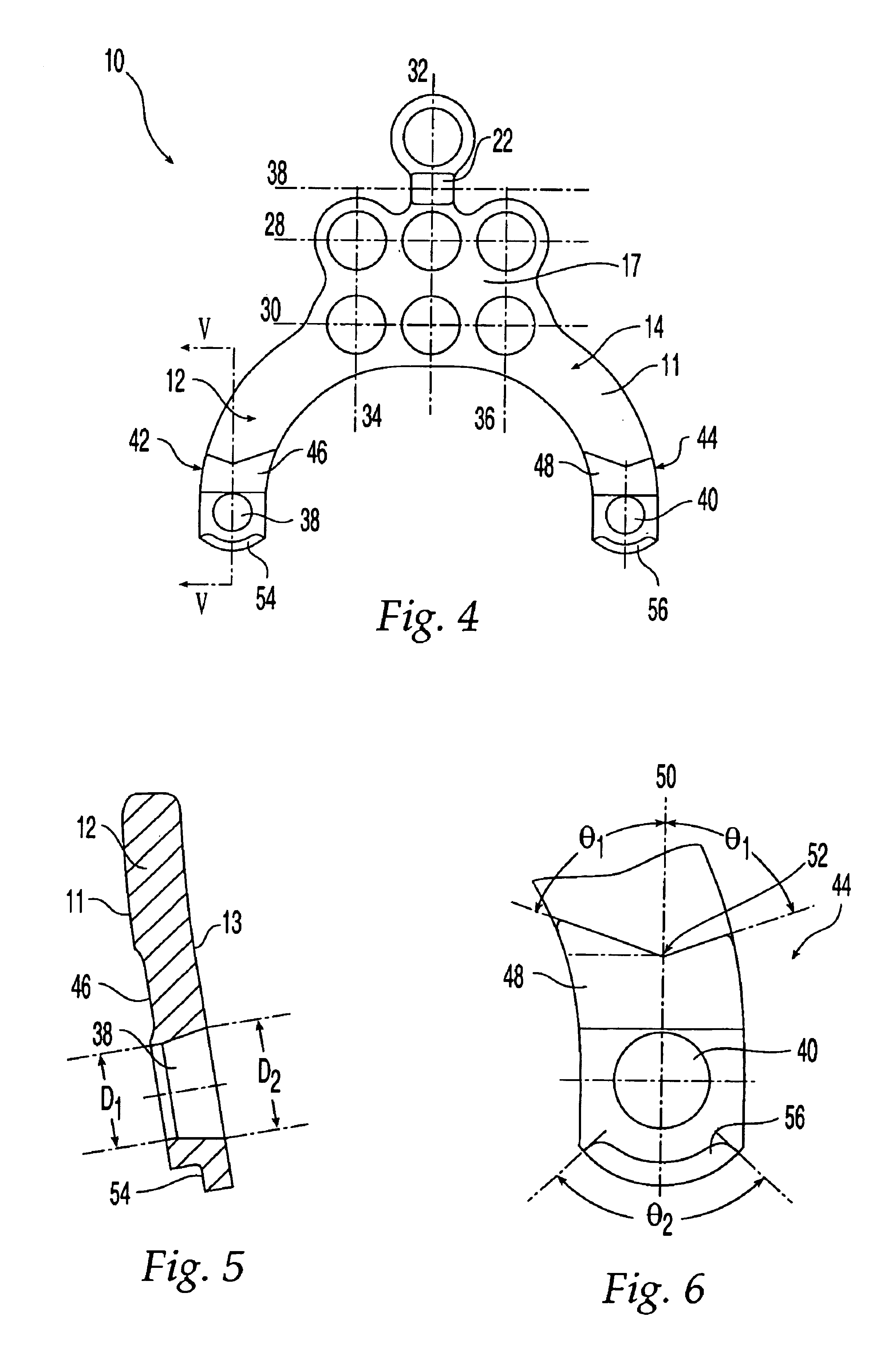
Adjustable Occipital Plate
InactiveUS20070299441A1Adjustability is providedEfficient and secure adjustabilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSet screwEngineering
An occipital plate for use in an occipito-cervico-thoracic (OCT) construct is mounted to a patient's occipital bone. The occipital plate includes an elongate base plate oriented with a midline of the base plate longitudinal on the occipital bone. A pair of lateral sections project in opposite directions from the central section and include attachment assemblies for securing a rod to the occipital plate. The position of the attachment assembly relative to the midline of the occipital plate is adjustable to thereby provide for medial-lateral adjustability. In specific embodiments, the attachment assemblies include a slide member which mates with the lateral section of the occipital plate in a dove-tail joint configuration and a set screw is threadably engaged with the slide member to secure the slide member relative to the midline of the occipital plate and the appropriate spacing and geometry for the specific patient. The set screw also secures a cam, which fixes the rod to the occipital plate.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Cervical support system
InactiveUS7371222B2Promote healingThe process is convenient and fastSurgeryFractureSupporting systemMedicine
A cervical support system for restricting head and neck movement of a patient recovering from an injury to or surgery on the spine. The support system includes a supporting member for mounting onto and around the head and neck of the patient. The supporting member includes an injection molded base portion integral with an occipital lobe supporting portion. The base portion is arranged to rest on the shoulder of the patient while the occipital lobe supporting portion is arranged to extend along the neck from the shoulder to the head of the patient. An arcuate member such as a C-collar is disposed on an outer surface of the supporting member. A plurality of adjustment devices such as a turn-tab adjustment mechanism on an outer surface of the arcuate member rotatably connect the arcuate member to the supporting member to position the arcuate member onto, and with respect to, the supporting member.
Owner:BIO CYBERNETICS INT INC
Cervical support system
A cervical support system for restricting head and neck movement of a patient recovering from an injury to or surgery on the spine. The support system includes a supporting member for mounting onto and around the head and neck of the patient. The supporting member includes an injection molded base portion integral with an occipital lobe supporting portion. The base portion is arranged to rest on the shoulder of the patient while the occipital lobe supporting portion is arranged to extend along the neck from the shoulder to the head of the patient. An arcuate member such as a C-collar is disposed on an outer surface of the supporting member. A plurality of adjustment devices such as a turn-tab adjustment mechanism on an outer surface of the arcuate member rotatably connect the arcuate member to the supporting member to position the arcuate member onto, and with respect to, the supporting member.
Owner:BIO CYBERNETICS INT INC
Calling device based on brain electric information demodulation
InactiveCN101159086AAvoid harmShort preparation timeAlarmsIdentification meansEngineeringVisual perception
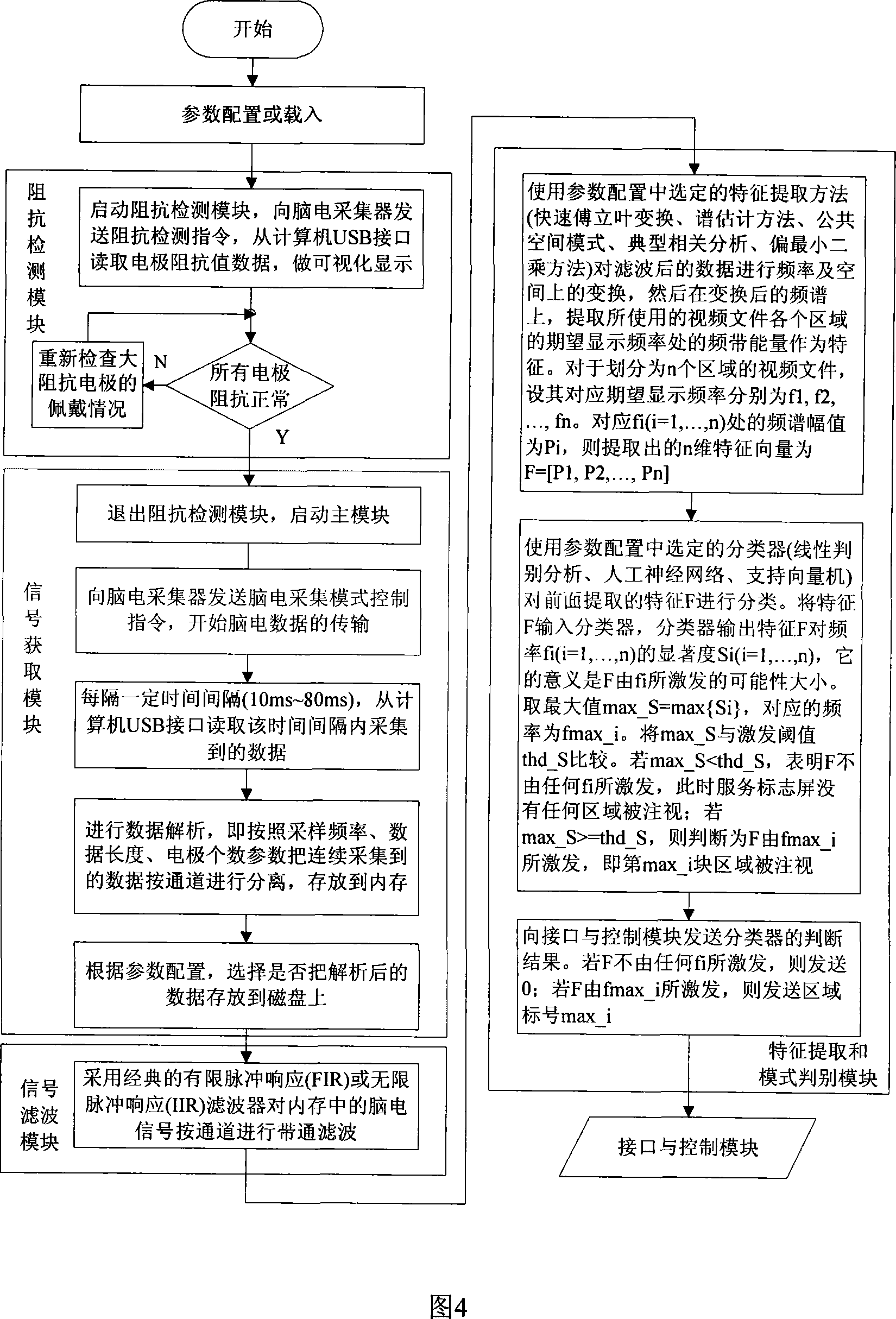
The invention discloses a calling device based on electrical brain information demodulation, which is to provide the calling device based on stable state visual induction electric potential demodulation for a ward calling system to substitute for a keypad type calling machine. The calling device consists of a service sign screen, an electrical brain collector, an electrical brain amplifier, an A / D converter and a calling extension machine; wherein the service sign screen is a LED display screen. The electric brain collector consists of 3-5 active electrodes, is fixed on the scalp on the position of occipital lobe of hind brain of a patient and is connected with the electric brain amplifier. Multi-lead electric brain signals are amplified