Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
313 results about "Drilling riser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
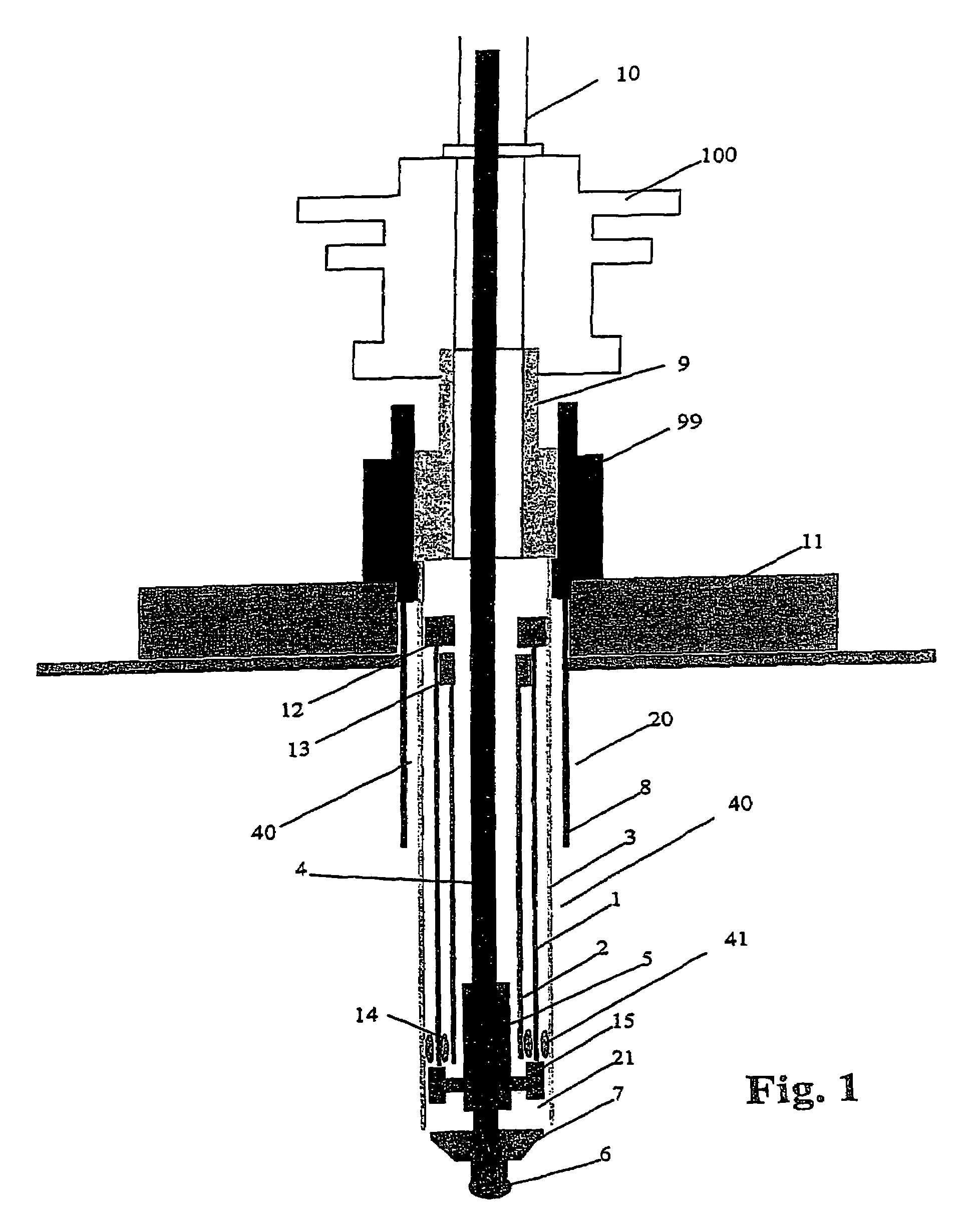
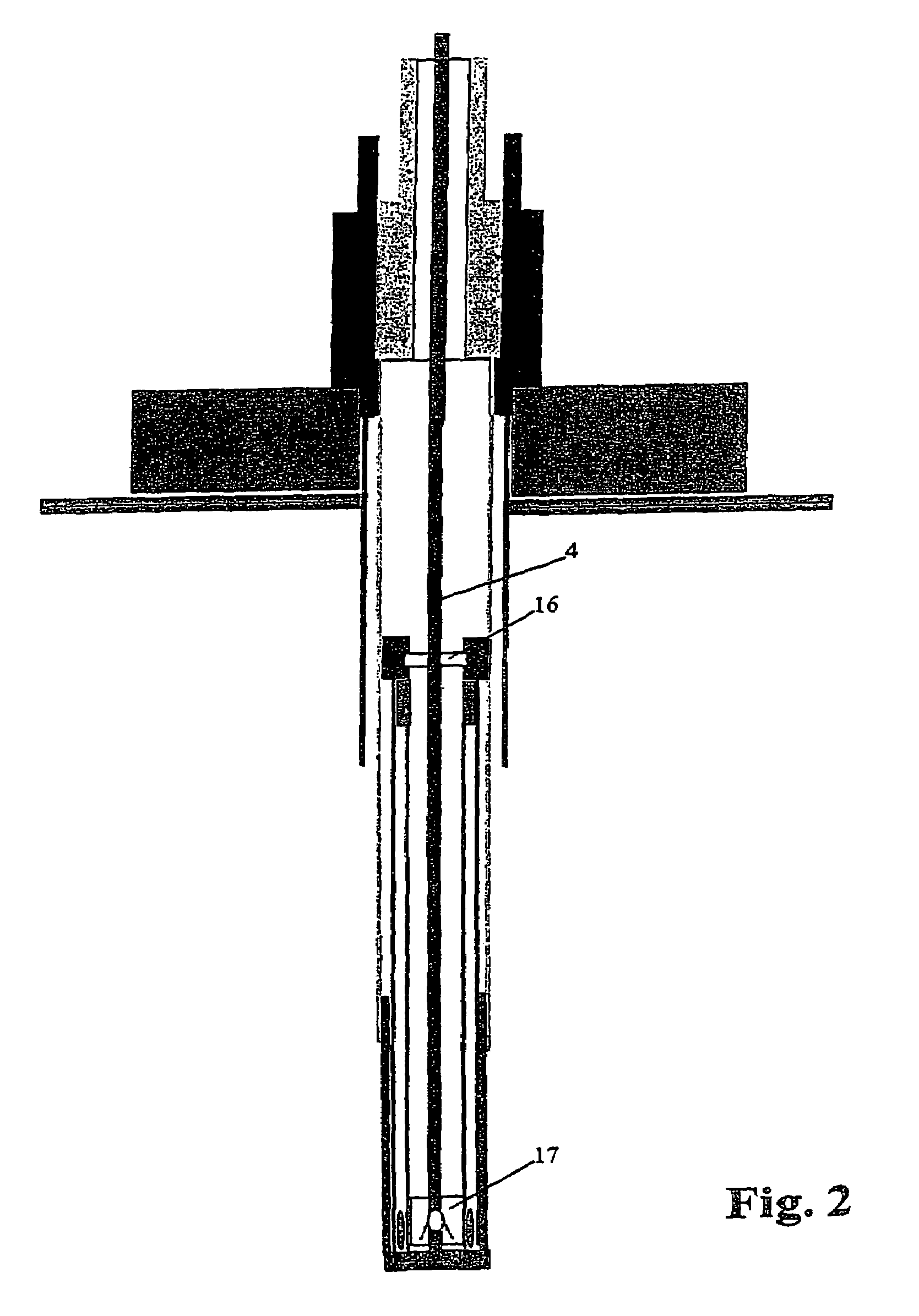
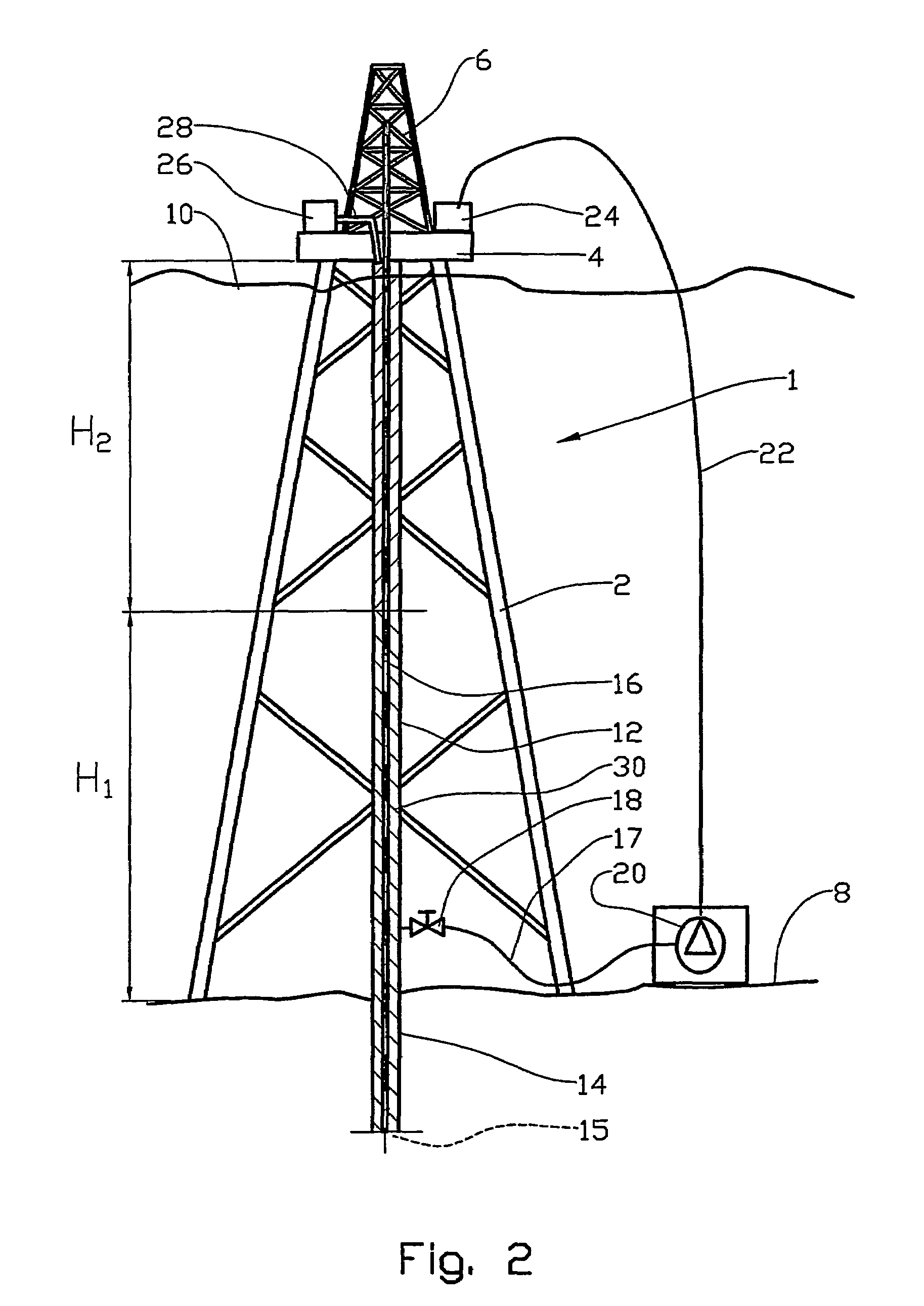
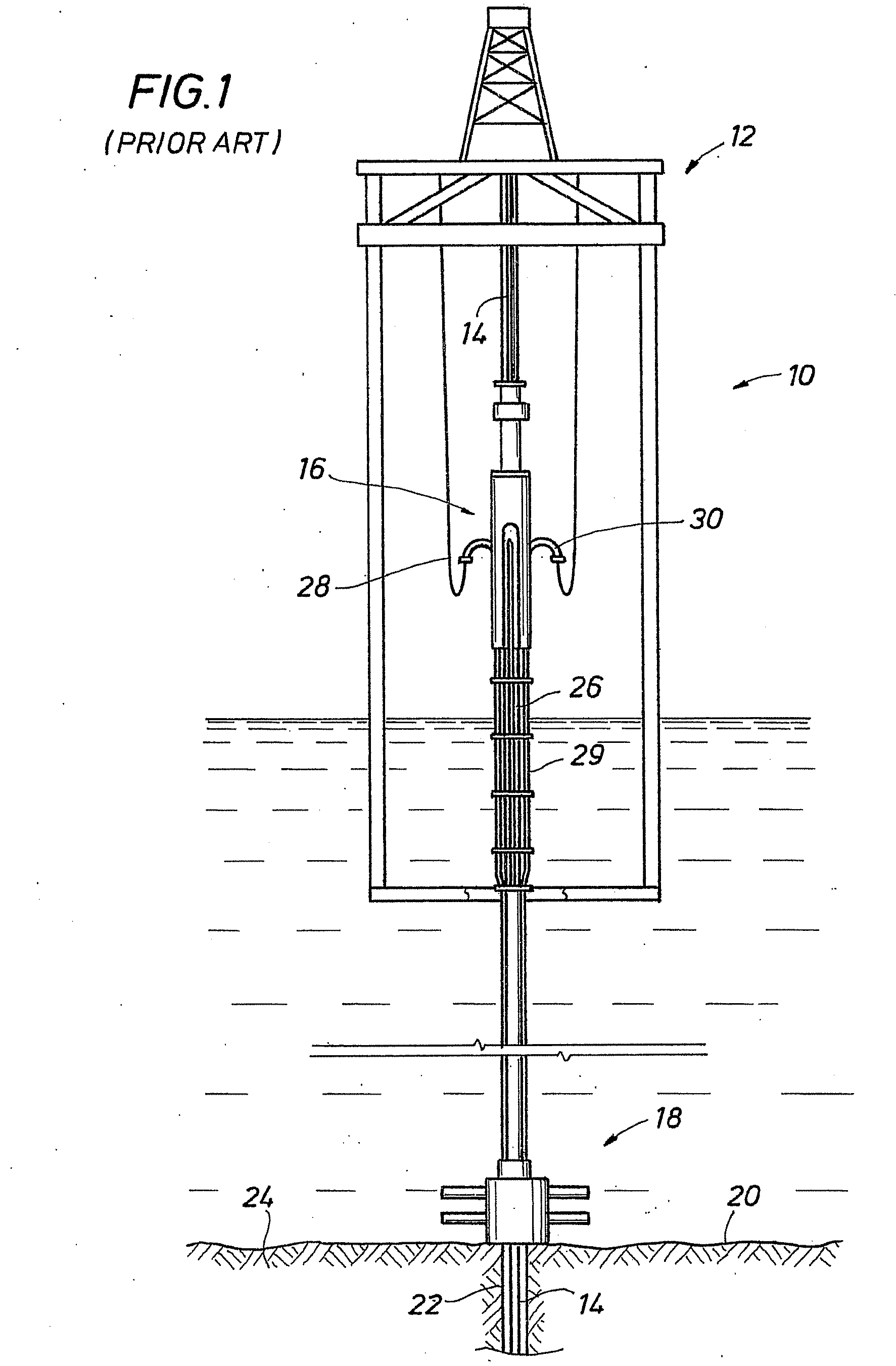
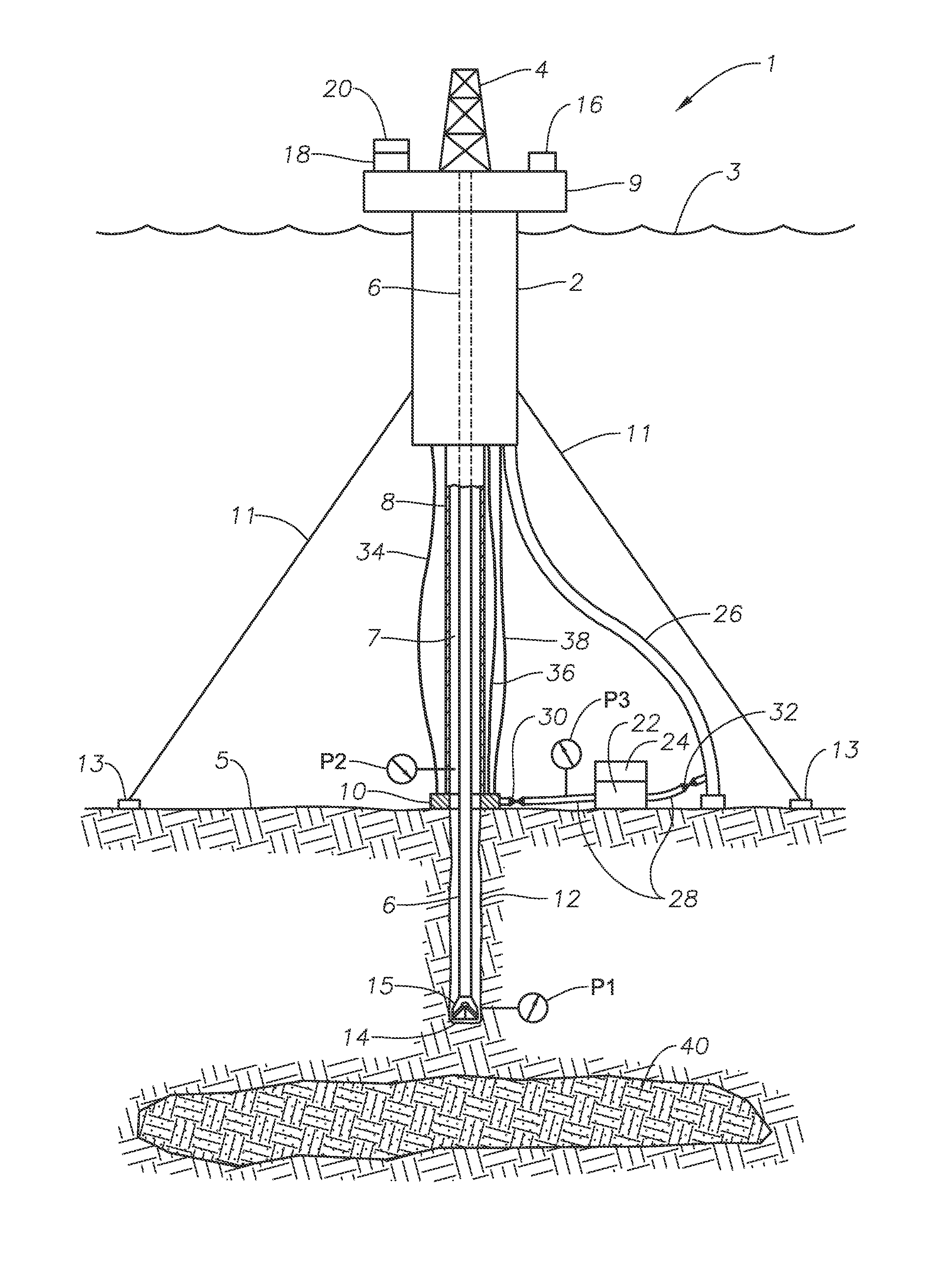
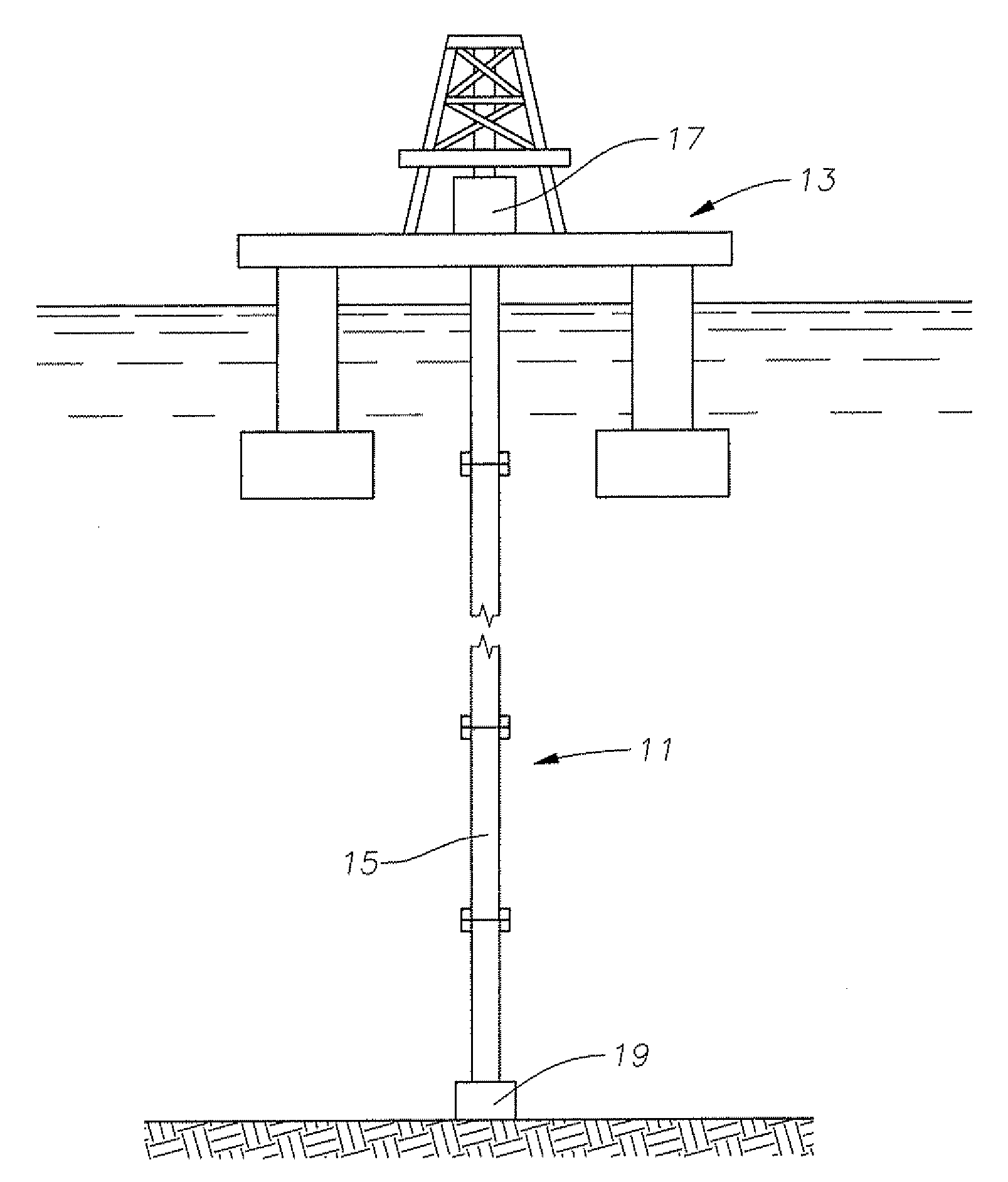
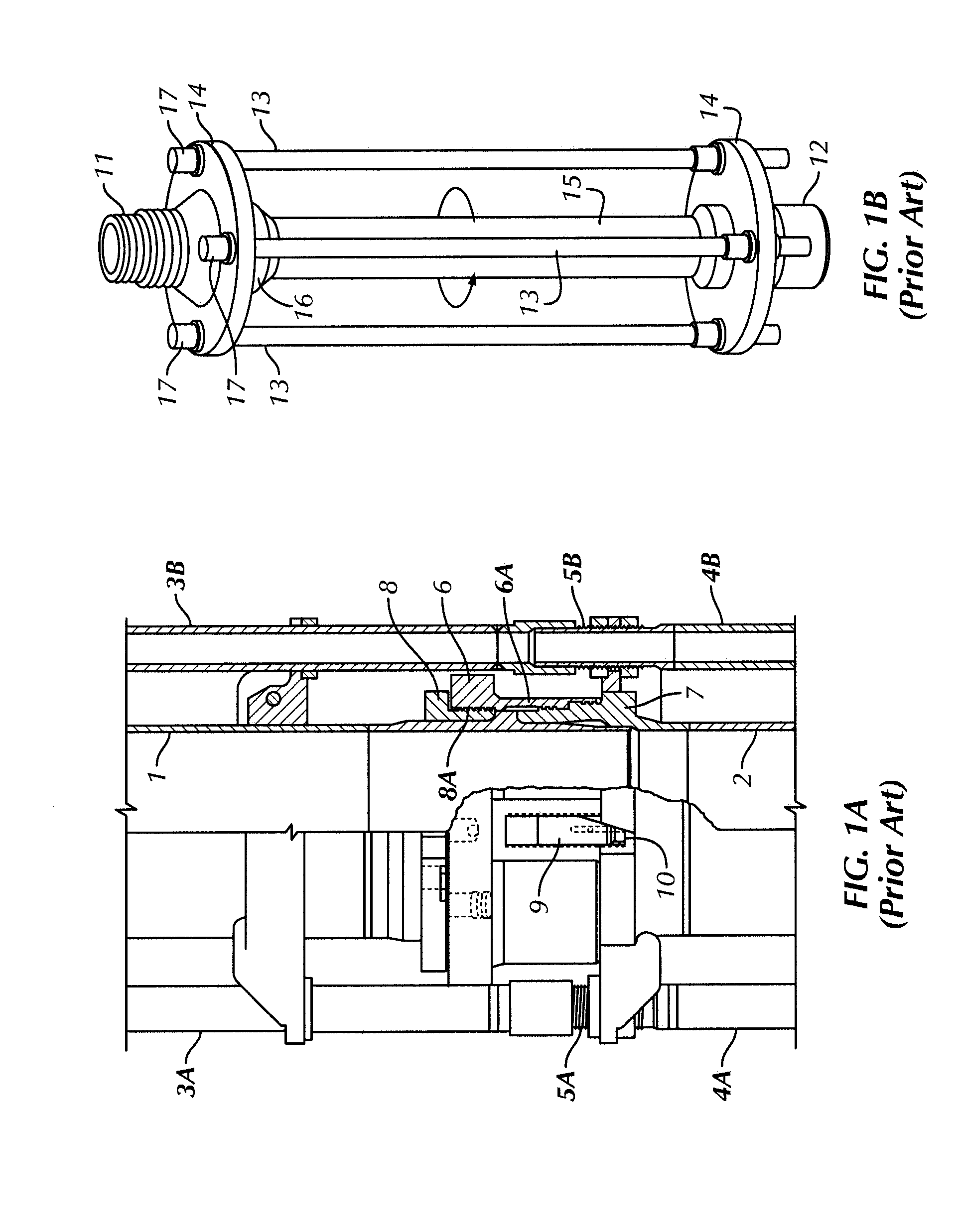
A drilling riser is a conduit that provides a temporary extension of a subsea oil well to a surface drilling facility. Drilling risers are categorised into two types: marine drilling risers used with subsea blowout preventer (BOP) and generally used by floating drilling vessels; and tie-back drilling risers used with a surface BOP and generally deployed from fixed platforms or very stable floating platforms like a spar or tension leg platform (TLP).
