Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Expiratory gas flow" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ventilation method and control of a ventilator based on same
InactiveUS7246618B2Prevents de-recruitmentLower Level RequirementsRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAirway pressuresIntensive care medicine
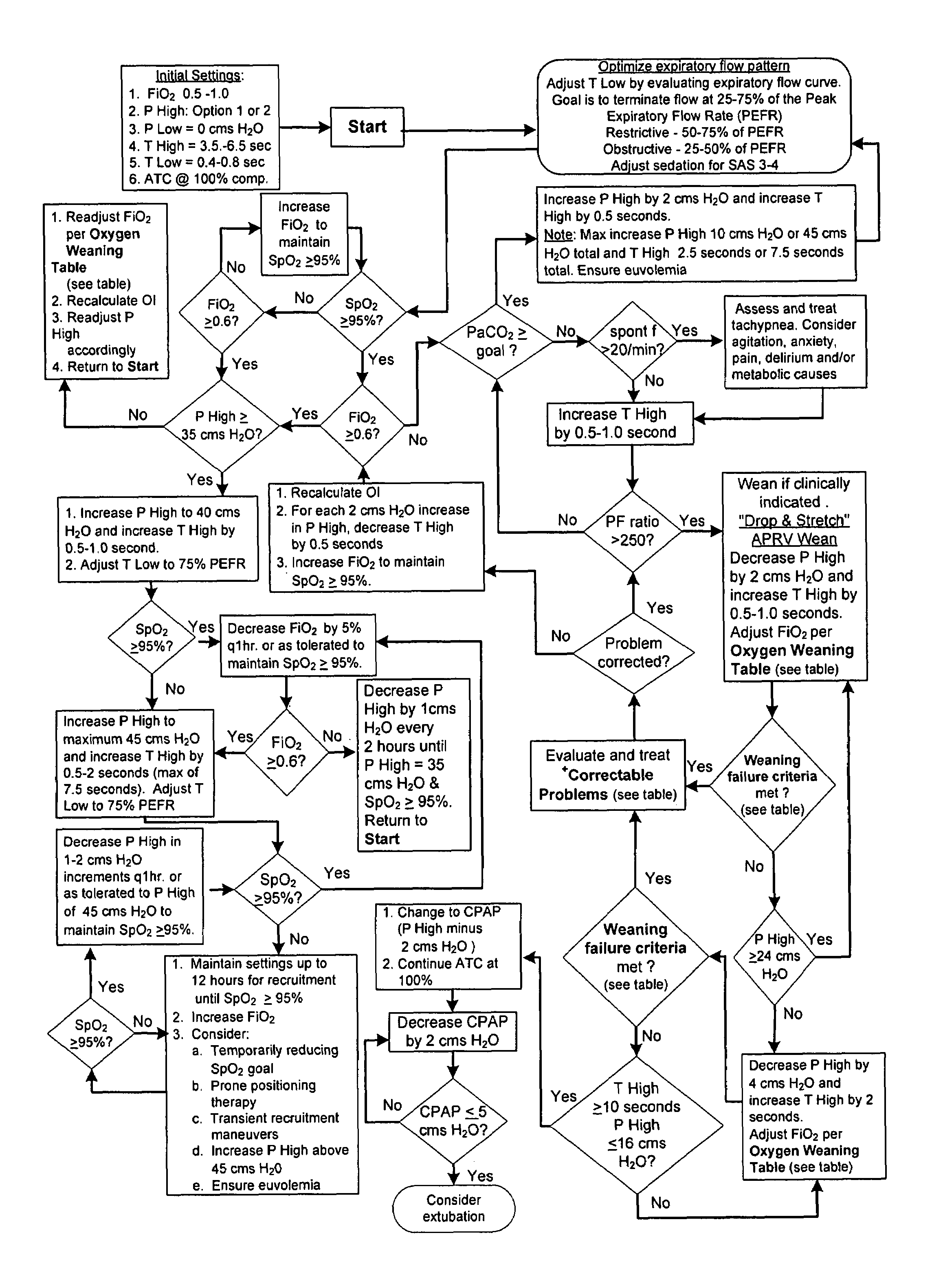
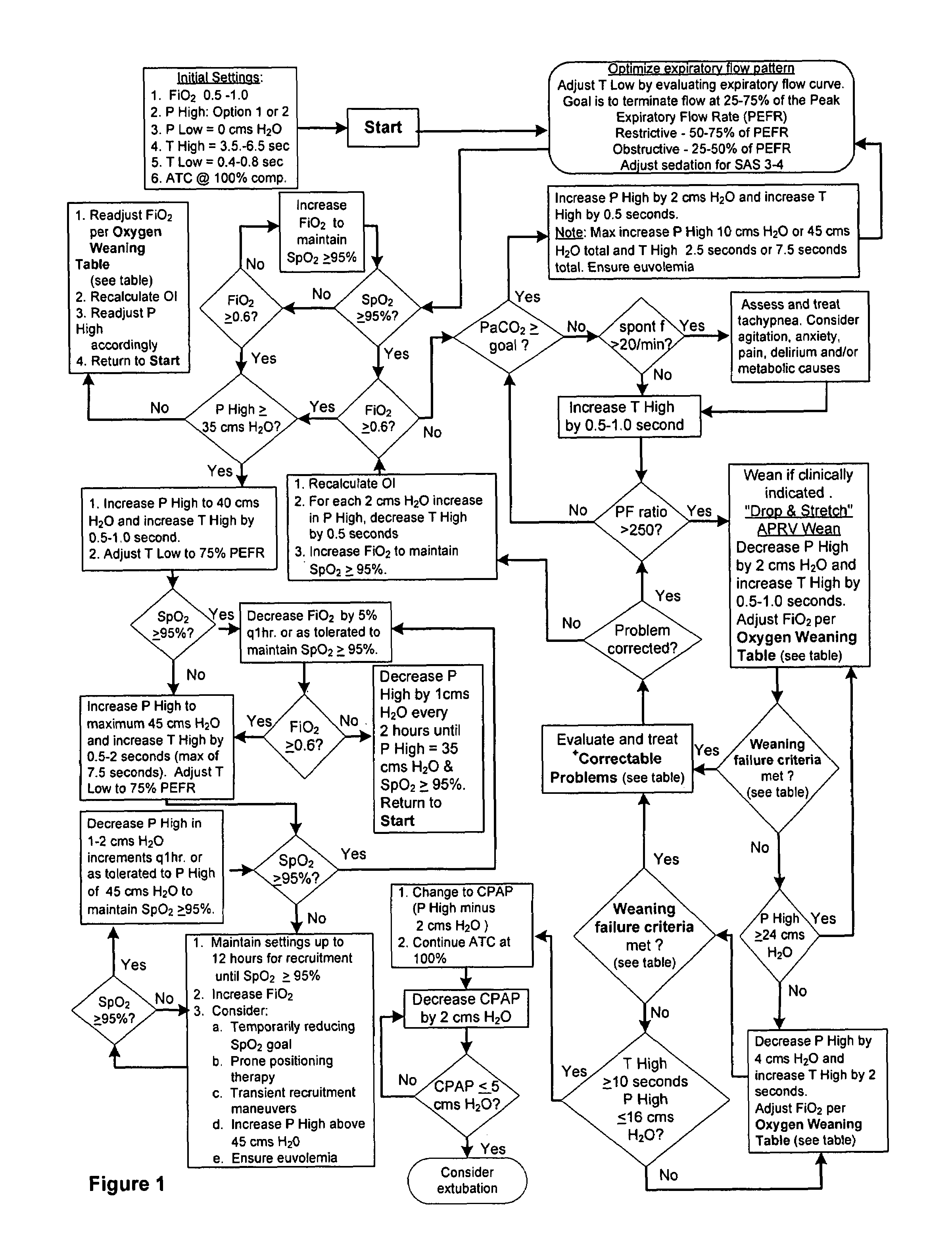
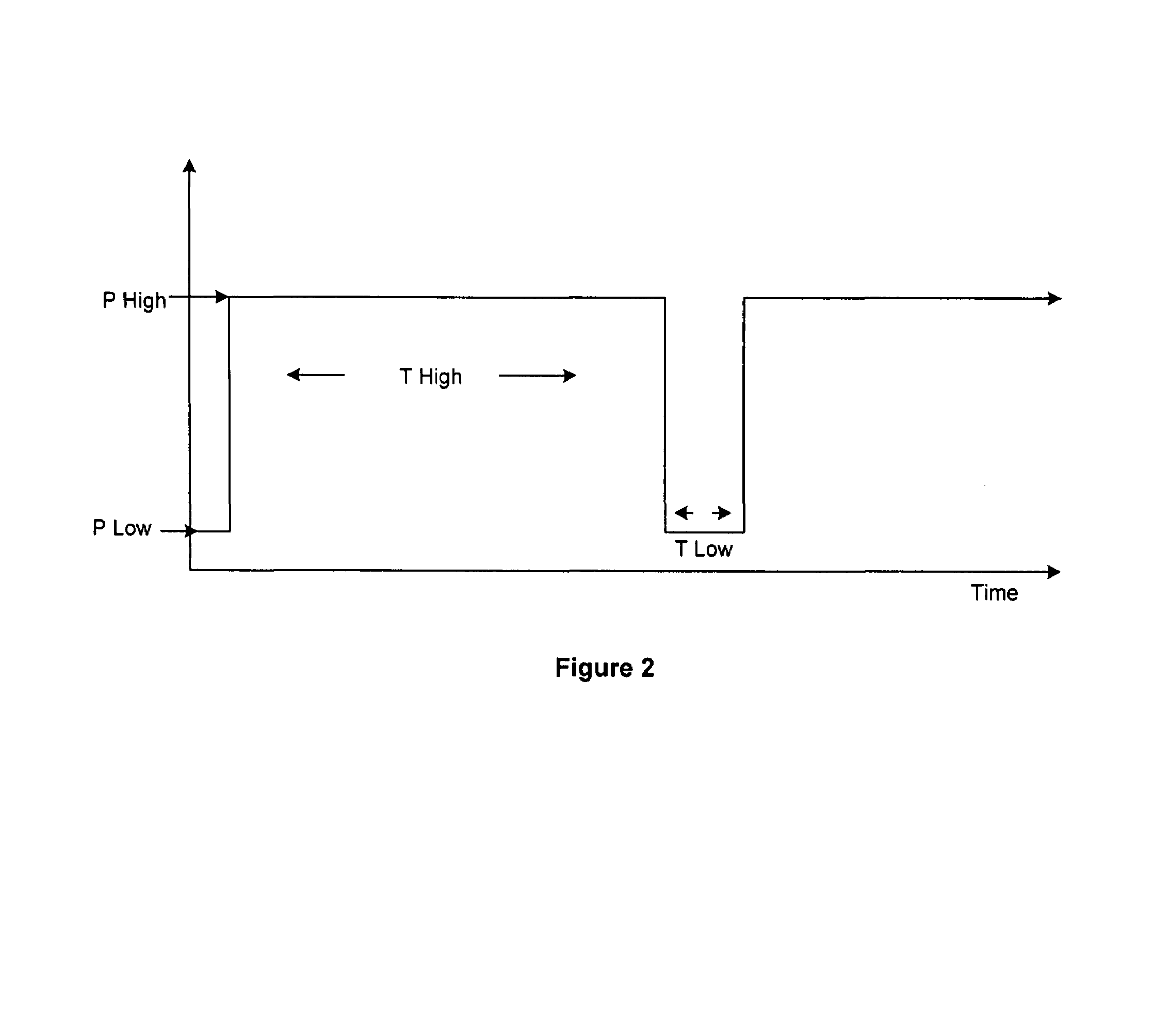
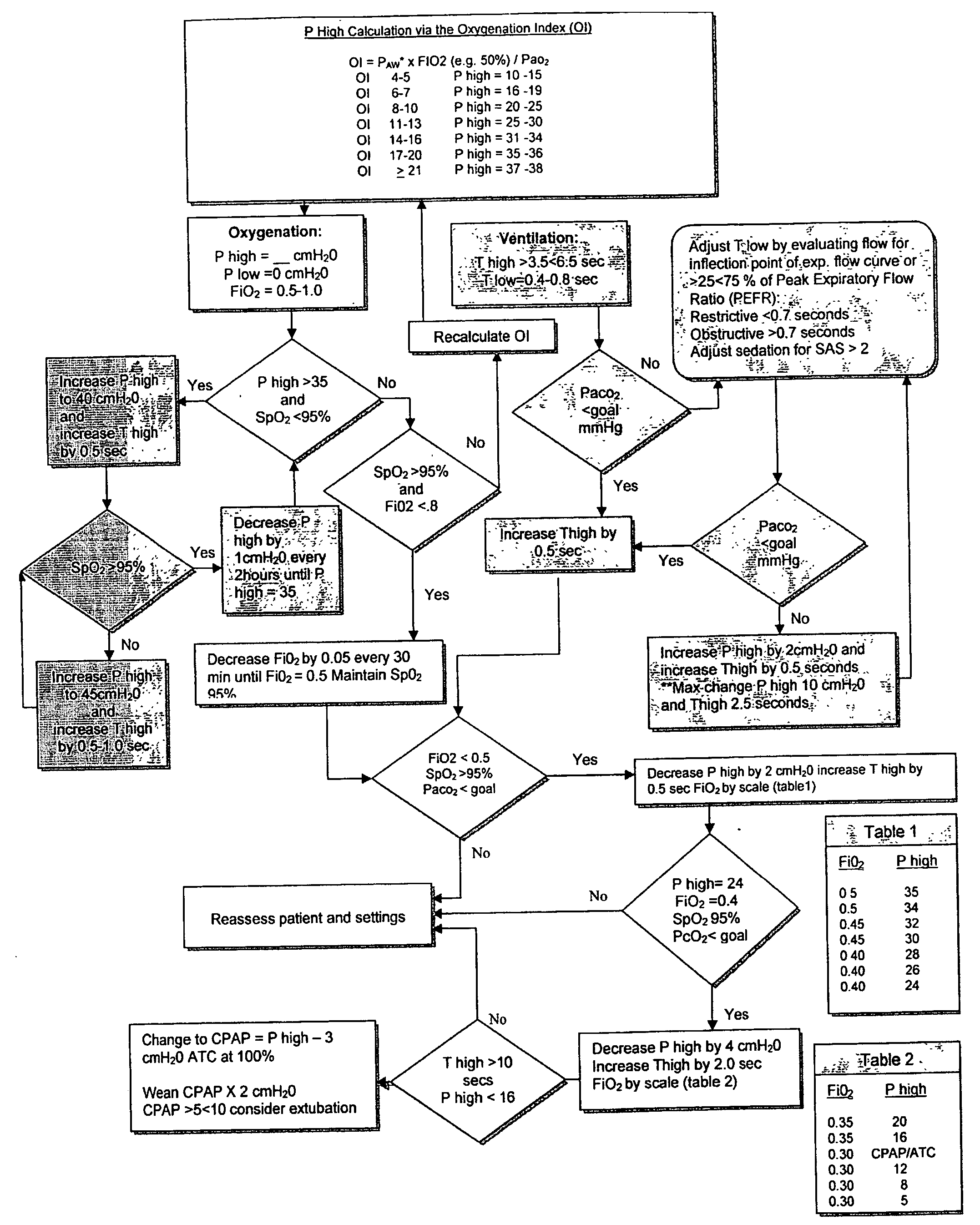
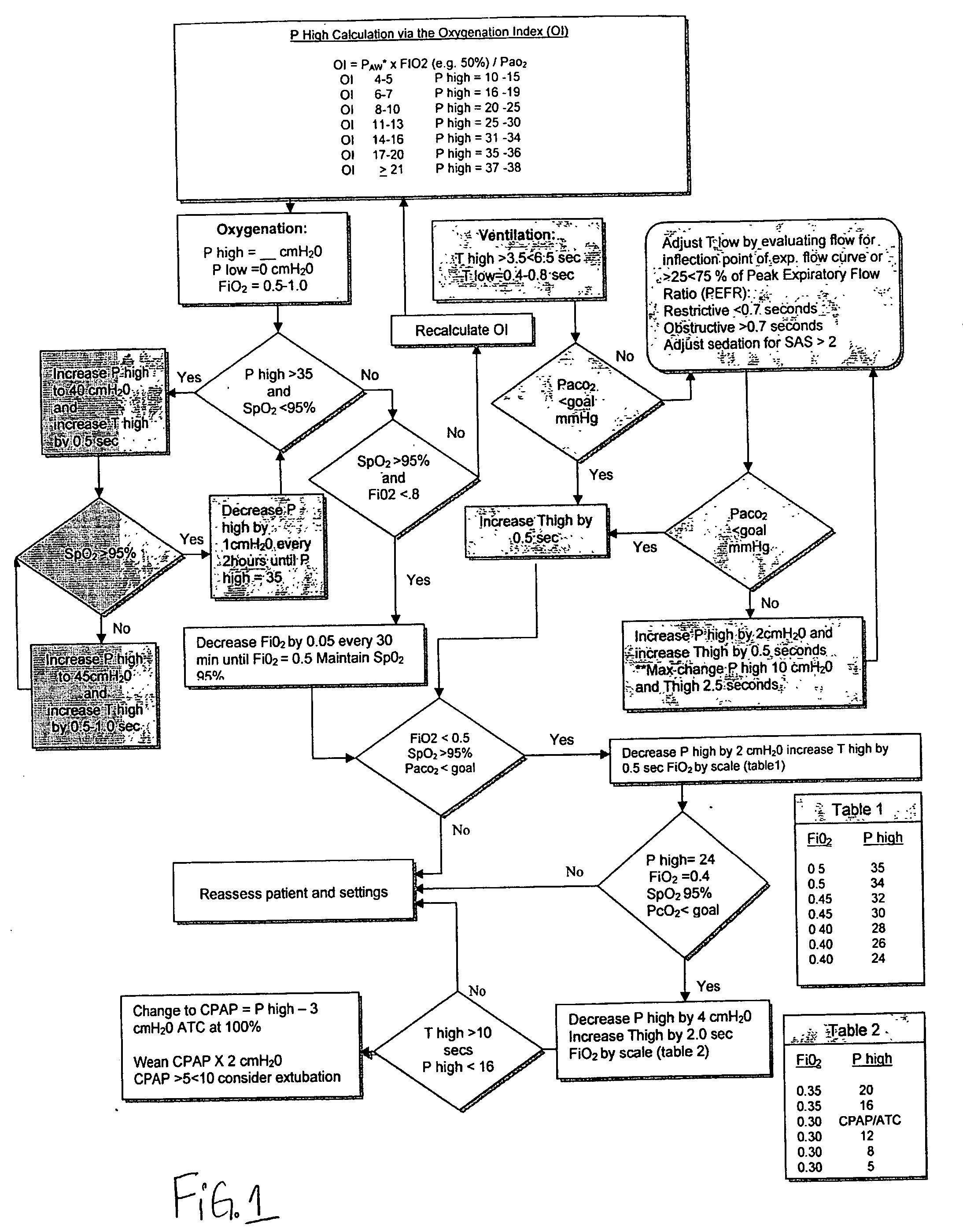
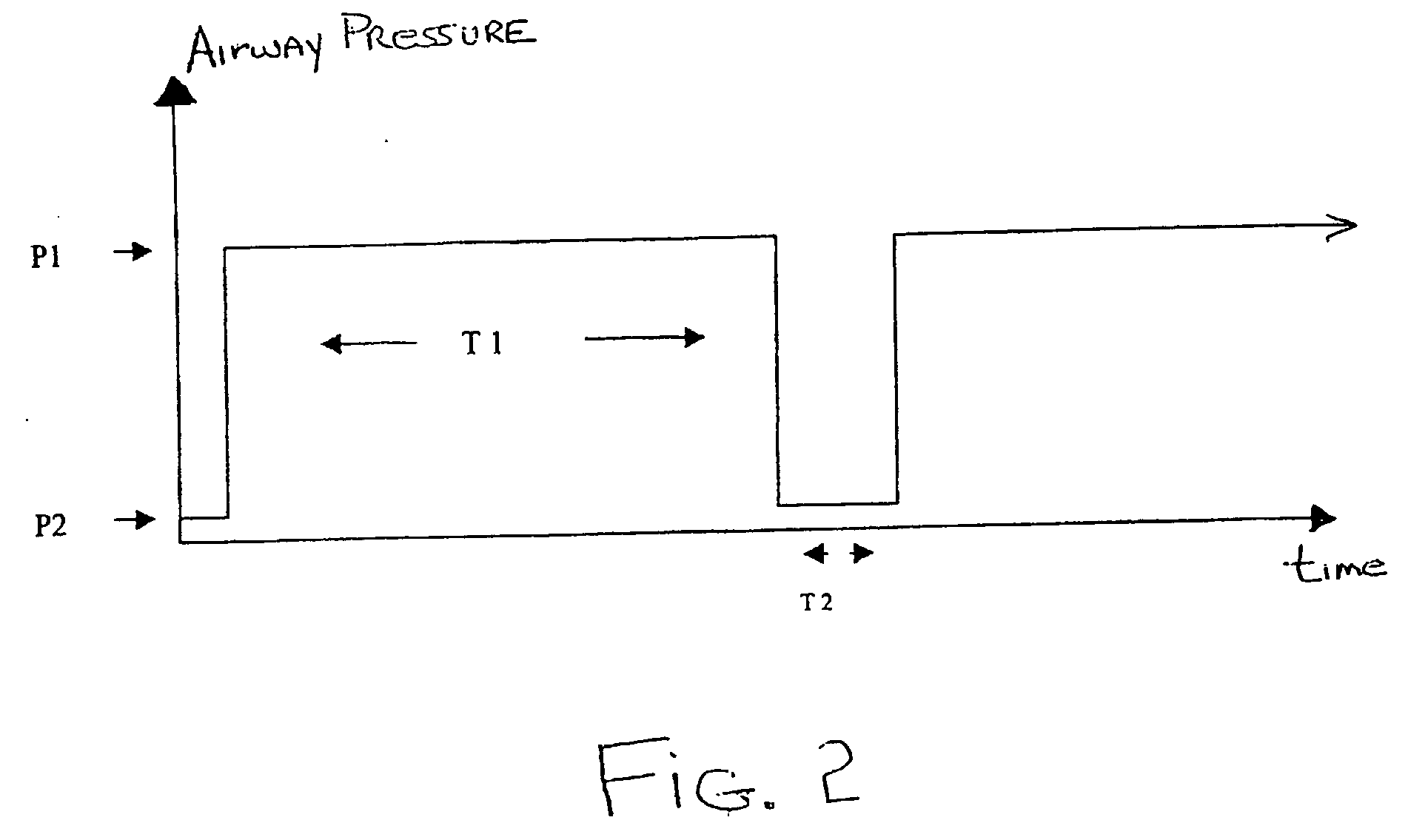
The invention provides an improved ventilation method and method for controlling a ventilator apparatus in accordance with same. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method of controlling a ventilator apparatus comprising the steps of placing a ventilator in a mode capable of adjusting airway pressure (P) and time (T), monitoring expiratory gas flow, analyzing the expiratory gas flow over time (T) to establish an expiratory gas flow pattern, and setting and / or adjusting a low time (T2) based on the expiratory gas flow pattern. Alternatively, the present invention relates to a method of controlling a ventilator apparatus comprising the steps of placing a ventilator in a mode capable of adjusting airway pressure (P) and time (T), and setting a low airway pressure (P2) of substantially zero cmH2O.
