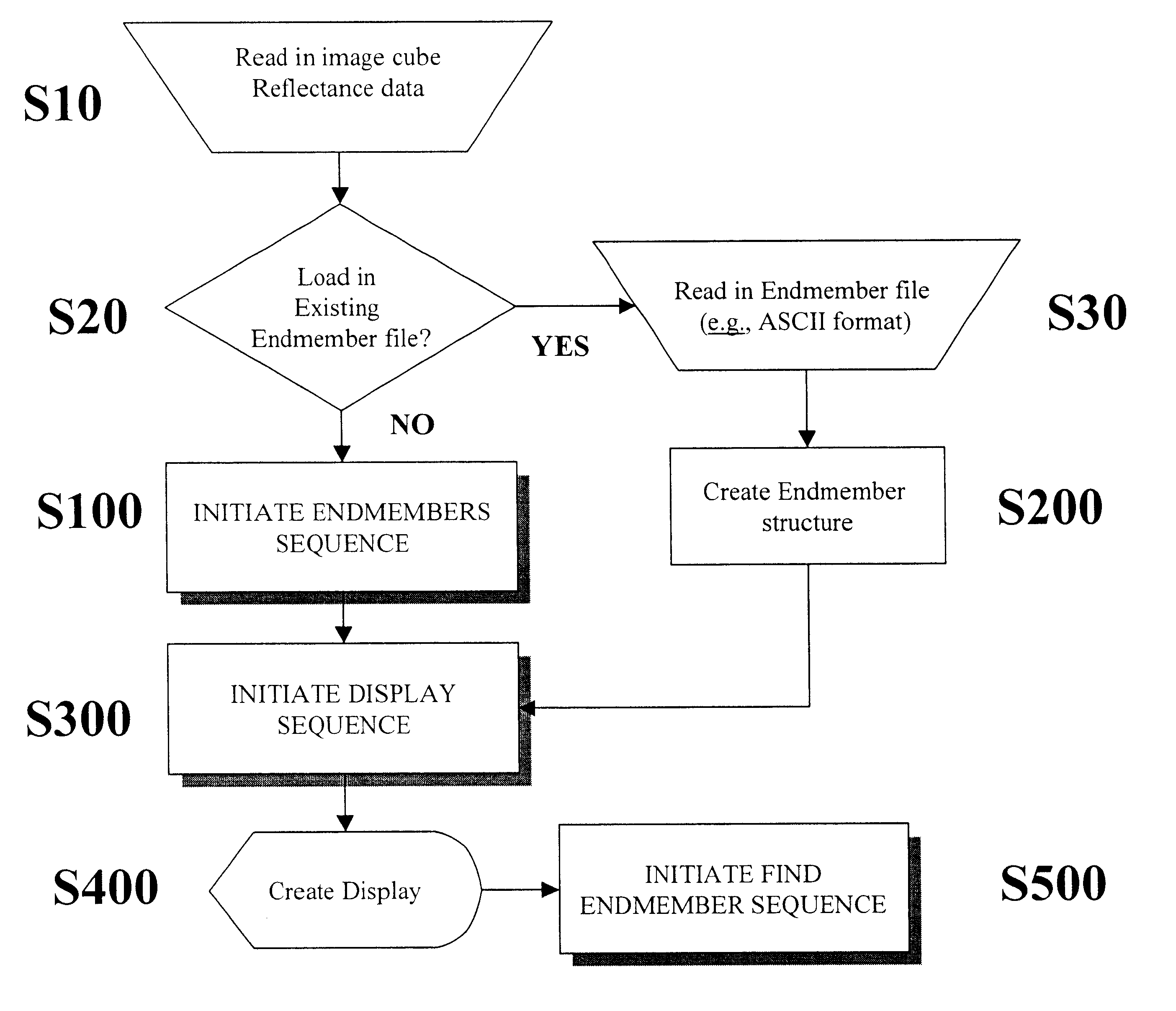
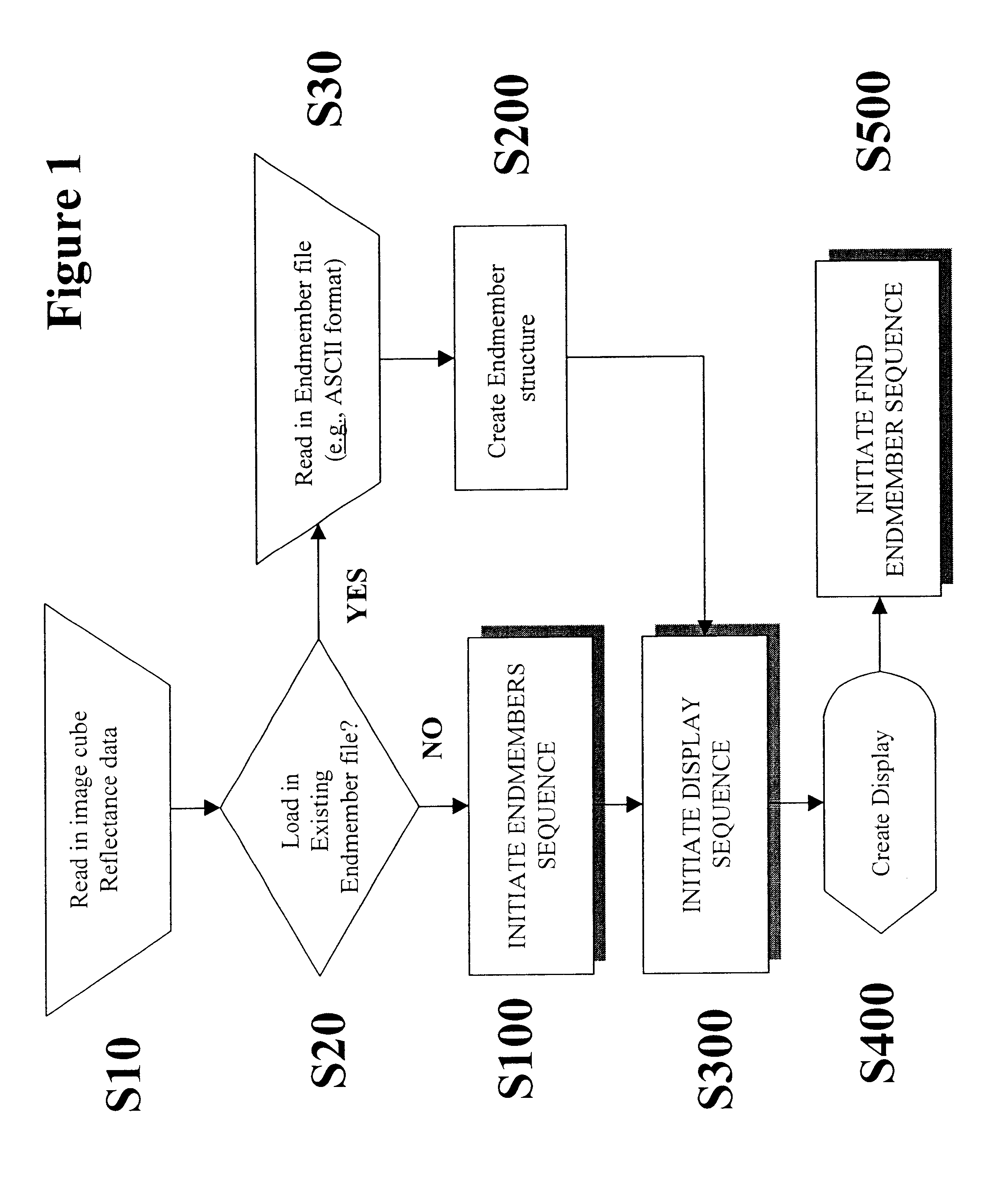
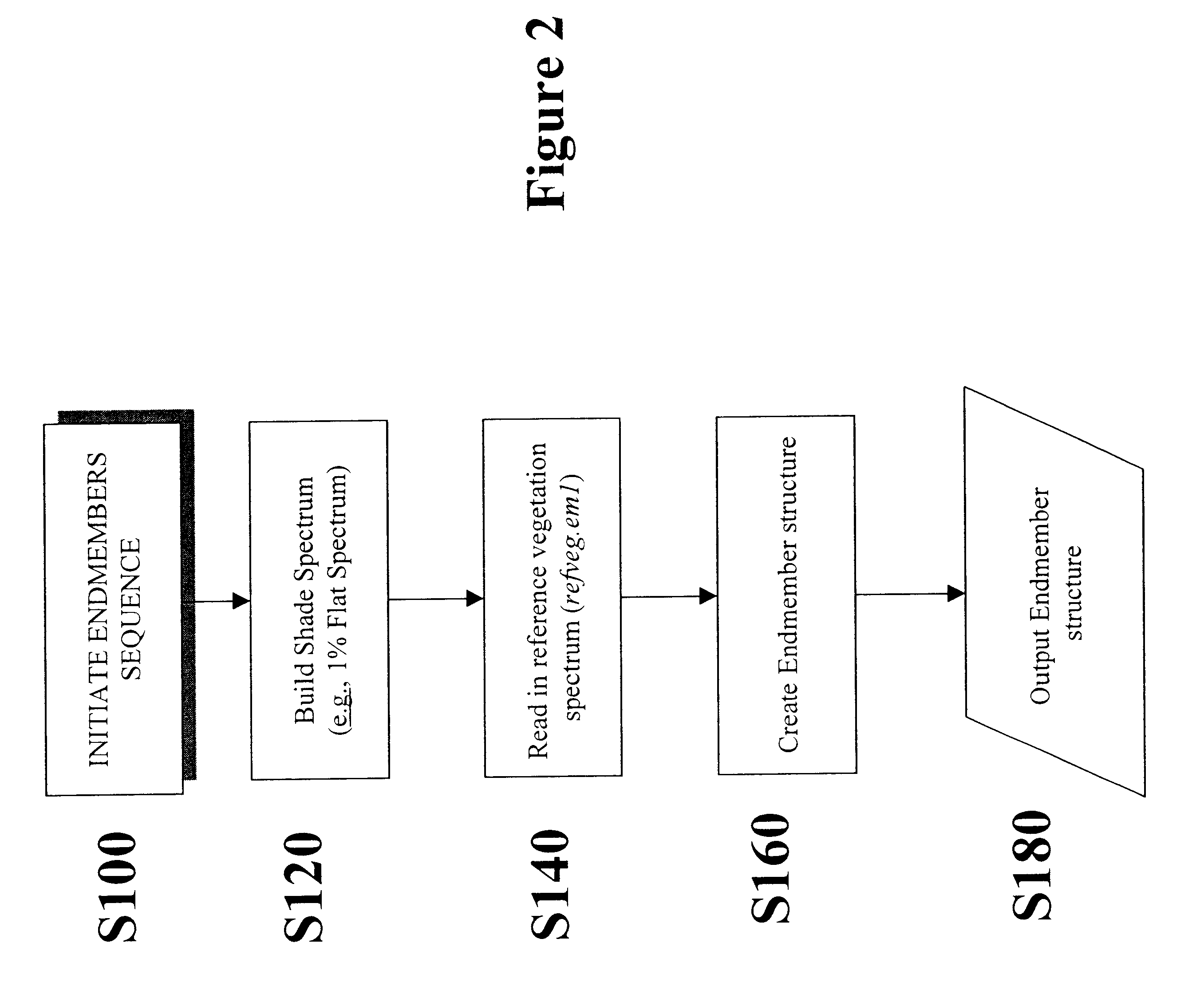
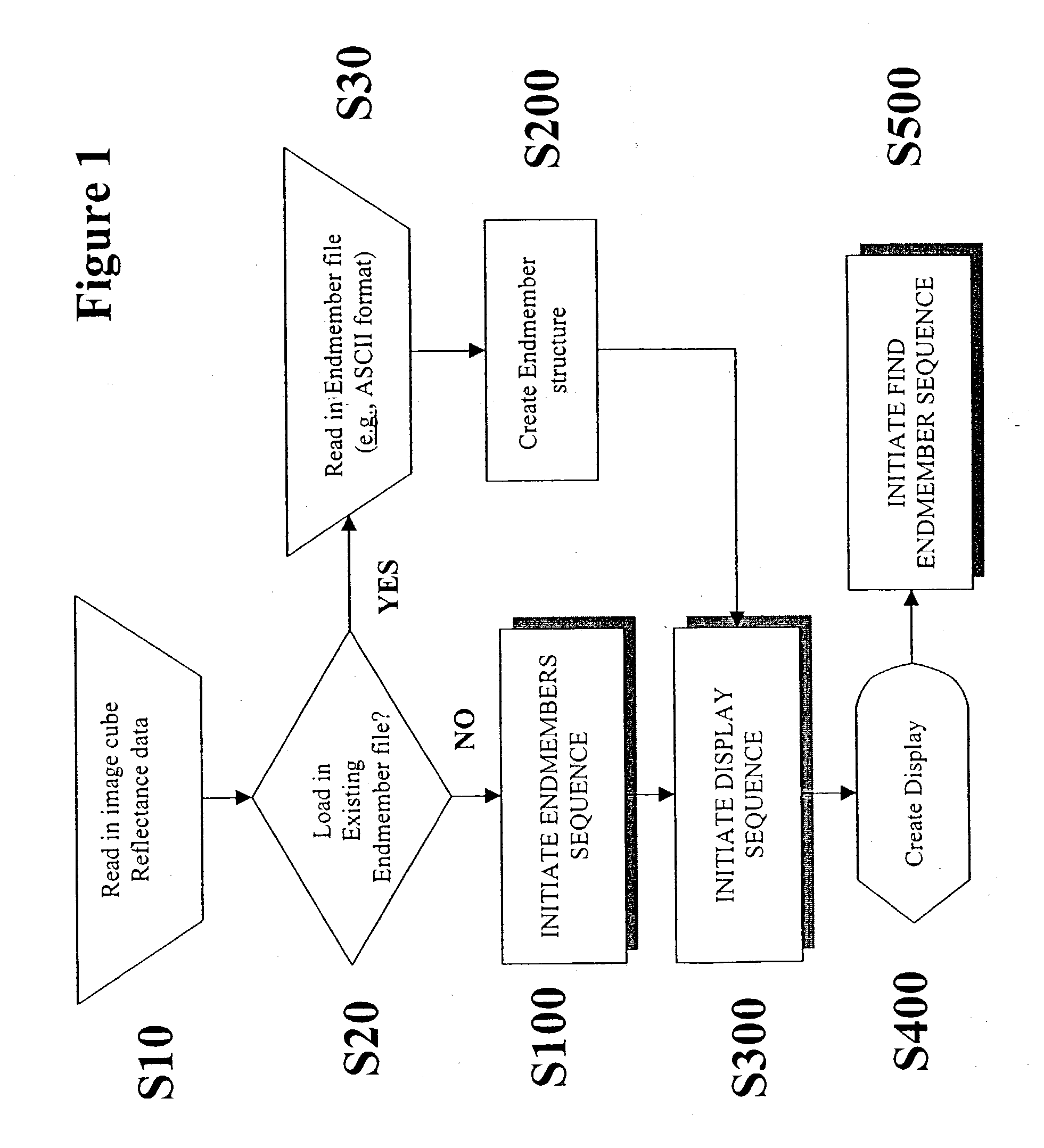
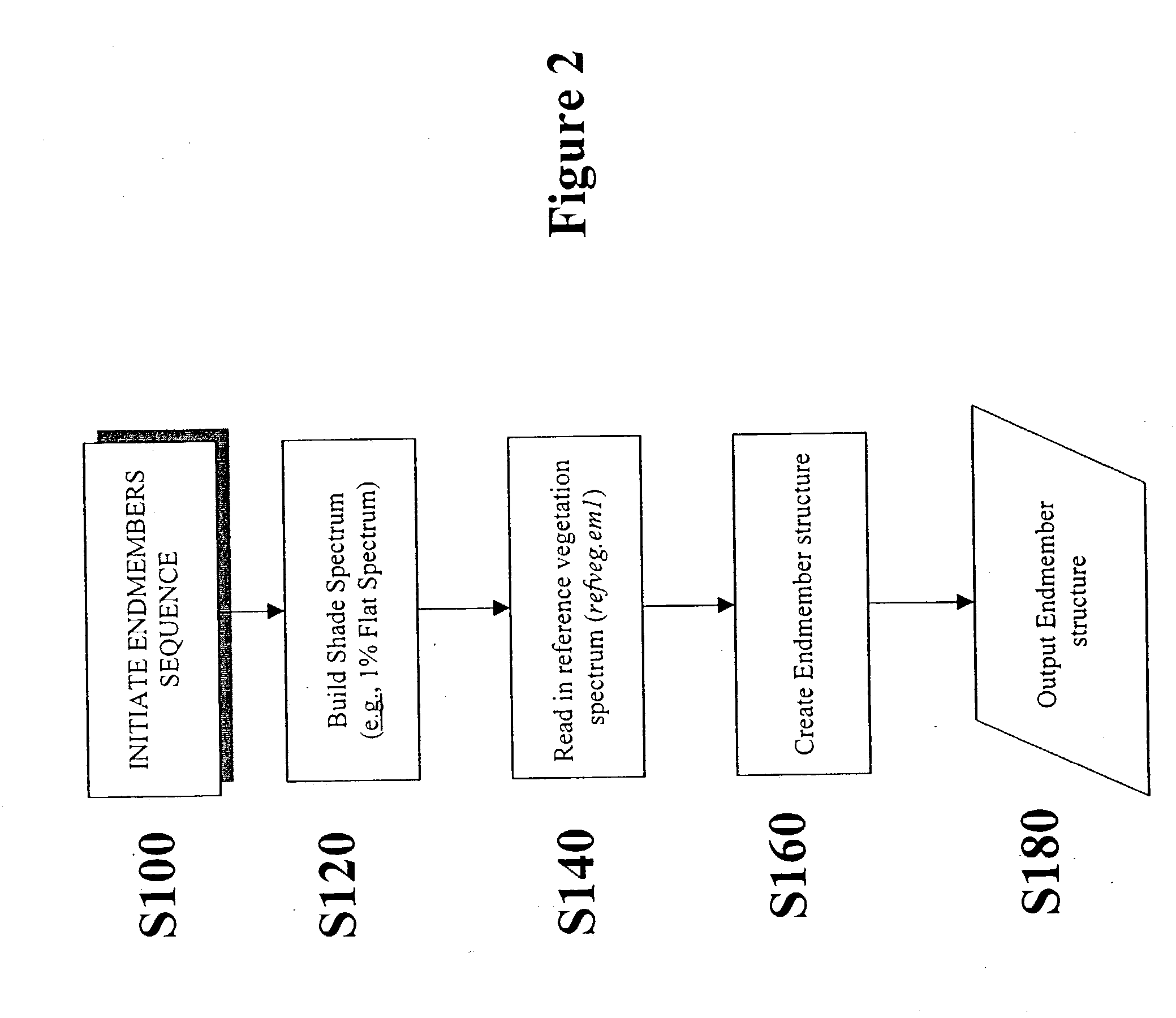
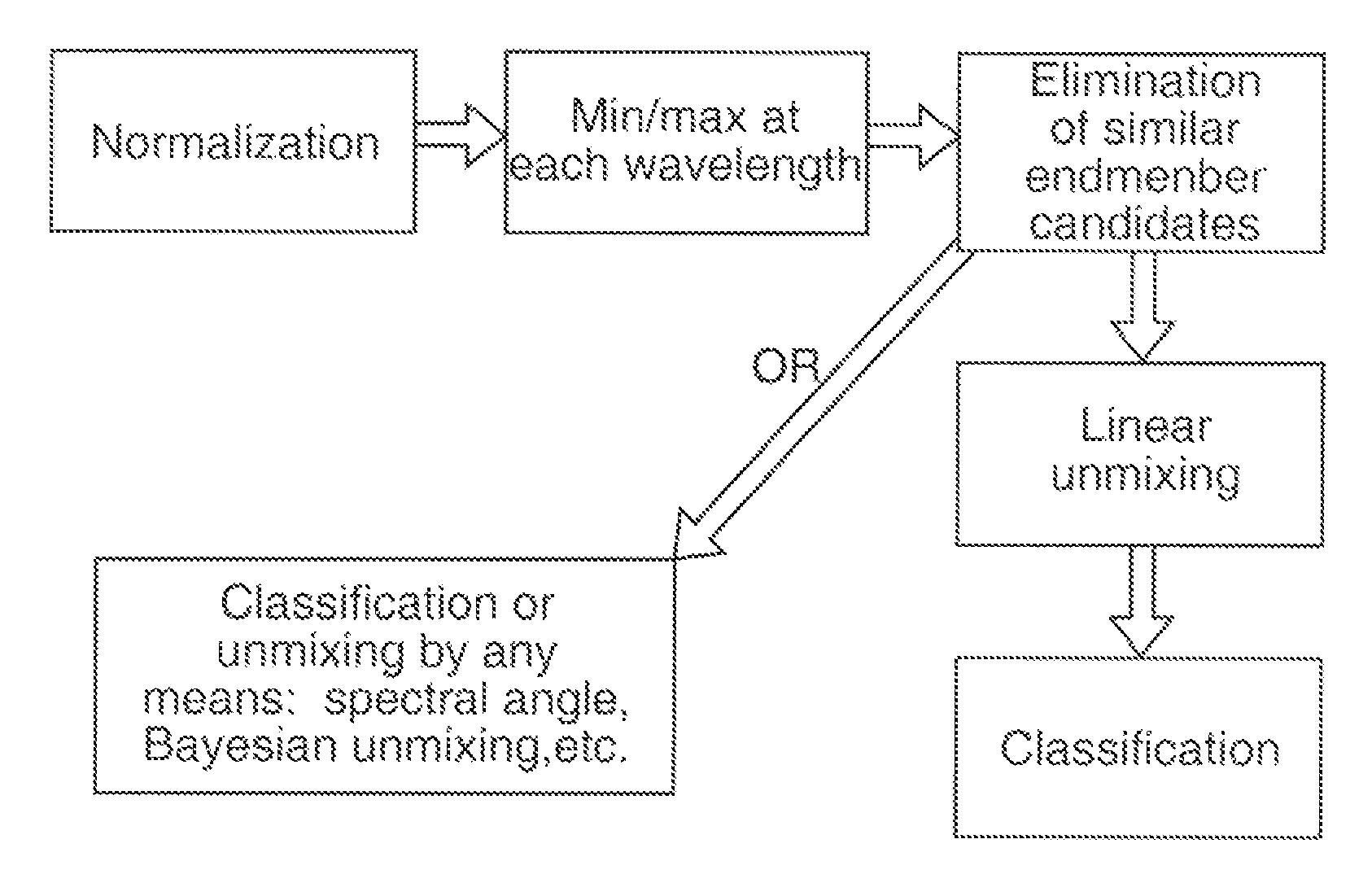
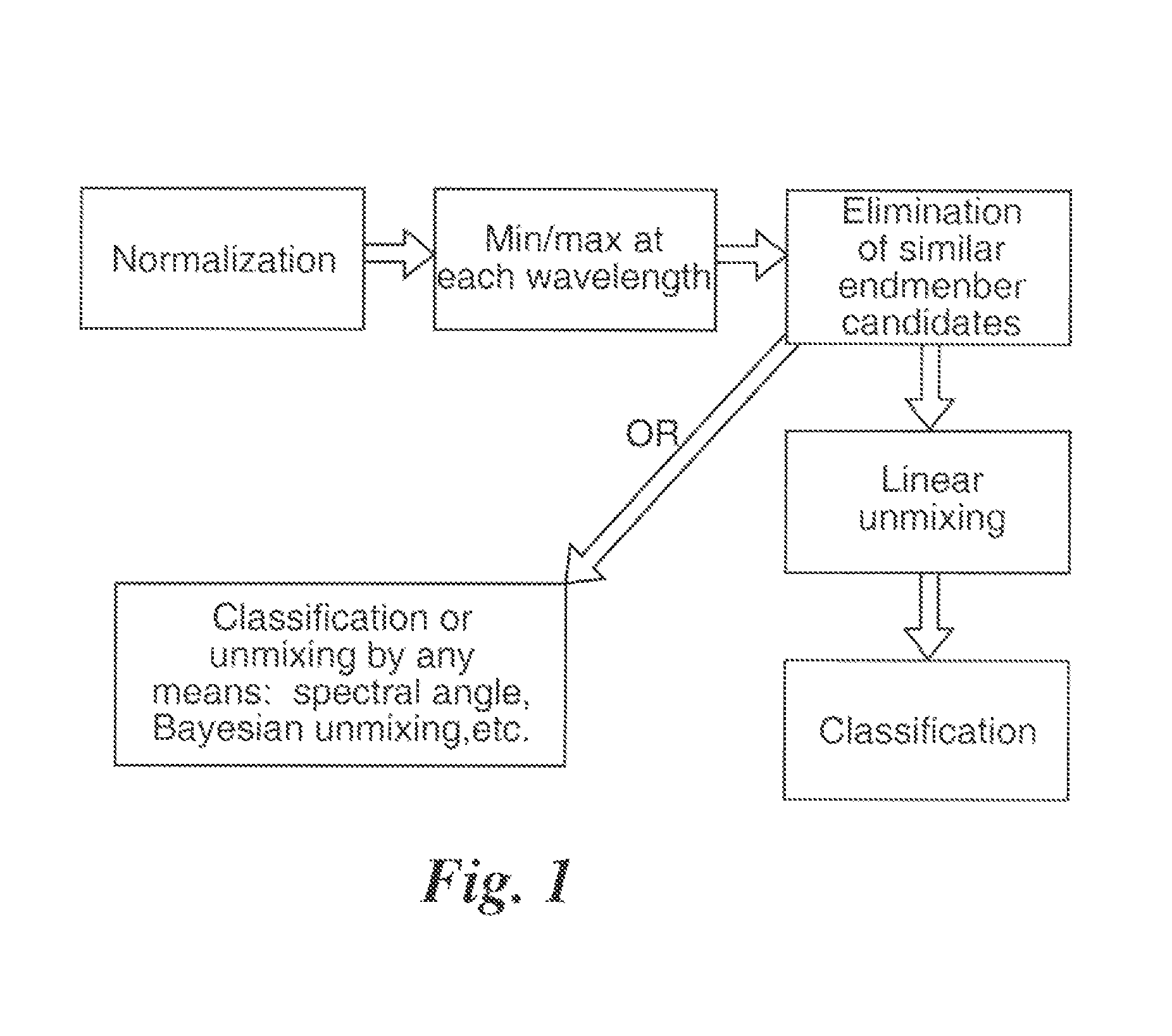
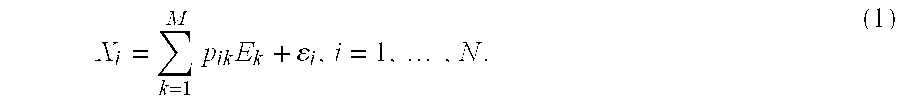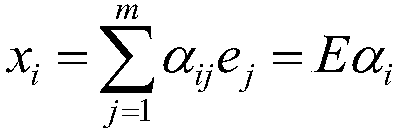Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57 results about "Endmember" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
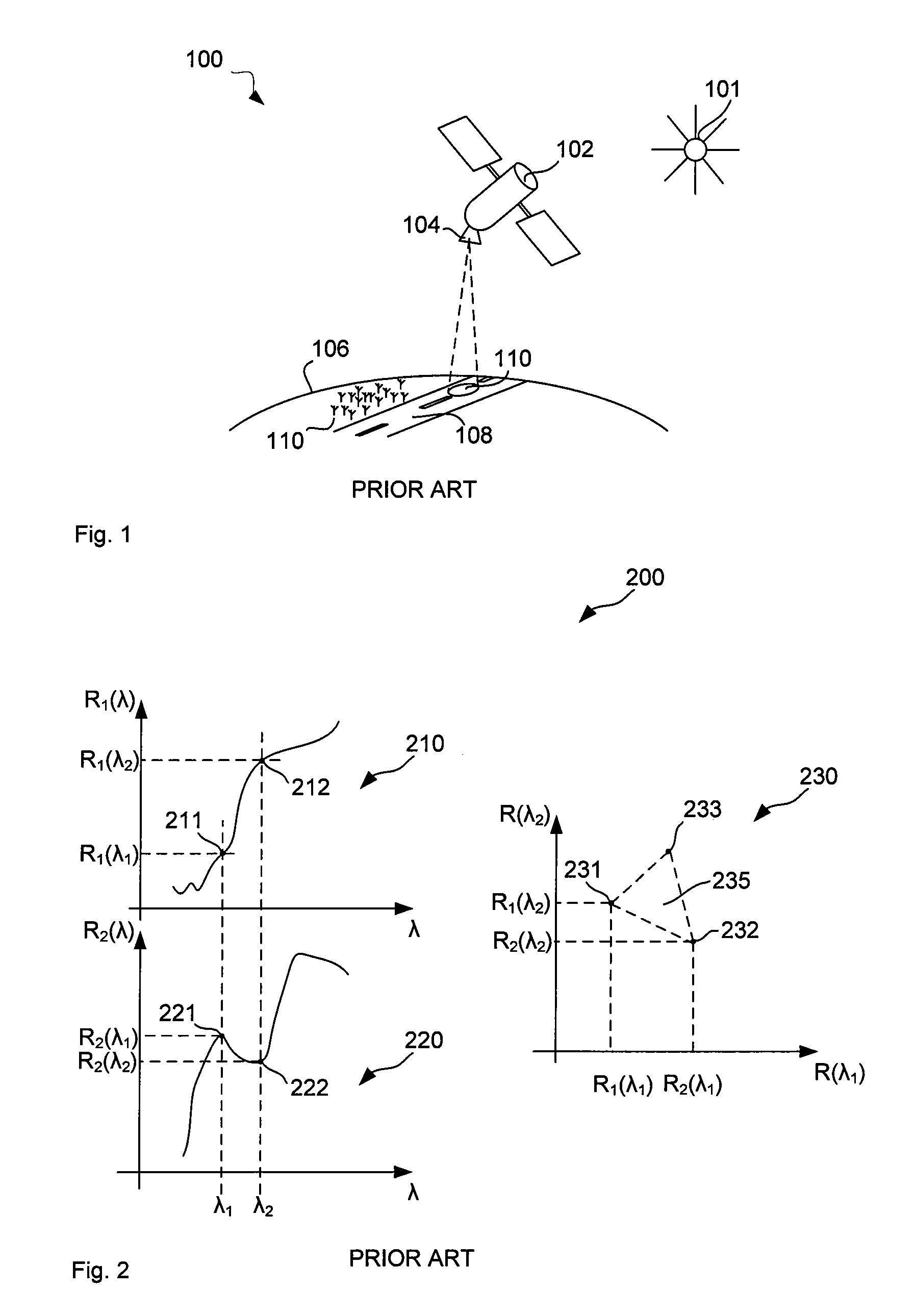
An endmember (also end-member or end member) in mineralogy is a mineral that is at the extreme end of a mineral series in terms of purity. Minerals often can be described as solid solutions with varying compositions of some chemical elements, rather than as substances with an exact chemical formula. There may be two or more endmembers in a group or series of minerals.