Arrangement and method for controlling and regulating bottom hole pressure when drilling deepwater offshore wells
InactiveUS7497266B2Handling is restrictedReduce pressureDrilling rodsConstructionsBottom hole pressureLine tubing
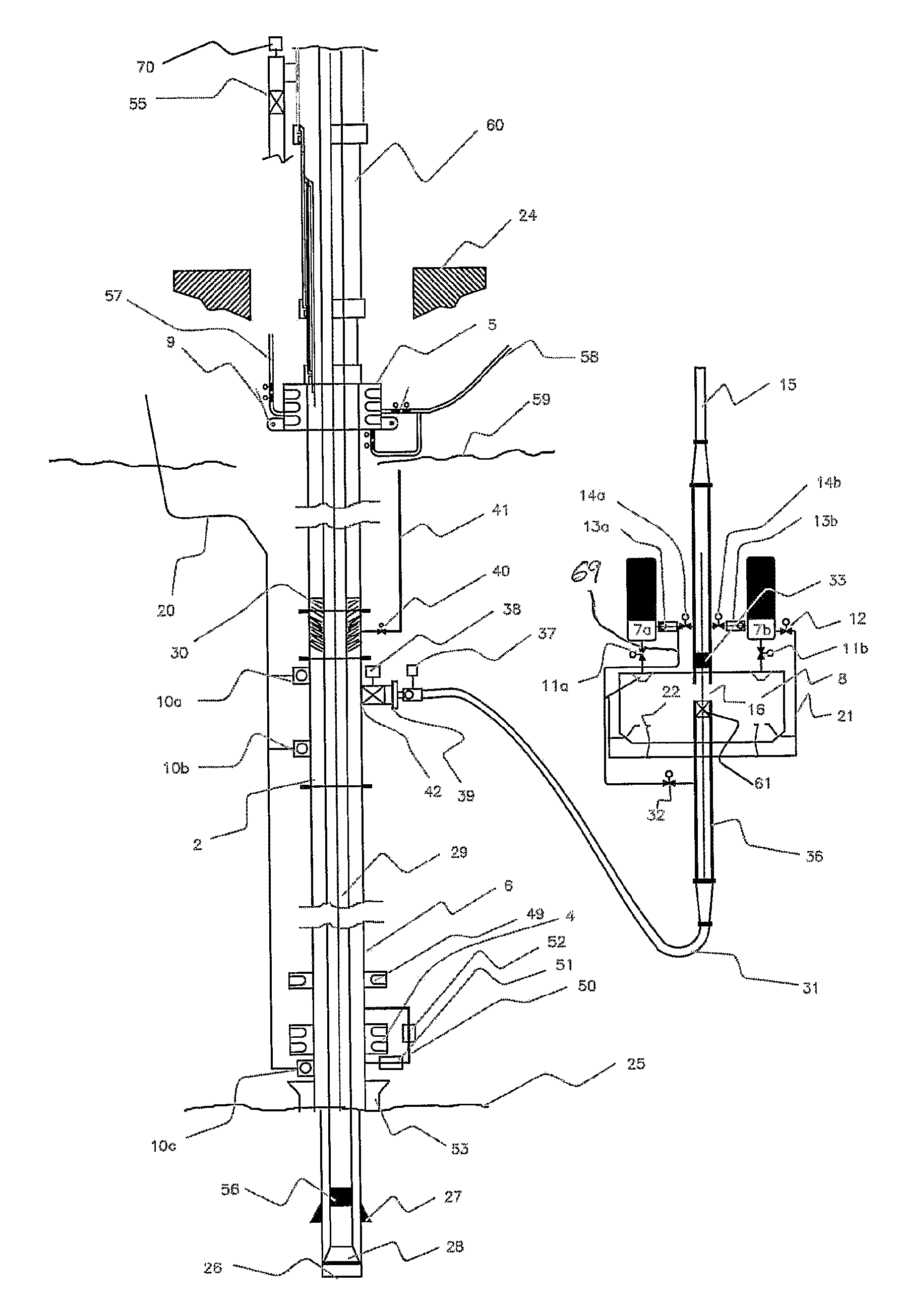
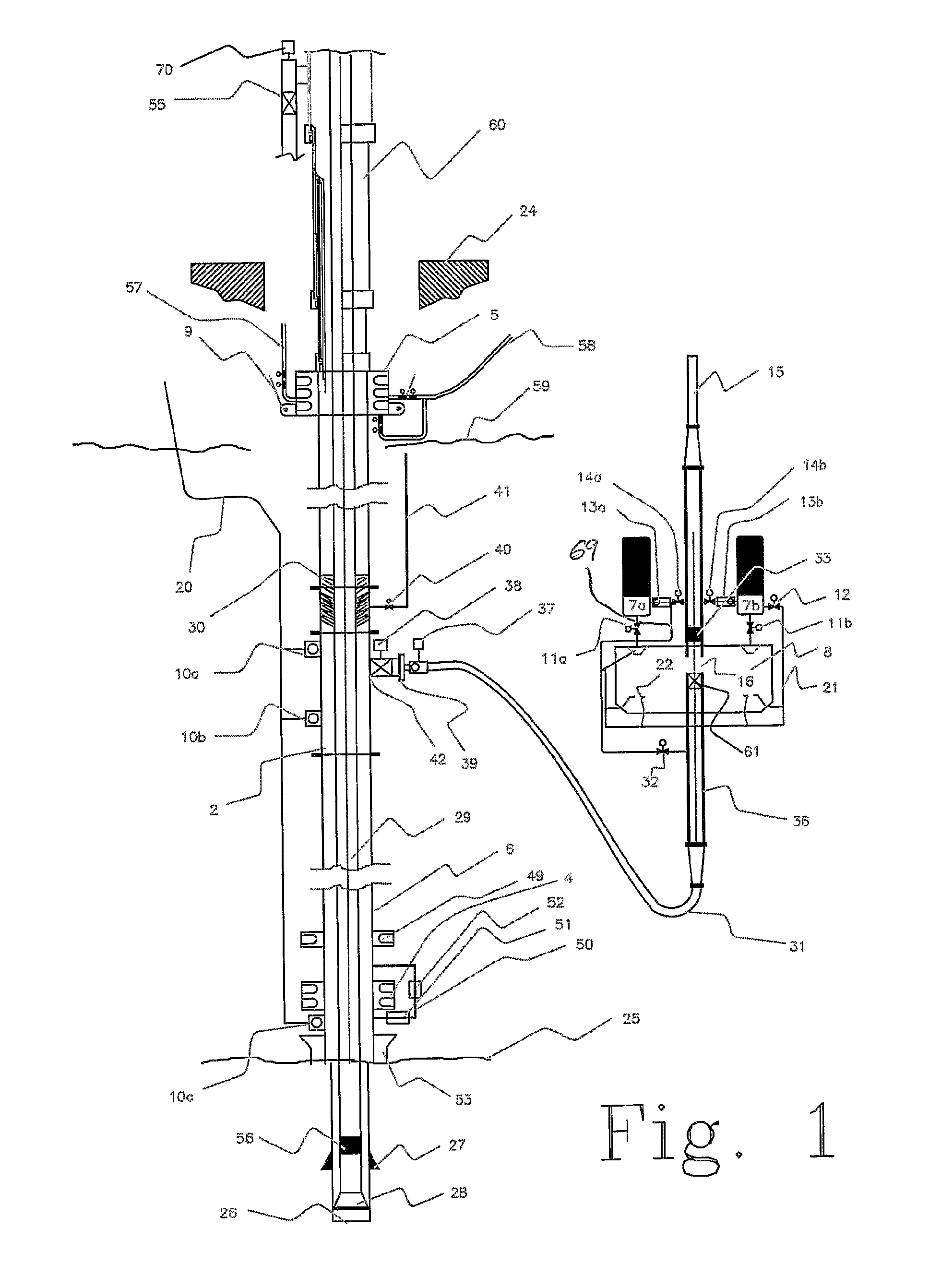
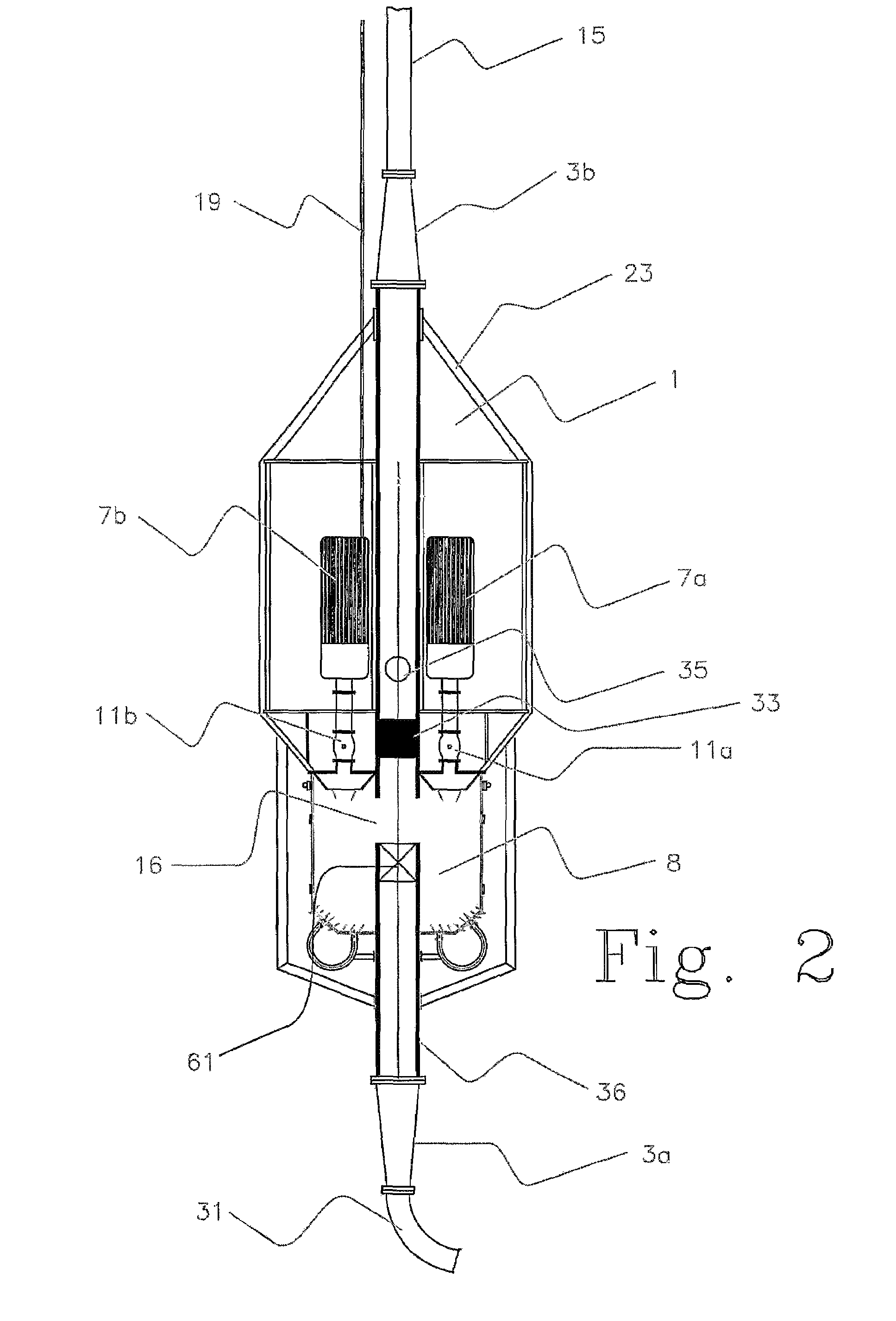
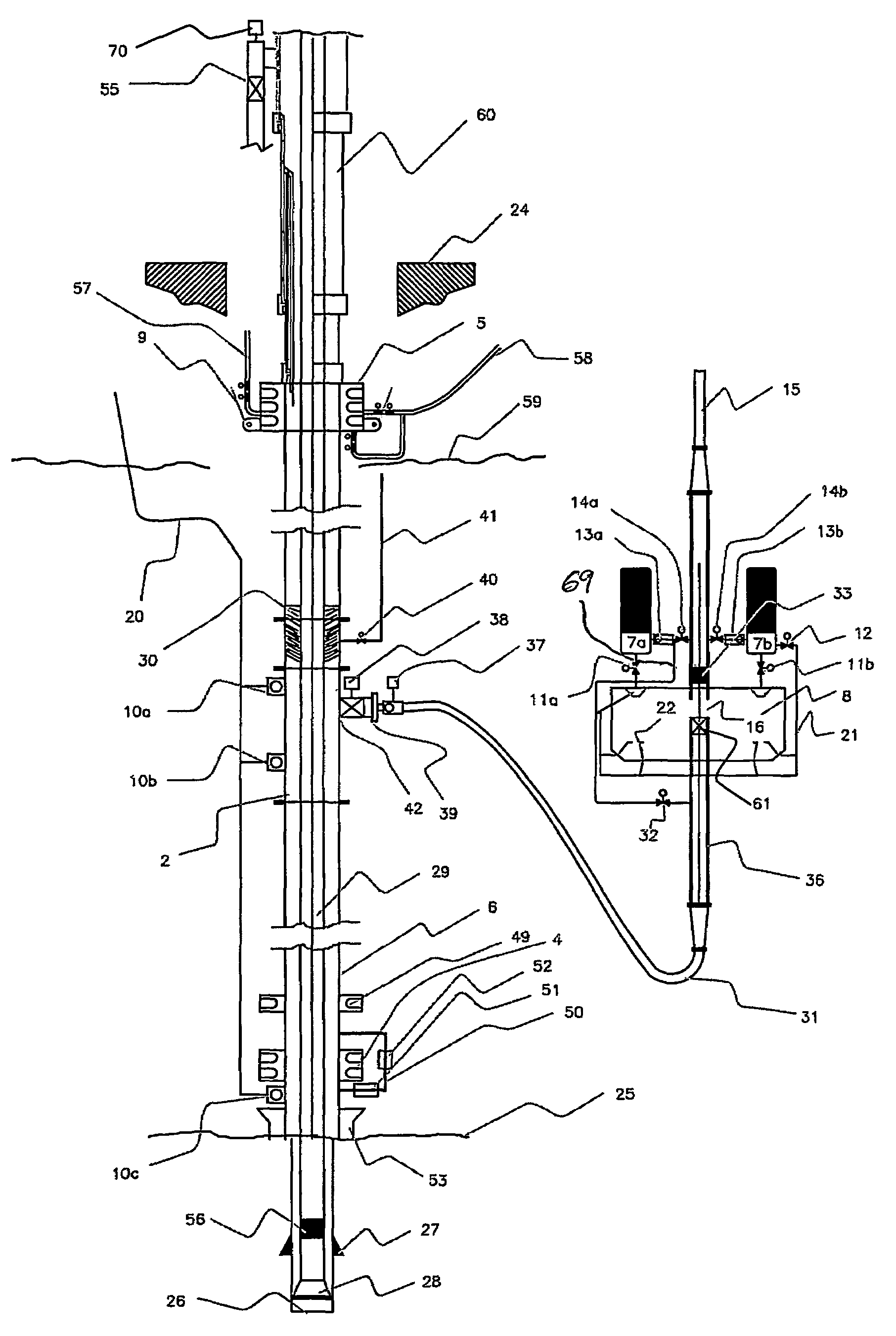
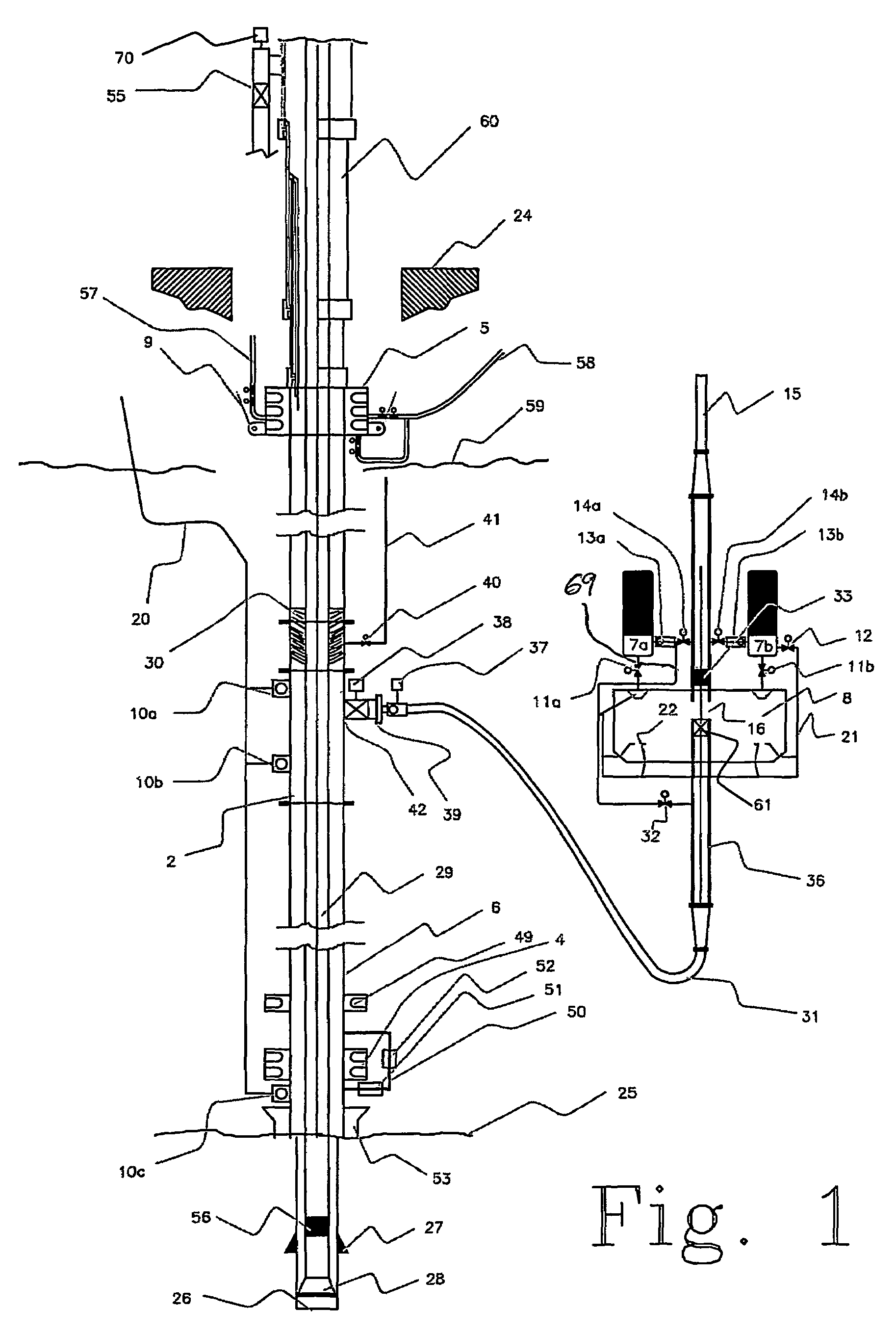
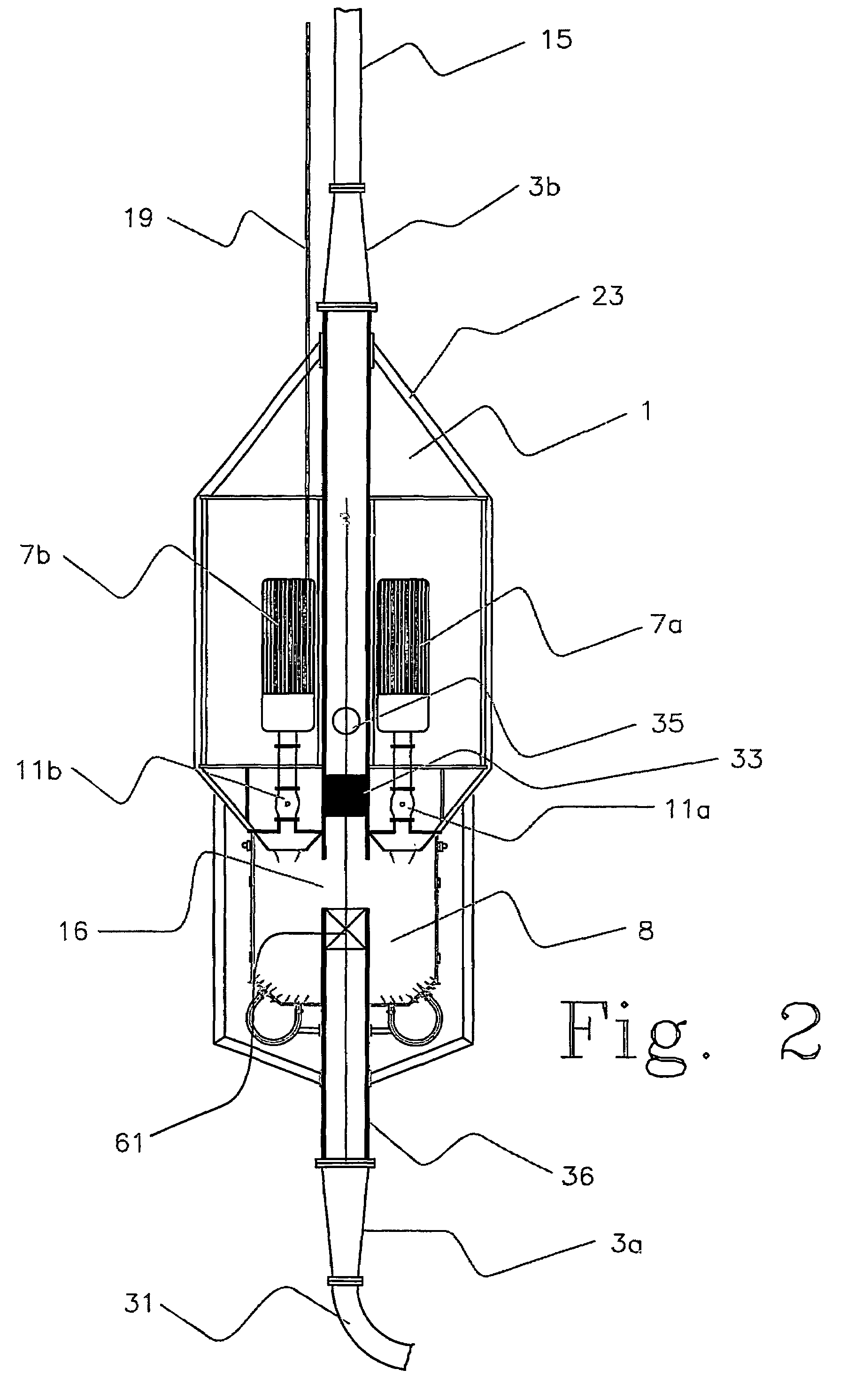
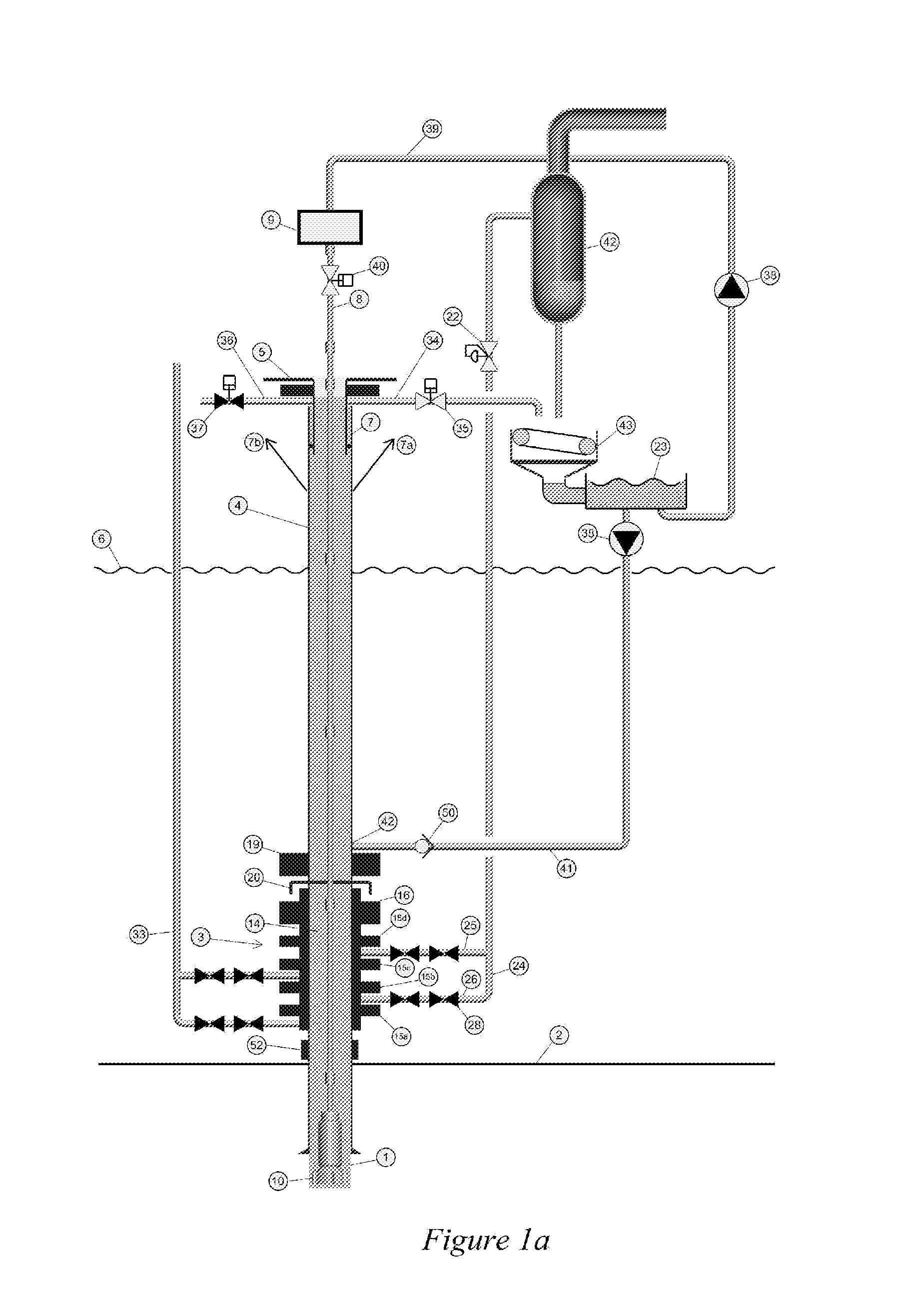
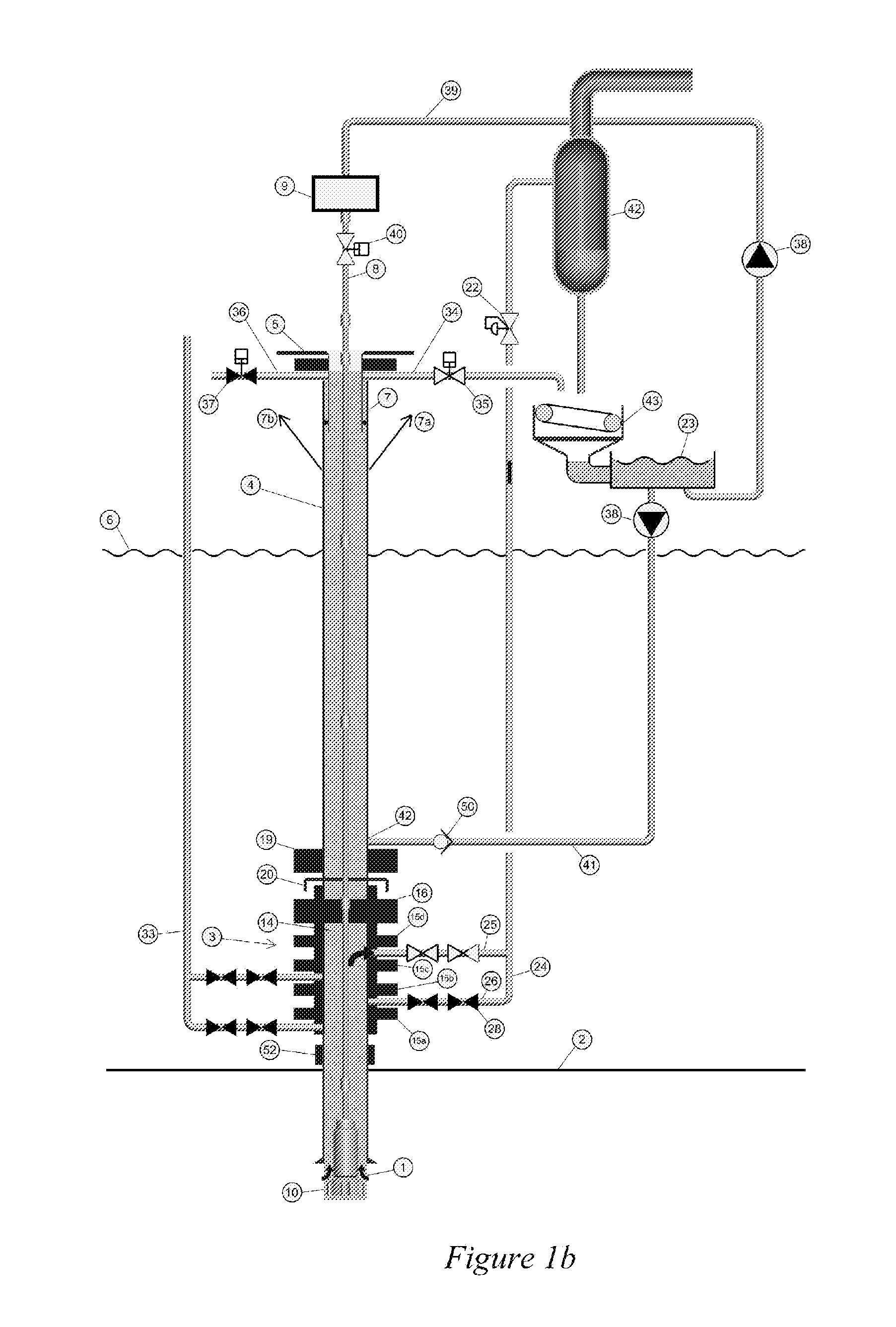
An arrangement and method for controlling and regulating bottom hole pressure in a well during subsea drilling in deep water involves adjustment of a liquid / gas interface level in a high pressure drilling riser up or down to change the slope and offset of the pressure gradient in the well. The arrangement may include a surface BOP and gas bleeding outlet at the upper end of the drilling riser, a lower BOP with a by-pass line, and an outlet at a depth below the water surface that is connected to a pumping system with a flow return conduit running back to a drilling vessel or platform.