Owner:HABASHI NADER M
Ventilation method and control of a ventilator based on same
InactiveUS20060174884A1Increase in vent free dayDrug costRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAirway pressuresIntensive care medicine
The invention provides an improved ventilation method and method for controlling a ventilator apparatus in accordance with same. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method of controlling a ventilator apparatus comprising the steps of placing a ventilator in a mode capable of adjusting airway pressure (P) and time (T), monitoring expiratory gas flow, analyzing the expiratory gas flow over time (T) to establish an expiratory gas flow pattern, and setting and / or adjusting a low time (T2) based on the expiratory gas flow pattern. Alternatively, the present invention relates to a method of controlling a ventilator apparatus comprising the steps of placing a ventilator in a mode capable of adjusting airway pressure (P) and time (T), and setting a low airway pressure (P2) of substantially zero cmH2O.
Owner:HABASHI NADER M
Methods and devices for providing inspiratory and expiratory flow relief during ventilation therapy
ActiveUS20090151724A1Breathe freelyUndesirable pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory supportAirway pressures
Respiratory support and / or controlled mechanical ventilation of a patient are provided. A ventilation apparatus may include a ventilator, a transtracheal prosthesis, and a respiratory relief device. The transtracheal prostheses and ventilation catheter may be arranged such that the patient can breathe freely through the upper airway and / or the tracheal prostheses. Respiratory sensors may measure a breathing rate, lung pressure, airway pressure, or a combination thereof. Pulses of gas may be provided to the patient through the ventilation catheter during inspiration. The pulses may have a first volume while the patient breathes normal and a second volume when the sensors detect a cessation of breathing or reduction in breathing volume. The second volume may be provided at 1-5 times the normal breathing rate, with a volume 25-500% times the first volume, or both.