Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
168 results about "Endoscopic manipulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
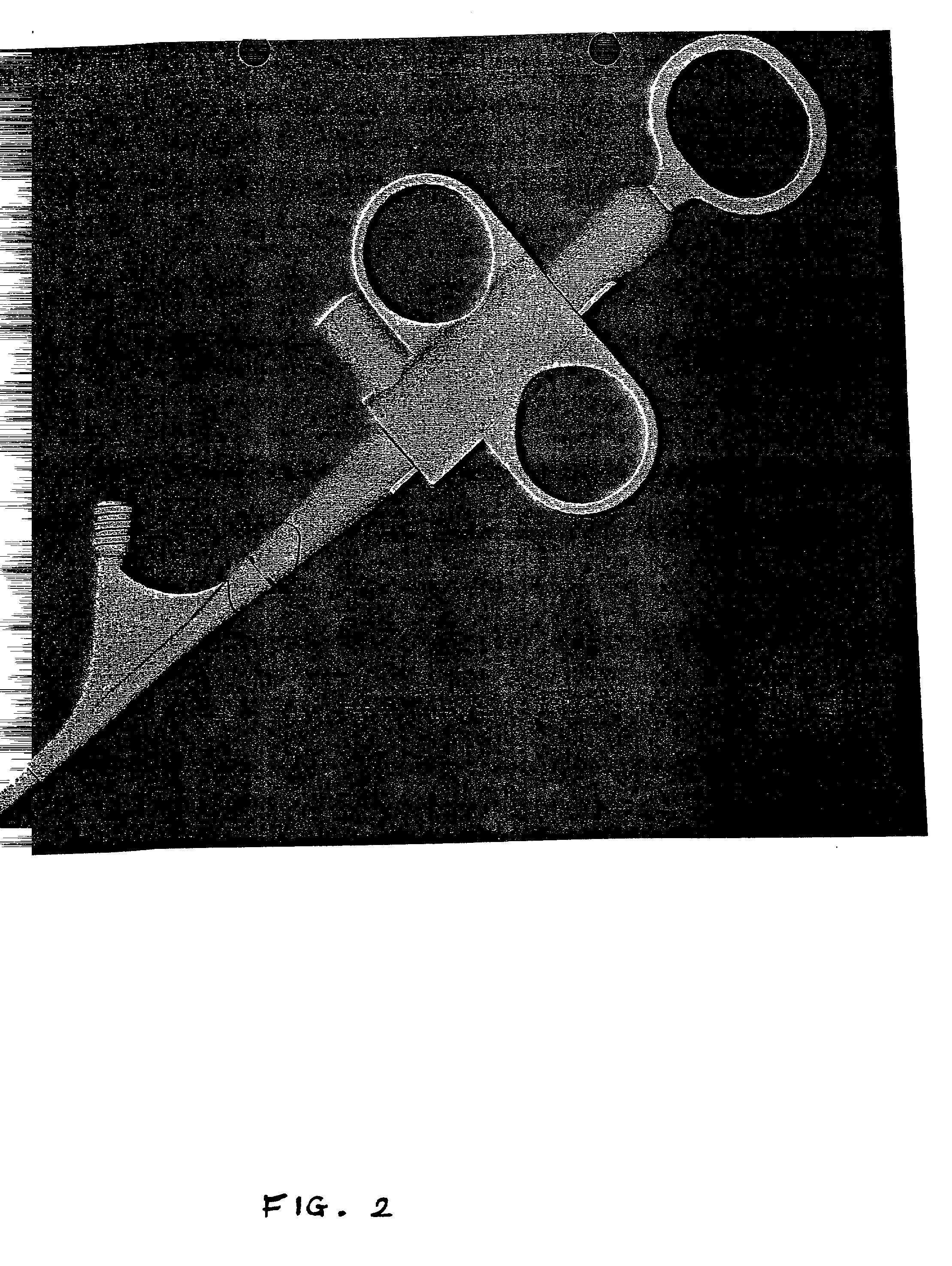
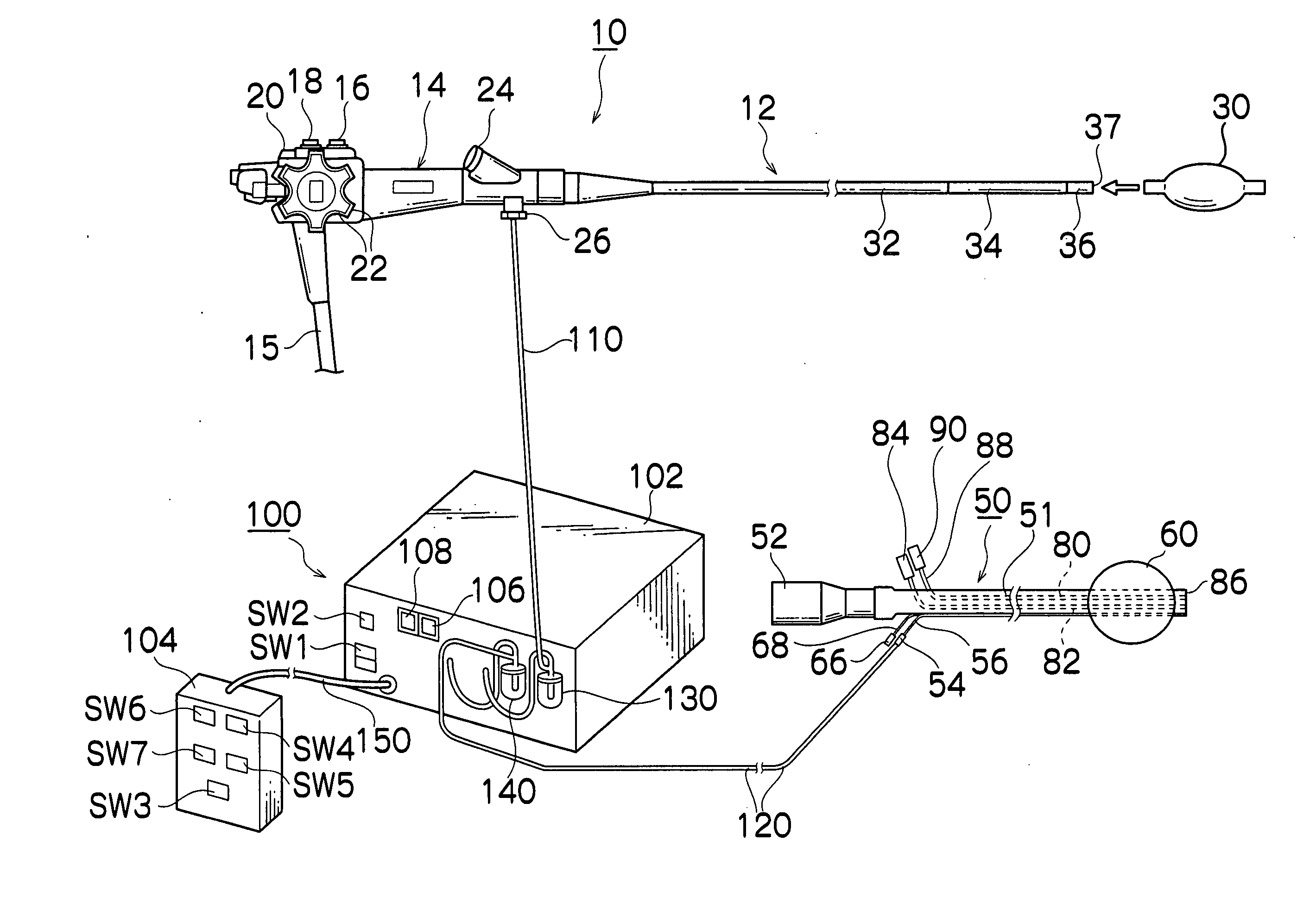
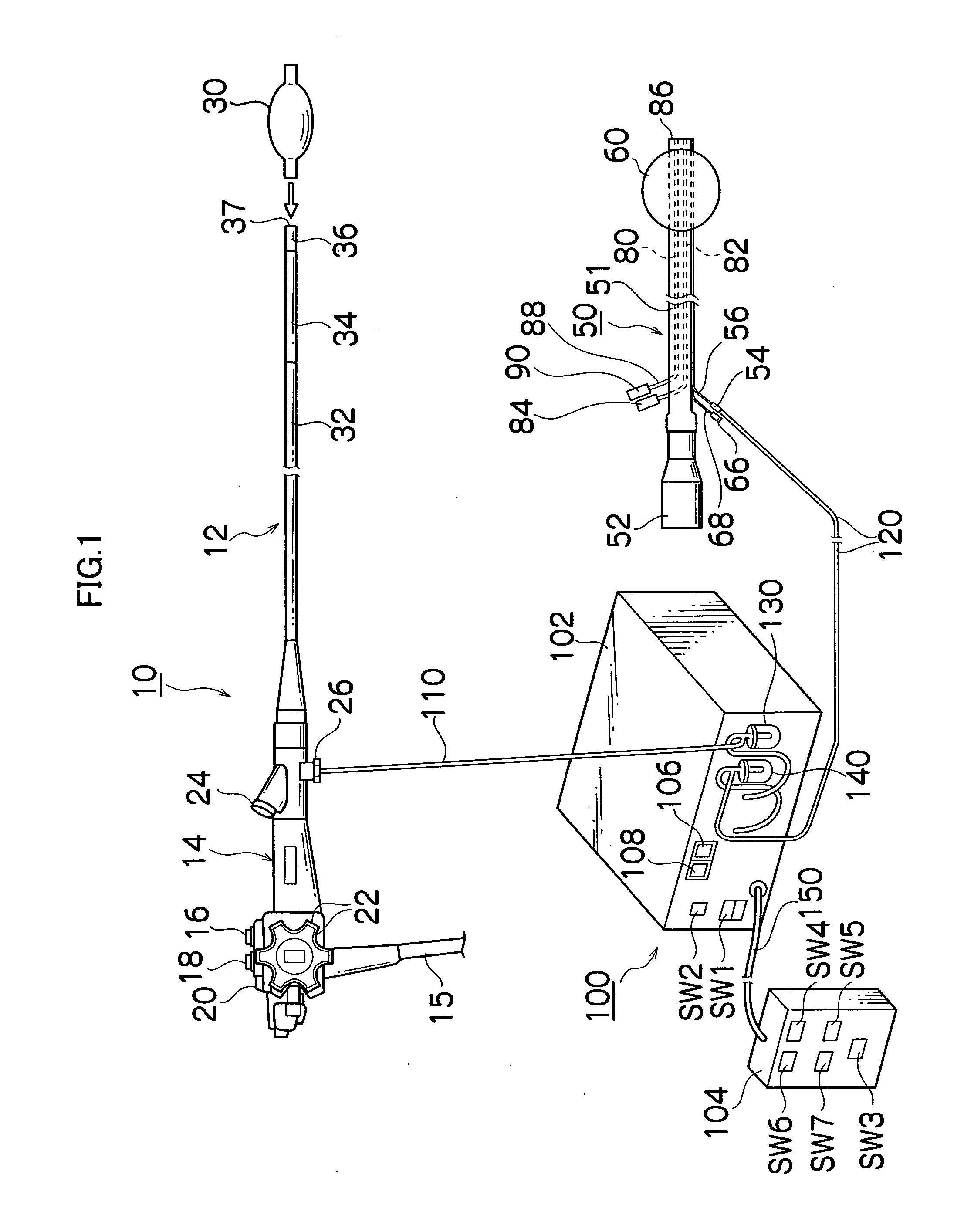
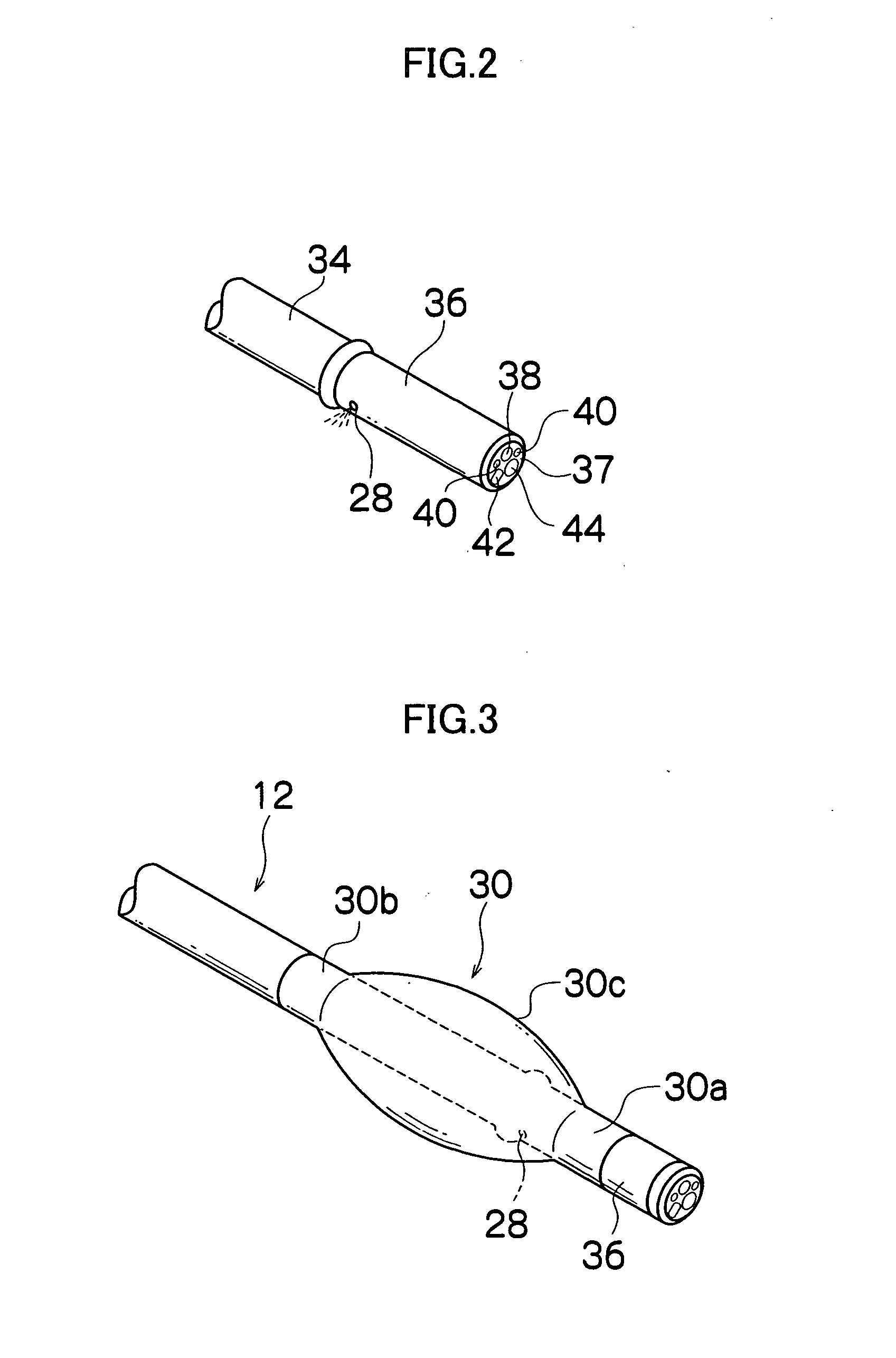
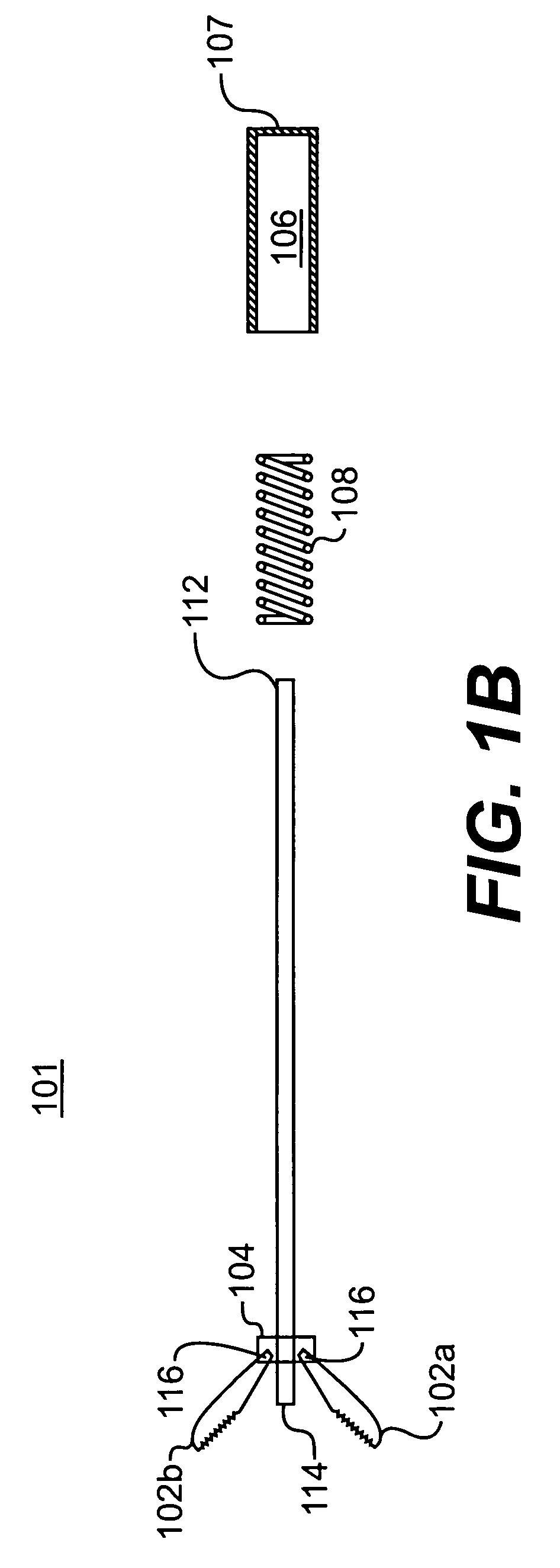
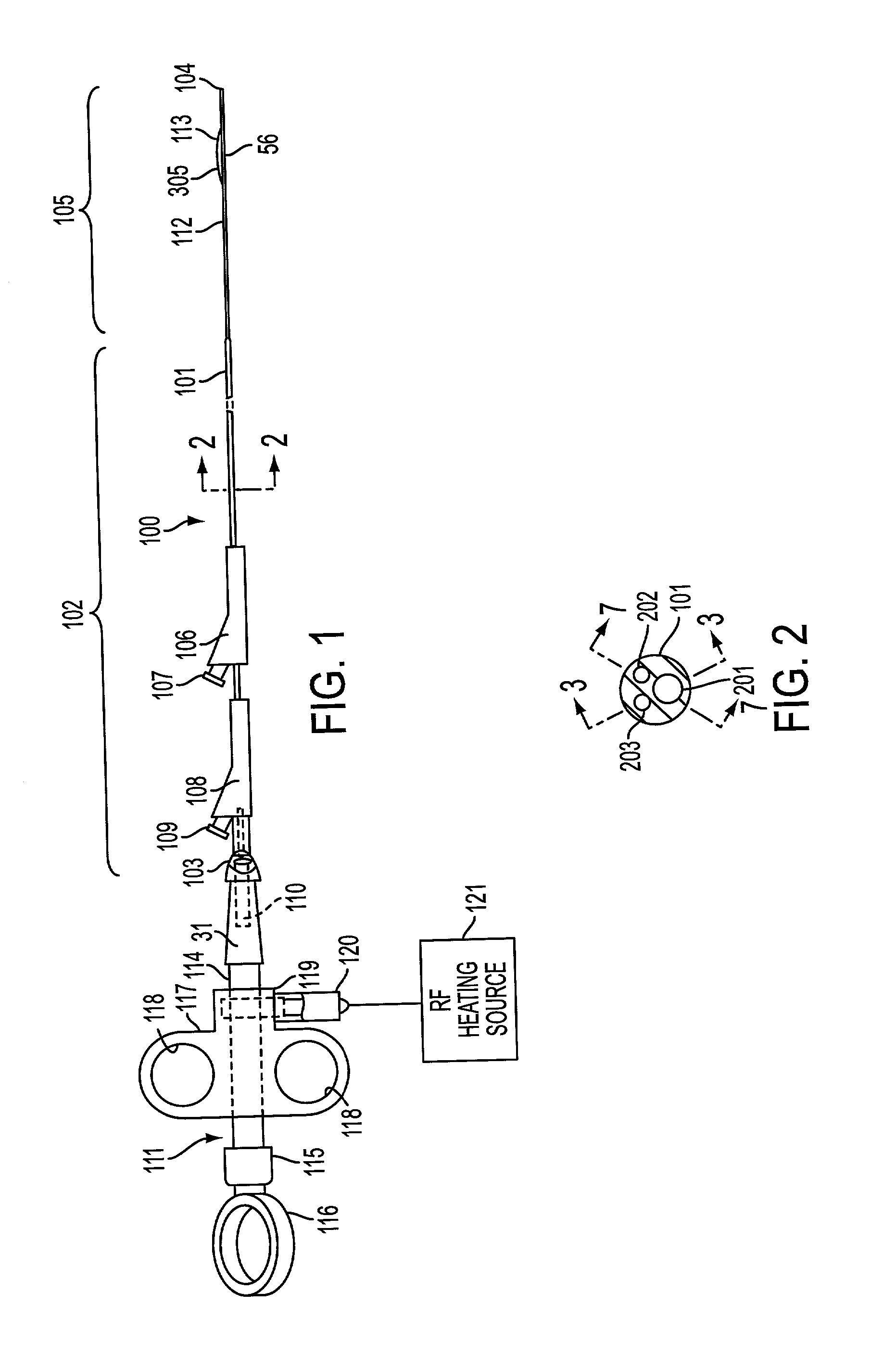
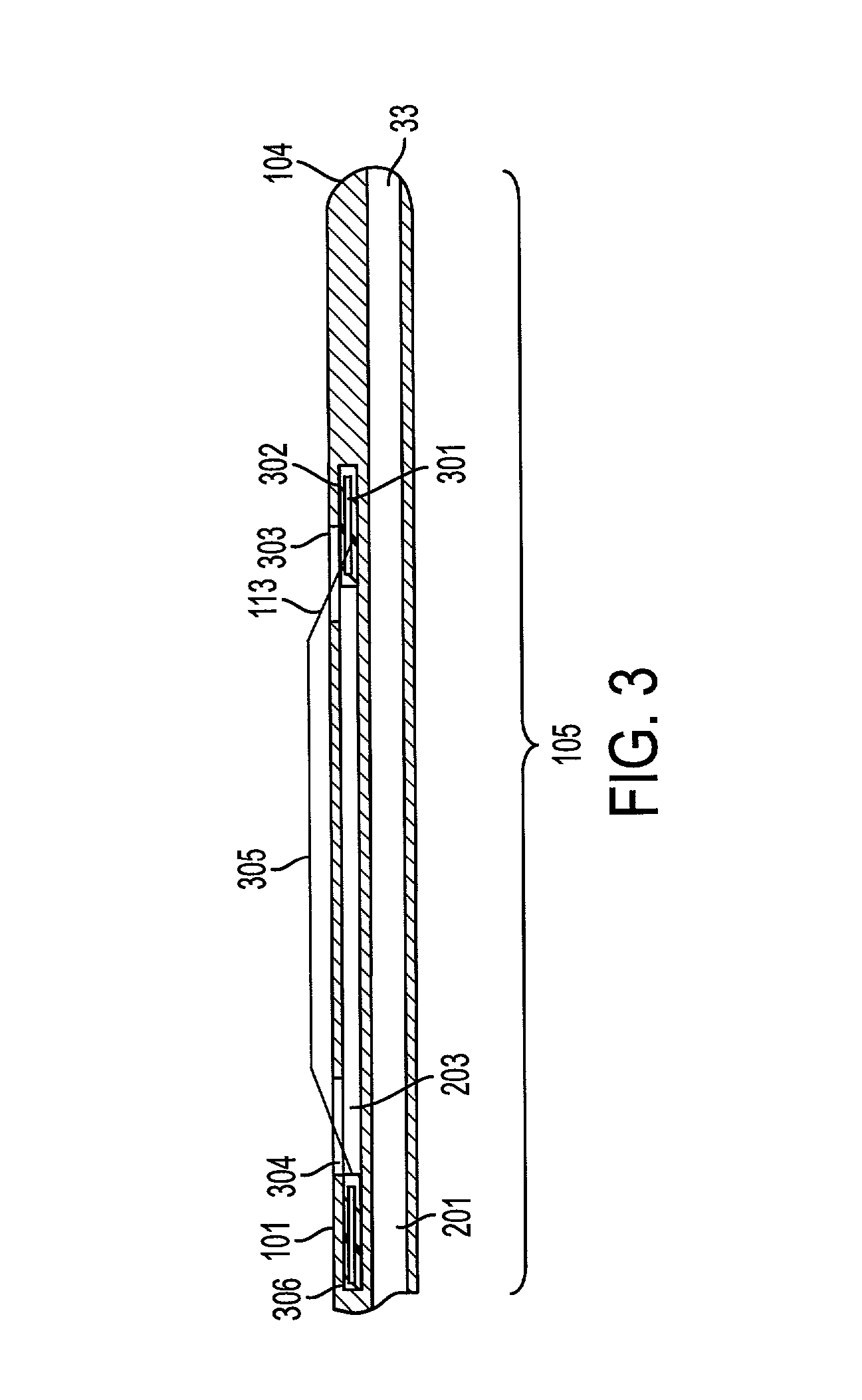
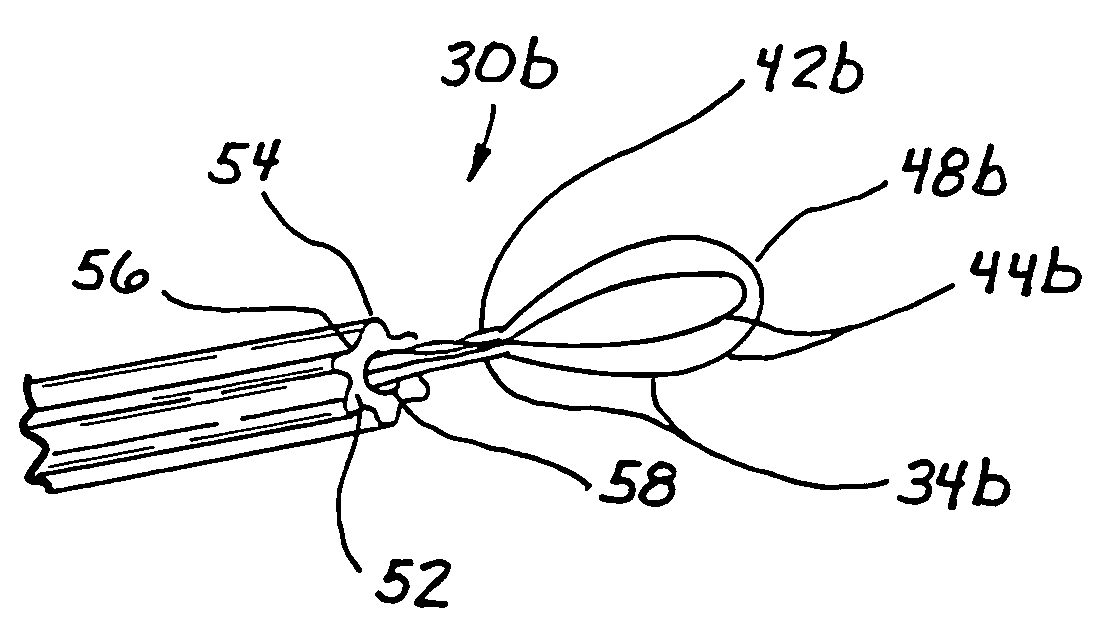
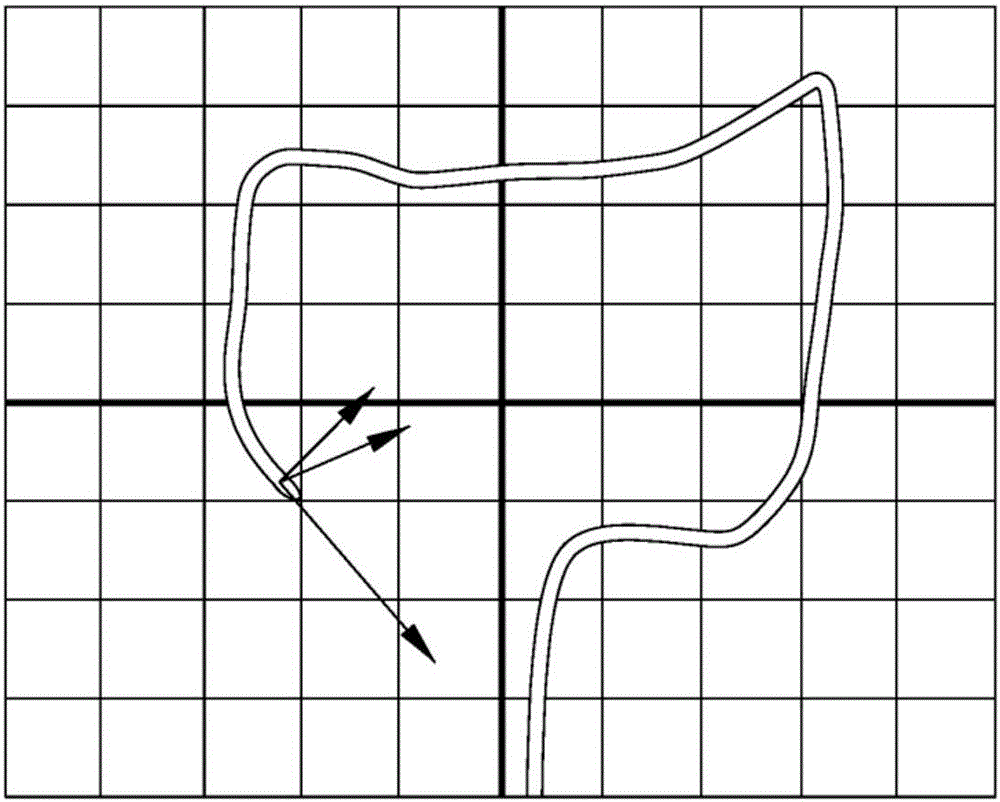
Steerable sphincterotome and methods for cannulation, papillotomy and sphincterotomy
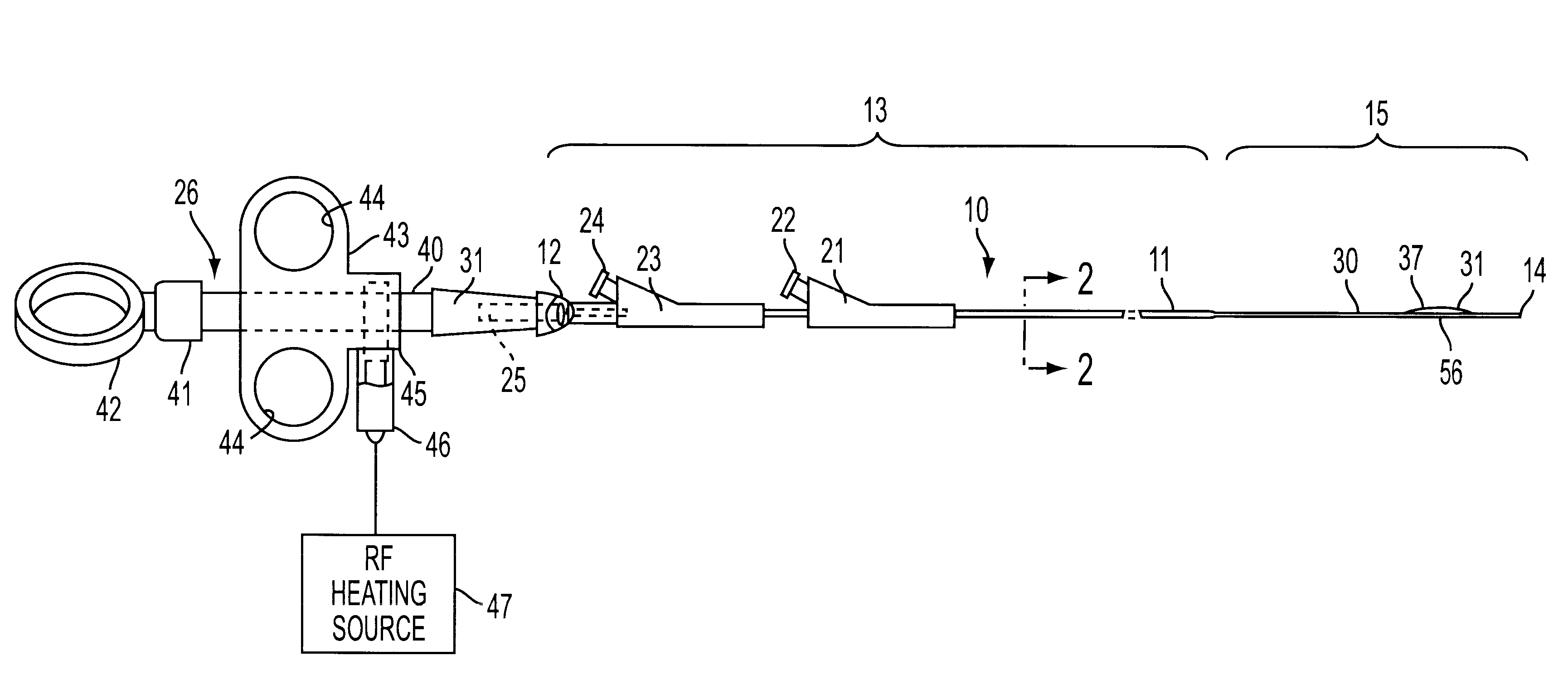
The present invention relates to methods and devices for performing endoscopic cannulation, papillotomy and sphincterotomy and similar procedures. According to the present state of the art, endoscopic cannulation of the common bile duct and papillotomy and similar procedures are accomplished by advancing the device into an endoscope / duodenoscope so that the distal tip of the device exits the endoscope adjacent the sphincter muscles at the Papilla of Vater. The endoscope mechanisms are then manipulated to orient the distal tip of the device to the desired position for proper cannulation of the duct. Due to inconsistencies in, for example, the sphincterotome, anatomy, and endoscope manipulation, it is difficult to accurately and consistently position the sphincterotome for proper cannulation. The steerable sphincterotome of the present invention allows the physician to control the position of the distal tip of the device independently of the endoscope and adjust for inconsistencies in the device and the anatomy. According to the present invention, the handle to which the cutting wire is attached is freely rotatable relative to the catheter. The handle, secured to the cutting wire but rotatable relative to the shaft of the catheter, provides a mechanism to rotate the wire, transmitting the force to rotate the device tip. With the handle rotating independently of the shaft at the proximal end, the force can be applied directly to the distal tip without twisting the entire shaft. Also a rotation lock to maintain the orientation of the tip and / or a rotation marking, to indicate the amount of rotation may be included.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and apparatus for continuous guidance of endoscopy
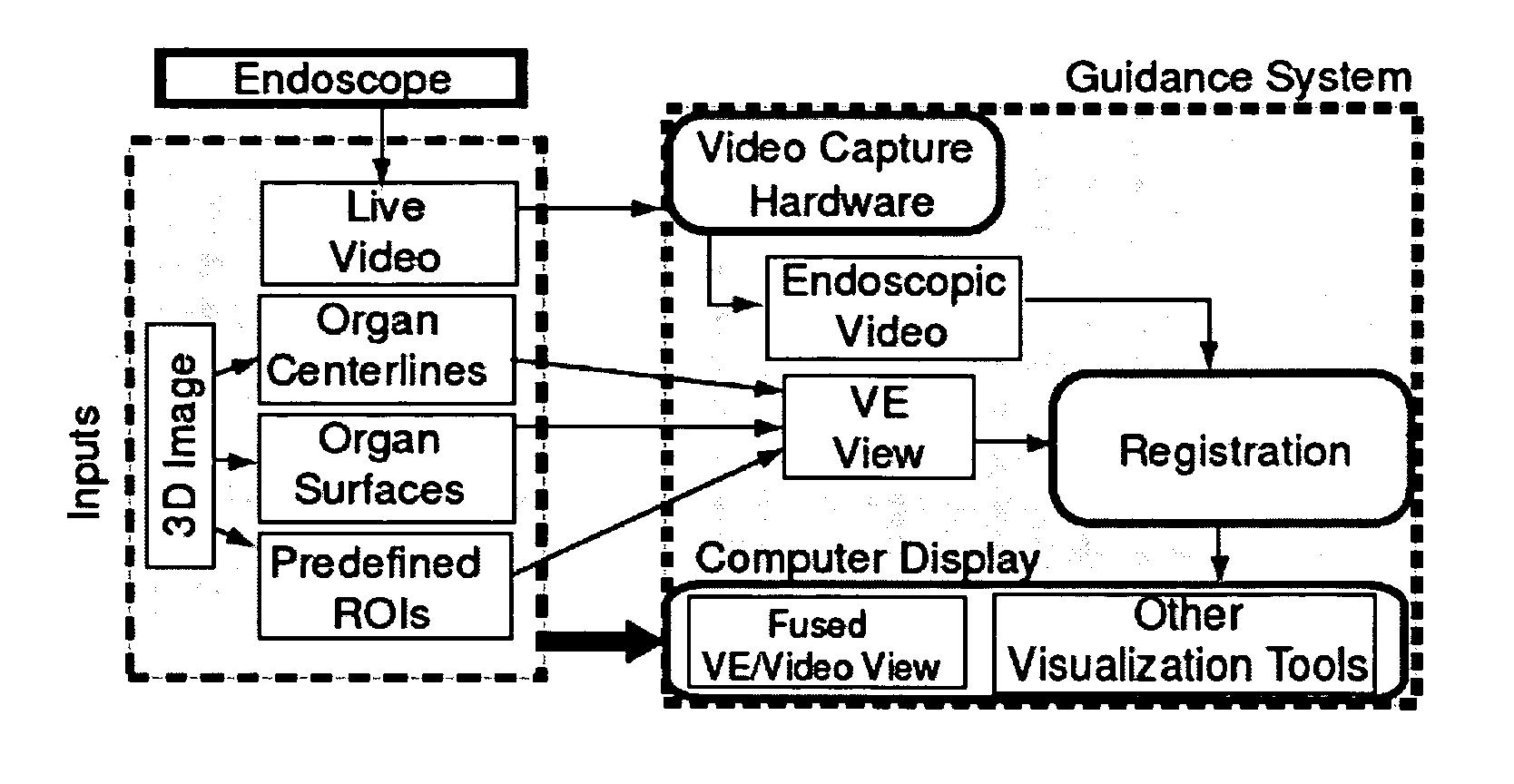
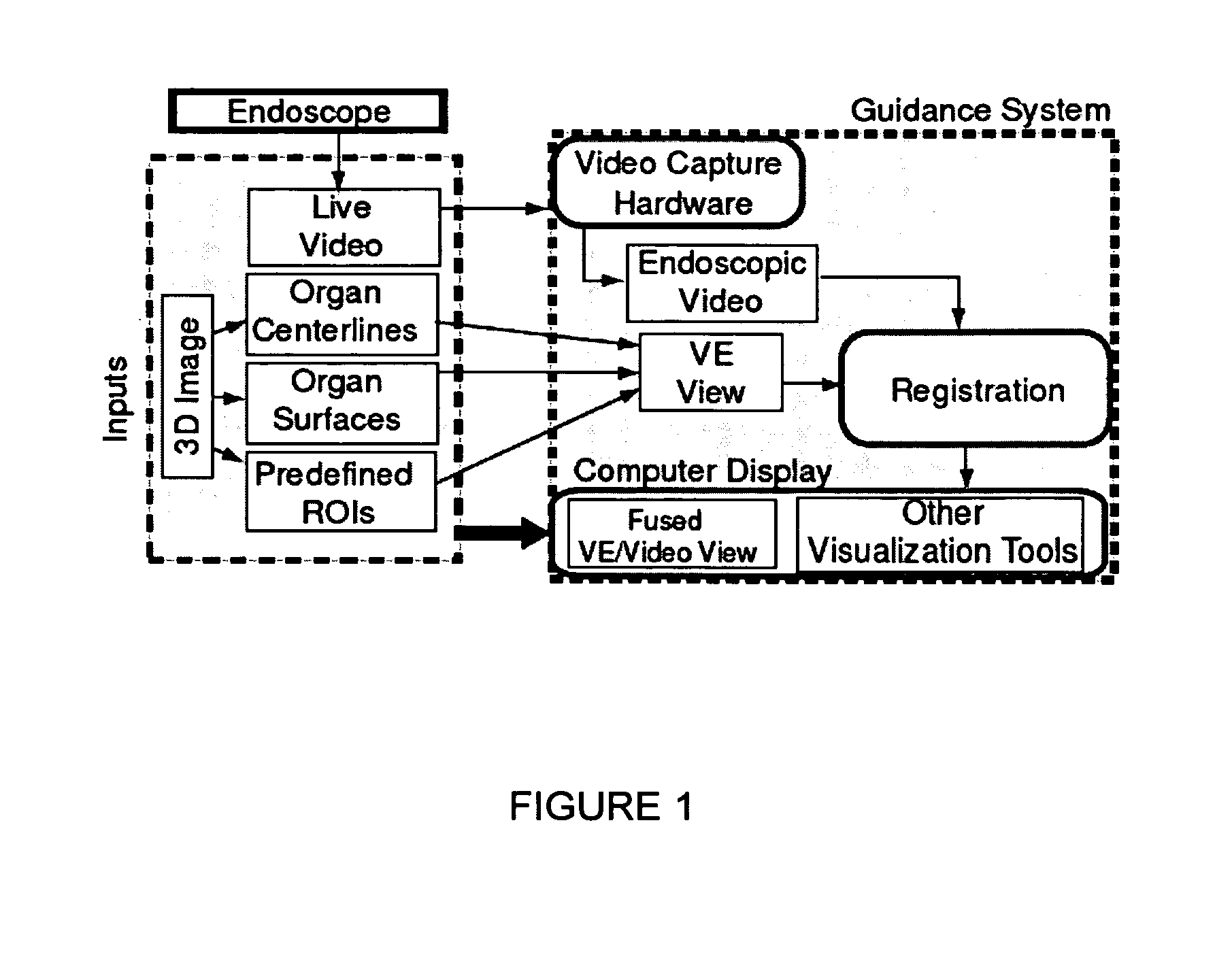
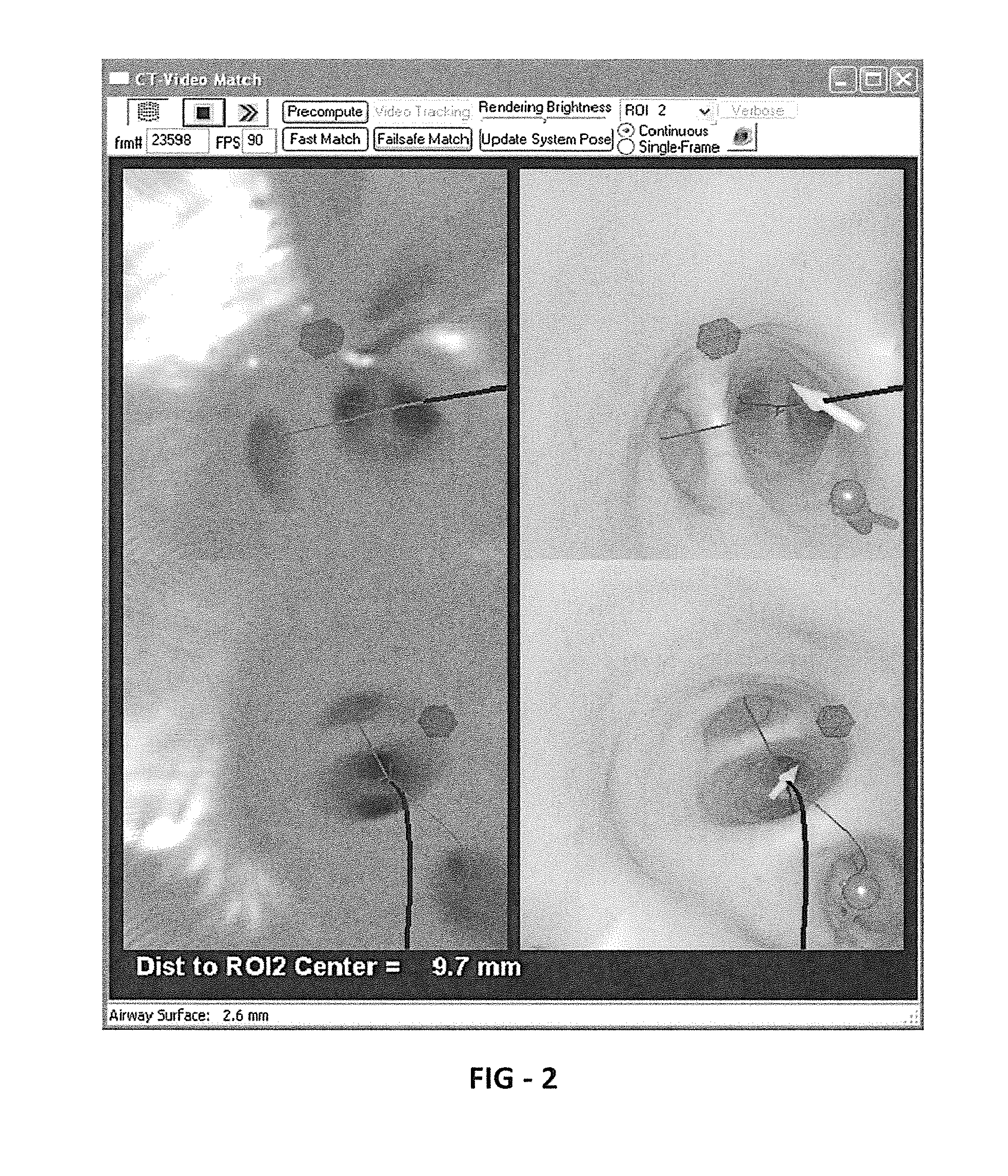
Methods and apparatus provide continuous guidance of endoscopy during a live procedure. A data-set based on 3D image data is pre-computed including reference information representative of a predefined route through a body organ to a final destination. A plurality of live real endoscopic (RE) images are displayed as an operator maneuvers an endoscope within the body organ. A registration and tracking algorithm registers the data-set to one or more of the RE images and continuously maintains the registration as the endoscope is locally maneuvered. Additional information related to the final destination is then presented enabling the endoscope operator