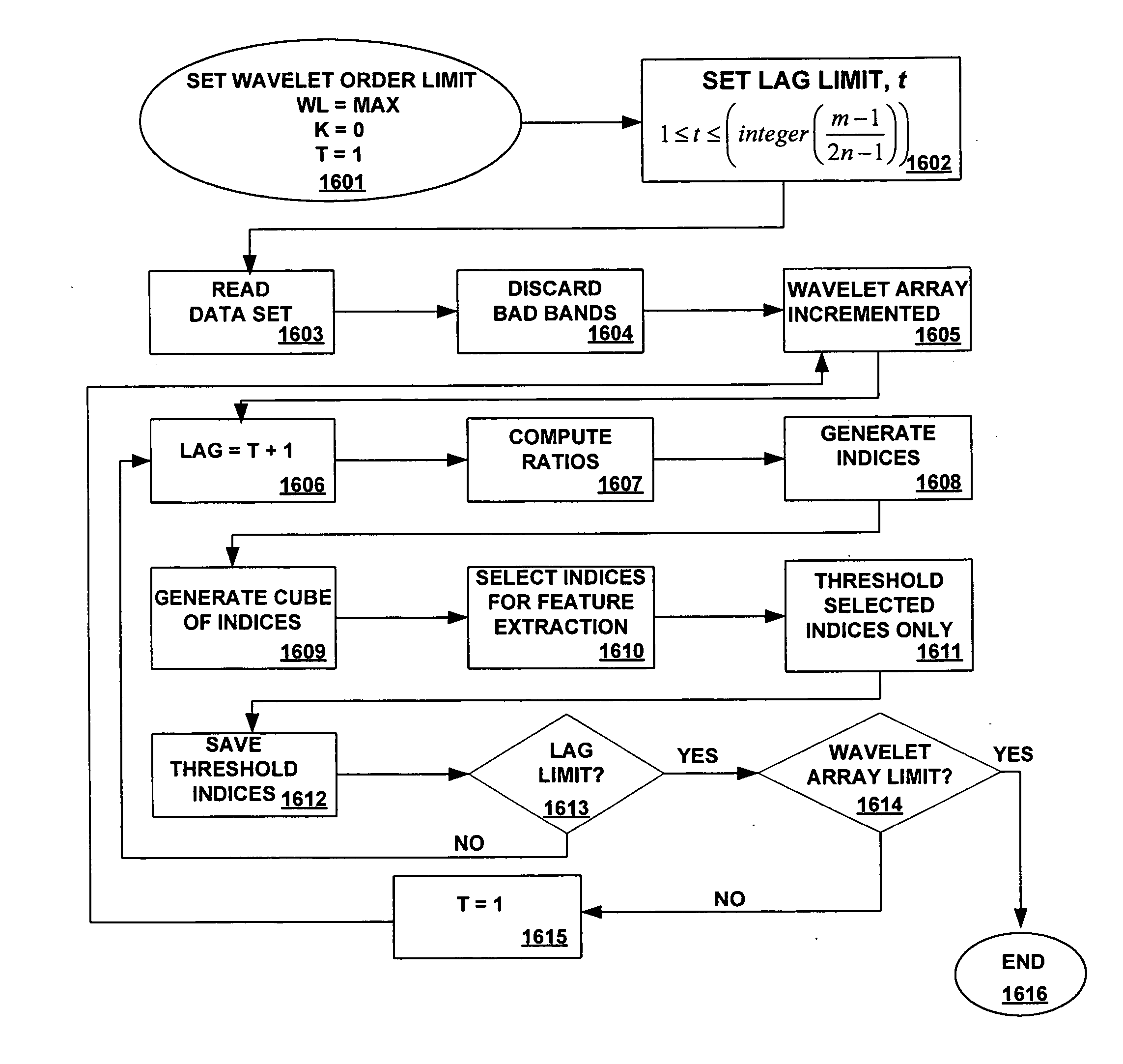
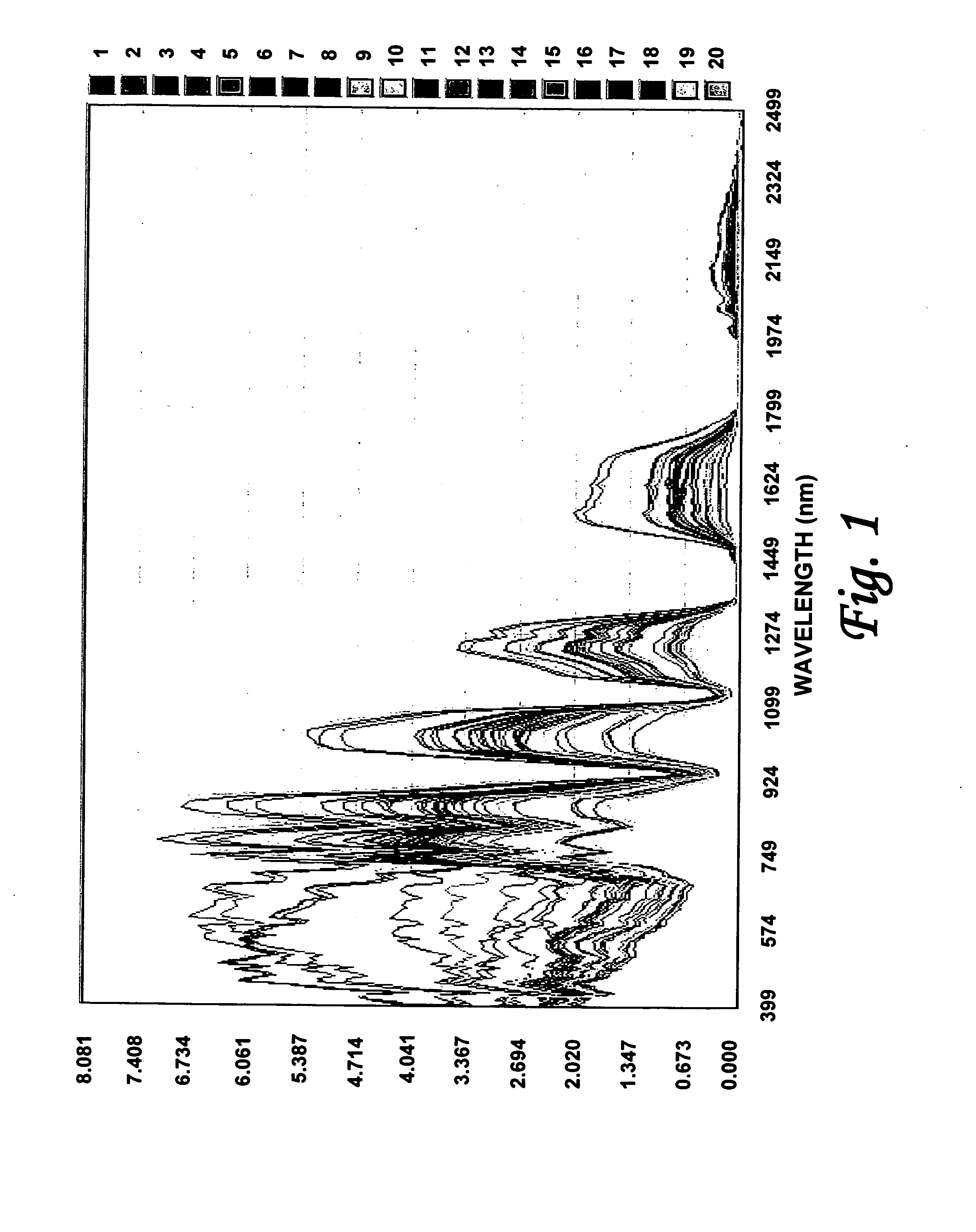
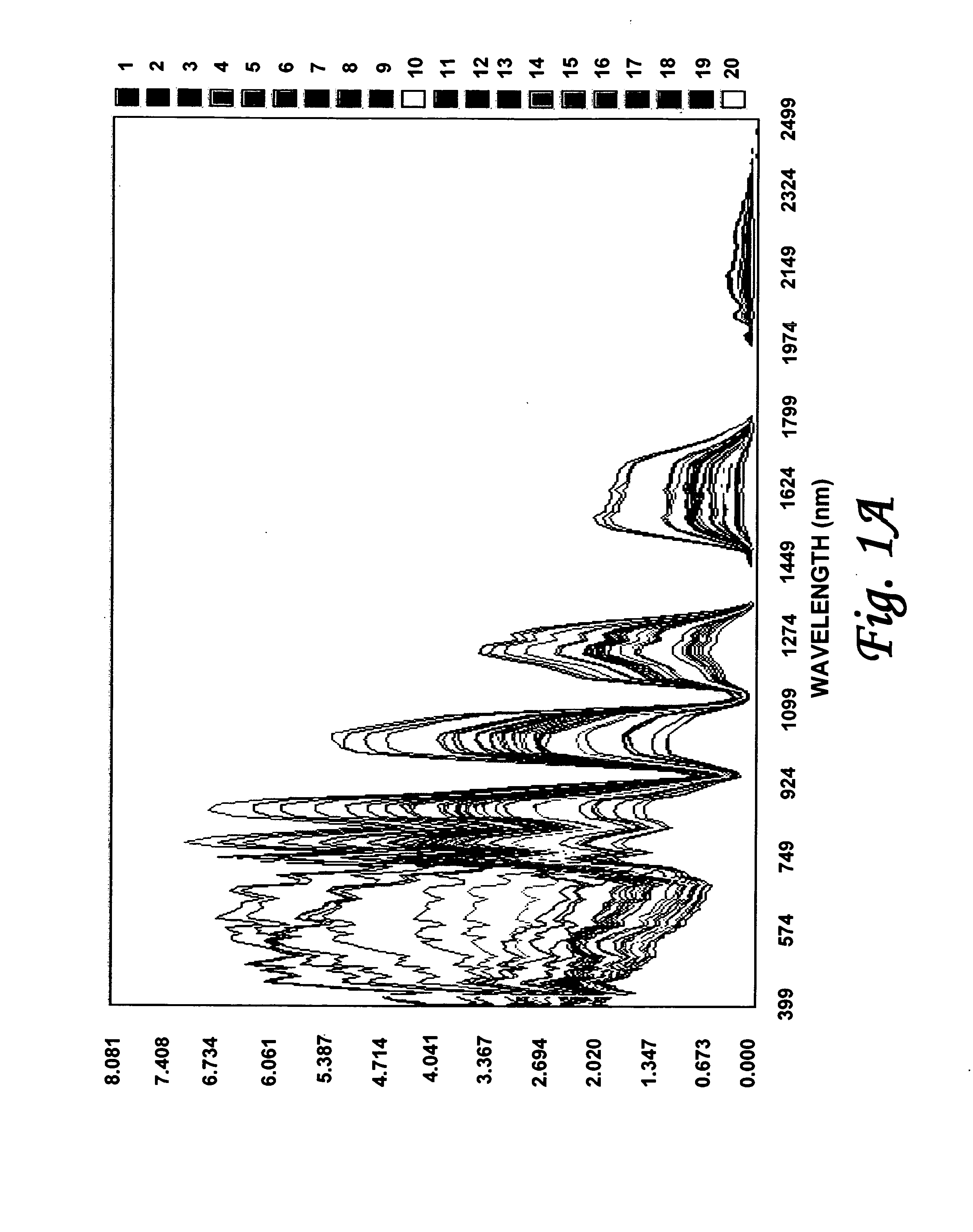
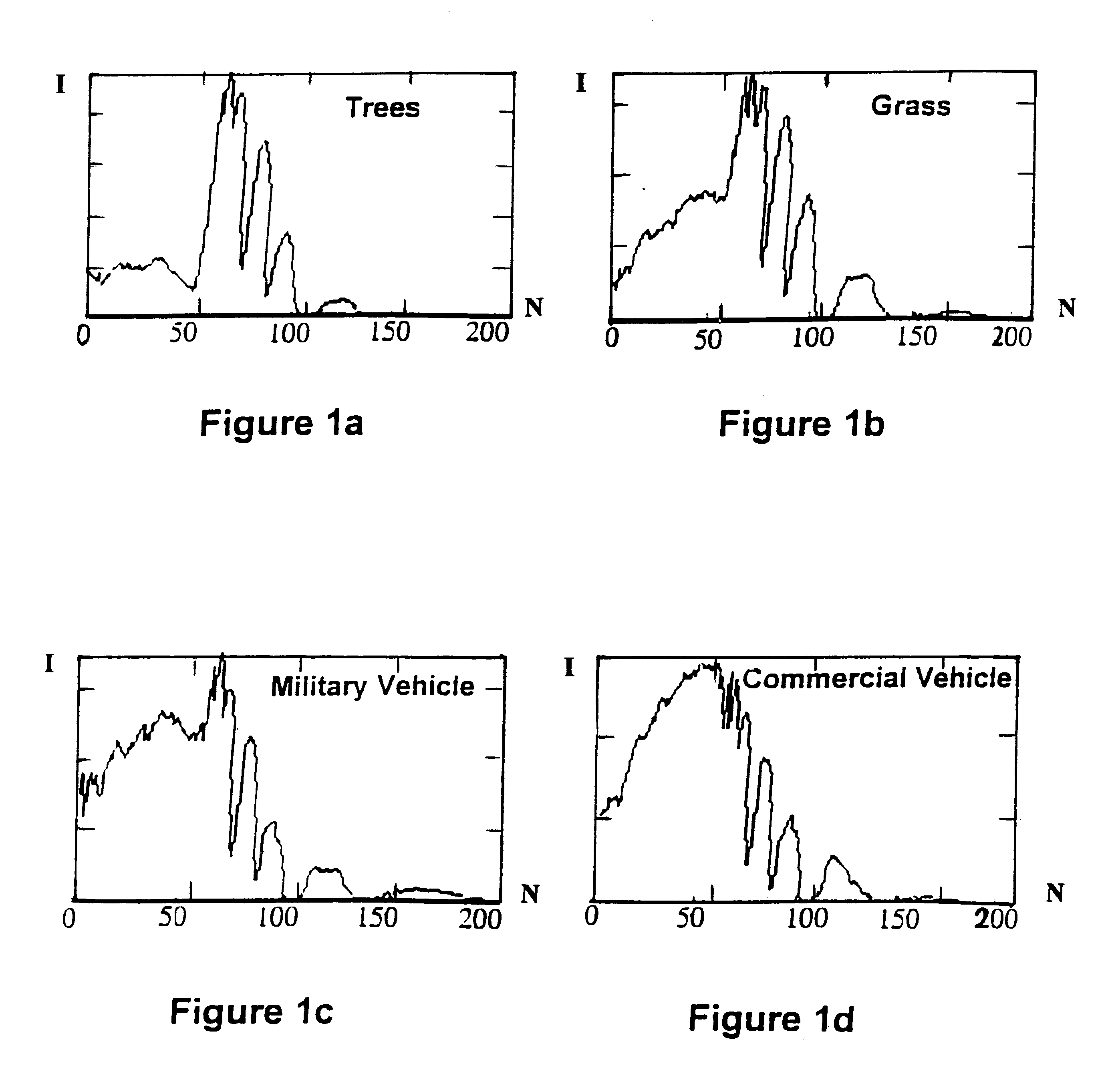
Efficient imagery exploitation employing wavelet-based feature indices
A wavelet-based band difference-sum ratio method reduces the computation cost of classification and feature extraction (identification) tasks. A Generalized Difference Feature Index (GDFI), computed using wavelets such as Daubechies wavelets, is employed in a method to automatically generate a large sequence of generalized band ratio images. In select embodiments of the present invention, judicious data mining of the large set of GDFI bands produces a small subset of GDFI bands suitable to identify specific Terrain Category / Classification (TERCAT) features. Other wavelets, such as Vaidyanathan, Coiflet, Beylkin, and Symmlet and the like may be employed in select embodiments. The classification and feature extraction (identification) performance of the band ratio method of the present invention is comparable to that obtained with the same or similar data sets using much more sophisticated methods such as discriminants, neural net classification, endmember Gibbs-based partitioning, and genetic algorithms.
Owner:US ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS
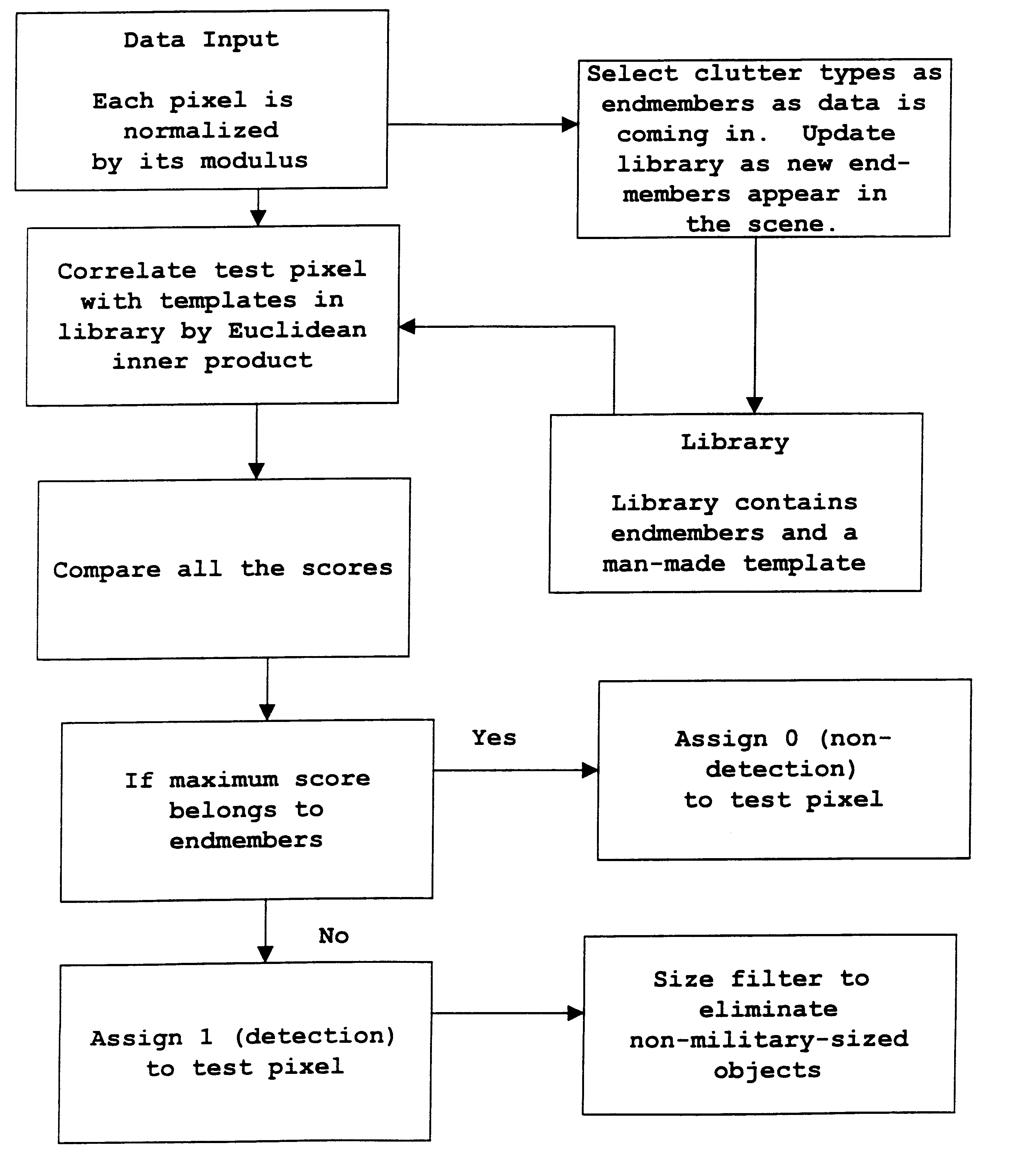
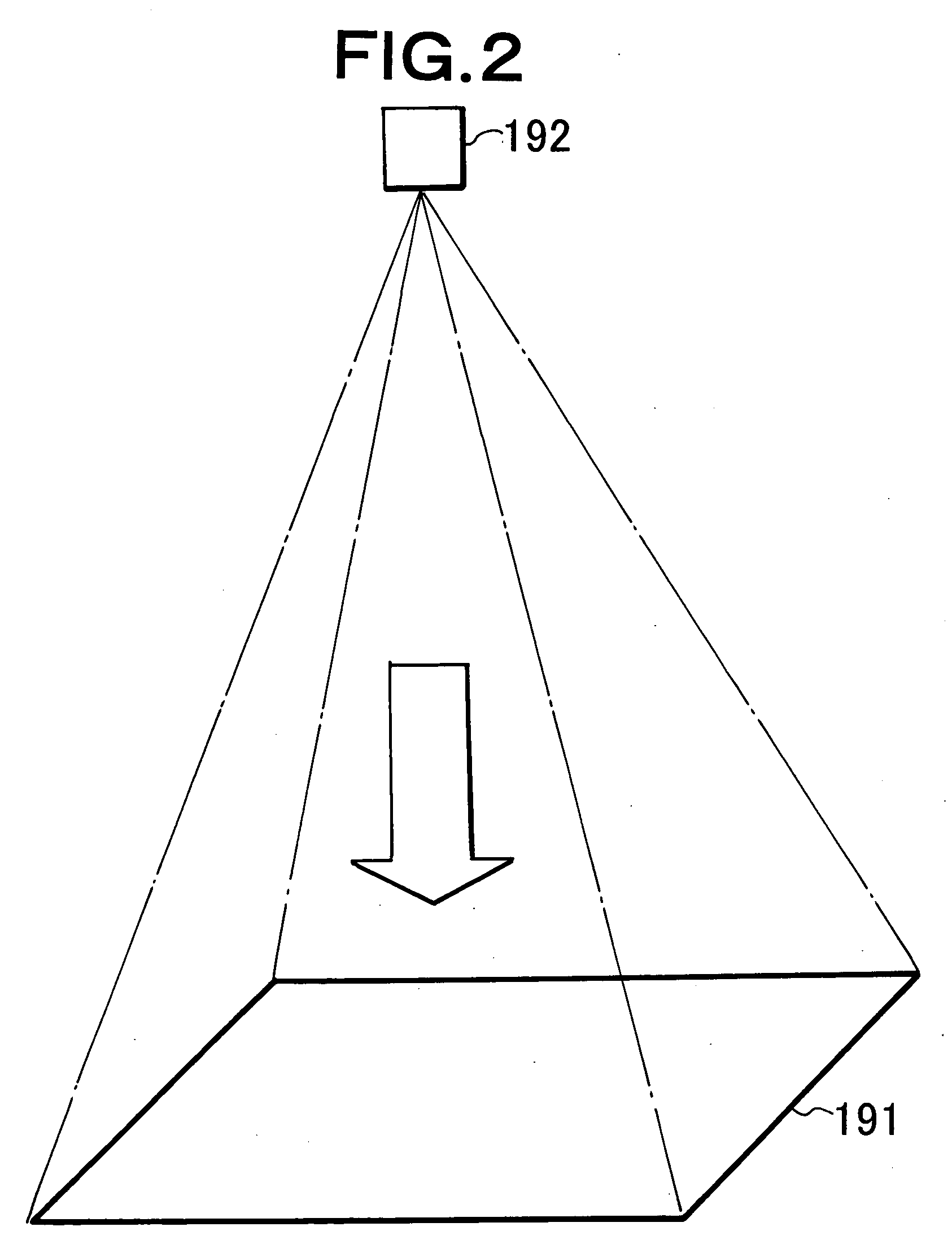
Ares method of sub-pixel target detection
Target detection using algorithms is based on the adaptive real-time endmembers selection from hyperspectral image data. New pixels are correlated with prestored clutter endmembers to obtain subsequently detected target and clutter pixels and then suppressing the latter, leaving about 10% of the image as targets. Targets are then reduced in number by size filtering.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Spectral mixture process conditioned by spatially-smooth partitioning
InactiveUS20050047663A1Accurate global labelingImprove global labelingScene recognitionClassification methodsEnergy functional
A method that facilitates identification of features in a scene enables enhanced detail to be displayed. One embodiment incorporates a multi-grid Gibbs-based algorithm to partition sets of endmembers of an image into smaller sets upon which spatial consistency is imposed. At each site within an imaged scene, not necessarily a site entirely within one of the small sets, the parameters of a linear mixture model are estimated based on the small set of endmembers in the partition associated with that site. An, enhanced spectral mixing process (SMP) is then computed. One embodiment employs a simulated annealing method of partitioning hyperspectral imagery, initialized by a supervised classification method to provide spatially smooth class labeling for terrain mapping applications. One estimate of the model is a Gibbs distribution defined over a symmetric spatial neighborhood system that is based on an energy function characterizing spectral disparities in both Euclidean distance and spectral angle.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Method to analyze remotely sensed spectral data