Owner:ENHANCED DRILLING
Arrangement and method for regulating bottom hole pressures when drilling deepwater offshore wells
InactiveUS7264058B2Improve abilitiesChange densityDrilling rodsConstructionsBottom hole pressureLine tubing
An arrangement and a method to control and regulate the bottom hole pressure in a well during subsea drilling at deep waters: The method involves adjustment of a liquid / gas interface level in a drilling riser up or down. The arrangement comprises a high pressure drilling riser and a surface BOP at the upper end of the drilling riser. The surface BOP havs a gas bleeding outlet. The riser also comprises a BOP, with a by-pass line. The drilling riser has an outlet at a depth below the water surface, and the outlet is connected to a pumping system with a flow return conduit running back to a drilling vessel / platform.
Owner:ENHANCED DRILLING
Method and system for connecting pipe to a top drive motor
Method and system for connecting a joint of pipe to a top drive motor just above the drilling platform of a drilling rig where the connection can be made quickly and safely by a drilling operator. The system includes a top drive motor that tilts about a horizontal axis and a pipe launcher that brings joints of pipe up to the drilling platform for connection with a top drive motor at a safe and convenient height above the platform. The top drive motor further includes a clamping assembly that grasps and pulls the joint of pipe to the motor as the connection is being made. The clamp assembly supports the motor-pipe connection as the top-drive motor is raised in the drilling mast of the rig bringing the joint of pipe up into a vertical orientation for connection with the drill tubing string.
Owner:LESKO GERALD
Drilling and producing deep water subsea wells
InactiveUS6968902B2Efficient separationMinimize flow disturbanceWaste water treatment from quariesLiquid separation auxillary apparatusOcean bottomWell drilling
Subsea wells are drilled and completed with an offshore floating platform in a manner that allows simultaneous work on more than one well. A first well is drilled and cased. Then a tubing hanger is run through a drilling riser and landed in the wellhead housing. Then, with the same floating platform, the drilling riser is disconnected and moved to a second well. While performing operations on the second well, the operator lowers a production tree from the floating platform on a lift line, and connects it to the first wellhead housing. An ROV assisted subsea plug removal tool is used for plug removal and setting operations. Seabed separation is configured upstream of a production choke valve.
Owner:VETCO GRAY
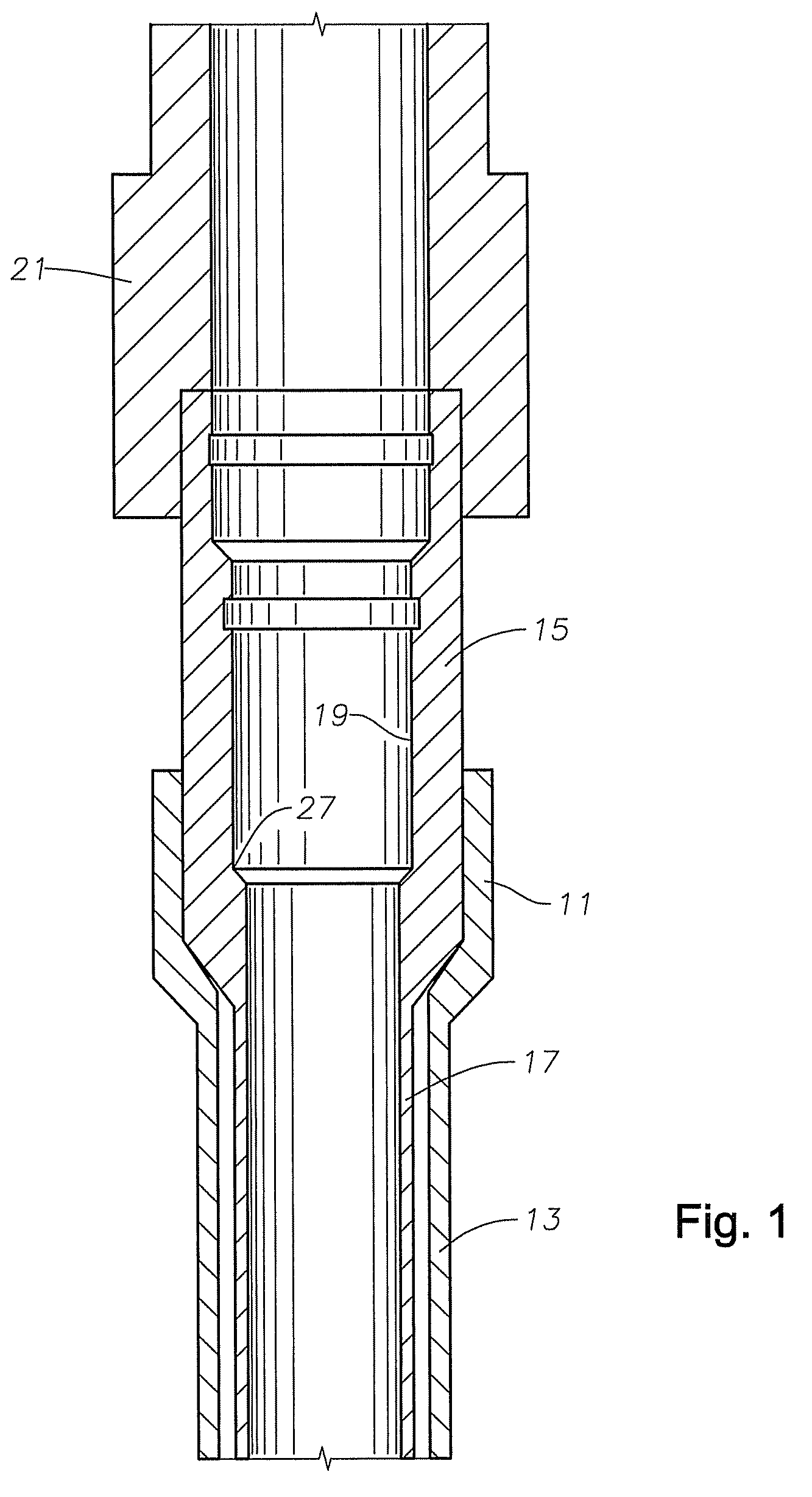
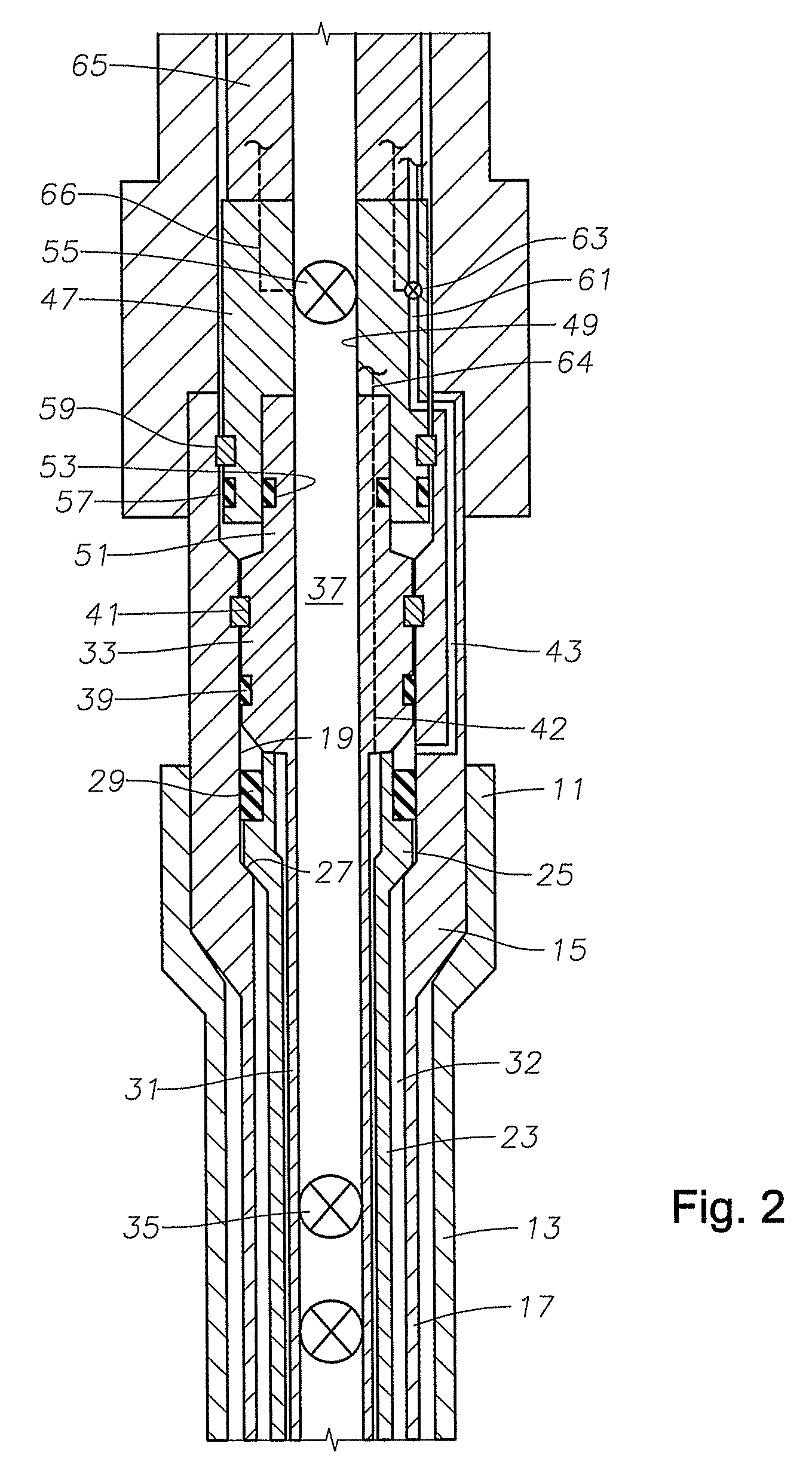
Drilling Riser Adapter Connection with Subsea Functionality
A drilling riser adapter variably connects and releases a riser from a subsea wellhead assembly. The drilling riser adapter has a hydraulically actuated engagement assembly for selectively engaging and disengaging a lower end of the marine riser. The drilling riser adapter also includes a control panel communicatively coupled to the engagement assembly for actuating the engagement assembly to engage and disengage the lower end of the marine riser. The drilling riser adapter also includes a hydraulic fluid pressure receptacle on the control panel for engagement by a remotely operated vehicle to supply hydraulic fluid pressure to the engagement assembly. The drilling riser adapter may be actuated subsea to release a first riser from the wellhead assembly, and connect to a second riser.