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Method and apparatus for assessing blood-concentration of a volatile constituent
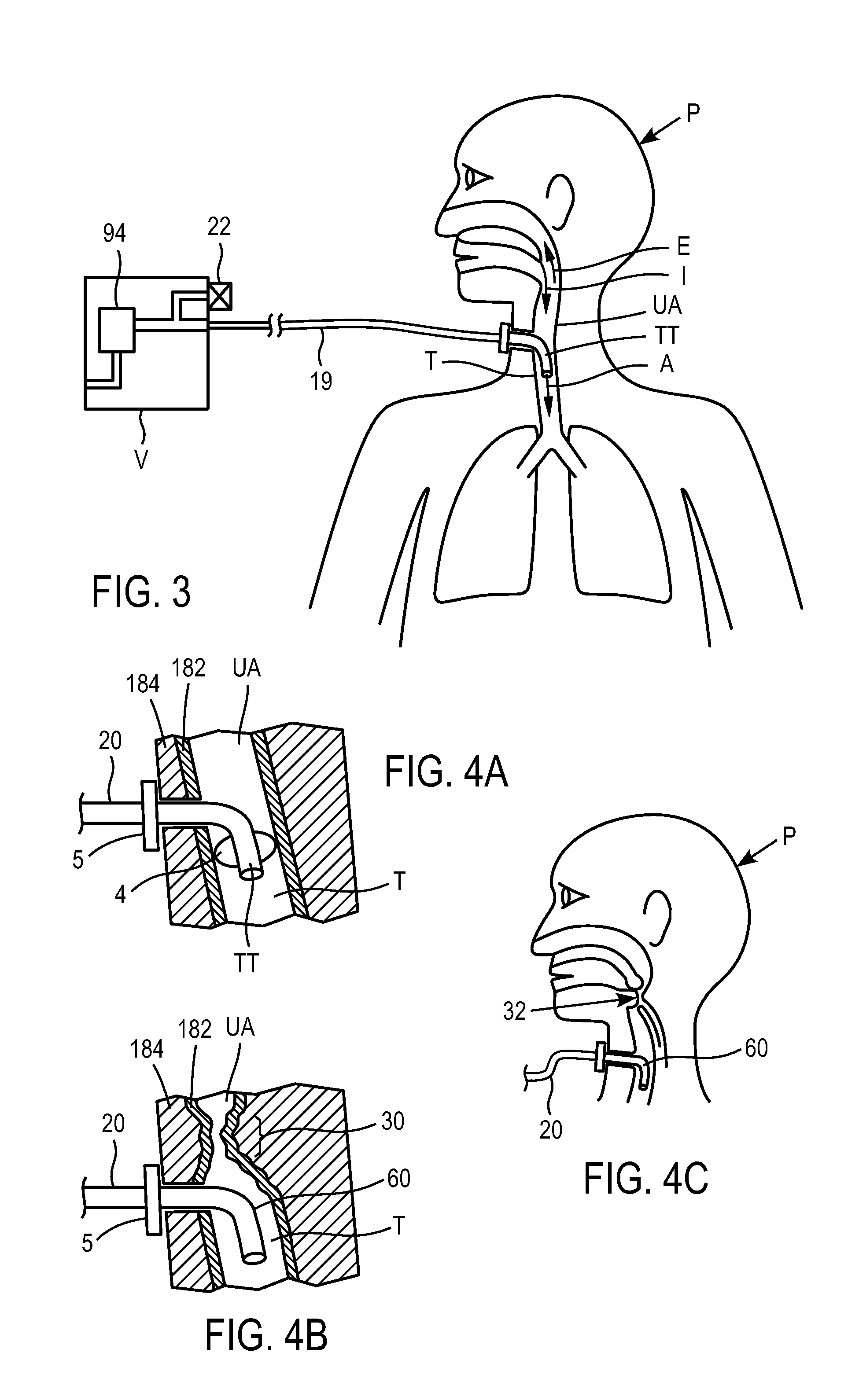
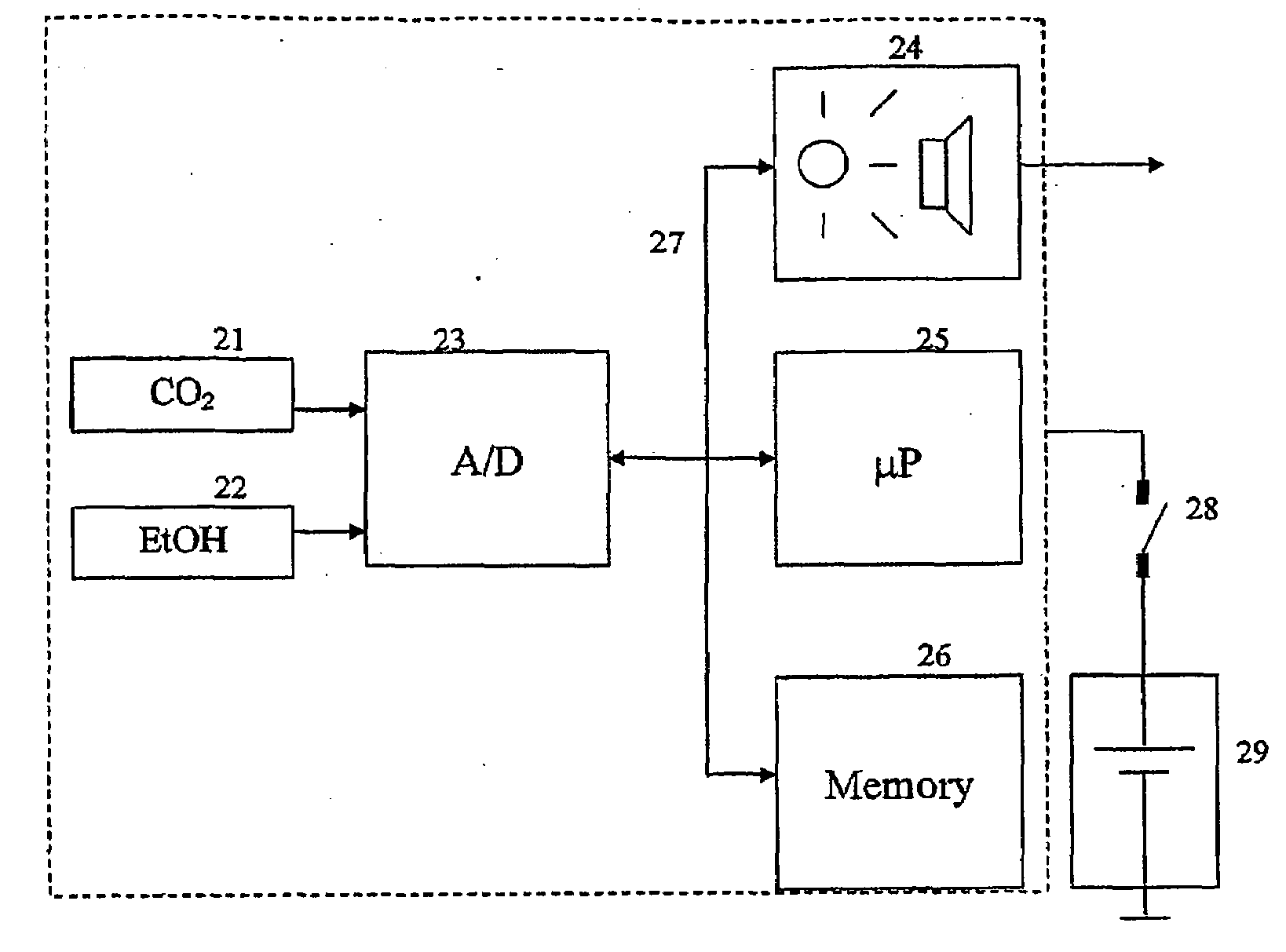
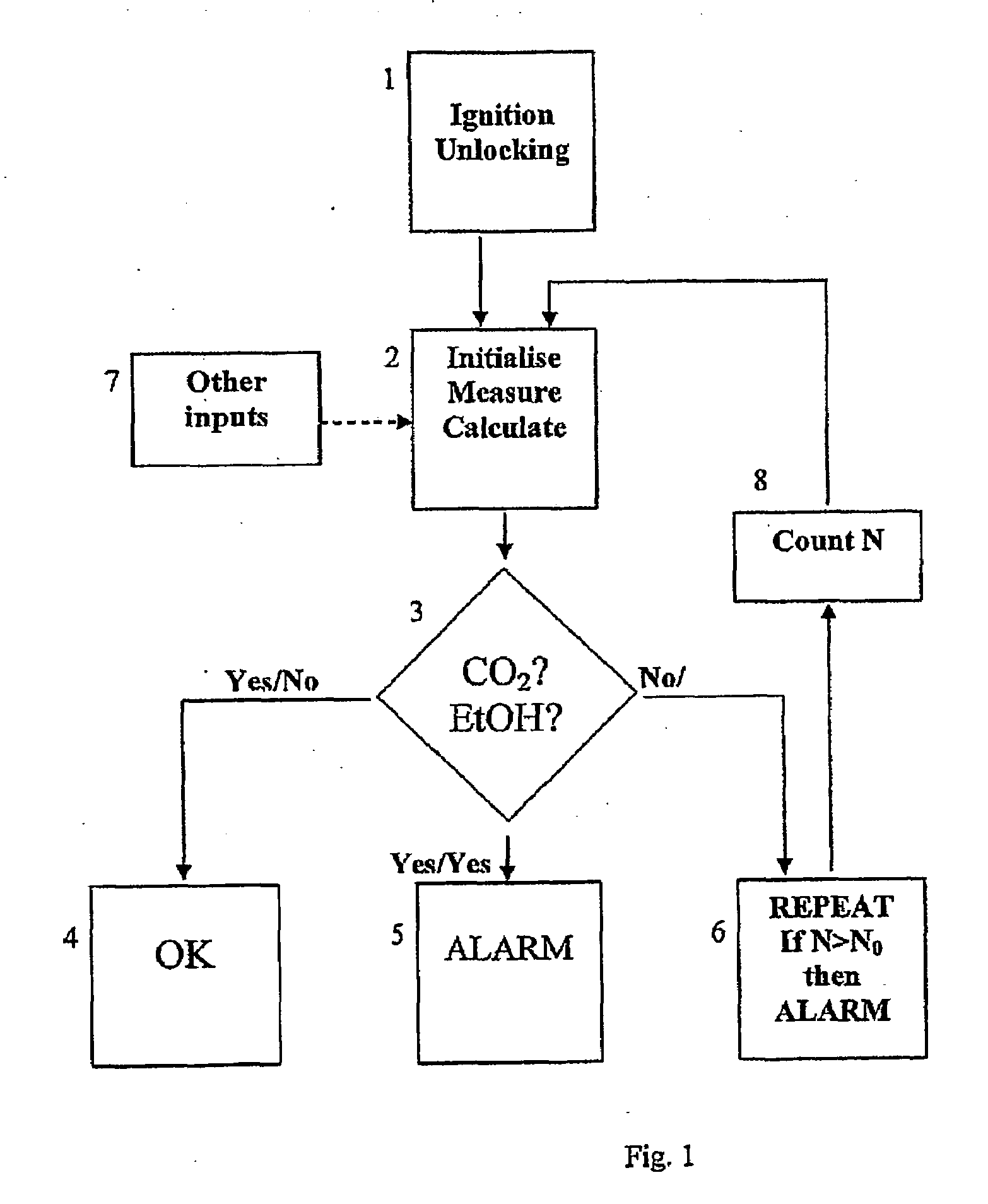
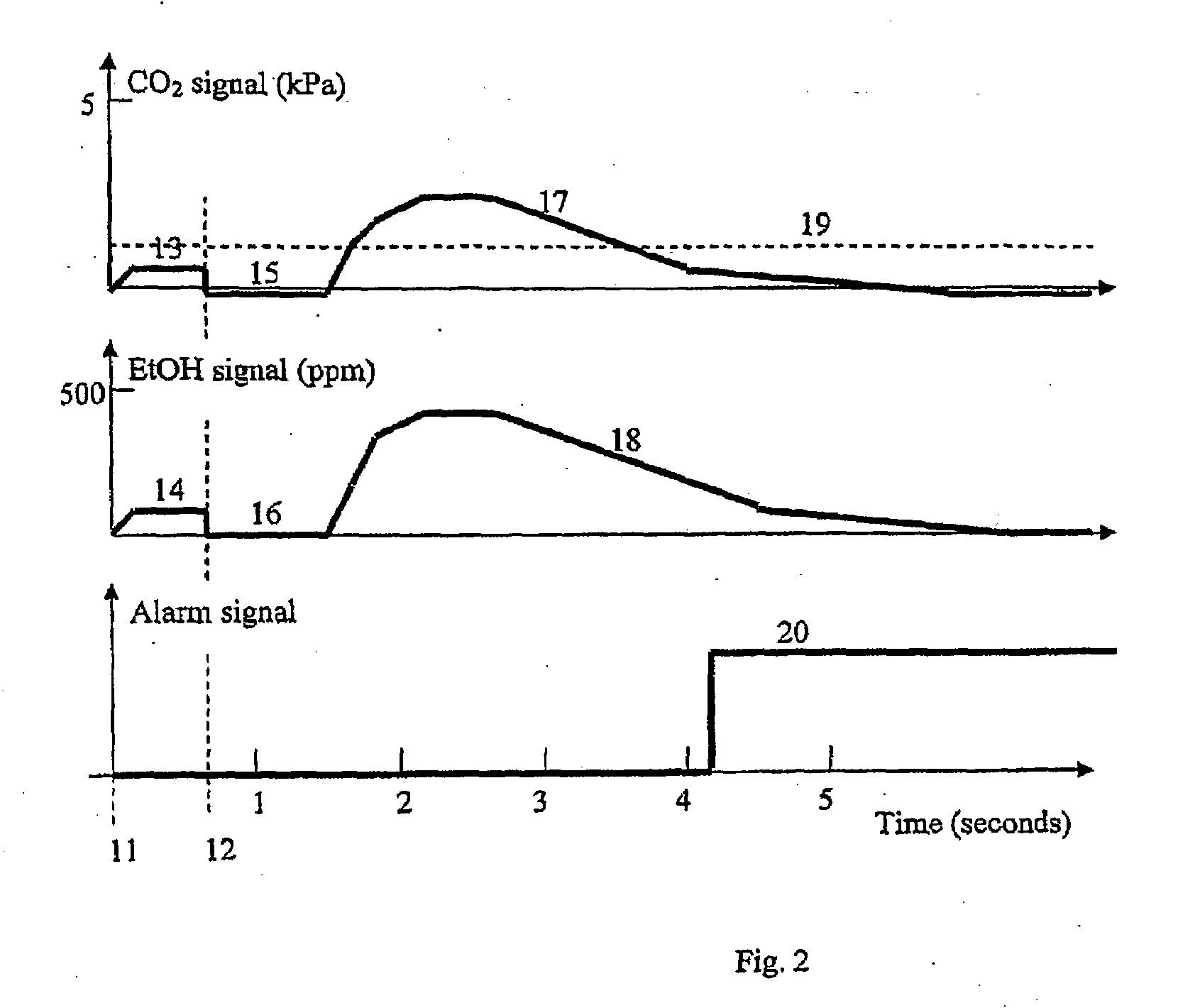
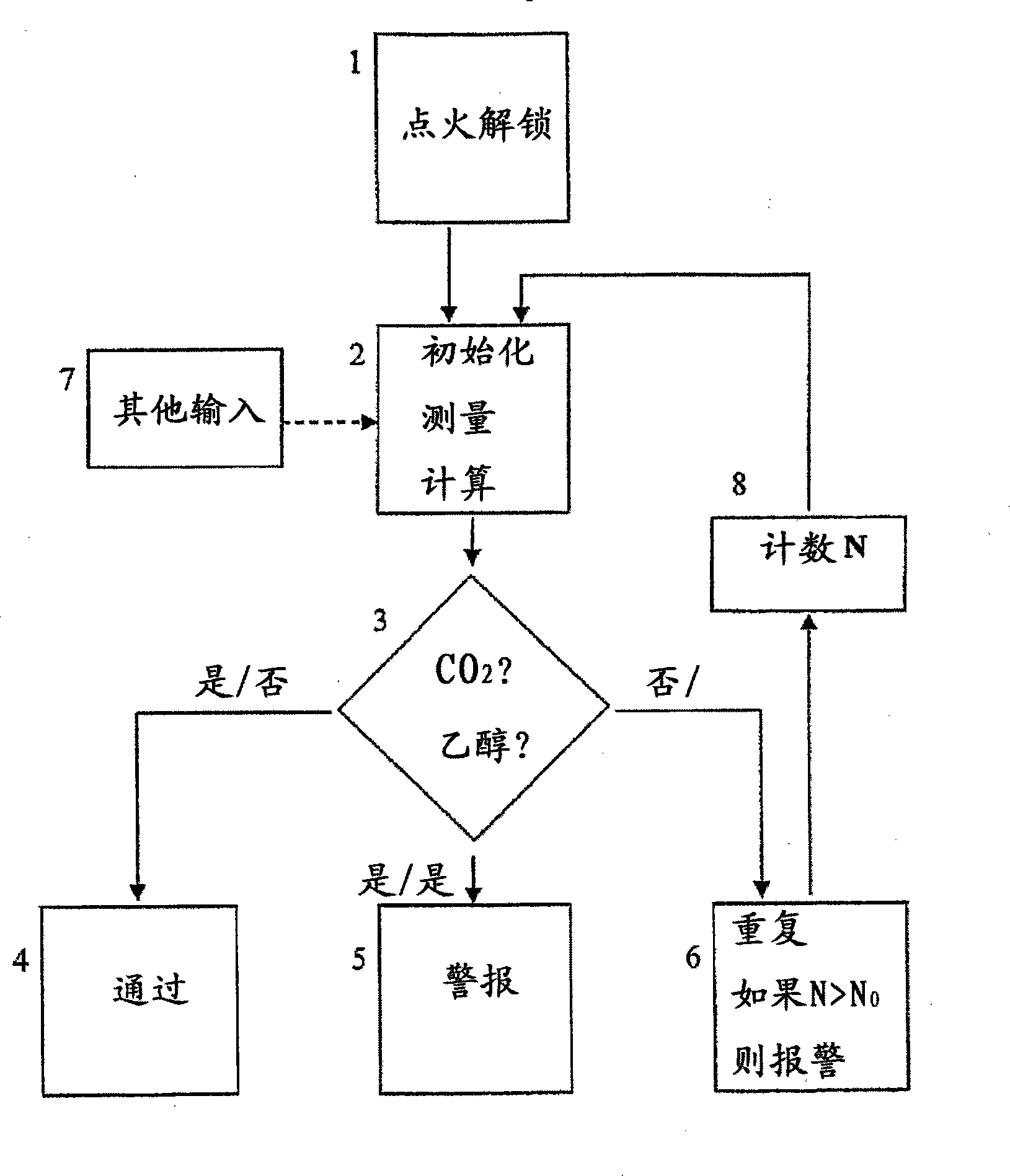
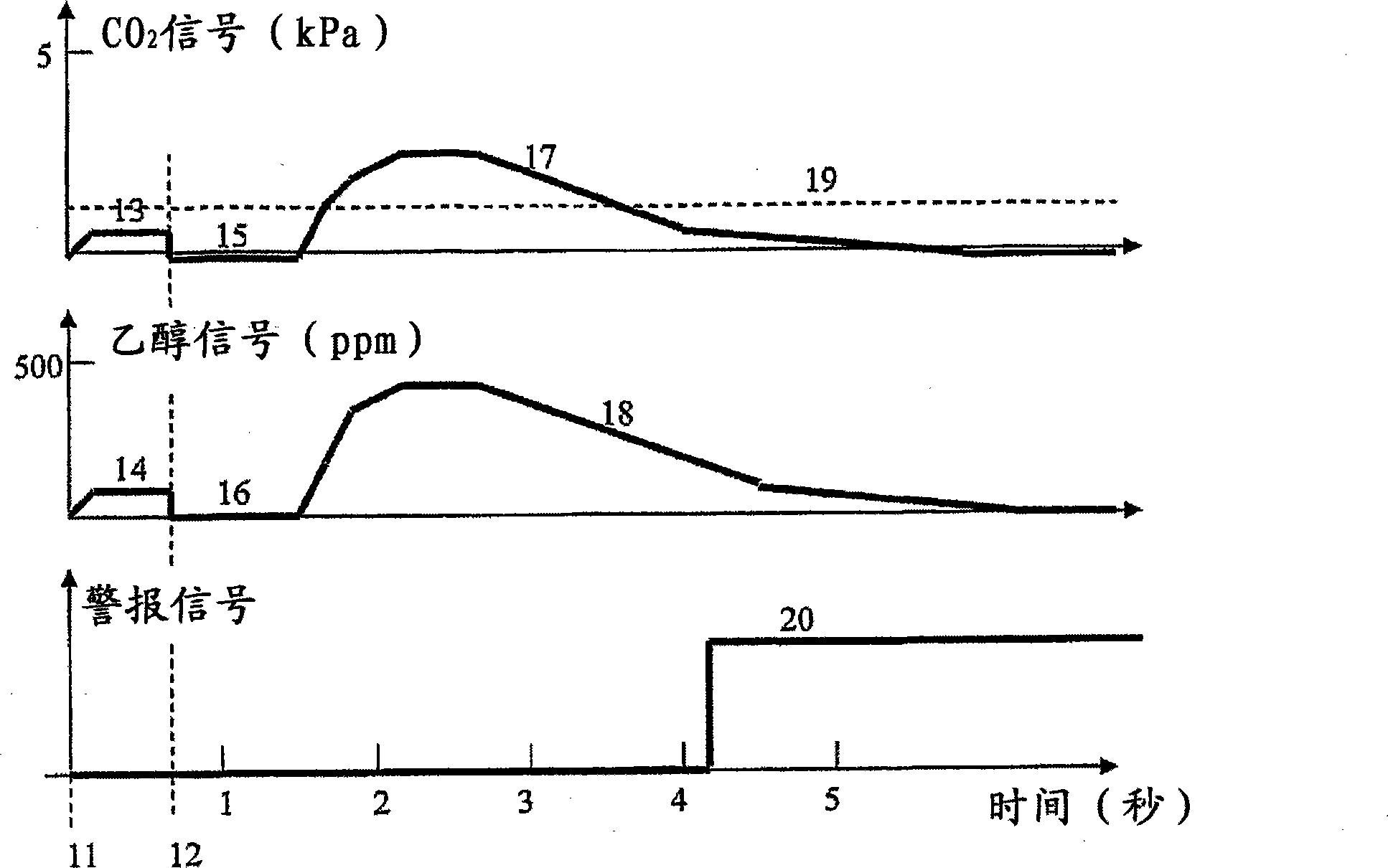
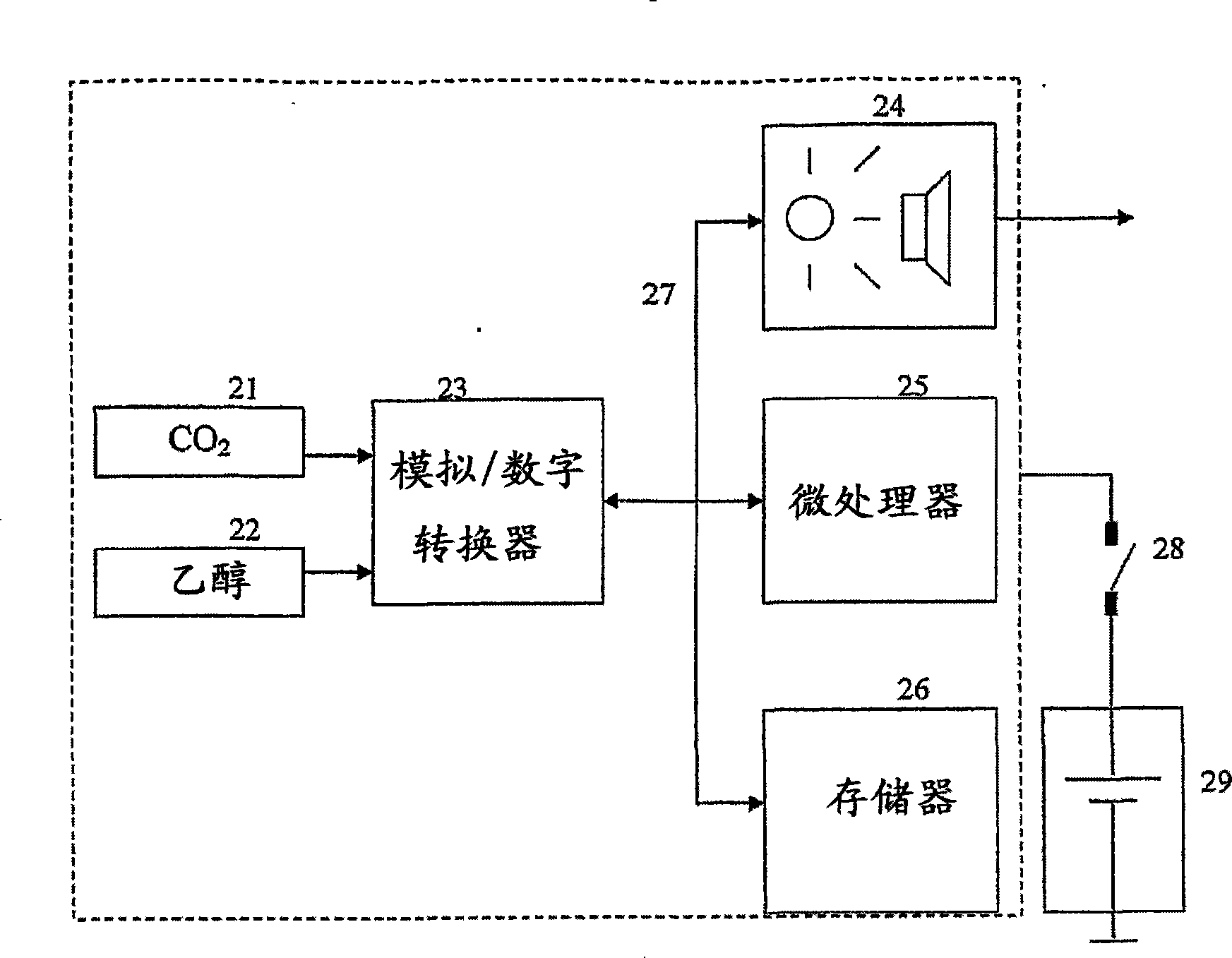
InactiveUS20090087920A1Simple methodWithdrawing sample devicesRespiratory organ evaluationExpiratory AirflowBlood concentration
A method and apparatus for of assessing the blood concentration level in a human or animal subject, of a volatile blood constituent (preferably alcohol) is disclosed. The method comprises steps of positioning a sensor (21, 22) within the expiratory gas flow of the subject, wherein the sensor (21, 22) is configured to detect the presence of the constituent and provide a first output signal representative of the concentration of said constituent in air, and also to detect a presence of carbon dioxide and to provide a second output signal representative of the concentration of carbon dioxide in air. The flow of expiratory gases from the subject is sampled to provide a first signal and second signal in respect of the expiratory gases substantially simultaneously. The method also comprises the step of inputting said first and second signals obtained by the sampling step into an algorithm configured to compare the variation of the first signal over time with the variation of the second signal over time and, depending on the result of the comparison, to make said second signal representative of the degree of dilution of said expiratory airflow. The invention further includes an apparatus for carrying out the method.