by the electric brain amplifier and are transmitted to the A / D converter. The A / D converter transforms simulation signals into digital signals and transmits the digital signals to the calling extension machine. LED display control software and electric brain processing and analyzing software are arranged on the calling extension machine. The LED display control software controls the display of the service sign screen. The electric brain processing and analyzing software processes and analyzes the electric brain data in real time and transmits calling information to a host machine. The invention can substitute non-contact and non-action type fixation operation for keypad type operation.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Occipital plate systems
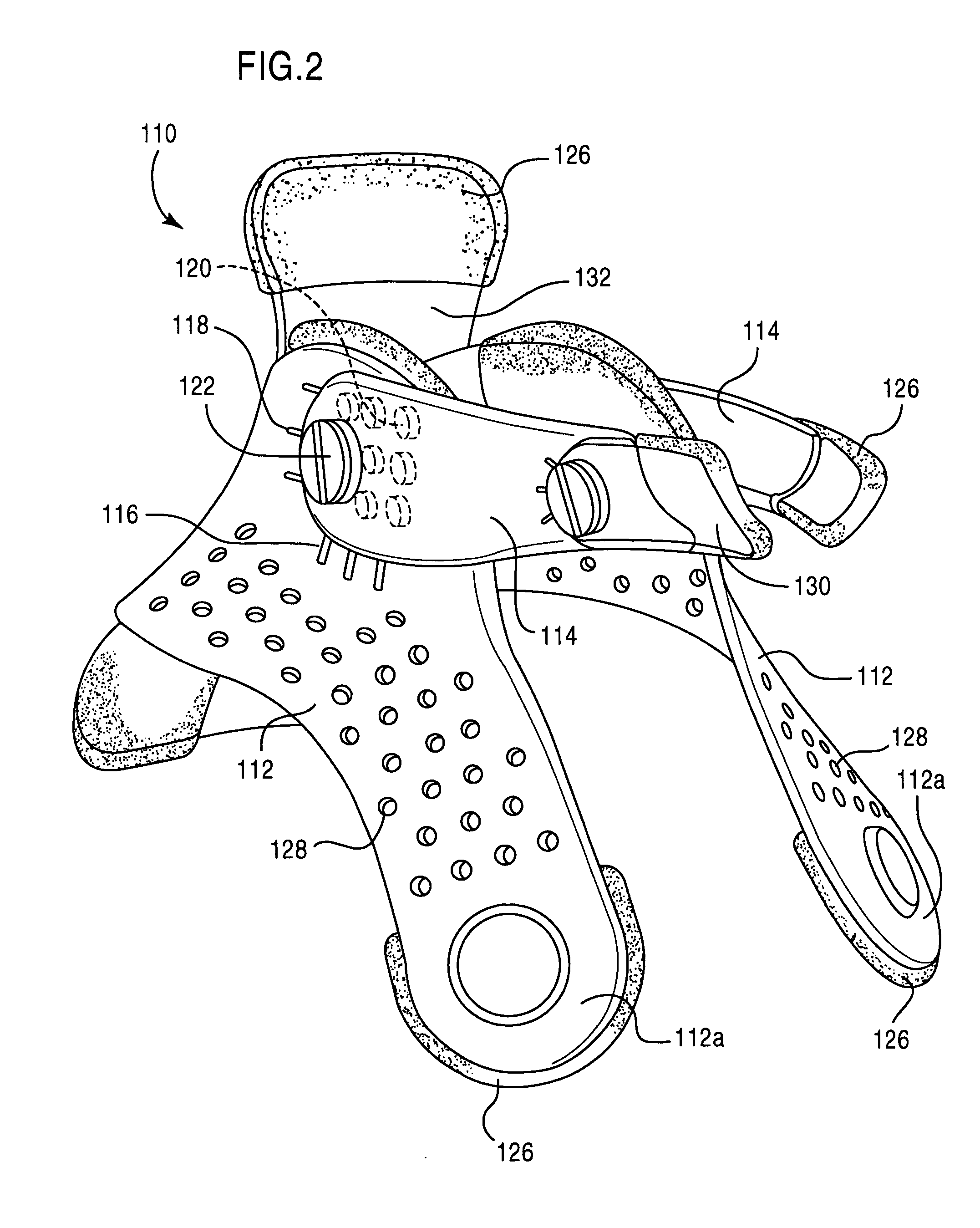
Occipital plate systems are described. The occipital plate systems can include a novel occipital plate having an upper portion and lower portion. The lower portion can include an opening for receiving one or more lateral members therethrough. The lateral members include top and / or side apertures for receiving lateral connectors that are attached to polyaxial screw receiving members. The occipital plate systems can also include low-profile clamping arms that are operably attached to an occipital plate via an extension member and articulating joint member. The clamping arms, along with tension cables attached intermittently along its length, can be used in addition to or instead of screws and hooks to secure an occipital plate system to vertebrae.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
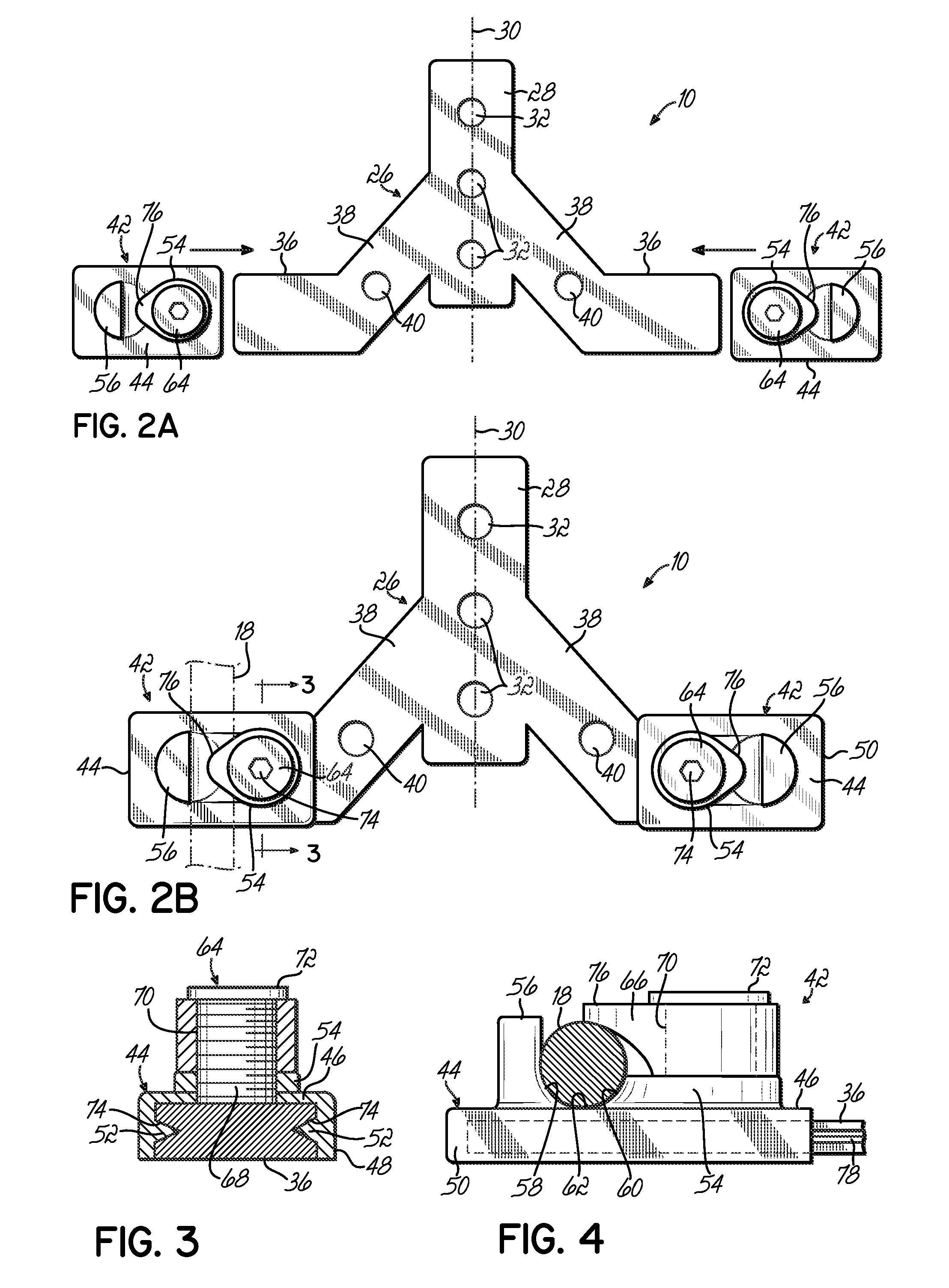
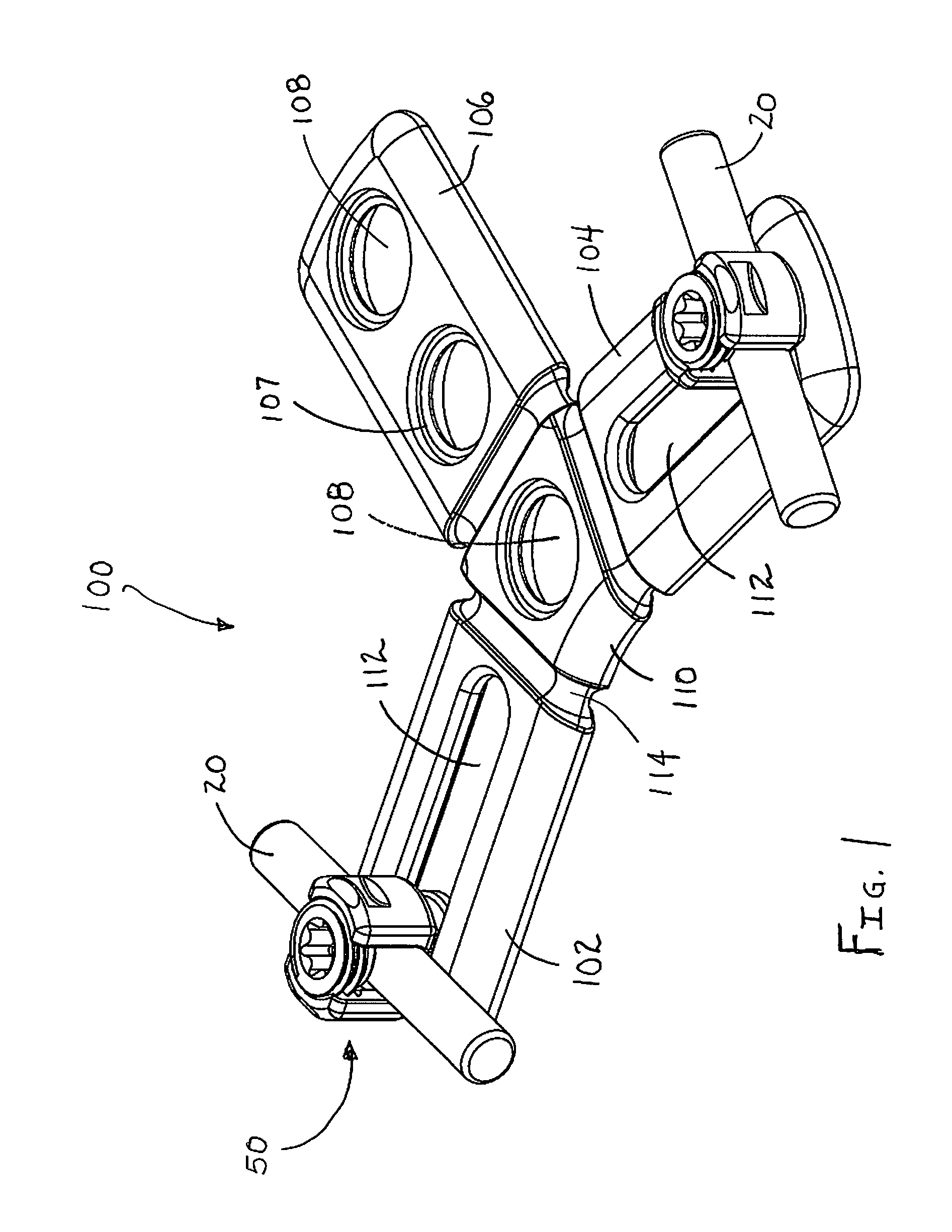
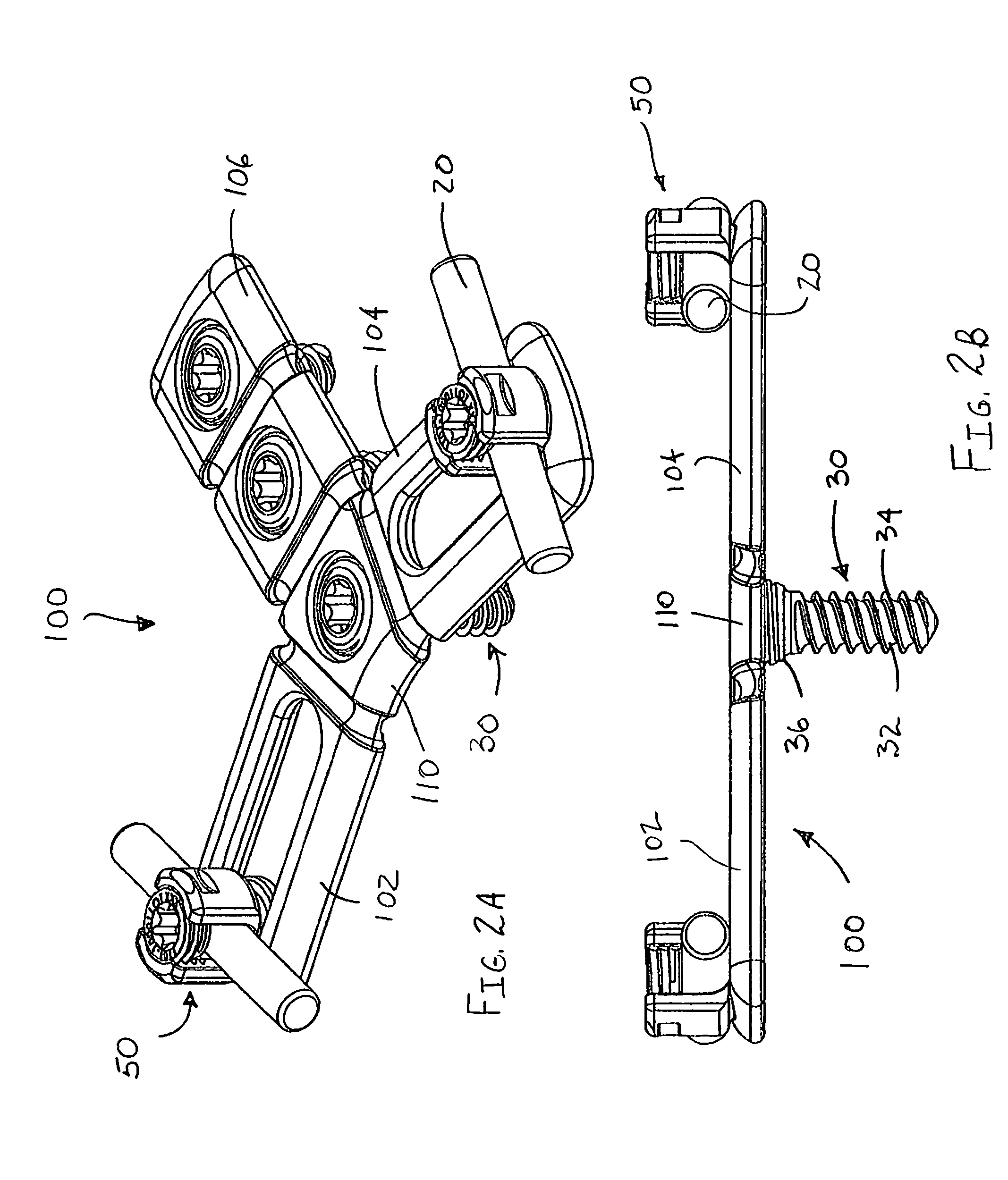
Occipital plate for cervical fixation
An adjustable occipital plate includes a central body portion having a plurality of arms extending therefrom in a generally Y-shaped configuration. Two of the arms include elongate slots for slidably receiving retaining members therein. Each retaining member includes a U-shaped channel for receiving a spine rod and a set screw. The central body portion and one arm include openings for receiving bone screws therein. Each of the arms may be angled with respect to the central body portion.
Owner:K2M
Adjustable occipital plate
An occipital plate for use in an occipito-cervico-thoracic (OCT) construct is mounted to a patient's occipital bone. The occipital plate includes an elongate central section aligned with a midline of the base and a pair of angled sections that project away from the central section and include attachment assemblies for securing a rod to the occipital plate. The attachment assemblies have multi-adjustability features. At least a portion of the attachment assemblies is rotatable with respect to the base so that the rods may be coupled to the occipital plate at a variety of angles with respect to the midline. The angular adjustability may accommodate any misalignments in the rods. Additionally, the position of the attachment assemblies relative to the midline of the occipital plate is adjustable to thereby provide for medial-lateral adjustability when attaching the rods to the occipital plate as part of the OCT construct.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
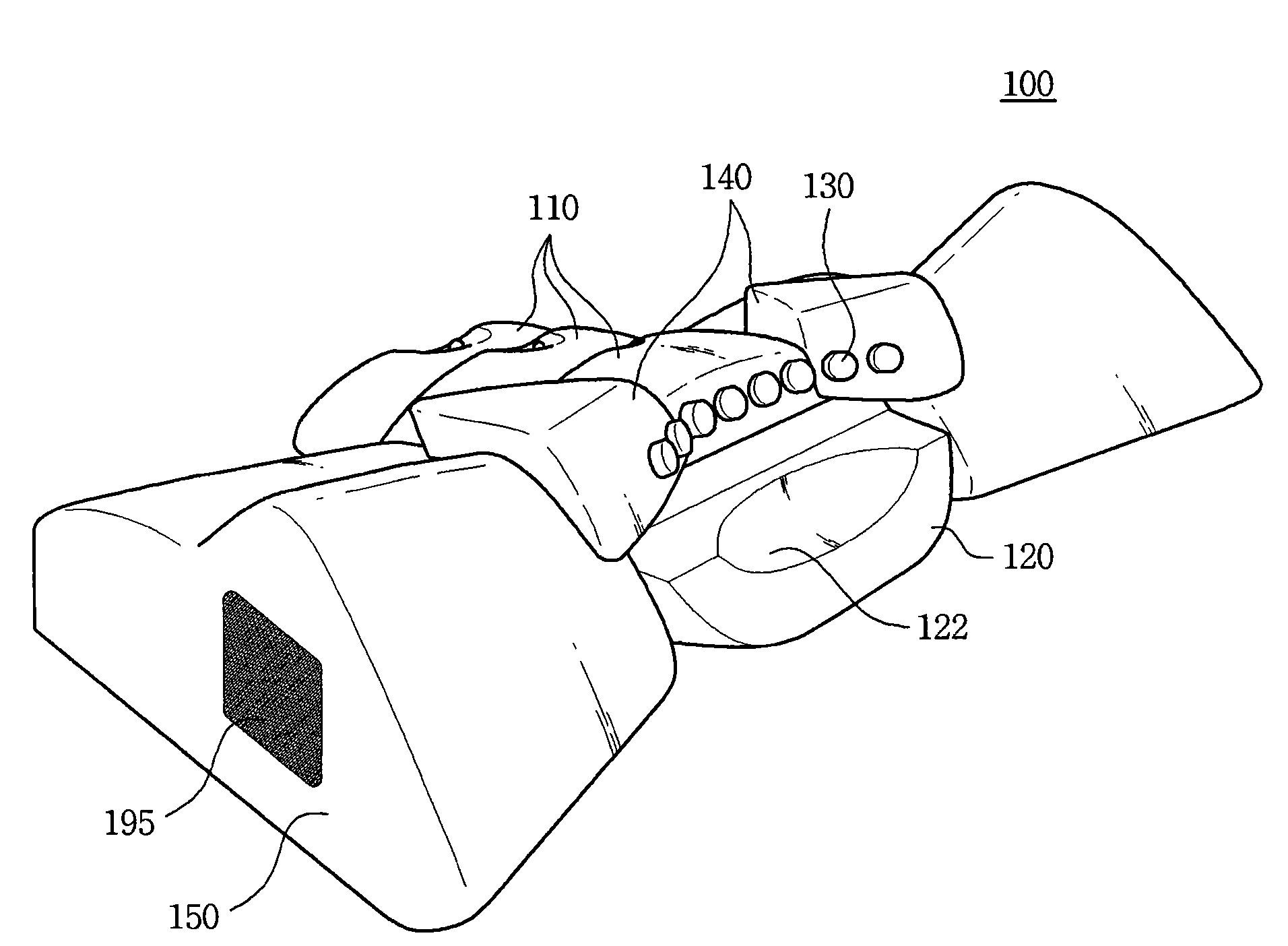
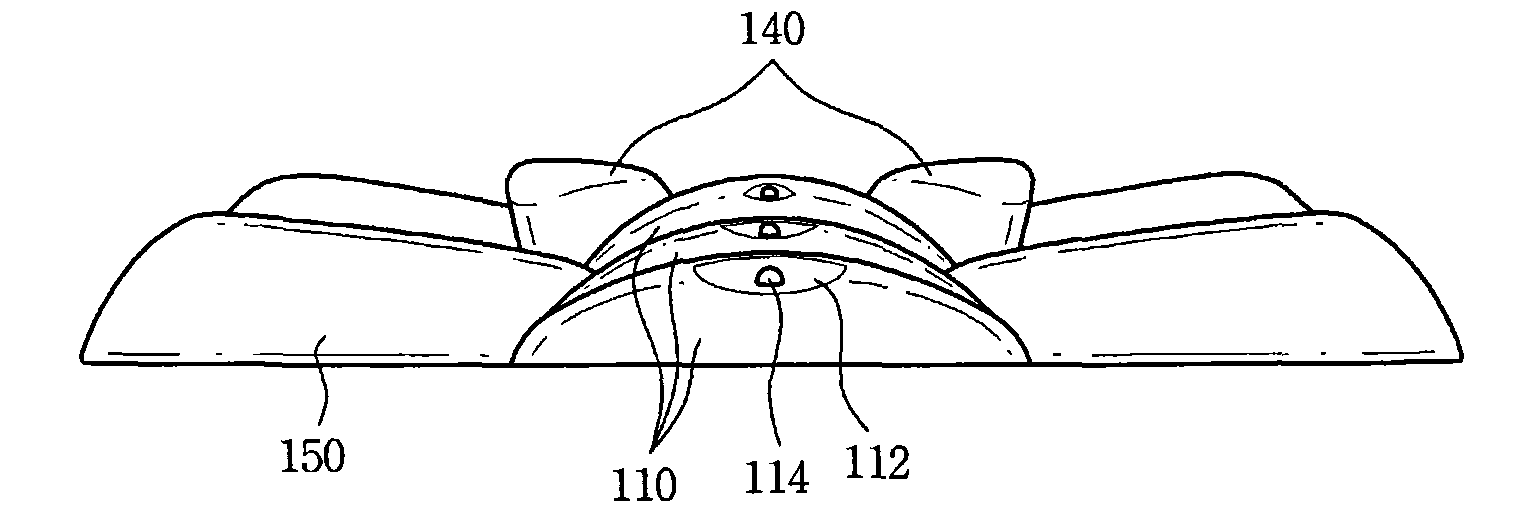
Headguard with an eccentric dimple for accommodating the occipital bone
The present claimed invention is directed to a protective headguard, comprising a rear pad to protectively cover at least the occipital lobe on the back of a human head. The rear pad has an eccentric dimple for accommodating the occipital lobe. A front pad is configured and arranged to protectively cover at least the forehead of a human. The front pad is releasably interconnected to the rear pad at separate and distinct upper and lower connection points on the rear pad positioned on opposite sides of the dimple. The fit of the headguard can be adjusted between a first and second configuration by disconnecting the front and rear pads, rotating the rear pad 180° and reconnecting the front and rear pads with the front pad connections to the rear pad exchanged as between the upper and lower connection points.