to decide on a final maneuver for the procedure. The reference information may include 3D organ surfaces, 3D routes through an organ system, or 3D regions of interest (ROIs), as well as a virtual endoscopic (VE) image generated from the precomputed data-set. The preferred method includes the step of superimposing one or both of the 3D routes and ROIs on one or both of the RE and VE images. The 3D organ surfaces and routes may correspond to the surfaces and paths of a tracheobronchial airway tree extracted, for example, from 3D MDCT images of the chest.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method and apparatus for continuous guidance of endoscopy
Methods and apparatus provide continuous guidance of endoscopy during a live procedure. A data-set based on 3D image data is pre-computed including reference information representative of a predefined route through a body organ to a final destination. A plurality of live real endoscopic (RE) images are displayed as an operator maneuvers an endoscope within the body organ. A registration and tracking algorithm registers the data-set to one or more of the RE images and continuously maintains the registration as the endoscope is locally maneuvered. Additional information related to the final destination is then presented enabling the endoscope operator to decide on a final maneuver for the procedure. The reference information may include 3D organ surfaces, 3D routes through an organ system, or 3D regions of interest (ROIs), as well as a virtual endoscopic (VE) image generated from the precomputed data-set. The preferred method includes the step of superimposing one or both of the 3D routes and ROIs on one or both of the RE and VE images. The 3D organ surfaces and routes may correspond to the surfaces and paths of a tracheobronchial airway tree extracted, for example, from 3D MDCT images of the chest.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Insertion assisting tool for endoscope and endoscope operating method
InactiveUS20050137457A1Guaranteed uptimeIncrease air pressureGuide needlesStentsExtremity PartEndoscope
An insertion assisting tool for an endoscope which is a tubular insertion assisting tool which is provided with an inflatable and deflatable balloon attached to a tip end outer peripheral part, and through which an insertion section for an endoscope is capable of being inserted, comprising: an air hole formed at an outer periphery and / or a tip end part of the insertion assisting tool.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Anti-twist casing for endoscopic manipulating head assembly
A casing of an endoscopic manipulating head assembly is largely constituted by and dividable into a main cover section adapted to support an operating means of an angulation control mechanism and a grip cover section provided between the main cover section and an insertion tube of the endoscope. Both of the main cover section and the grip cover section are formed of a synthetic resin material. A support plate of a rigid metal is provided internally of the manipulating head assembly to support the angulation control mechanism. A plural number of