Owner:AUTOLIV DEV AB
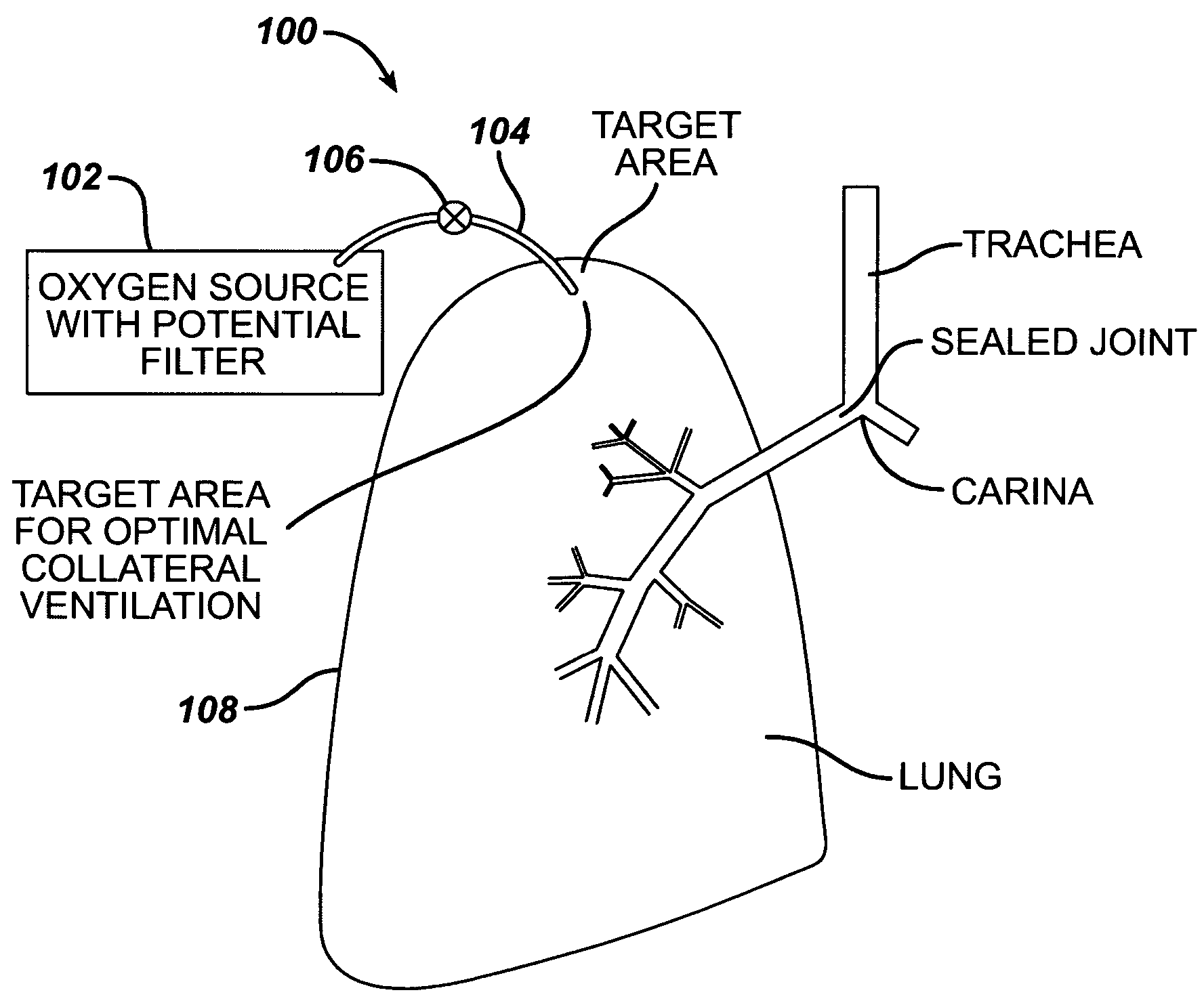
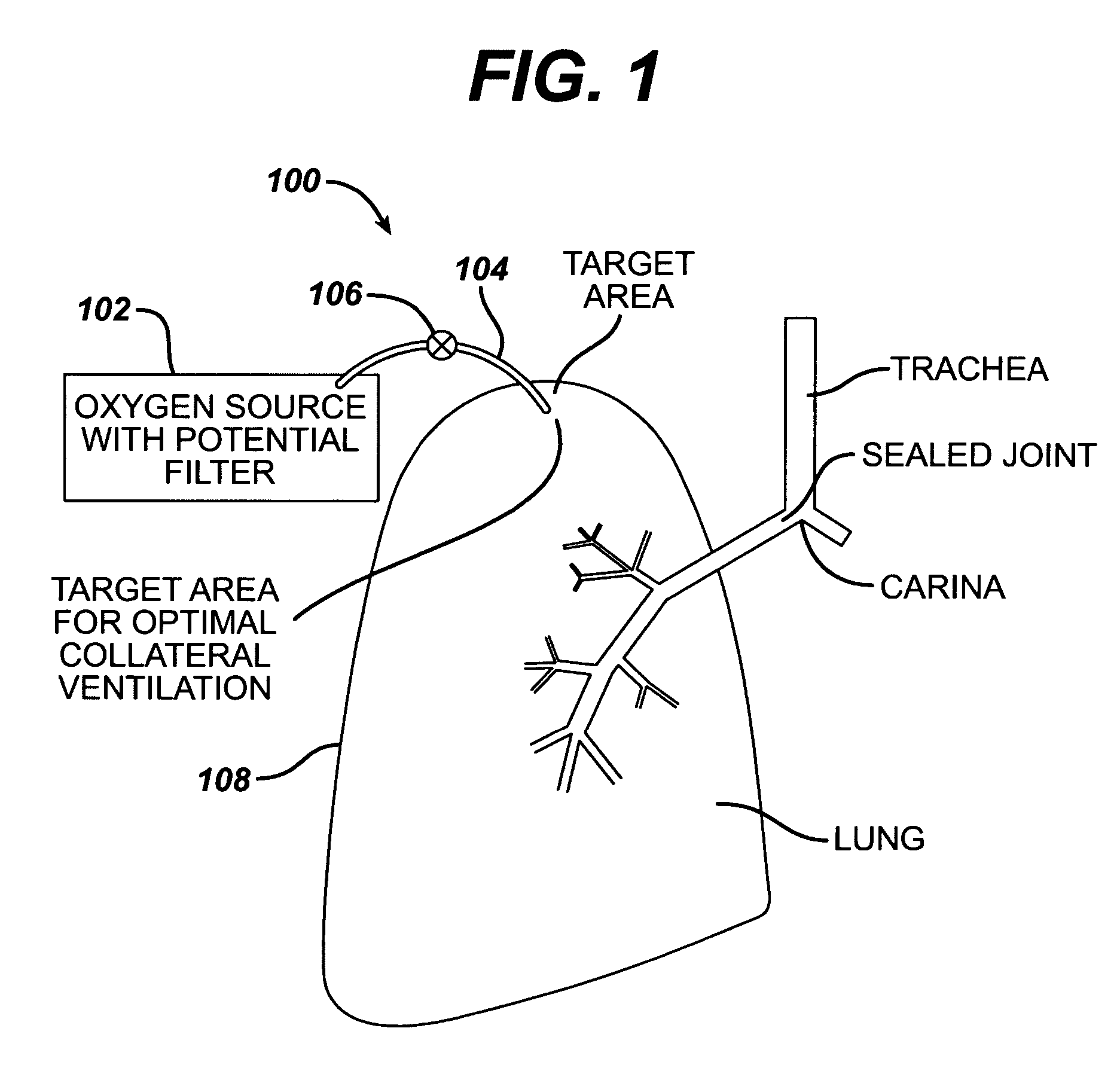
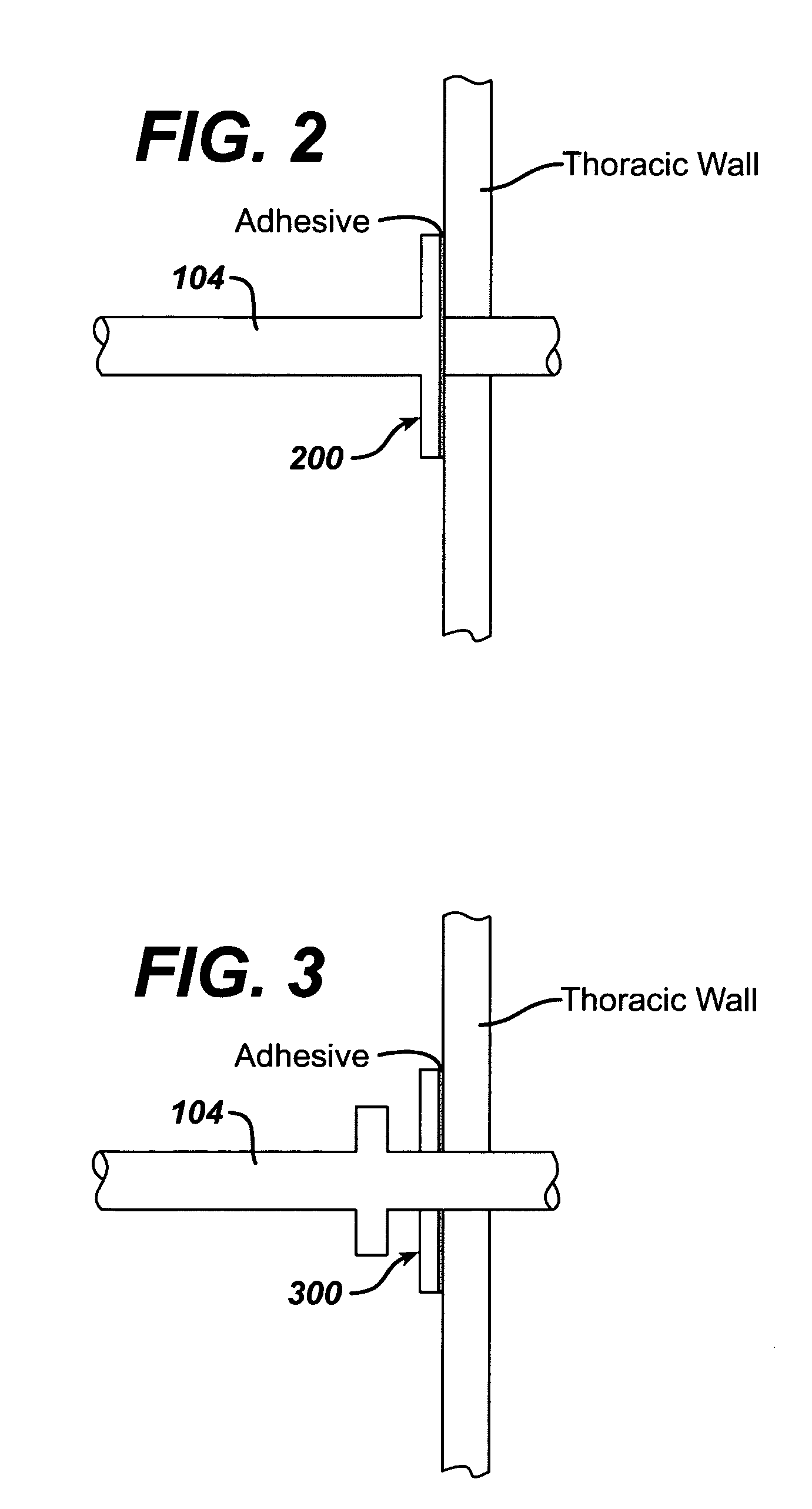
Intra/extra-thoracic collateral ventilation bypass system and method
InactiveUS7426929B2Speed up the flowPromote absorptionTracheal tubesDiagnosticsObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesObstructive chronic bronchitis
A long term oxygen therapy system having an oxygen supply directly linked with a patient's lung or lungs may be utilized to more efficiently treat hypoxia caused by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease such as emphysema and chronic bronchitis. The system includes an oxygen source, one or more valves and fluid carrying conduits. The fluid carrying conduits link the oxygen source to diseased sites within the patient's lungs. A collateral ventilation bypass trap system directly linked with a patient's lung or lungs may be utilized to increase the expiratory flow from the diseased lung or lungs, thereby treating another aspect of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The system includes a trap, a filter / one-way valve and an air carrying conduit. In various embodiments, the system may be intrathoracic, extrathoracic or a combination thereof. In order for the system to be effective, an airtight seal between the parietal and visceral pleurae is required. Chemical pleurodesis is utilized for creating the seal.
Owner:PORTAERO
Methods and systems for venitilation with unknown exhalation flow and exhalation pressure
ActiveUS20140224250A1Tracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesIntensive care medicineExhalation
This disclosure describes systems and methods for providing novel back-up ventilation. Further, this disclosure describes systems and methods for delivering ventilation when exhalation pressure and / or exhalation flow are unknown or unreliable by the ventilator.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Control for pressure of a patient interface
ActiveUS20160256660A1Low efficiencyHigh outputRespiratory masksMedical devicesExhaust valveTidal volume
A method of an apparatus control pressure in the patient interface. A vent valve may be used with a respiratory device, where the vent valve may selectively block fluid communication between components, such as the flow generator, the patient interface, and / or the vent. An expiratory flow model may be used to determine an expiratory characteristic such as an expiratory flow rate or pressure in the patient interface where an indicative measure may not be available. The expiratory flow model may receive inputs based on a measure of the patient's respiration, such as the tidal volume, peak inspiratory flow rate or length of inspiration. The expiratory characteristic may be used by a controller to control a pressure in the patient interface to provide respiratory therapy to a patient at or close to a target pressure.
Owner:RESMED LTD
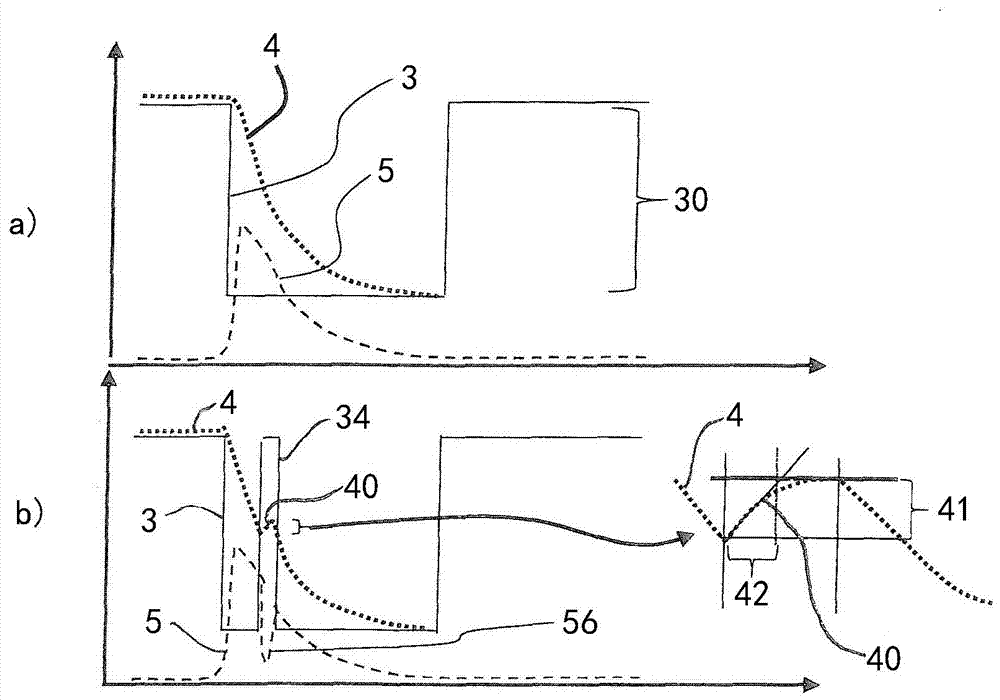
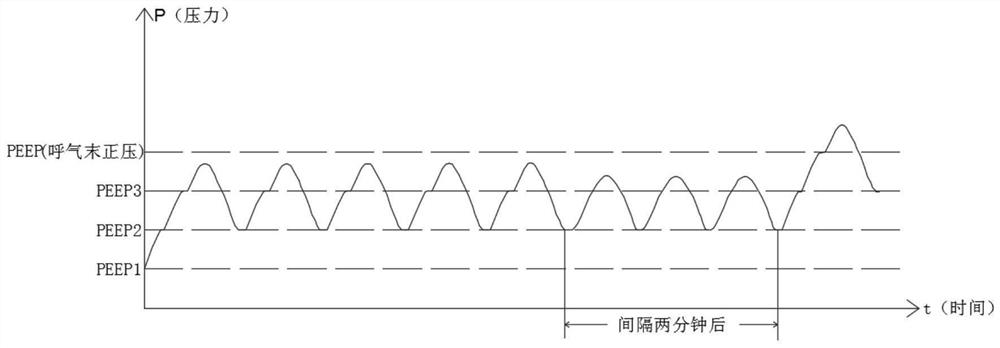
Method and device for the adaptive regulation of a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)
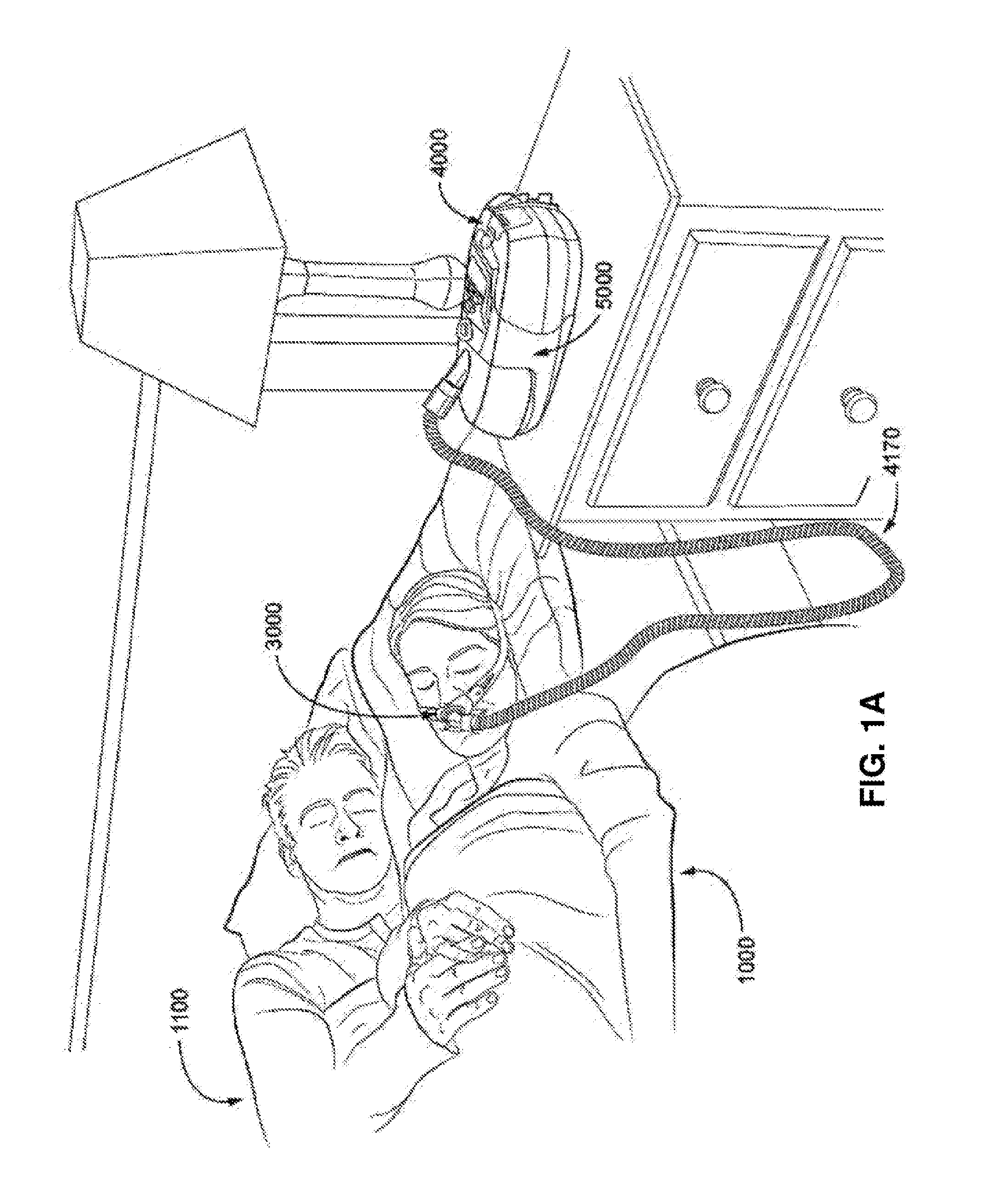
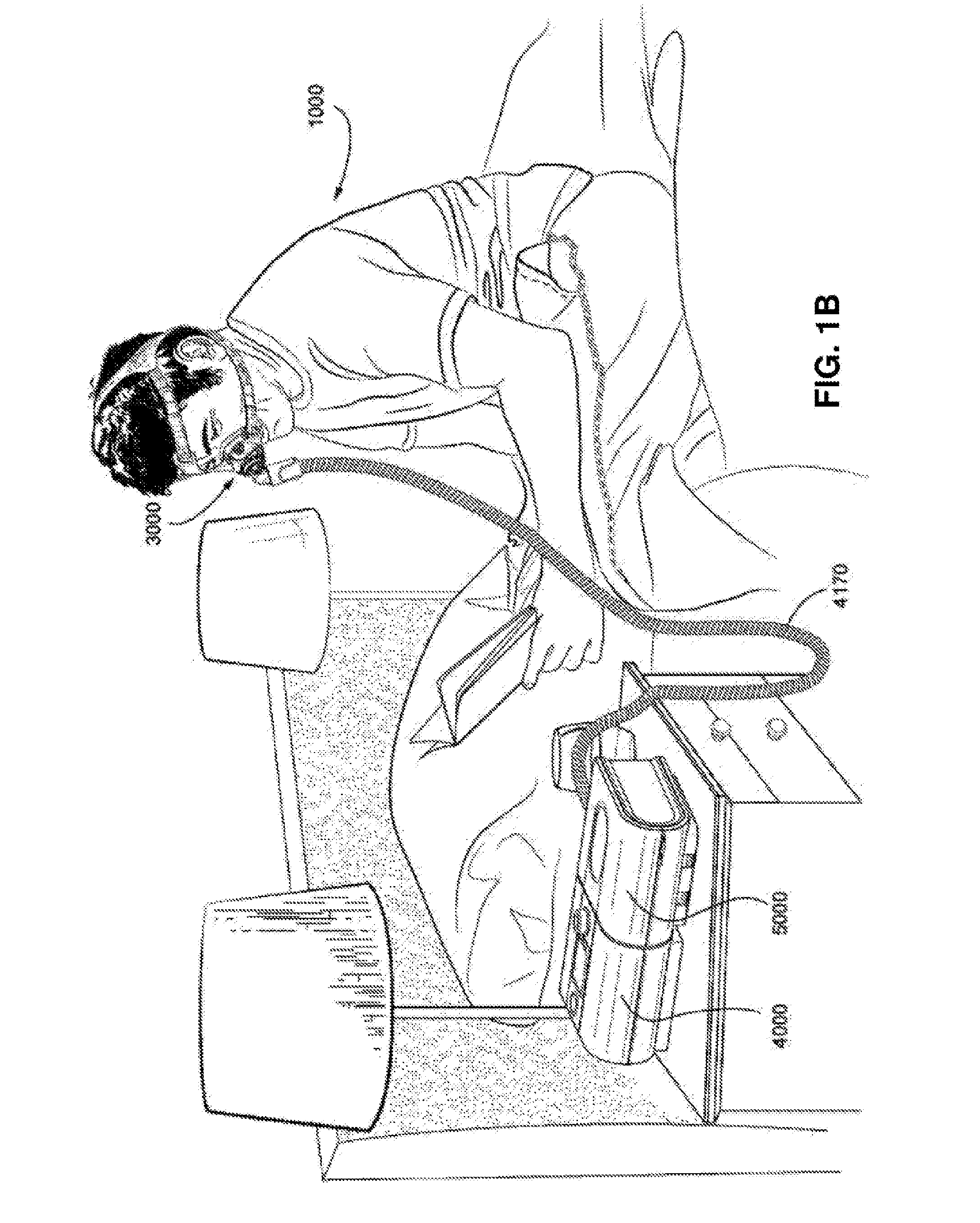
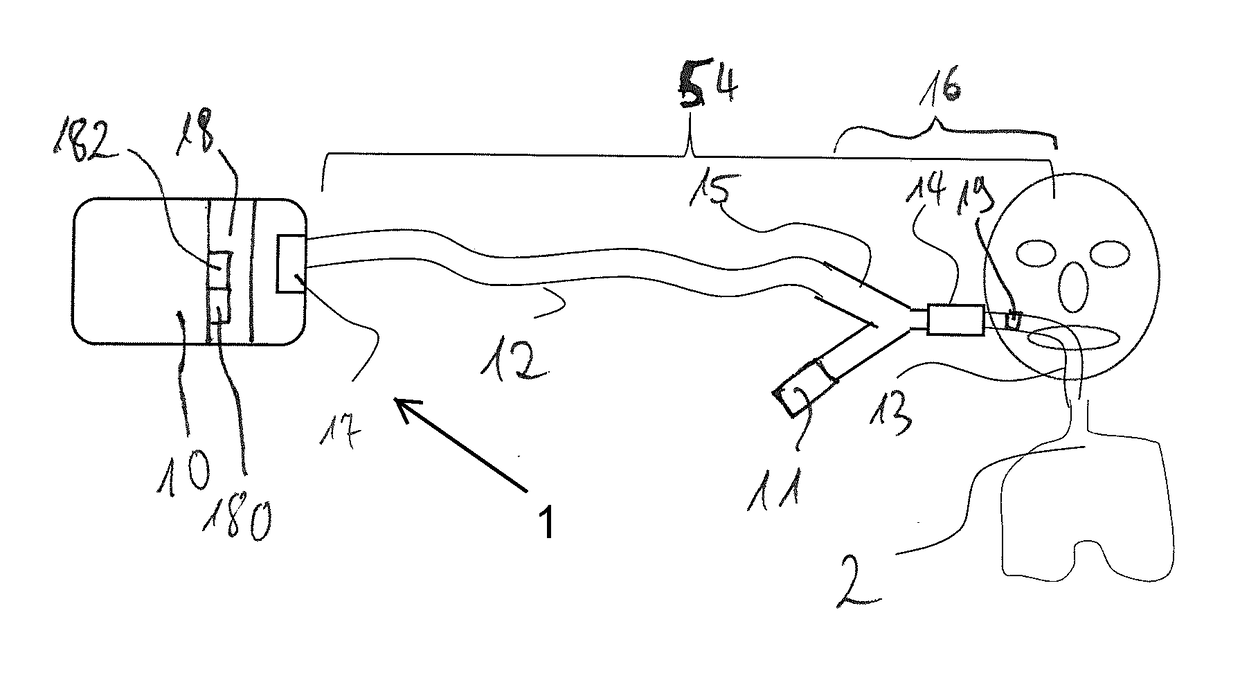
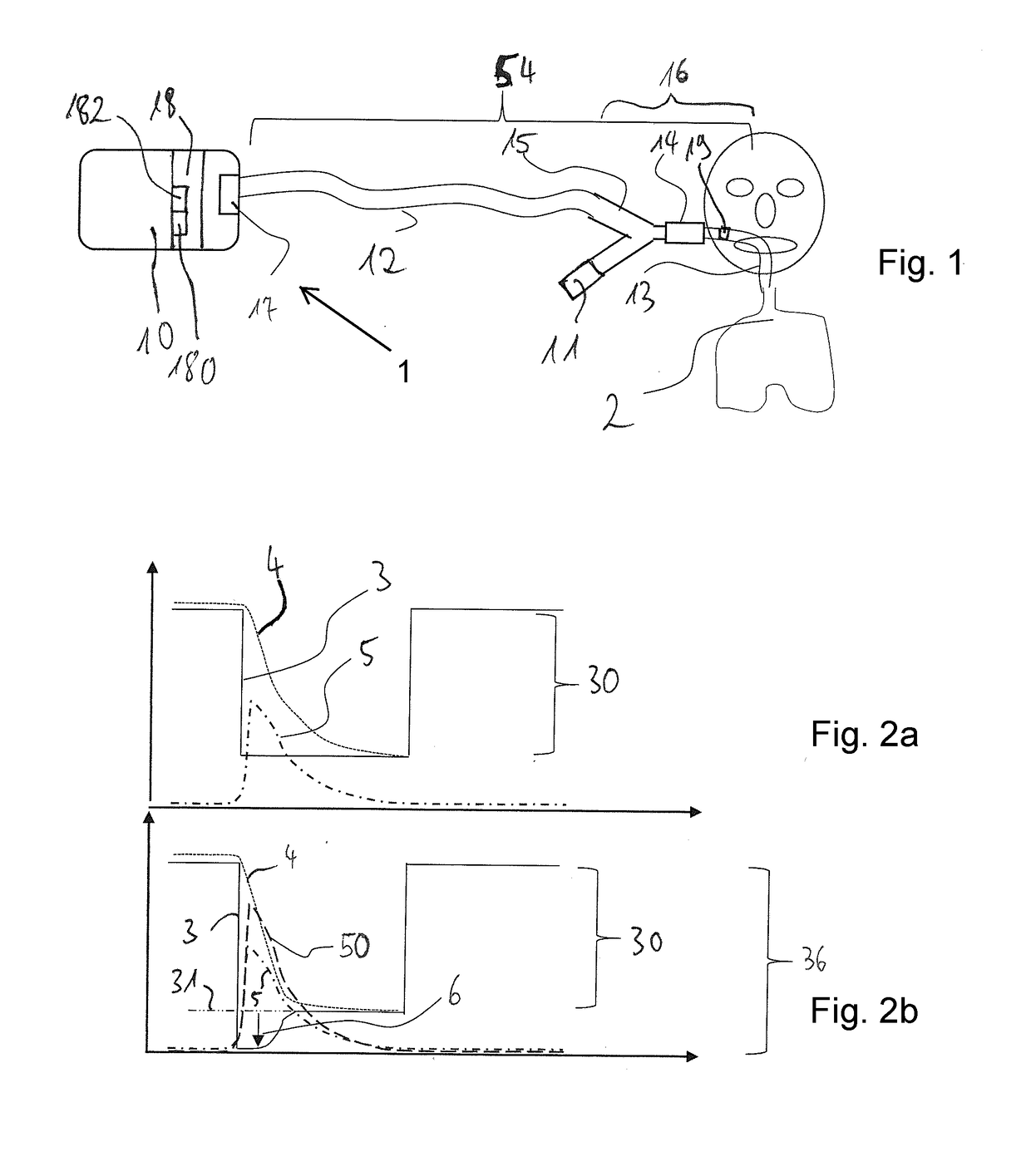
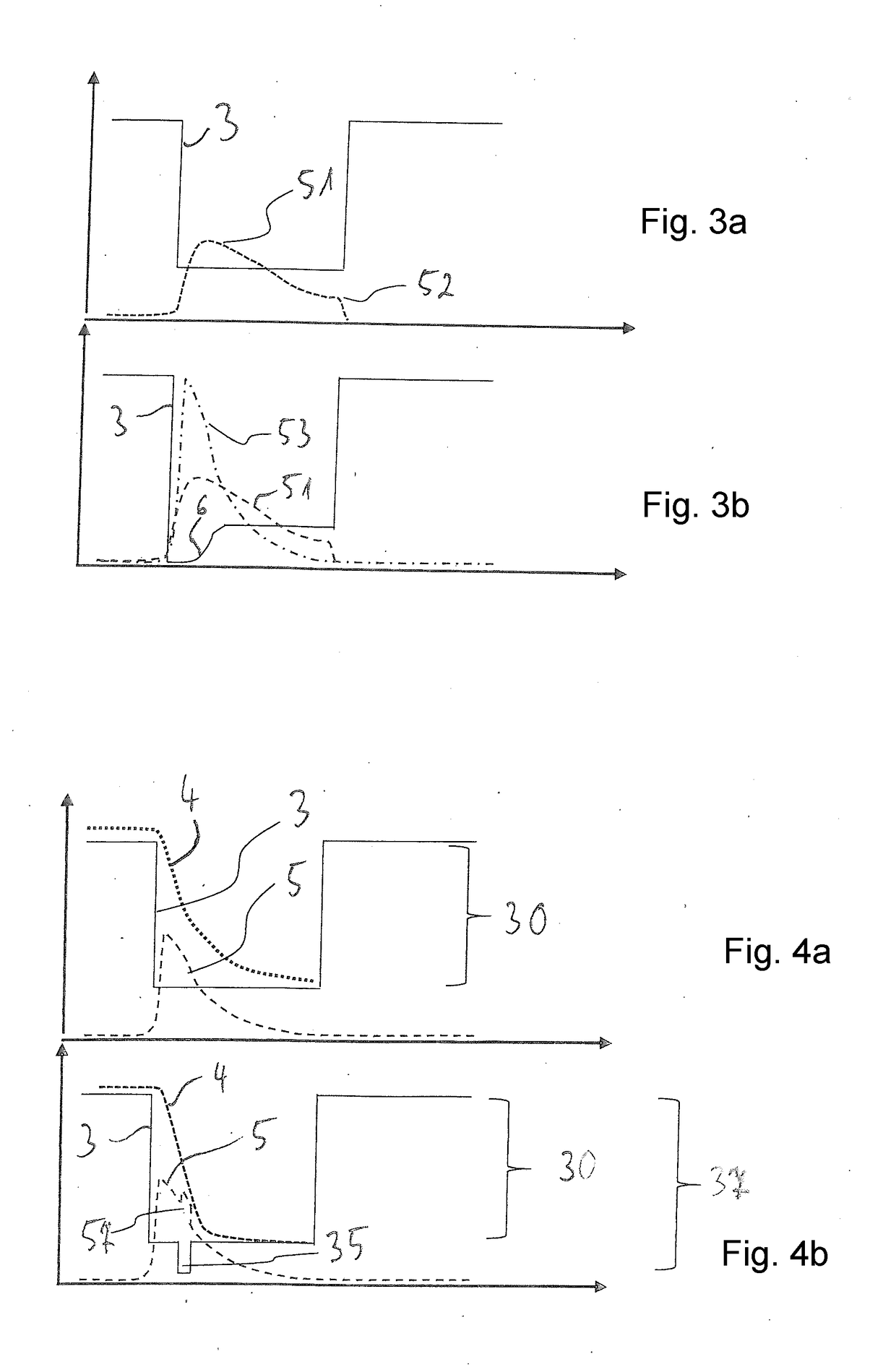
A method controls an expiratory gas flow at a user interface (16) of a ventilator (1) wherein the user interface (16) has an exhalation valve (11), which provides a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP). The method includes the following steps during a phase of exhalation: changing the positive end-expiratory pressure from a basic PEEP value (31) with the exhalation valve (11); returning the positive end-expiratory pressure to the basic PEEP value (31) with the exhalation valve (11); and determining an exhalation parameter. The method permits an adaptive change in the expiratory flow during the exhalation. Air trapping can be avoided, and it is possible to respond to changed exhalation parameters within one and the same phase of exhalation.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Method for controlling pressure of anesthesia machine and breathing machine pressure control by using expiration flow sensor