Owner:FULL90 SPORTS
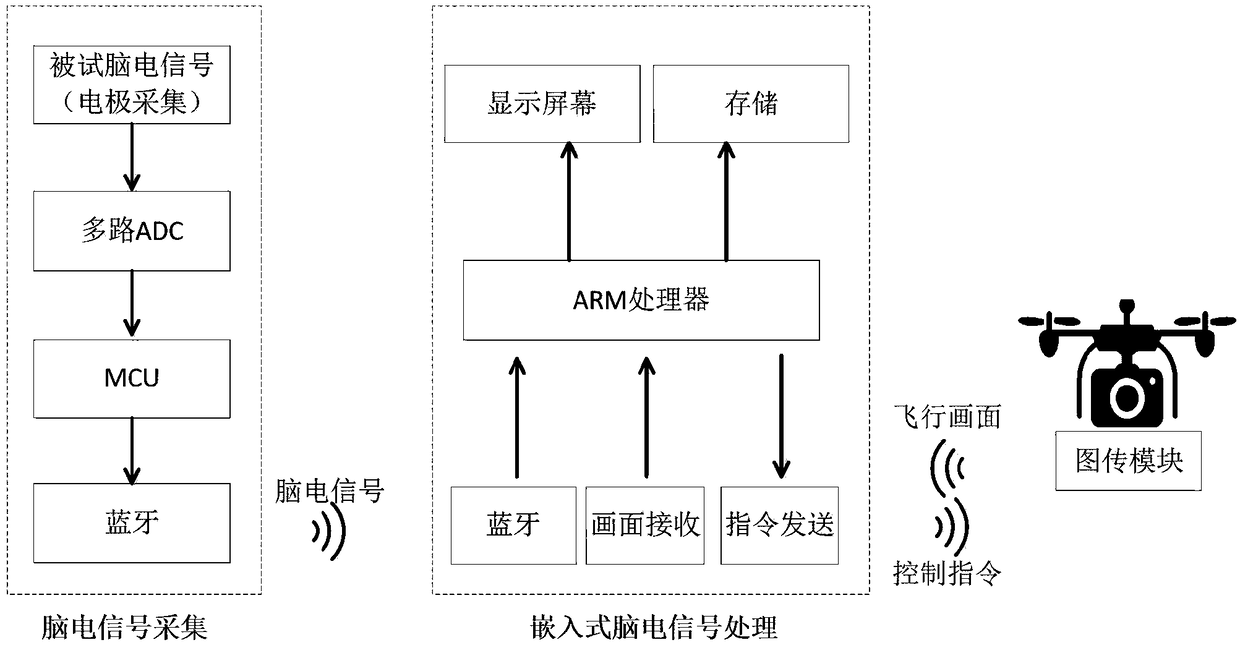
Motion-imagination-based portable brain-controlled unmanned aerial vehicle system and control method thereof
PendingCN108762303AReduce volumeReduce power consumptionInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingSystems designBrain computer interfacing
The invention, which belongs to the field of brain-computer interfaces, relates to a motion-imagination-based portable brain-controlled unmanned aerial vehicle system and a control method thereof. Thesystem is composed of an EEG signal acquisition device, an embedded EEG signal processing device, and a flight portion. The EEG signal acquisition device uses a high-precision and high-integration analog front end and a high-precision and high-integration AD conversion chip, so that power consumption of the EEG signal acquisition module is reduced, the system design is simplified, and the signal-to-noise ratio is improved; and signal processing is carried out well and thus the size of the EEG signal acquisition device is reduced substantially. According to the system, the EEG signal acquisition device is installed at an occipital lobe part of an electrode cap in an integration manner and the bluetooth is used as a data transmission mode, so that the collection part of the EEG signal is combined with the electrode cap and an independent part is formed. Therefore, the comfort and flexibility of the user are improved substantially.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
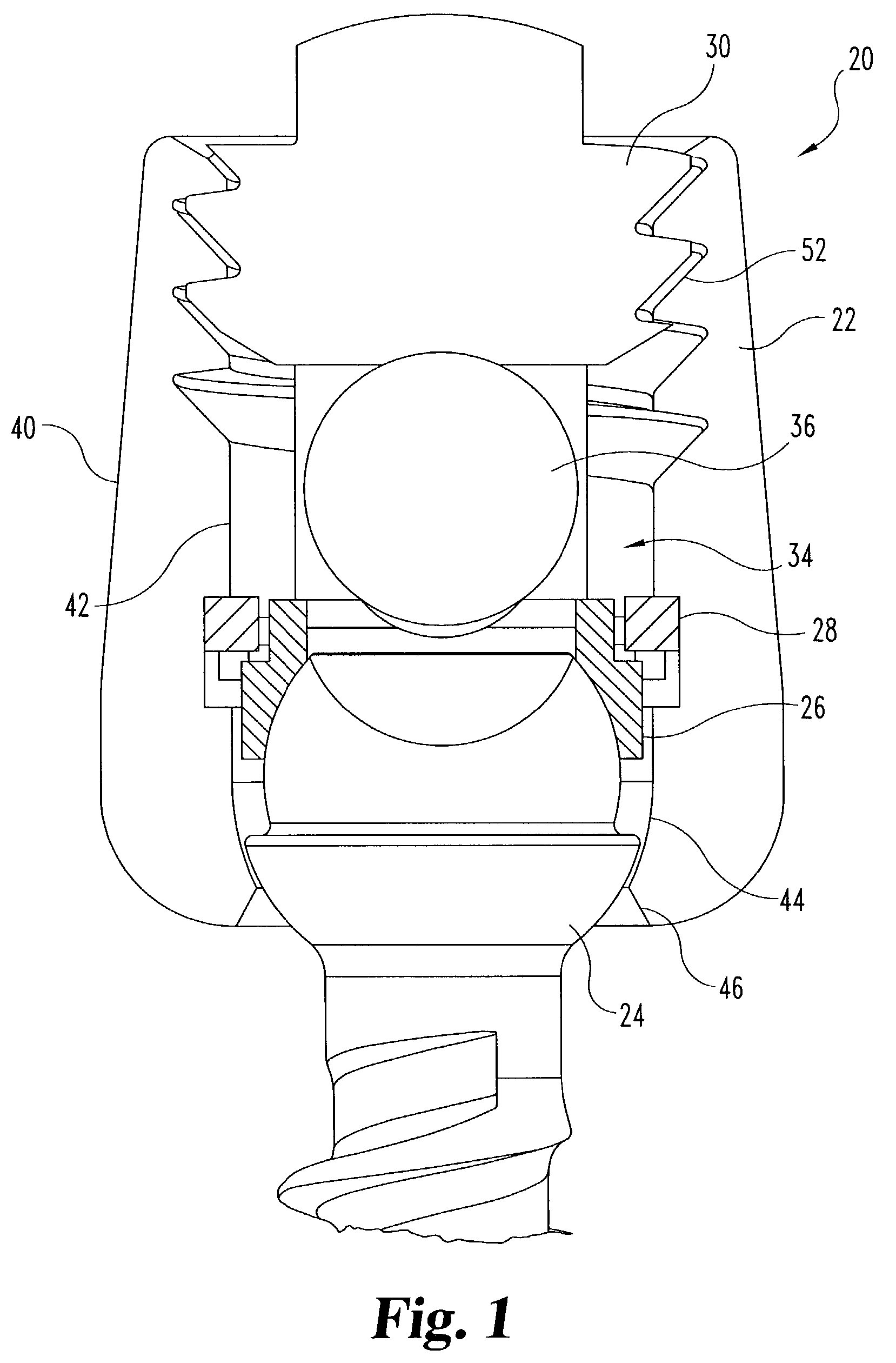
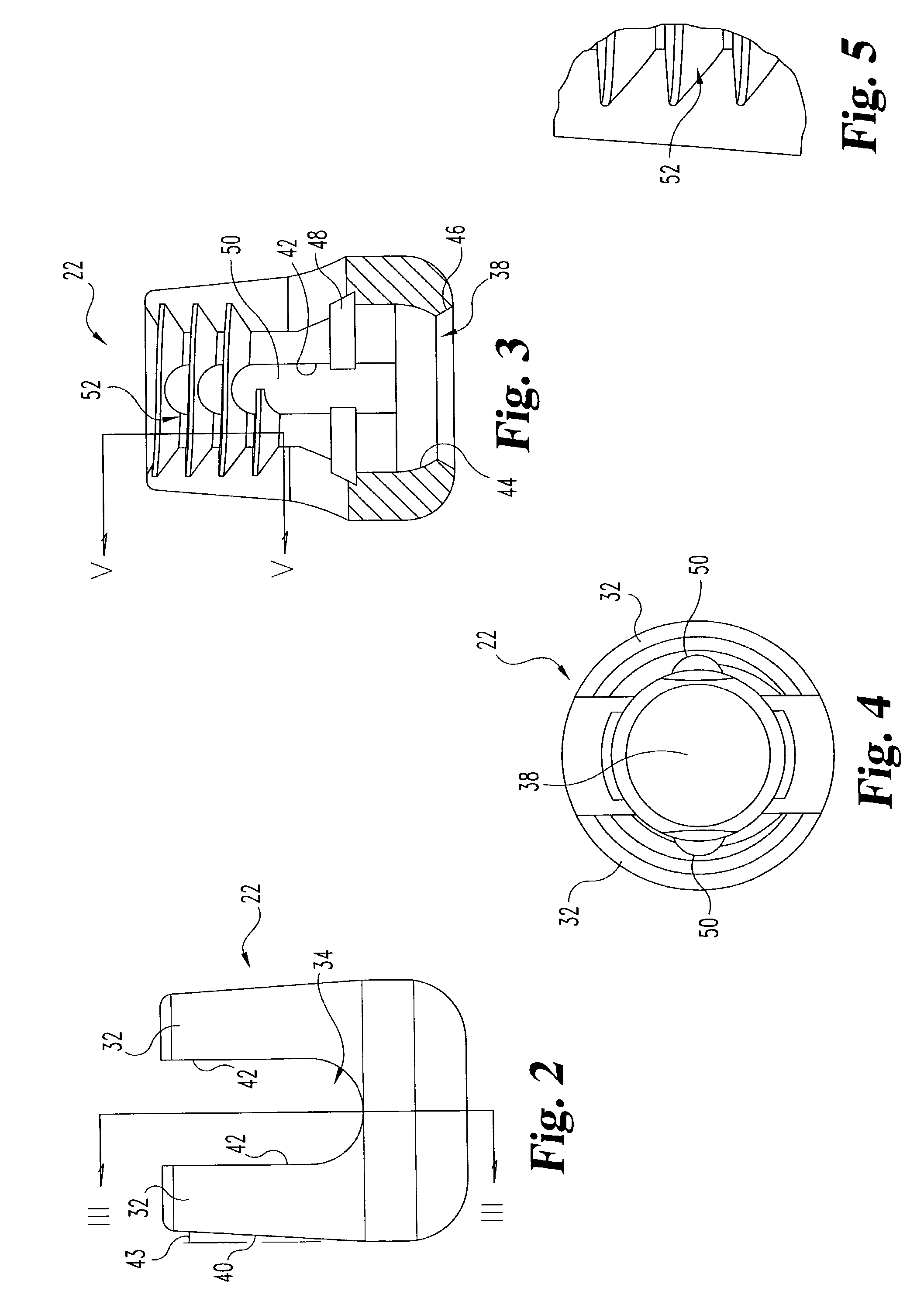
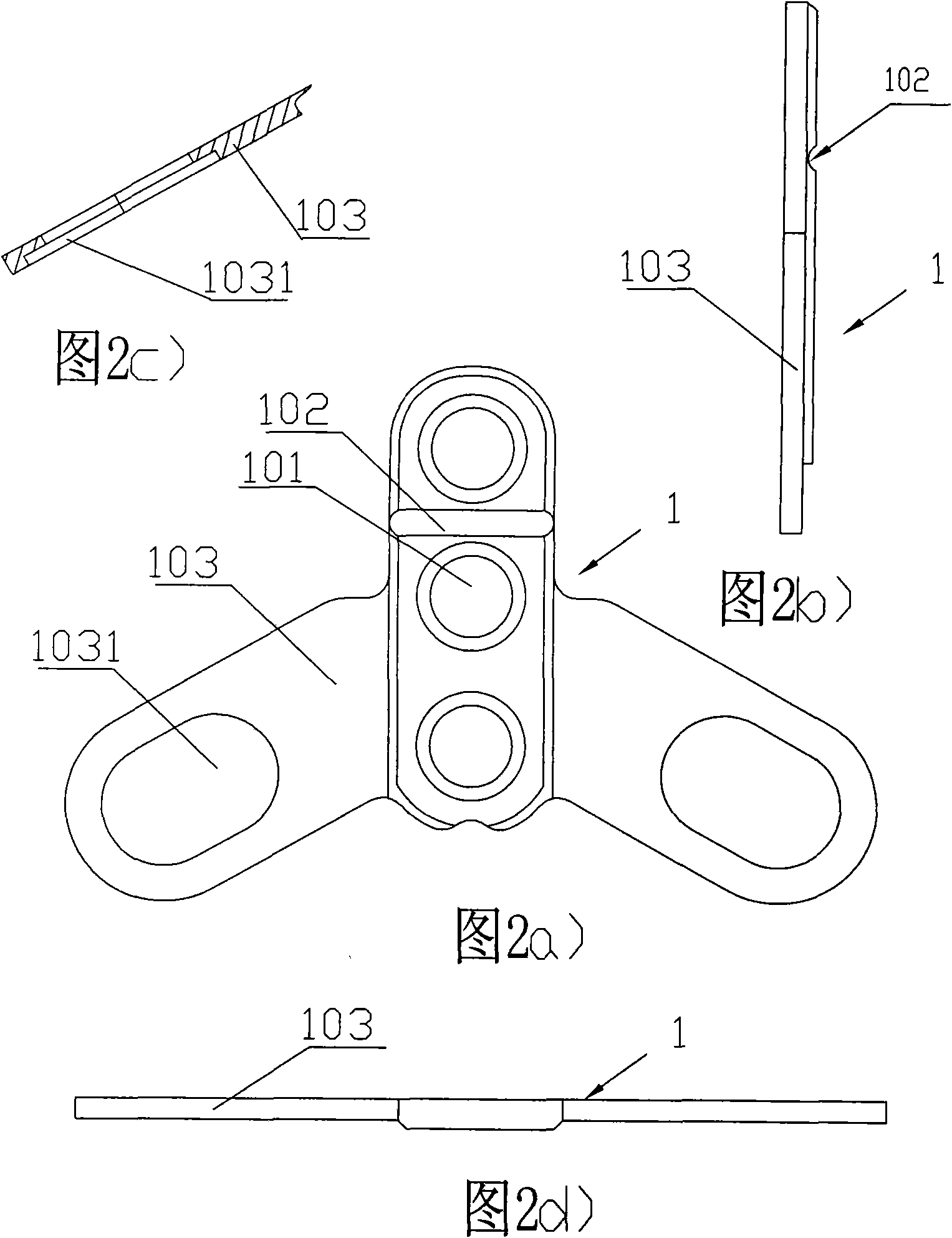
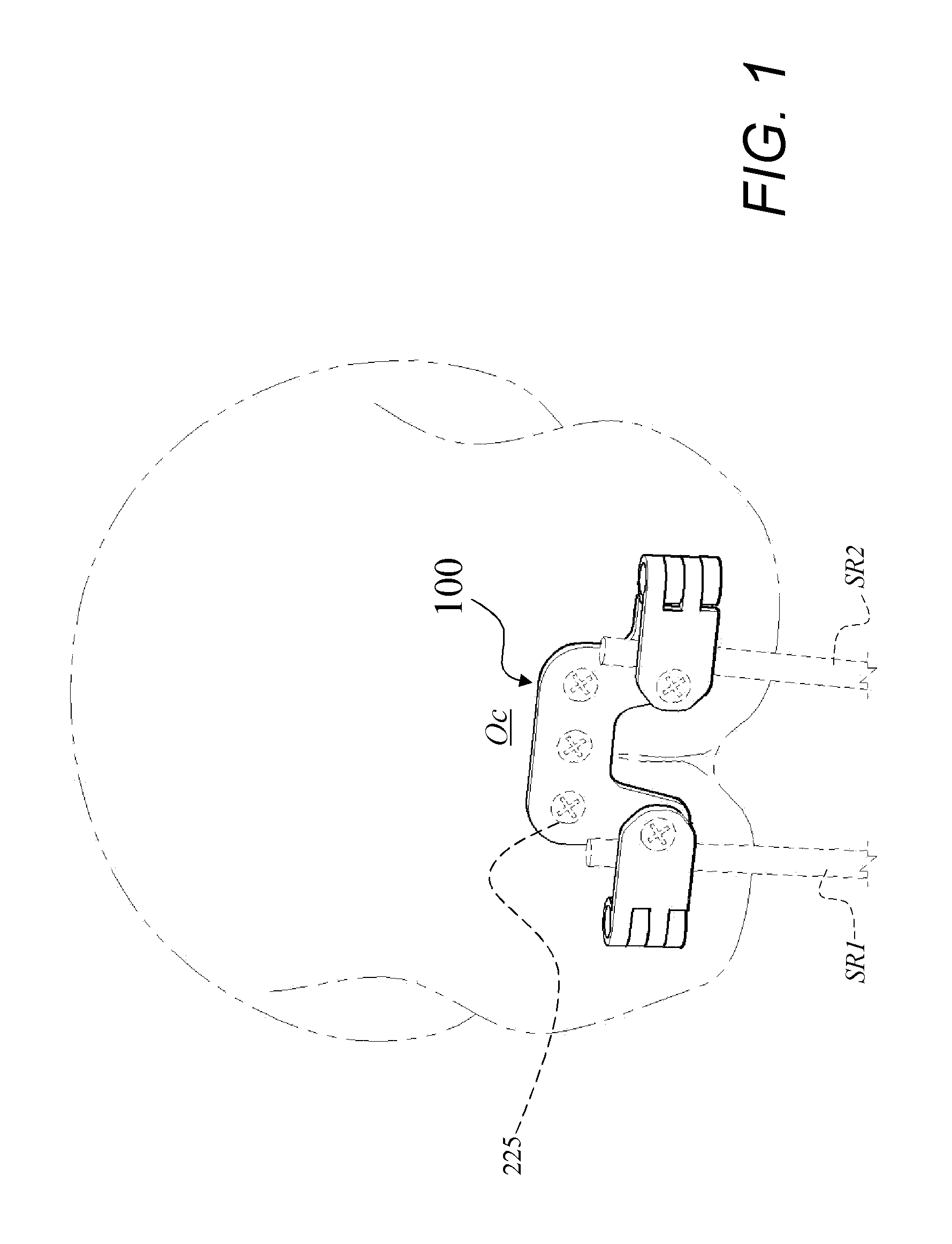
Occipital plate
An occipital plate for use in an occipitocervical fixation procedure to stabilize the base of a patient's skull with respect to the patient's neck. The occipital plate of the invention is made up of a middle portion having left and right sides, and left and right hinged legs extending outward in opposite directions from the left and right sides of the middle portion. Each of the left and right hinged legs uses a hinge mechanism to secure a spinal rod to the occipital plate.
Owner:MACKALL JOHN L
Atlas fusion prosthesis
The invention discloses an atlas fusion prosthesis which is arranged between an occipital bone and an axis to replace a physiological atlas. The atlas fusion prosthesis comprises a prosthesis body, an upper joint fusion face which is arranged at the upper part of the prosthesis body and used for sticking with an occipital condyle joint face of the occipital bone and a lower joint fusion face which is arranged at the lower part of the prosthesis body and used for sticking with an