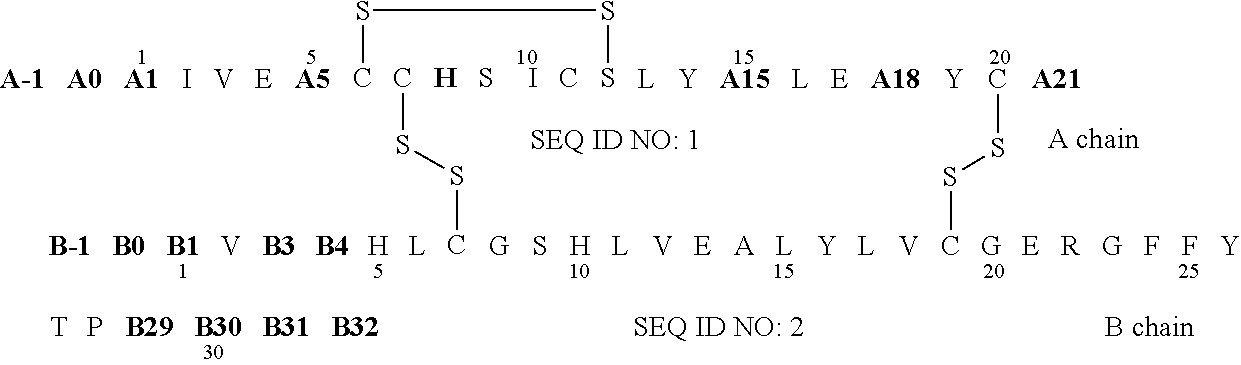Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
165 results about "Insulin analog" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An insulin analog is an altered form of insulin, different from any occurring in nature, but still available to the human body for performing the same action as human insulin in terms of glycemic control. Through genetic engineering of the underlying DNA, the amino acid sequence of insulin can be changed to alter its ADME (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion) characteristics. Officially, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) refers to these as "insulin receptor ligands", although they are more commonly referred to as insulin analogs.
Stabilized insulin formulations
InactiveUS6852694B2Easy to separateBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsINSULIN PREPARATIONSEndocrinology
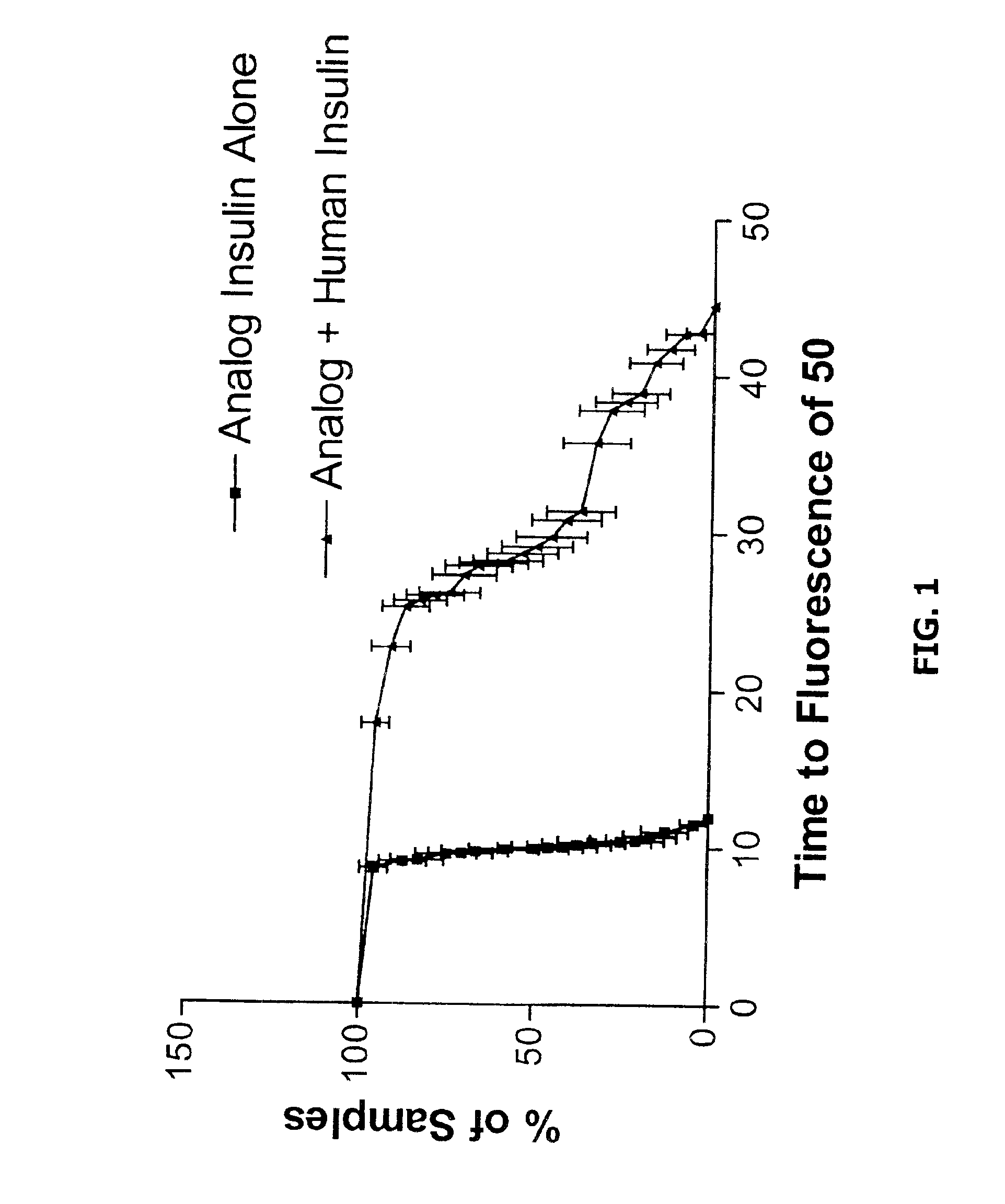
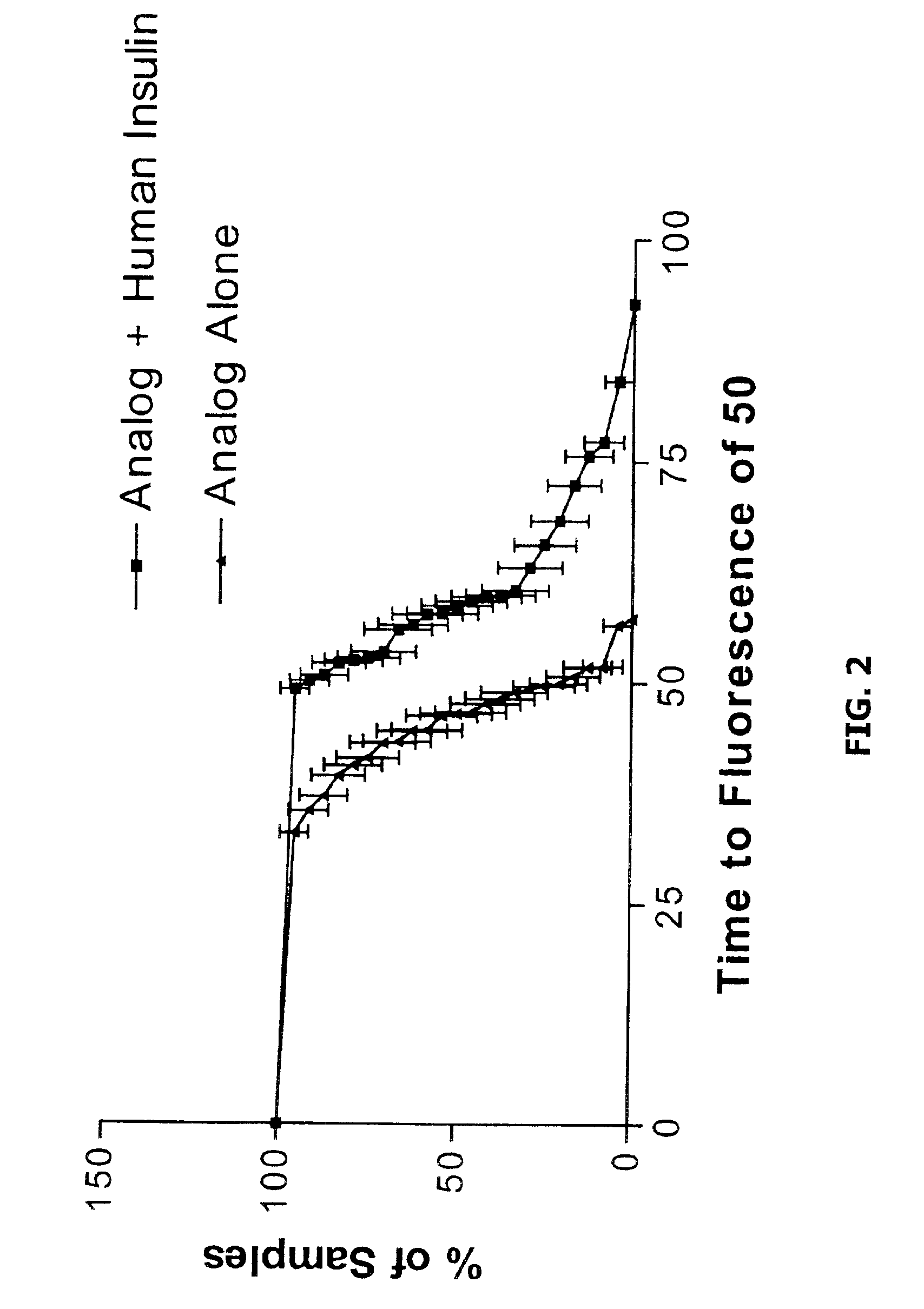
The present invention is directed to stabilized insulin composition comprising a mixture of insulin species such as insulin and an insulin analog. As disclosed herein, insulin compositions comprising a mixture of insulin and insulin analog species form heterodimeric complexes having a greater stability than the homodimeric complexes formed in compositions comprising single insulin species. Consequently, the present invention provides methods for stabilizing insulin molecules, methods for identifying stable heterodimeric insulin complexes and stabilized insulin compositions.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Acidic insulin preparations having improved stability
ActiveUS7476652B2Improve stabilityHigh stressOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMetabolitePreservative
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical formulation comprising a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of insulin, an insulin metabolite, an insulin analog, an insulin derivative and combinations thereof; a surfactant or combinations of two or more surfactants; optionally a preservative or combinations of two or more preservatives; and optionally an isotonicizing agent, buffers or further excipients or combinations thereof, the pharmaceutical formulation having a pH in the acidic range.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Insoluble compositions for controlling blood glucose
InactiveUS6531448B1Easy to controlReduce rateBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineDivalent metal
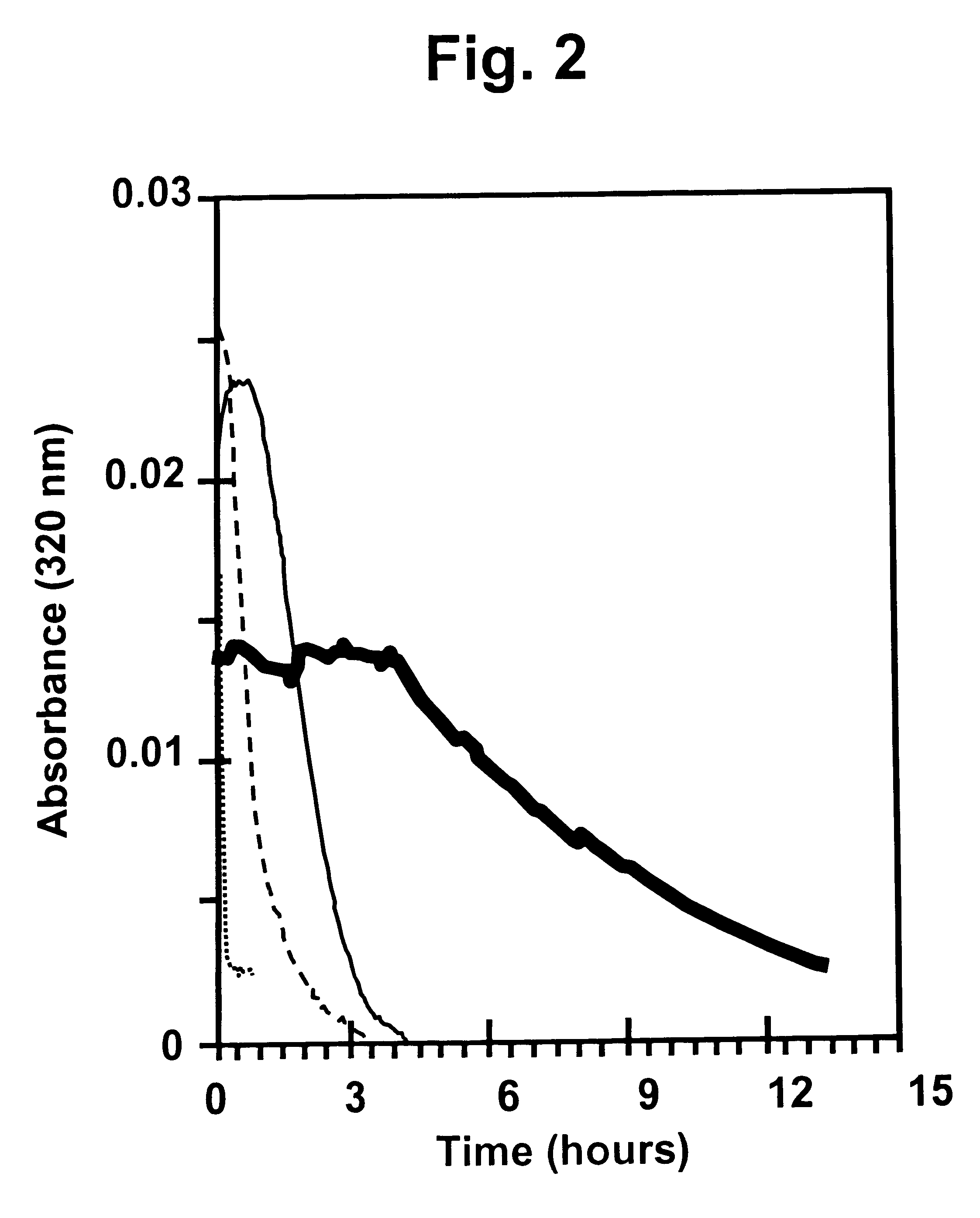
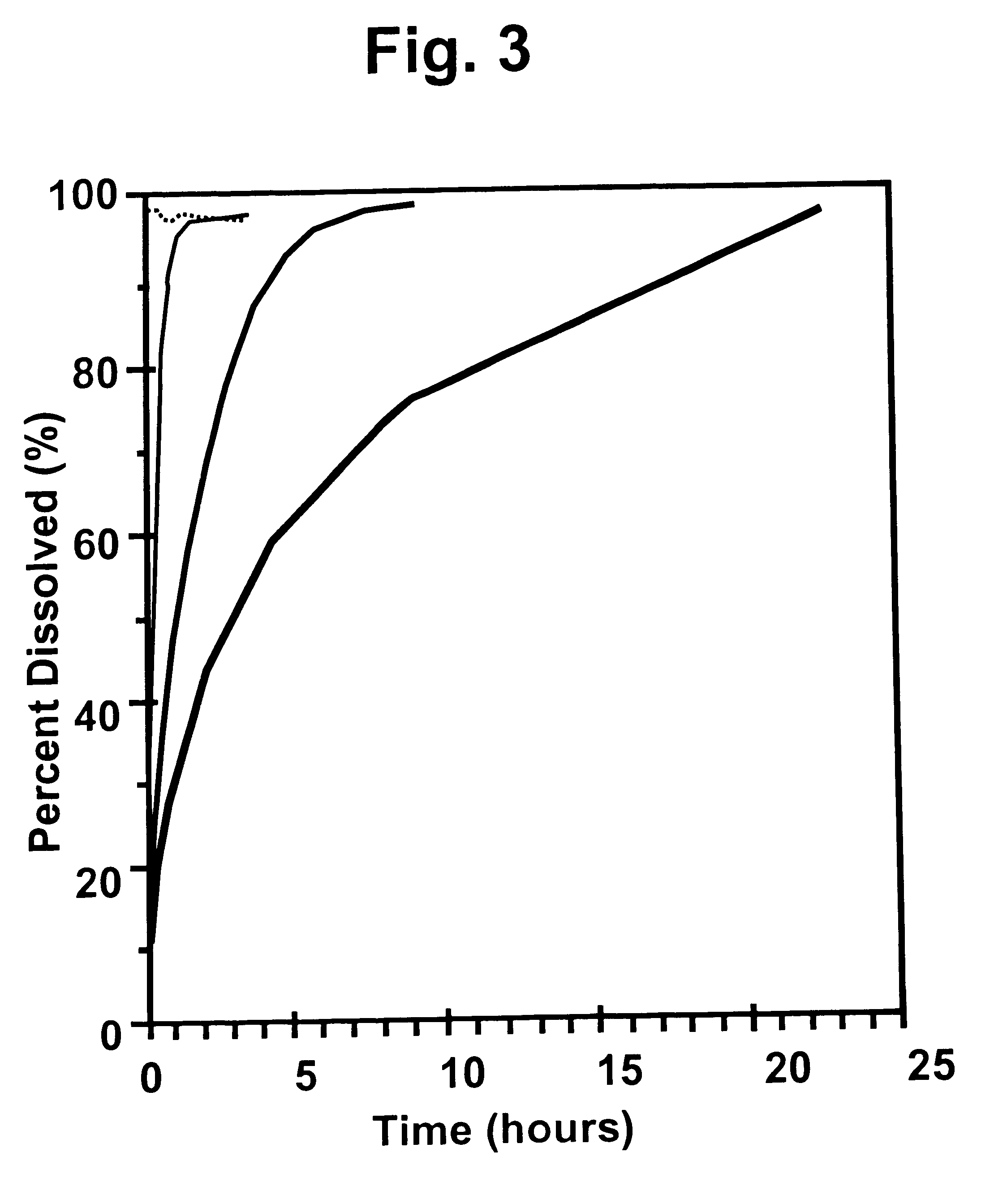