passage-forming tubular structural members are successively connected within the grip cover section for passing internal components to and from the insertion tube of the endoscope. The support plate is connected to one of the tubular structural members which is located at the proximal end of the grip cover section. A first anti-twist lock portion is formed between the support plate and joined end portions of the main and grip cover sections, while a second anti-twist lock portion is formed between the grip cover section and joined end portions of the tubular structural members.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Endoscopic apparatus and method
InactiveUS7169167B2Vaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSurgical forcepsEndoscopic operationsDistal portion
The present invention is directed to a medical device, such as an endoscopic device, configured to be loaded into a channel of an endoscope prior to insertion of the endoscope into a body, and a method of performing an operative procedure with an endoscopic device. The endoscopic device comprises an elongate member for insertion into the channel of the endoscope, wherein a length of the elongate member is greater than a length of the channel of the endoscope. The endoscopic device also comprises a distal assembly connected to a distal portion of the elongate member and operable to perform an endoscopic operation, wherein the distal assembly has an open configuration and a closed configuration with a profile larger than a diameter of the channel of the endoscope, wherein the distal assembly is adapted to be exterior to the channel when the endoscope is inserted into the body.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
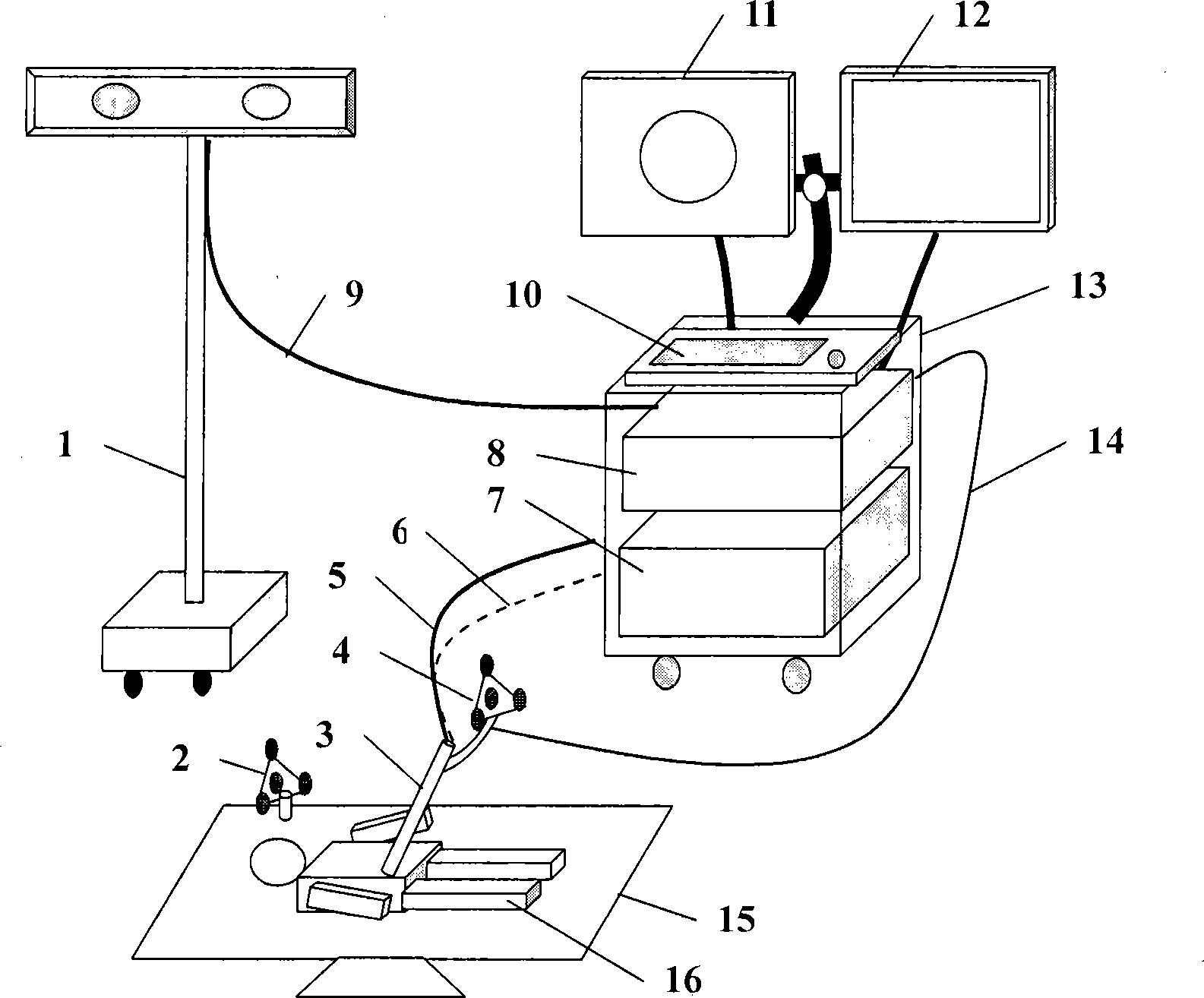
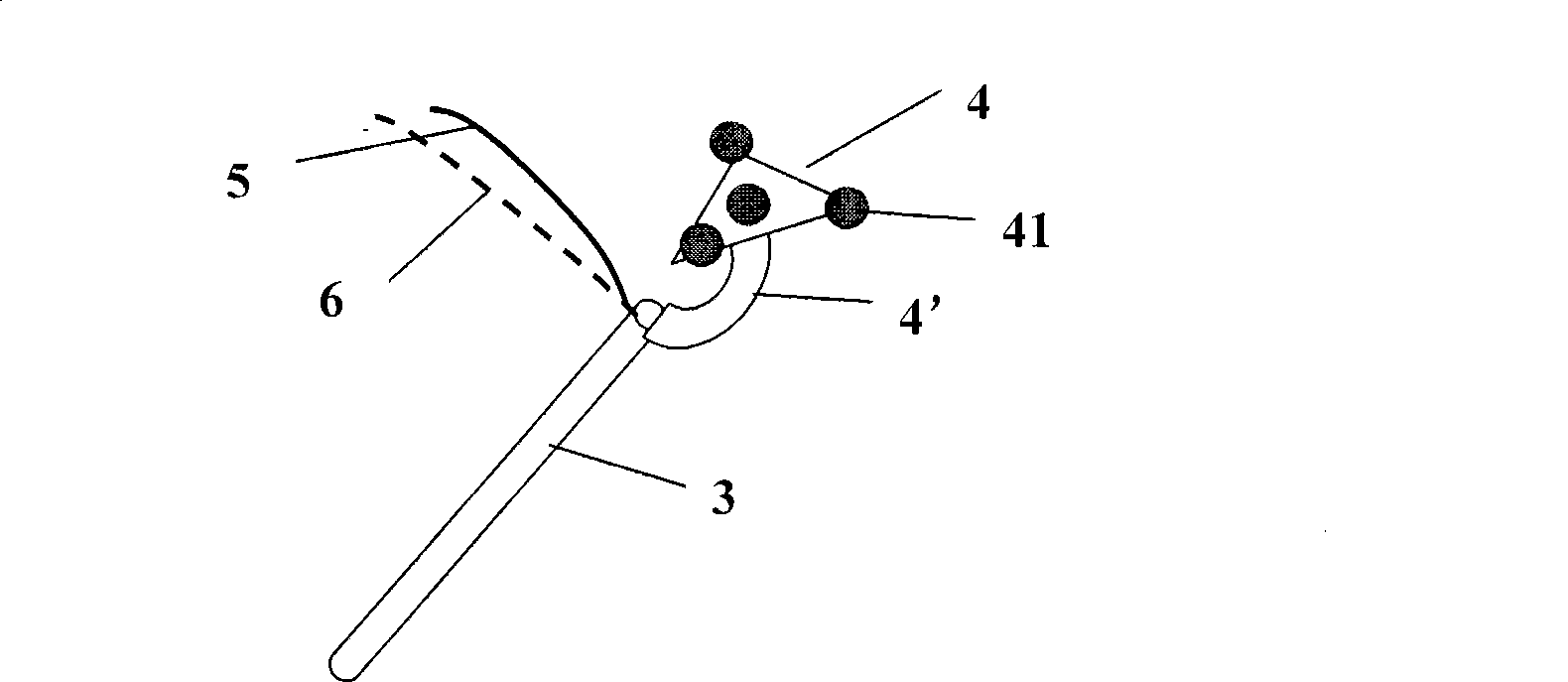
Method and system for guiding operation of electronic endoscope by auxiliary computer
InactiveCN101375805ASuccessfully completedClear structured informationSurgeryRadiation diagnosticsImaging processingComputer-aided
The invention discloses a method and a system for introducing an electronic endoscope into operation with the assistance of a computer. The system comprises an electronic endoscope system, a space orientation system used for tracking a position and a direction of the probe head of the endoscope, an image workstation used for producing a planar or three-dimensional image of a surgery area of a patient according to an input image and blending and displaying an image of the probe head of the endoscope and the planar or three-dimensional image by connecting with the space orientation system, and auxiliary image orientation and processing software. The system tracks the position and the direction of the probe head of the endoscope through a space track technology and a computerized image processing technology, so that by combing the planar image with the image of the endoscope with the assistance of images as CT or X-ray pictures, a doctor can not only see the planar image captured by the probe head of the endoscope, but also see the position of the probe head of the endoscope and the conditions of the peripheral tissue. Therefore, the doctor can fully control the comparative position of the probe head of the endoscope in the body, thereby improving the quality of endoscope surgery and shortening the time of a surgery.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