upper joint face of the axis. The atlas fusion prosthesis disclosed by the invention has the main advantages that the atlas prosthesis with a fusion face matching both the occipital bone and the axis is implanted to replace the physiological atlas so as to rapidly recover functions of the atlas, promote sacralization, realize the purpose of reconstructing cervical stability and facilitate postoperative recovery.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
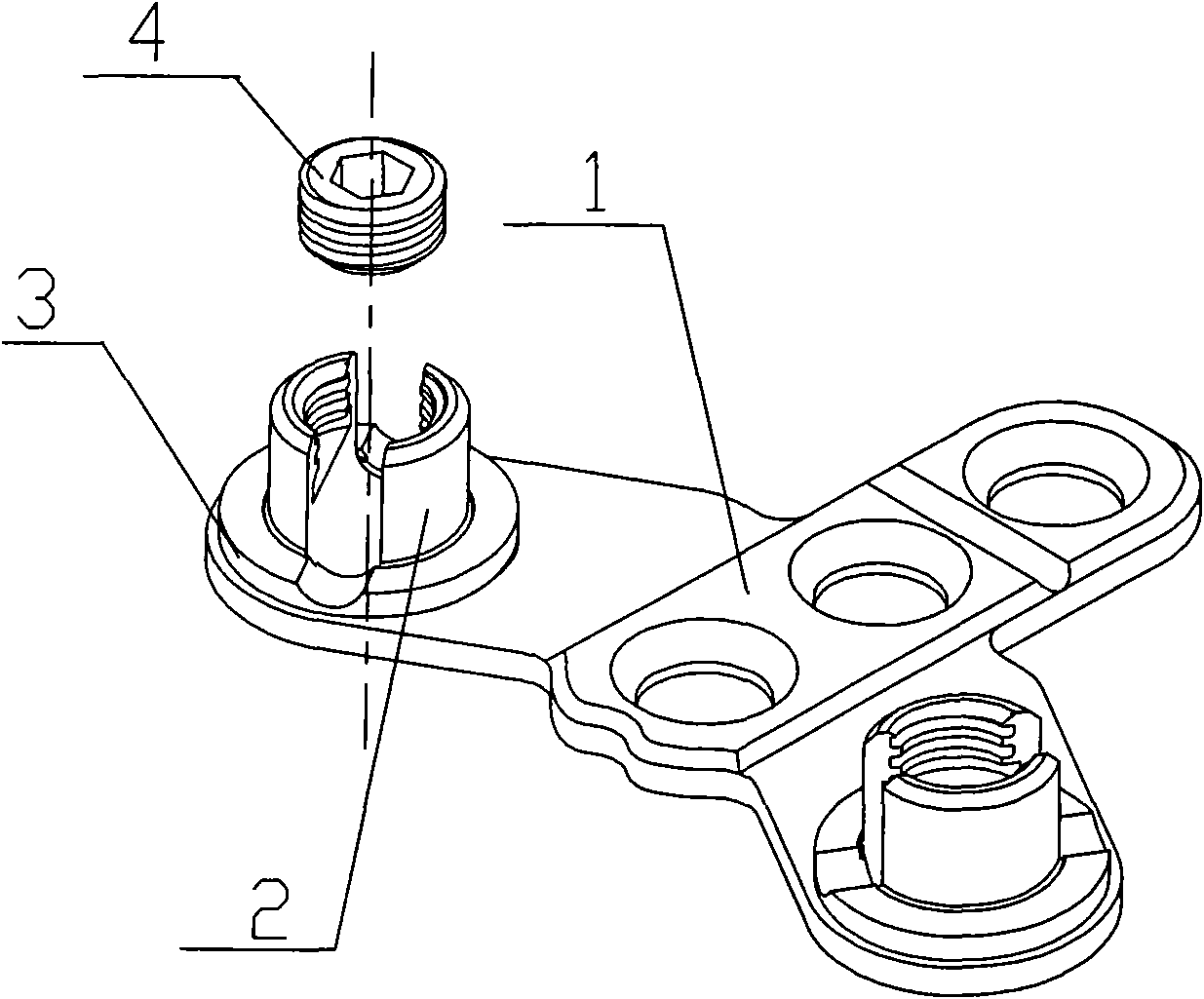
Occipital screw rod connector
InactiveCN101669838AEasy to operateEasy to adjustInternal osteosythesisArchitectural engineeringOccipital bone
The invention discloses an occipital screw rod connector which consists of an occipital plate, a U-shaped connecting base, a screw plug and a retainer ring, wherein the occipital plate is a swallow-shaped triplex plate with a straight plate in the middle and oblique arm plates at two lower sides, the straight plate is provided with a group of screw holes in which occipital screws are screwed, theoblique arm plate is provided with an elongated slot for adjustment; the U-shaped connecting base is provided with a U-shaped opening groove for receiving a connecting rod in need of connection, a U-shaped opening inner hole of the U-shaped connecting base is provided with the screw plug, and the bottom part of the U-shaped connecting base is provided with an outer edge platform; and the retainerring is an opening-type gasket. The occipital plate and the U-shaped connecting base can be connected into one body with the retainer ring, and the U-shaped connecting base can be movable and rotatable along the elongated slot of the oblique arm plate. When the connecting rod in need of connection is placed in the U-shaped groove of the U-shaped connecting base and the screw plug is screwed, the occipital plate, the U-shaped connecting base, the opening-type retainer ring and the connecting rod can be firmly fixed together.
Owner:郭谦
Meditation pillow using craniosacral therapy
InactiveUS8316855B2Promote circulationOperating chairsDevices for pressing relfex pointsAcupressureNerve fiber bundle
A meditation pillow using craniosacral therapy is disclosed. The meditation pillow includes a columna vertebralis supporting part formed in a user's neck direction to support a part of a columna vertebralis located thereon, an occipital region supporting part formed at a rear of the columna vertebralis supporting part to support an occipital region of a head located thereon, and an occipital region acupressure part protrudingly formed along a superior nuchal line between an atlas and an occipital bone to stimulate nerve fibers of the occipital region.