InactiveCN102397613ASolve problems when working togetherGuaranteed accuracyRespiratorsClosed loopCurve fitting
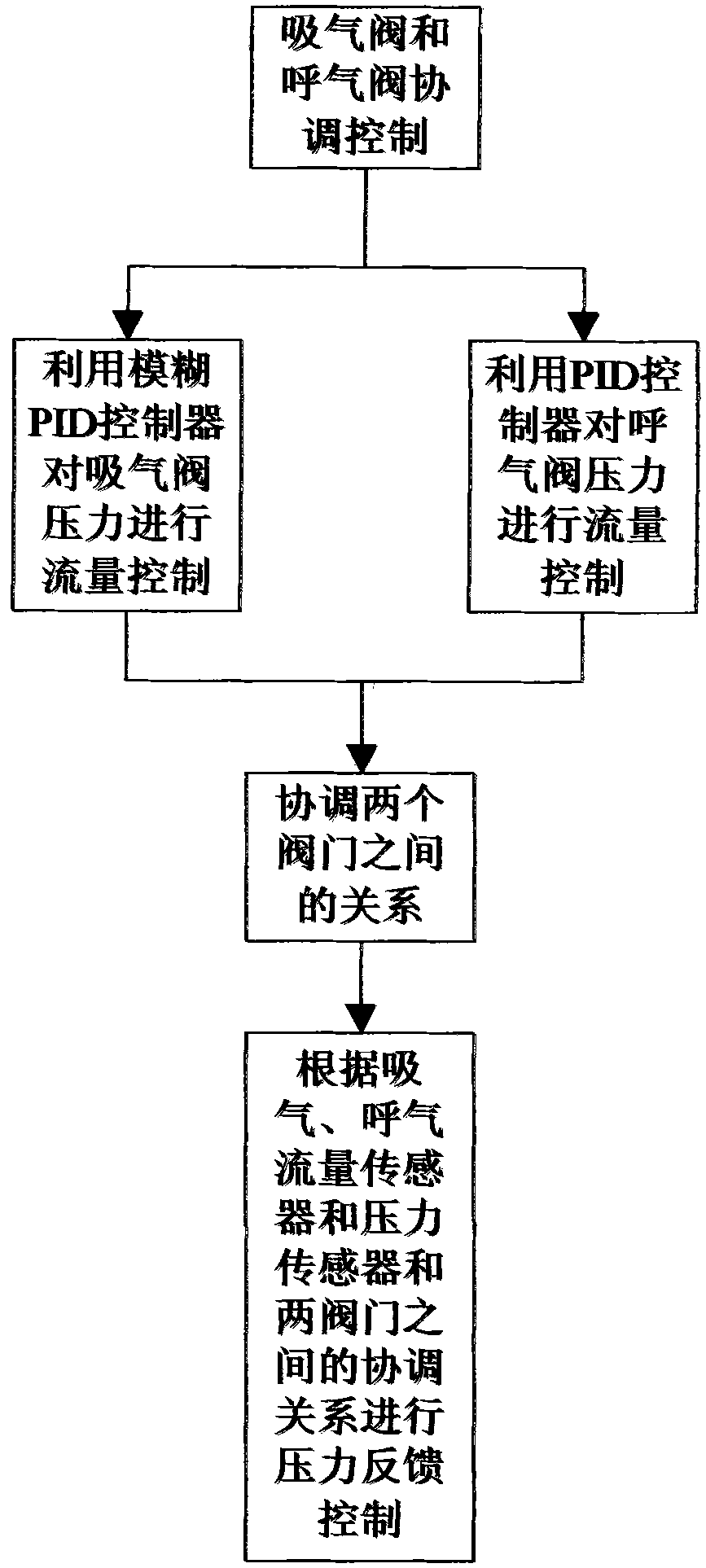
The invention discloses a method for controlling pressure of an anesthesia machine and a breathing machine by using an expiration flow sensor. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) monitoring expiration flow by using an expiration flow monitoring sensor which is arranged at the expiration mouth of an expiration valve; (2) establishing a closed-loop proportion integration differentiation (PID) flow control system for the expiration valve and the expiration flow monitoring sensor; (3) grading expiration valve controlled flow PID control parameters according to required focus points in the grading range of 1LPM to 300LPM, and fitting the PID control parameters under flow values at the focus points by a curve fitting method or a broken line approximate method; (4) calculating suction valve controlled output flow and expiration valve controlled output flow under set control pressure according to a formula P=F*R; and (5) performing pressure feedback control on the anesthesia machine and the breathing machine in a suction valve and expiration valve cooperative control mode according to the suction valve controlled output flow and the expiration valve controlled output flow.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE CHANGFENG CO LTD
Method and device for the adaptive regulation of a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)
A method controls an expiratory gas flow at a user interface (16) of a ventilator (1) wherein the user interface (16) has an exhalation valve (11), which provides a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP). The method includes the following steps during a phase of exhalation: changing the positive end-expiratory pressure from a basic PEEP value (31) with the exhalation valve (11); returning the positive end-expiratory pressure to the basic PEEP value (31) with the exhalation valve (11); and determining an exhalation parameter. The method permits an adaptive change in the expiratory flow duringthe exhalation. Air trapping can be avoided, and it is possible to respond to changed exhalation parameters within one and the same phase of exhalation.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Methods and systems for ventilation with unknown exhalation flow and exhalation pressure
This disclosure describes systems and methods for providing novel back-up ventilation. Further, this disclosure describes systems and methods for delivering ventilation when exhalation pressure and / or exhalation flow are unknown or unreliable by the ventilator.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Variable resistance pulmonary ventilation bypass valve
InactiveUS20080127982A1Eliminating or substantially reducing trapped airIncrease air pressureRespiratorsBreathing masksCollateral ventilationFlow limitation
A collateral ventilation bypass trap system directly linked with a patient's lung or lungs may be utilized to increase the expiratory flow from the diseased lung or lungs, thereby treating one aspect of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The system includes a trap, a filter / one-way valve, an air carrying conduit and a retention device for securing system elements in position. The system also includes a flow restriction device for controlling the flow of air through the air carrying conduit.