Owner:HYDRIL USA DISTRIBUTION LLC
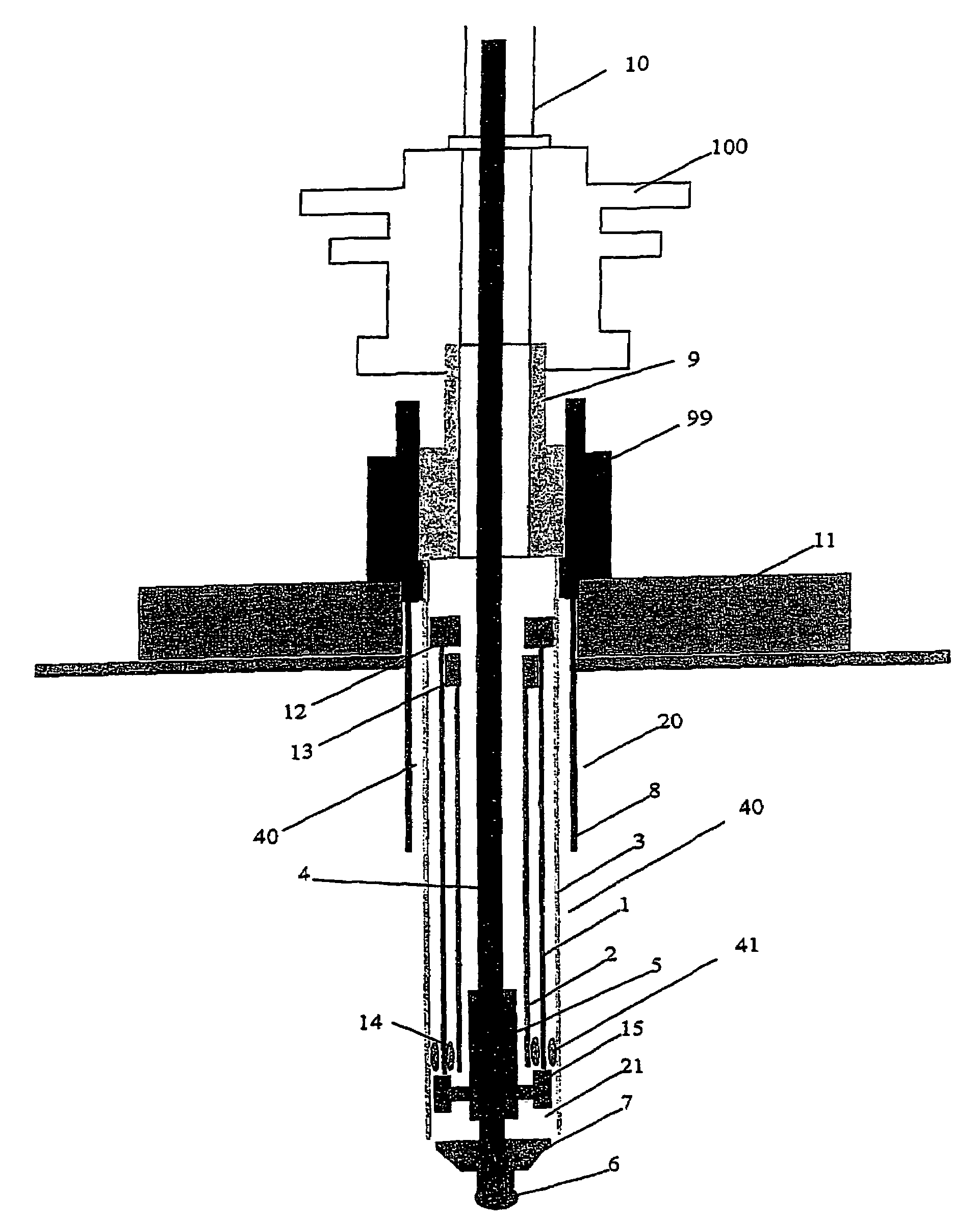
Method and device for liner system
ActiveUS7367410B2Reduce the overall diameterLow costDrilling rodsDerricks/mastsDrilling riserWater pipe
Method for drilling and lining a well wherein at least one liner (1, 2, 32) with a larger external diameter than the substantial part of a drilling riser (10) is pre-installed at a point below the substantial part of the drilling riser (10). A bore hole section (21) is drilled after the drilling riser (10) has been installed, the bore hole section having a larger diameter than the at least one pre-installed liner (1, 2, 32). The at least one pre-installed liner (1, 2, 32) is subsequently lowered into the bore hole section (21, 22). A drilling and liner system for implementing the method is also described.
Owner:ENHANCED DRILLING
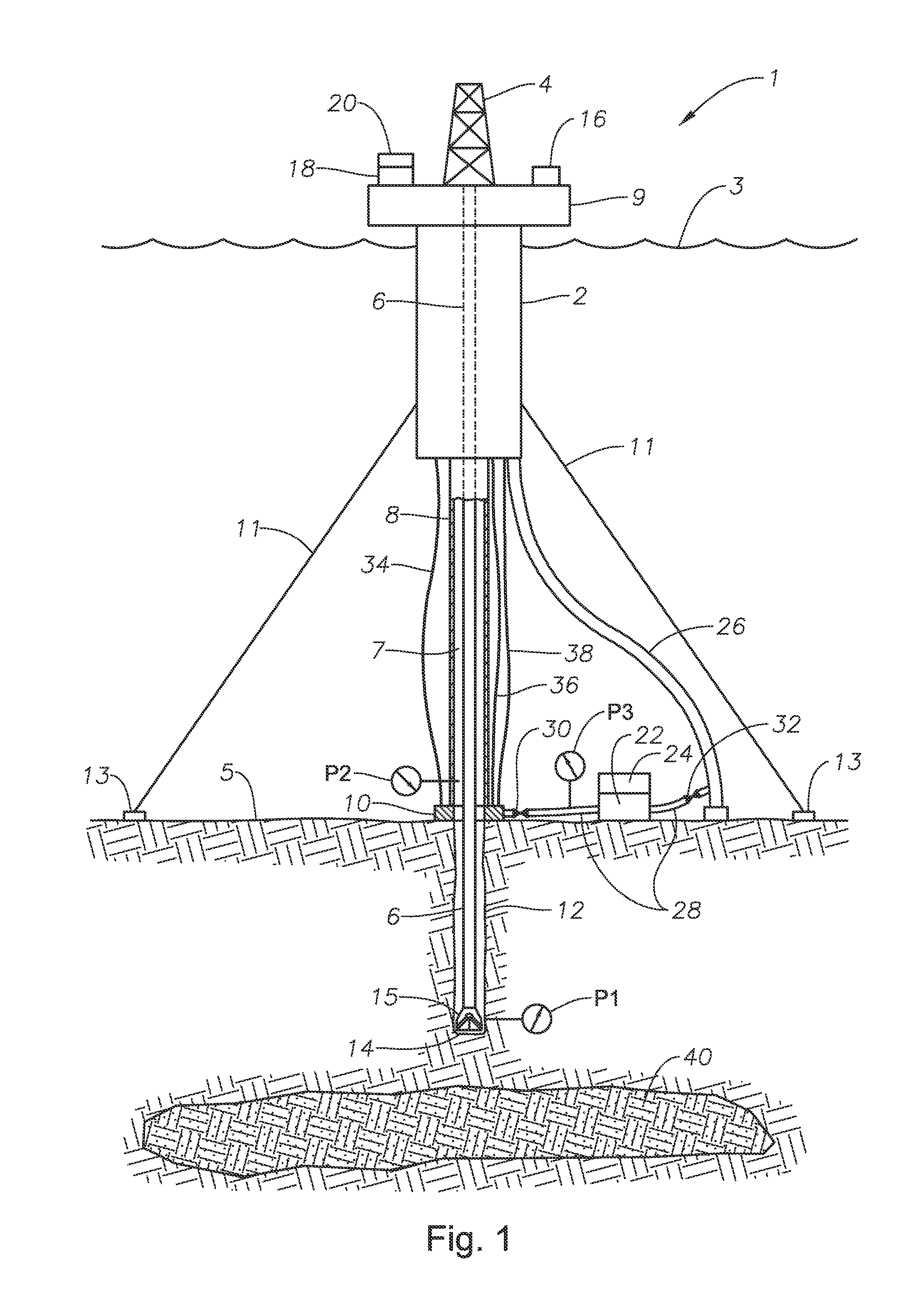
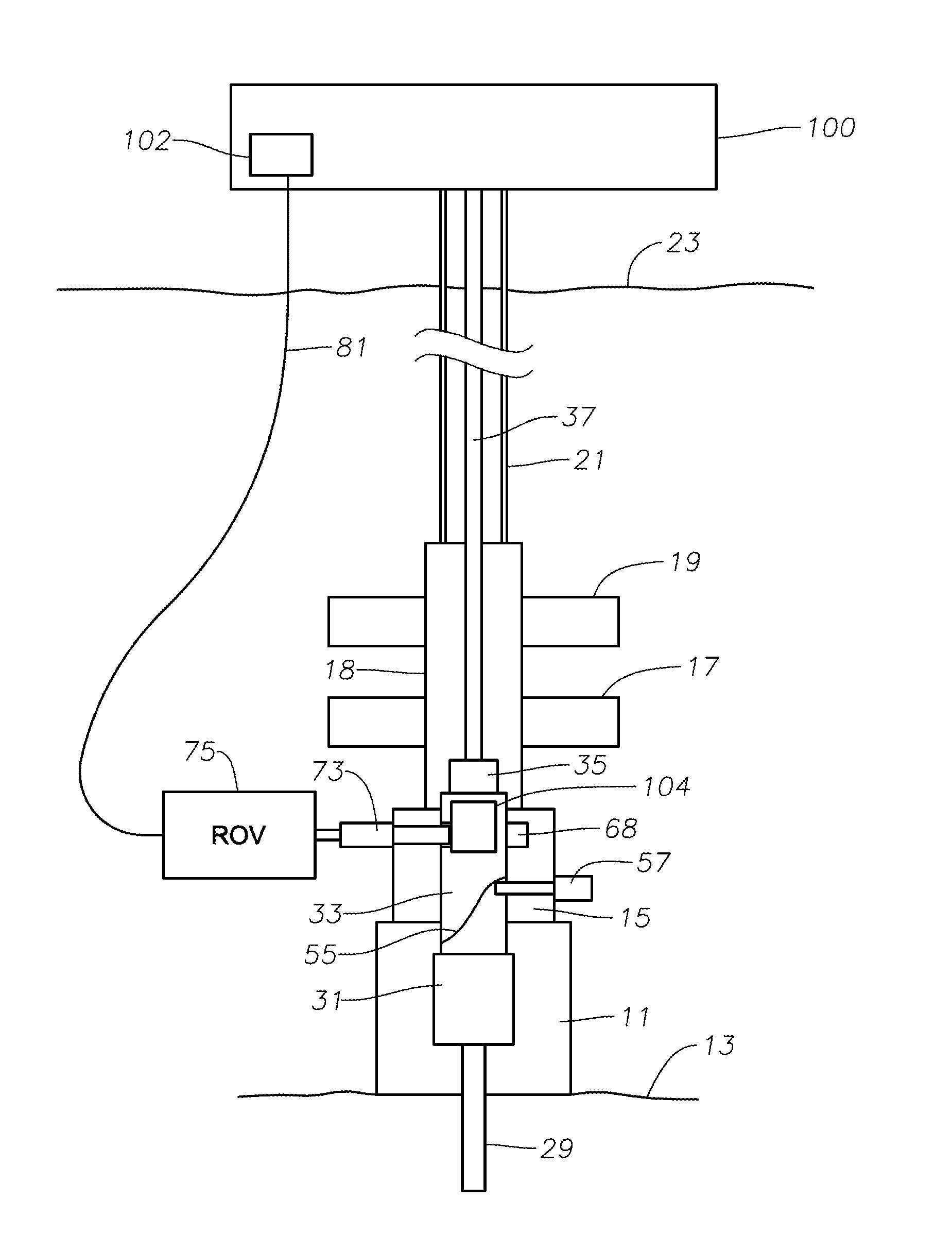
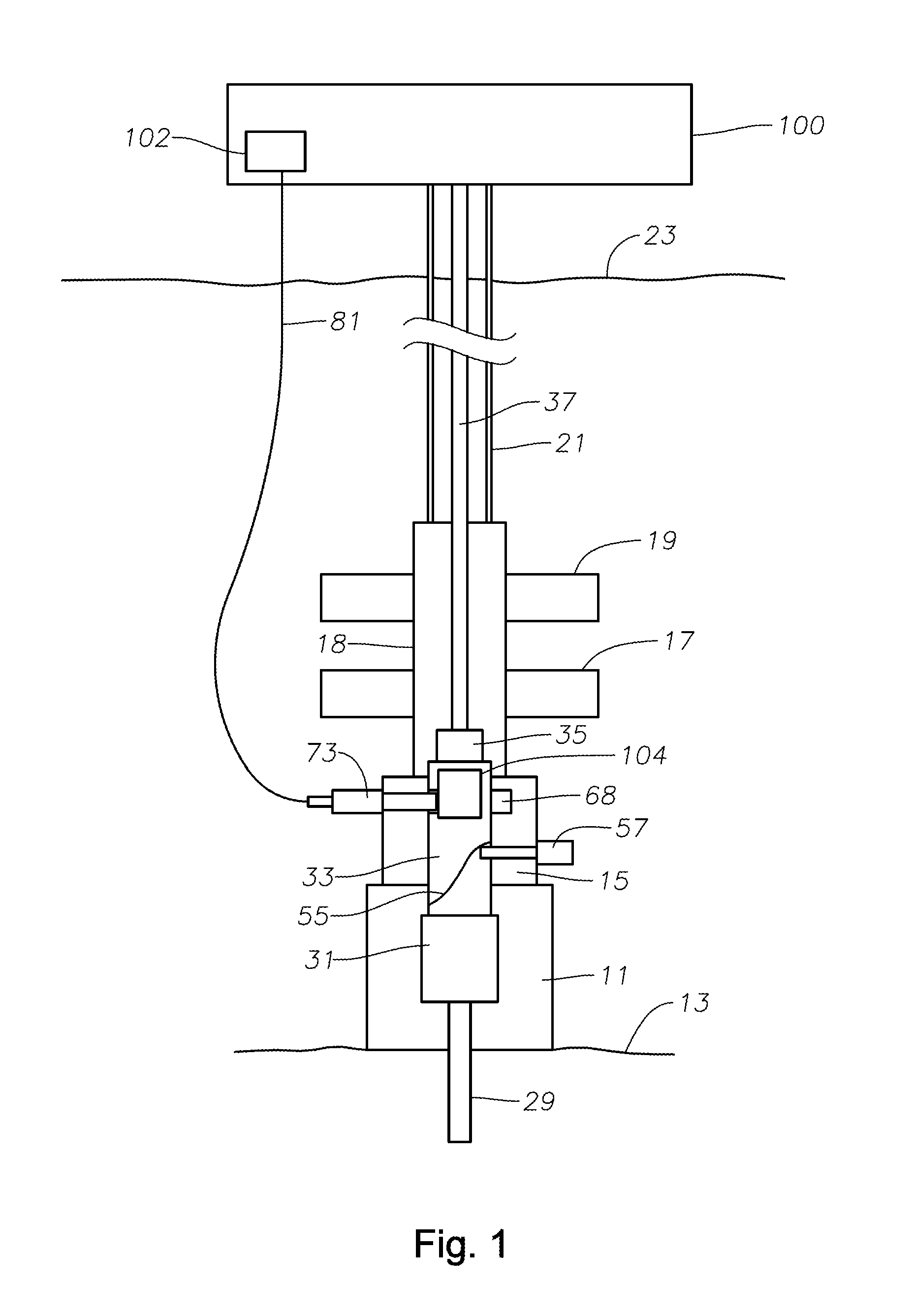
Systems and methods for subsea drilling
ActiveUS20110100710A1Improve securityReduce pressure requirementsDrilling rodsDerricks/mastsWell drillingHydrostatic head
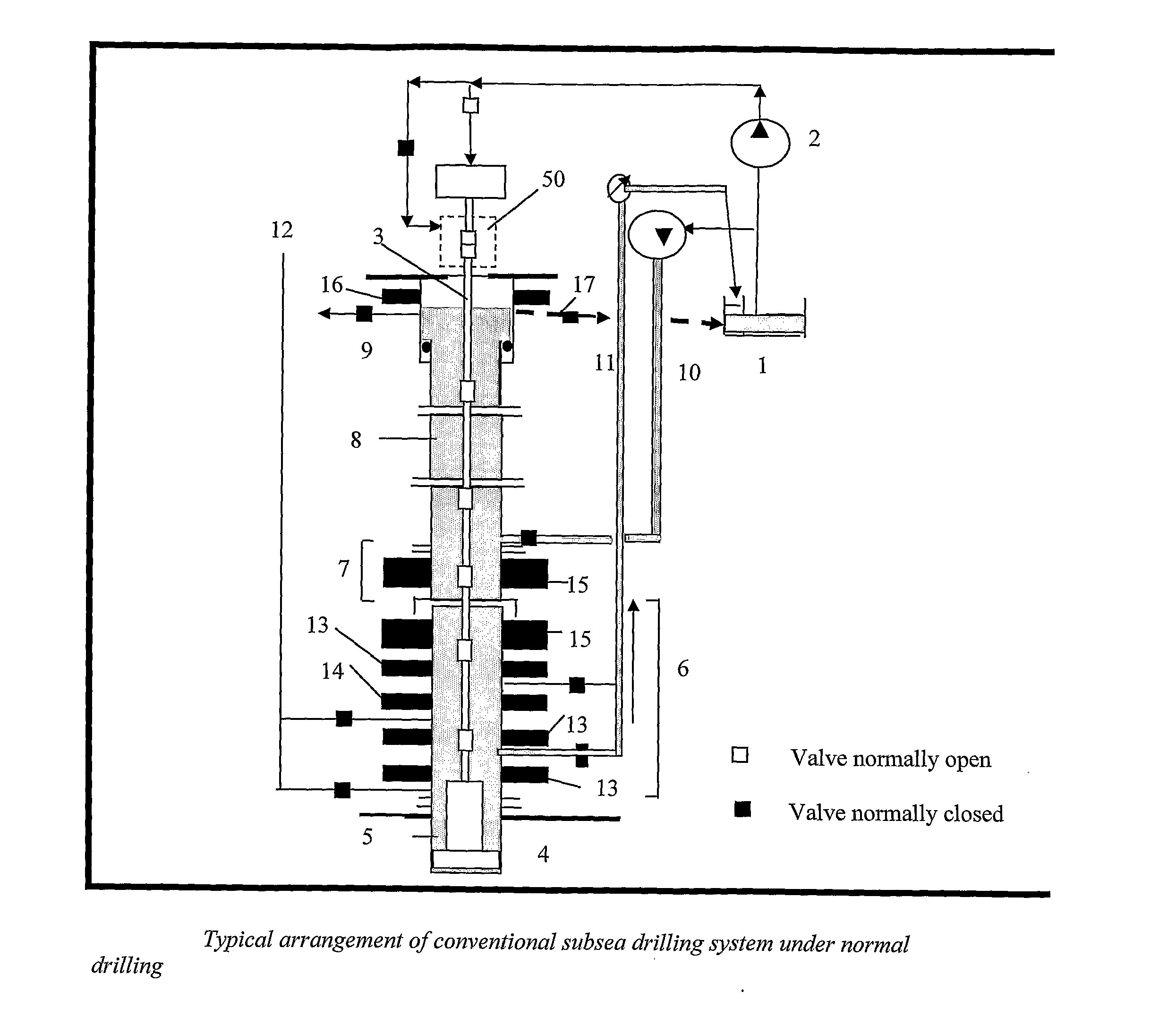
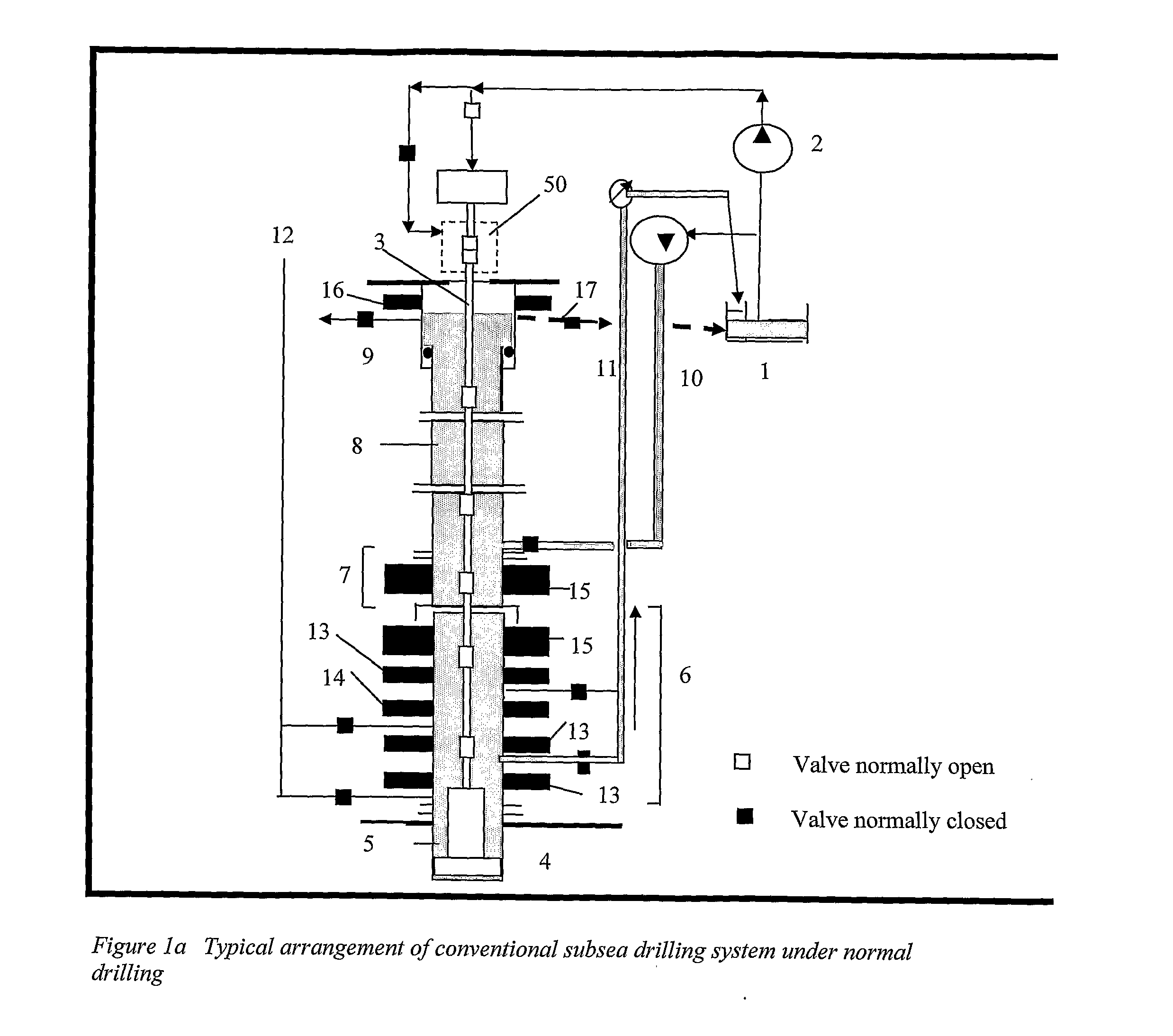