Owner:JINBIOTECH
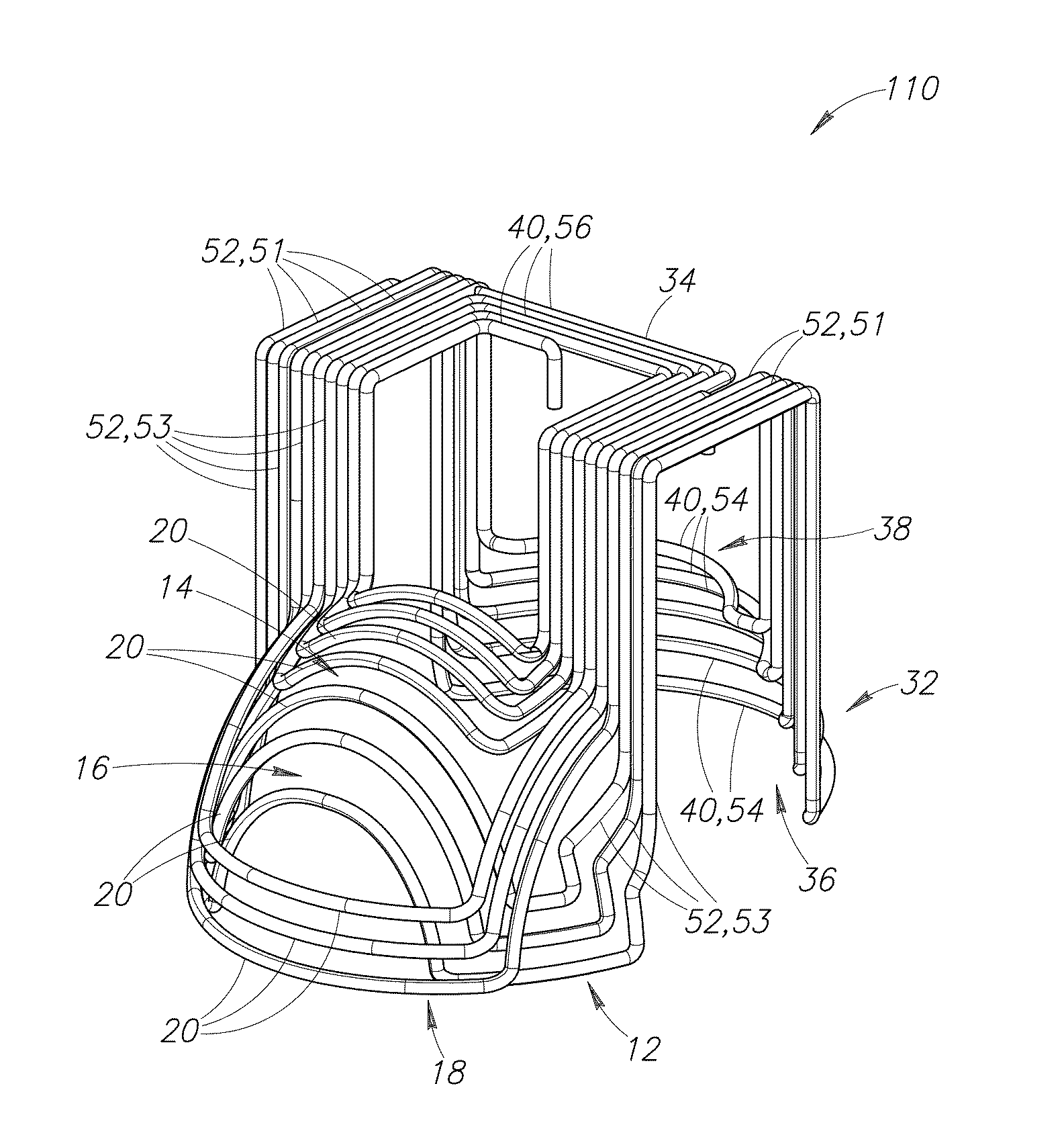
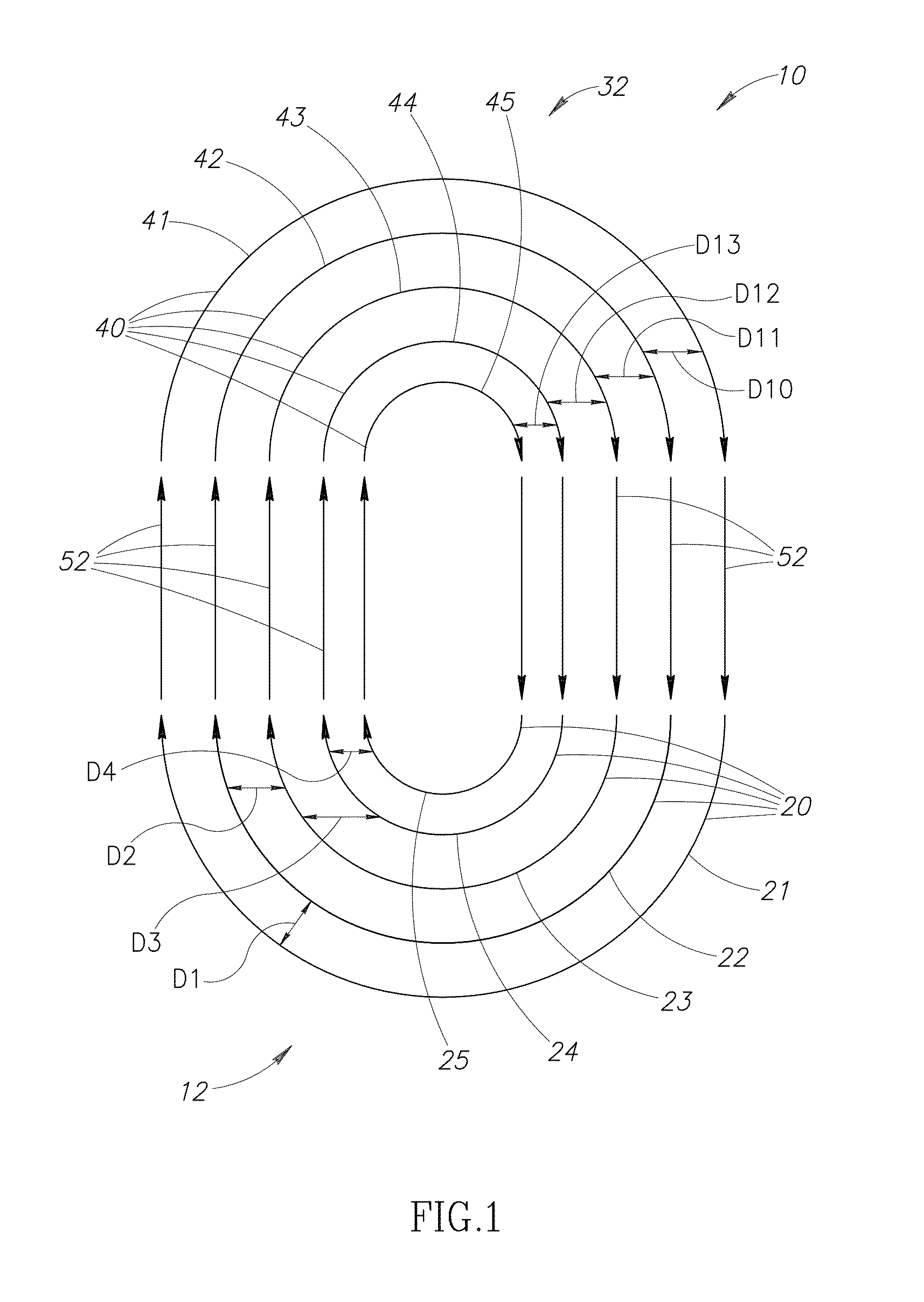
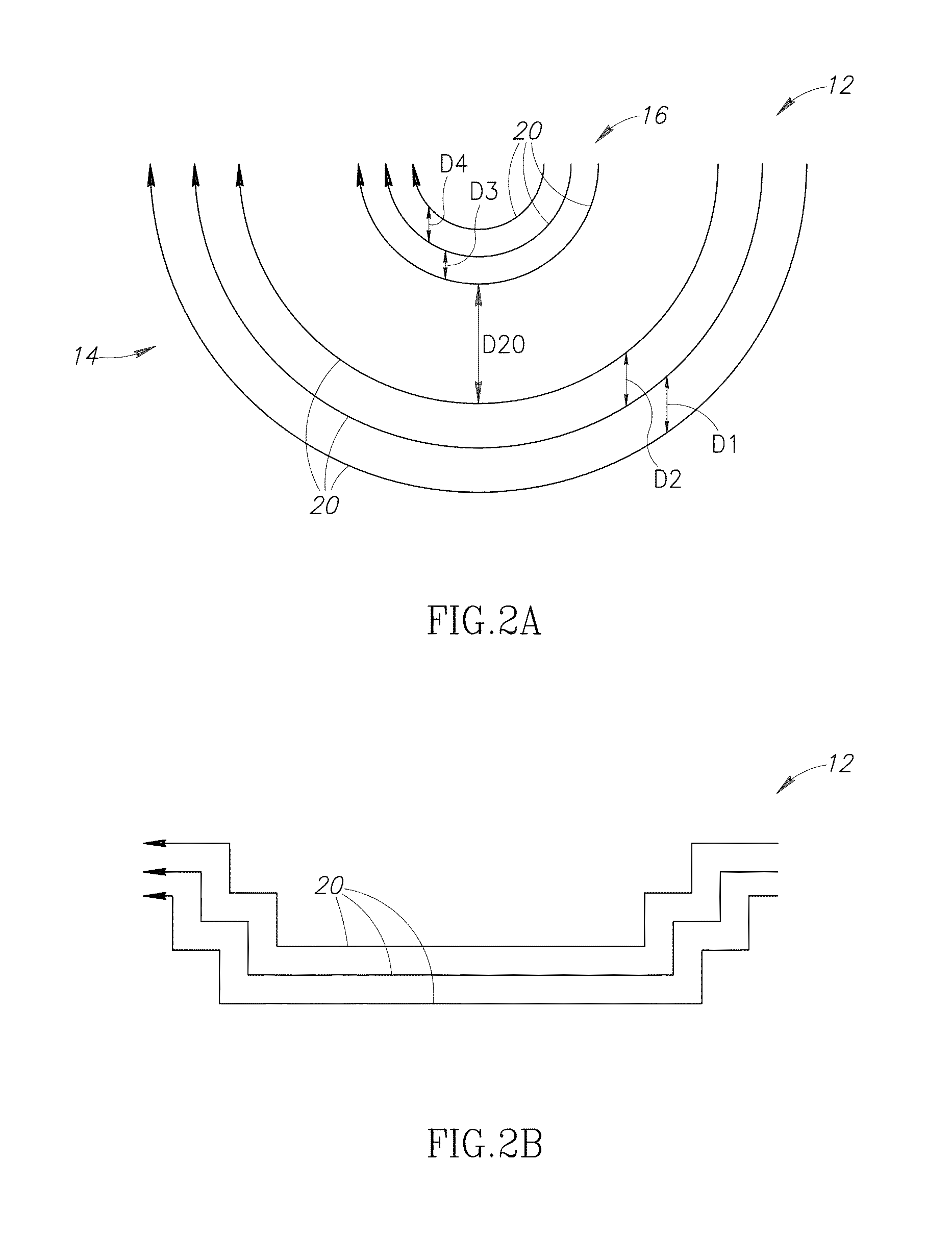
Circular coils for deep transcranial magnetic stimulation
ActiveUS20140235926A1Better depth penetration profileImprove depth penetration profileElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsPower flowTemporal Regions
A transcranial magnetic stimulation coil which is location-specific for frontal lobe regions, occipital lobe regions, parietal lobe regions, right temporal regions and left temporal regions is designed with multiple spaced apart stimulating elements having current flow in a substantially circular direction, and multiple return elements having current flow in substantially the same circular direction.
Owner:BRAINSWAY
Occipital plate
An occipital plate for use in an occipitocervical fixation procedure to stabilize the base of a patient's skull with respect to the patient's neck. The occipital plate is made up of a middle portion having left and right sides, and left and right hinged legs extending outward in opposite directions from the left and right sides of the middle portion. Each of the left and right hinged legs uses a hinge mechanism to secure a spinal rod to the occipital plate.
Owner:MACKALL JOHN
Meditation pillow using craniosacral therapy