The present invention relates to insoluble compositions comprising a protein selected from the group consisting of insulin, insulin analogs, and proinsulins; a derivatized protein selected from the group consisting of derivatized insulin, derivatized insulin analog, and derivatized proinsulin; a complexing compound; a hexamer-stabilizing compound; and a divalent metal cation. Formulations of the insoluble composition are suitable for both parenteral and non-parenteral delivery for treating hyperglycemia and diabetes. Microcrystal forms of the insoluble precipitate are pharmaceutically analogous to the neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin crystal form. Surprisingly, it has been discovered that suspension formulations of such insoluble compositions possess unique and controllable dissolution properties that provide therapeutically advantageous glucodynamics compared with insulin NPH formulations.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Crystalline compositions for controlling blood glucose
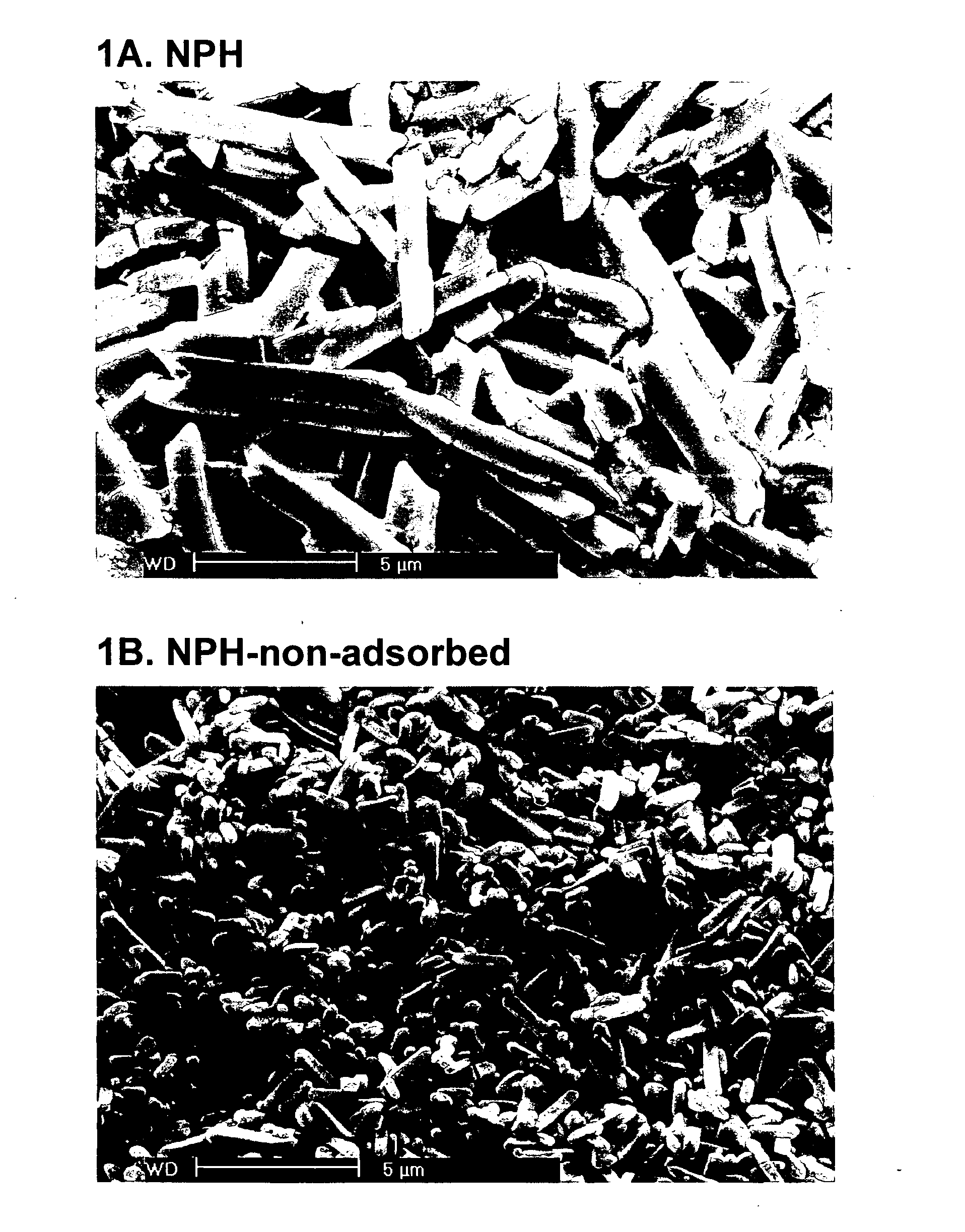
The present invention relates to insulin crystals formed from zinc, protamine, a hexamer-stabilizing compound, and a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of insulin, an insulin analog, and a derivatized insulin. The crystals are suitable for administering to a patient for control of blood glucose levels. The crystals have been derived from the neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH) form in a process utilizing precisely determined protamine concentrations and fortification of NPH crystals formed at a first lower concentration of protamine to achieve a second higher concentration of protamine.
Owner:BRADER MARK LAURENCE +2
Pulmonary insulin crystals
InactiveUS20020198140A1Promote absorptionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsInsulin analogCrystal
The present invention provides methods and compositions for treating diabetes by administering acylated insulin or an acylated insulin analog via a pulmonary route. The insulin or insulin analog may be in the form of a dry powder or a solution.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Crystalline compositions for controlling blood glucose
InactiveUS20050054818A1Easily resuspendedPose of reactionPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsGlucose polymersD-Glucose
The present invention relates to a process for forming non-adsorbed insulin crystals from zinc, protamine, a hexamer-stabilizing compound, and a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of insulin, an insulin analog, a derivatized insulin, and a derivatized insulin analog. The crystals are suitable for administering to a patient for control of blood glucose levels. The crystals are formed in a process utilizing precisely determined protamine concentrations.