ActiveUS7491944B1Radiation pyrometryComputation using non-contact making devicesThermionic emissionThermal infrared
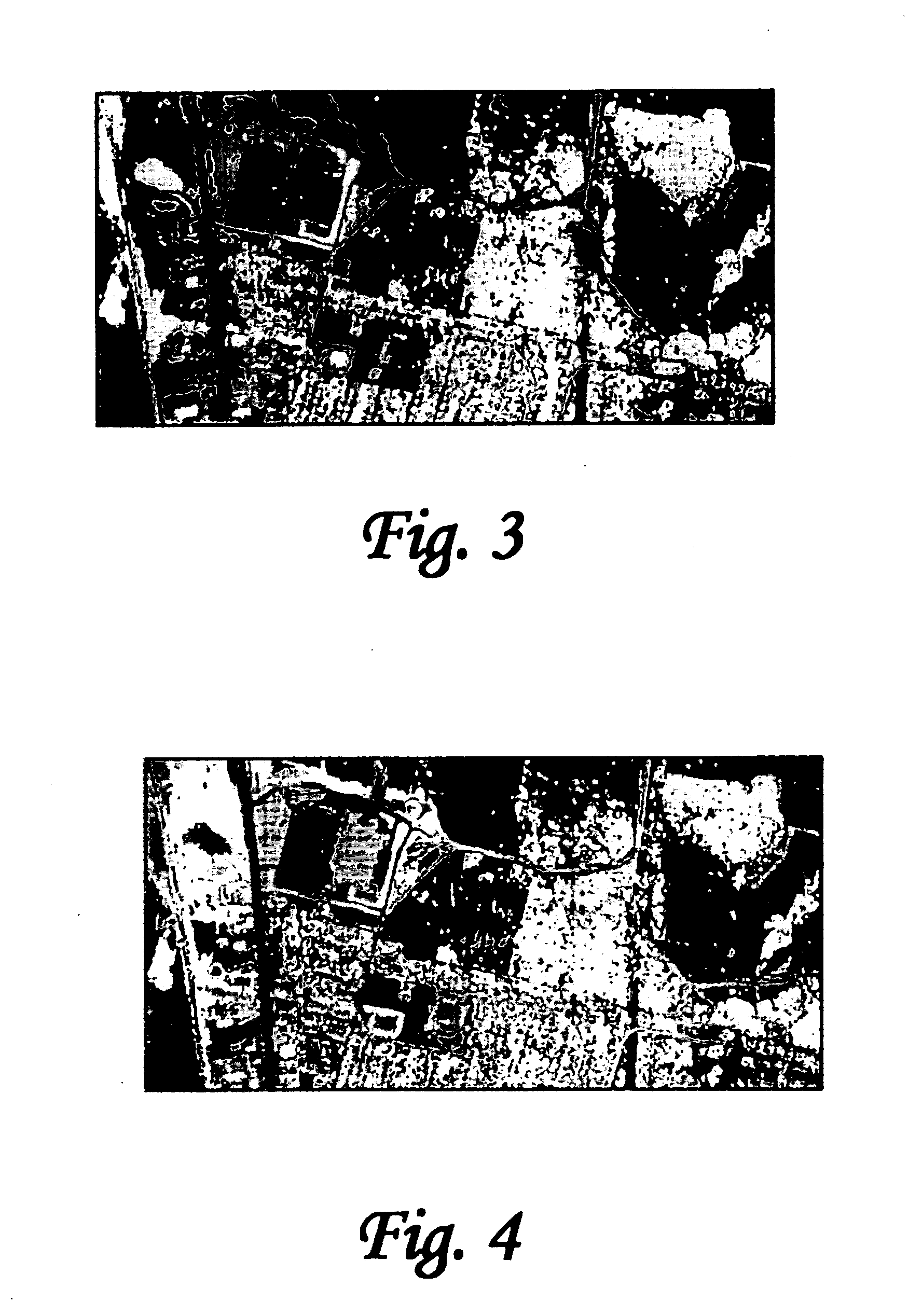
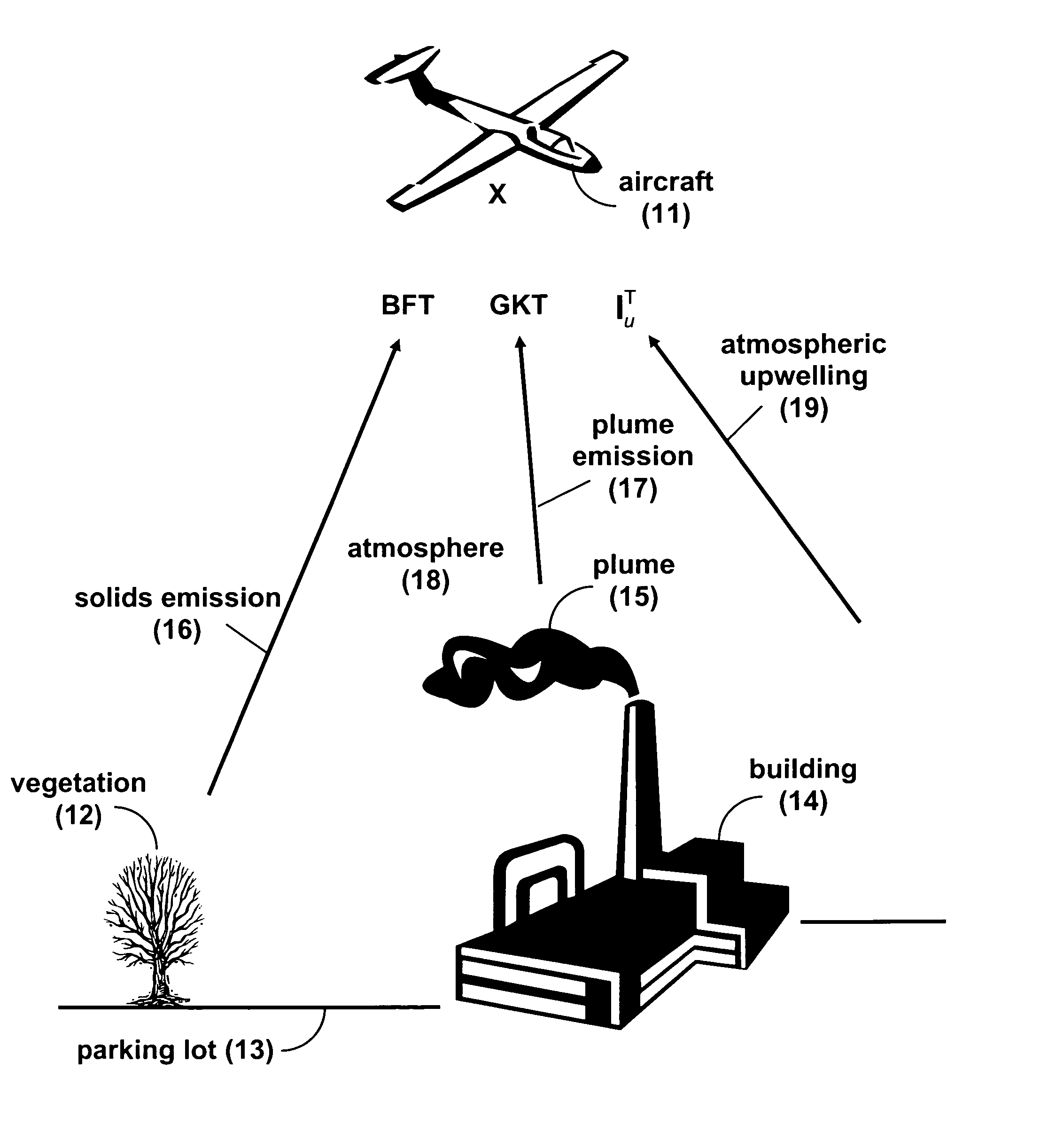
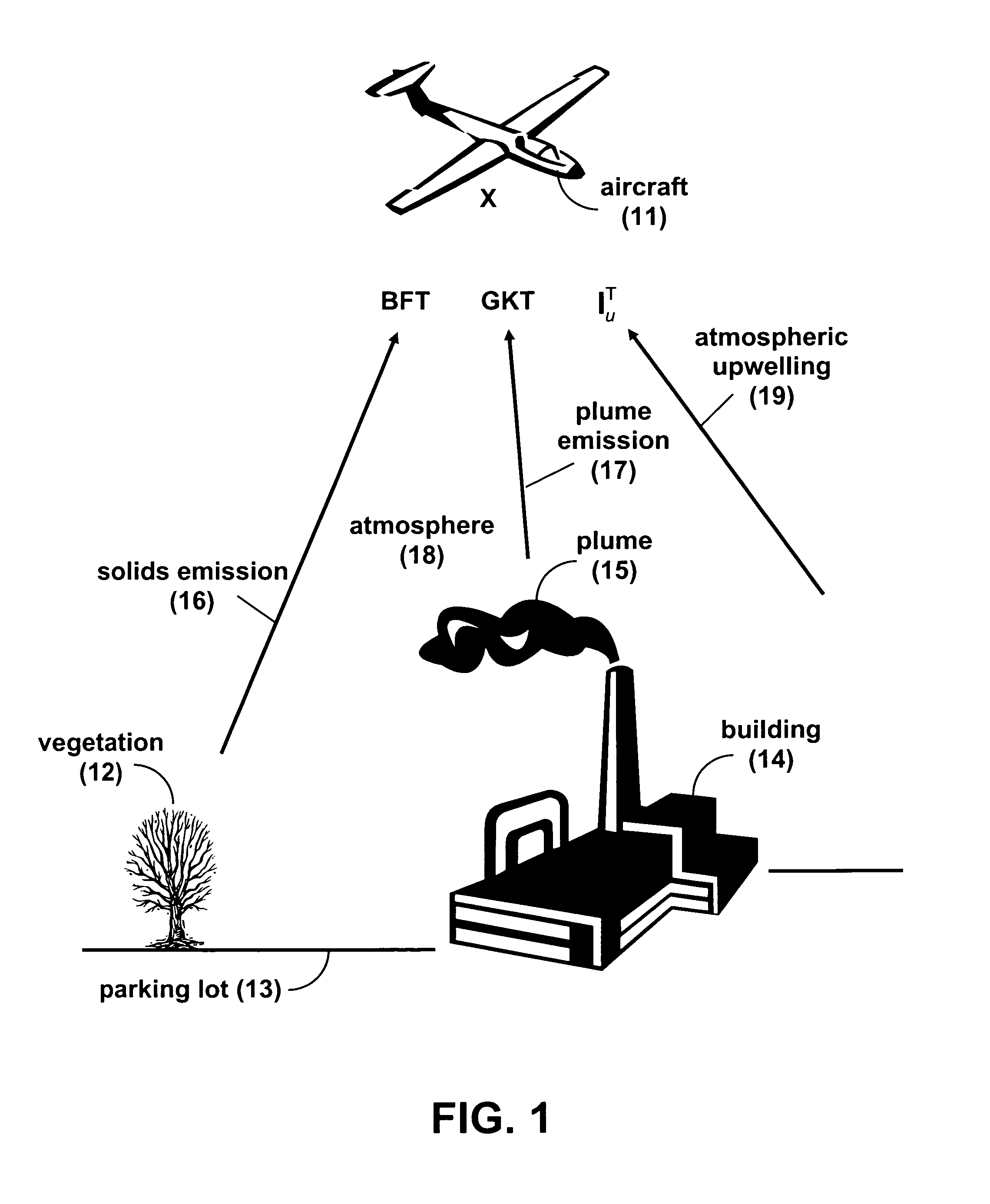
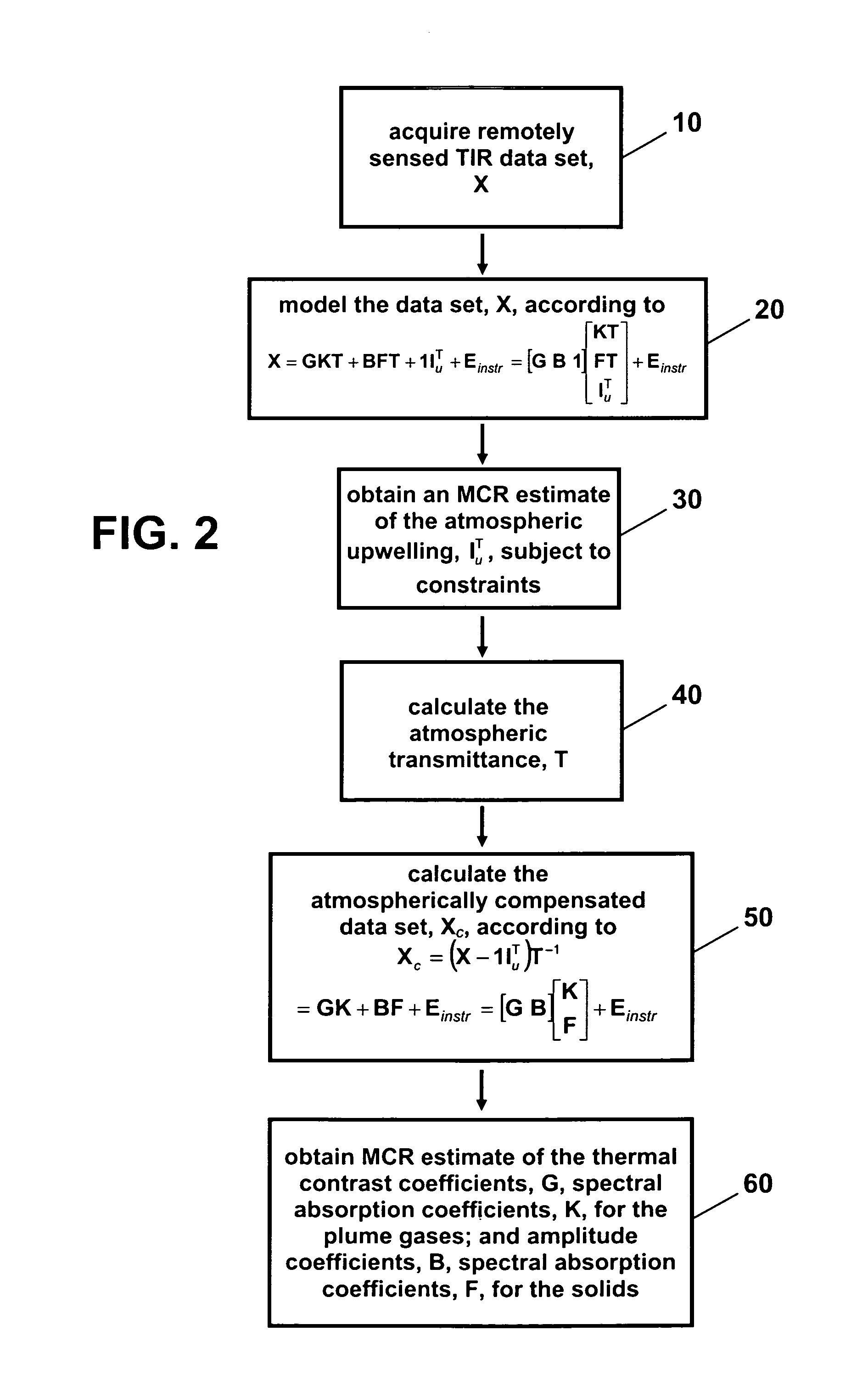
A fast and rigorous multivariate curve resolution (MCR) algorithm is applied to remotely sensed spectral data. The algorithm is applicable in the solar-reflective spectral region, comprising the visible to the shortwave infrared (ranging from approximately 0.4 to 2.5 μm), midwave infrared, and thermal emission spectral region, comprising the thermal infrared (ranging from approximately 8 to 15 μm). For example, employing minimal a priori knowledge, notably non-negativity constraints on the extracted endmember profiles and a constant abundance constraint for the atmospheric upwelling component, MCR can be used to successfully compensate thermal infrared hyperspectral images for atmospheric upwelling and, thereby, transmittance effects. Further, MCR can accurately estimate the relative spectral absorption coefficients and thermal contrast distribution of a gas plume component near the minimum detectable quantity.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Method for selecting representative endmember components from spectral data
InactiveUS20030012398A1Increase profitIncreased complexityImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceUser Friendly
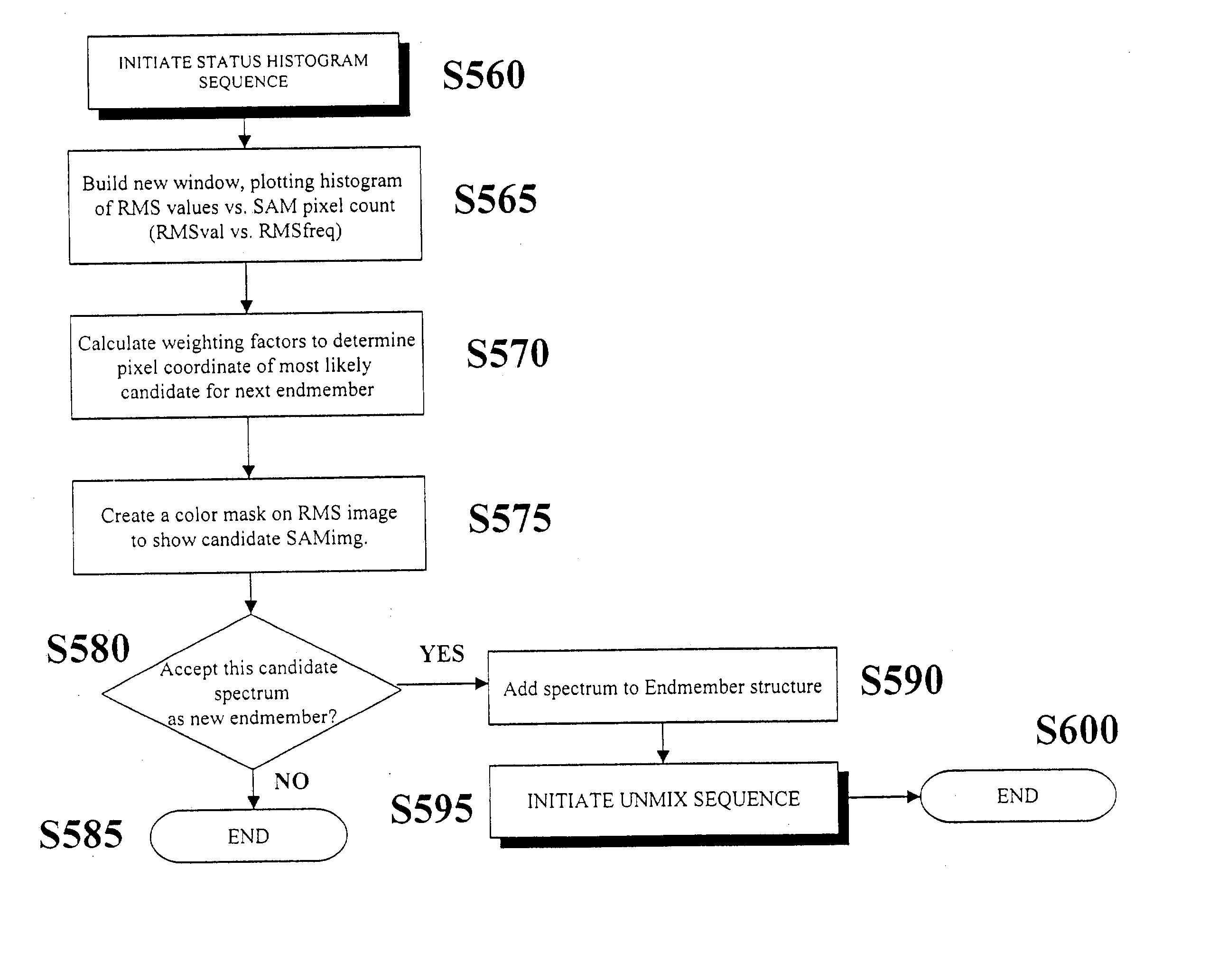
Described herein is a process for objectively and automatically determining spectral endmembers and transforming Spectral Mixture Analysis (SMA) from a widely used research technique into a user-friendly tool that can support the needs of all types of remote sensing. The process extracts endmembers from a spectral dataset using a knowledge-based approach. The process identifies a series of starting spectra that are consistent with a scene and its environment. The process then finds endmembers iteratively, selecting each new endmember based on a combination of physically and statistically-based tests. The tests combine spectral and spatial criteria and decision trees to ensure that the resulting endmembers are physically representative of the scene.
Owner:LEIDOS
Decomposing hyperspectral or multispectral image data
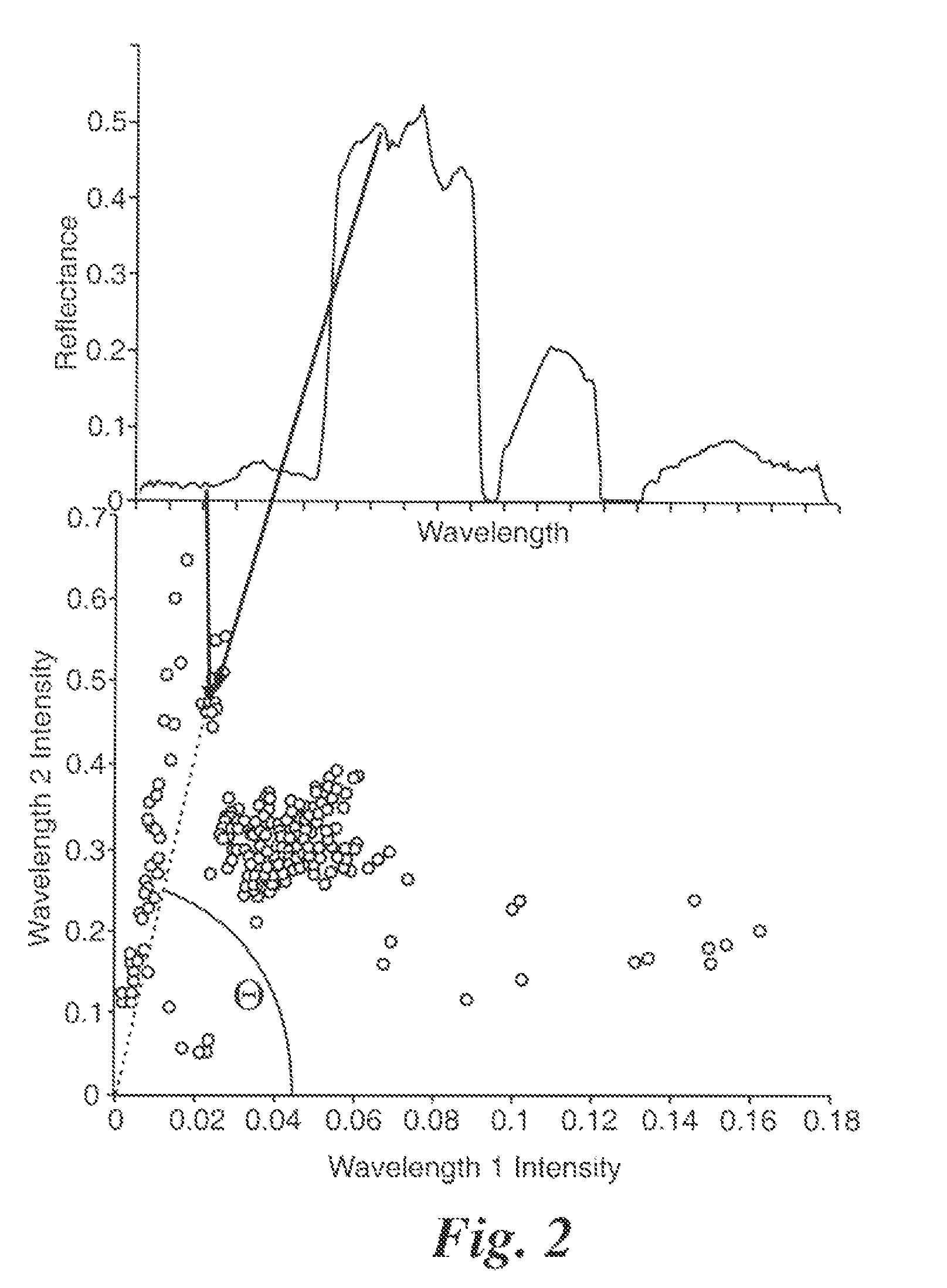
ActiveUS20130039580A1Easy to useMaximize independenceScene recognitionFrequency spectrumReflectance spectroscopy