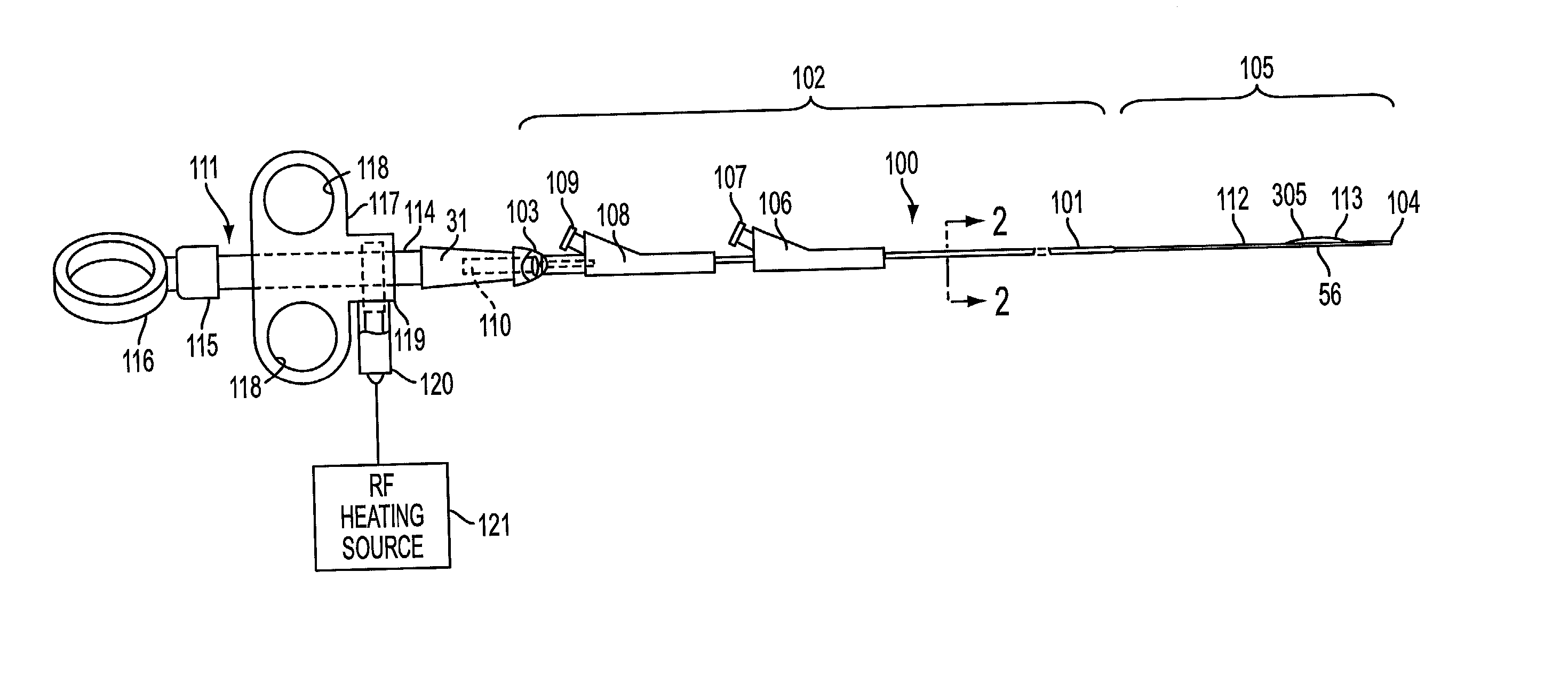
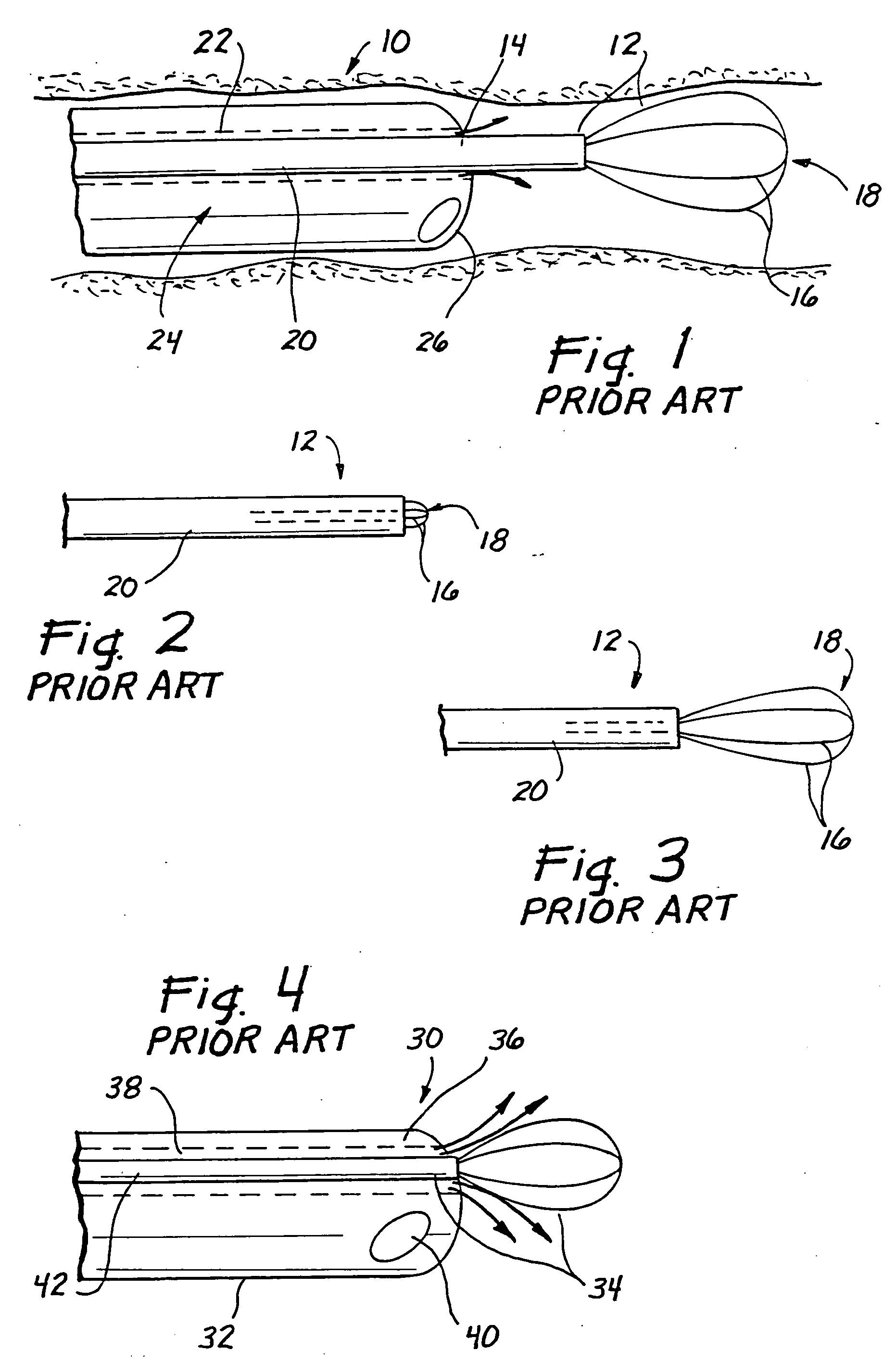
Method and apparatus for measuring and controlling blade depth of a tissue cutting apparatus in an endoscopic catheter
InactiveUS20030060842A1Surgical needlesDiagnostic markersPrecut sphincterotomyCommon bile duct dilatation
According to the present state of the art, endoscopic cannulation of the common bile duct and papillotomy and / or sphincterotomy of the Papilla of Vater and / or the Sphincter of Oddi is accomplished by advancing a sphincterotome (or papillotome or cannulotome) into an endoscope / duodenoscope so that the distal tip of the sphincterotome exits the endoscope adjacent the sphincter muscles at the Papilla of Vater. The endoscope mechanisms are then manipulated to orient the distal tip of the sphincterotome to the desired position for proper cannulation of the duct. Accurate and consistent control of the length of the exposed blade is made difficult due to a number of factors. These factors include: 1) differences in the inside diameters of the outer tube and the needle knife wire, 2) the orientation of the needle knife wire within the outer tube, 3) the mismatch of tolerance of the needle knife wire and the inside diameter of the extrusion, 4) anatomy, and 5) endoscope manipulation. A sphincterotome incorporating the present invention will provide the user with an indication of the exposed blade length and will allow the physician to control the length of the exposed blade. According to one embodiment of the present invention, various visual indications are presented to the user as the needle knife is advanced from its outer sheath. These visual indications, combined with a mechanical method to hold the knife in position during catheter placement allows the user to perform precise incisions. Presently available products that may be modified according to the present invention include, but are not limited to, Boston Scientific Sphincterotomes and Needle Knives.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Laparoscopic Instrument
InactiveUS20080319459A1Slow down the feedingSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesEndoscopic operationsPERITONEOSCOPE
The present invention relates to a system of laparoscopic instruments that provides the possibility of an effective and fast laparoscopic / endoscopic suturing method in order to facilitate 5 laparoscopic / endoscopic operation. The system consists of the following main parts: a novel, specially made laparoscopic instrument that in one end has a specially made needle through which a thread can be fed; a novel, specially made laparoscopic instrument that in one end has a specially made needle that has the capability of receiving and holding 10 the end of the thread, a novel, special clips machine and a new clip; a novel thread feeder, eventually integrated in a forceps; and specially made double forceps.