Owner:BRADER MARK LAURENCE +1
Magnesium Compositions for Modulating the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Insulin and Insulin Analogs, and Injection Site Pain
ActiveUS20140113856A1Improved injection site tolerabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderEthylenediamineMagnesium salt
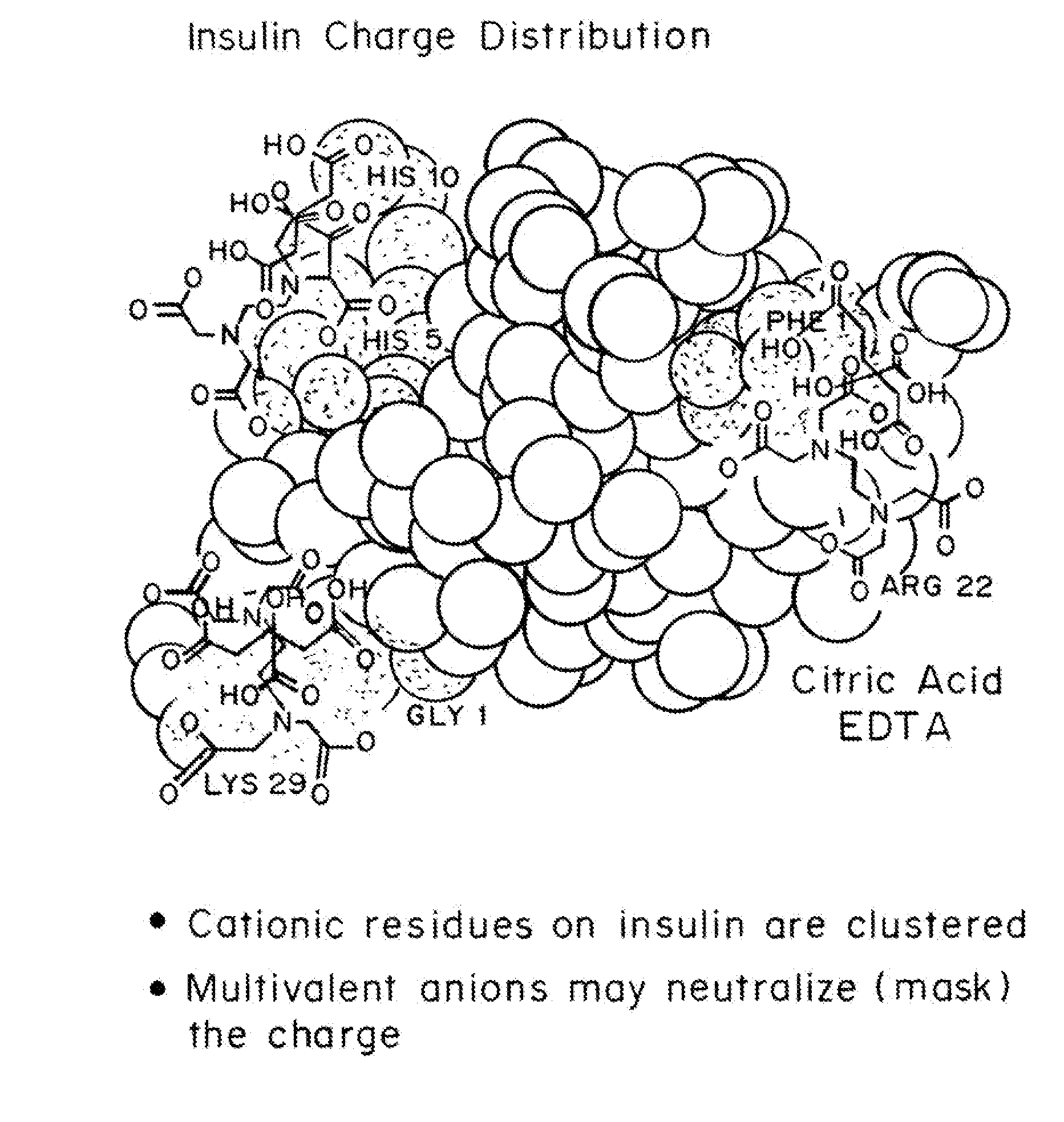
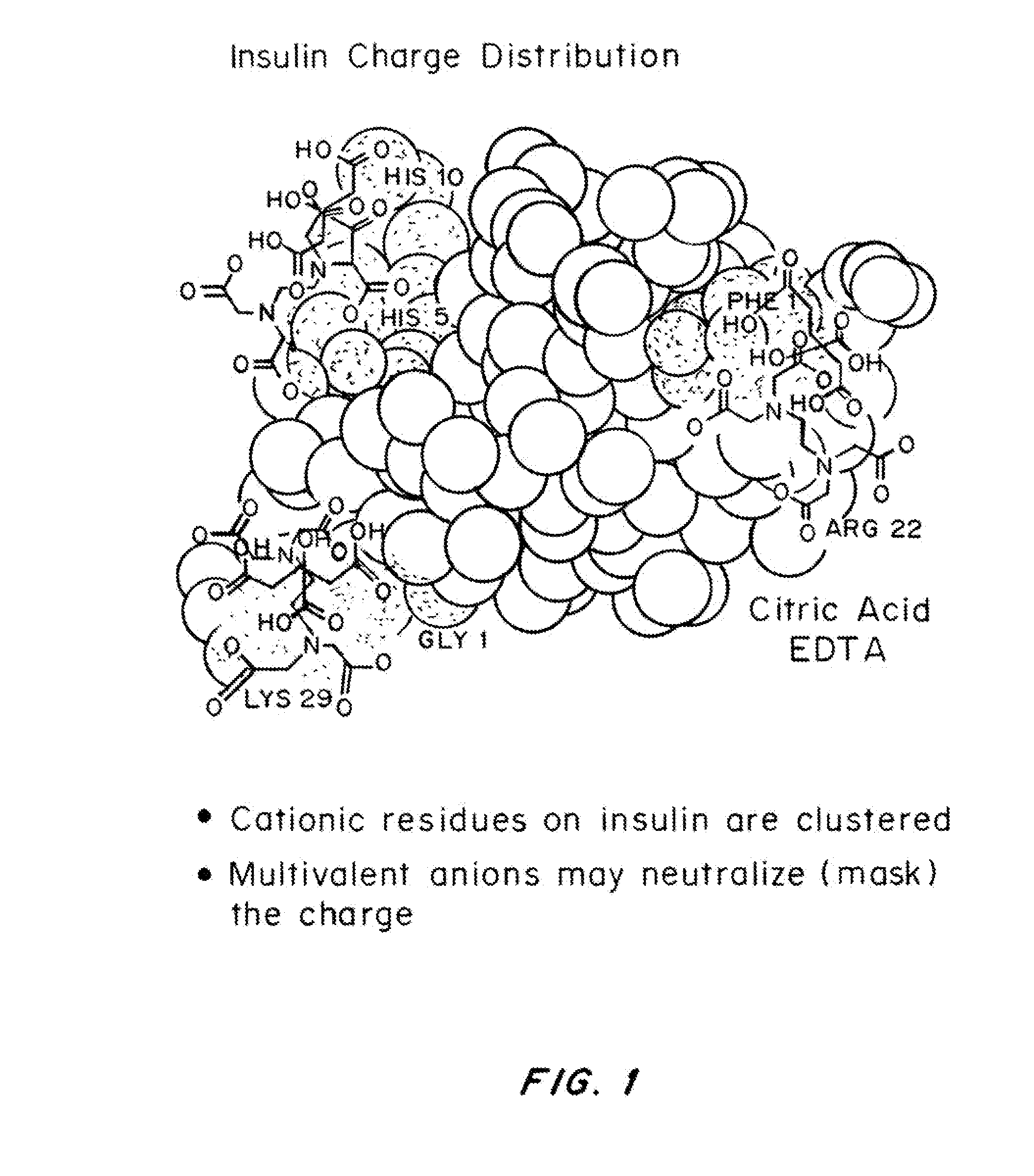
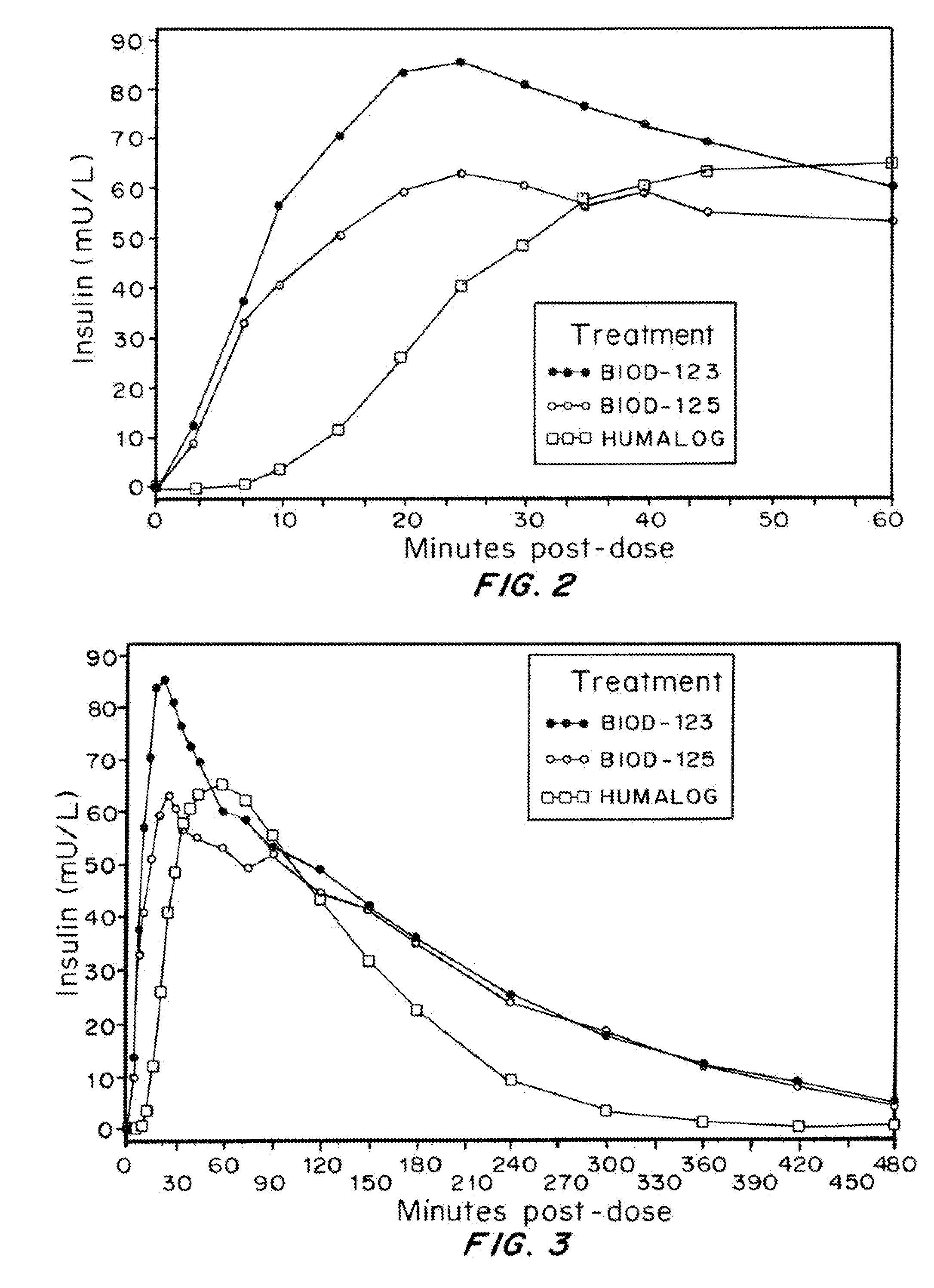
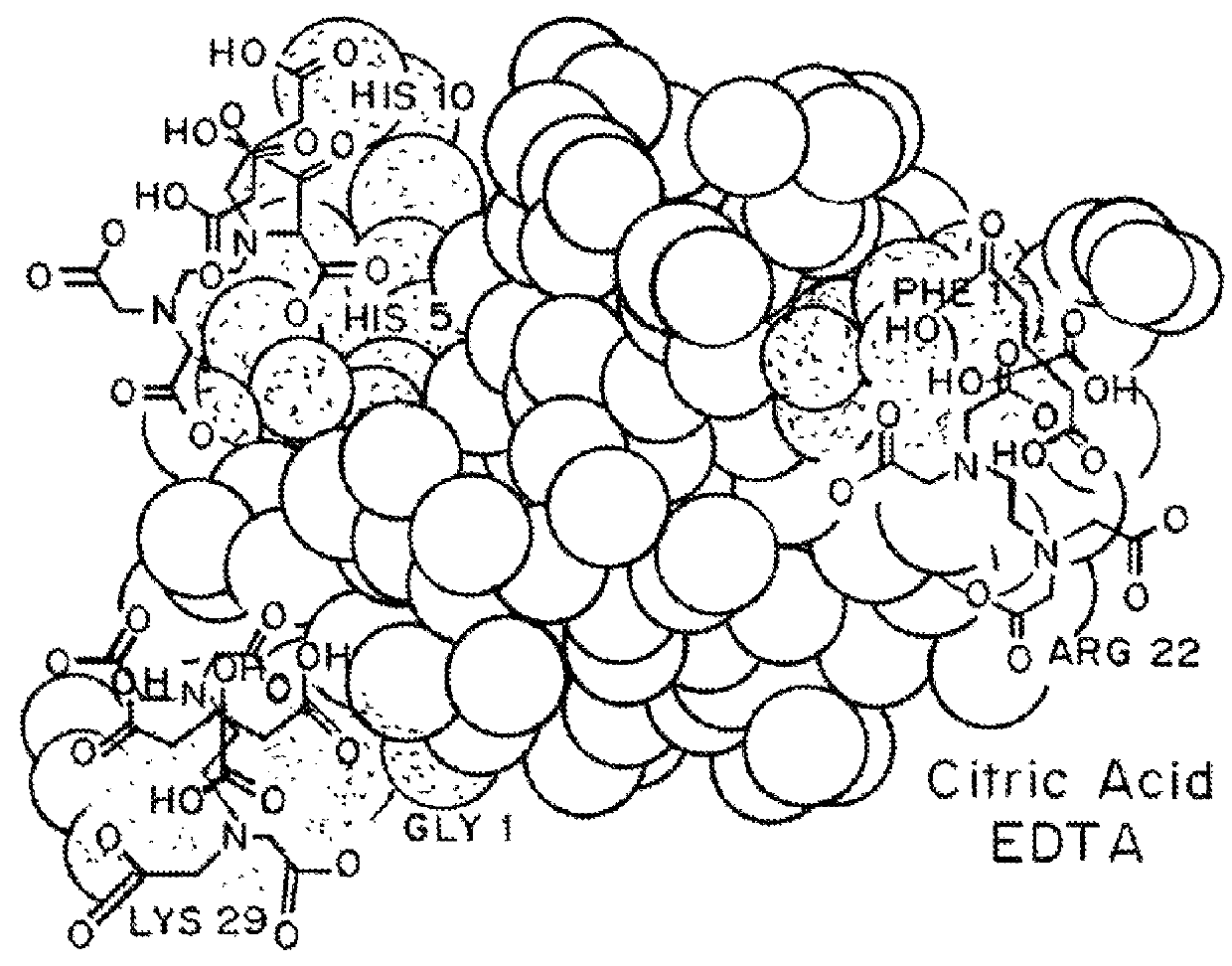
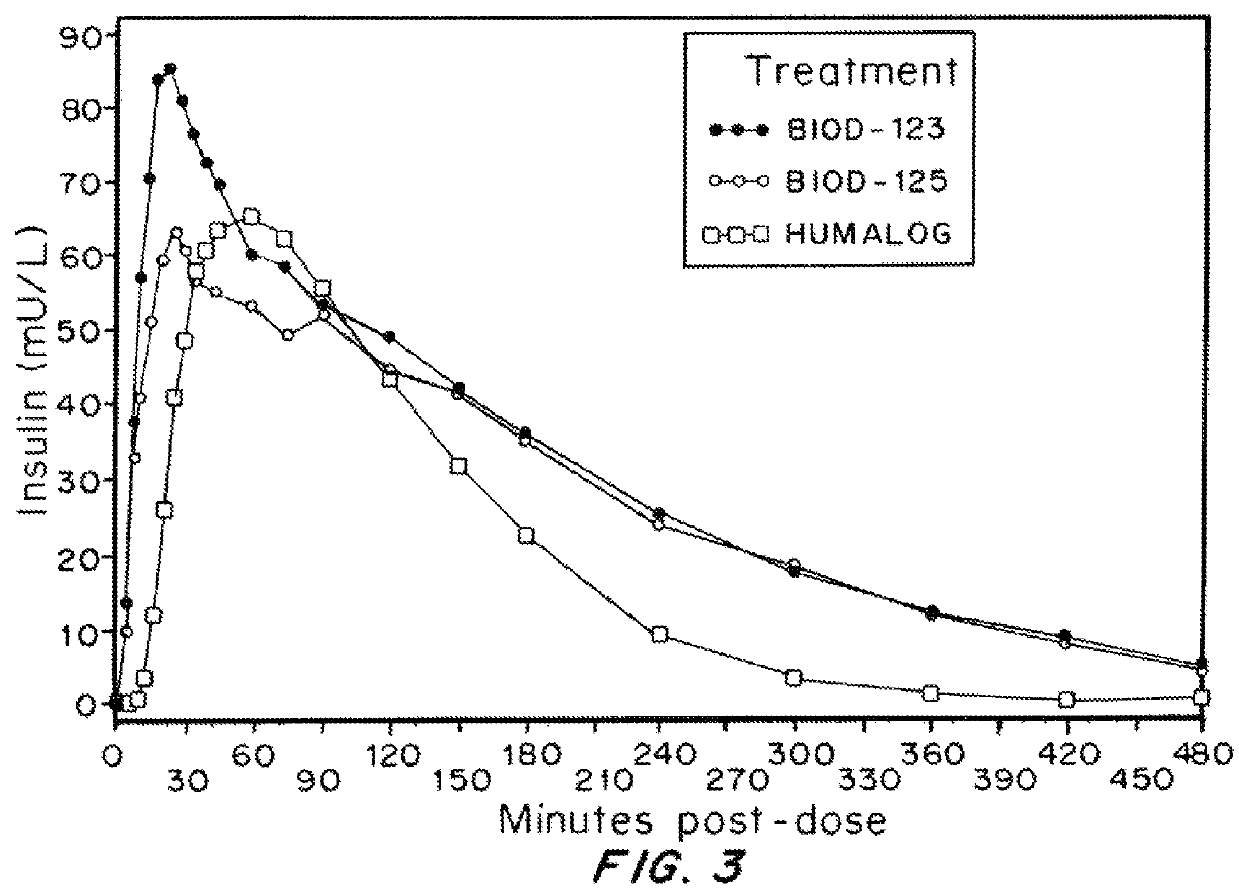
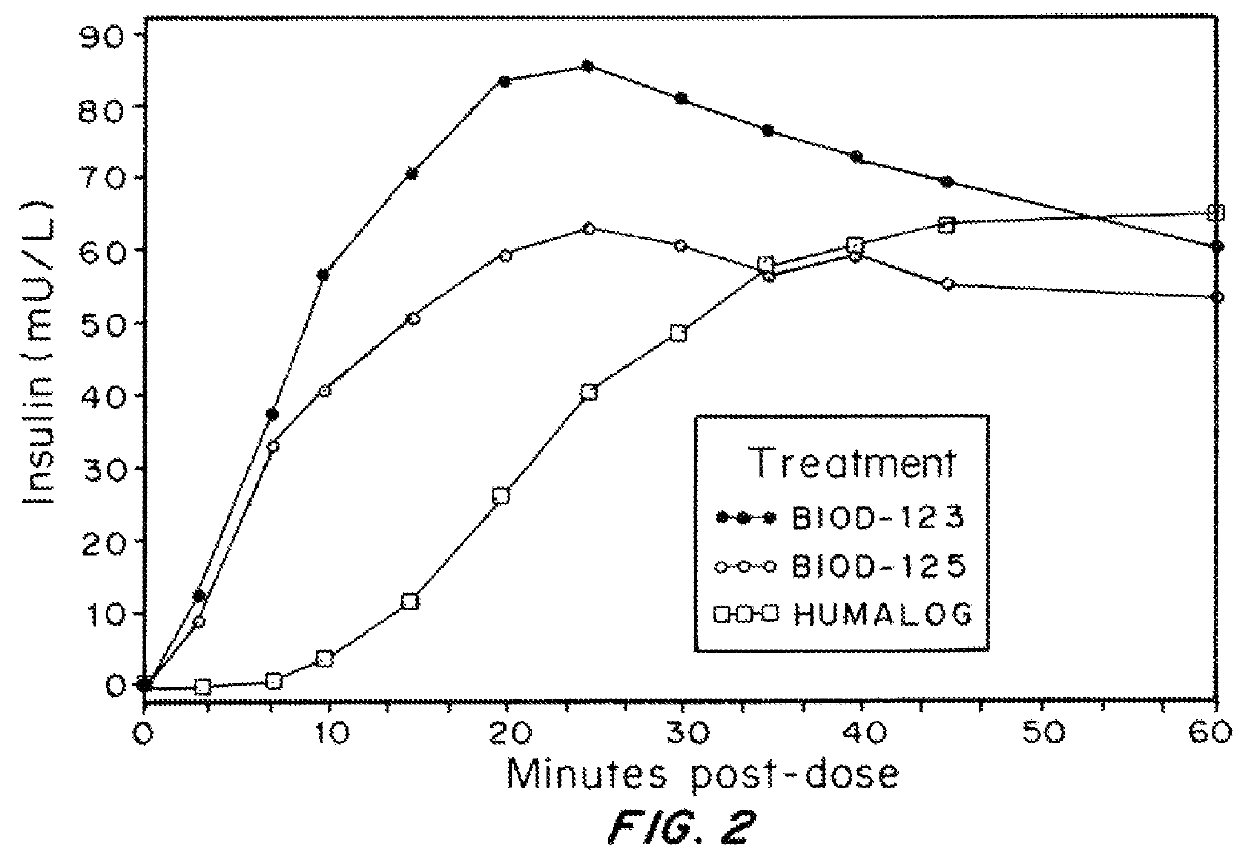
Compositions and methods for modulating injection site pain associated with rapid acting injectable insulin formulations have been developed for subcutaneous injection. The formulations contain insulin in combination with a zinc chelator such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (“EDTA”), a dissolution / stabilization agent such as citric acid, a magnesium salt, and, optionally, additional excipients. New presentations include rapid acting concentrated insulin formulations and a way to enhance the absorption of commercially available rapid acting analog formulations by mixing them with a vial containing dry powder excipients that accelerate their absorption. Devices for mixing excipient and insulin together at the time of administration, while minimizing residence time of the mixture, are also described.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Stable insulin formulations
InactiveUS6906028B2Improve stabilityEasy to separatePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderArginineBuffering agent
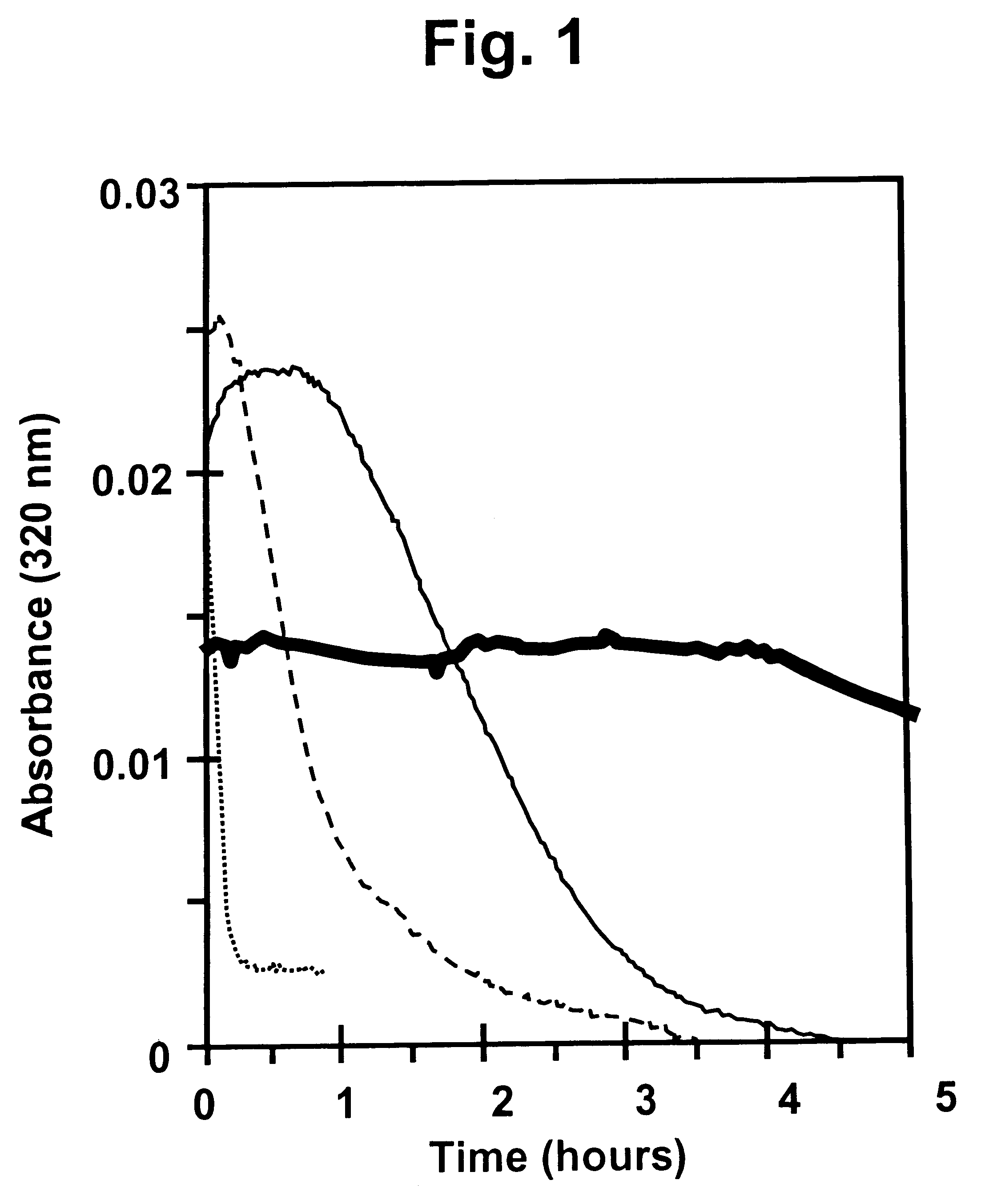
The present invention provides a monomeric insulin analog formulation stabilized against aggregation in which the buffering agent is either TRIS or arginine. The stable formulations of the present invention are useful for treating diabetes, and are particularly advantageous in treatment regimes requiring lengthy chemical and physical stability, such as, in continuous infusion systems.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Stabilized acylated insulin formulations