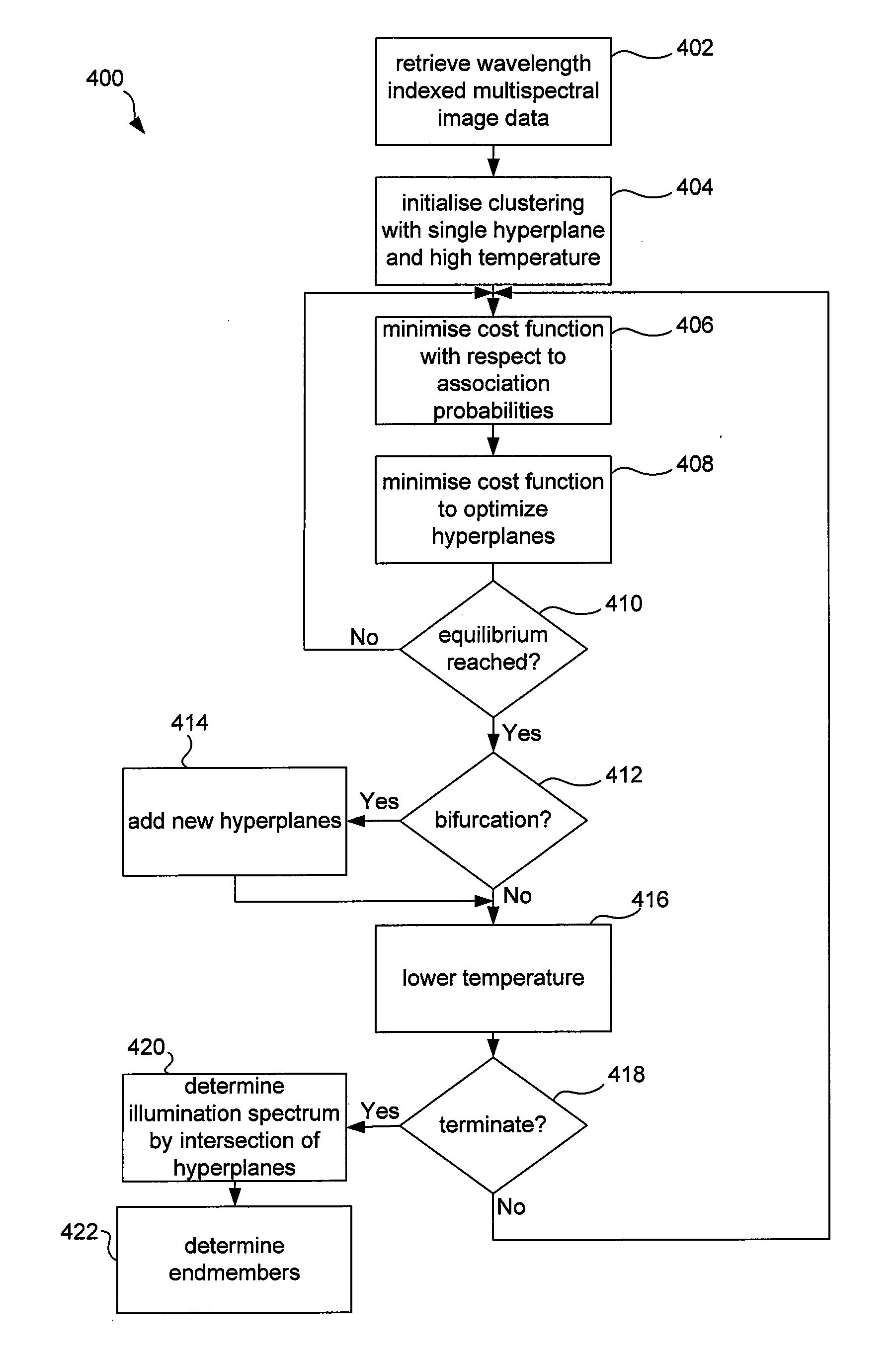
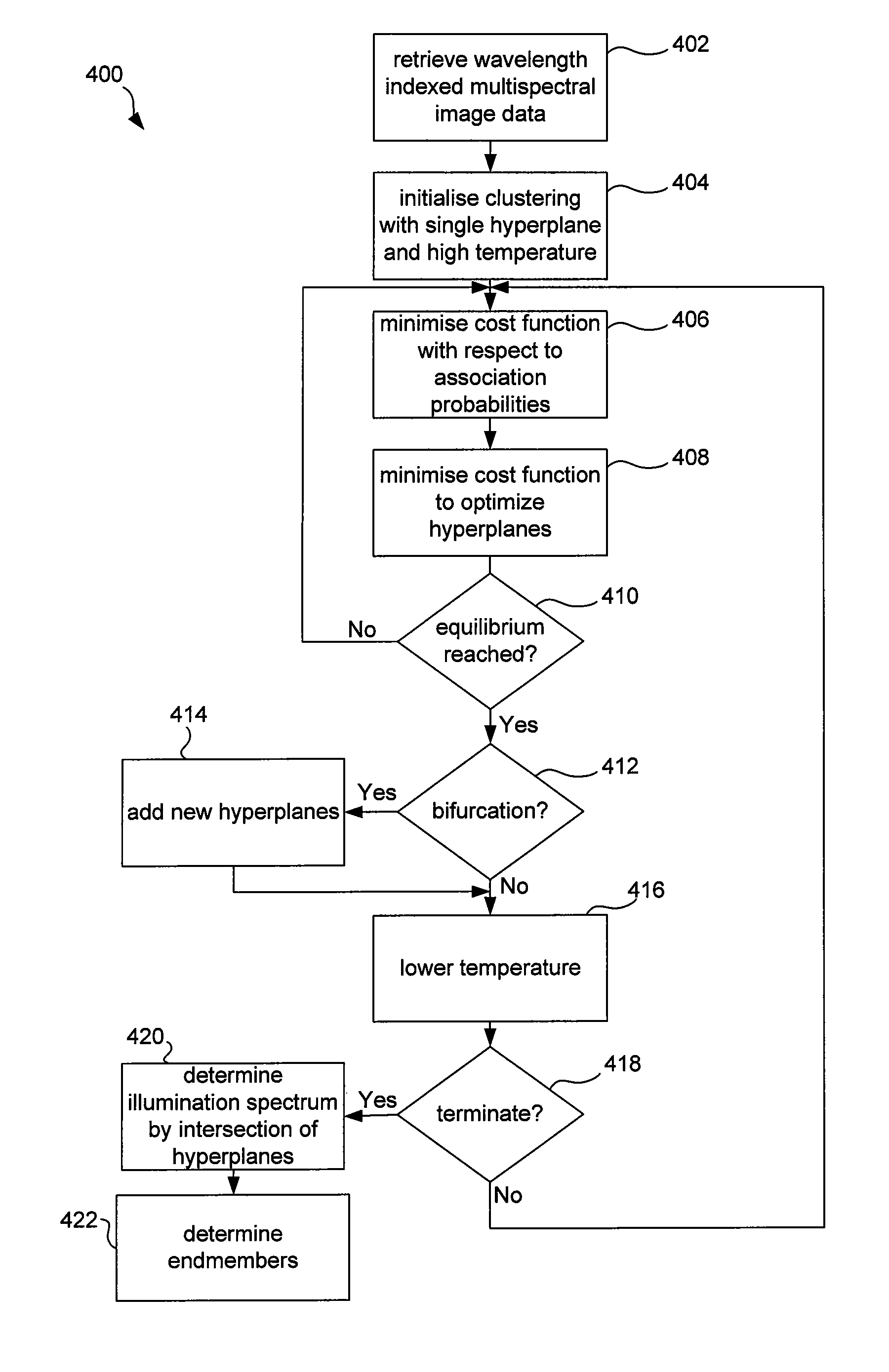
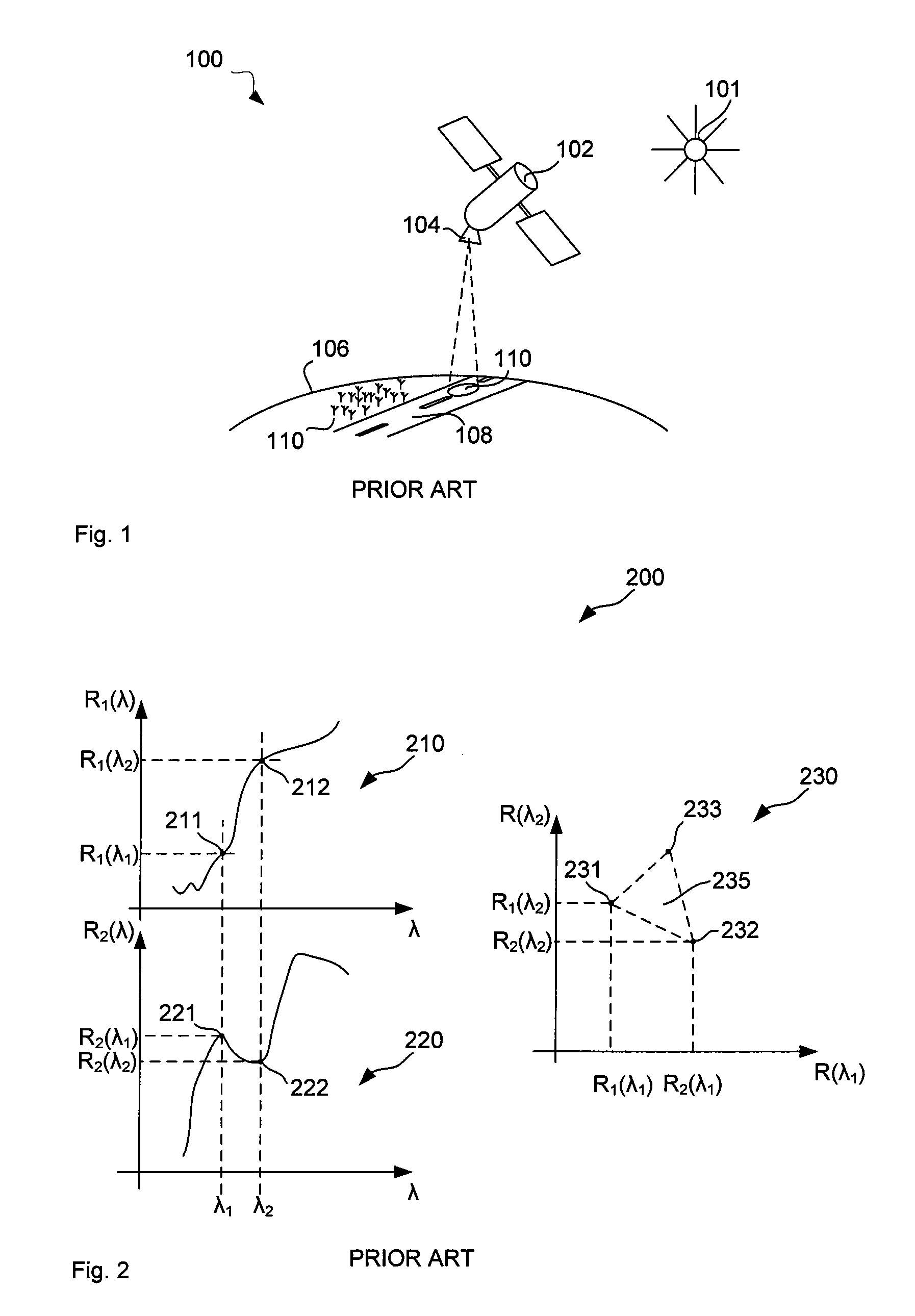
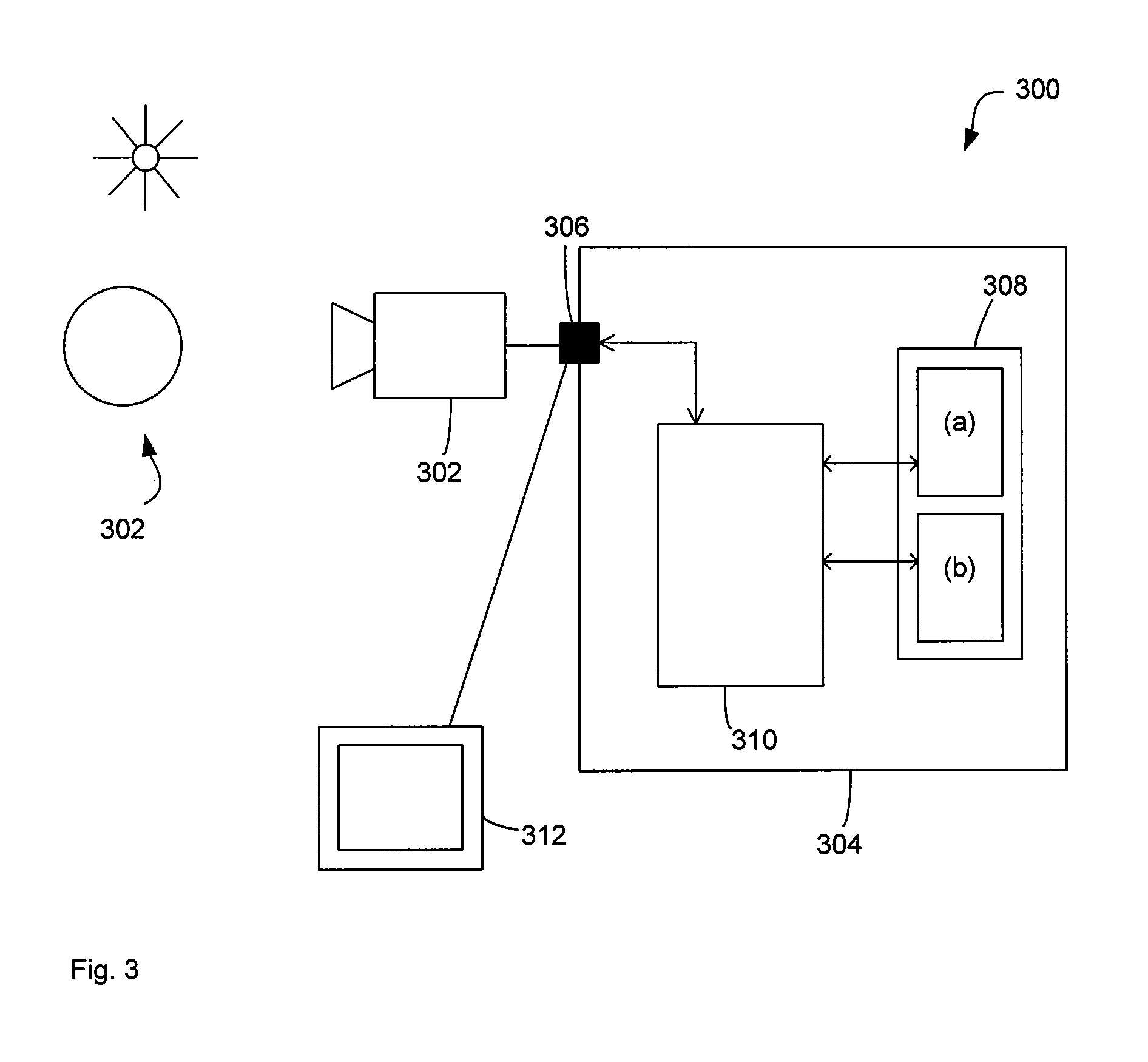
The disclosure concerns processing of electronic images, such as hyperspectral or multispectral images. In particular, but is not limited to methods, software and computer systems for determining underlying spectra of an image of a scene. The image data comprises for each pixel location a sampled image spectrum that is a mixture of plural reflectance spectra. Processor 310 determines or accesses plural hyperplanes that each have plural linearly independent basis vectors. Each hyperplane represents an estimate of one of the plural reflectance spectra. The processor 310 then determines for each pixel location, a contribution of the plural basis vectors of each hyperplane to the image spectrum of that pixel location. The processor 310 determines or accesses plural hyperplanes and not plural endmembers directly. Hyperplanes are two-dimensional while endmembers are only one-dimensional. As a result, hyperplanes carry more information, such as the illumination spectrum and are therefore of greater use. The decomposition of the image data into hyperplanes is possible without knowing the illumination spectrum. This decomposition allows for a range of new applications such as endmember extraction and compact representation.
Owner:NAT ICT AUSTRALIA
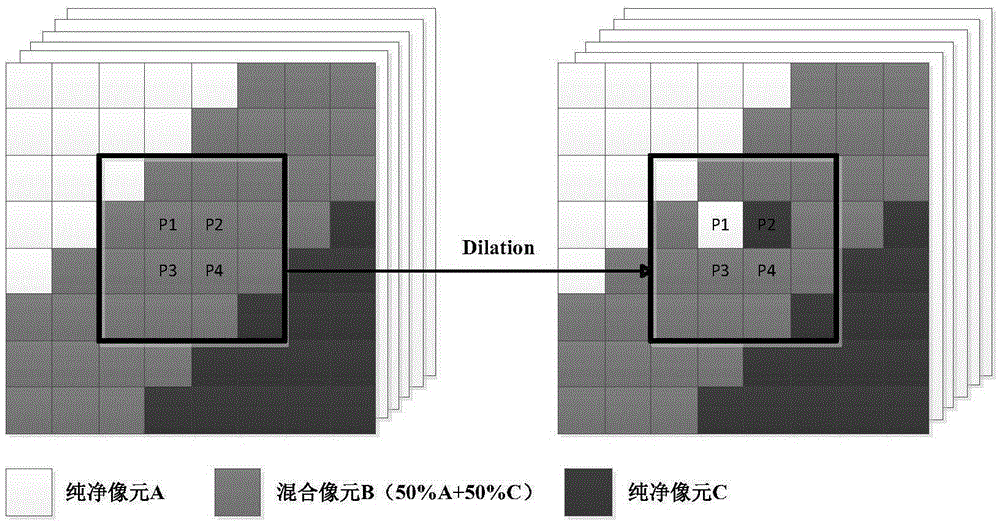
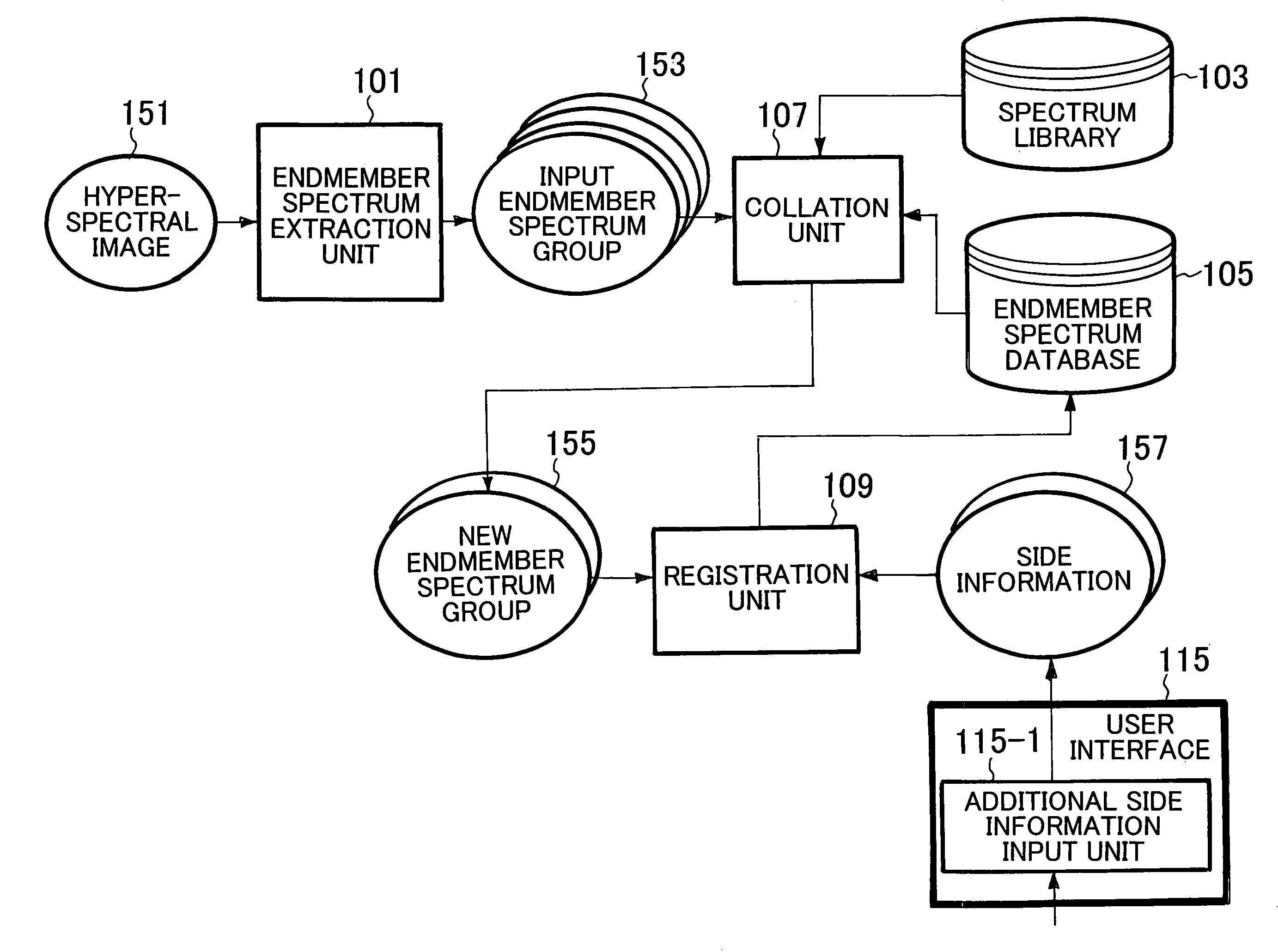
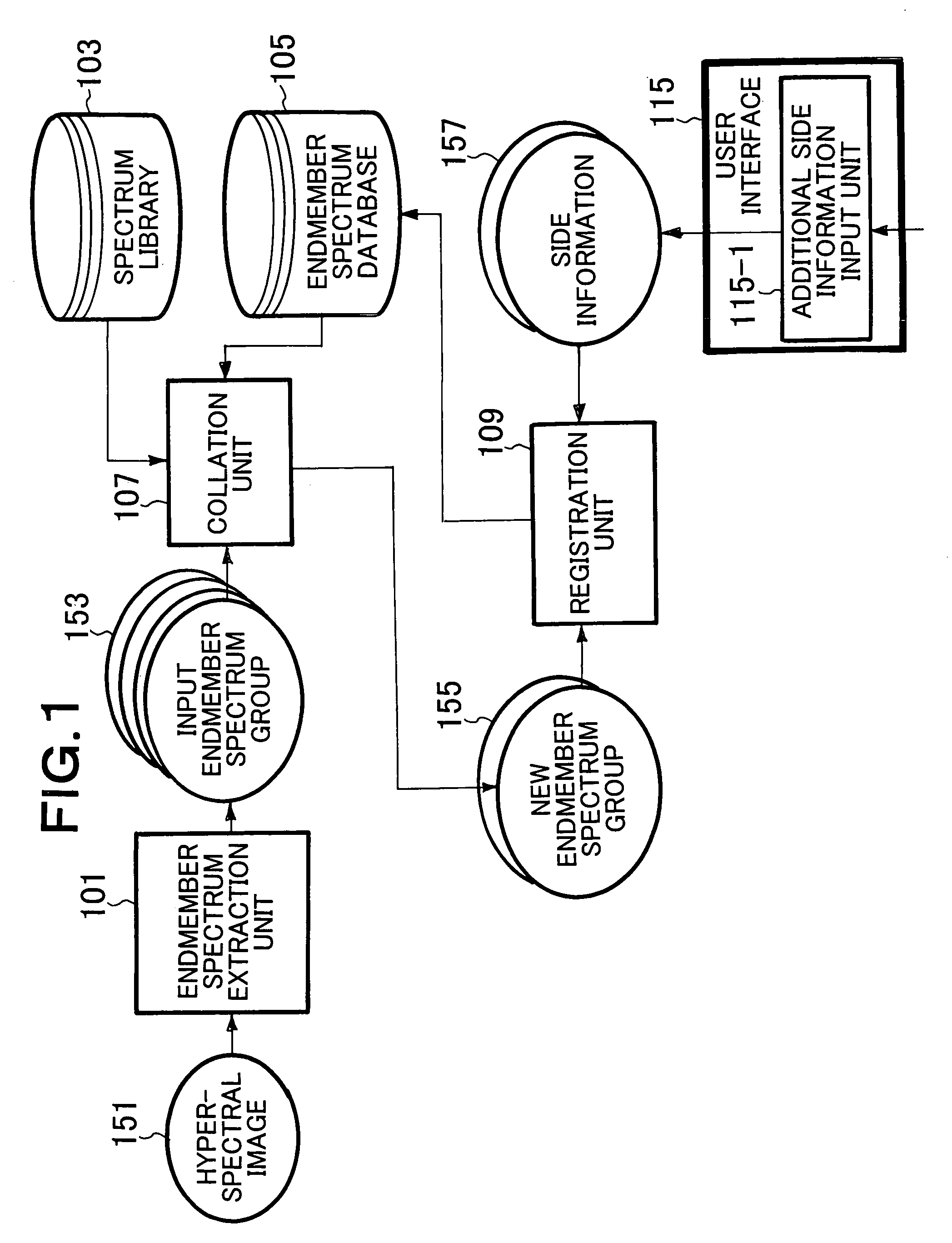
Endmember spectrum database construction method, endmember spectrum database construction apparatus and endmember spectrum database construction program
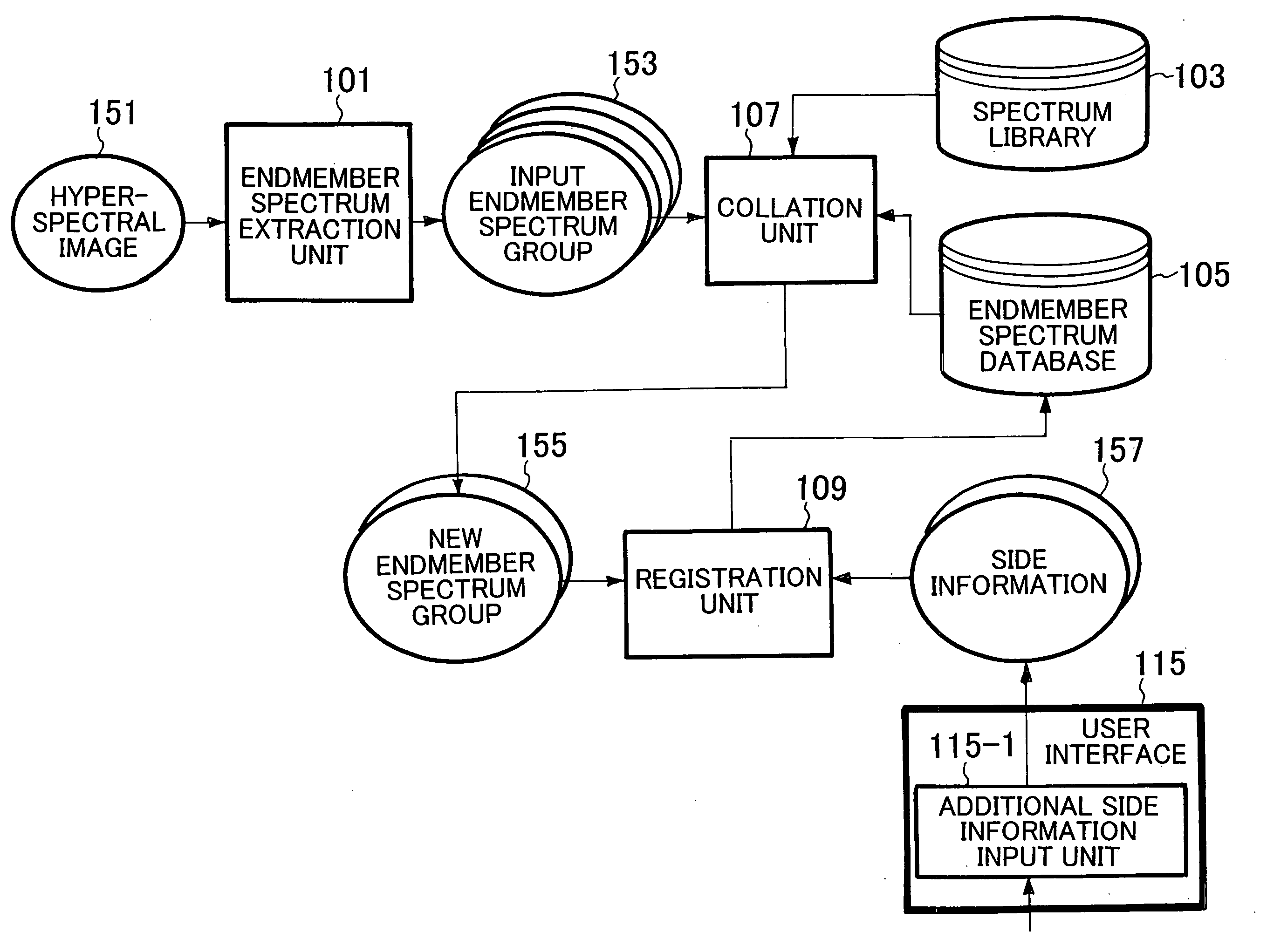
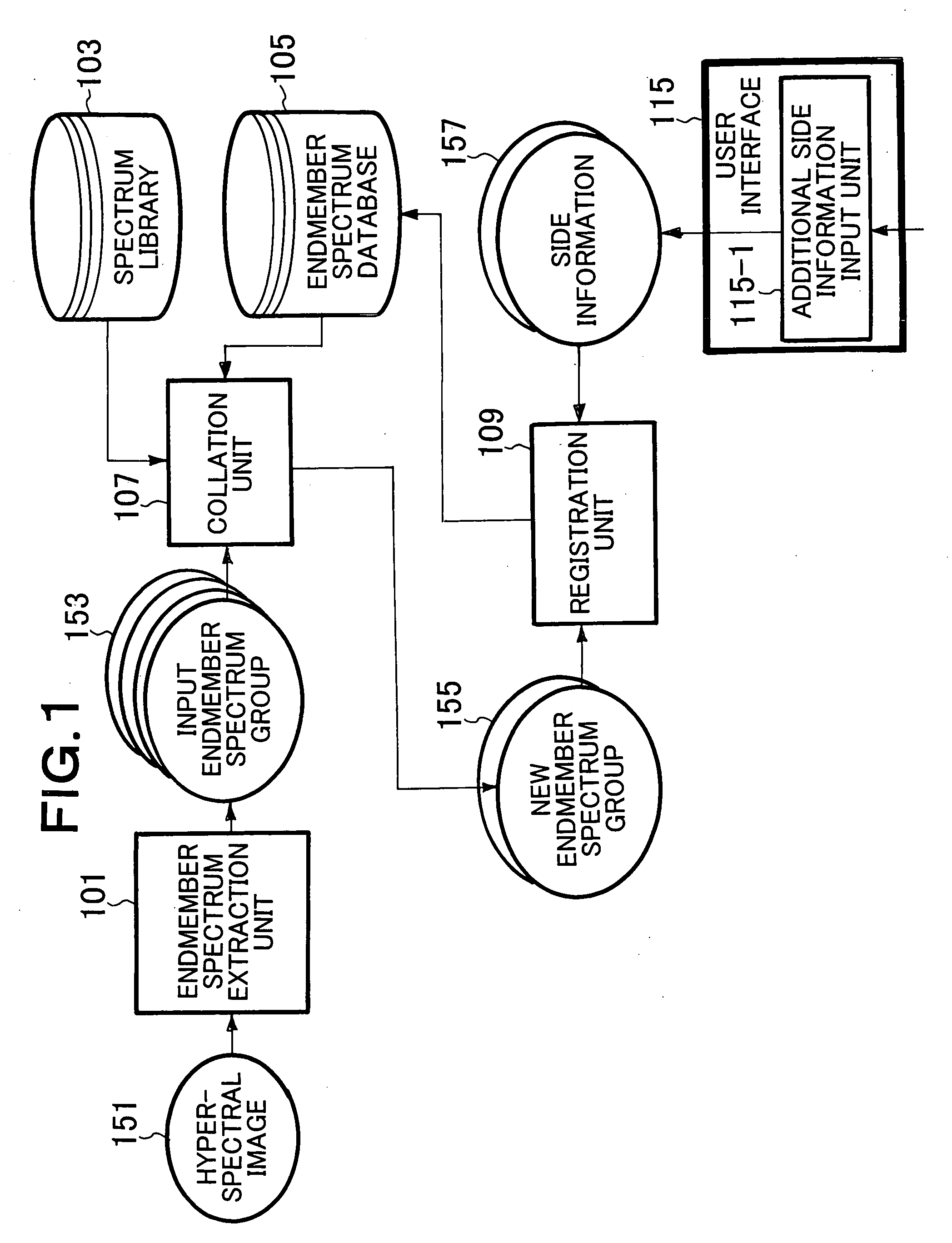
According to one embodiment, an endmember spectrum extraction unit generates an input endmember spectrum group from a hyperspectral image. A collation unit outputs an endmember spectrum group including endmember spectra that are registered with neither a spectrum library nor an endmember spectrum database as a new endmember spectrum group. An input endmember spectrum distribution image generation unit generates an input endmember distribution image every input endmember spectrum. A new endmember spectrum distribution image selection unit selects an input endmember spectrum distribution image that is included in input endmember spectrum distribution images and that corresponds to new endmember spectrum as a new endmember distribution image. The user recognizes what kind of object corresponds to each new endmember spectrum on the basis of the new endmember spectrum distribution image, the hyperspectral image and a high resolution image, and determines and orders whether to register each new endmember spectrum with the endmember spectrum database.