Owner:NAJJAR AZAD
Surgical Instrument
InactiveUS20090254075A1Fluid jet surgical cuttersSurgical instruments for heatingEndoscopic operationsEndoscope
A surgical instrument suitable for endoscopic operations having a gripping handle, tubular body and an operational tip. Jetting outlets laterally disposed at the operational tip provides for jetting pressurized liquid delivered by the tubular body. The jetting outlets are configured as to emit converging jets. Two or more jets converge at a convergence point laterally displaced at a predefined distance from the surface of the operational tip. The operational tip includes a heating member having an active face for contact heating a bleeding tissue. A rotating mechanism provides for independently rotating the jetting outlets and the active surface of the heating member relative to the gripping handle. A method for regulating the operating temperature of the heating member is provided.
Owner:ULTRASURGE TECH
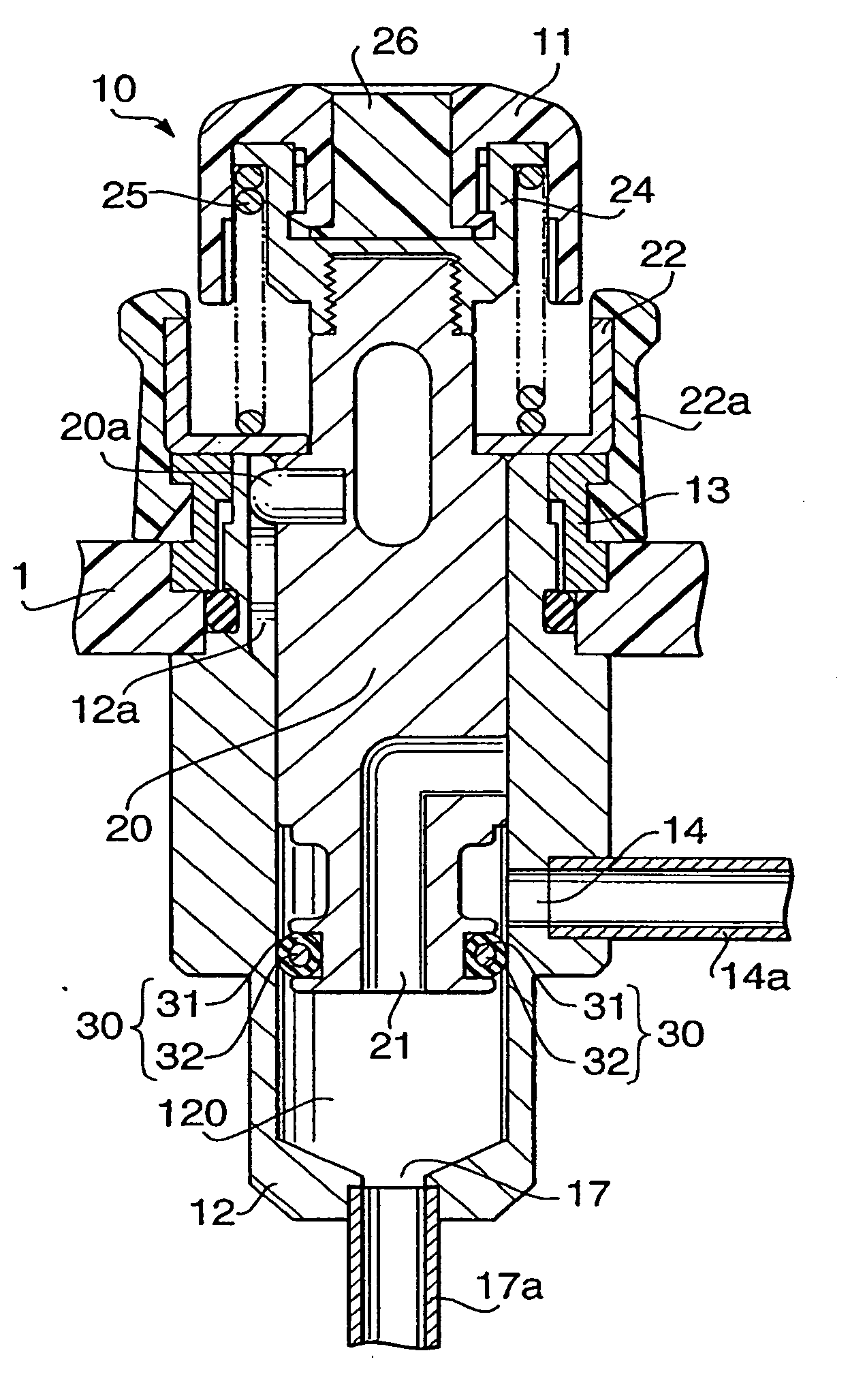
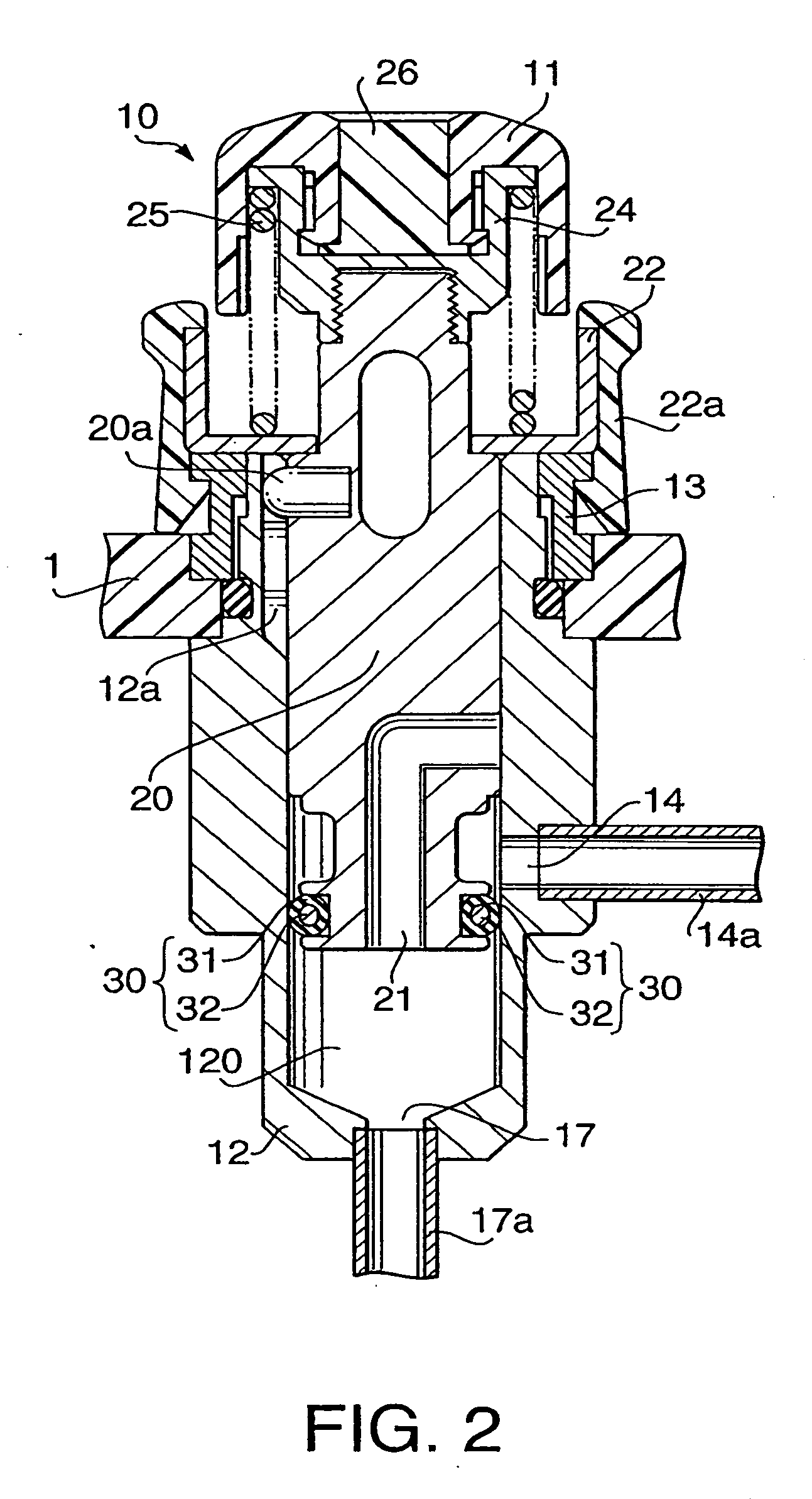
Operation button for endoscope
An operation button for an endoscope is provided with a cylinder and a piston reciprocally slidable inside a lumen of the cylinder. A first flow channel and a second flow channel are formed to communicate with the lumen. When the piston is located at a first position, the first and second flow channel communicate with each other, while the first flow channel and the second flow channel are disconnected when the piston is located at a second position. A sealing member is provided on an outer periphery of the piston to provide secure airtightness between the cylinder and the piston. The sealing member includes a core member mainly made of one of poly-para-xylylene and poly-para-xylylene derivatives and a coating layer allocated on an outer periphery of the core member.
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
Steerable sphincterotome and methods for cannulation, papillotomy and sphincterotomy
The present invention relates to methods and devices for performing endoscopic cannulation, papillotomy and sphincterotomy and similar procedures. According to the present state of the art, endoscopic cannulation of the common bile duct and papillotomy and similar procedures are accomplished by advancing the device into an endoscope / duodenoscope so that the distal tip of the device exits the endoscope adjacent the sphincter muscles at the Papilla of Vater. The endoscope mechanisms are then manipulated to orient the distal tip of the device to the desired position for proper cannulation of the duct. Due to inconsistencies in, for example, the sphincterotome, anatomy, and endoscope manipulation, it is difficult to accurately and consistently position the sphincterotome for proper cannulation. The steerable sphincterotome of the present invention allows the physician to control the position of the distal tip of the device independently of the endoscope and adjust for inconsistencies in the device and the anatomy. According to the present invention, the handle to which the cutting wire is attached is freely rotatable relative to the catheter. The handle, secured to the cutting wire but rotatable relative to the shaft of the catheter, provides a mechanism to rotate the wire, transmitting the force to rotate the device tip. With the handle rotating independently of the shaft at the proximal end, the force can be applied directly to the distal tip without twisting the entire shaft. Also a rotation lock to maintain the orientation of the tip and / or a rotation marking, to indicate the amount of rotation may be included.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
High flow stone basket system
A medical device for viewing inside a body and for retrieving an object from a location within the body, the medical device comprising an endoscope having a tube defining a working channel and a basket engageable with the object. In one embodiment of the invention, the basket does not require a sheath and is disposed through the working channel such that the endoscope operates to contain or activate the sheathless basket. In another embodiment of the invention, a single push wire with a collar at its end is used in place of a sheath to control the opening and closing of the basket. In another embodiment of the invention, a tapered and funnel-shaped sheath surrounding the basket is used to contain or activate the basket. The invention minimizes the basket crossing profile so as to improve fluid flow in the working channel.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Endoscopic soft tissue working space creation
A device for creating endoscopic operating space includes an external cannula, an internal cannula disposed in the external cannula, and an expandable retractor disposed at a distal end of the device and cooperable with the external cannula and the internal cannula. The expandable retractor is displaceable between an unexpanded position and an expanded position. An actuator is cooperable with the expandable retractor to displace the expandable retractor between the unexpanded position and the expanded position.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
Method and Apparatus for Measuring and Controlling Blade Depth of a Tissue Cutting Apparatus in an Endoscopic Catheter
InactiveUS20090005637A1Precise depth controlProviding resistance to movementSurgical needlesEndoscopesPrecut sphincterotomyCommon bile duct dilatation
According to the present state of the art, endoscopic cannulation of the common bile duct and papillotomy and / or sphincterotomy of the Papilla of Vater and / or the Sphincter of Oddi is accomplished by advancing a sphincterotome (or papillotome or cannulotome) into an endoscope / duodenoscope so that the distal tip of the sphincterotome exits the endoscope adjacent the sphincter muscles at the Papilla of Vater. The endoscope mechanisms are then manipulated to orient the distal tip of the sphincterotome to the desired position for proper cannulation of the duct. Accurate and consistent control of the length of the exposed blade is made difficult due to a number of factors. These factors include: 1) differences in the inside diameters of the outer tube and the needle knife wire, 2) the orientation of the needle knife wire within the outer tube, 3) the mismatch of tolerance of the needle knife wire and the inside diameter of the extrusion, 4) anatomy, and 5) endoscope manipulation. A sphincterotome incorporating the present invention will provide the user with an indication of the exposed blade length and will allow the physician to control the length of the exposed blade. According to one embodiment of the present invention, various visual indications are presented to the user as the needle knife is advanced from its outer sheath. These visual indications, combined with a mechanical method to hold the knife in position during catheter placement allows the user to perform precise incisions. Presently available products that may be modified according to the present invention include, but are not limited to, Boston Scientific Sphincterotomes and Needle Knives.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Measuring endoscope system
ActiveUS7048685B2Improve inspectionEasy to operateSurgeryEndoscopesEndoscopic operationsComputer module
A measuring endoscope system includes a menu display module that selects a menu according to display data which is associated in advance with any of a plurality of optical adaptors, and a measuring program for performing measurement according to the result of the selection performed by the menu display module. Consequently, in the measuring endoscope system, when a user designates an optical adaptor using an optical adaptor selection screen image displayed on an LCD by the menu display module, a measuring technique associated with the optical adaptor is automatically selected. When a user wants to perform measurement using the measuring endoscope system, the user should merely press a measurement execution switch included in an endoscopic operation unit. Thus, measurement in which the selected measuring technique is implemented is carried out. Consequently, the present invention has succeeded in improving the maneuverability of a measuring endoscope system in measurement and improving the efficiency thereof in inspection.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Systems and methods for tracking and displaying endoscope shape and distal end orientation
InactiveCN106455908ALoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreSurgical navigation systemsEndoscopic ProcedureEndoscope
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Insertion assisting tool for endoscope and endoscope operating method
An insertion assisting tool for an endoscope which is a tubular insertion assisting tool which is provided with an inflatable and deflatable balloon attached to a tip end outer peripheral part, and through which an insertion section for an endoscope is capable of being inserted, comprising:an air hole formed at an outer periphery and / or a tip end part of the insertion assisting tool.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Endoscopic fluid control valve and endoscope
An embodiment of the invention discloses an endoscopic fluid control valve. The endoscopic fluid control valve is simple in structure and internal-space-saving by arranging only one fluid outlet, capable of preventing fluid backflow without arranging a one-way valve in an operation portion of an endoscope and easy to clean. The endoscopic fluid control valve comprises a valve cover, a valve stem, a valve element, an elastic member, buttons, a first seal ring, a second seal ring, a third seal ring, a fourth seal ring, a gas inlet, a liquid inlet and a fluid outlet.