InactiveUS20010041786A1Peptide/protein ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsFatty acidAqueous solution
A storage stable formulation comprising an aqueous solution suitable for parenteral delivery, particularly as an injectable formulation to a patient, preferably having a pH of 7.1 to 7.6, containing a fatty acid-acylated insulin or a fatty acid-acylated insulin analog and stabilized using zinc and preferably a phenolic compound.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Albumin-insulin fusion proteins
ActiveUS20080057004A1Efficient deliveryPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsInsulin activityIn vivo
Owner:TEVA BIOPHARM USA
Insoluble compositions for controlling blood glucose
InactiveUS20030144181A1Easy to controlReduce ratePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicineDivalent metal
The present invention relates to insoluble compositions comprising a protein selected from the group consisting of insulin, insulin analogs, and proinsulins; a derivatized protein selected from the group consisting of derivatized insulin, derivatized insulin analog, and derivatized proinsulin; a complexing compound; a hexamer-stabilizing compound; and a divalent metal cation. Formulations of the insoluble composition are suitable for both parenteral and non-parenteral delivery for treating hyperglycemia and diabetes. Microcrystal forms of the insoluble precipitate are pharmaceutically analogous to the neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin crystal form. Surprisingly, it has been discovered that suspension formulations of such insoluble compositions possess unique and controllable dissolution properties that provide therapeutically advantageous glucodynamics compared with insulin NPH formulations.