Owner:NEC CORP
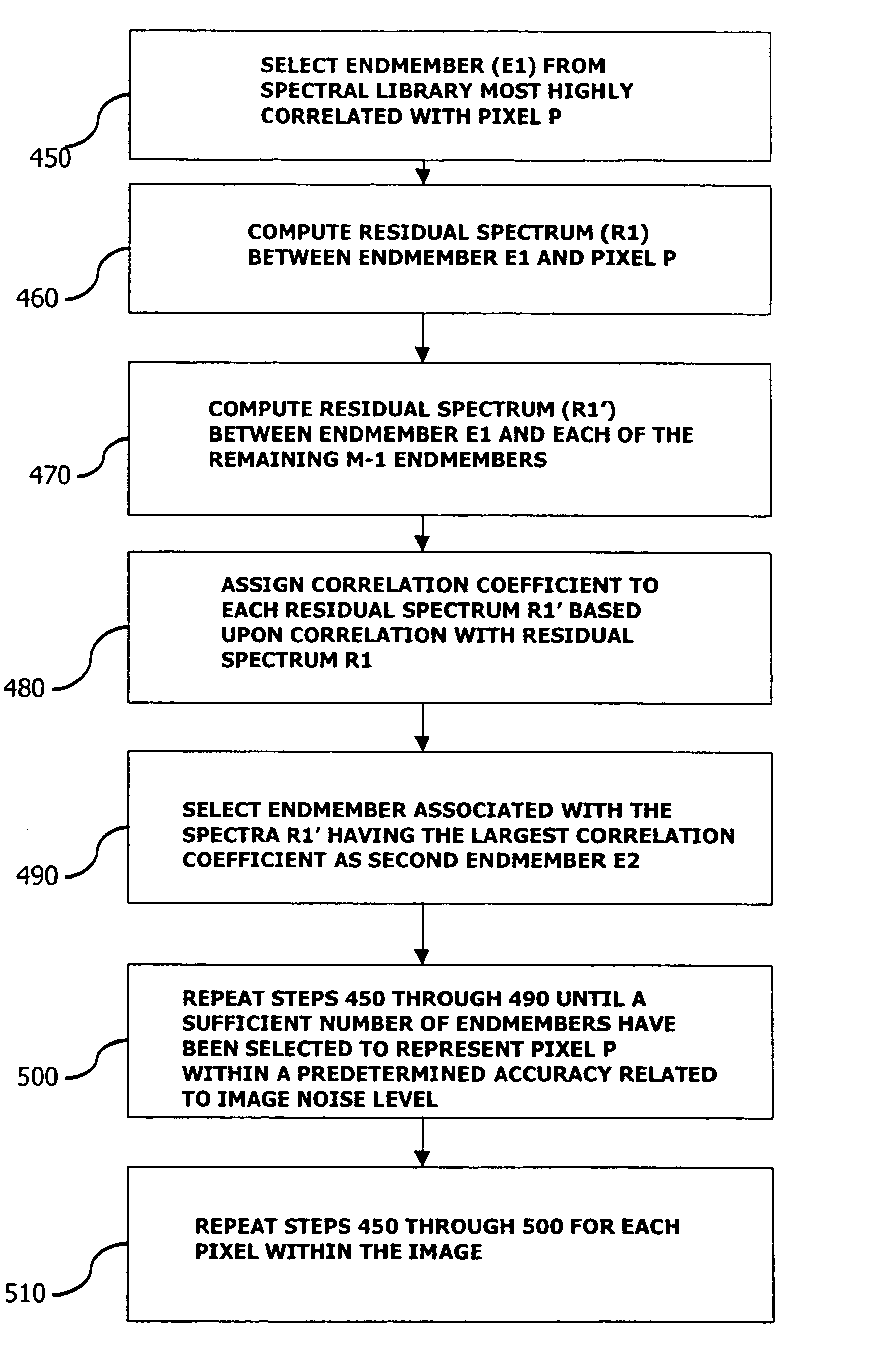
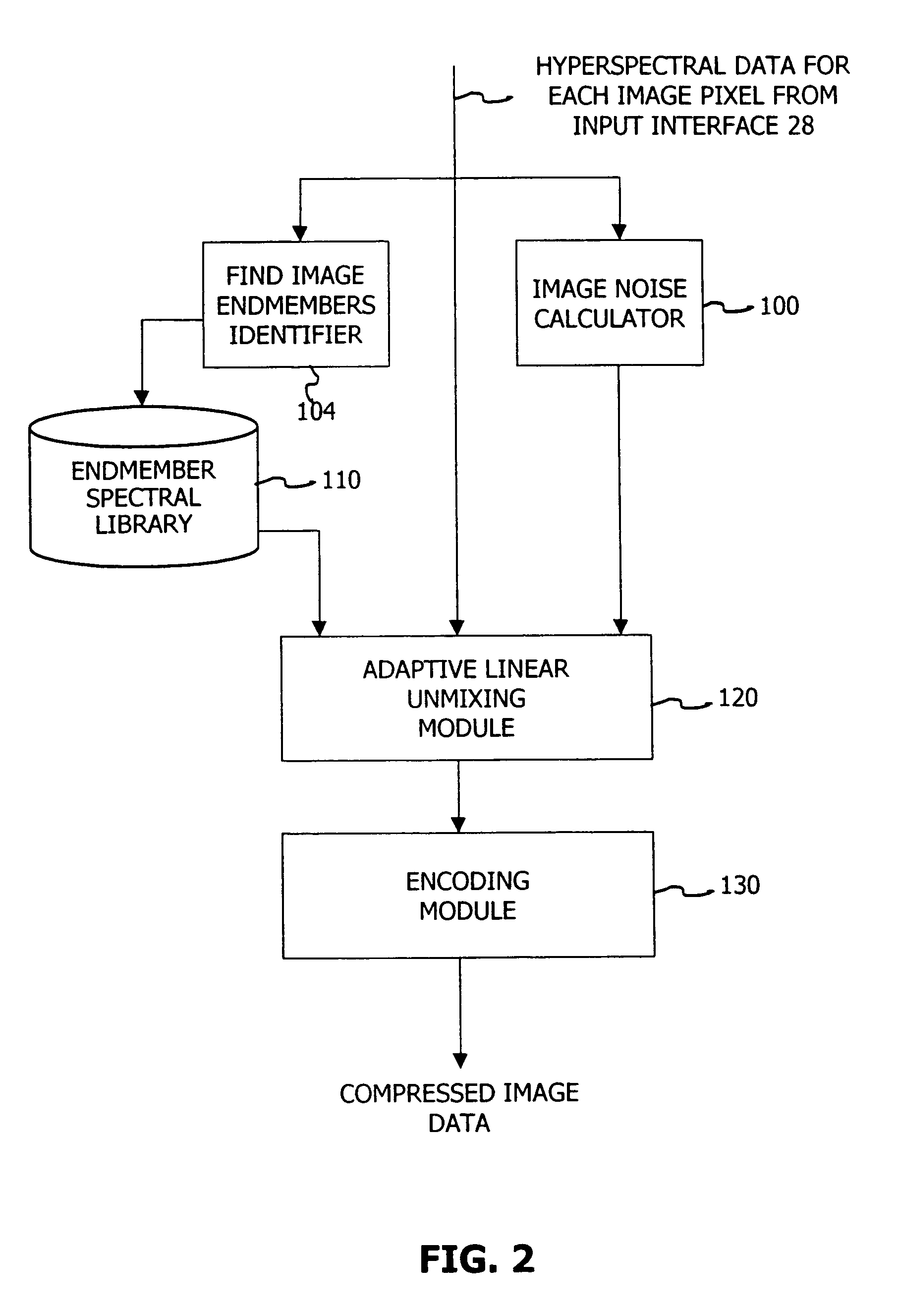
Adaptive hyperspectral data compression
A method is disclosed herein for compressing spectral data corresponding to an image comprising a plurality of pixels. The method includes the step of creating a set of potential endmembers. A first plurality of the potential endmembers are identified as a first set of endmembers based upon their respective correlations with a first spectral signature of a first of the plurality of pixels. The first pixel is then represented as a combination of the first set of endmembers. Processing of the image preferably continues by identifying a second plurality of the potential endmembers as a second set of endmembers based upon their respective correlations with a second spectral signature of a second of the plurality of pixels. The second pixel is then represented as a combination of the second set of endmembers.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Method for selecting representative endmember components from spectral data
InactiveUS6608931B2Increase profitIncreased complexityImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceUser Friendly
Described herein is a process for objectively and automatically determining spectral endmembers and transforming Spectral Mixture Analysis (SMA) from a widely used research technique into a user-friendly tool that can support the needs of all types of remote sensing. The process extracts endmembers from a spectral dataset using a knowledge-based approach. The process identifies a series of starting spectra that are consistent with a scene and its environment. The process then finds endmembers iteratively, selecting each new endmember based on a combination of physically and statistically-based tests. The tests combine spectral and spatial criteria and decision trees to ensure that the resulting endmembers are physically representative of the scene.
Owner:LEIDOS
Process for finding endmembers in a data set
ActiveUS7680337B2Extended transfer timeRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansPattern recognitionData set
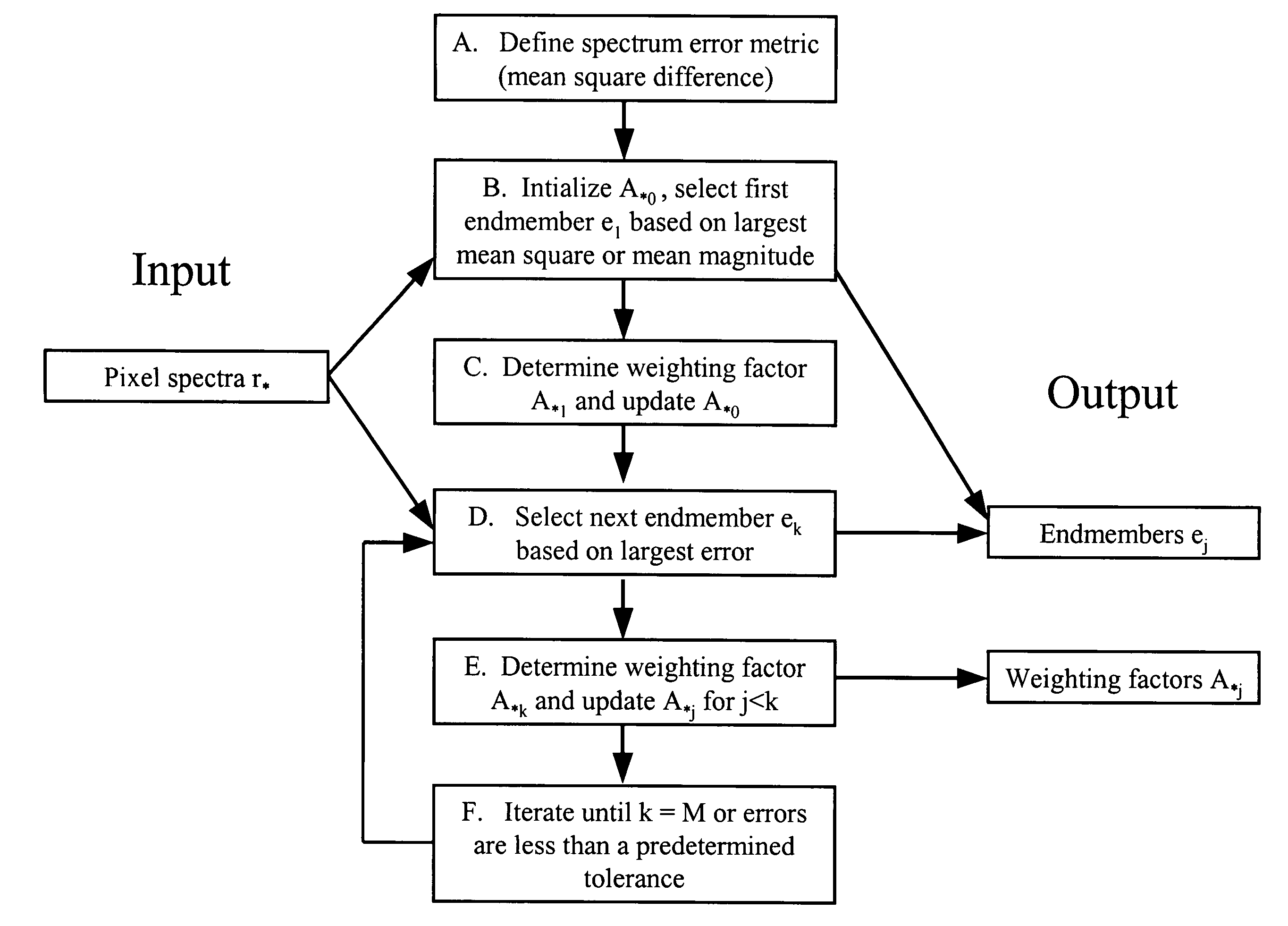
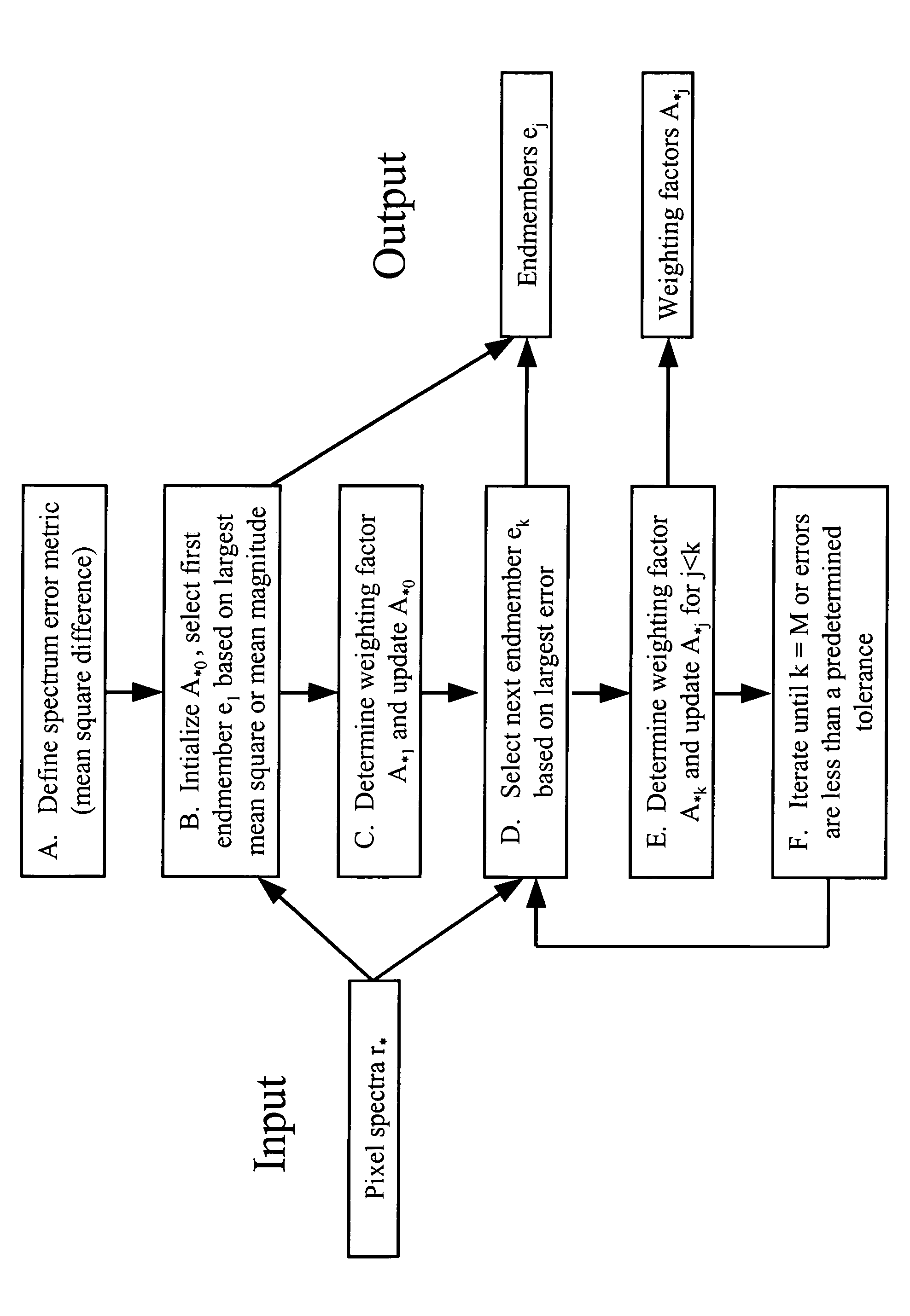
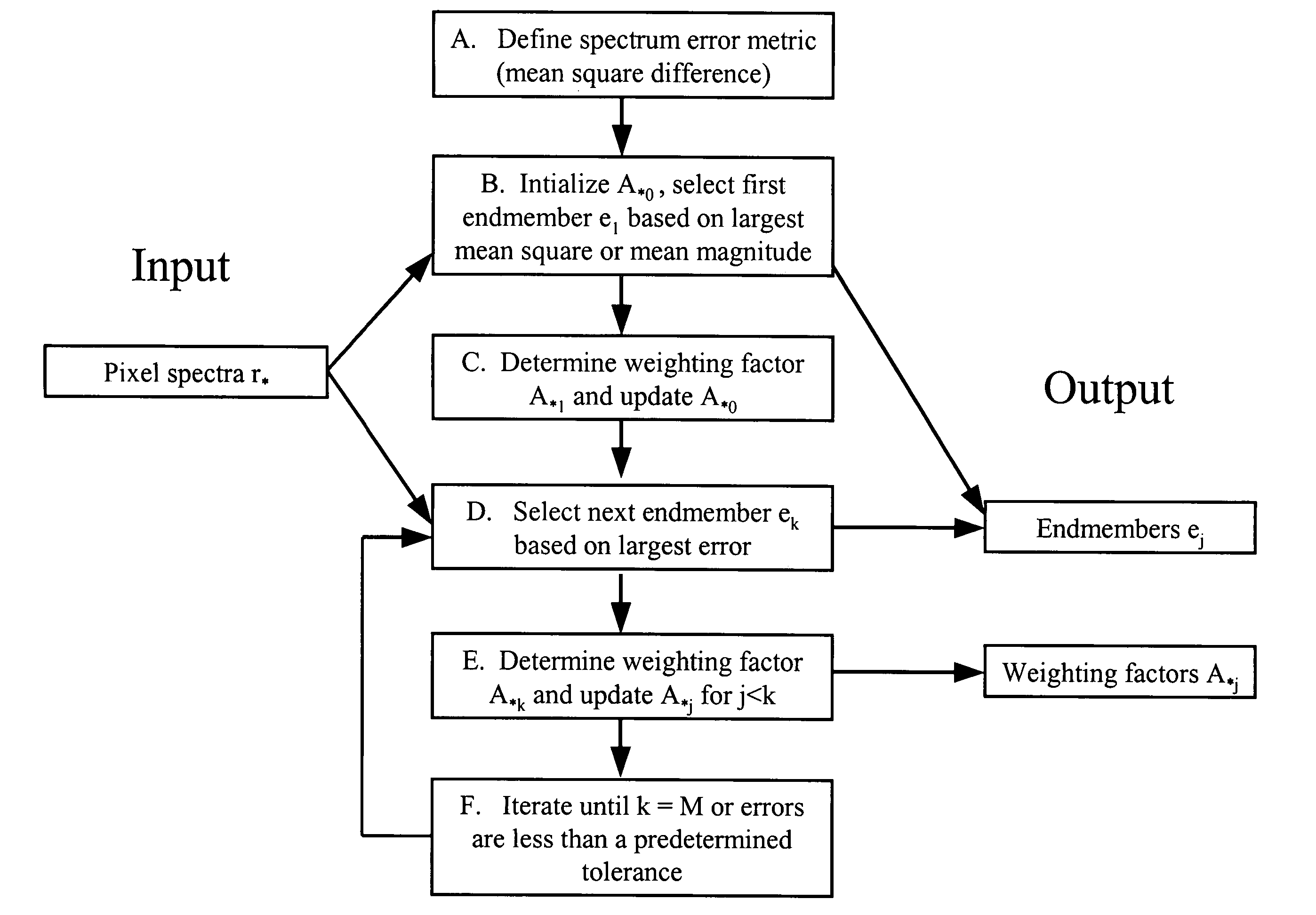
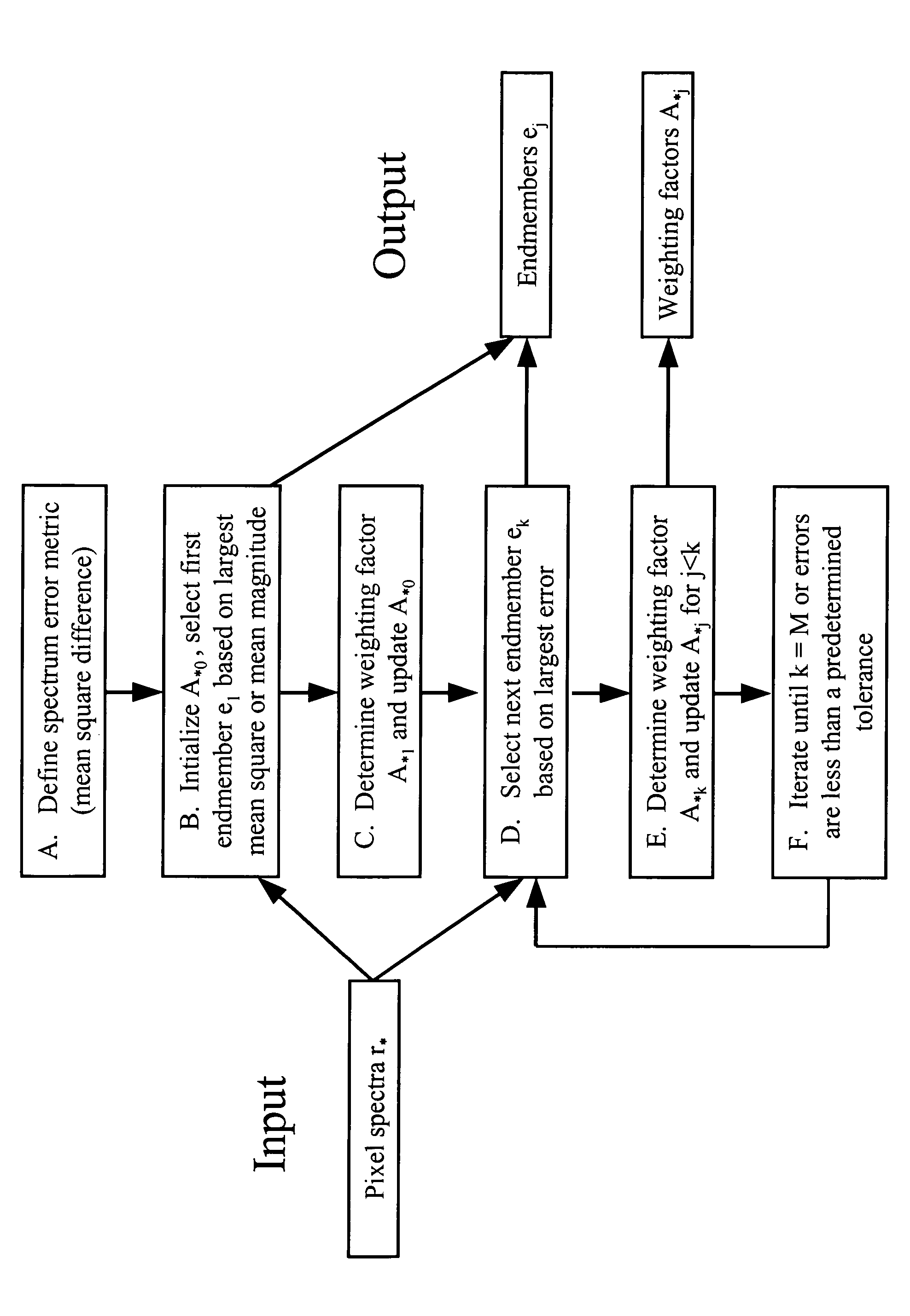
The invention provides a method for identifying one or more materials in a scene by determining a set of spectral vectors, called endmembers, from a data set comprised of spectra from the image data, and matching the set of endmembers to predefined library materials. The image data of the scene is captured with a sensor, and comprises a plurality of spectra. The method applies an iterative mathematical criterion, termed residual minimization, to find the endmembers. The first endmember may be selected based on the largest mean square value or the largest mean magnitude value. Subsequent endmembers are determined by calculating weighting factors, such that the weighting factors are non-negative and the calculated vector differences, or residuals, generate the smallest error metric. The error metric is dependent upon the vector difference between two spectra in the image data set, and may be the mean squared vector difference between two spectra.