Owner:SONOSCAPE MEDICAL CORP
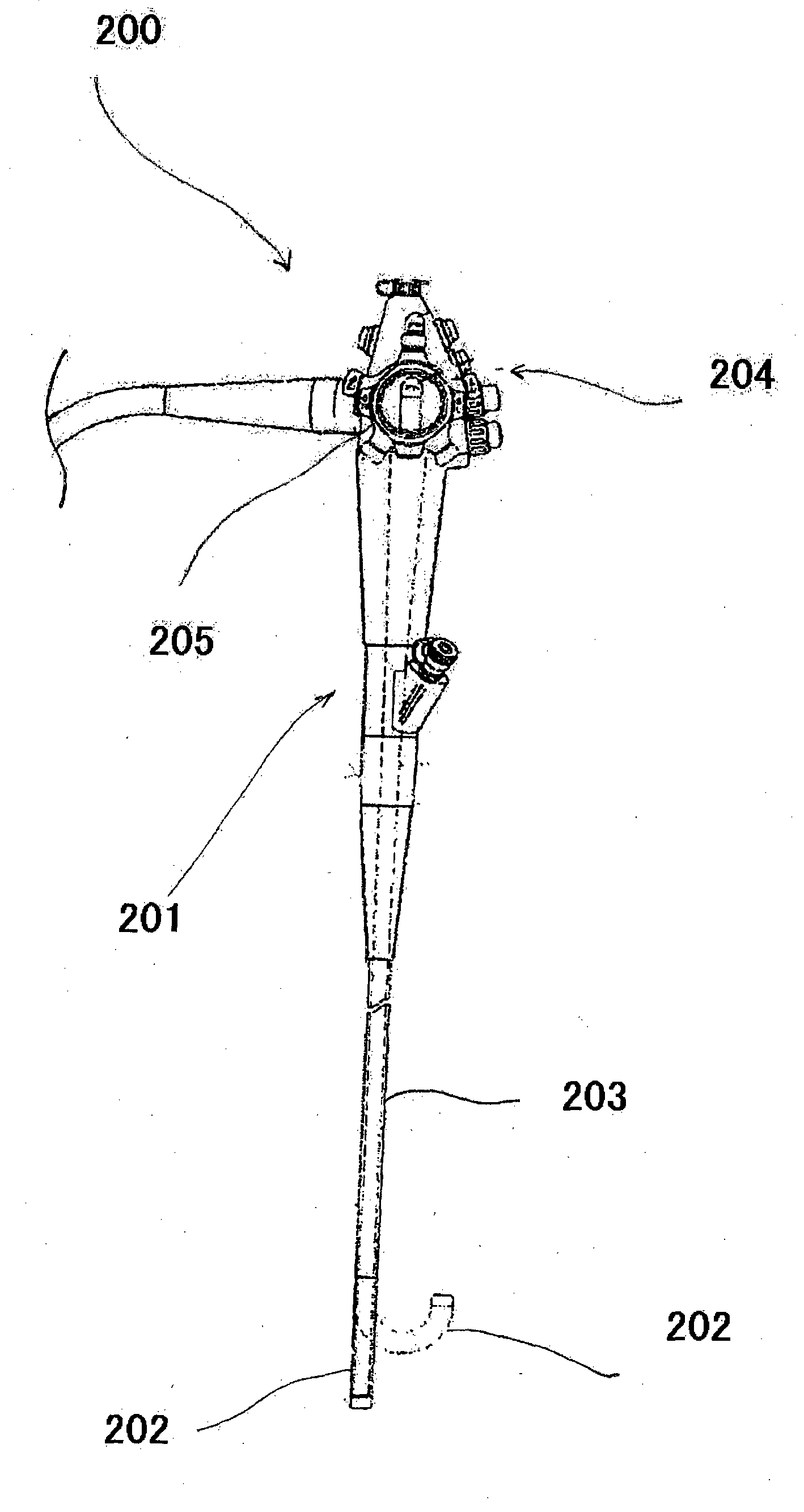
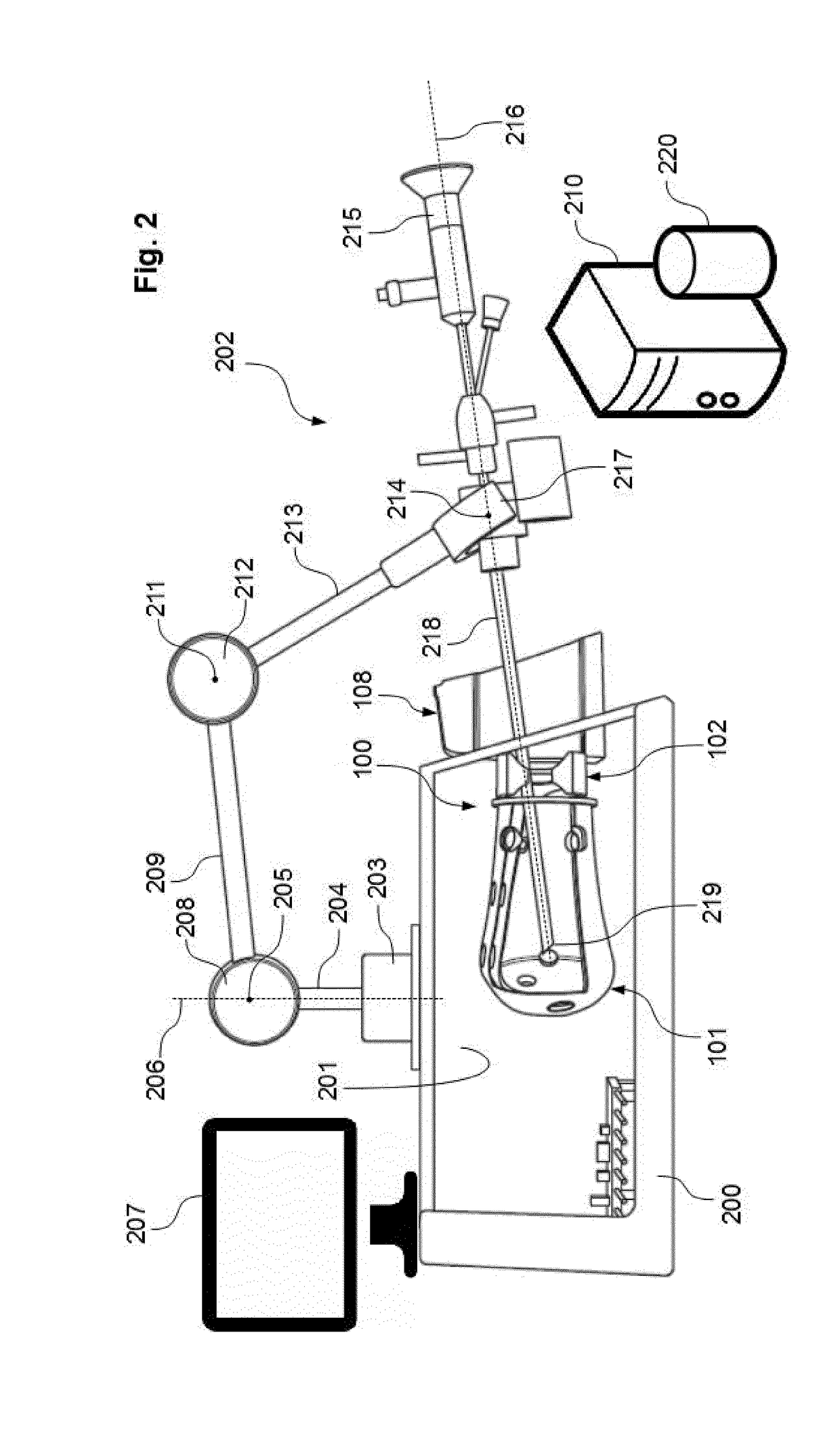
Endoscope Manipulator and Method for Controlling the Same
An endoscope manipulator for performing robot-assisted endoscope manipulation comprises a movable robot base with a hollow trunk and a vertical lifting joint; a passive joint set with one end mounted to an upper end of the vertical lifting joint, for manually setting an initial pose of the endoscope; an active joint set mounted to another end of the passive joint set, for adjusting pose control of the endoscope intra-operatively; and a compliant endoscope holder mountable to an end-effector of the active joint set, which passively changes to a compliant state upon an external force exceeding a threshold being applied to an endoscopic lens held by the compliant endoscope holder.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
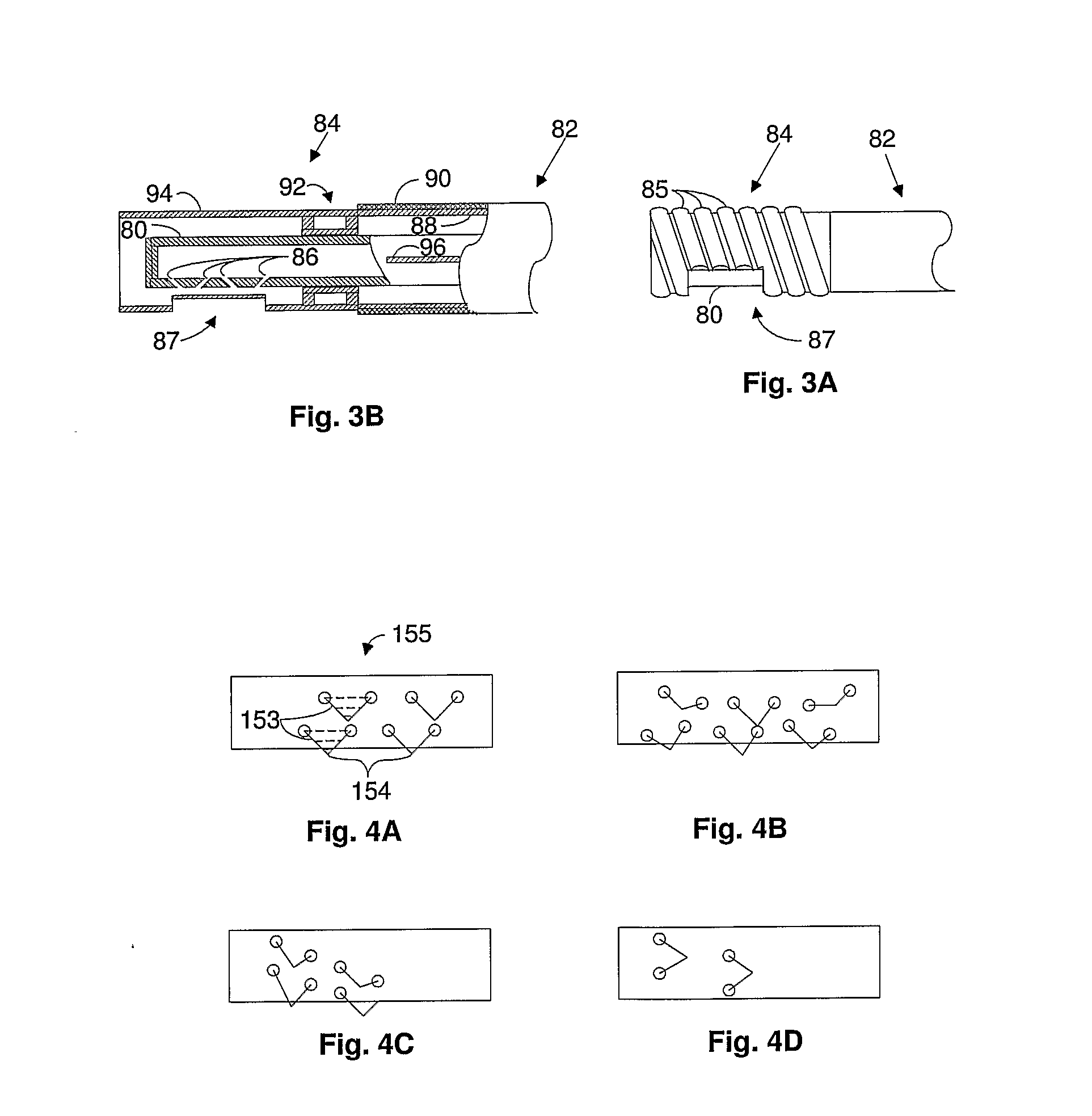
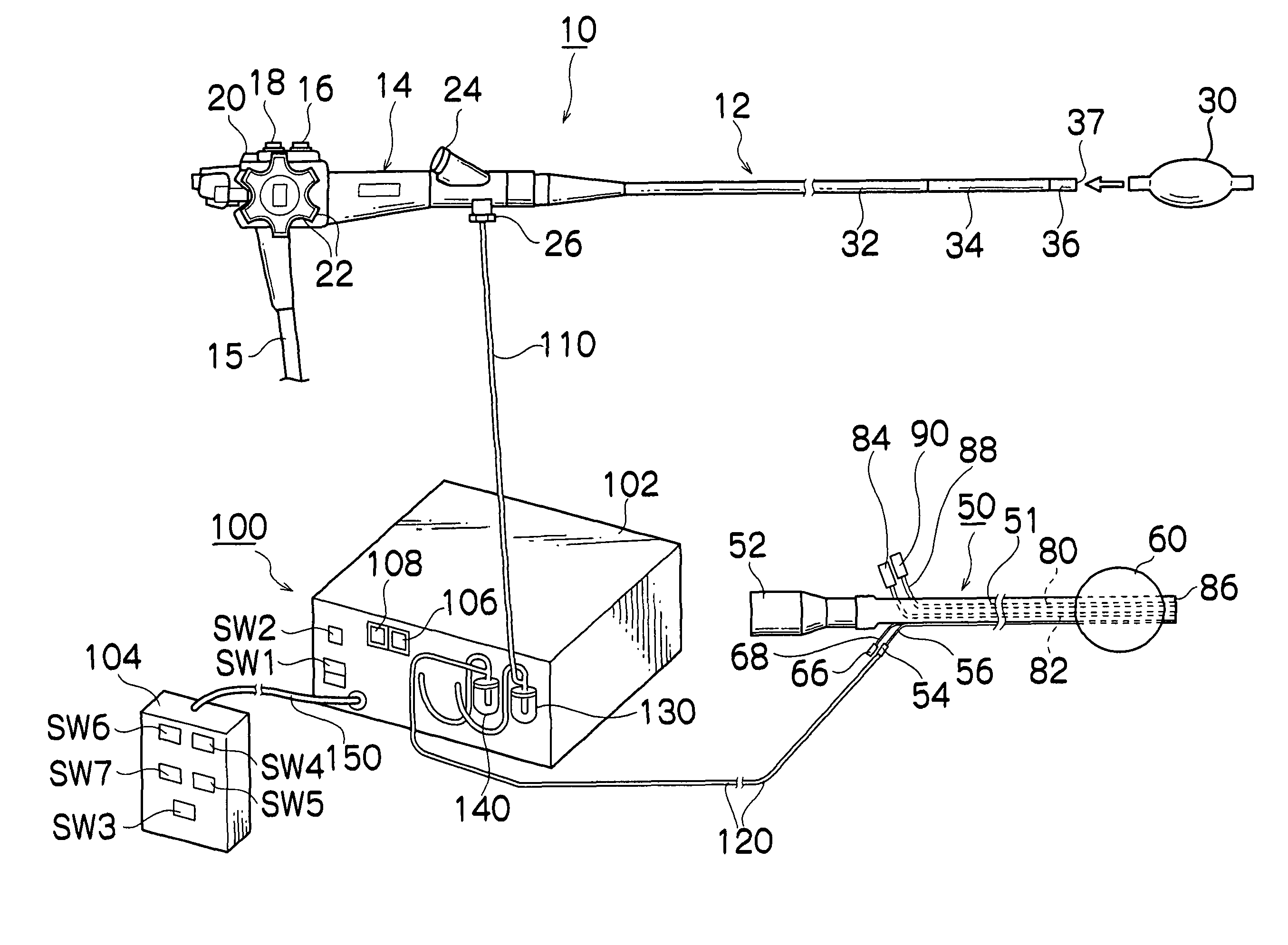
Endoscope
In this endoscope, an endoscope connector is provided at a base end portion of a universal cable extending from an endoscope operating unit. The endoscope connector is provided with: a first unit, which is provided at the base end portion of the universal cable, and which has inserted therein a fluid pipe line and a signal transmitting line, which are inserted into the universal cable; a second unit, which is connected and fixed to the first unit, and which has a connecting pipe line provided therein, said connecting pipe line being connected to the fluid pipe line; and a signal transmitting cable, which is integrally formed at a side portion of the first unit, and has an electric connector provided at an end portion thereof.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
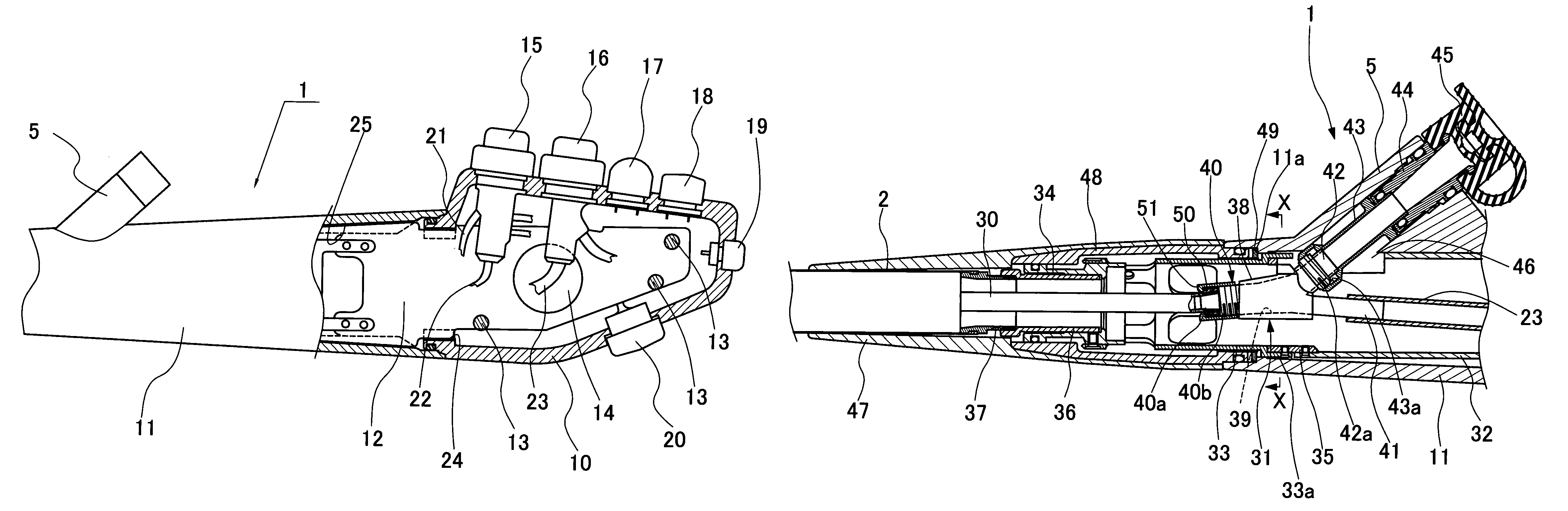
Endoscope operation section and endoscope
Bending operation knobs, a first switch button provided in a first surface, and a second switch button provided side by side with the first switch button in the first surface and positioned on the side distant from the bending operation knobs relative to the first switch button are included. The second switch button is formed so as to have an outer diameter smaller than that of the first switch button, an outer circumferential side of the second switch button is covered by a fitting portion, and a projection portion is formed at a site of the fitting portion, the site facing the first switch button, on an outer circumference of the second switch button, the projection portion projecting toward the side away from the first surface relative to another site of the fitting portion.