The invention discloses a meditation pillow using craniosacral therapy. The meditation pillow includes a columna vertebralis supporting part formed in a user's neck direction to support a part of a columna vertebralis located thereon, an occipital region supporting part formed at a rear of the columna vertebralis supporting part to support an occipital region of a head located thereon, and an occipital region acupressure part protrudingly formed along a superior nuchal line between an atlas and an occipital bone to stimulate nerve fibers of the occipital region.
Owner:JINBIOTECH
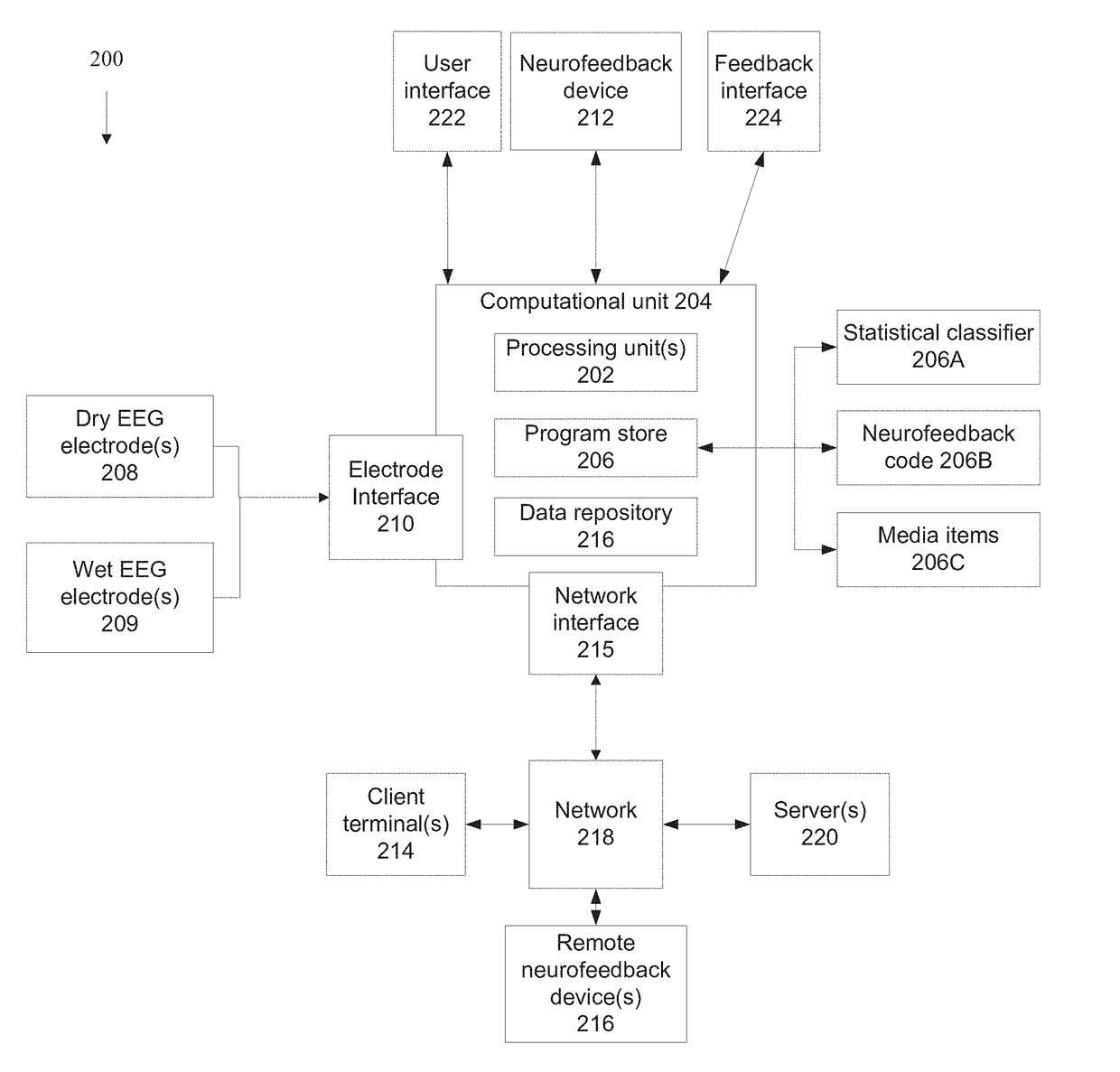
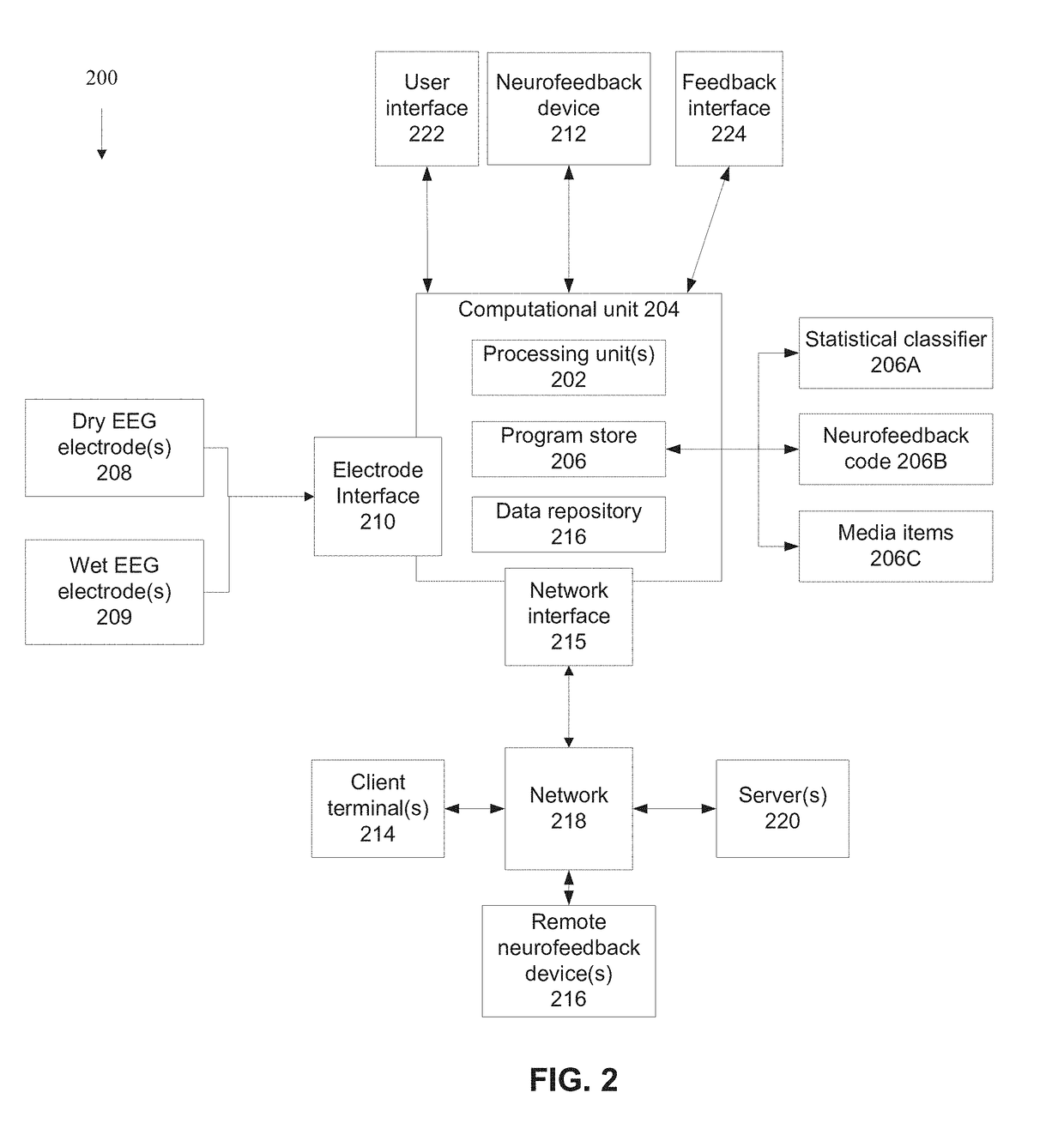
Systems and methods for processing eeg signals of a neurofeedback protocol
ActiveUS20180184937A1Improve Feedback AccuracyImprove performanceElectroencephalographyMedical data miningFrontal lobeComputer science
Owner:MYNDELEVATOR LTD
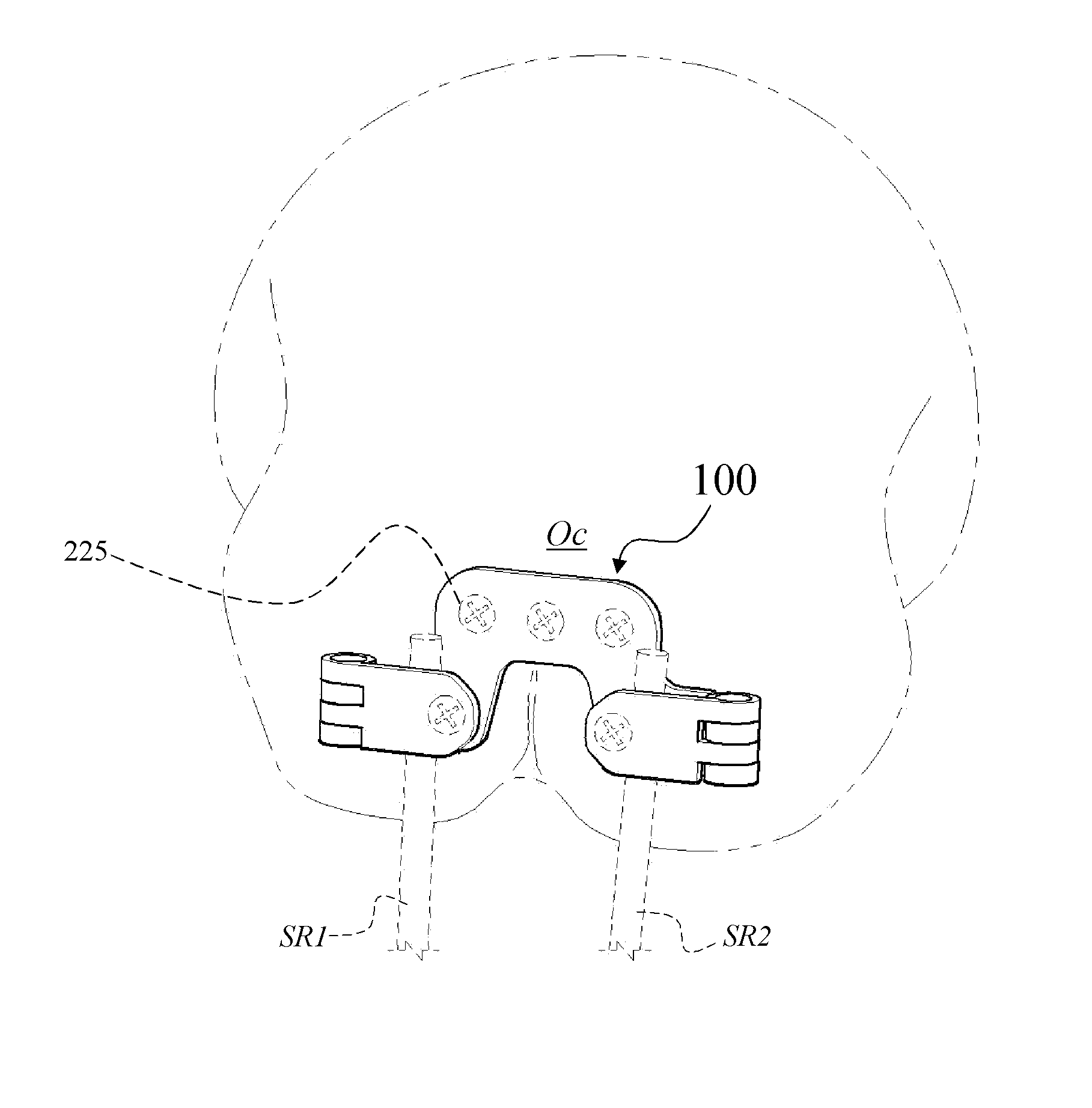
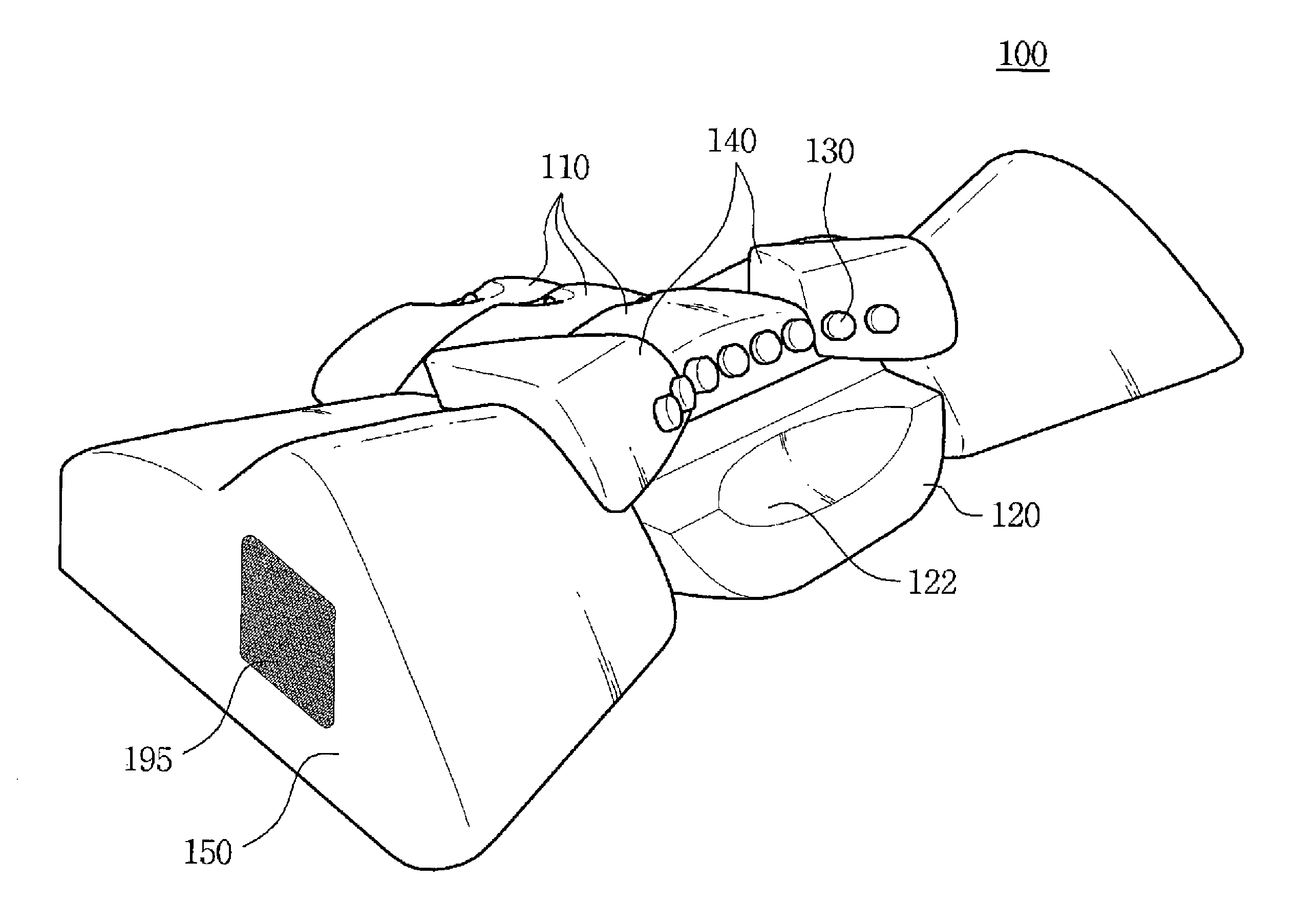
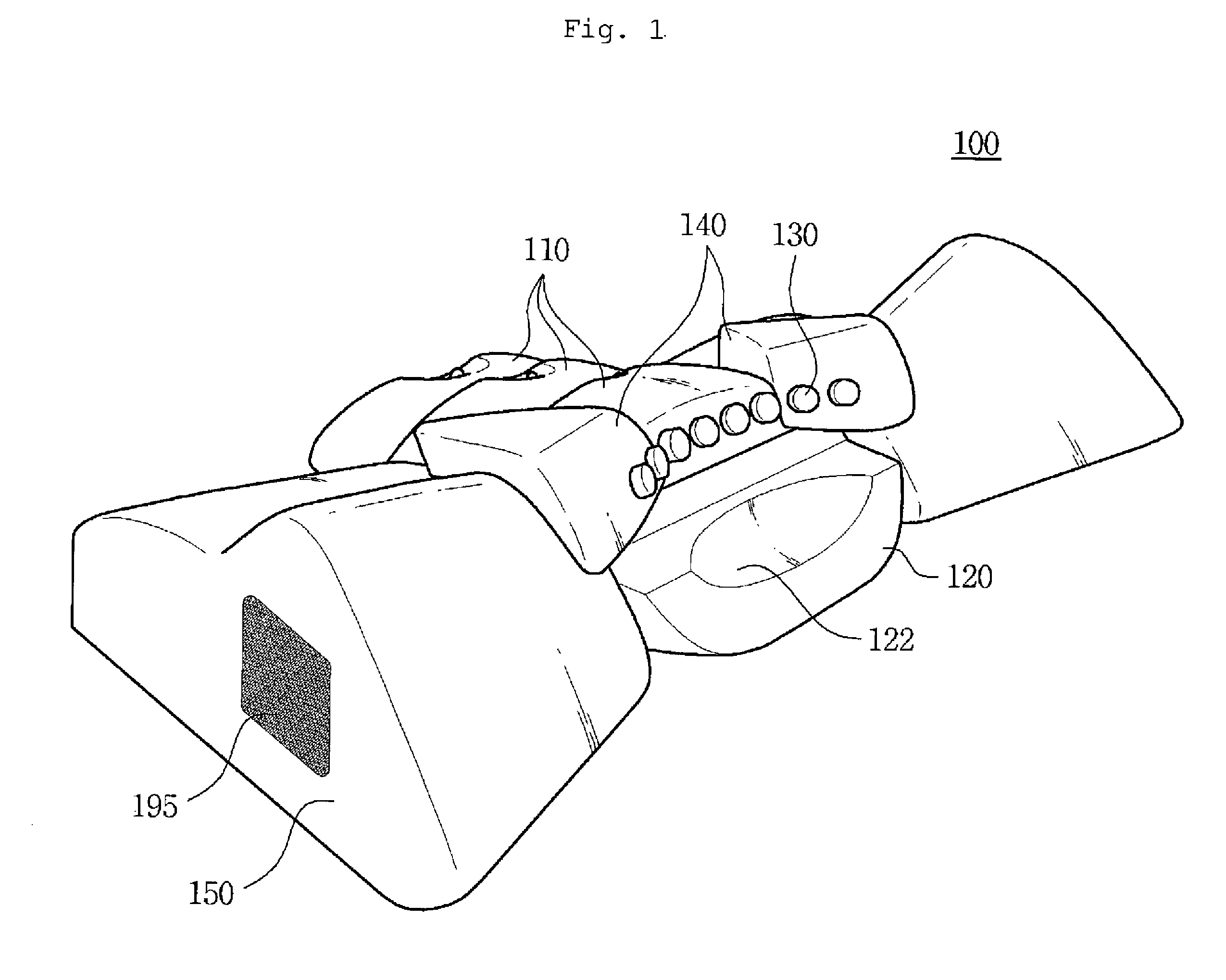
Head mountable device
PendingCN110612059ASensorsTelemetric patient monitoringPhysical medicine and rehabilitationLED display
A head mountable device for detecting a functional disorder of the brain in a patient is disclosed, the device comprising an LED display and at least one electrode for measuring electrical potential.The device is configured to be mountable on the head of a patient such that when mounted on the head of a patient the LED display is positioned before the eyes of a patient and the at least one electrode is positioned adjacent to the occipital lobe of the patient.