Owner:BRADER MARK LAURENCE
Insoluble insulin compositions
The present invention relates to an insoluble composition comprising an acylated protein selected from the group consisting of acylated insulin, acylated insulin analogs and acylated proinsulin and preparations thereof. The formulations are suitable for parenteral or other delivery to a patient for prolonged control of blood glucose levels. More specifically, the present invention relates to compositions comprising an acylated protein complexed with zinc, protamine and a phenolic compound such that the resulting microcrystals resemble the neutral protamine zinc (NPH) insulin crystalline form. Surprisingly; this acylated protein composition has been found to have therapeutically superior subcutaneous release pharmacokinetics, and longer and flatter glucose kinetics than currently marketed NPH insulin formulations. Furthermore, the crystals of the present invention retain some of the advantageous properties of NPH crystals, namely being able to be easily resuspended and also mixed with soluble insulin.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Fibrillation resistant proteins
ActiveUS20090304814A1Improve the immunityIncreased susceptibilityBiocideFungiFibrillationHistidine residue
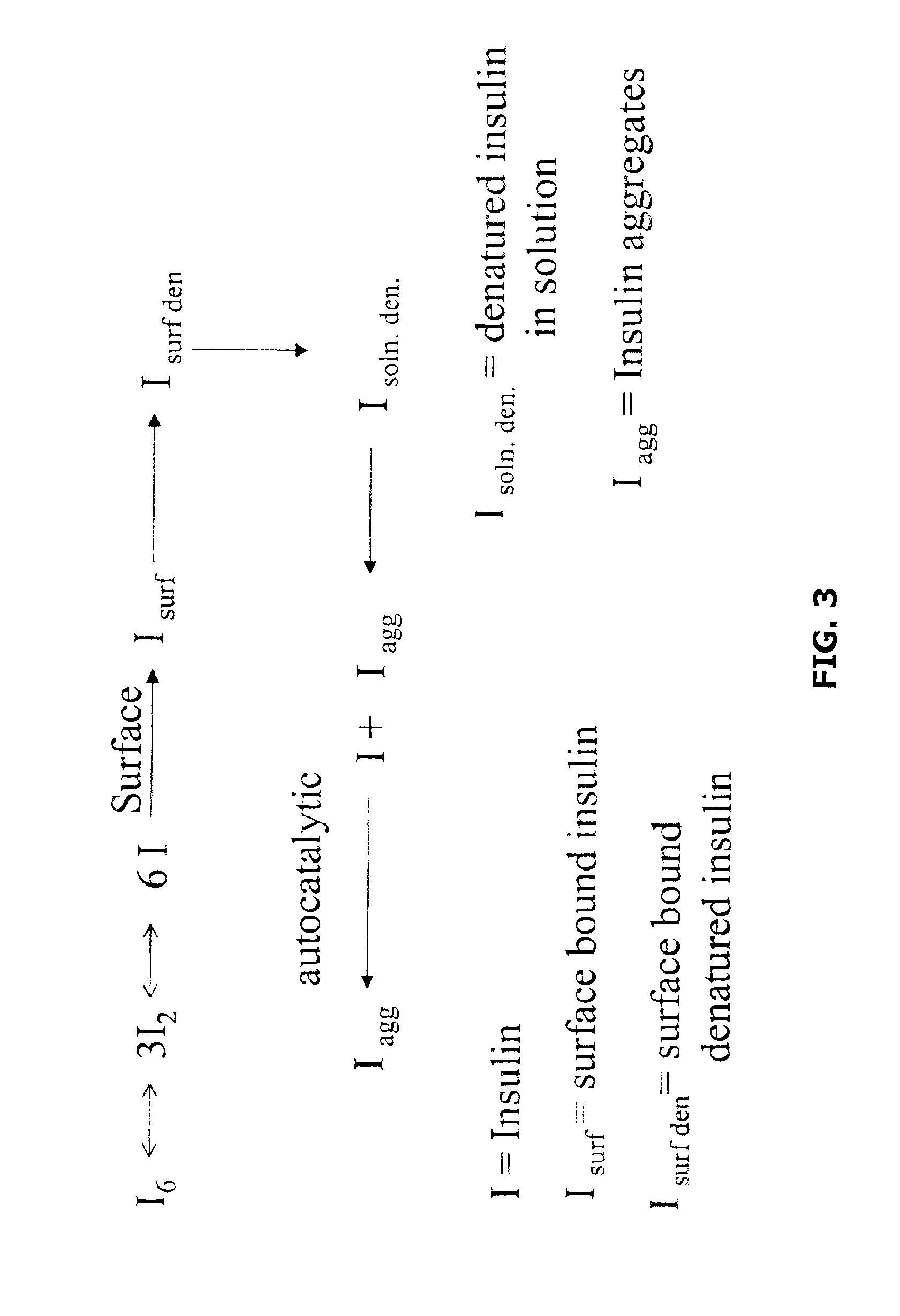
Protection of proteins against fibrillation may be afforded by introduction of certain histidine substitutions into the protein, such that a pair of histidines are present with sufficient spacing as to allow the histidines to coordinate with zinc. In the case of insulin, introduction of histidine residue substitutions at residues A4 and A8 together or a histidine residue substitution at residue B1, provides increased resistance to fibrillation while maintaining at least a majority of the activity of the insulin analogue. Introduction of a histidine residue substitution at residue A8 restores at least a portion of fibrillation resistance that may have been harmed by substitutions present on the B-chain such as those present in fast-acting insulins. Proteins protected by such histidine substitutions may be used to provide a pharmaceutical composition. A method of treating a patient includes administering a physiologically effective amount of the pharmaceutical composition to the patient.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Crystals of insulin analogs and processes for their preparation
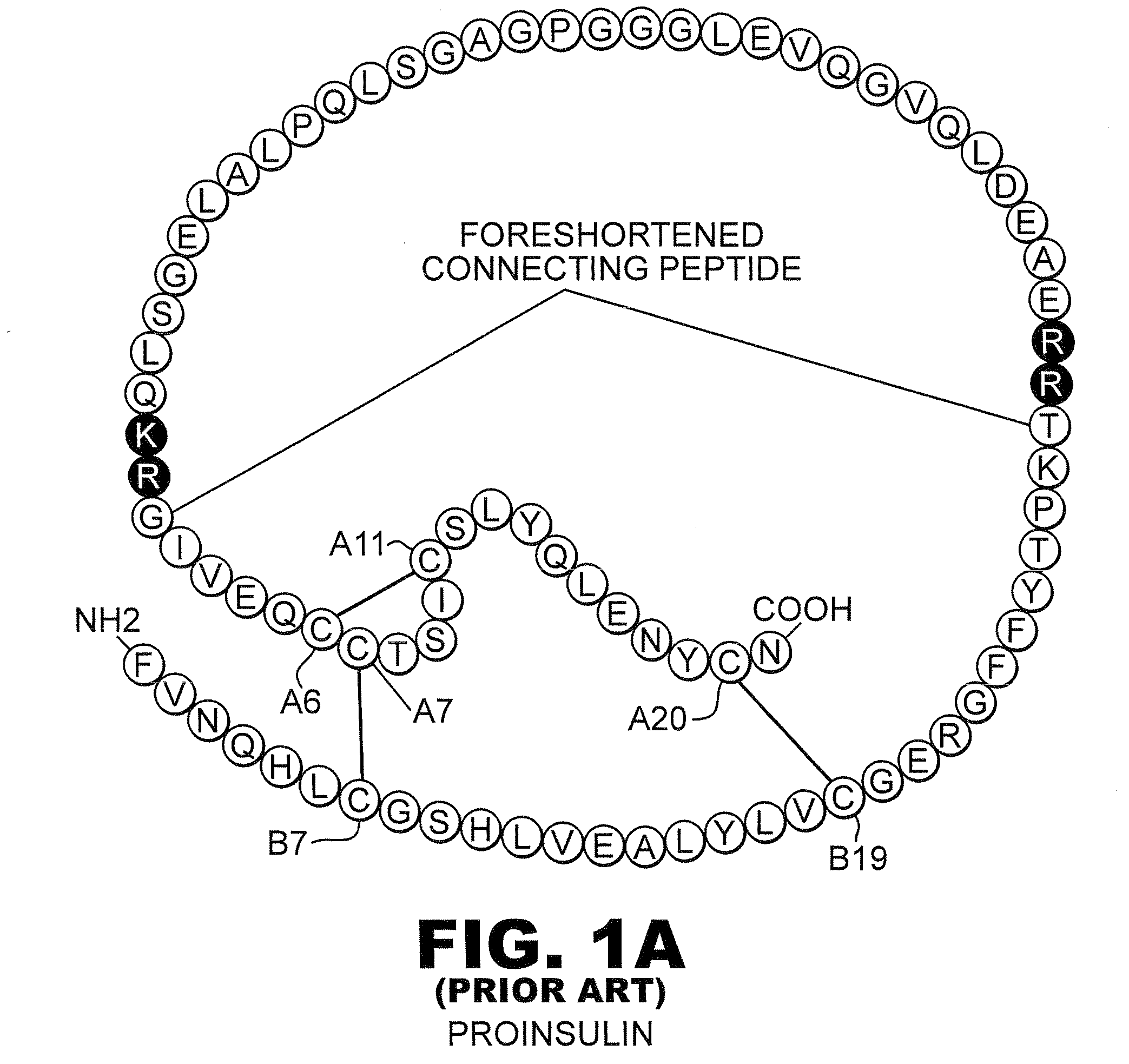
The invention relates to crystals of an insulin analog in which asparagine (Asn) in position B3 of the B chain is replaced by a naturally occurring basic amino acid residue and at least one amino acid residue in the positions B27, B28 or B29 of the B chain is replaced by another naturally occurring neutral or acidic amino acid residue, where phenylalanine (Phe) in position B1 of the B chain can optionally be absent, the crystals being present in the space group R3 (No. 146) with the cell axes A=81.5 ű1 Å and C=33.3 ű1 Å, their preparation and use, and a pharmaceutical composition comprising these crystals.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Multiple agent diabetes therapy
InactiveUS7323543B2Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsActrapid insulinPancreatic hormone
A pharmaceutical composition includes at least two of agents I)-iii), wherein agent i) is selected from the group consisting of an insulin, an insulin analog, a physiologically active fragment of said insulin and a physiologically active fragment of said insulin analog, agent ii) is selected from the group consisting of an insulin-related peptide, an insulin-related peptide analog, a physiologically active insulin-related peptide fragment and a physiologically active insulin-related peptide analog fragment, and agent iii) is an insulin sensitizer.