A subsea drilling method and system for controlling the drilling fluid pressure, where drilling fluid is pumped down into the borehole through a drill string and returned back through the annulus between the drill string and the well bore. The drilling fluid pressure is controlled by draining drilling fluid out of the drilling riser (8) or BOP (6) at a level between the seabed and the sea water in order to adjust the hydrostatic head of drilling fluid. The drained drilling fluid and gas is separated in a subsea separator (28) where the gas is vented to surface through a vent line (39), and the fluid is pumped to surface via pump (40).
Owner:ENHANCED DRILLING
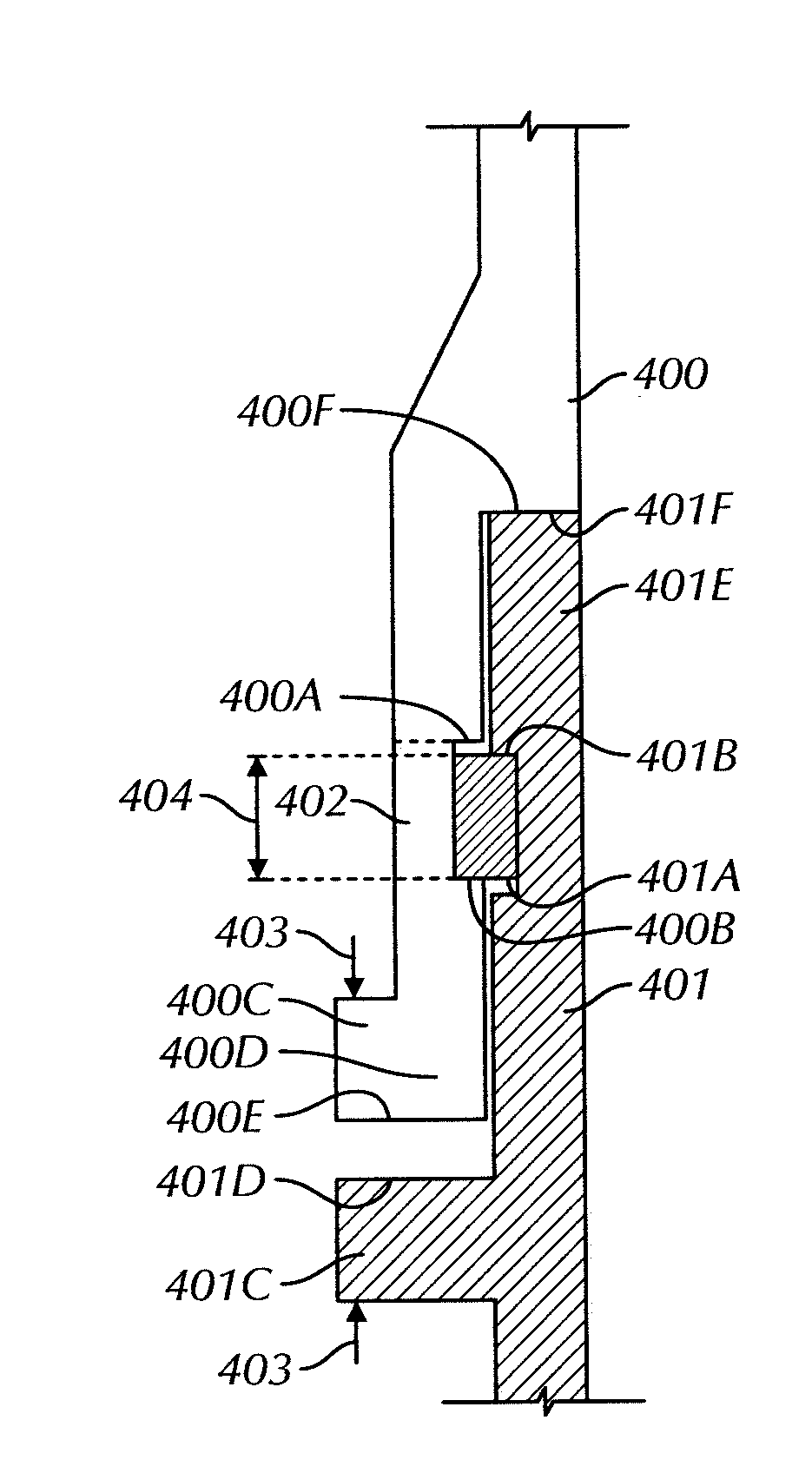
Rapid makeup drilling riser
ActiveUS7686087B2Avoid passingRapid make-upSleeve/socket jointsDrilling rodsWell drillingEngineering
A connector for connecting sections of drilling riser pipe wherein a first riser contains a pin assembly with an external first grooved profile and a second riser contains a housing assembly. An internal split pivoting latch segment assembly carried by the housing assembly contains a second grooved profile adapted to mate to the first grooved profile and a split actuation ring movably carried by the housing assembly forces the second grooved profile of the latch segment assembly into engagement with the first grooved profile of the pin assembly. A plurality of retraction links engage an upper edge of the latch segment assembly to disengage the second grooved profile of the latch segment assembly from the first grooved profile of the pin assembly if the risers are to be disconnected.