Owner:PORTAERO
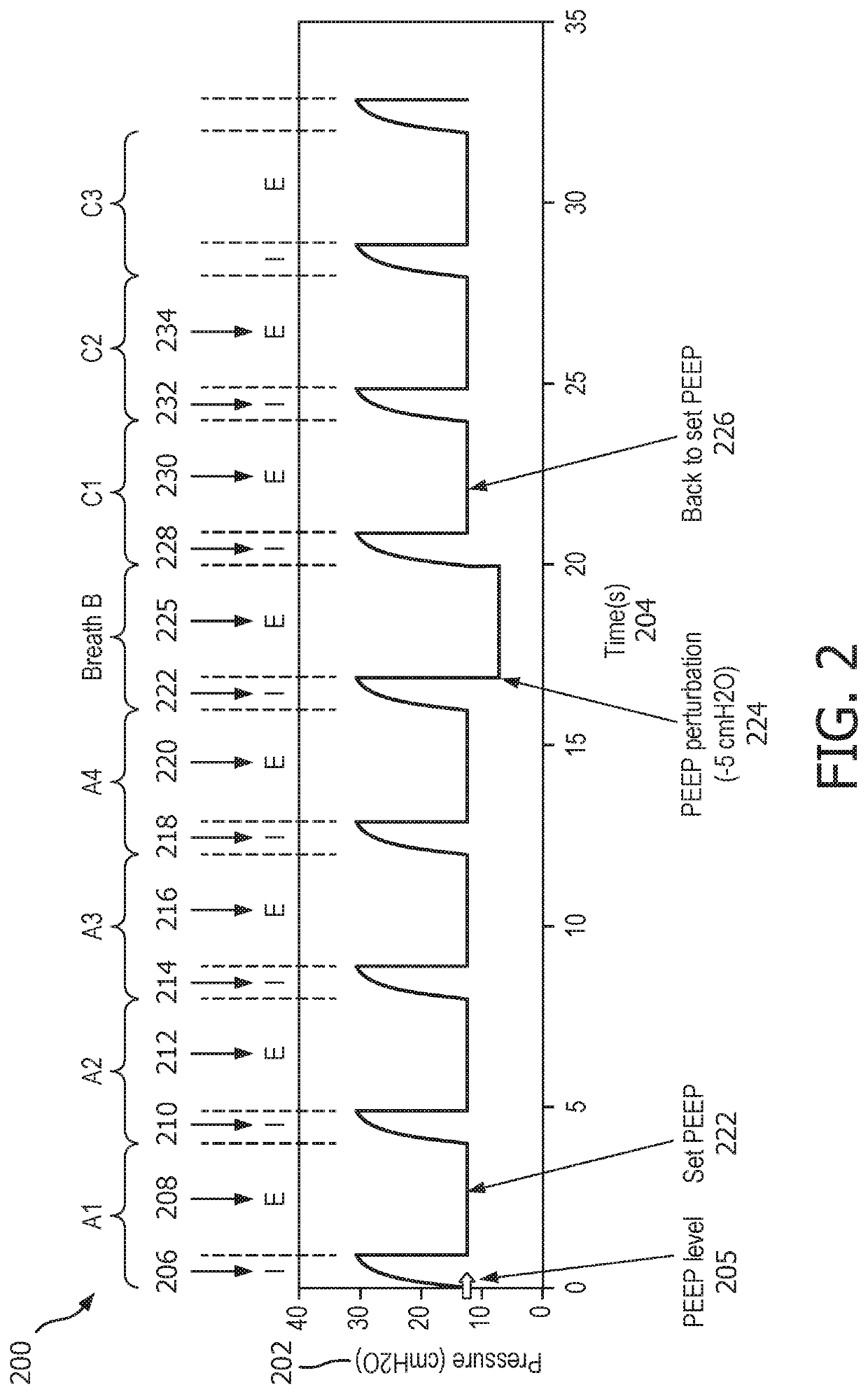
Expiratory flow limitation detection using pressure perturbations
A system and a method for expiratory flow limitation (EFL) detection by controlling positive pressure (e.g., PEEP) applied during expiration for a subject is based on a temporary perturbation or adjustment of a pressure level of positive pressure during exhalation on selected breaths. The different responses to such a perturbation of flow-limited breaths compared to non-flow limited breaths is used to assess EFL in a subject. Automatic adjustments of the positive pressure applied to the patient are used in the disclosed algorithm to abolish EFL, and are implemented through existing ventilators and other respiratory devices.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Expiratory flow limitation detection via flow resistor adjustment
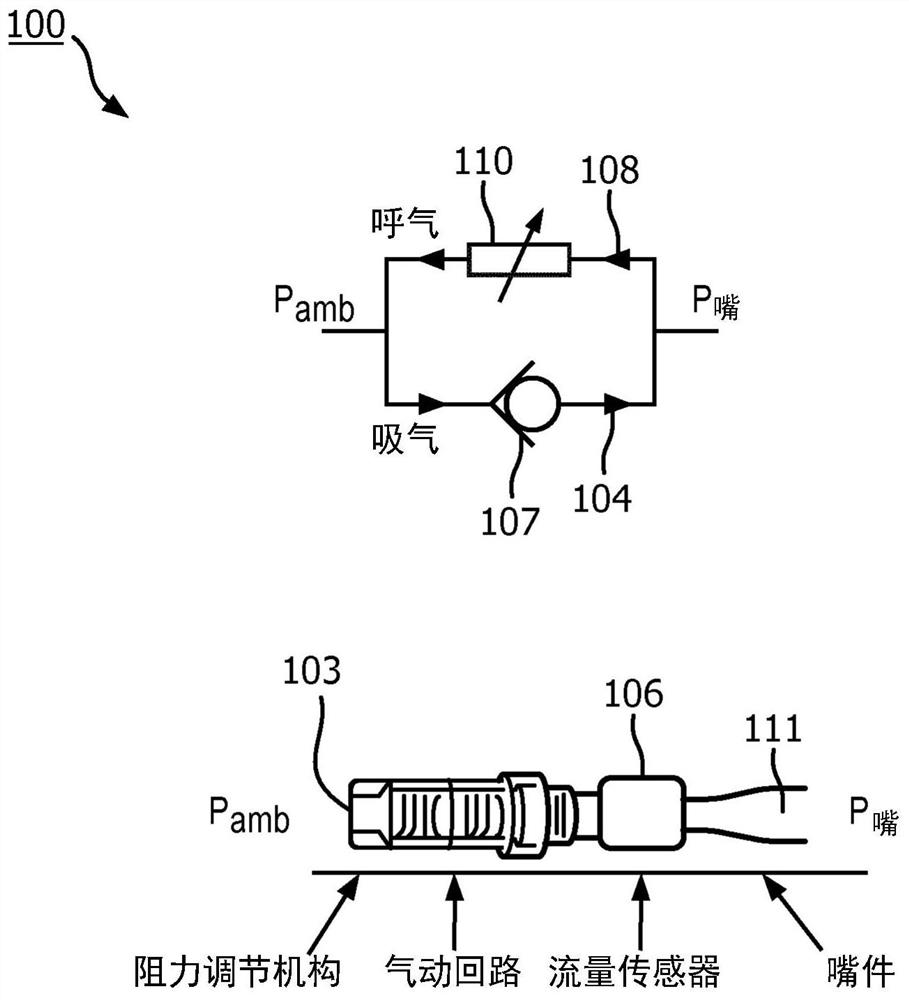
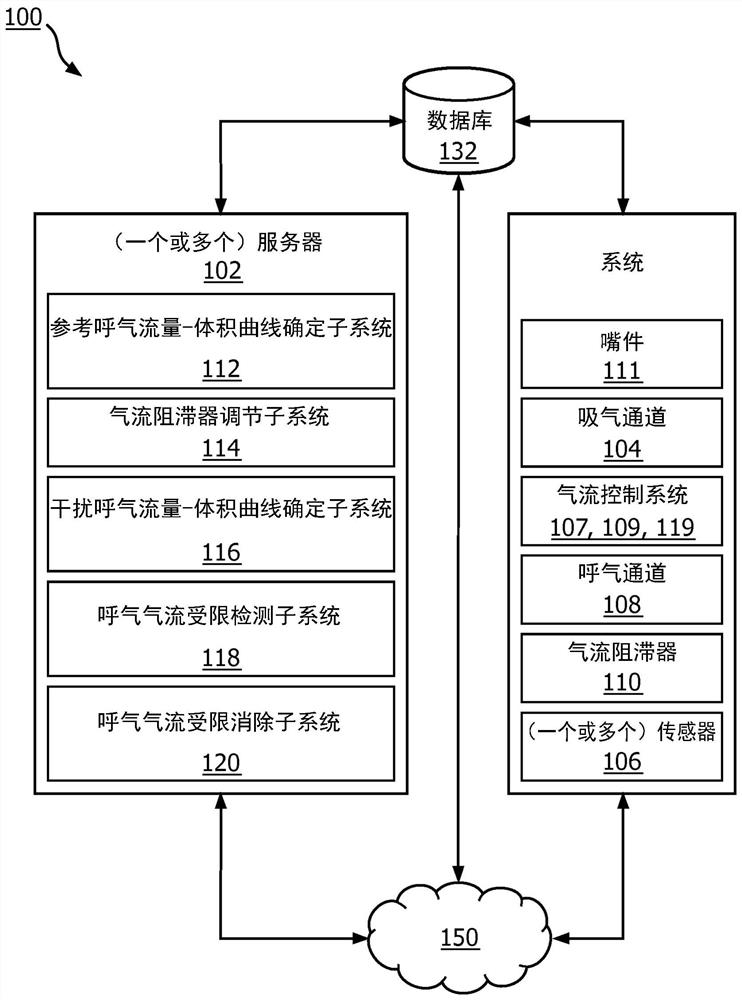
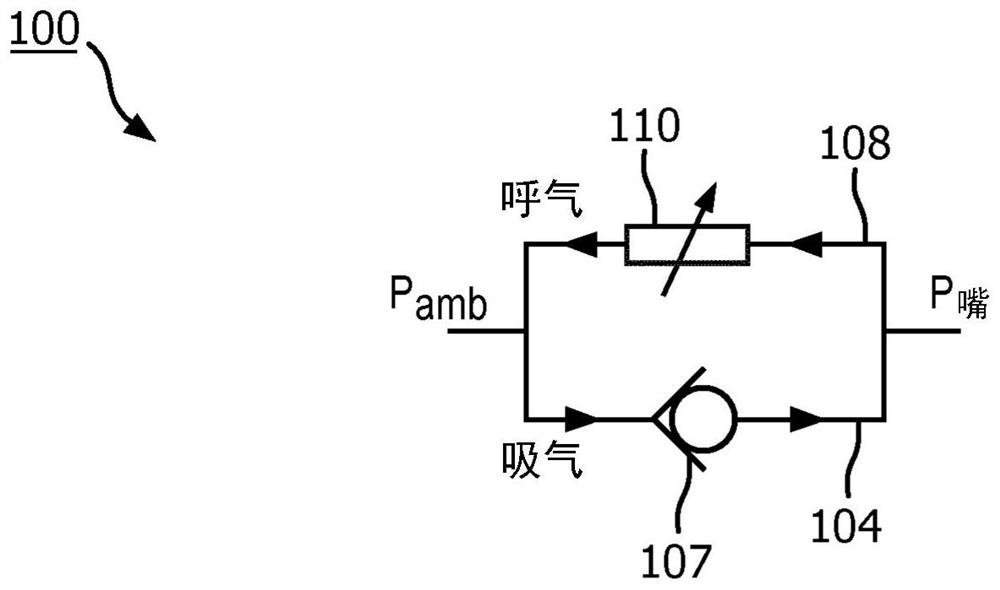
A system for detecting EFL of a patient is provided. The system comprises an inhalation passage; an exhalation passage; a sensor for measuring flow-volume information of the exhaled air through an exhalation passage; a flow resistor positioned in the exhalation passage and being adjustable to provide an exhalation resistance in the exhalation passage; and a computer system. In one embodiment, oneor more physical processors of the computer system are programmed with computer program instructions which, when executed cause the computer system to: determine a reference expiratory flow-volume curve using flow-volume information of the exhaled air through the exhalation passage when a reference exhalation resistance is provided by the flow resistor in the exhalation passage; and determine a perturbed expiratory flow- volume curve using flow-volume information of the exhaled air through the exhalation passage when a lowered exhalation resistance is provided by the flow resistor in the exhalation passage.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Arrangement for passive gas sampling
InactiveUS7040183B2Withdrawing sample devicesRespiratory organ evaluationInspiratory flowBreathing gas
An arrangement for passive gas sampling of a breathing gas in a breathing system allows sampling during both inspiration and expiration. The arrangement has a tube-piece having a first connector for receiving an inspiratory gas flow, a second connector for delivering an expiratory gas flow and a third connector for delivering the inspiratory gas flow and receiving the expiratory gas flow, a first port arranged between the second connector and the third connector and connected to a measurement chamber, a second port arranged between the first connector and the third connector and connected to the measurement chamber and a third port arranged between the first connector and the second connector and connected to the measurement chamber. The tube-piece is formed such that when an inspiratory flow passes through the tube-piece, a flow is established principally between the first port, the measurement chamber and the second port, and that when an expiratory flow passes through the tube-piece a flow is established principally between the third port, the measurement chamber and the first port.
Owner:MAQUET CRITICAL CARE
Nasal interfaces for respiratory therapy
ActiveUS10576233B2Improve comfortImprove stabilityRespiratory masksBreathing masksNasal prongsNasal congestion
Patient interfaces for respiratory therapy in the form of nasal interfaces or nasal masks include features that enhance or provide lateral stability of the interface. At least some of the embodiments provide multiple facial contact points or areas located in the general areas of the user's cheeks and / or upper lip. Some embodiments of the nasal interfaces provide advantageous sealing characteristics. The nasal interfaces may provide a controlled expiratory flow to reduce noise. Some embodiments include nasal pillows instead of or in addition to nasal prongs. The nasal pillows can have exhaust vents or can change in length in response to a pressure level within the nasal pillow.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL HEALTHCARE LTD
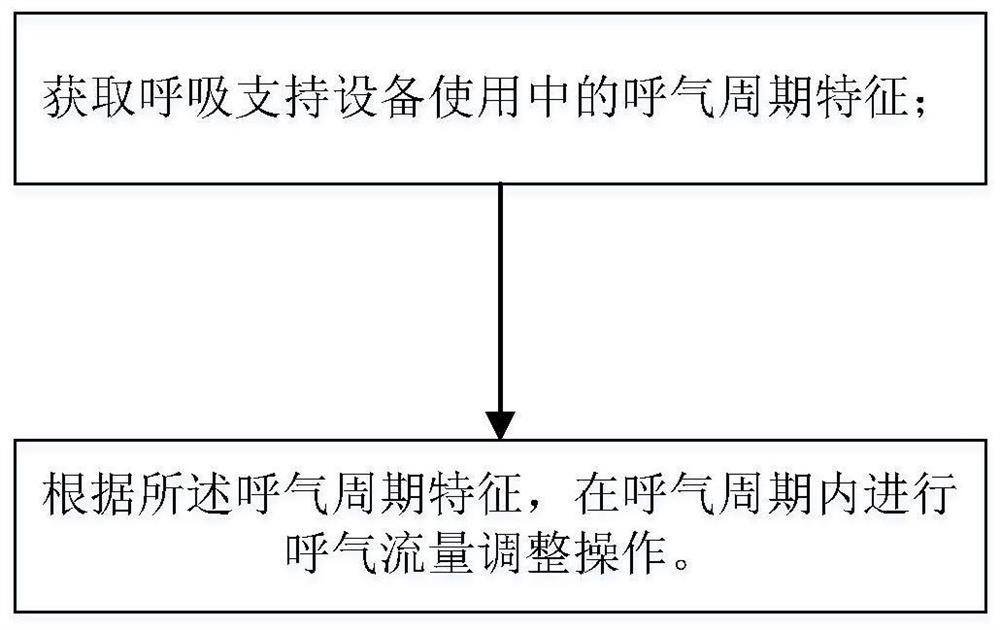
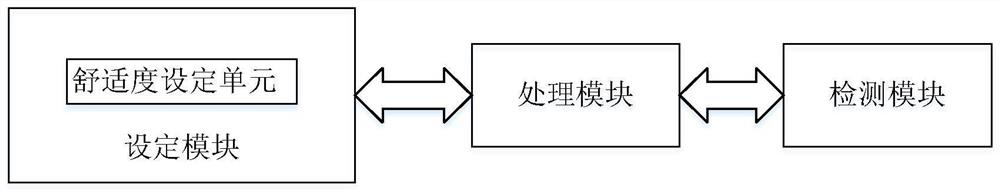
Respiratory support method capable of dynamically adjusting flow and respiratory support equipment
PendingCN112274740AImprove comfortReal-time controlRespiratorsMedical devicesExpiratory TimeEngineering
The invention relates to a respiratory support method capable of dynamically adjusting flow and respiratory support equipment. The respiratory support method capable of dynamically adjusting flow comprises the following steps: acquiring expiration period characteristics of the respiratory support equipment in use; and according to the expiration period characteristics, carrying out expiration flowadjustment operation is in the expiration period. According to the respiratory support method provided by the invention, through a flow control mode capable of setting comfort, when the expiration ofthe patient is detected, the expiration flow is dynamically adjusted, so that the use comfort of a user is improved; and the flow is reduced according to the set comfort level, and then the flow is controlled in real time according to the detected expiration time of the patient, so that the use comfort of the patient is improved and the tolerance is improved under the condition that the use requirements of the patient are met.
Owner:HUNAN MICOME ZHONGJIN MEDICAL SCI & TECH DEV CO LTD
Decontamination Device for Inhaled and Exhaled Ventilator Gases
PendingUS20210361892A1Reducing ventilator flowImprove the immunityRespiratorsMechanical apparatusExpiratory AirflowUltraviolet
The invention discloses a decontamination device for decontaminating inhaled and / or exhaled gases in a ventilator. The decontamination device comprises a gas inlet and outlet for inspiratory and expiratory gas flow, and a chamber for gas flow. The chamber is configured to connect the gas inlet and outlet. The chamber comprises at least one ultraviolet (UV) light source integrate inside the chamber that preferably emits in the UVC range, wherein the UV light source is preferably a UVC light-emitting diode. The UV light source is configured to produce UV light to decontaminate contaminants in the inhaled and / or exhaled gases by minimizing the distance between the contaminants in the gas flow and the light source, maintaining the gas flow in a gas flow path long enough to deactivate the contaminants, increasing the intensity of the light source to optimize decontamination, and increasing turbulence to redirect the gas flow and prevent boundary layers and shadowing.
Owner:HABASHI NADER M
Apparatus, method and system for monitoring respiratory state
Owner:HEFEI BOE OPTOELECTRONICS TECH +1
Respirator and using method
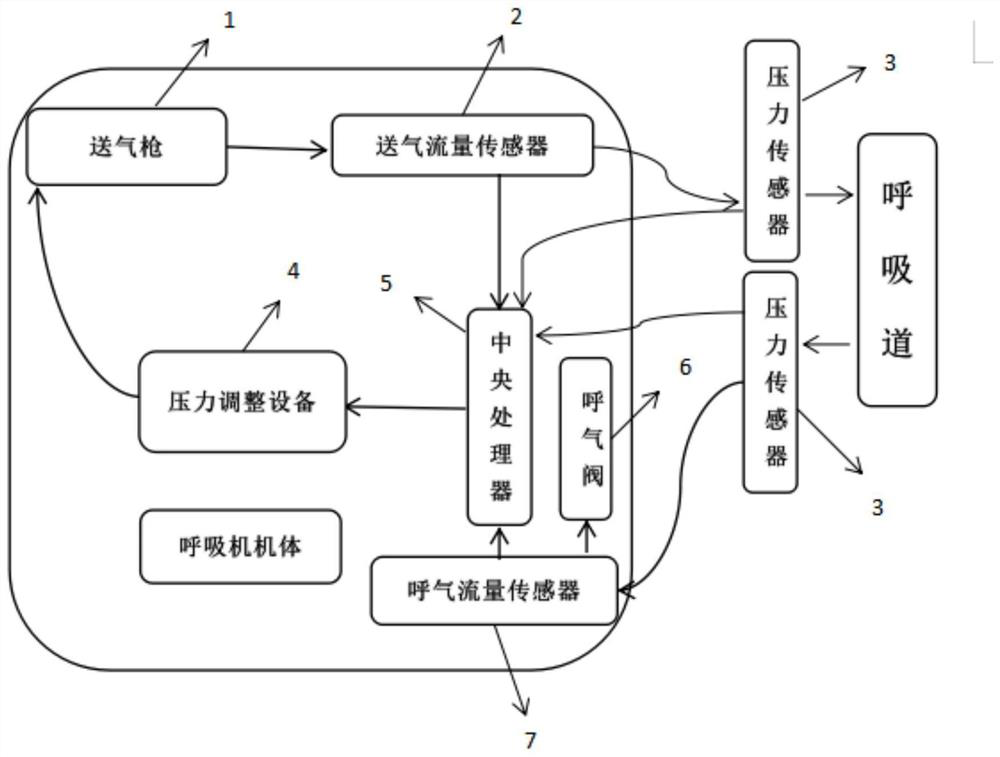
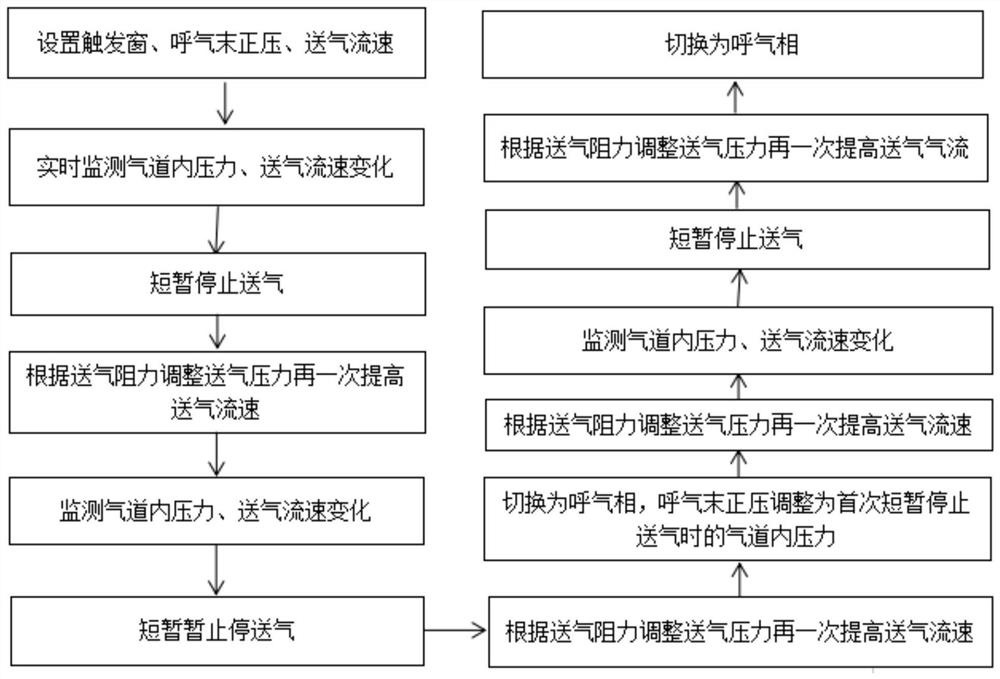
PendingCN112057714AImprove the success rate of rescueImprove lung ventilationRespiratorsMedical devicesMedical equipmentExpiratory Airflow
The invention relates to the technical field of medical equipment, and discloses a respirator and a using method thereof. The respirator comprises an expiration flow sensor, an air supply flow sensorand a plurality of pressure sensors, a central processing unit, pressure adjusting equipment, an air supply gun and an exhalation valve, wherein the pressure sensors are used for measuring the air supply flow pressure and the expiration flow pressure and arranged on an air supply pipe and an expiration pipe; the central processing unit is used for receiving the data of the air supply flow sensor and the expiration flow sensor, comparing, integrating and calculating the data of the air supply flow and the expiration flow, and controlling the pressure adjusting equipment according to the integrated and calculated data and the data of the plurality of pressure sensors; the pressure adjusting equipment is used for adjusting the pressure of the air supply flow according to an instruction of thecentral processing unit and adjusting the pressure of the air supply flow; the air supply gun is used for conveying airflow with corresponding pressure according to data of the pressure adjusting equipment; and the exhalation valve is used for controlling and exhausting exhalation air flow. According to the respirator and the using method, the treatment success rate of the ARDS patient can be increased.