Owner:OLYMPUS MEDICAL SYST CORP
Simulation system for training in endoscopic operations
ActiveUS20110212426A1Simple and secure detectionEducational modelsFlexible endoscopyEndoscopic operations
A simulation system for training in endoscopic operations includes an endoscope apparatus, including at least one input for inserting an endoscopic working instrument, a sensor arrangement to detect a movement of the endoscopic working instrument, a control device to generate a virtual image of an endoscopic operation scene depending on a movement of the endoscopic working instrument, transmission means to transmit measured values supplied by the sensor arrangement to the control device for use in generating the virtual image and a display device to display the virtual image, where the sensor arrangement includes at least one optic sensor that interacts with a surface of a shaft of the endoscopic working instrument to detect the movement of the endoscopic working instrument. A flexible endoscope, an endoscopic working instrument and a method for recording a movement of an endoscopic working instrument as well as a method for training in endoscopic operations.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
Endoscope operating apparatus
To provide an endoscope operating apparatus where an operator who is a user can recognize a locked state and a free state clearly with his / her fingers grasping an operating part under an examining environment, and the number of constituent parts can be decreased to reduce a manufacturing cost and achieve weight reduction. An operating apparatus of an endoscope which is provided with a flexible tube inserted into a body to be examined and having a bending part at a distal end thereof and which performs work by bending the bending part according to a manual operation, comprising: a drive part which can pull a wire which is disposed in the flexible tube, a distal end of the wire being fixed to the bending part and the wire bending the bending part; and an operating part which operates the drive part.
Owner:SG ENDOSCOPY
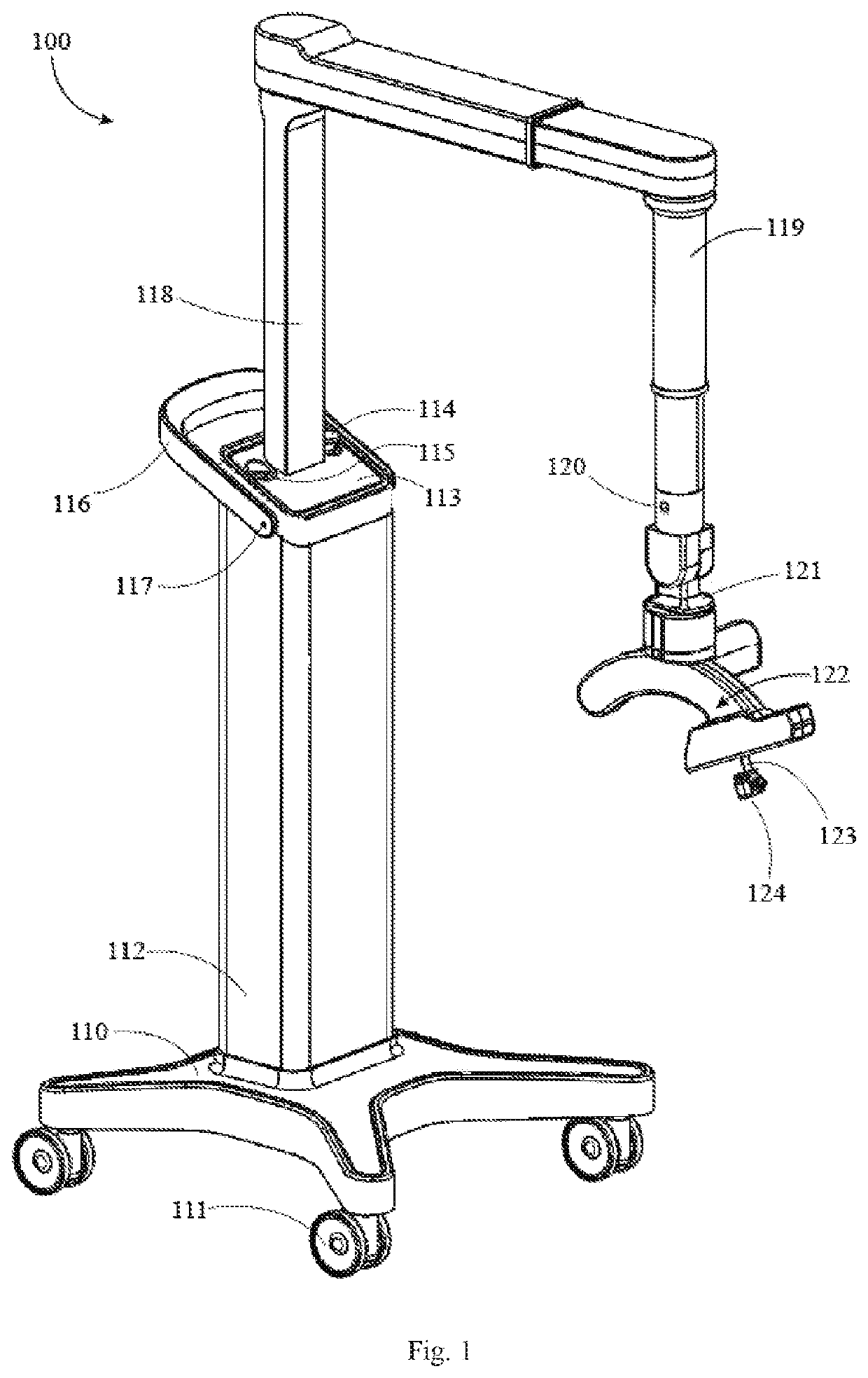
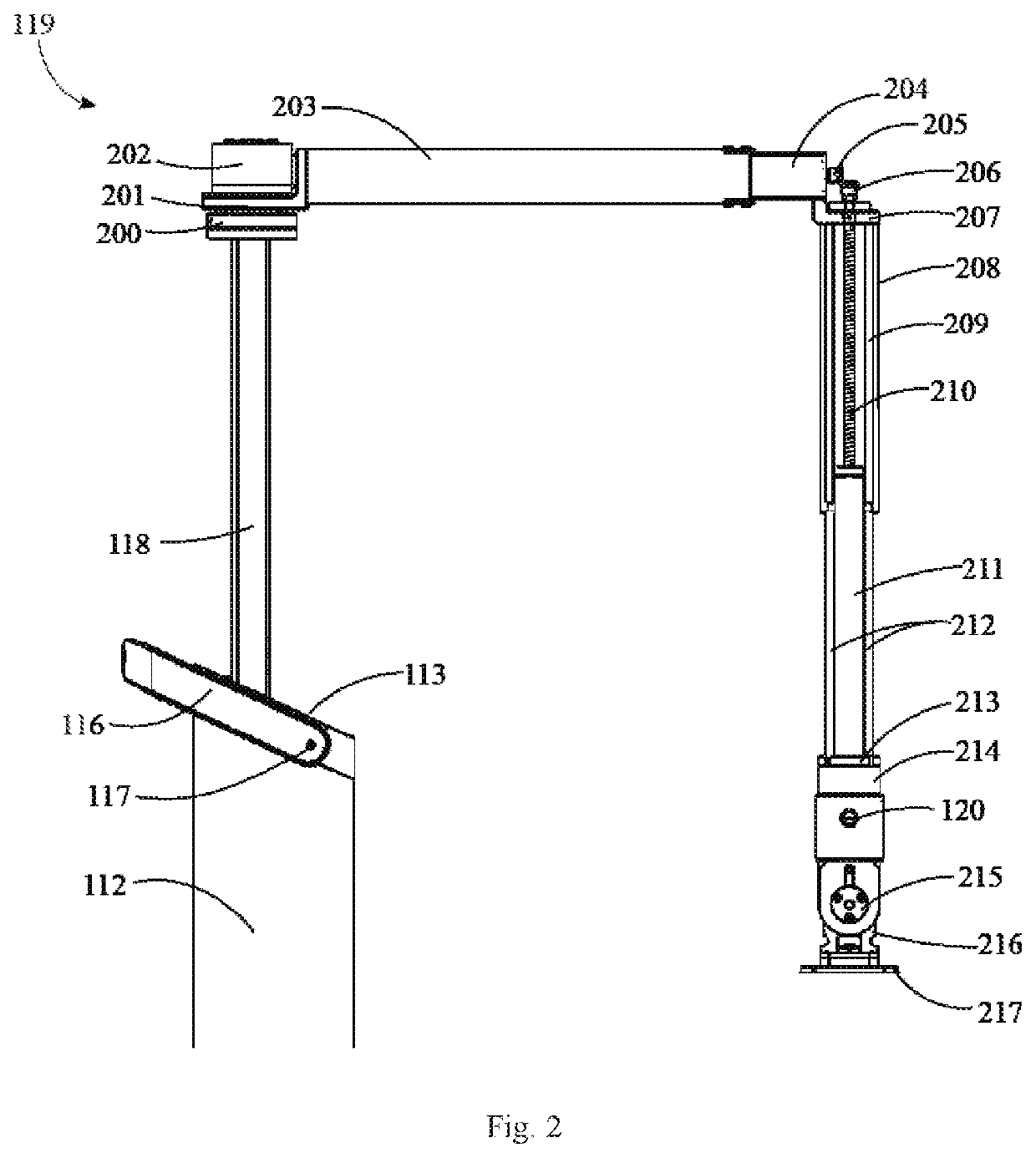
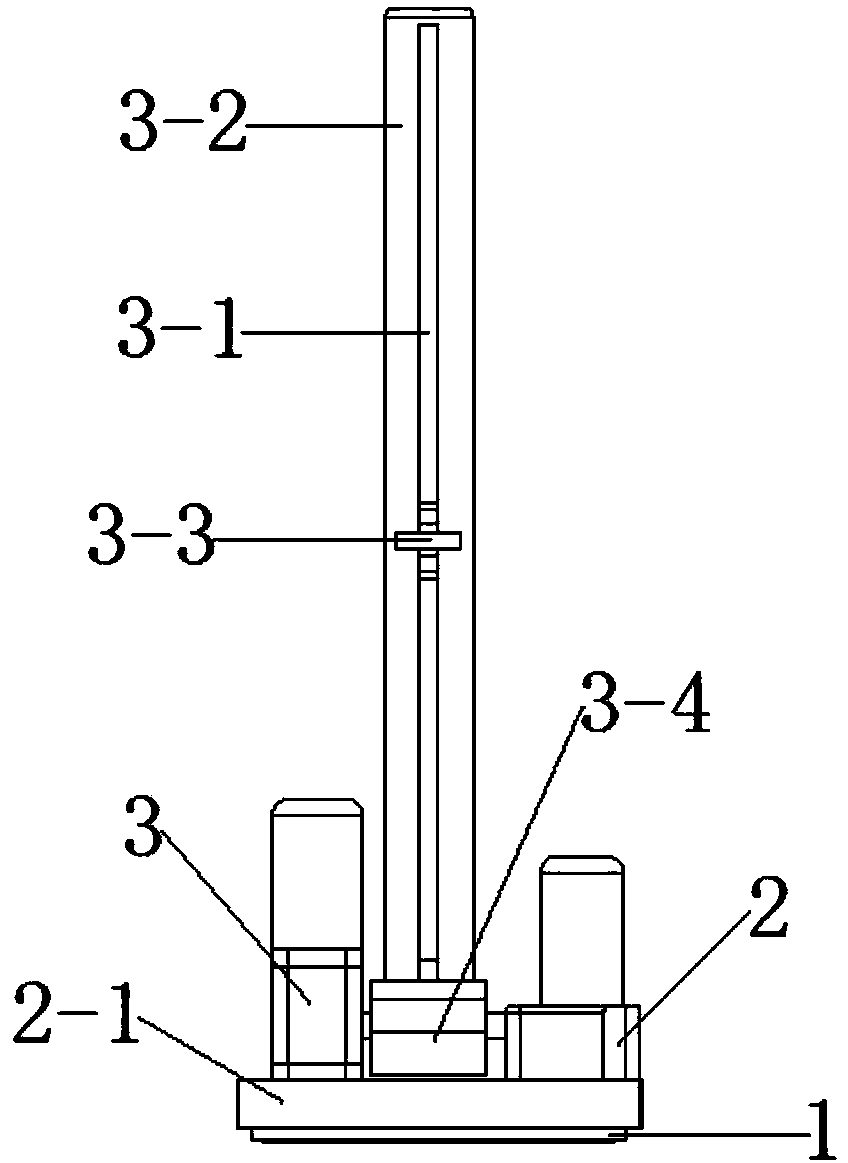
Portable mechanical endoscope fixture
ActiveCN104188613AProtection against sudden fall hazardsAvoid changing the position of the speculumSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisThree degrees of freedomEndoscope
The invention provides a portable mechanical endoscope fixture comprising a base, a horizontal rotating mechanism and a lifting pitching mechanism. Through adjustment of three degrees of freedom, an endoscope being fixed can be horizontally rotated, lifted up and down and pitched. The portable mechanical endoscope fixture has the advantages that manual fixing of the endoscope is completely replaced; the lifting pitching mechanism and a vertical lifting mechanism are arranged at the edge of the horizontal rotating mechanism, more operating space is saved, and more medical instruments can be used in surgery; in addition, a sound-operated or foot-operated control device can be added to the portable mechanical endoscope fixture, and medical labor cost is saved.