Owner:HEADSAFEIP PTY LTD
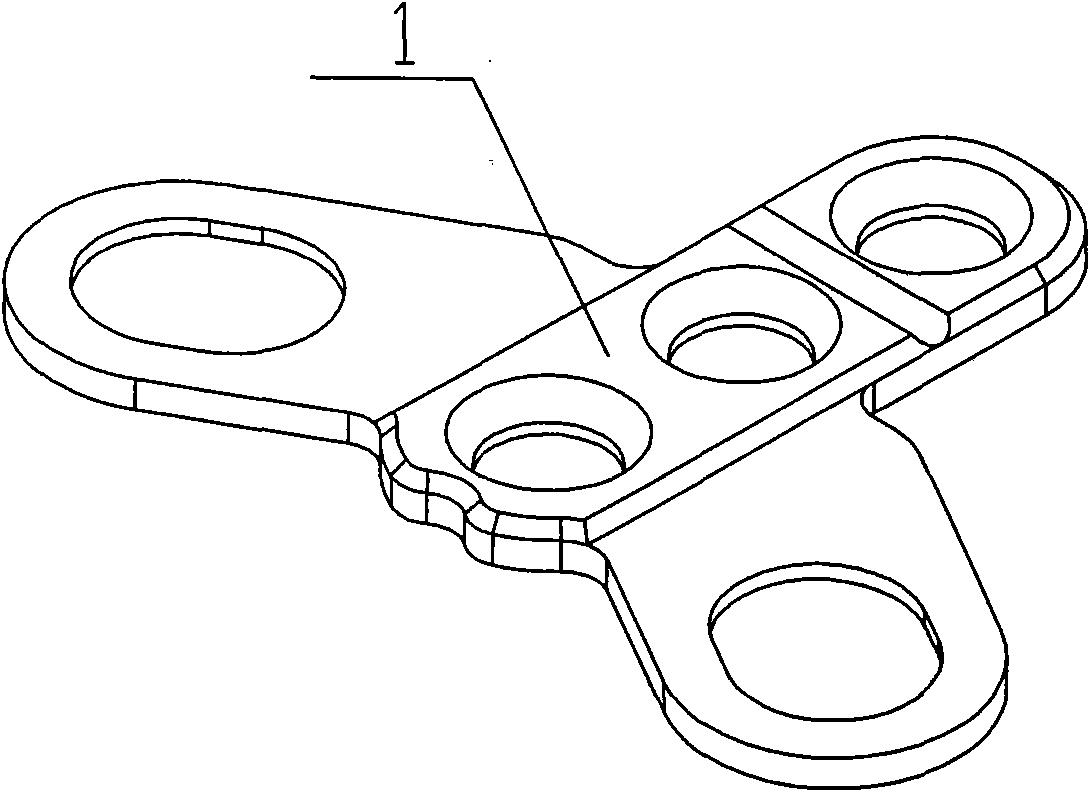
Occipitocervical plate
Methods and systems for occipital-cervical spinal fixation. A plate configured for attachment to the occipital bone has two arms extending out from either side, which turn downwards parallel to one another. A first bend is disposed in the arms, such that the arms extend down from the occipital bone behind the spinous process of the C1 and C2 vertebrae, upon installation. A second bend in the arms allows attachment to the C2 vertebra. The system may be dimensioned for pediatric installation. A bone graft material may be held in place between the cervical vertebrae and the skull by installing a cable to the installed system to retain the bone graft material in place. Methods and kits for occipital-cervical spinal fixation are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND +1
Methods of Using Brain Temporal Dynamics
ActiveUS20180228419A1Reduce complexityElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyAutobiographical memoryCognitive response
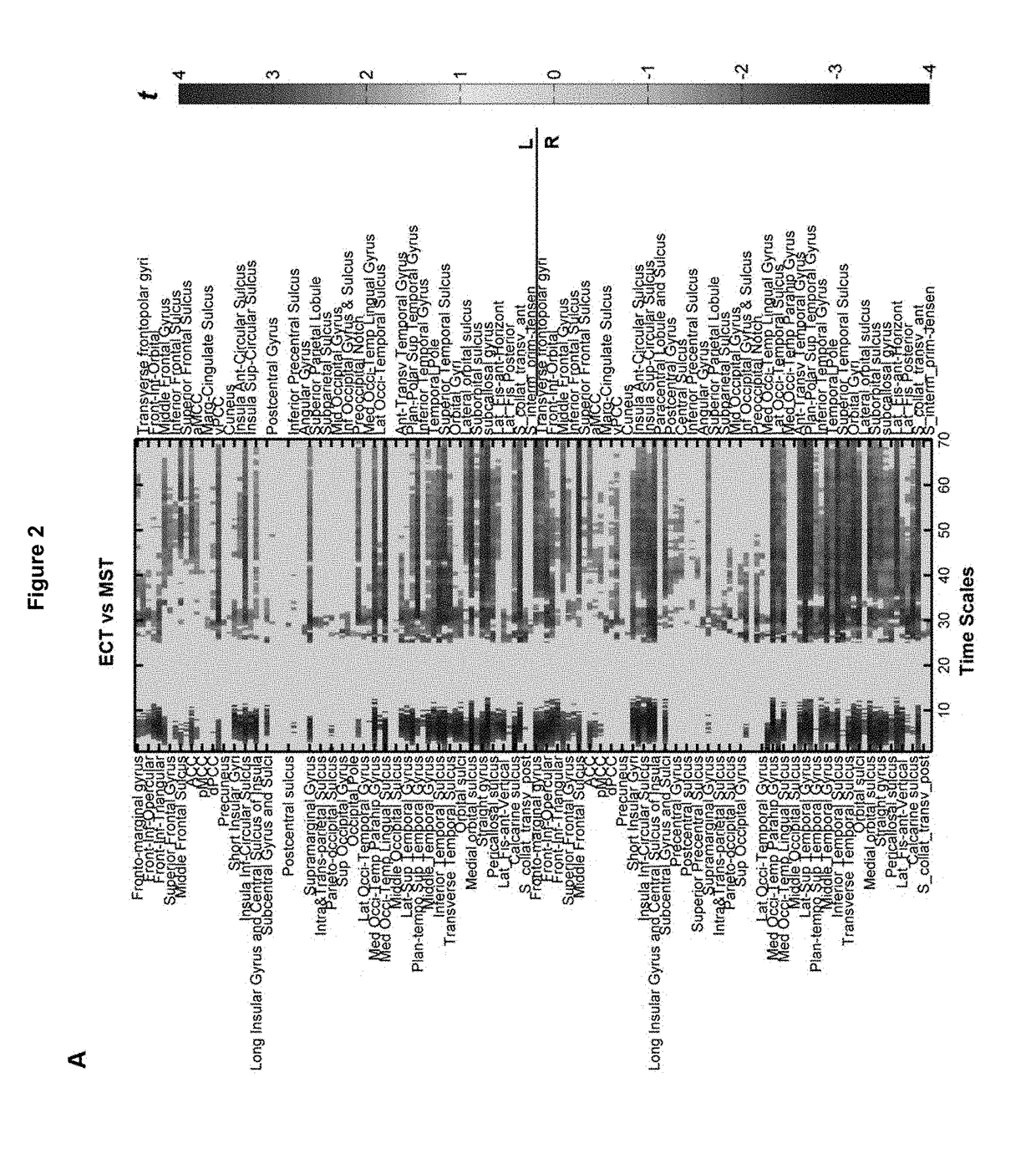
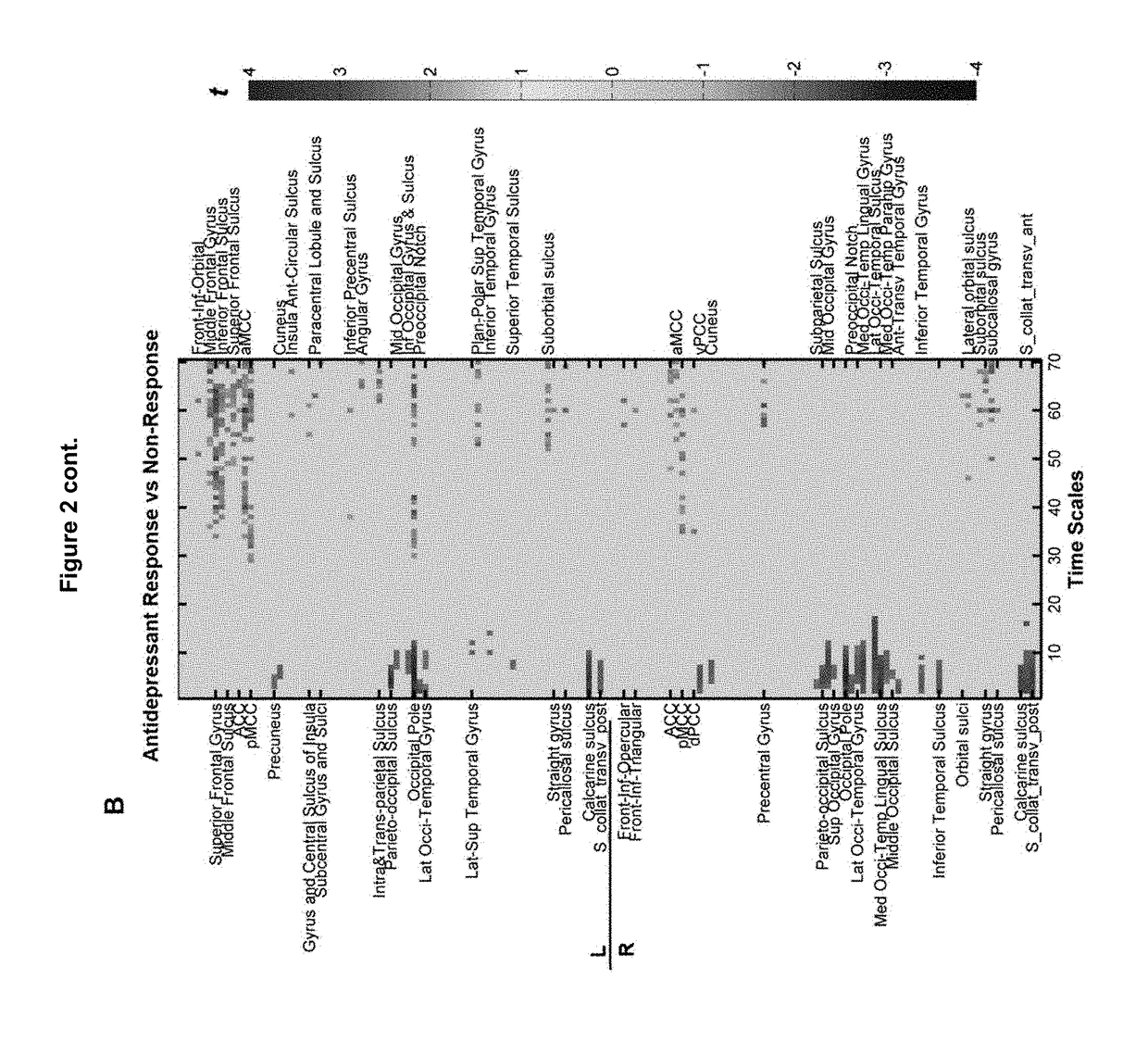
Over 350 million people worldwide suffer from depression, a third of whom are medication resistant. Seizure therapy remains the most effective treatment in depression, even when many treatments fail. The utility of seizure therapy is limited due to its cognitive side effects and stigma. The biological targets of seizure therapy remain unknown, hindering design of new treatments with comparable efficacy. Seizures impact the brains temporal dynamicity observed through electroencephalography. This dynamicity reflects richness of information processing across distributed brain networks subserving affective and cognitive processes. We investigated the hypothesis that seizure therapy impacts mood (depressive symptoms) and cognition by modulating brain temporal dynamicity. We obtained resting-state EEG from thirty-four patients (age=46.0±14.0, 21 females) receiving two types of seizure treatments—electroconvulsive therapy or magnetic seizure therapy. We employed multi-scale entropy to quantify the complexity of brain's temporal dynamics before and after seizure therapy. We discovered that reduction of complexity in fine time scales underlined successful therapeutic response to both seizure treatments. Greater reduction in complexity of fine time scales in parieto-occipital and central brain regions was significantly linked with greater improvement in depressive symptoms. Greater increase in complexity of coarse time scales was associated with greater decline in cognition including the autobiographical memory. These findings were region- and time-scale specific. That is, change in complexity in occipital regions (e.g., O2 electrode or right occipital pole) at fine time-scales was only associated with change in depressive symptoms, and not change in cognition, and change in complexity in parieto-central regions (e.g., Pz electrode or intra and transparietal sulcus) at coarser time-scale was only associated with change in cognition, and not depressive symptoms. Finally, region and time-scale specific changes in complexity classified both antidepressant and cognitive response to seizure therapy with good (80%) and excellent (95%) accuracy, respectively. In this study, we discovered a novel biological target of seizure therapy; complexity of the brain resting-state dynamics. Region and time-scale dependent changes in complexity of the brain resting-state dynamics is a novel mechanistic marker of response to seizure therapy that explains both the antidepressant response and cognitive changes associated with this treatment. This marker has tremendous potential to guide design of the new generation of antidepressant treatments.
Owner:FARZAN FARANAK
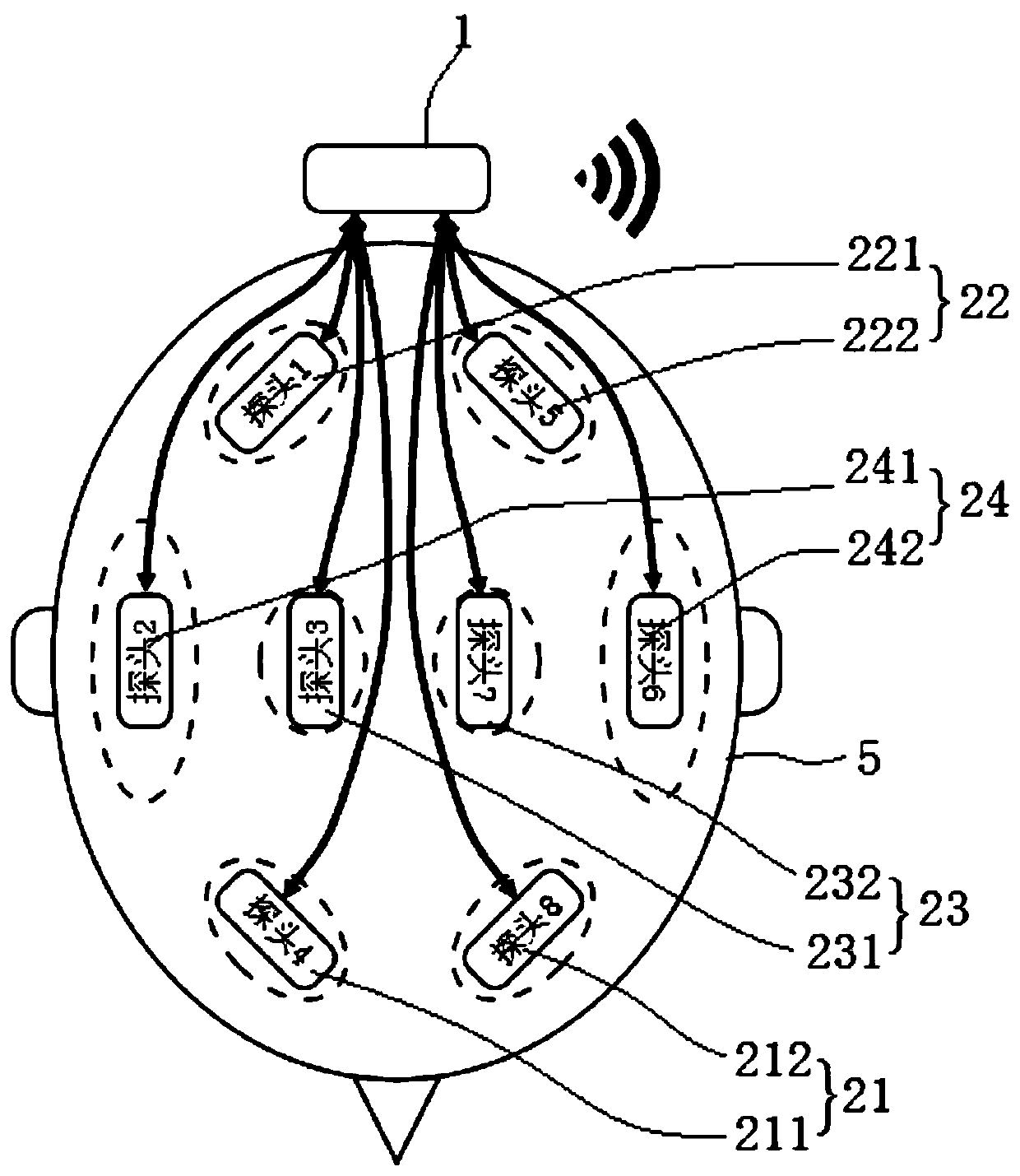
Wireless multi-brain-region brain blood oxygen wearable detection system and method
PendingCN111568440AImprove spatial resolutionImprove space efficiencyMedical imagingSensorsPrefrontal lobePosterior Circulation Brain Infarction
The invention discloses a wireless multi-brain-region brain blood oxygen wearable detection system and method. The system comprises a collector and a plurality of probes, wherein the plurality of probes communicate with the collector through cables; the probes include prefrontal lobe brain region probes covering the left side and the right side of the brain and any brain region probe or a combination of multiple brain region probes of occipital lobe brain region probes, parietal lobe brain region probes and temporal lobe brain region probes covering the left side and the right side of the brain; the plurality of probes are correspondingly attached to divided functional brain regions; the probes are driven and controlled to emit detection light to the corresponding brain regions; the probessimultaneously receive the emitted detection light of the functional brain regions, and collect brain blood oxygen signals of the brain regions; and the collected brain blood oxygen signals of the brain regions are processed to obtain brain blood oxygen collection information of the brain regions. Through simultaneous detection of the multiple brain regions, the brain regions of partial anteriorcirculation cerebral infarction and posterior circulation cerebral infarction can be covered, and the limitation that only the anterior circulation infarction of the brain can be reflected is overcome.