Owner:MINIMED
Formulations of insulin
InactiveUS7387996B2Superior long-term physical stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBiochemistryINSULIN PREPARATIONS
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Acidic insulin preparations with improved stability
ActiveUS20050171009A1Improve long-term stabilityIncrease pressureBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMetaboliteMedicine
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical formulation comprising a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of insulin, an insulin metabolite, an insulin analog, an insulin derivative and combinations thereof; a surfactant or combinations of two or more surfactants; optionally a preservative or combinations of two or more preservatives; and optionally an isotonicizing agent, buffers or further excipients or combinations thereof, the pharmaceutical formulation having a pH in the acidic range.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Novel insulin derivatives having an extremely delayed time-action profile
InactiveUS20110173722A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganismsInsulin A ChainCombinatorial chemistry
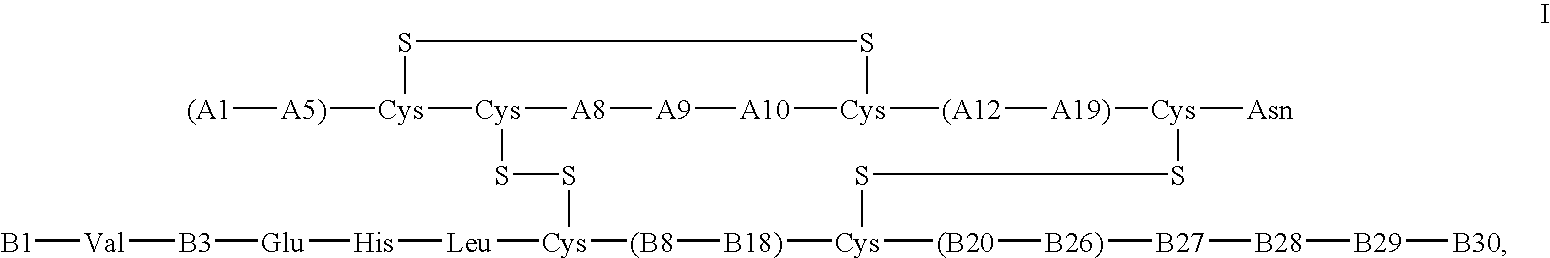
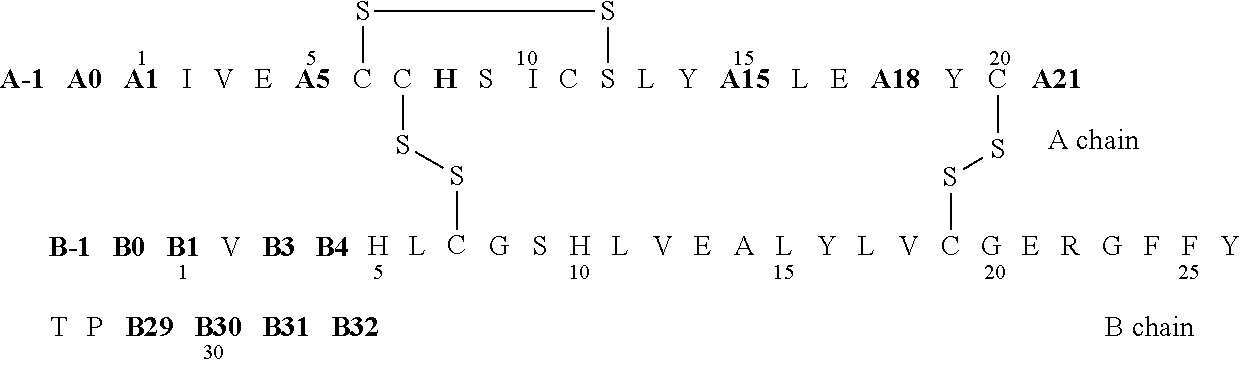
The invention relates to novel insulin analogs having a basal time-action profile, which are characterized by the addition and / or substitution of negatively and positively charged amino acid residues and by an amidation of the C-terminal carboxy group of the B chain and histidine in position 8 of the insulin A chain. The invention also relates to the production and use thereof.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Insulin analogs having protracted time action
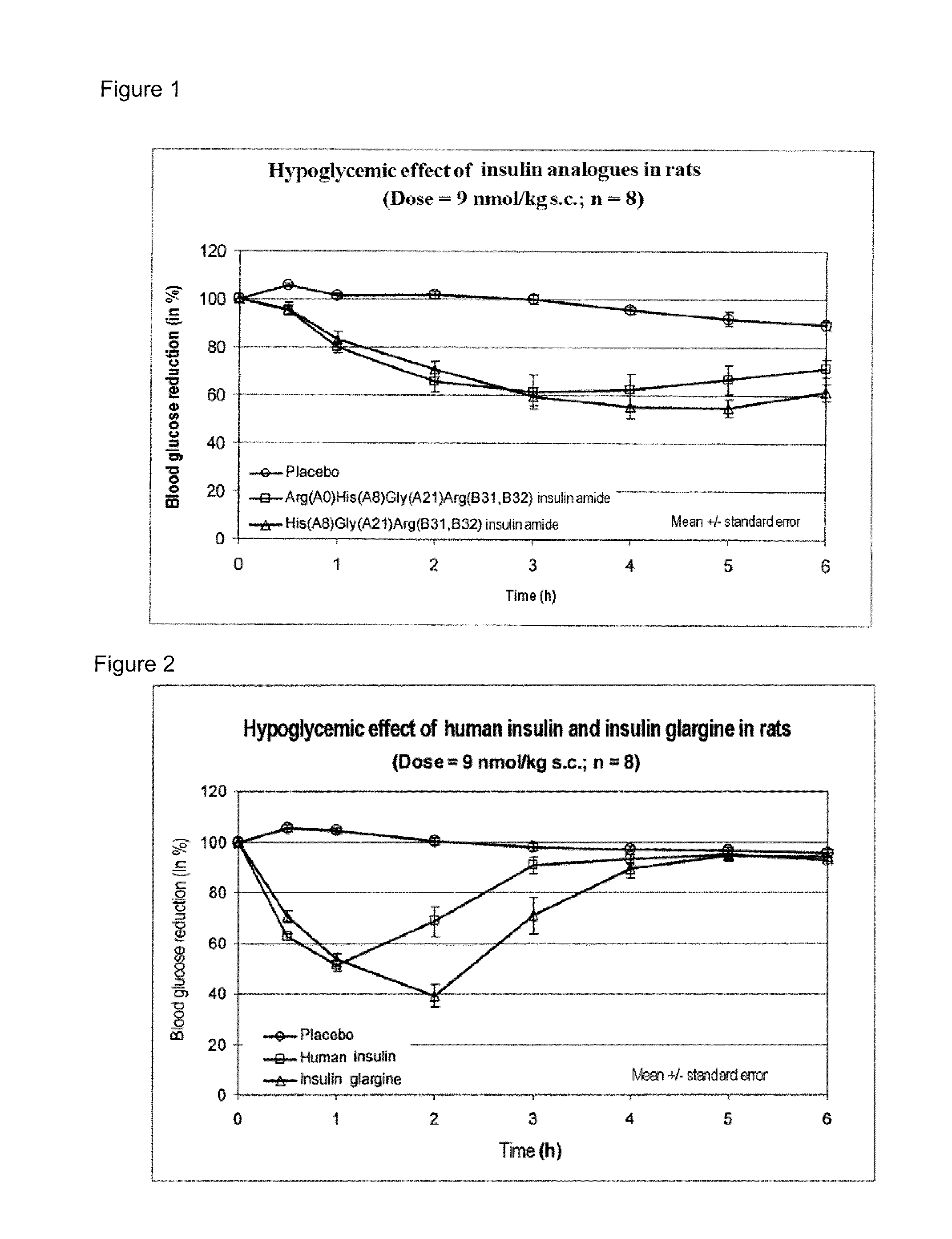
The present invention provides the insulin analog A0Arg A21Gly B31Arg B32Arg, which provides a protracted, even basal duration of action. The present invention also provides a method of treating diabetes mellitus comprising administering the insulin analog.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Stabilized polypeptide insulin receptor modulators
InactiveUS20160215036A1Increase helix stabilizationIncreased target affinitySenses disorderNervous disorderPharmaceutical drugPancreatic hormone
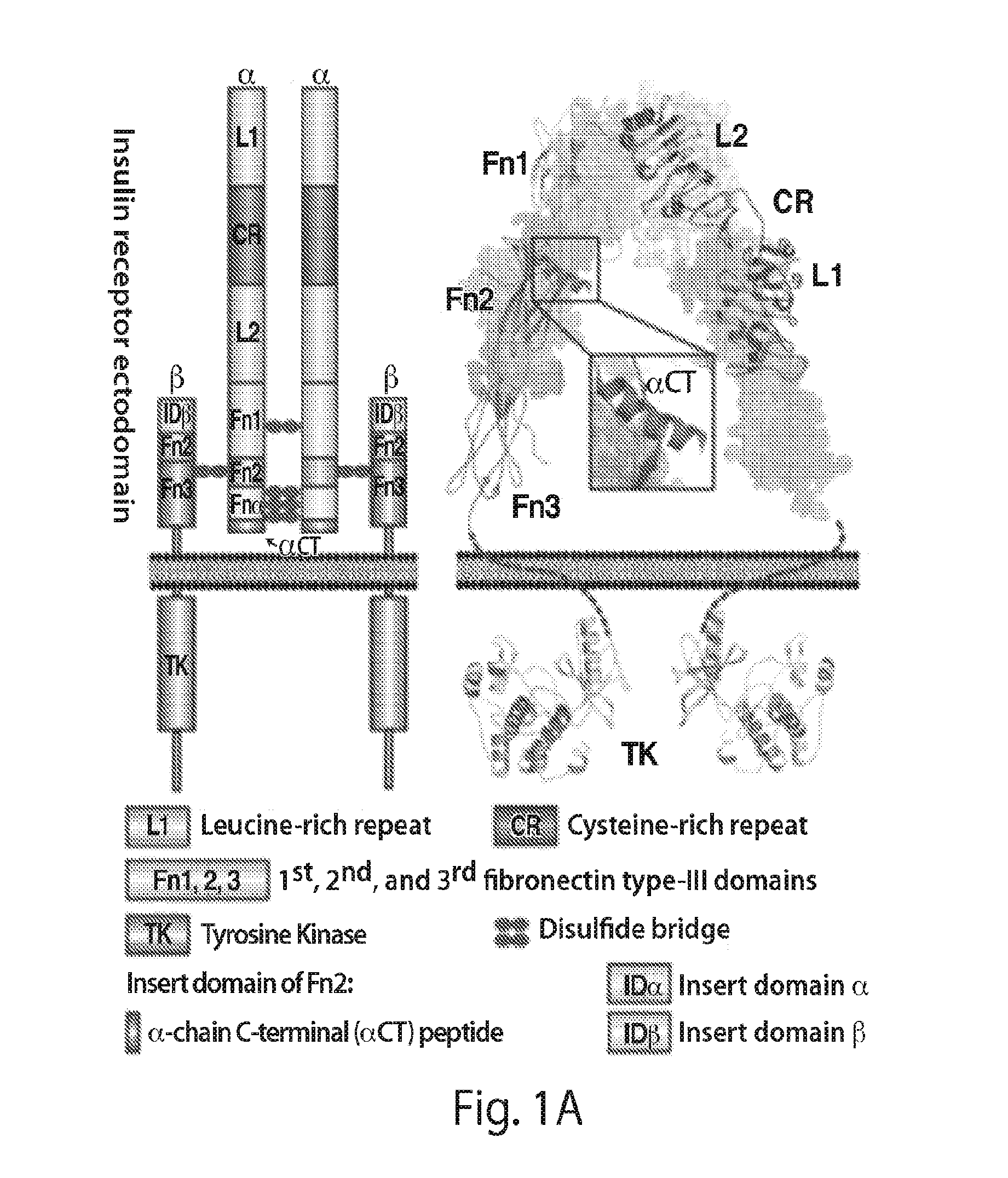
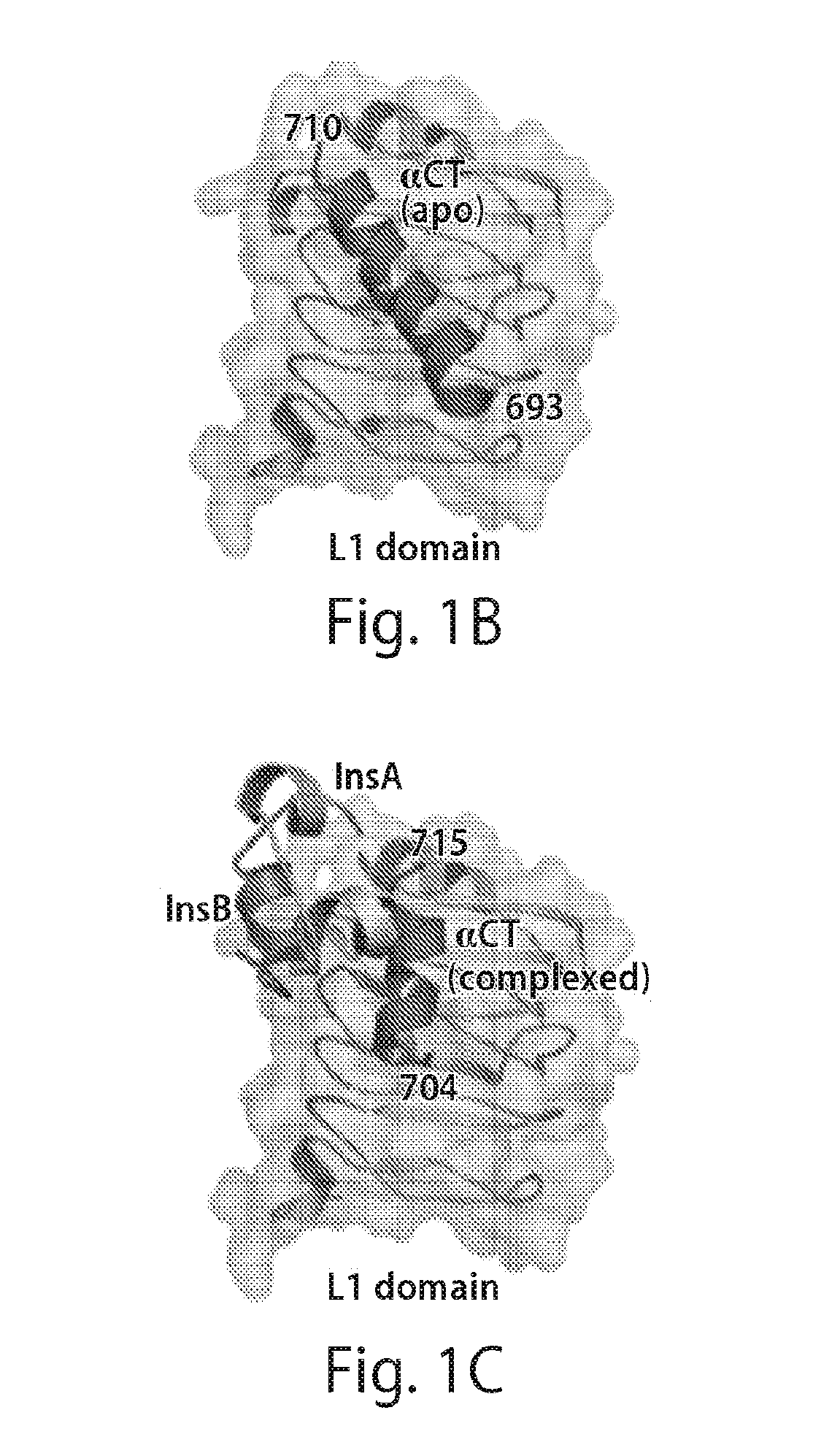
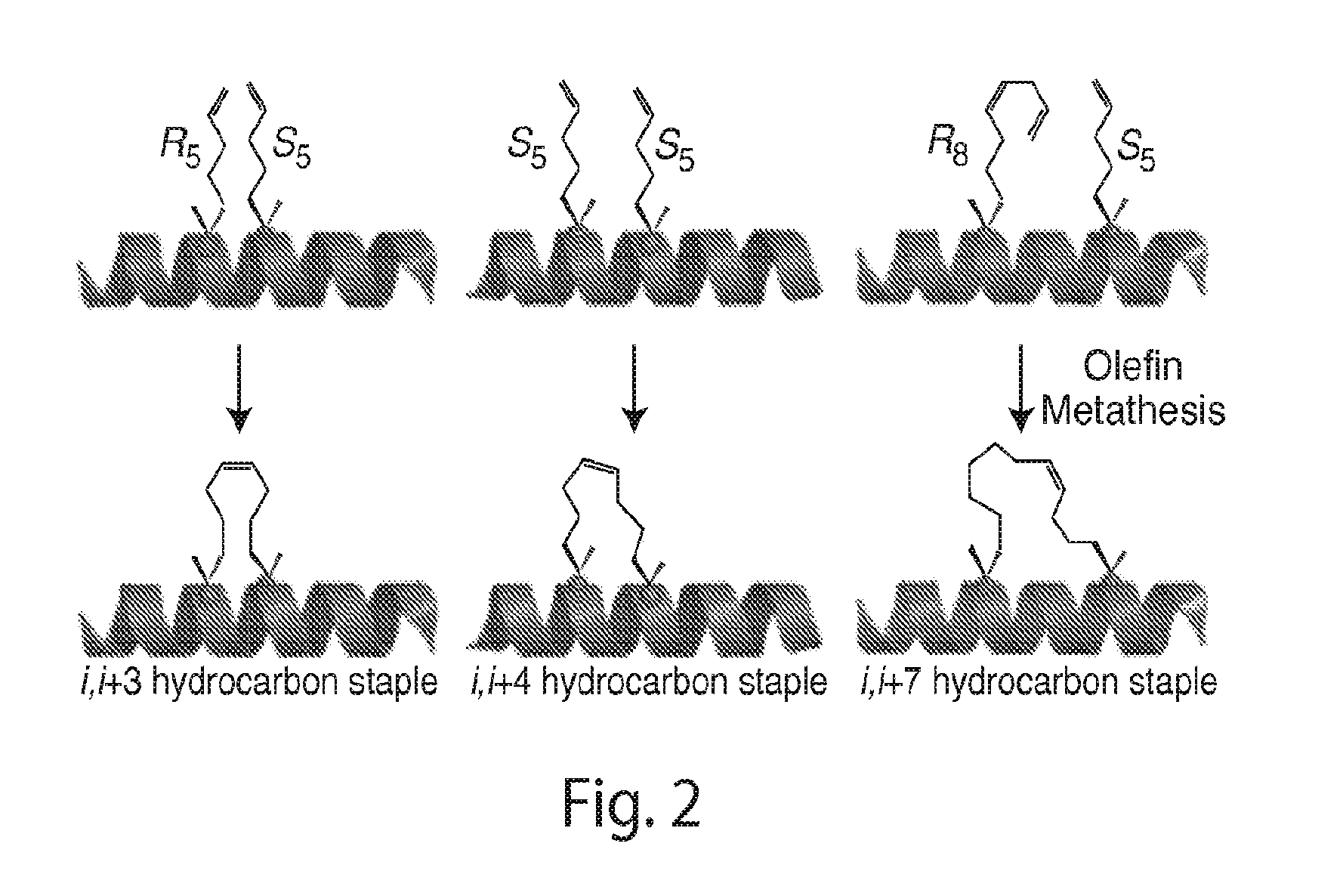
Provided herein are stabilized α-CT polypeptides comprising an alpha-helical segment, and wherein the polypeptide is of Formula (I-1) or Formula (I-2): Rf—[XAA]s—XA1—XA2—XA3—XA4—XA5—XA6—XA7—XA8—XA9—XA10—XA11—XA12—XA13—XA14—[XAA]t—Re (I-1) Rf—[XAA]s—XC1—XC2—XC3—XC4—XC5—XC6—XC7—XC8—XC9—XC10—XC11—XC12—XC13—XC14—XC15—XC16—XC17—XC18—XC19—XC20—[XAA]t—Re (I-2) wherein the α-CT polypeptide binds to the insulin receptor, and wherein the α-CT polypeptide includes at least one staple (i.e. two cross-linked amino acids) and / or at least one stitch (i.e. three cross-linked amino acids). Further provided are insulin analogues including the stapled or stitched α-CT polypeptides, pharmaceutical compositions thereof, methods of use, e.g., methods of treating a diabetic condition or complications thereof.