Owner:SPECTRAL SCI
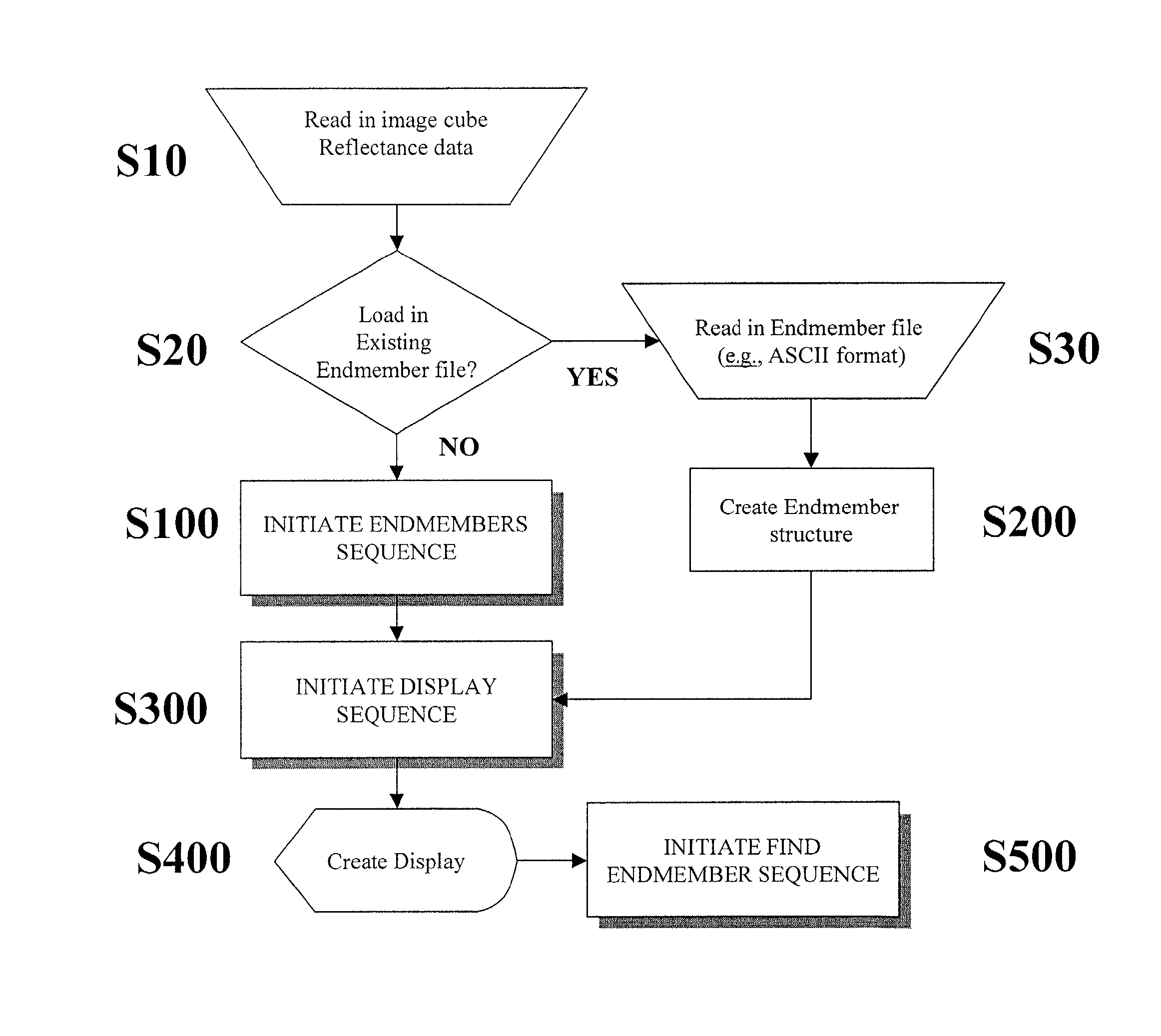
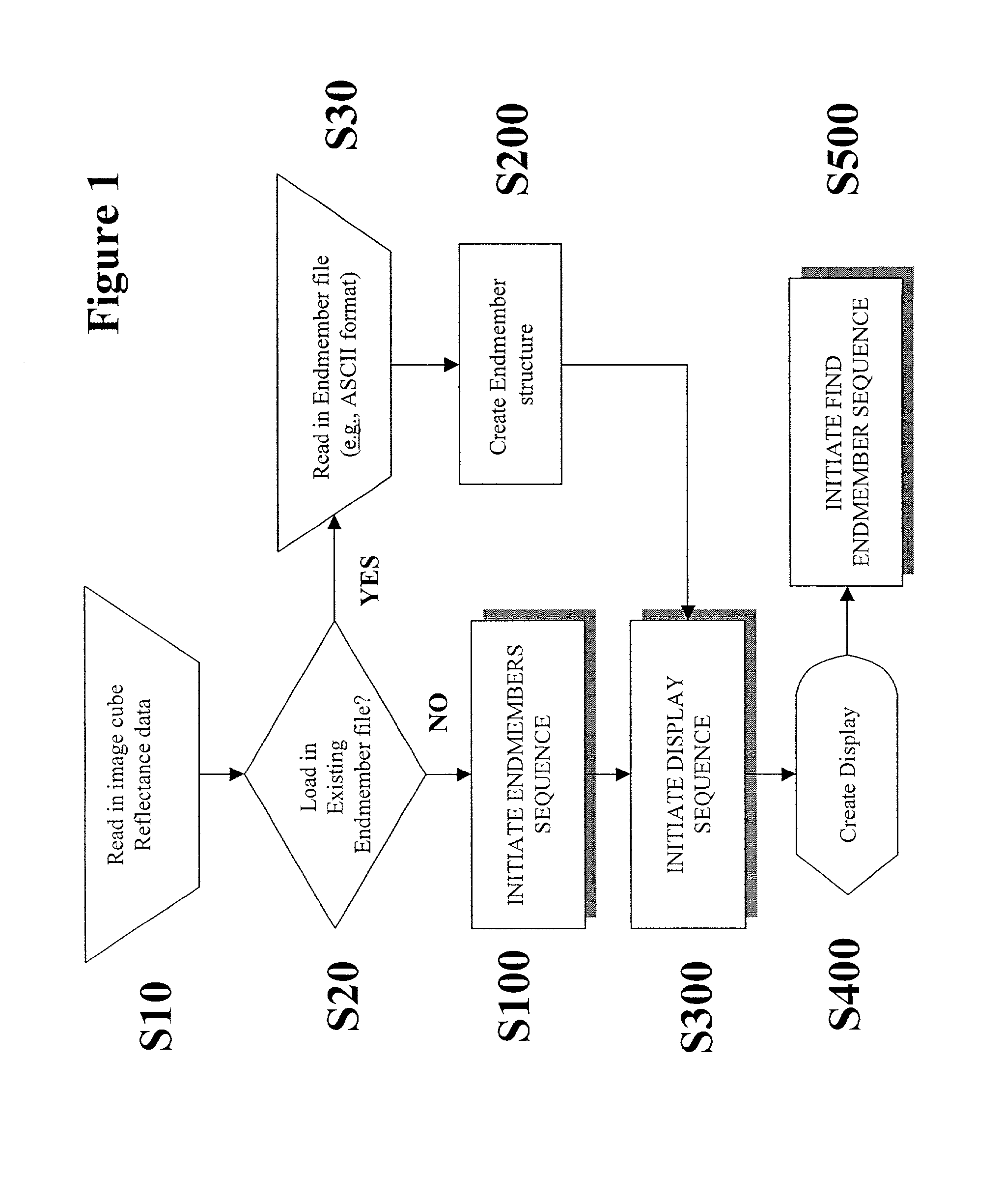
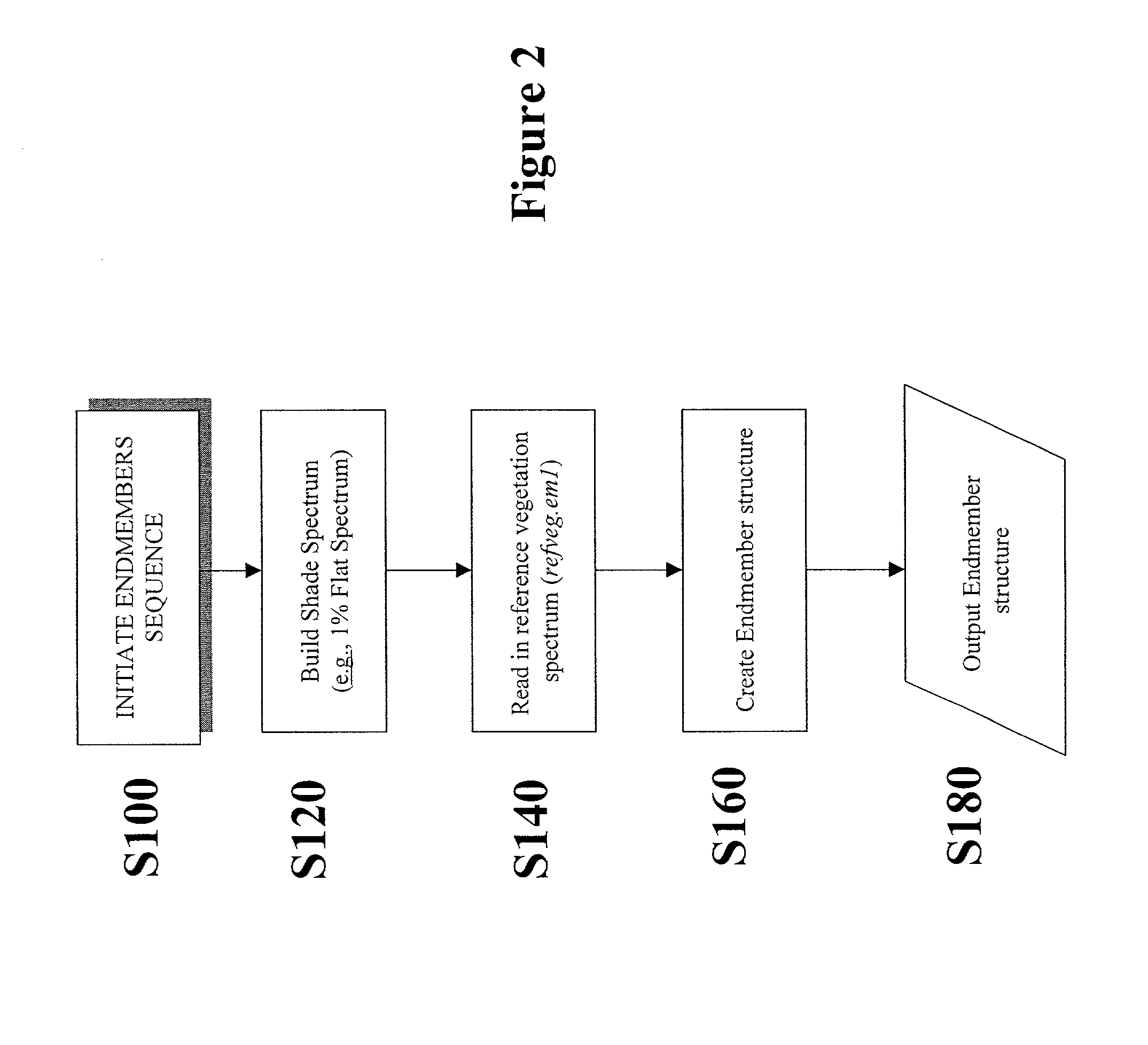
Method of identifying endmember spectral values from hyperspectral image data
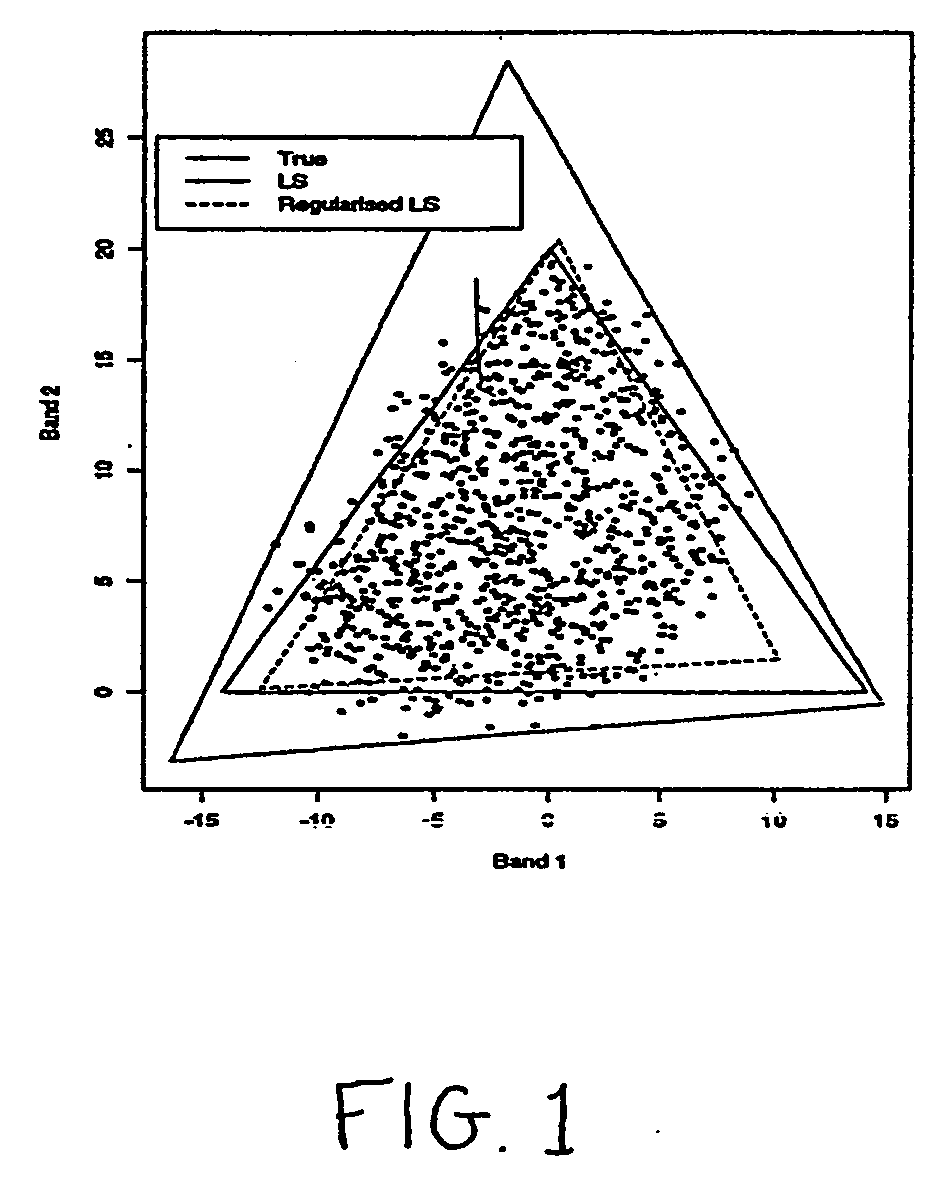
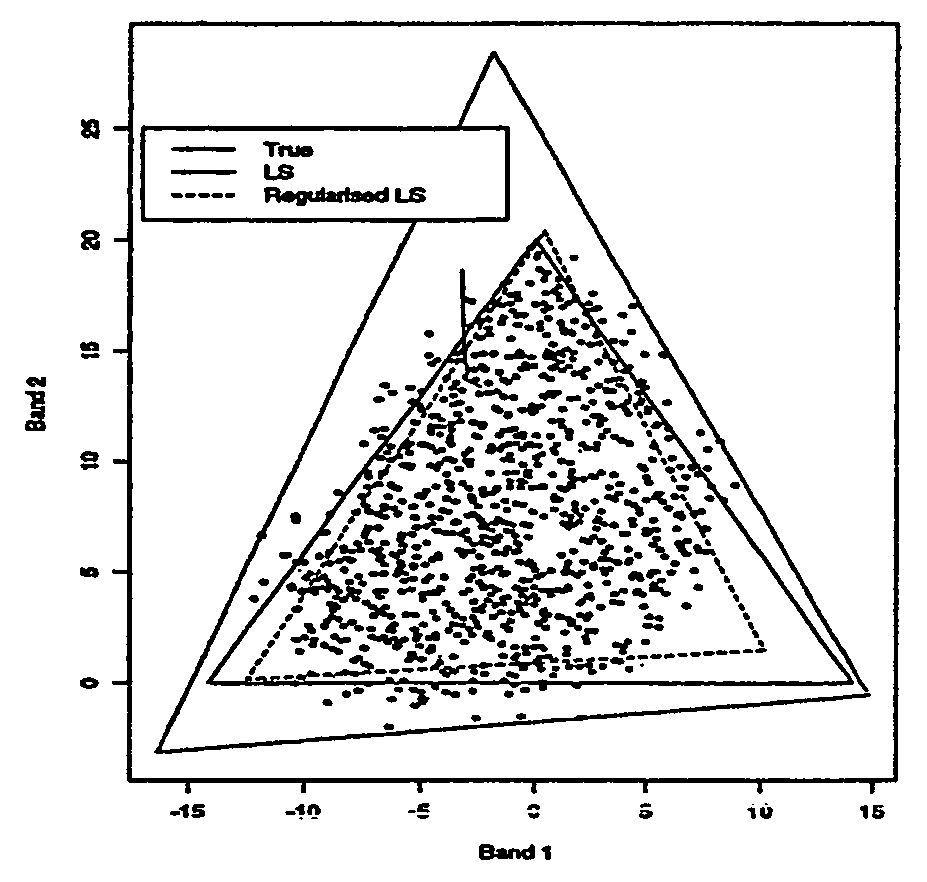
A method of identifying endmember spectral values from multispectral image data, where each multispectral data value is equal to a sum of mixing proportions of each endmember spectrum. The method comprises the steps of processing the data to obtain a multidimensional simplex having a number of vertices equal to the number of endmembers. The position of each vertex represents a spectrum of one of the endmembers. Processing the data is conducted by providing starting estimates of each endmember spectrum for each image data value. The mixing proportions for each data value is estimated from estimates of the spectra of all the endmembers. The spectrum of each endmember is estimated from estimates of the mixing proportions of the spectra of all the endmembers for each image data value. The estimation steps are repeated until a relative change in the regularised residual sum of squares is sufficiently small. The regularised residual sum of squares includes a term which is a measure of the size of the simplex.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Process for finding endmembers in a data set
A method of representing spectral data, such as hyperspectral imaging data (HSI) and multispectral imaging data (MSI), as a set of simplex models. The method finds end-images or end-spectra in the data (termed “endmembers”) as extreme points, and simultaneously determines the abundance of the endmembers.
Owner:SPECTRAL SCI
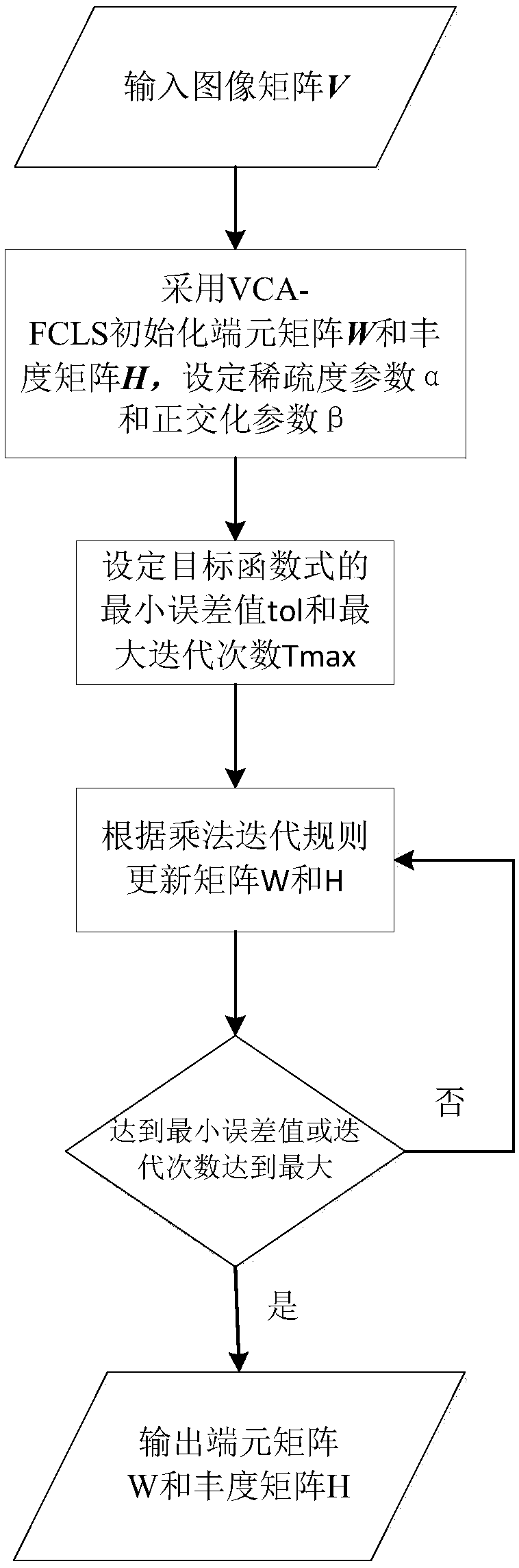
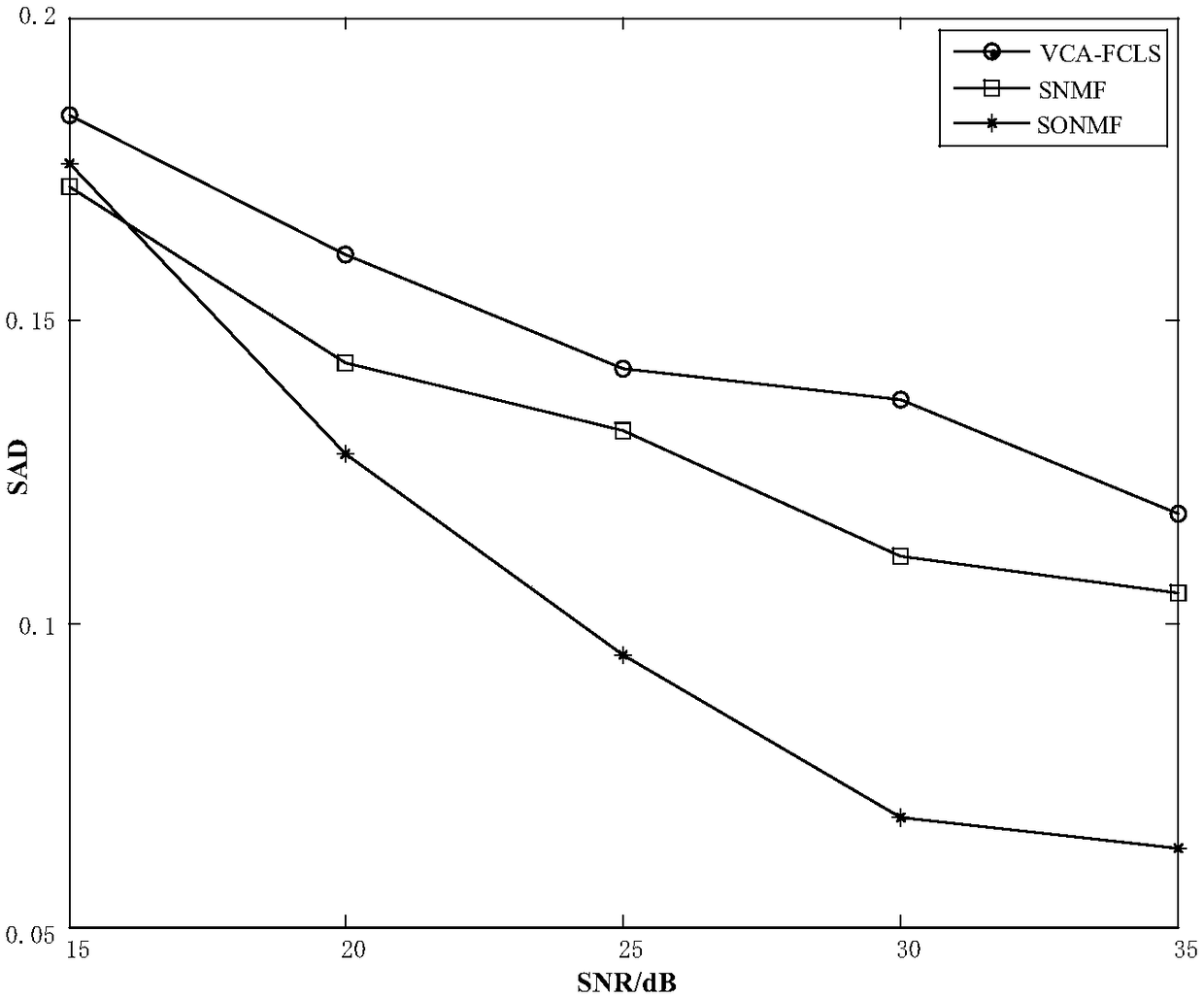
Spectral unmixing scheme based on abundance sparse and endmember orthogonal constraint NMF(Non-negative Matrix Factorization)
InactiveCN109085131AGuaranteed independenceGood unmixing effectColor/spectral properties measurementsAlgorithmDecomposition
A spectral unmixing scheme based on abundance sparse and endmember orthogonal constraint NMF(Non-negative Matrix Factorization) is an algorithm of a spectral image decomposition field. A classical NMFtarget function is a non-convex function, and a constraint condition needs to be added into the target function for solving the problems. The characteristics of spectral images are combined to put forward the spectral image unmixing algorithm which combines endmember orthogonality with abundance sparse constrains NMF on the basis of a linear spectral mixture model. The endmember orthogonal constraint guarantees independence among spectral endmembers, meanwhile, the abundance sparsity fully utilizes the sparsity of spectral data, two constraint conditions are introduced into the target function, a least square method is adopted to obtain the iteration rules of an endmember matrix and an abundance matrix, and a final result is obtained through the setting of an iterative termination condition. Through the experiments of simulation data and truthful data, the effectiveness of the algorithm is verified.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
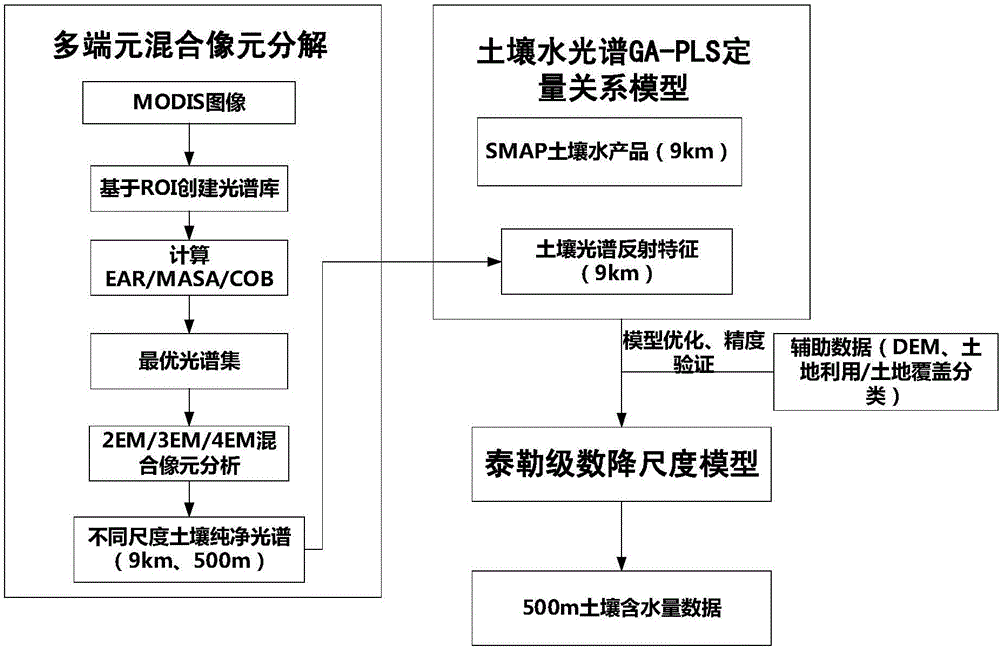
A downscaling method for a soil water content product
ActiveCN106501186AImprove accuracySatisfying large-scale watershed-scale regional researchColor/spectral properties measurementsMoisture content investigation using microwavesRelational modelDynamic monitoring
A downscaling method for a soil water content product is disclosed. The method includes A) acquiring passive microwave soil water content products of a region to be researched and optical remote sensing data at the same time, B) subjecting the optical remote sensing data to soil spectrum extraction based on a multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis process, C) building a model of a quantitative relation between soil spectrum reflection characteristics and soil water contents acquired from the passive microwave soil water content products by utilizing GA-PLS, and D) based on the model of the quantitative relation, building a soil water content downscaling model by utilizing the Taylor series expansion and acquiring soil water content data having a high spatial resolution. Advantages of passive microwave remote sensing data and optical remote sensing data on the temporal-spatial resolution are utilized in the method, and the passive microwave remote sensing data and the optical remote sensing data are effectively combined to acquire the soil water content data having the high spatial resolution, and therefore large-scale watershed scale region researching can be met, real-time or quasi real-time dynamic monitoring on watershed scale soil water contents is achieved, accuracy is high, building is easy and time and labor are saved.
Owner:中科卫星应用德清研究院 +1
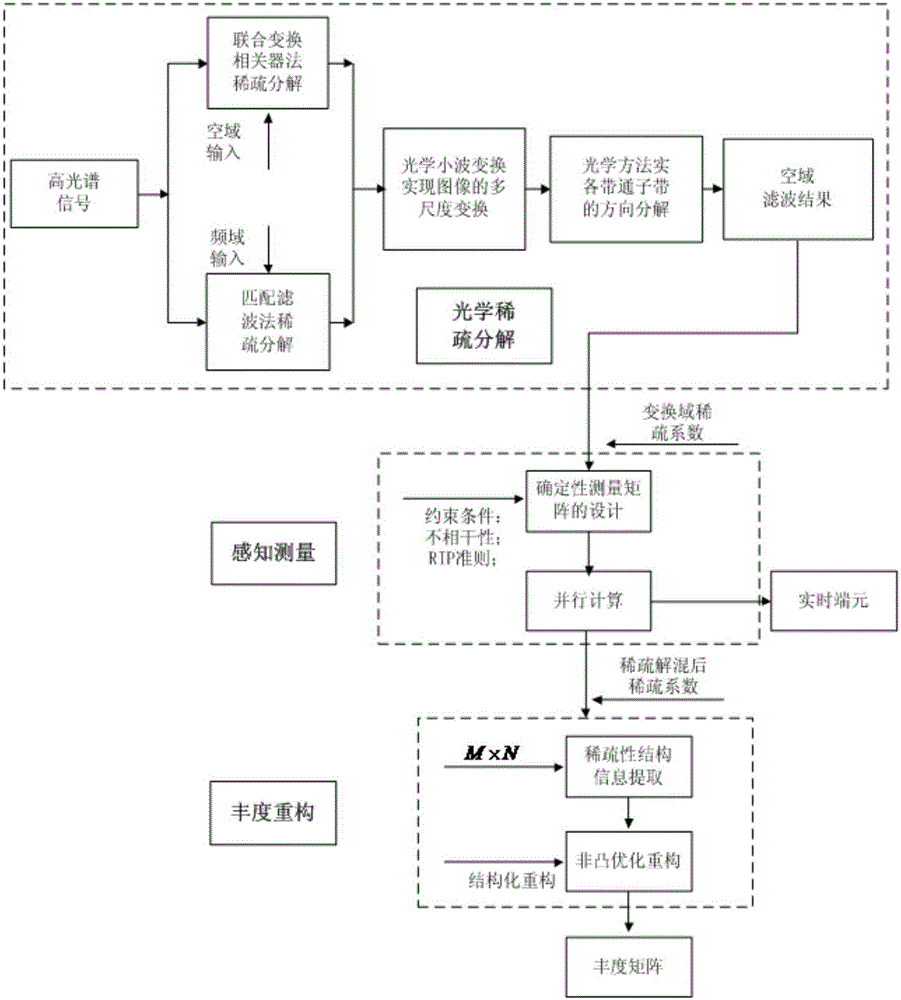
Sparse unmixing method based on optical calculation
InactiveCN106788714AGuaranteed reconstruction accuracyIncrease storage capacityCharacter and pattern recognitionFree-space transmissionAlgorithmDecomposition
The invention relates to a sparse unmixing method based on optical calculation. The method comprises the following steps: S1, an optical filtering method is adopted to acquire a transform domain sparse coefficient matrix for hyperspectral signals; S2, a deterministic measurement matrix is designed to realize perception measurement on the hyperspectral signals; S3, parallel multiplication calculation is carried out on the sparse coefficient matrix and the deterministic measurement matrix through a hardware FPGA for acquiring endmember signals; and S4, the sparse structural information of the hyperspectral signals and a structured reconstruction algorithm are used for reconstructing an abundance matrix. The optical filtering technology and an electrical system are adopted to realize multiscale geometric analysis, the sparse unmixing efficiency is greatly improved on the premise of ensuring the reconstruction precision, and quick and effective sparse decomposition can be realized.