Owner:TIANJIN BOLANG SCI TECH DEV
Simulation system for training in endoscopic procedures
A simulation system for training in endoscopic procedures includes an endoscope apparatus, which includes an operating part with at least one valve, a control device to generate a virtual image of an endoscopic operating scene depending on an actuation of the valve and a display device to display the virtual image, the endoscope apparatus includes for example a siphoning line, an insufflation line and / or a flushing line upon which the valve acts. The simulation system includes pressure-generating means to impact the siphoning line, the insufflation line and / or the flushing line with reduced or excess pressure, sensor means to measure pressure and / or flow in the siphoning line, the insufflation line and / or the flushing line and transmission means to transmit the measured values provided by the sensor means to the control device to be used in generating the virtual image.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
Apparatus for endoscopic procedures
The present disclosure provides for a surgical device. The surgical device includes a jaw assembly and a camera assembly coupled to the jaw assembly. The camera assembly includes a camera housing defining an interior space having at least one opening on a side thereof, first and second support arms pivotally coupled within the camera housing and deployable therefrom, and a camera body coupled to the first and second support arms and moveable between a first position, in which the camera body is positioned within the interior space of the camera housing, and a second position, in which the camera body extends from the at least one opening of the camera assembly.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Device for simulating an endoscopic operation via natural orifice
InactiveUS20180366034A1Simple to executeMore realistic simulation scenariosEducational modelsEndoscopic operationsPhysical model
A device for simulating an endoscopic operation via natural orifice, including a physical model of a biological organ including main and inlet modules detachable from each other. The main module may define a main body of the organ with a cavity and the inlet module may define an inlet opening to the cavity of the main module corresponding to the inlet of the biological organ. The cavity of the main module is accessible through the inlet module by an endoscopic tool to actuate in the cavity of the main module. The main module may be configured in such a way that, in use, one or more simulation modules are attachable with the main module to simulate one or more events representative of the actuation of the endoscopic tool in the cavity of the main module.
Owner:FUNDACIO INSTITUT DE RECERCA DE LHOSPITAL DE LA SANTA CREU I SANT PAU +2
Endoscope joint ring, endoscope bent part and corresponding endoscope device
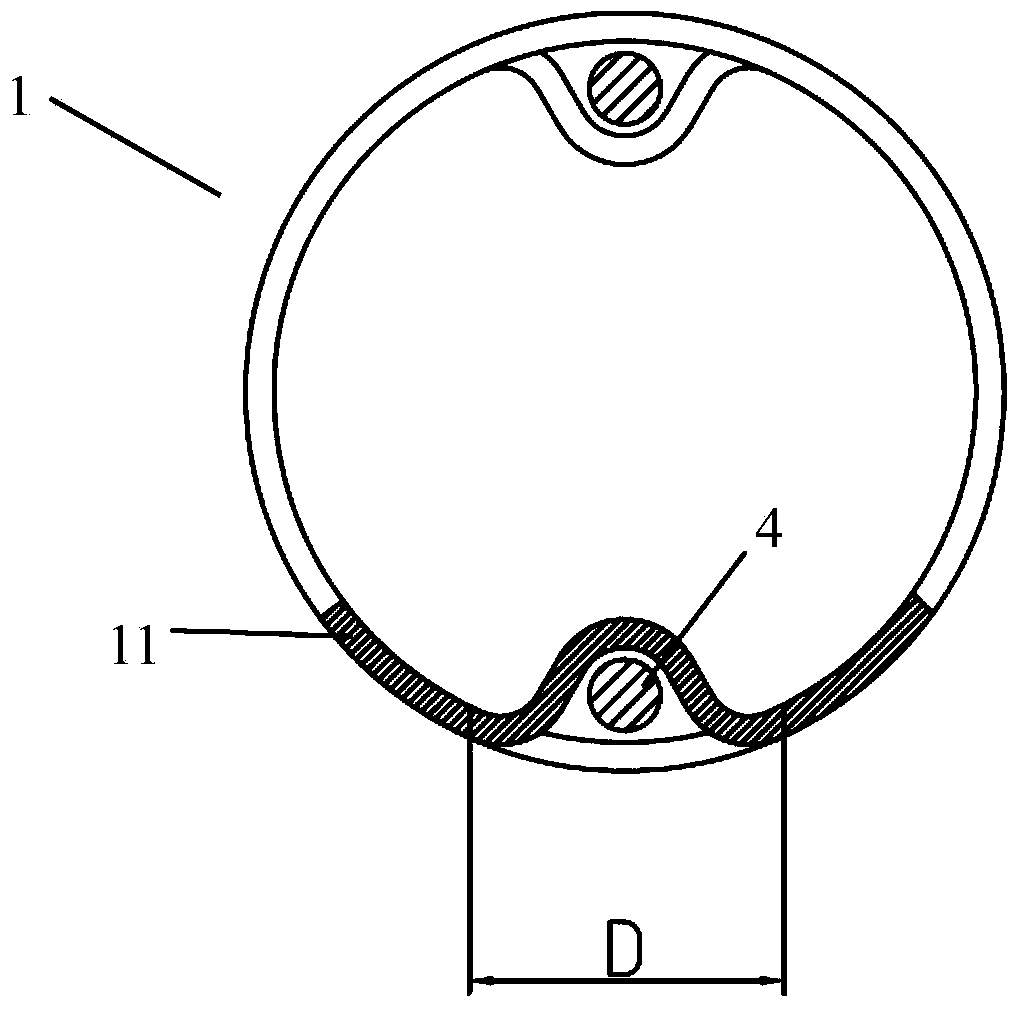
InactiveCN103690140ACooperate wellGrasp the accuracySurgeryEndoscopesBiomedical engineeringEndoscopic manipulation
The invention relates to an endoscope joint ring, an endoscope bent part and a corresponding endoscope device. The endoscope joint unit comprises a ring part and a restraint positioning part, wherein the periphery of the restraint positioning part is closed, and the restraint positioning part is a part independent from the ring part; the restraint positioning part is fixedly arranged at one side of the inner wall of the ring body. The endoscope bent part comprises at least two endoscope joint units, and adjacent endoscope joint units are in mutually movable connection. One end of the endoscope device is an insert end, and the endoscope bent part is positioned at the insert end. The size and shape of the restraint positioning part are not influenced by the size of the ring body, so that the restraint positioning part can be better matched with the periphery of an endoscope operation part; the consistence of each restraint positioning part is maintained, so that when a metal material is stamped, tiny changes due to inconsistent metal rebound shrinking rates can be avoided; the restraint positioning part is convenient to treat, trim, burr and other phenomena influencing extra resistance generated in a process of drawing a steel cable cannot occur.
Owner:SHANGHAI OUTAI MEDICAL EQUIP
Electrically curvable endoscope device
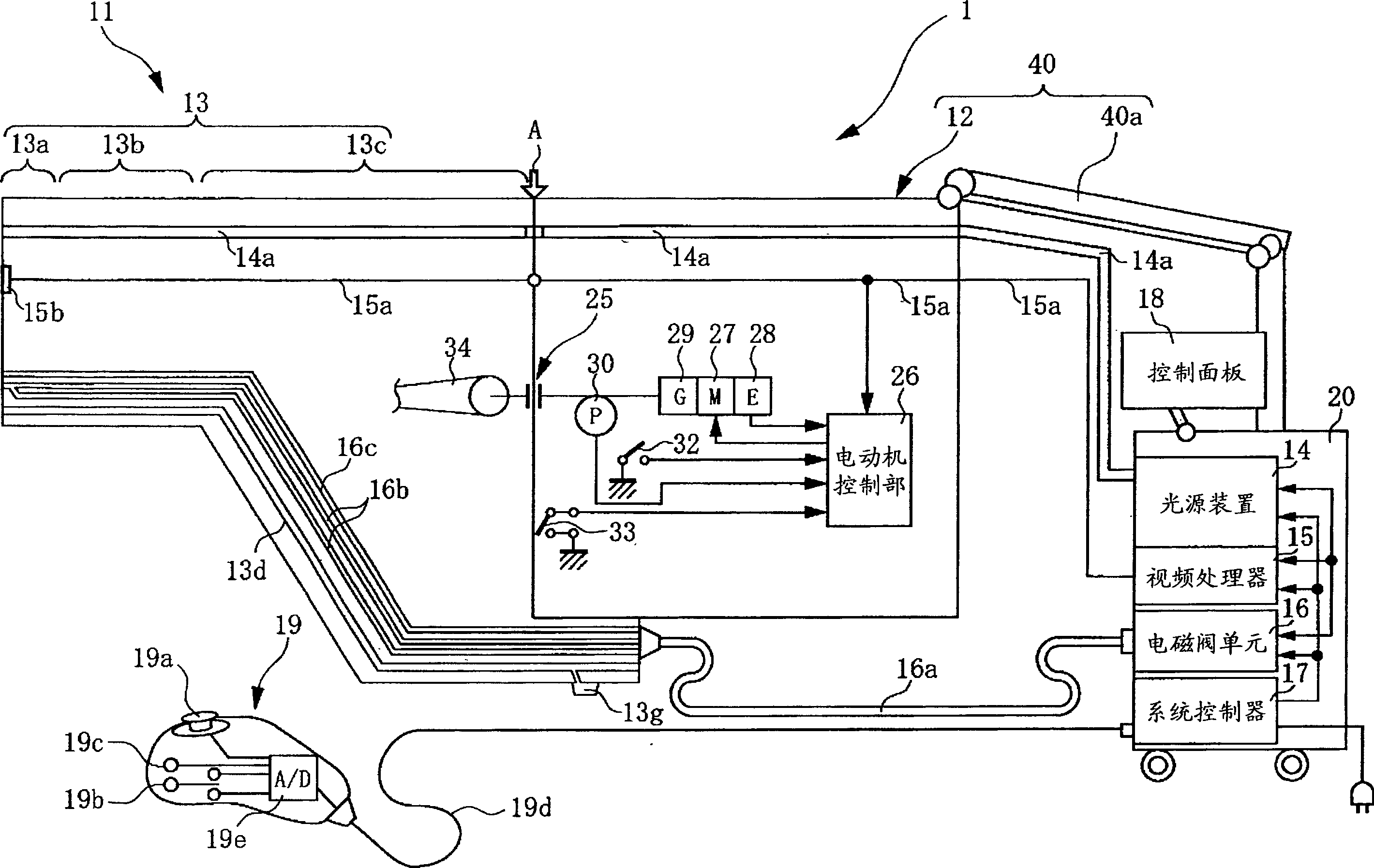
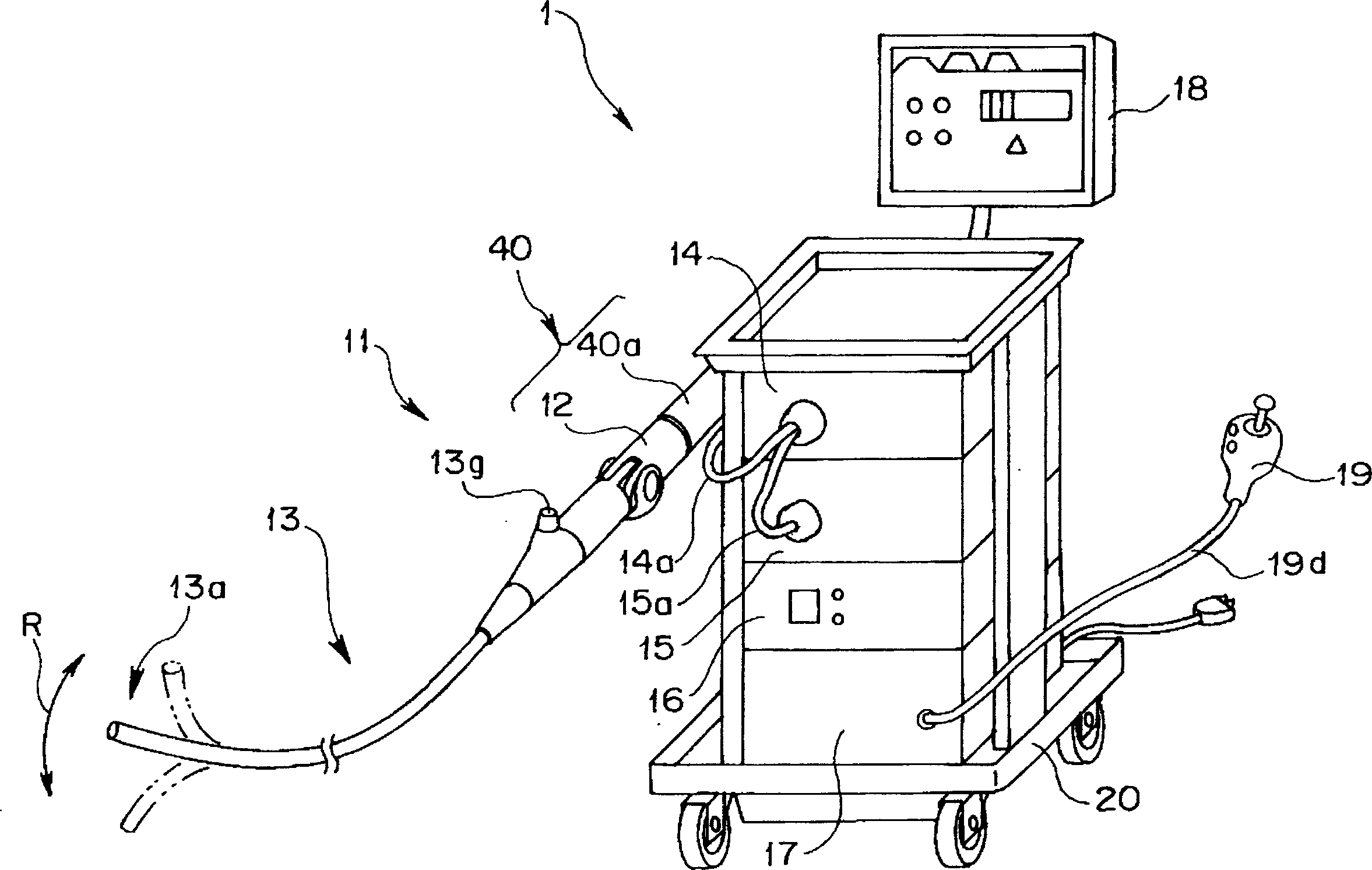
To provide an electric bending endoscope device which can always ensure good operability when using the endoscope without imposing a weight burden on the operator during the operation of the endoscope. The electric bending endoscope device includes at least: an electric bending endoscope capable of observation and treatment in a body cavity, including an elongated insertion portion inserted into the body cavity, and a device for electrically bending and driving a part of the insertion portion. A bending drive device, and an operating part that is separate from the bending drive device and electrically connected to the bending drive device; a system controller, electrically connected to the electric bending endoscope, and controls the electric bending endoscope as a whole; and An endoscope holding device, which includes a bending drive unit with a built-in bending drive device and holds a part of the electric bending endoscope, and an arm connected to and held on the bending drive unit; by attaching and detaching the bending drive unit It is freely connected and arranged on the base end side of the insertion part, and electrically connects the electric bending endoscope and the bending driving device.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com