Owner:王军
Ventilation equipment and expiration flow correction method
The invention provides ventilation equipment and an expiration flow correction method, and the correction method comprises the steps: in a current respiratory cycle, obtaining a first measurement signal output by a first flow sensor for detecting the expiration flow, and obtaining a second measurement signal output by a second flow sensor for detecting the expiration flow; the drift distance of the second flow sensor is inversely calculated according to the first measurement signal and the second measurement signal; correcting a second corresponding relation between the second measurement signal and the expiratory flow according to the drift distance; in the next respiratory cycle of the current respiratory cycle, the second flow sensor obtains a fourth flow value according to the corrected second corresponding relation and at least displays the fourth flow value; wherein the drift distance generated by the first flow sensor due to environment change is smaller than the drift distance generated by the second flow sensor due to environment change. According to the expiration flow correction method, the detection accuracy of the expiration flow can be effectively improved.
Owner:深圳市普博医疗科技股份有限公司
Ventilation control unit and ventilation control system
PendingUS20210338954A1Regulation of gas flowIncrease airflowRespiratorsMedical devicesControl theoryInspiratory gas flow
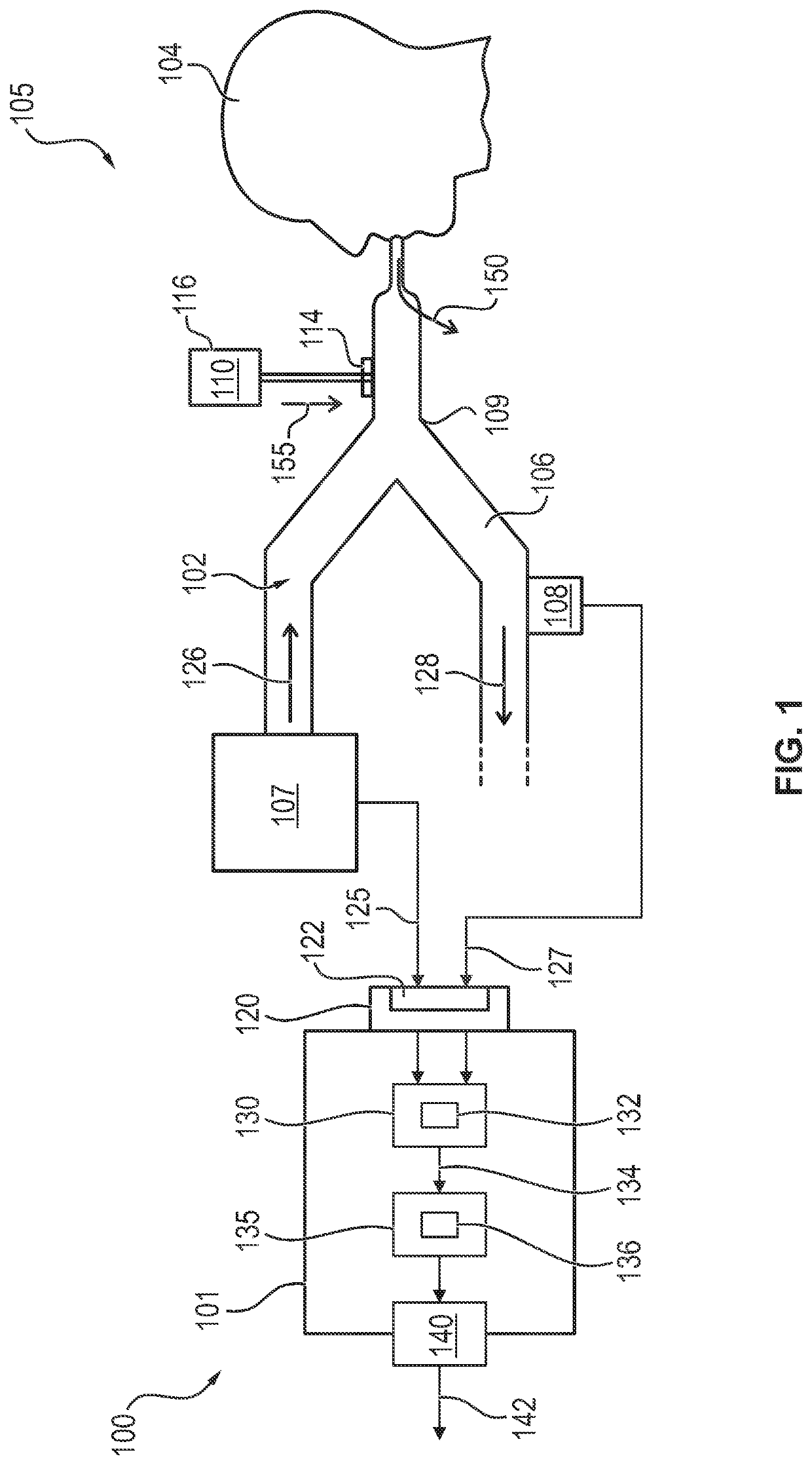
A ventilation control unit (100), regulating a gas flow (102) within a ventilation system (105), includes a reception module (120), first and second calculation modules (130, 135) and an output module (140). The reception module has a signal interface (122) receiving inspiratory and expiratory flow signals (125, 127) at regular time intervals. The first calculation module calculates a leak flow (132) based on a difference between the current inspiratory gas flow and the current expiratory gas flow, with an external gas flow source (110) separated from a ventilation circuit of the ventilation system. The second calculation module calculates an external gas flow (136) after connecting the external gas flow source to the ventilation circuit based on the leak flow and the difference between the current inspiratory gas flow and the current expiratory gas flow. The output module outputs an output signal (142), based on the external gas flow.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Intelligent evaluation system for ventilation function examination
PendingCN114869267AImprove accuracyImprove inspection efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationSimulation
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
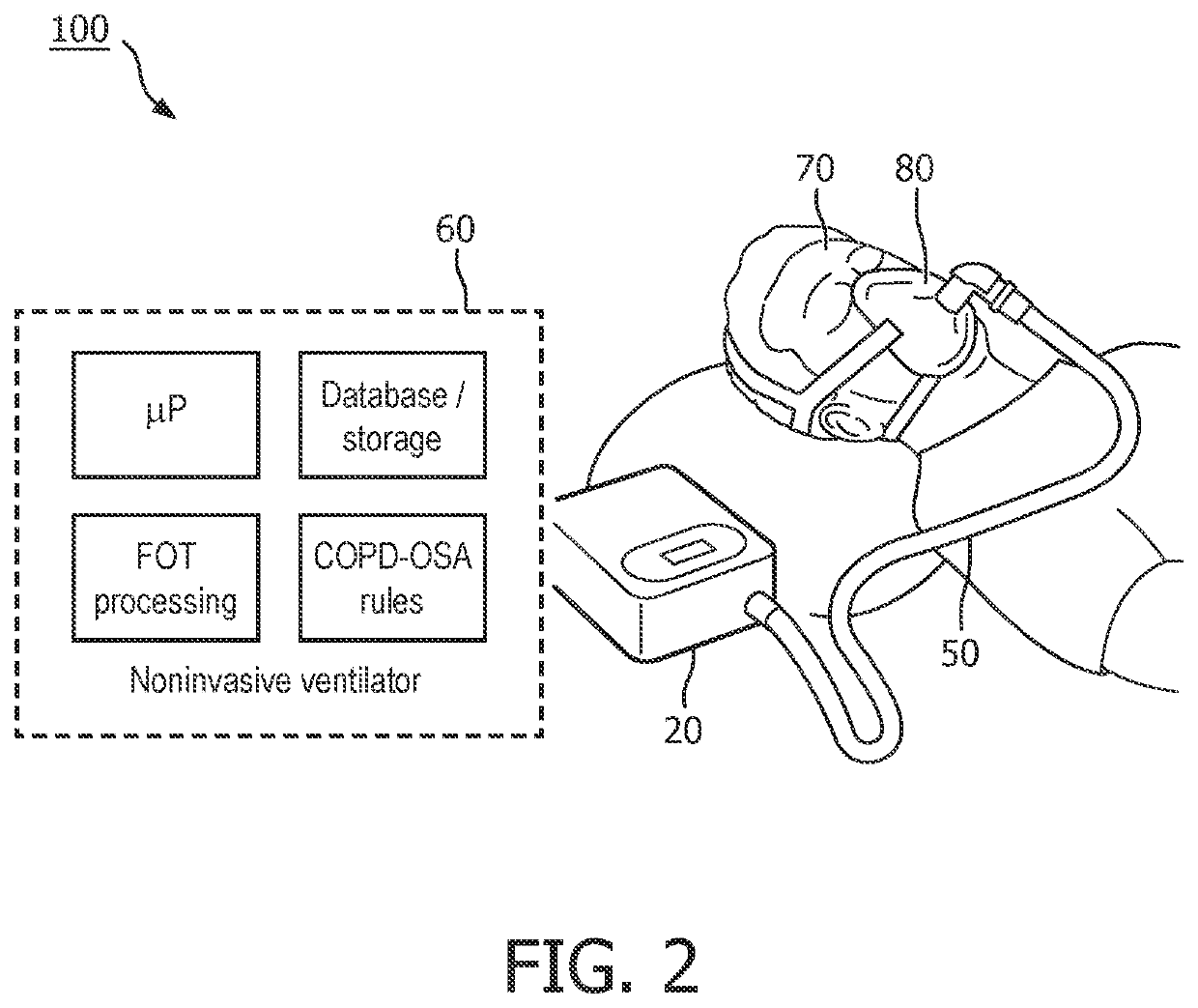
Detecting and treating copd-osa overlap syndrome
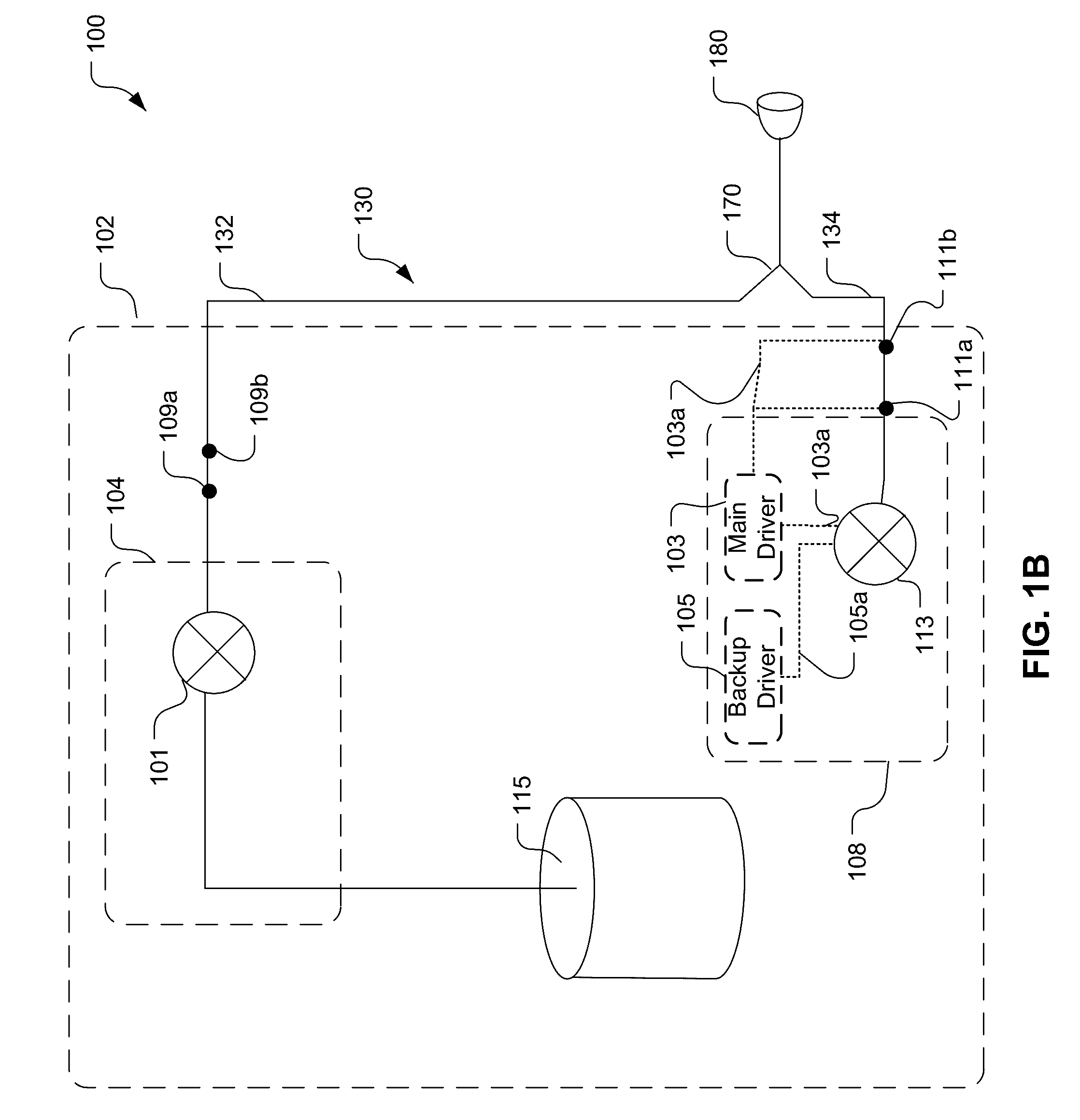
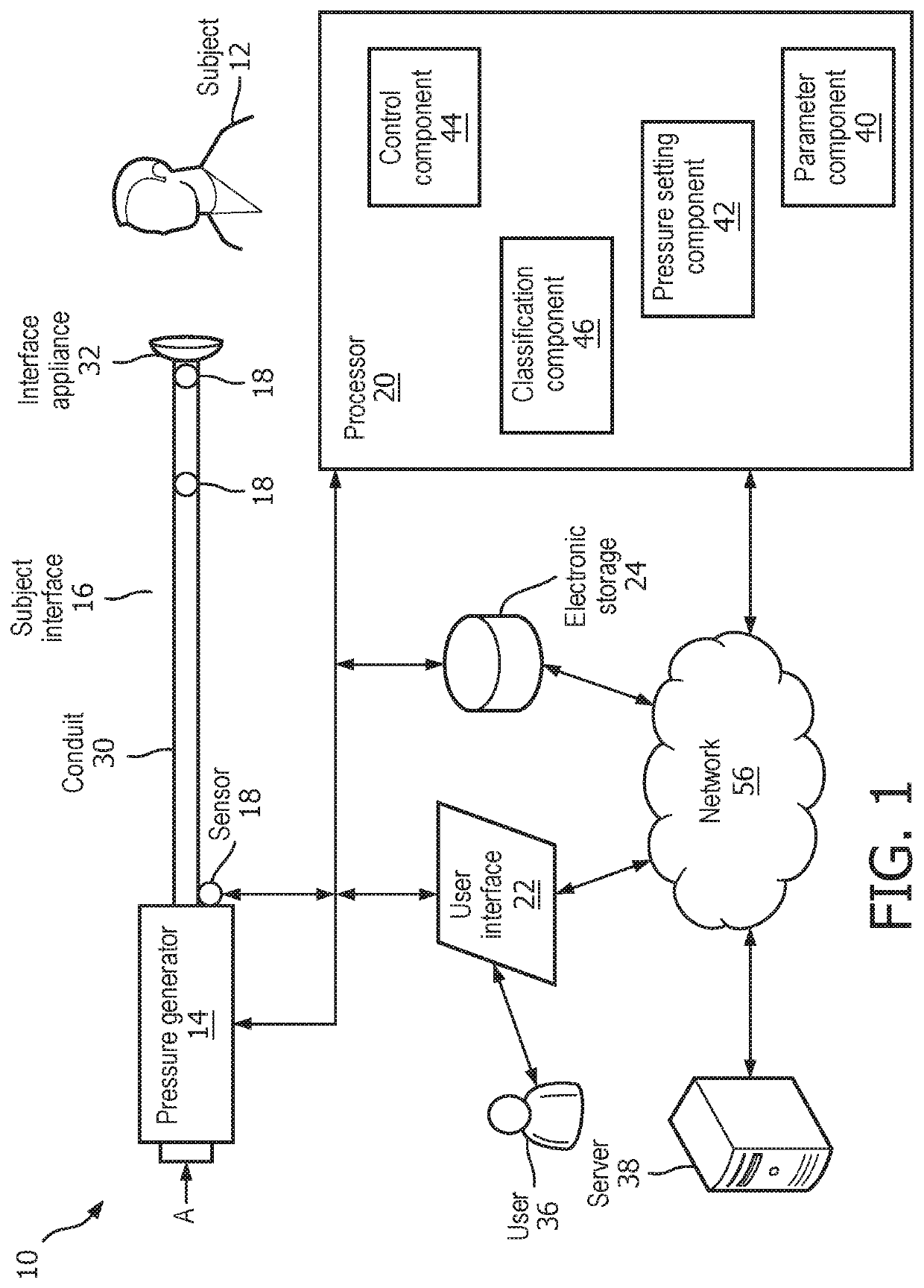
The present ventilator system, for detecting and treating concurrent chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA event(s)) overlap syndrome, comprises a pressure generator for generating a pressurized flow of breathable gas for delivery to an airway of a subject; sensor(s) for generating output signals conveying information related to breathable gas parameters; and processor(s) operatively connected to the sensor(s) and the pressure generator, configured to: detect presence of OSA event(s) and / or expiratory flow limitation (EFL) in the subject based on the output signals. Responsive to detecting concurrent presence of OSA event(s) and EFL, the processors are configured to determine OSA EVENT(S) therapy parameters for treating the detected OSA event(s) in the subject; determine EFL therapy parameters for treating the detected EFL in the subject; determine a priority treatment based on a comparison between the OSA event(s) therapy parameters and the EFL therapy parameters; and control the pressure generator to deliver the determined priority treatment.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Interactive guidance related to a subject's expiratory flow limitation results
In certain embodiments, a ventilator may provide interactive guidance for obtaining a subject's expiratory flow limitation results. In some embodiments, the ventilator may cause a progressive color component to be presented, where the progressive color component indicates a progression from one color proximate one side of the progressive color component to another color proximate another side of the progressive color component. The ventilator may cause a forced oscillation to be continuously applied to an airway of the subject for a time period. The ventilator may monitor the subject's degree of expiratory flow limitation based on output signals generated by one or more sensors as the forced oscillation is continuously applied for the time period. The ventilator may cause, based on the monitoring, a movable component's position on the progressive color component to be continuously updated during the time period to indicate the degree of expiratory flow limitation.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
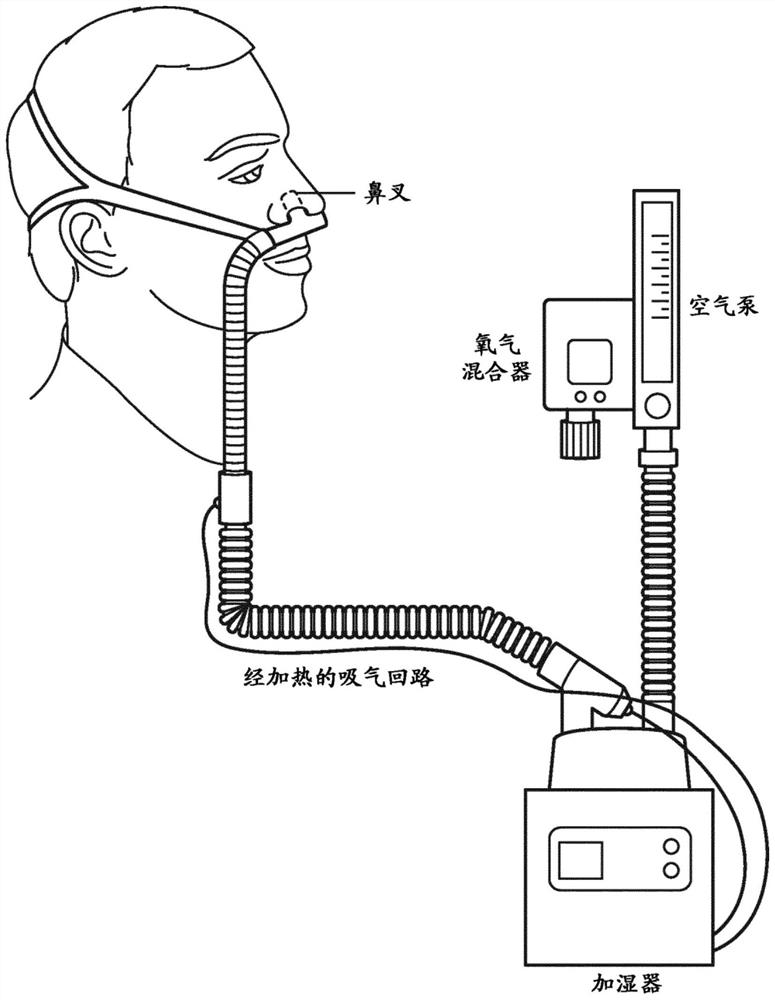
Oxygen recovery during nasal therapy