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Stabilized Pharmaceutical Formulations of Insulin Analogues and/or Insulin Derivatives
ActiveUS20150216941A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical formulationInsulin Analogue
Owner:SANOFI SA
Stabilized acylated insulin formulations
A storage stable formulation comprising an aqueous solution suitable for parenteral delivery, particularly as an injectable formulation to a patient, preferably having a pH of 7.1 to 7.6, containing a fatty acid-acylated insulin or a fatty acid-acylated insulin analog and stabilized using zinc and preferably a phenolic compound.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Meal-time insulin analogues of enhanced stability
InactiveUS20110059887A1Increase propensityImprove stabilitySugar derivativesBacteriaInsulin A ChainWild type
A method treating a patient includes administering a physiologically effective amount of a fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to the patient. The fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof, contains an insulin A-chain sequence modified at position A8 and an insulin B-chain sequence or an analogue thereof. The fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue may exhibit thermodynamic stability similar to or exceeding that of wild-type human insulin and displays a susceptibility to fibrillation similar to or exceeding that of wild-type human insulin. An insulin analogue may display greater in vitro insulin receptor binding than normal insulin while displaying binding to IGFR less than twice that of normal insulin and less than that of fast-acting insulin analogs. The fibrillation-resistant insulin may be used to treat a patient by subcutaneous injection or by using an implantable or external insulin pump, due to its fibrillation resistance.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Novel insulin analog and use thereof
InactiveUS20160008483A1Avoids in vivo clearance mechanismReduced receptor binding affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin humulinInsulin receptor binding
The present invention relates to an insulin analog that has a reduced insulin titer and a reduced insulin receptor binding affinity compared to the native form for the purpose of increasing the blood half-life of insulin, a conjugate prepared by linking the insulin analog and a carrier, a long-acting formulation including the conjugate, and a method for preparing the conjugate.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