Owner:中科搏锐(北京)科技有限公司 +1
Head mountable device
PendingUS20200060573A1Neuronal activity can be objectively analysedLow costElectroencephalographySensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationLED display
A head mountable device for detecting a functional disorder of the brain in a patient, comprising an LED display; at least one electrode for measuring electrical potential; the device being configured to be mountable on the head of a patient such that when mounted on the head of a patient the LED display is positioned before the eyes of a patient and the at least one electrode is positioned adjacent to the occipital lobe of the patient.
Owner:HEADSAFEIP PTY LTD
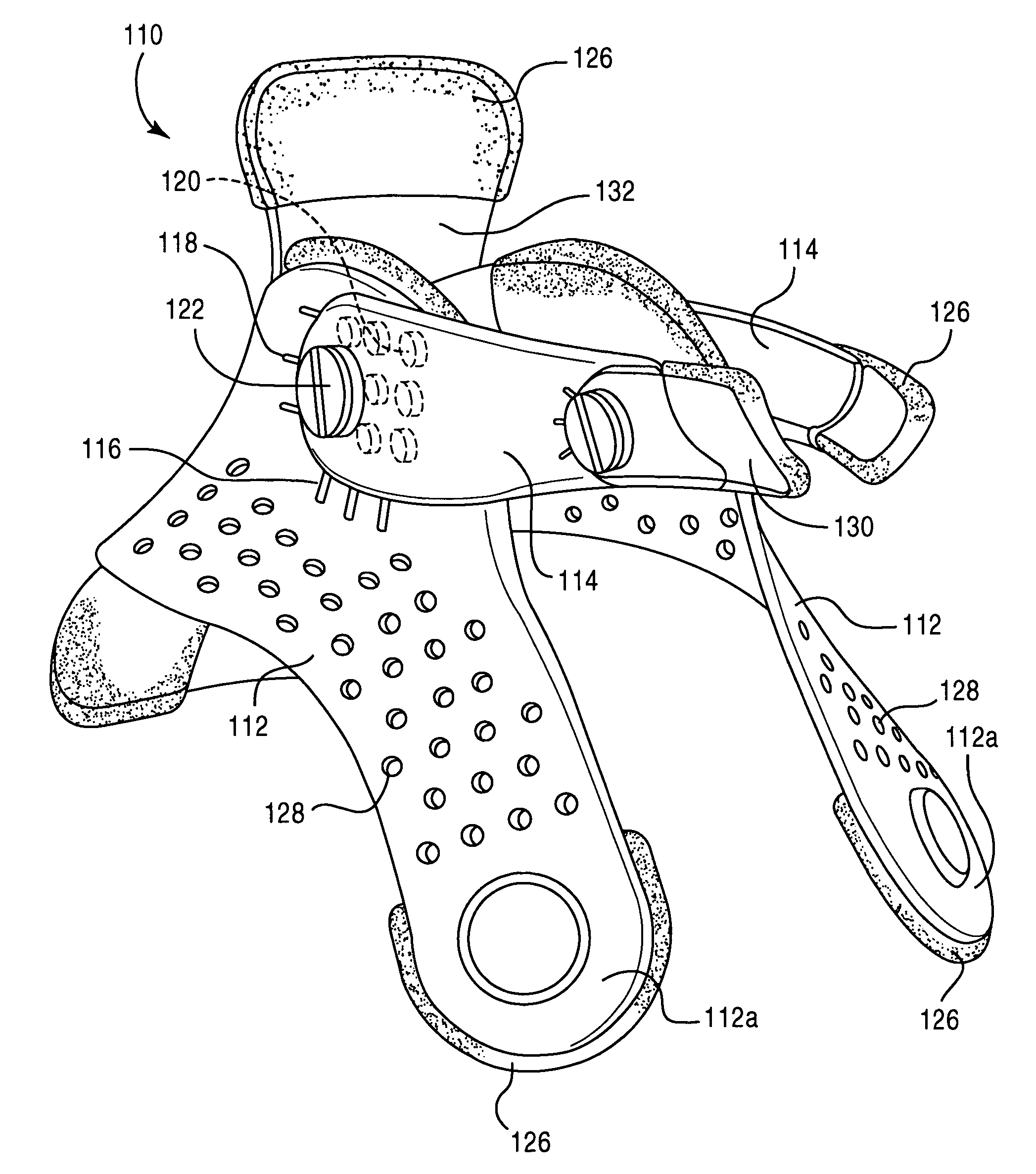
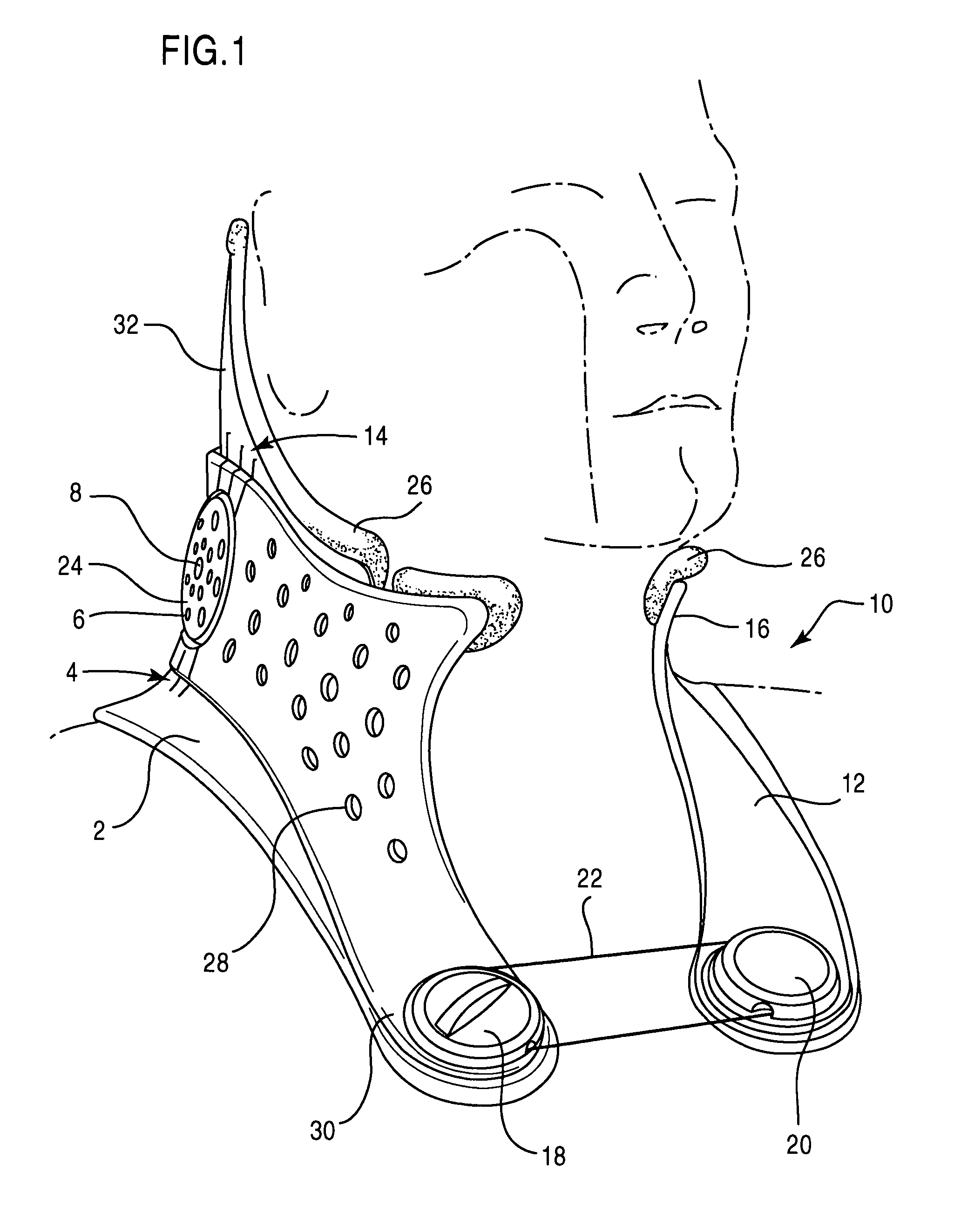
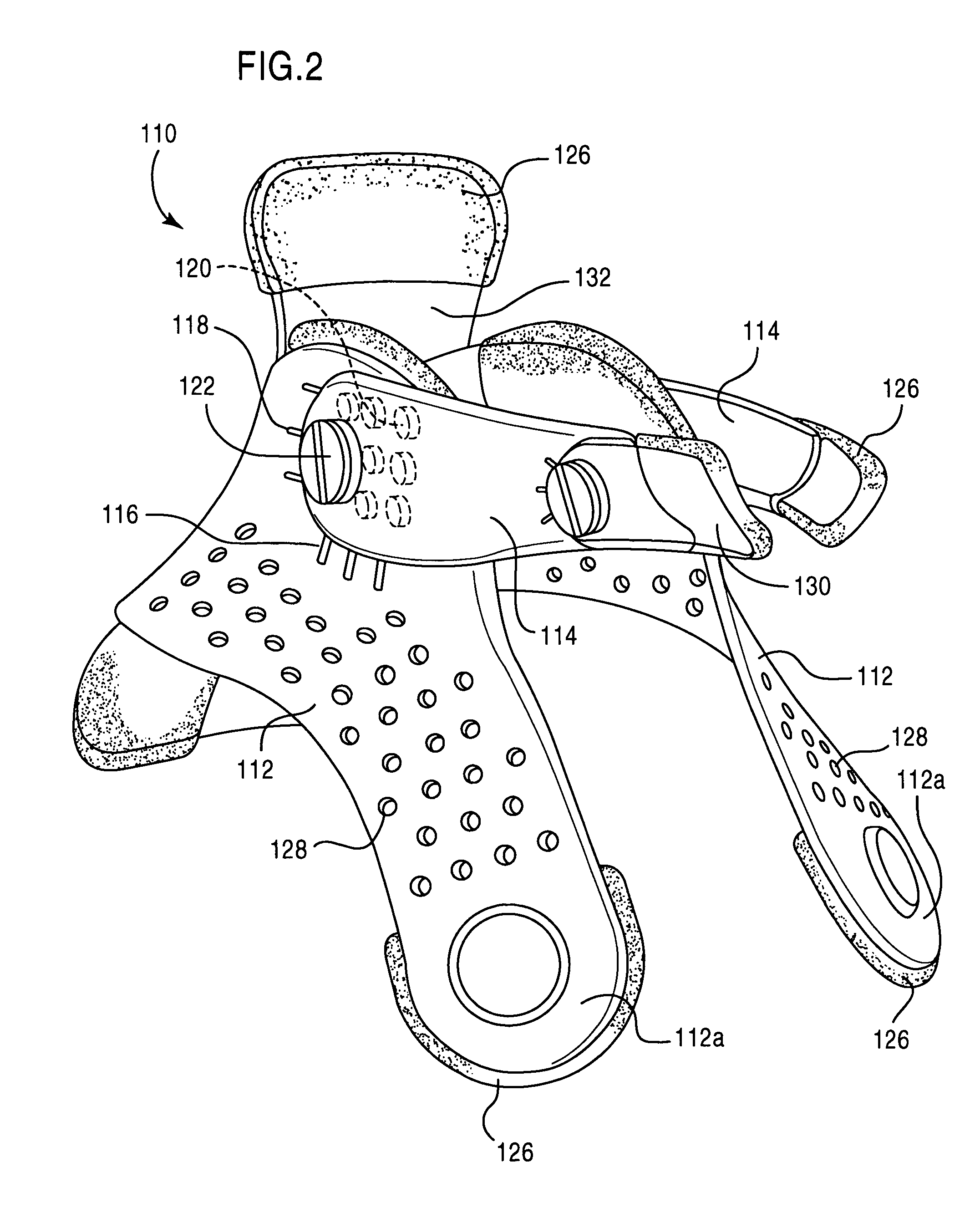
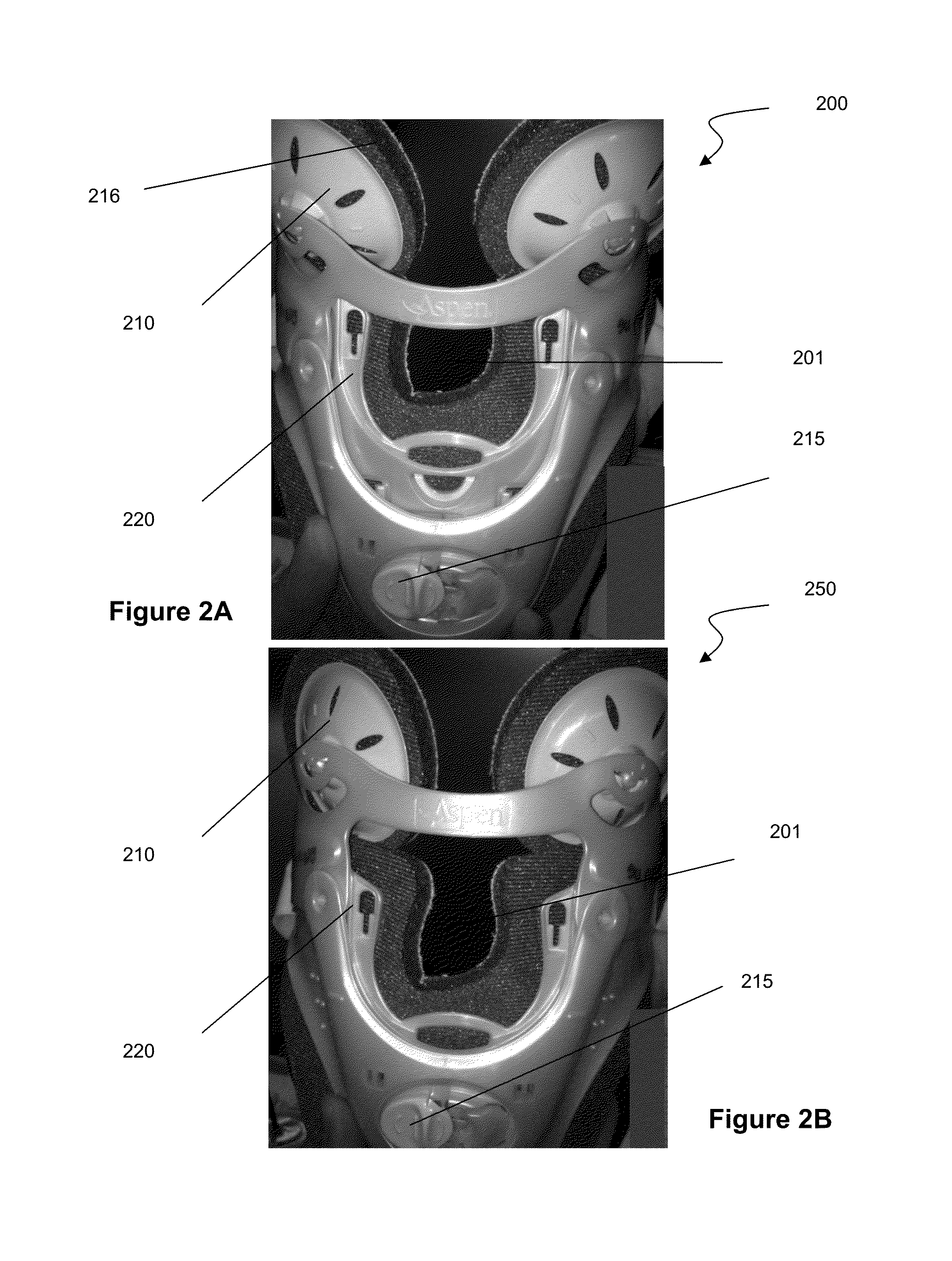
Cervical collar spinal height adjustment system
Neck braces having versatile rear braces are provided. Some rear braces comprise various components including a rear panel having notches, a height adjustment mechanism, and at least one occipital lobe support. Each component can be movably attached to another component via a fastener (e.g., ball snap, snap connector, etc.), thereby allowing one component to rotate, tilt or otherwise move in relation to the other component.
Owner:FIJI MFG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com