Owner:CHONGQING TECH & BUSINESS UNIV
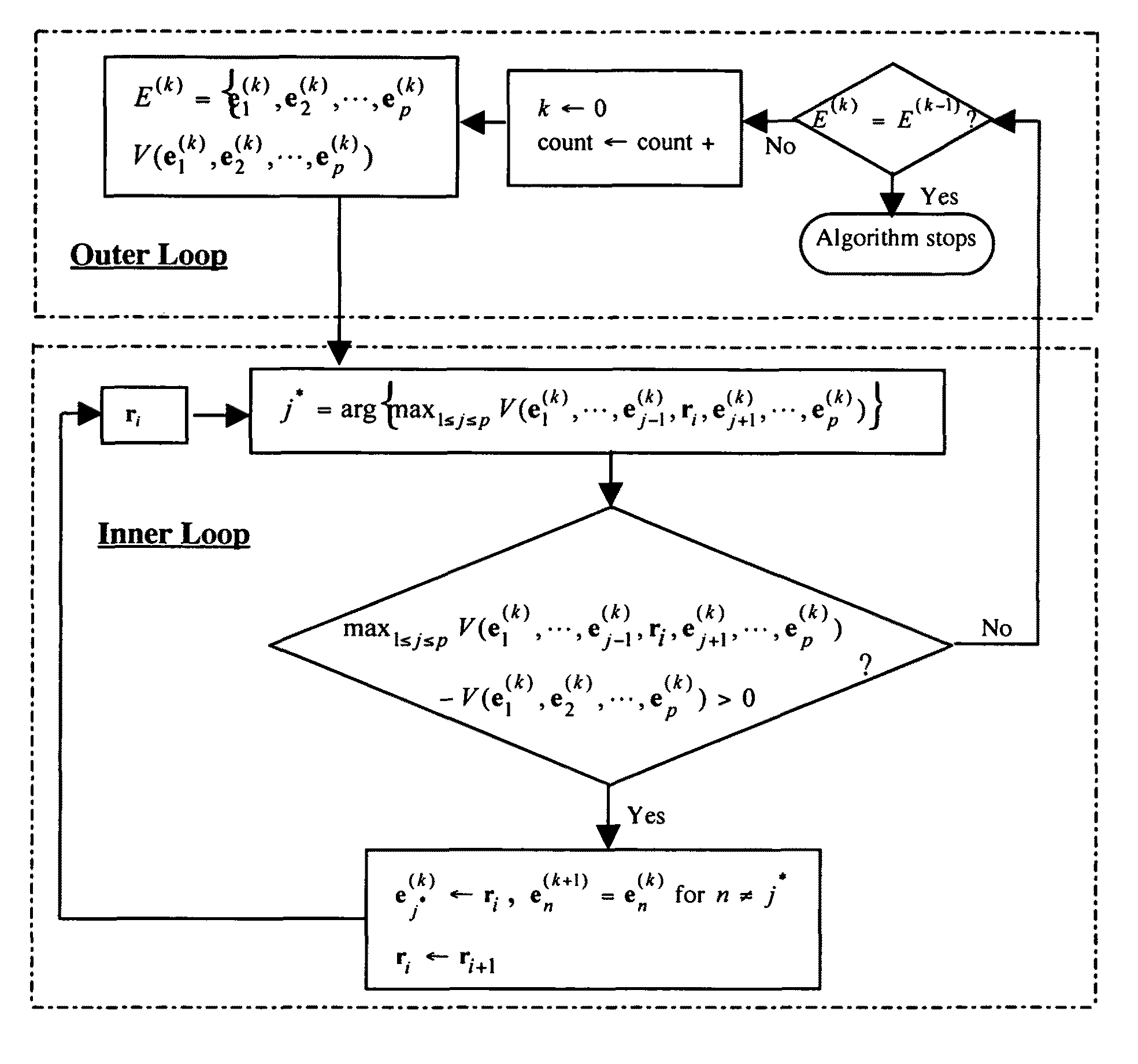
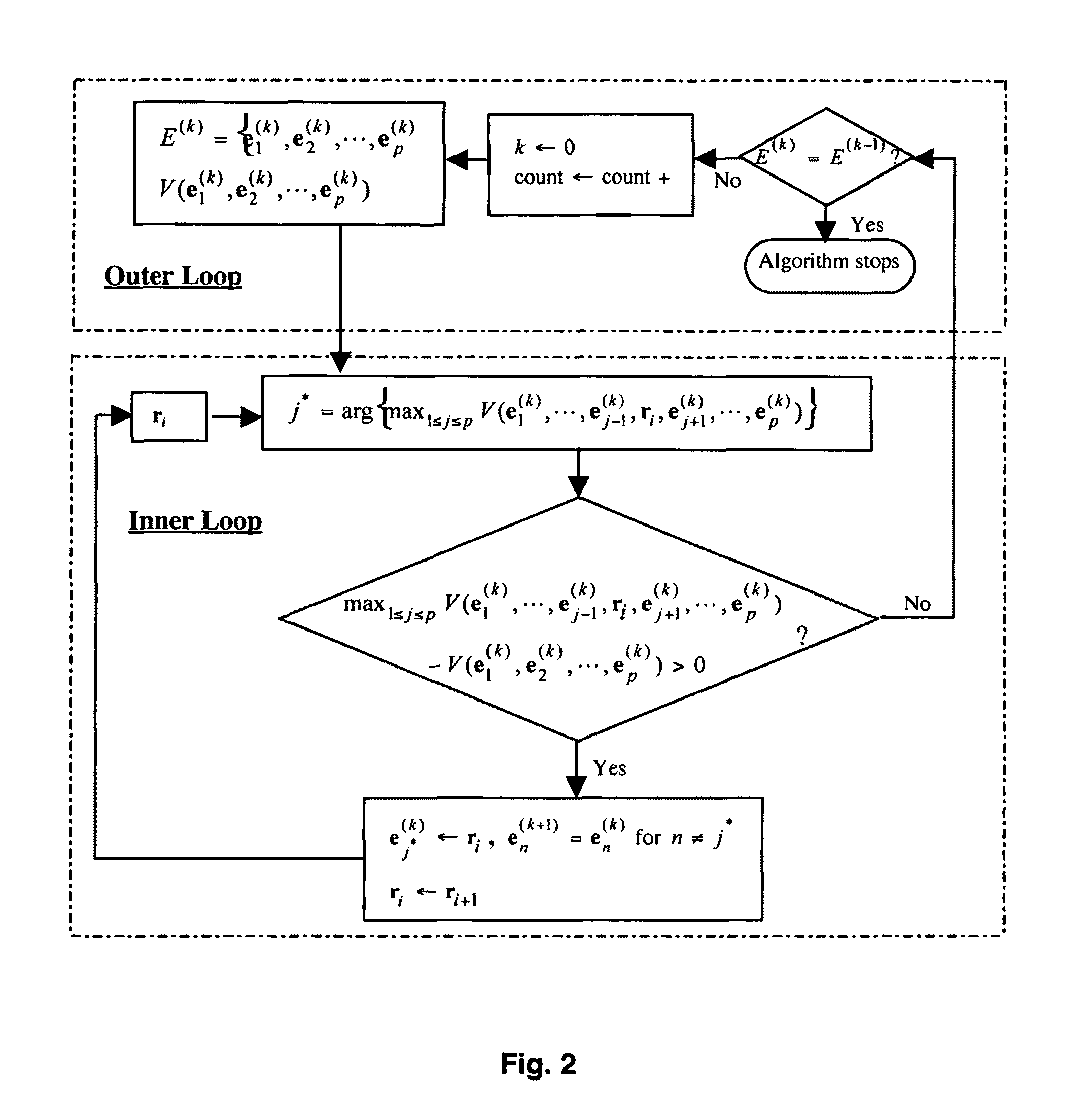
Maximum simplex volume criterion-based endmember extraction algorithms
InactiveUS20090144350A1Reduce dimensionalityReduce dataDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsImaging dataExtraction algorithm
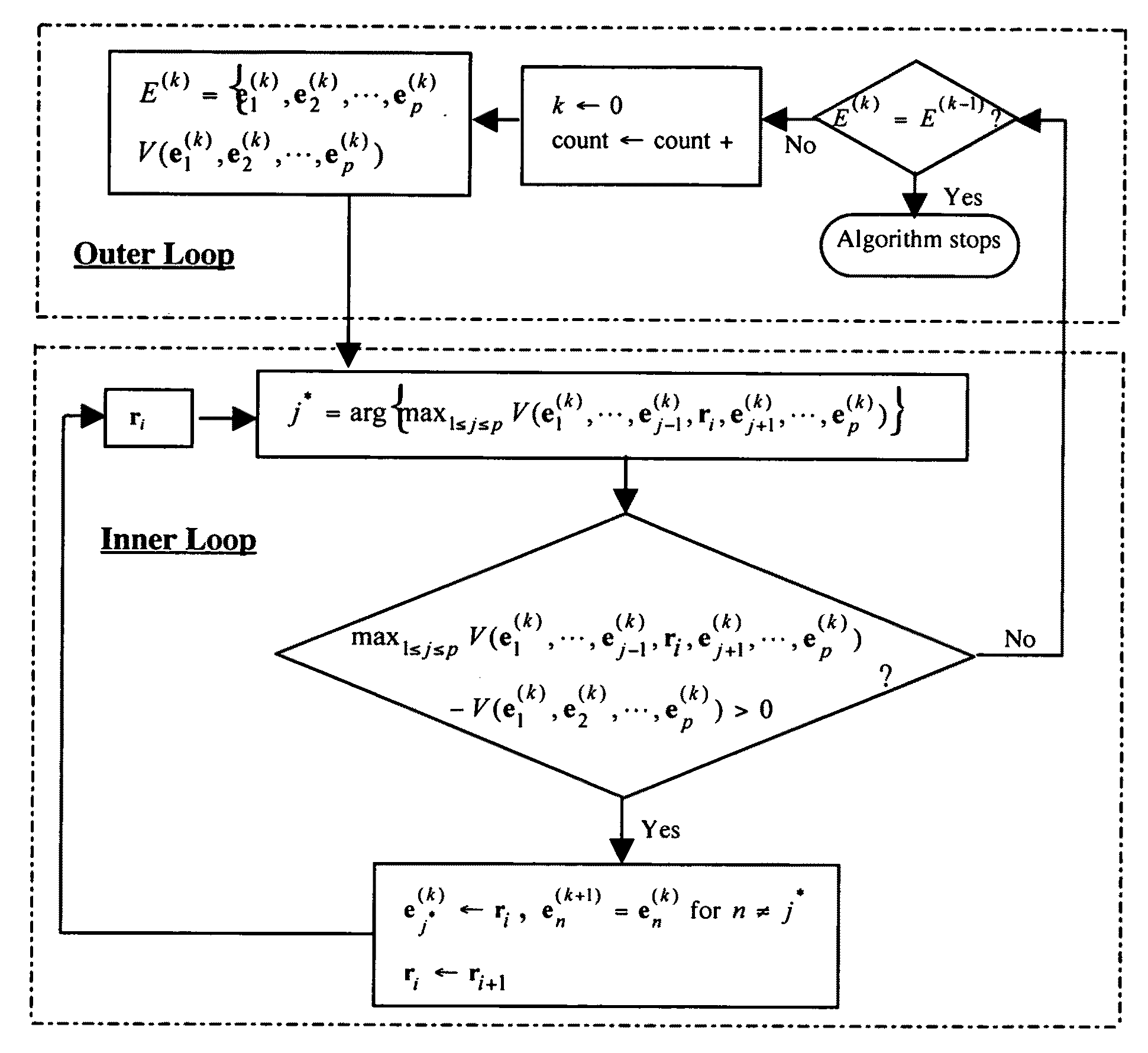
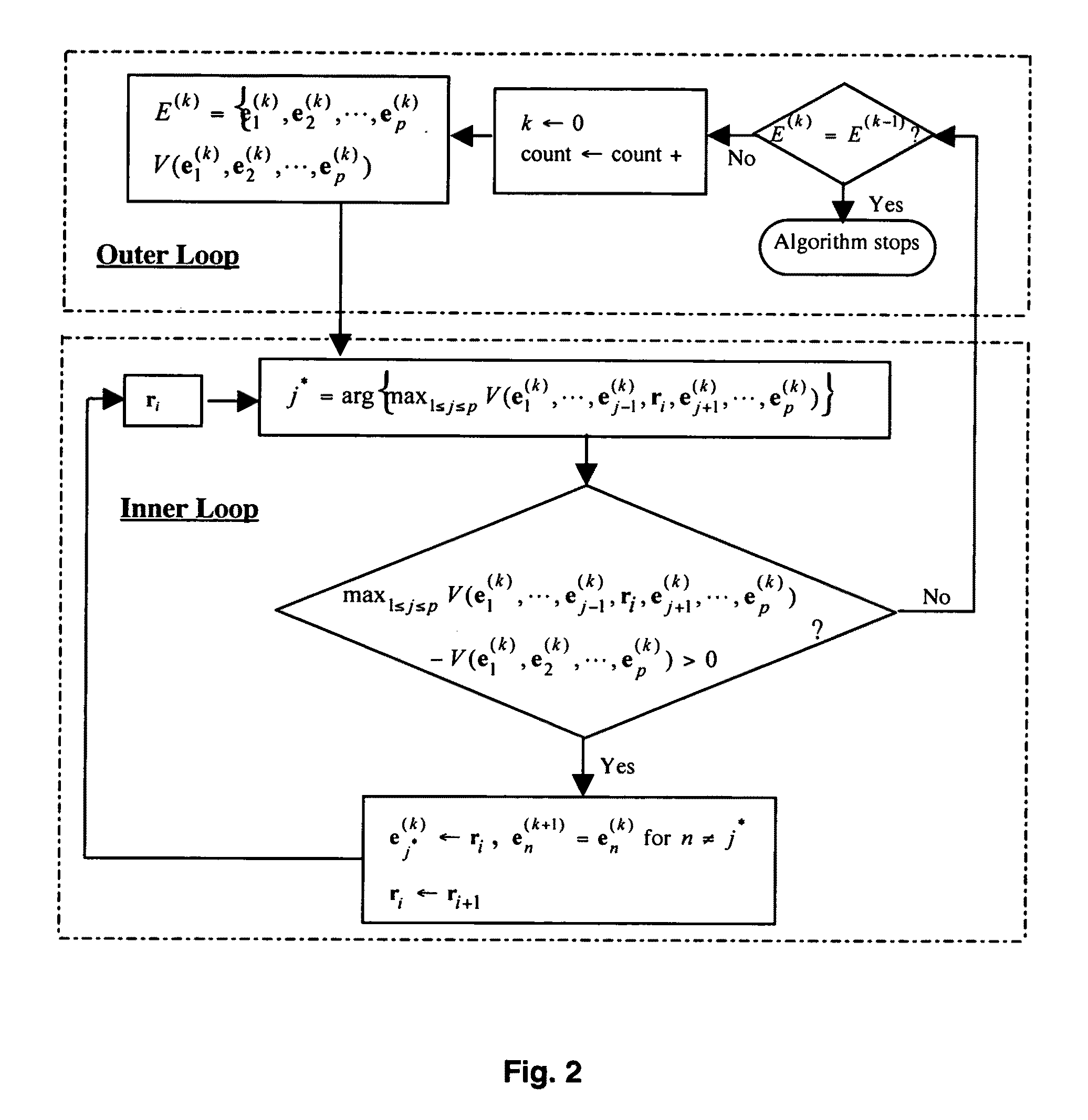
Provided herein are algorithms and processes to extract endmembers from hyperspectral image data in real time. A Simplex Growing Algorithm is effective to estimate a p number of endmembers to be generated, to select one or more initial endmembers as a simplex of k members and to add a k+1 endmember to the simplex that yields a maximum simplex volume until k=p, thereby extracting one or more endmembers from the data. Alternatively, N-FINDR algorithms form an initial simplex set of p endmembers obtained from the hyperspectral image data, find a maximum volume of one or more initial p endmembers therewithin, replace one or more of the p endmembers within the simplex with one or more of the found p endmembers of maximum volume, and refind a maximum volume of p endmember(s) and replace p endmember(s) until no increase in p endmember(s) volume is found.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Method for selecting representative endmember components from spectral data
InactiveUS20030161533A1Increase profitIncreased complexityImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceUser Friendly
Described herein is a process for objectively and automatically determining spectral endmembers and transforming Spectral Mixture Analysis (SMA) from a widely used research technique into a user-friendly tool that can support the needs of all types of remote sensing. The process extracts endmembers from a spectral dataset using a knowledge-based approach. The process identifies a series of starting spectra that are consistent with a scene and its environment. The process then finds endmembers iteratively, selecting each new endmember based on a combination of physically and statistically-based tests. The tests combine spectral and spatial criteria and decision trees to ensure that the resulting endmembers are physically representative of the scene.
Owner:LEIDOS INC
Algorithm for rapid endmembers determination (ALRED) in hyperspectral data
InactiveUS8041121B1Useful resultSelection process is extremely rapidSpectrum investigationScene recognitionData setRapid processing
A method for rapid processing of large sets of hyperspectral data. A hyperspectral image, with hundreds of thousands to millions of pixels measured at hundreds of wavelengths, can contain over a gigabyte of data. Even modern computers can be quite slow when performing involved calculations on data sets of this size. An algorithm requiring a minimal amount of floating point calculations that still yielded useful results is disclosed.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNITED STATES
Decomposing hyperspectral or multispectral image data
ActiveUS8670620B2Easy to useMaximize independenceScene recognitionFrequency spectrumReflectance spectroscopy
The disclosure concerns processing of electronic images, such as hyperspectral or multispectral images. In particular, but is not limited to methods, software and computer systems for determining underlying spectra of an image of a scene. The image data comprises for each pixel location a sampled image spectrum that is a mixture of plural reflectance spectra. Processor 310 determines or accesses plural hyperplanes that each have plural linearly independent basis vectors. Each hyperplane represents an estimate of one of the plural reflectance spectra. The processor 310 then determines for each pixel location, a contribution of the plural basis vectors of each hyperplane to the image spectrum of that pixel location. The processor 310 determines or accesses plural hyperplanes and not plural endmembers directly. Hyperplanes are two-dimensional while endmembers are only one-dimensional. As a result, hyperplanes carry more information, such as the illumination spectrum and are therefore of greater use. The decomposition of the image data into hyperplanes is possible without knowing the illumination spectrum. This decomposition allows for a range of new applications such as endmember extraction and compact representation.
Owner:NAT ICT AUSTRALIA
Latent fingerprint image enhancement method for hyperspectral imaging
ActiveCN105160642AAchieve separationReduce the difficulty of operationImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionLatent fingerprintOrthogonal subspace
The invention discloses a latent fingerprint image enhancement method for hyperspectral imaging. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, acquiring a fingerprint endmember spectrum set; step 2, acquiring a background endmember spectrum set based on the fingerprint endmember spectrum set in the step 1 or combination of the fingerprint endmember spectrum set in the step 1 and average spectrum of different background regions marked with a user, and adopting orthogonal subspace iteration for extracting the background endmember spectrum set; step 3, separating fingerprints from backgrounds to realize fingerprint enhancement; and step 4, postprocessing fingerprint features: adopting morphological open-close mixed reconstruction for performing morphology-reserving and noise-inhibiting post-processing on the fingerprint features after enhancement in the step 3. The method is simple and practical, greatly lowers the difficulty of user operation, can smooth noises and fill holes on the premise of keeping enhanced fingerprint information, and is high in fingerprint enhancement reliability, high in efficiency and high in practicality and feasibility.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of identifying endmember spectral values from hyperspectral image data
A method of identifying endmember spectral values from multispectral image data, where each multispectral data value is equal to a sum of mixing proportions of each endmember spectrum. The method comprises the steps of processing the data to obtain a multidimensional simplex having a number of vertices equal to the number of endmembers. The position of each vertex represents a spectrum of one of the endmembers. Processing the data is conducted by providing starting estimates of each endmember spectrum for each image data value. The mixing proportions for each data value is estimated from estimates of the spectra of all the endmembers. The spectrum of each endmember is estimated from estimates of the mixing proportions of the spectra of all the endmembers for each image data value. The estimation steps are repeated until a relative change in the regularised residual sum of squares is sufficiently small. The regularised residual sum of squares includes a term which is a measure of the size of the simplex.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
High-quality spectrum reconstruction method based on few-wave-band high-resolution image and low-resolution hyperspectral image
ActiveCN106780423AImproving the accuracy of reconstructed spectraImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionDecomposition
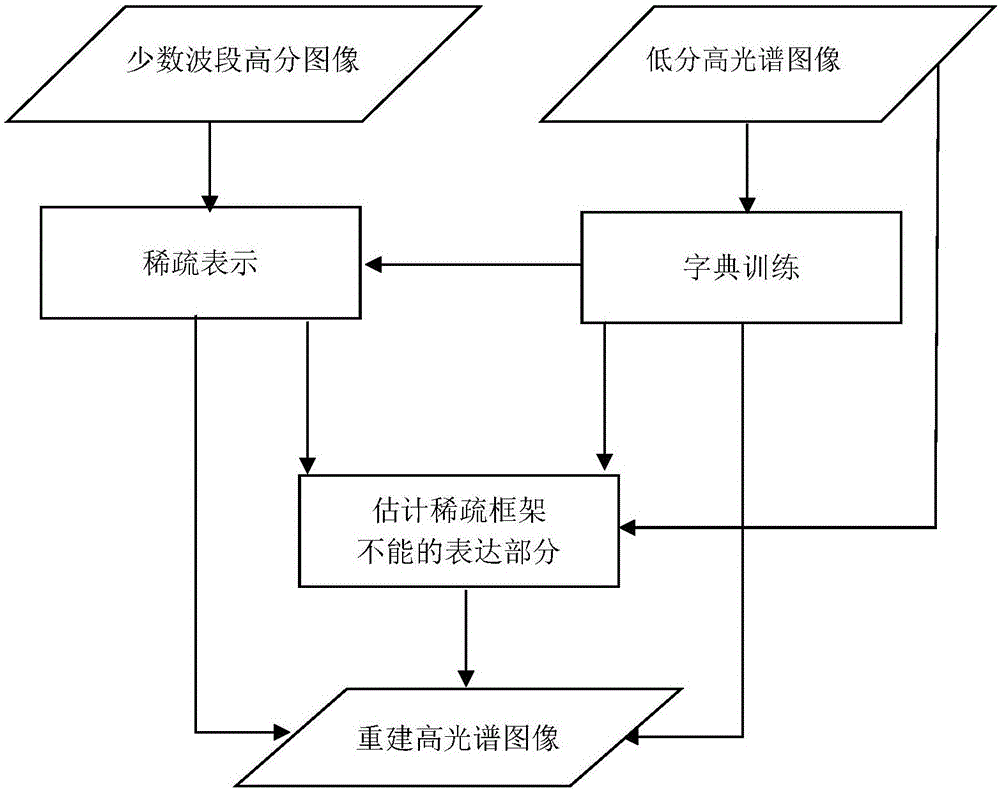
Provided is a high-quality spectrum reconstruction method based on a few-wave-band high-resolution image and a low-resolution hyperspectral image. The method comprises the steps that the high-resolution image having few wave bands and the low-resolution hyperspectral image under the same scene are obtained; the low-resolution hyperspectral image is trained in a non-decomposition mode to obtain a spectrum dictionary; then, the high-resolution image having the few wave bands is subjected to sparse representation under the condition of being free of non-negative restriction, and a sparse representation coefficient is obtained; the part which cannot be represented by a sparse representation framework is estimated through spatial structure information; the dictionary, the sparse coefficient and the estimation part are utilized for reconstructing the hyperspectral image with high resolution. Accordingly, under the sparse representation framework, the non-decomposition mode is introduced to solve the spectrum dictionary, the deficiency of descriptive power of endmember decomposition to spectral characteristics of the hyperspectral image is made up, and the reconstructed spectrum precision, the effectiveness of hyperspectral image reconstruction and the spatial accuracy of reconstructing the hyperspectral image are effectively improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Thermal infrared fusion reconstruction method based on hyperspectral image
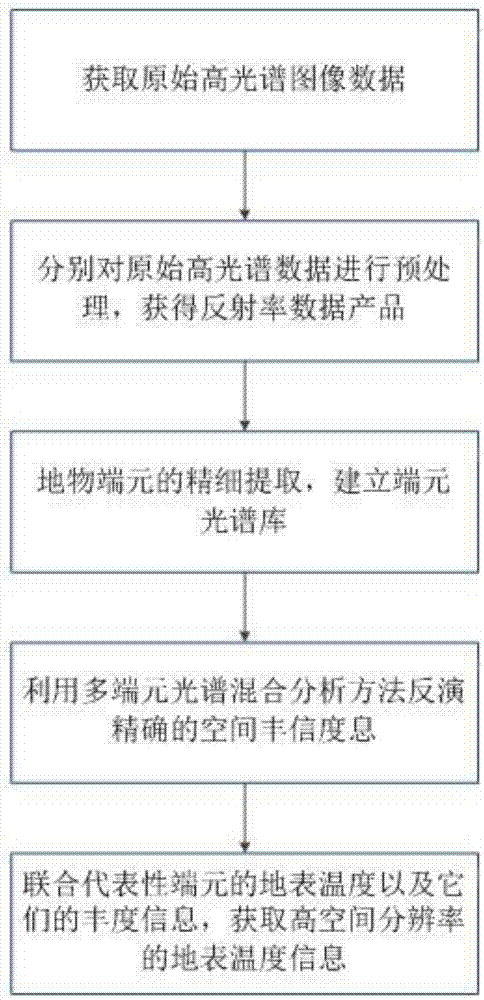
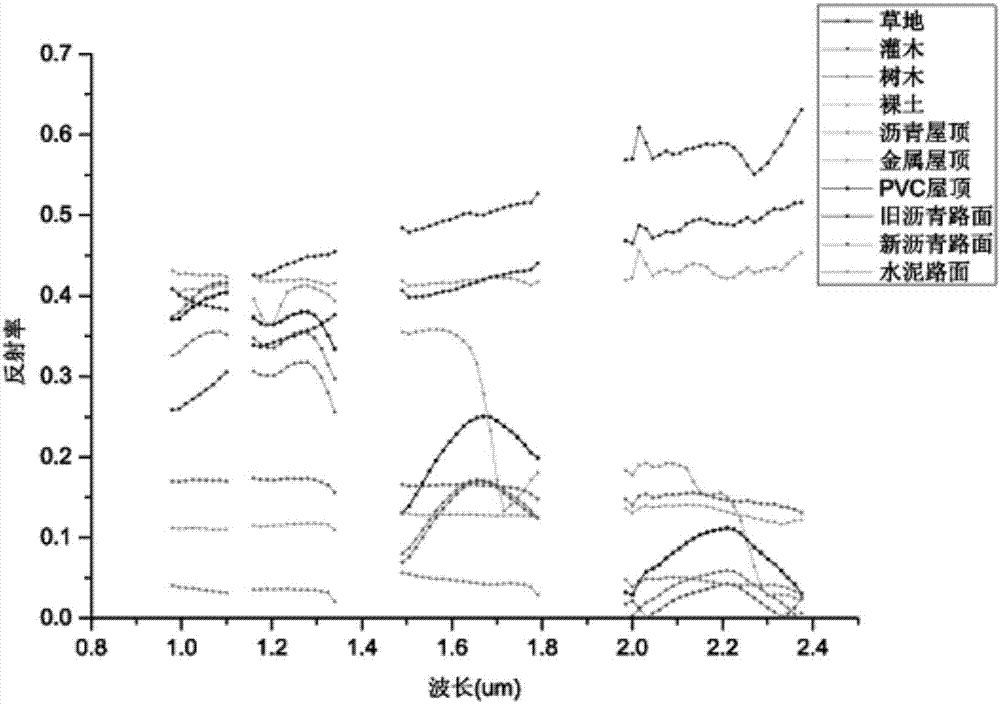
ActiveCN107966210AImprove spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometryDrawing from basic elementsTerrainReconstruction method
The invention relates to the technical field of remote sensing, and particularly relates to a thermal infrared fusion reconstruction method based on a hyperspectral image. The method comprises the following steps: A, pure endmembers are selected based on spectral reflectance characteristics and thermal response characteristics of an urban material; B, a multi-endmember spectral mixed analysis method is used to invert accurate terrain spatial abundance information; and C, through the surface temperature of joint representative endmembers and the spatial abundance information of the endmembers,a surface temperature image with a high spatial resolution is acquired. In the technical scheme of the invention, through a data fusion means, based on a hyperspectral remote sensing data reconstruction theory, the urban surface temperature image with a high spatial resolution is obtained, the image can significantly improve the spatial resolution of the urban temperature, and research on a seriesof problems brought about by an urban heat island and global changes can be done conveniently.