CTP-based insulin analogs for treatment of diabetes
Insulin analogs comprising a non-native glycosylation site sequence are provided having high potency and specificity for the insulin receptor. In one embodiment a peptide sequence of greater than 18 amino acids is used as a linking moiety to link human insulin A and B chains, or analogs or derivatives thereof, to provide high potency single chain insulin analogs. In one embodiment the linking moiety comprises one or more glycosylation sites. Also disclosed are prodrug and conjugate derivatives of the insulin analogs.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Compositions and methods of treating diabetes
InactiveUS20100216693A1Marked depressionReduce aggregationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderC-peptideInsulin Analogue
Owner:CREATIVE PEPTIDES SWEDEN
Liposome-encapsulated insulin formulations
InactiveUS20030068361A1High encapsulation efficiencyPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAcute hyperglycaemiaLiposome
Owner:ARADIGM
Insulin assay
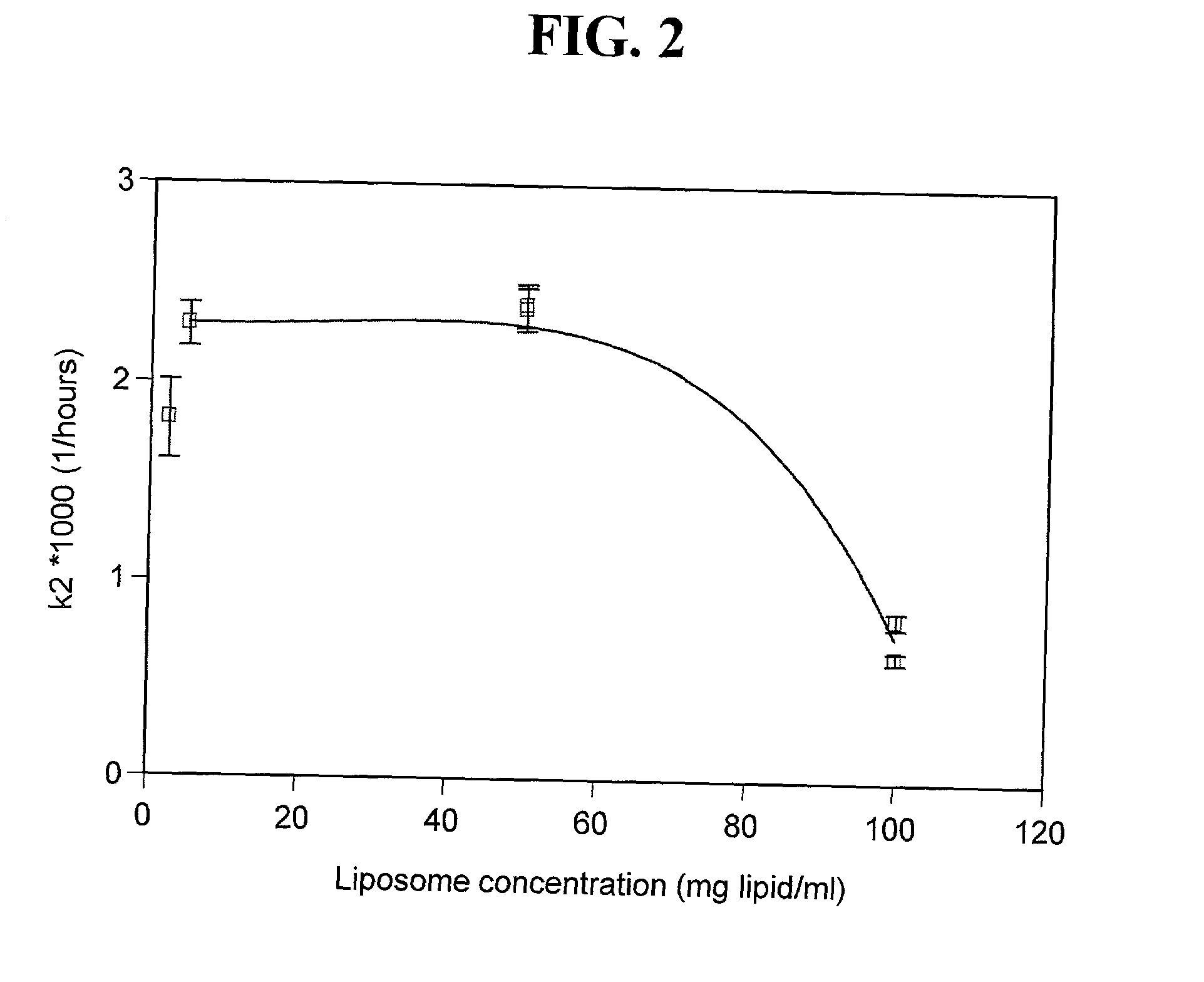
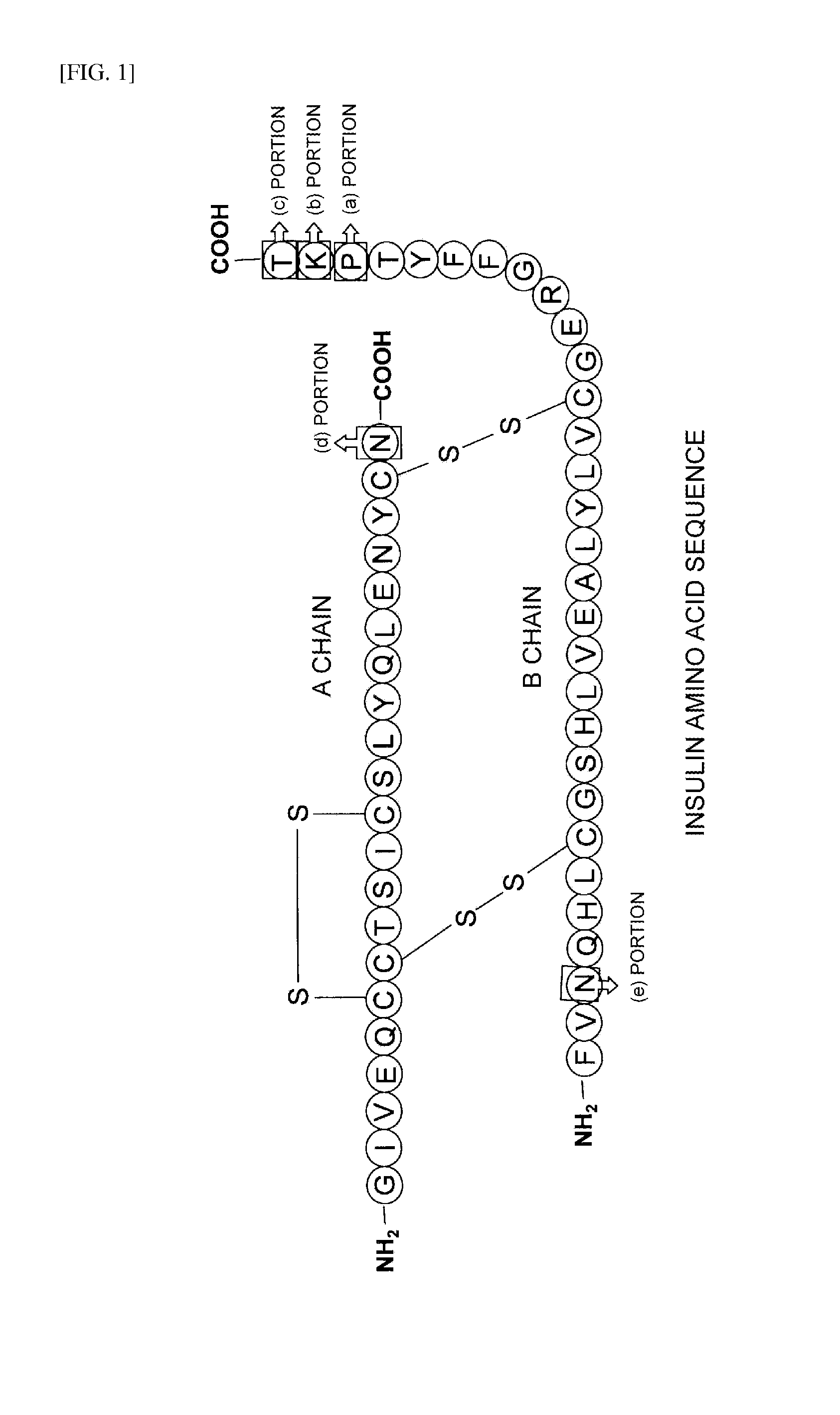
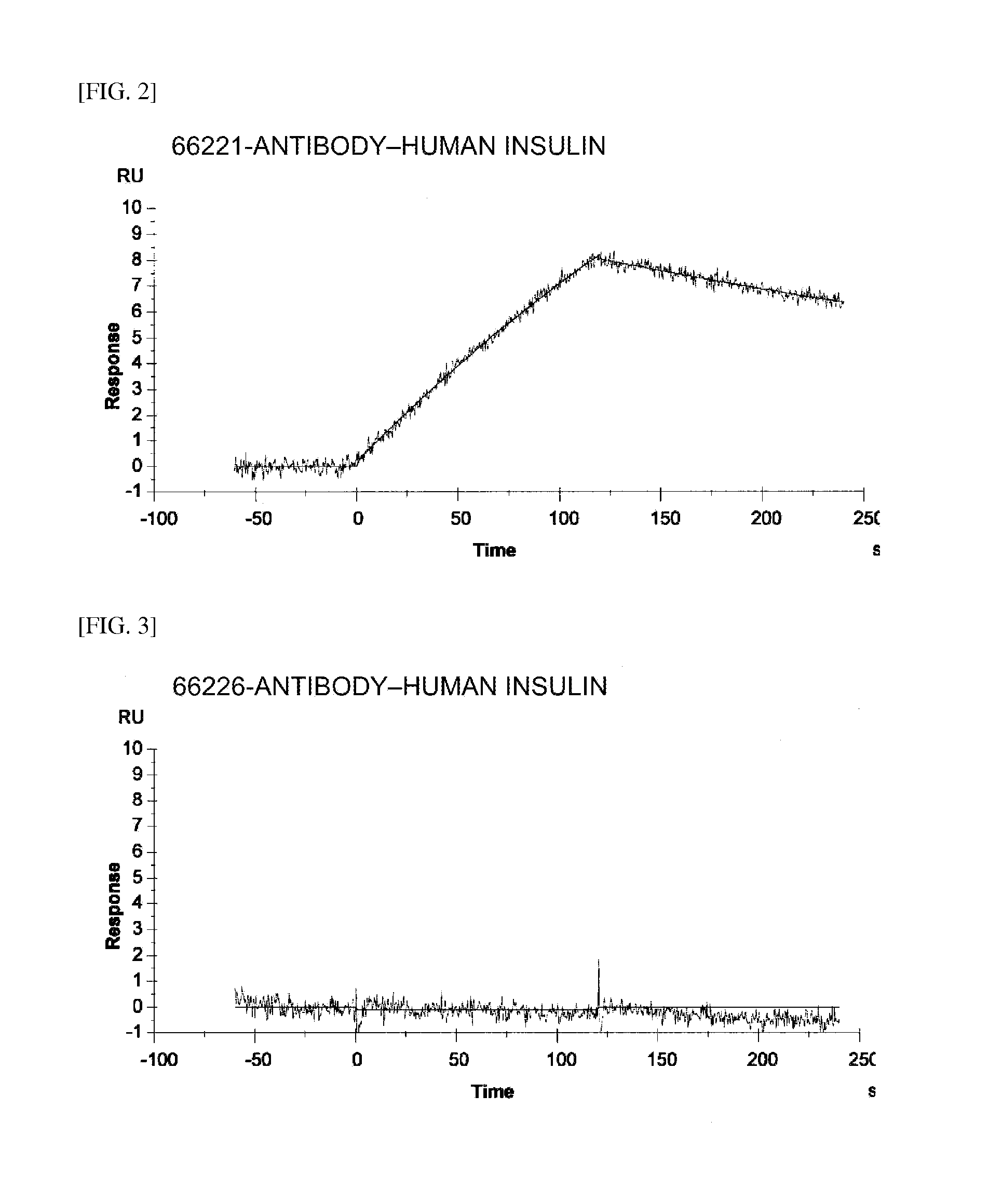
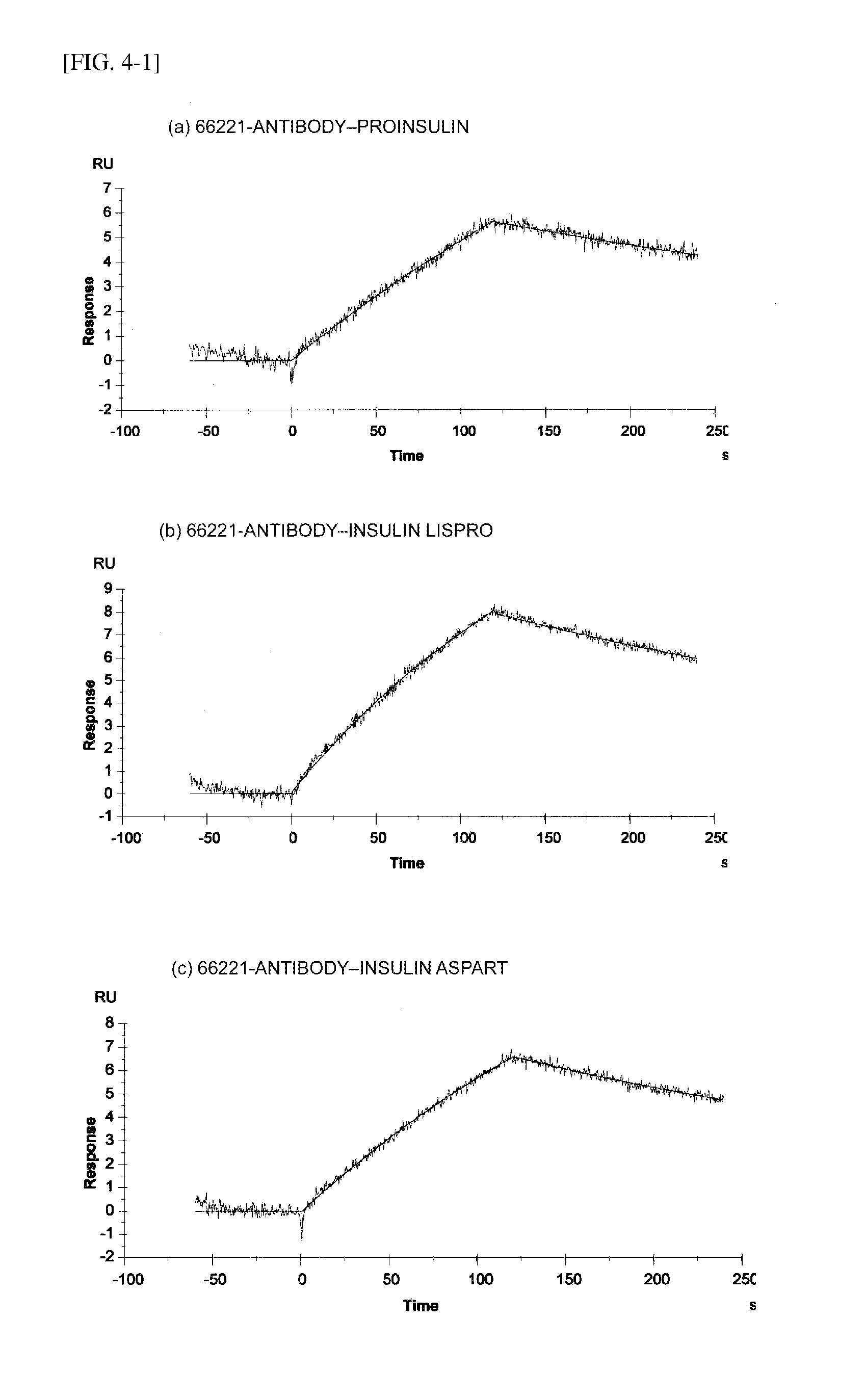
ActiveUS20110195438A1Sensitively and specifically assayedAccurate monitoringImmunoglobulins against hormonesBiological testingINSULIN USEBiochemistry
The present invention provides an insulin-specific assay and an assay reagent capable of sensitively and specifically assaying insulin using an antibody having a property of reacting with insulin bound to an anti-insulin antibody while not reacting with insulin not bound to an anti-insulin antibody, without being affected by proinsulin and insulin analogs.
Owner:SEKISUI MEDICAL CO LTD
Magnesium compositions for modulating the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of insulin and insulin analogs, and injection site pain
Compositions and methods for modulating injection site pain associated with rapid acting injectable insulin formulations have been developed for subcutaneous injection. The formulations contain insulin in combination with a zinc chelator such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (“EDTA”), a dissolution / stabilization agent such as citric acid, a magnesium salt, and, optionally, additional excipients. New presentations include rapid acting concentrated insulin formulations and a way to enhance the absorption of commercially available rapid acting analog formulations by mixing them with a vial containing dry powder excipients that accelerate their absorption. Devices for mixing excipient and insulin together at the time of administration, while minimizing residence time of the mixture, are also described.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com