The system comprises an oxygen supply device; one or more sensors configured to generate an output signal conveying information about whether the patient is in an inspiration phase or an expiration phase; one or more valves; and a computer system. The one or more valves have: a) a first configuration in which the one or more valves operate to recover an excess flow of oxygen-enriched breathing gas during an inspiration phase; and b) a second configuration in which the one or more valves discharge the patient's expiratory flow to the atmosphere during the expiratory phase. The one or more physical processors are programmed with computer program instructions that, when executed, cause the computer system to provide input to the one or more valves based on the output signal, the provided input causing the one or more valves to move between the first and second configurations.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
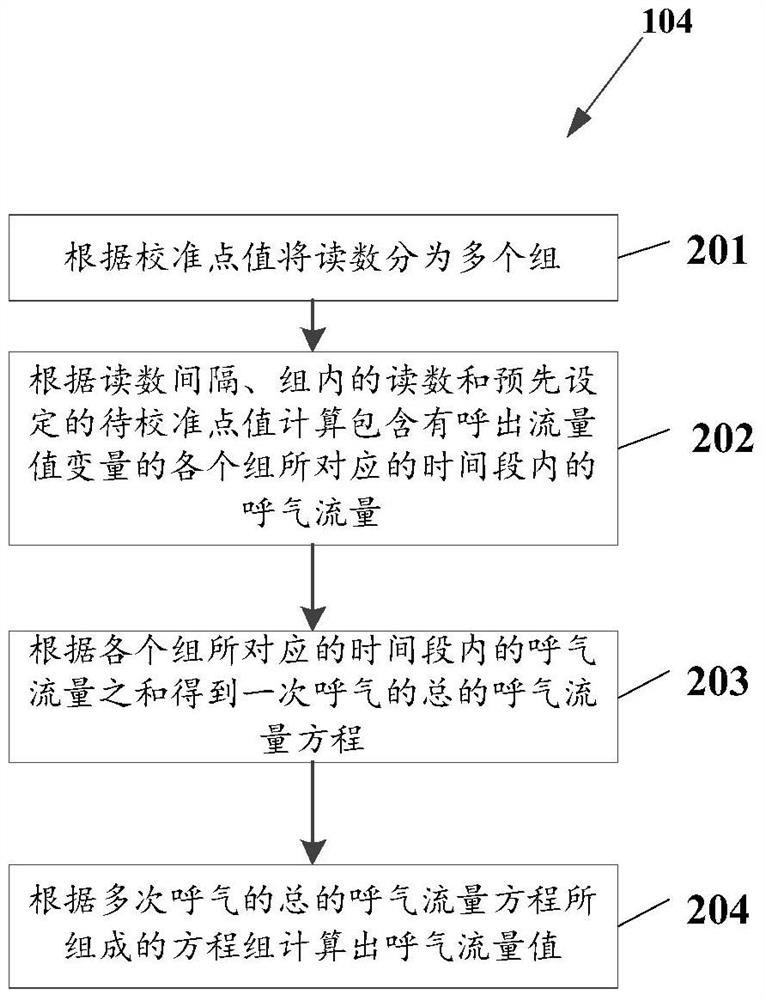
Method and device for calibrating expiratory flow sensor of anesthesia machine
The invention relates to a method and device for calibrating an expiratory flow sensor of an anesthesia apparatus. The method comprises: enabling a simulated lung disposed on the anesthesia apparatus to inhale through the anesthesia apparatus; recording tidal volume provided to the simulated lung by the anesthesia apparatus; recording a reading of the expiratory flow sensor when the simulated lung exhales; and calculating an expiratory flow value corresponding to a point value to be calibrated, according to the tidal volume, the reading and a preset point value to be calibrated.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Expiratory pressure automatic titration method and system based on expiratory flow limited index
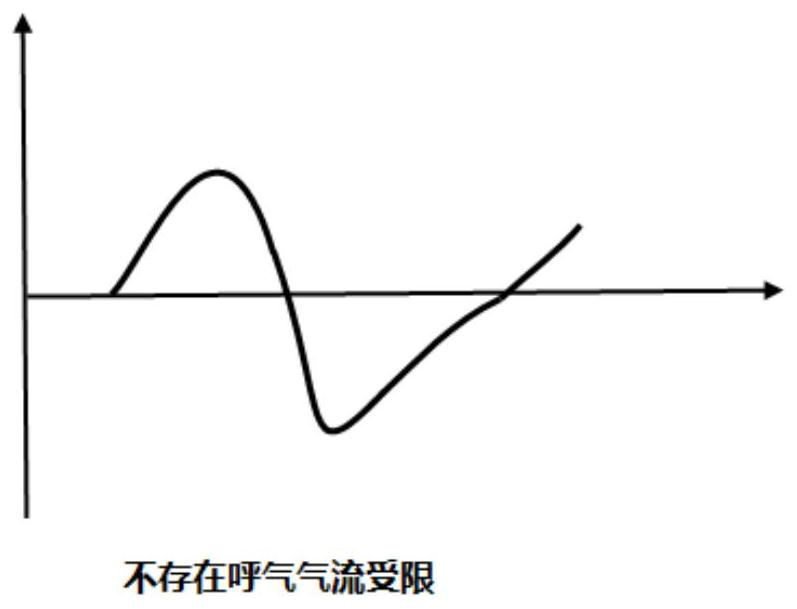
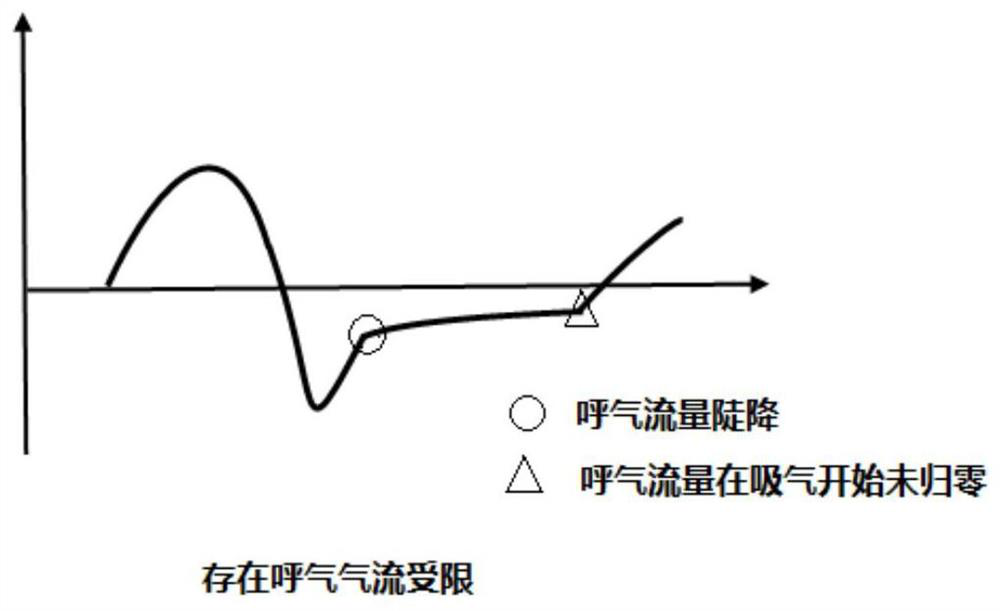
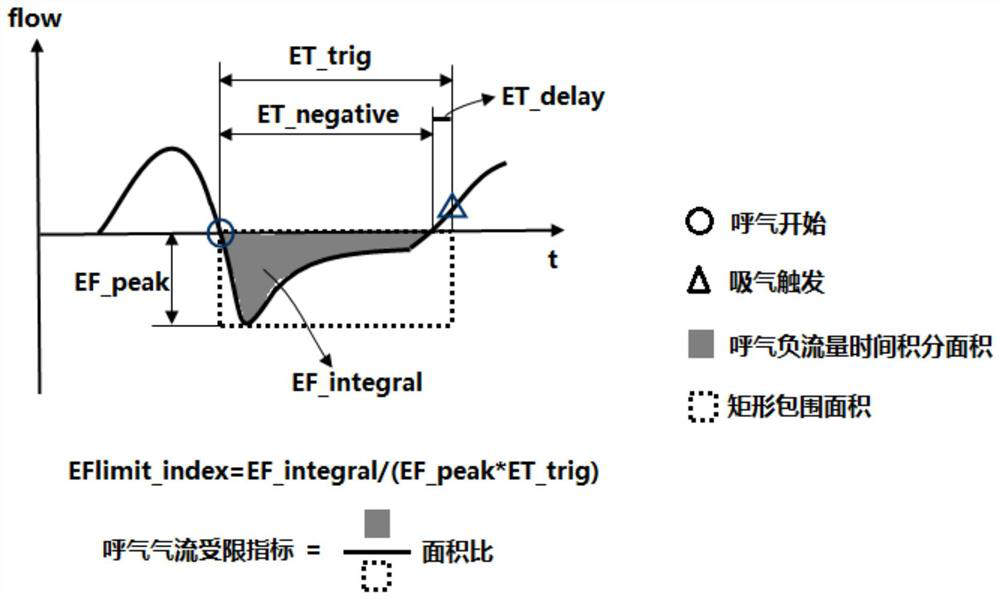
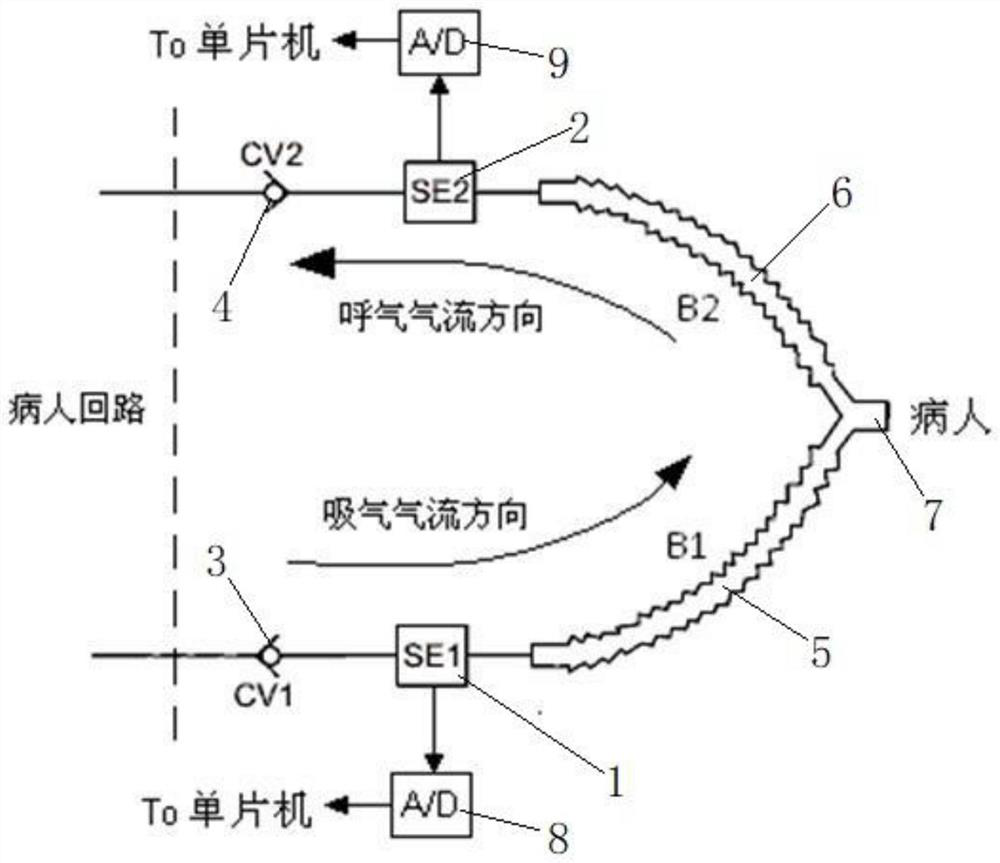
ActiveCN112827030ASimple calculationLow costRespiratorsDiagnostic recording/measuringExpiratory AirflowExpiratory Time
The invention discloses an expiration pressure automatic titration method and system based on an expiration flow limited index; the method comprises the steps: in a maintenance stage, when a preset maintenance time is reached, calculating a current expiration flow limited index according to a negative expiration flow, an expiration peak flow and expiration time which are monitored in real time, and entering a regulation stage; determining whether the current expiratory flow limited index is smaller than the expiratory flow limited index at the end moment of the previous adjustment stage or not, and if yes, increasing the positive end expiratory pressure; if not, carrying out the operation of lowering the positive end expiratory pressure; and when the positive end expiratory pressure increasing operation or the positive end expiratory pressure decreasing operation is ended, recording the expiratory flow limitation index when the adjusting stage is ended. The exhaled air flow limitation index provided by the invention has vivid description significance and can be used as an indication of the actual exhaled air flow limitation degree; the method is relatively simple in calculation, does not need hardware support with high complexity requirements, and reduces the product cost.
Owner:BEIJING AEONMED
Dynamic calibration device for zero position of flow sensor of anaesthesia machine and dynamic calibration method
PendingCN112569440AReal-time calibrationReal-time zero calibrationRespiratorsMedical devicesFlow transducerPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention discloses a dynamic calibration device for a zero position of a flow sensor of an anaesthesia machine and a dynamic method thereof, and the device and method can achieve the zero calibration of an expiration flow sensor during inspiration and the zero calibration of the inspiration flow sensor during expiration, and achieve the real-time zero calibration of the anaesthesia machine during operation without shutdown for zero calibration. The zero calibration of the inspiration flow sensor and the expiration flow sensor can be completed in one ventilation period. The inspiration andexpiration are alternately carried out, zero calibration and measurement are also alternately carried out, the device can be immediately used for next flow measurement after zero calibration each time, even if zero drift occurs in the using process, zero drift can be immediately eliminated, and real-time, non-stop and dynamic zero calibration is truly achieved. The zero calibration is automatically carried out, manual operation is not needed, and zero calibration errors caused by human factors are eliminated.
Owner:上海力申科学仪器有限公司
Method and apparatus for assessing blood concentration of volatile constituent
A method and apparatus for of assessing the blood concentration level in a human or animal subject, of a volatile blood constituent (preferably alcohol) is disclosed. The method comprises steps of positioning a sensor (21, 22) within the expiratory gas flow of the subject, wherein the sensor (21, 22) is configured to detect the presence of the constituent and provide a first output signal representative of the concentration of said constituent in air, and also to detect a presence of carbon dioxide and to provide a second output signal representative of the concentration of carbon dioxide in air. The flow of expiratory gases from the subject is sampled to provide a first signal and second signal in respect of the expiratory gases substantially simultaneously. The method also comprises the step of inputting said first and second signals obtained by the sampling step into an algorithm configured to compare the variation of the first signal over time with the variation of the second signal over time and, depending on the result of the comparison, to make said second signal representative of the degree of dilution of said expiratory airflow. The invention further includes an apparatus for carrying out the method.
Owner:VEONEER SWEDEN AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com