Owner:SHENZHEN ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING CENT
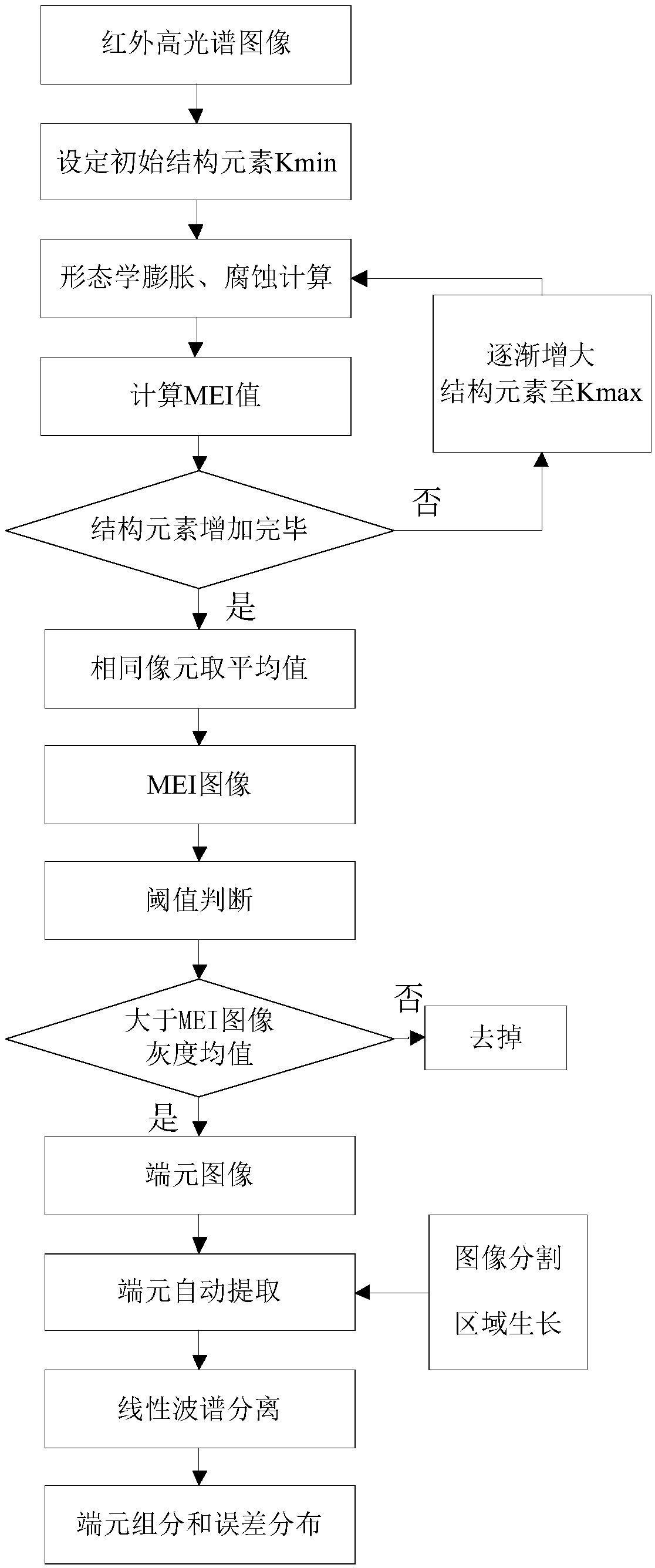
Automated morphological endmember extraction based hyperspectral image data unmixing method
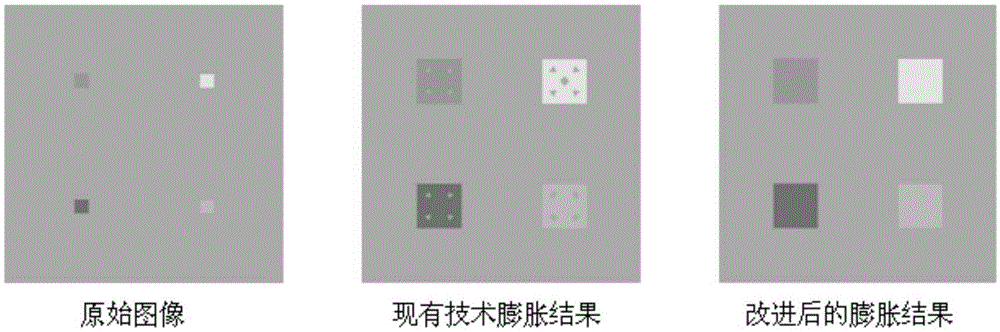
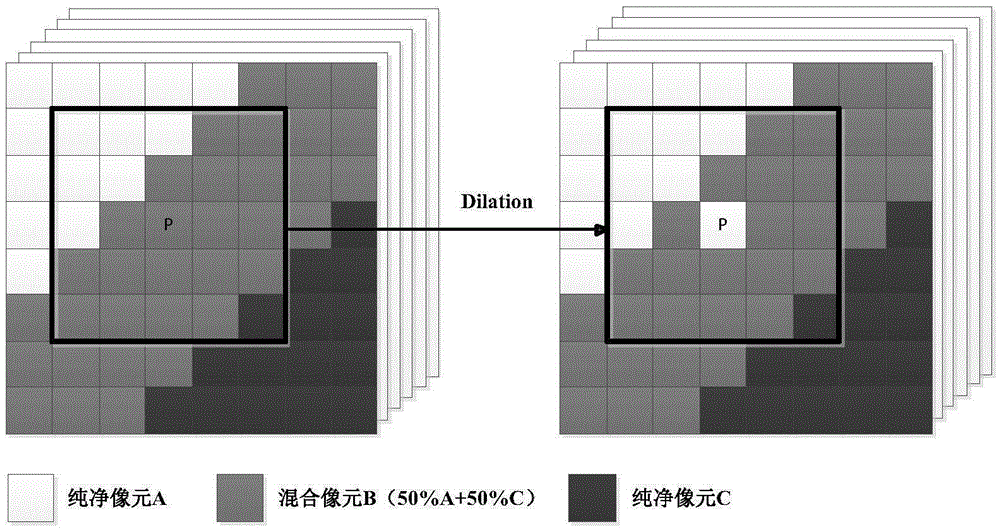
ActiveCN105427319AImprove clarityAvoid lossImage enhancementImage analysisSpectral vectorStructuring element
The invention relates to an automated morphological endmember extraction based hyperspectral image data unmixing method and belongs to the technical field of image data processing. According to the method, calculation is performed by utilizing a reference spectral vector to obtain an image element with highest mixing degree in a whole image, and based on this, a morphological operator is improved; an original structural element is improved with a new MEI calculation method; a structural element of an odd size is replaced with a structural element of an even size; and four candidate endmembers are selected from each structural element, so that possible information loss is effectively avoided, the accuracy of data processing is further improved, and finally the definition of the image obtained after data processing is improved; and the automated morphological endmember extraction based hyperspectral image data unmixing method is quite simple and convenient to implement.
Owner:CHONGQING BIO NEWVISION MEDICAL EQUIP LTD
Endmember spectrum database construction method, endmember spectrum database construction apparatus and endmember spectrum database construction program
ActiveUS7630990B2Improve accuracyScene recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionSpectral database
According to one embodiment, an endmember spectrum extraction unit generates an input endmember spectrum group from a hyperspectral image. A collation unit outputs an endmember spectrum group including endmember spectra that are registered with neither a spectrum library nor an endmember spectrum database as a new endmember spectrum group. An input endmember spectrum distribution image generation unit generates an input endmember distribution image every input endmember spectrum. A new endmember spectrum distribution image selection unit selects an input endmember spectrum distribution image that is included in input endmember spectrum distribution images and that corresponds to new endmember spectrum as a new endmember distribution image. The user recognizes what kind of object corresponds to each new endmember spectrum on the basis of the new endmember spectrum distribution image, the hyperspectral image and a high resolution image, and determines and orders whether to register each new endmember spectrum with the endmember spectrum database.
Owner:NEC CORP
Maximum simplex volume criterion-based endmember extraction algorithms
InactiveUS8417748B2Reduce dimensionalityReduce dataDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsImaging dataExtraction algorithm
Provided herein are algorithms and processes to extract endmembers from hyperspectral image data in real time. A Simplex Growing Algorithm is effective to estimate a p number of endmembers to be generated, to select one or more initial endmembers as a simplex of k members and to add a k+1 endmember to the simplex that yields a maximum simplex volume until k=p, thereby extracting one or more endmembers from the data. Alternatively, N-FINDR algorithms form an initial simplex set of p endmembers obtained from the hyperspectral image data, find a maximum volume of one or more initial p endmembers therewithin, replace one or more of the p endmembers within the simplex with one or more of the found p endmembers of maximum volume, and refind a maximum volume of p endmember(s) and replace p endmember(s) until no increase in p endmember(s) volume is found.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
An improved hyperspectral end member extraction method based on discrete variables
InactiveCN109816090AImprove extraction accuracySolve the accuracy problemGenetic modelsPattern recognitionGenetic algorithm
The invention discloses an improved hyperspectral end member extraction method based on discrete variables, and the method comprises the steps of firstly, taking the minimum root-mean-square error between unmixed spectral data and original spectral data as an objective function, and building an end member extraction optimization model in combination with a constraint condition; calculating the food source information based on an artificial bee colony algorithm, selecting NP pieces of food source information as initial solutions and inputting the initial solutions into a genetic algorithm; andfinally, obtaining an optimal solution of the end member extraction optimization model based on a genetic algorithm. According to the method, the end member extraction precision optimization in the hyperspectral image is realized by applying the discrete artificial bee colony algorithm and the genetic algorithm to the hyperspectral end member extraction, so that the problems that a traditional endmember extraction method is low in precision and a linear constraint model is liable to fail are solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A hyperspectral image emissivity spectrum extraction method based on endmember abundance inversion
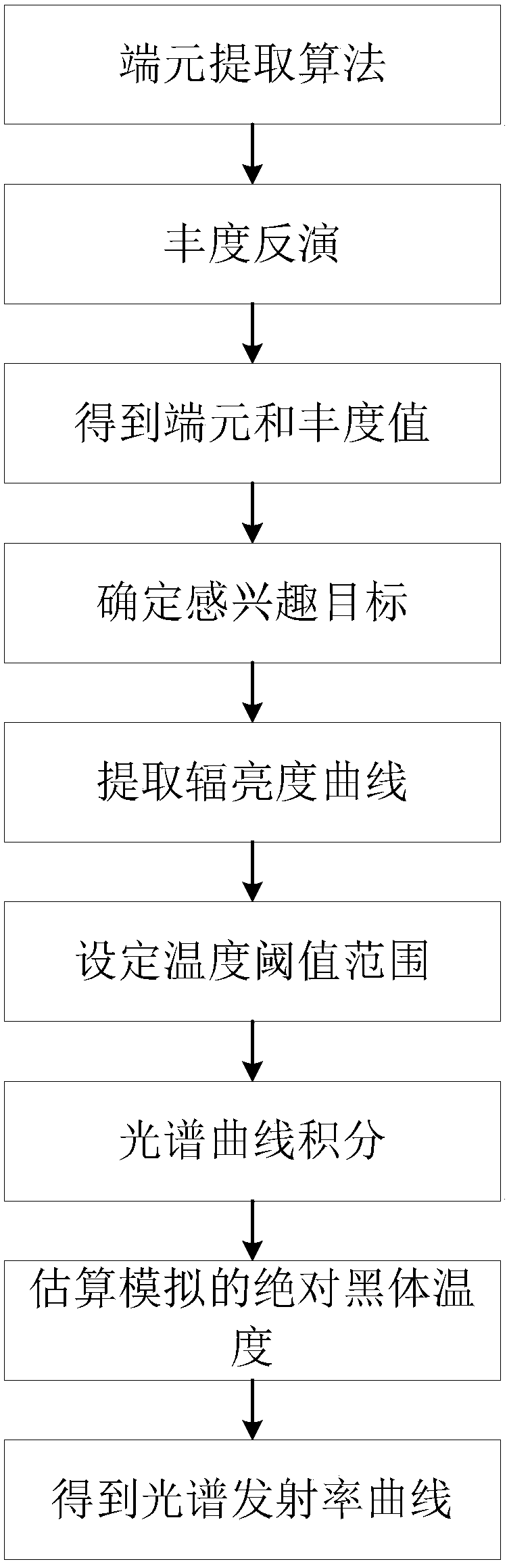
ActiveCN106056044BTroubleshoot problems introducing mixed cellsImprove extraction accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSpectral emissionDecomposition
The invention provides a hyperspectral image emissivity spectrum extraction method based on endmember abundance inversion. First, the whole infrared hyperspectral image is decomposed into mixed pixels to obtain the pure endmembers in the image and the corresponding endmembers. The abundance value of the target, and then obtain the radiance spectrum curve of each pixel point in the image, and then perform curve integration on the radiance spectrum of the target of interest within the set temperature threshold range, and estimate the infrared hyperspectral emissivity according to the integrated area The absolute black body temperature simulated by the curve, and then the emissivity spectrum curve is obtained. When extracting the radiance curve of the target of interest, the present invention considers the influence of mixed pixels, obtains the real radiance curve of the target through end-member extraction and abundance inversion, improves the extraction accuracy of the radiance curve, and then makes the emissivity The extraction accuracy of curves has been improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
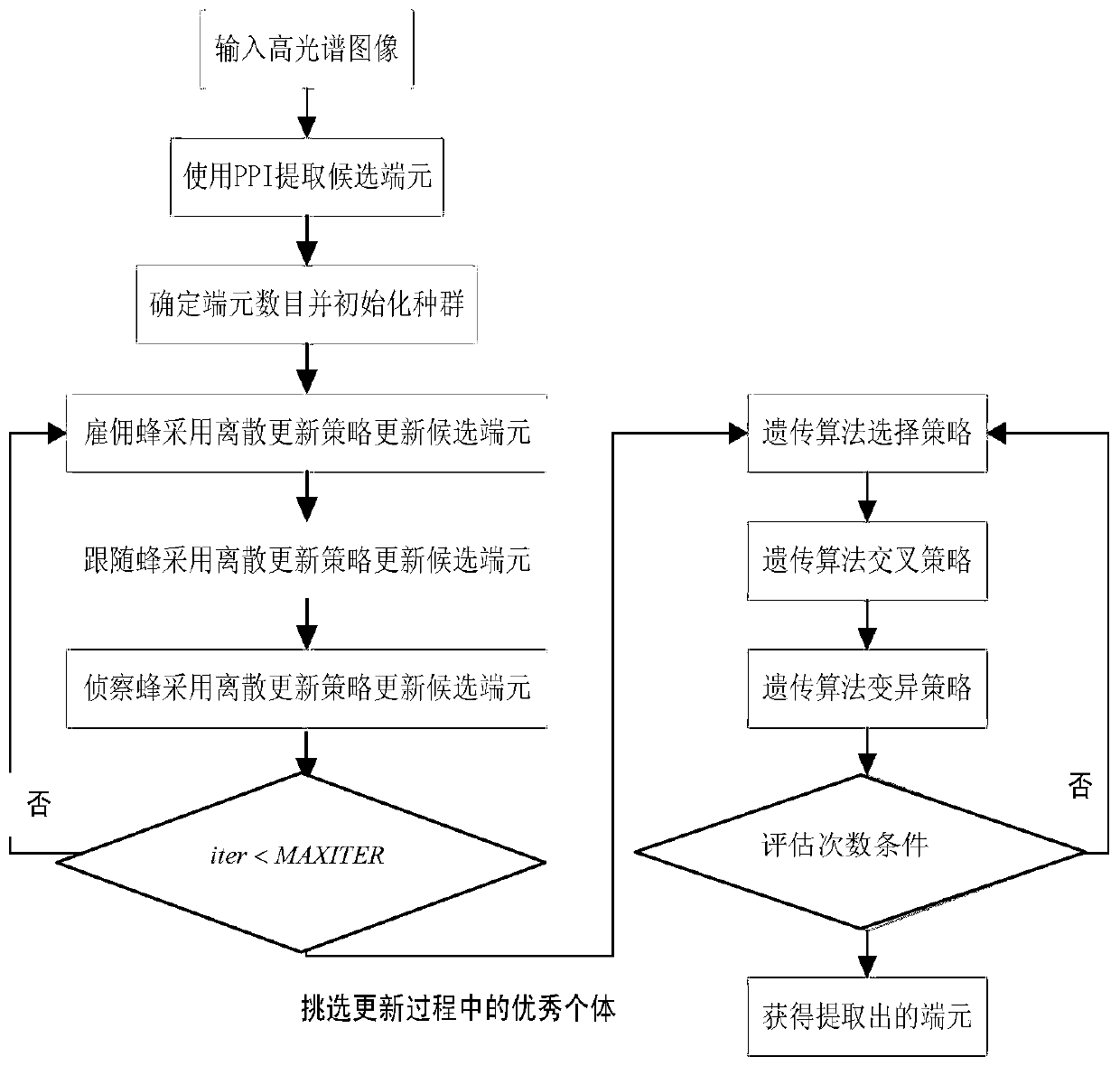
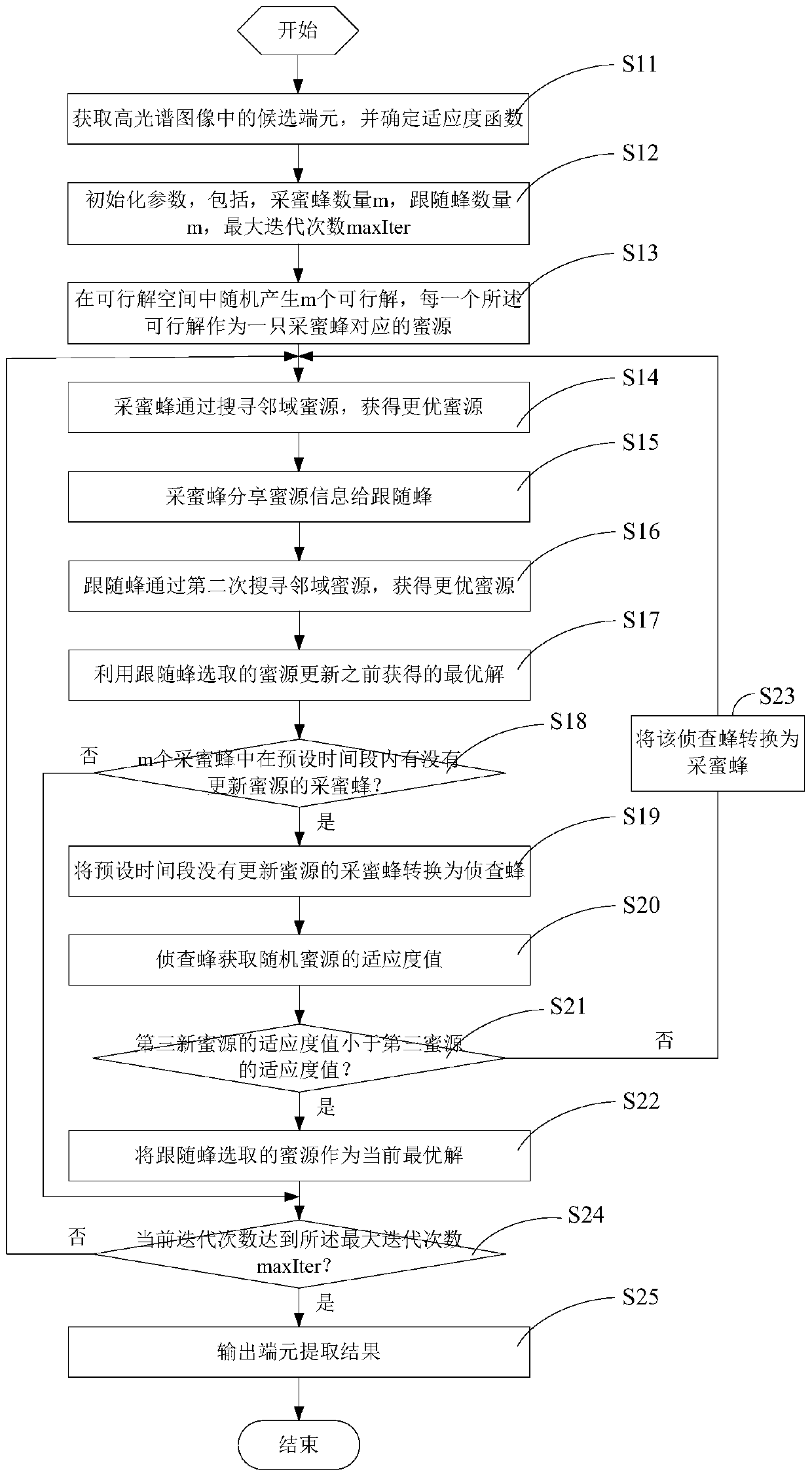
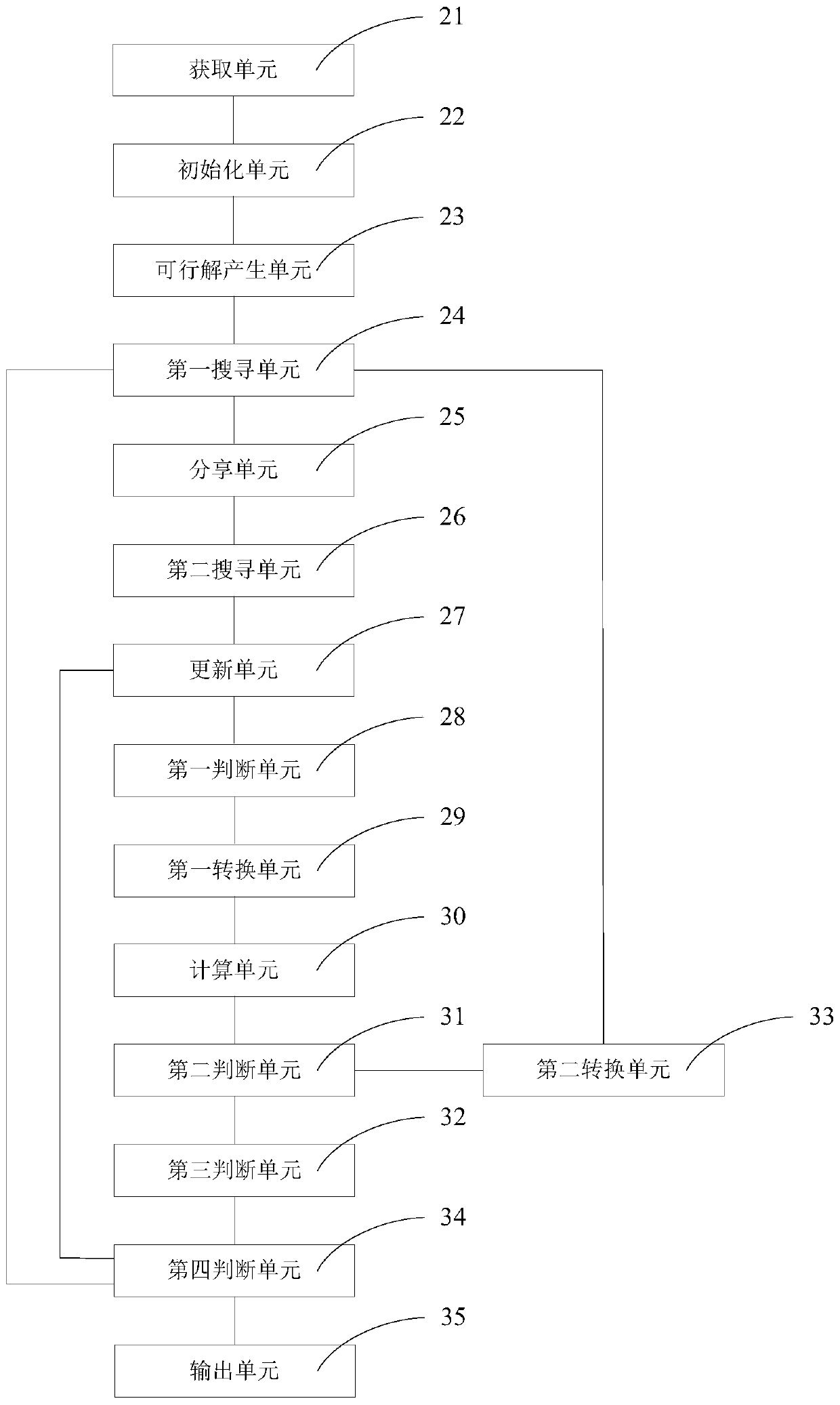
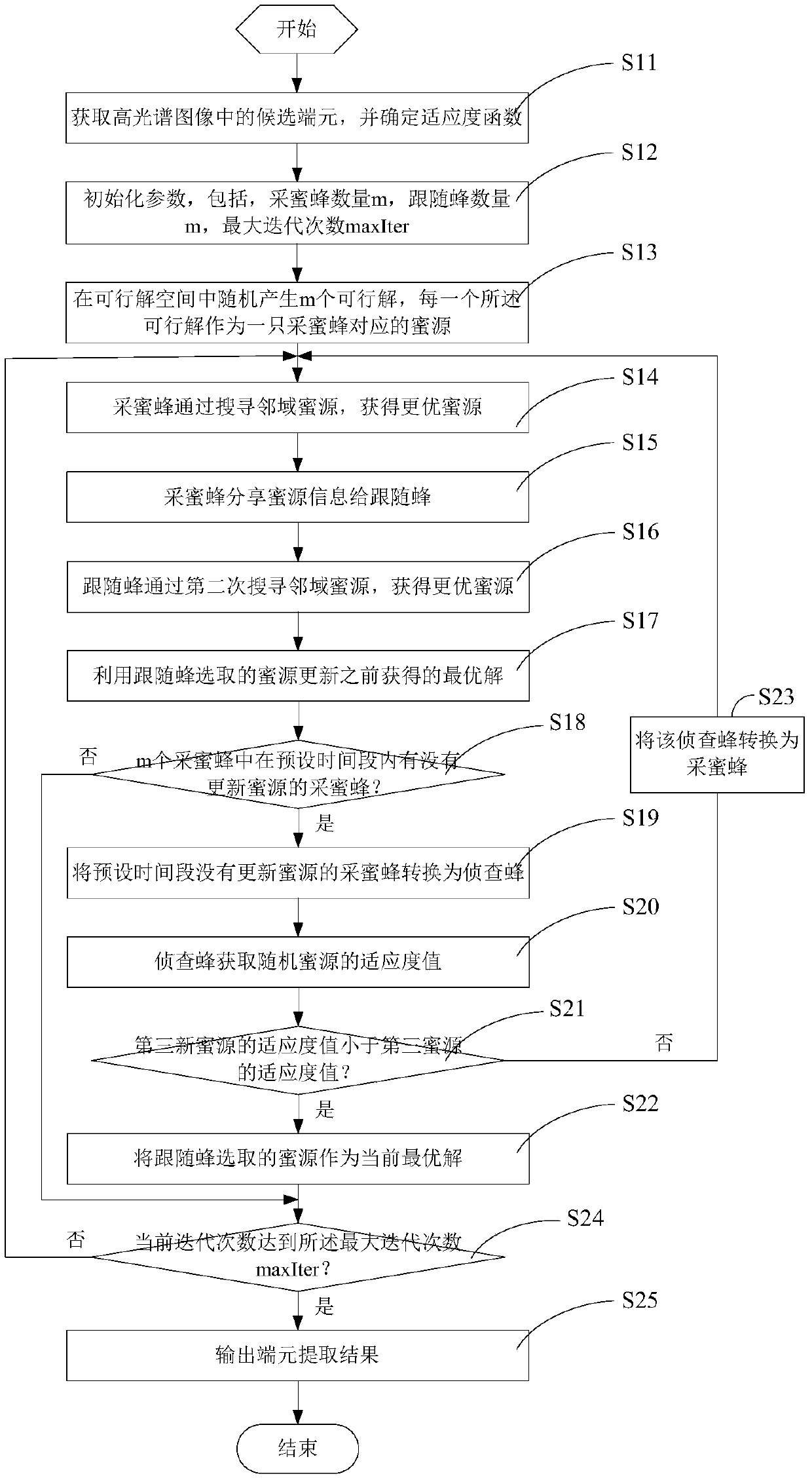
A kind of hyperspectral image endmember extraction method and system
The invention discloses a hyper-spectral image end member extraction method and a hyper-spectral image end member extraction system. Optimized variables in the problem of hyper-spectral image end member extraction correspond to nectar source locations in an artificial bee colony algorithm, and optimization of each nectar source is determined by a fitness function. Nectar collecting bees search for an optimal nectar source, and sends nectar source information to follower bees after search; the follower bees search for an optimal nectar source the second time, and use a selected optimal nectar source to update a previously obtained optimal solution; and when there is a nectar collecting bee not updating the nectar source in a preset period of time, the nectar collecting bee is transformed into an investigation bee, and the investigation bee compares the fitness value of a randomly selected nectar source with the fitting value of a nectar source used as an optimal solution and calibrates the nectar source used as an optimal solution. According to the invention, the end member extraction problem is converted into a combination optimization problem solving process based on the artificial bee colony algorithm, the advantages of the artificial bee colony algorithm are given full play, and the nectar source used as an optimal solution is calibrated by the investigation bee to reduce the risk that the optimization process is trapped into a local optimal solution.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Xylanase activity measuring method
The invention discloses a method for determining the activity of xylanase, which is characterized by comprising: A, producing a standard corresponding relation curve between an absorbance value of xylose measured by an MBTH method and concentration of the xylose; and B, using the MBTH method to detect the absorbance value which is produced after the xylanase to be tested hydrolyzes xylan and is equivalent to that of the xylose; and determining the content of reducing sugar which is produced in unit time and is equivalent to the xylose in an enzymolysis product of the xylanase to be tested according to the standard corresponding relation curve which is produced in step A between the concentration of the xylose and the measured absorbance value of the xylose to calculate the activity of thexylanase. The method uses the MBTH method to detect the quantity of terminal groups of the xylose produced after the xylanase hydrolyzes the xylan to determine the activity of the xylanase. The detectability and work concentration range of xylose determination by the method are apparently lower than those of a DNS method and a potassium ferricyanide method, so the sensitivity of the method is apparently higher than that of the DNS method and the potassium ferricyanide method.
Owner:WUHAN SUNHY BIOLOGICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com