Owner:VETCO GRAY
System and method for drilling a subsea well
ActiveUS20120227978A1Increase the differential pressureFluid removalUnderwater drillingBottom hole pressureSuction stress
A subsea mud pump can be used to return heavy drilling fluid to the surface. In order to provide a less stringent requirement for such a pump and to better manage the bottom hole pressure in the case of a gas kick or well control event, the gas should be separated from the drilling fluid before the drilling fluid enters the subsea mud pump and the pressure within the separating chamber. The mud pump suction should be controlled and kept equal or lower than the ambient seawater pressure. This can be achieved within the cavities of the subsea BOP by a system arrangement and methods explained. This function can be used with or without a drilling riser connecting the subsea BOP to a drilling unit above the body of water.
Owner:ENHANCED DRILLING
Method and device for controlling drilling fluid pressure
Owner:ENHANCED DRILLING
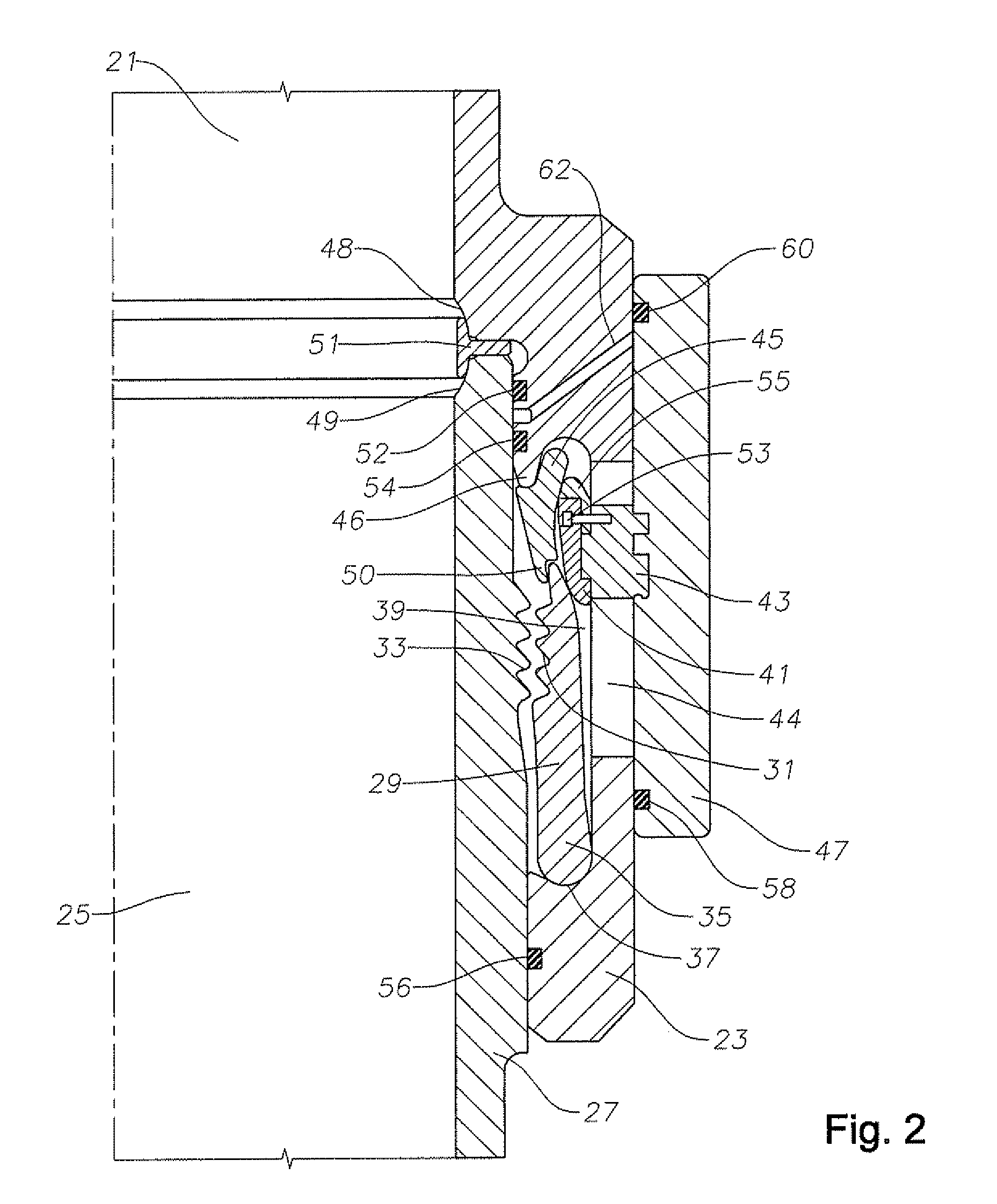
System and method for connecting tubular members
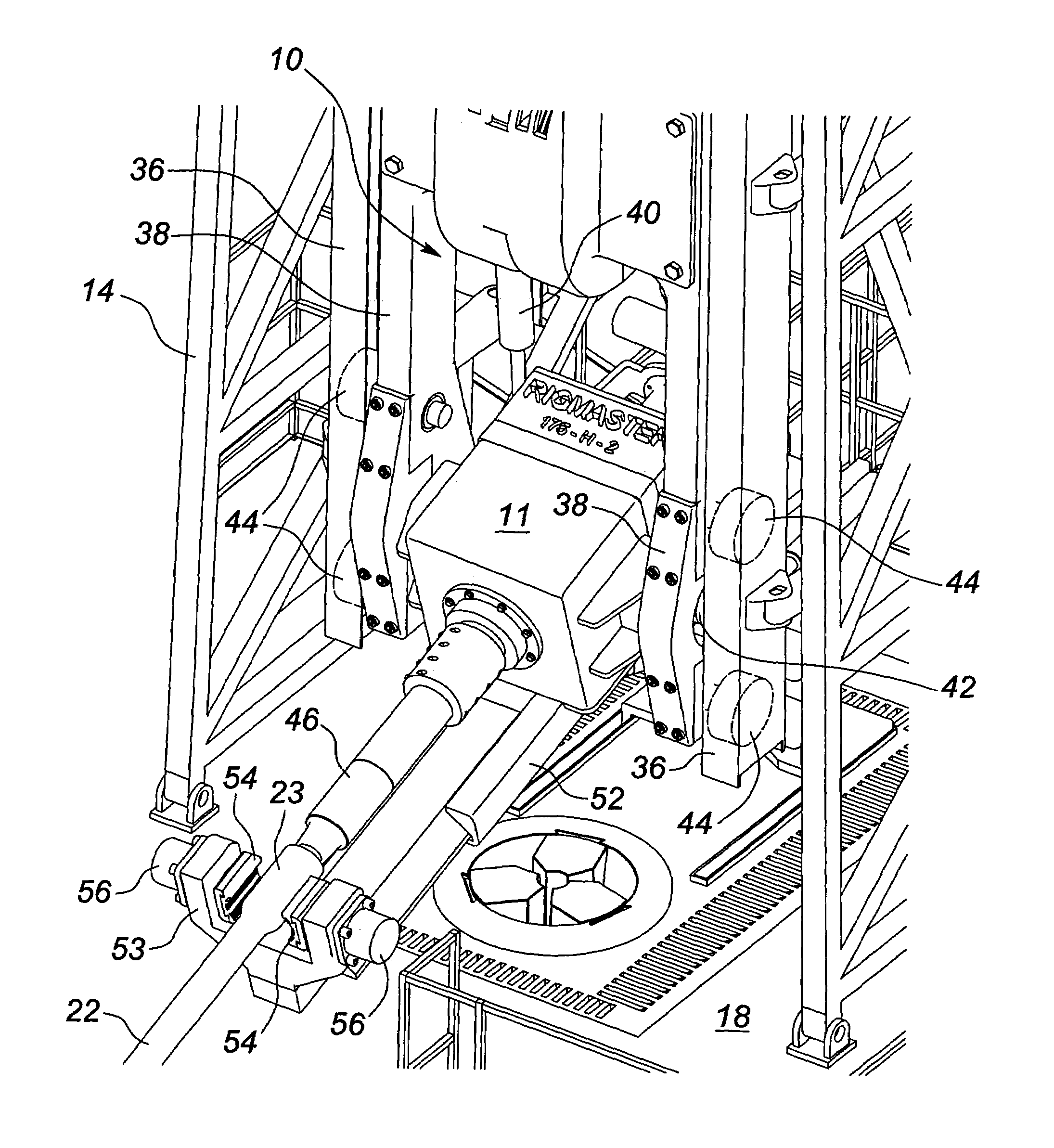
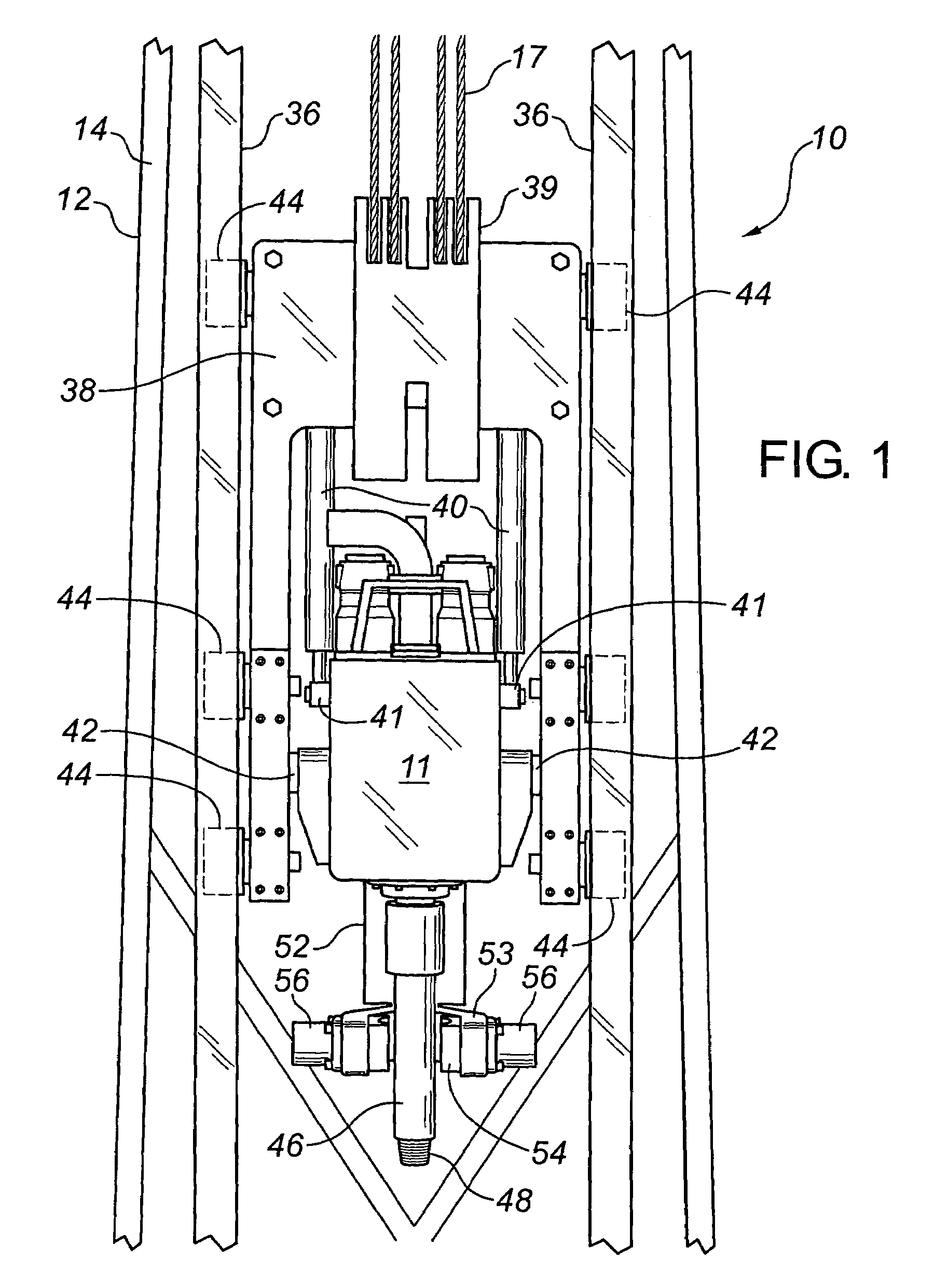
A technique for securing drilling riser joints in a drilling riser string is presented. The drilling riser joints have a tubular housing that has a box configuration on one end and a pin configuration on the other end. The drilling riser string is assembled by connecting the pin end of one drilling riser joint to the box end of an adjoining drilling riser joint. A moveable ring is used to connect adjoining drilling riser joints. The moveable ring is used to drive a fastener of one drilling riser joint against the adjoining drilling riser joint. The moveable ring is driven axially from a position where the fastener is not engaged against the adjoining drilling riser joint to a position where the fastener is engaged against the adjoining drilling riser joint. A latch is used to prevent the moveable ring from moving inadvertently from the second position.
Owner:HYDRIL USA DISTRIBUTION LLC
Fluid Connection To Drilling Riser
A riser for use in boring a subsea wellbore having a gooseneck assembly connected onto the riser. The gooseneck assembly has an outlet that couples with a flowline on the riser and a connector assembly that selectively decouples the gooseneck assembly from the flowline. A release member, such as a wire, cable, or rod, is attached to the connector so the connector assembly can be actuated by manipulating the release member from a remote location.
Owner:DETAIL DESIGNS
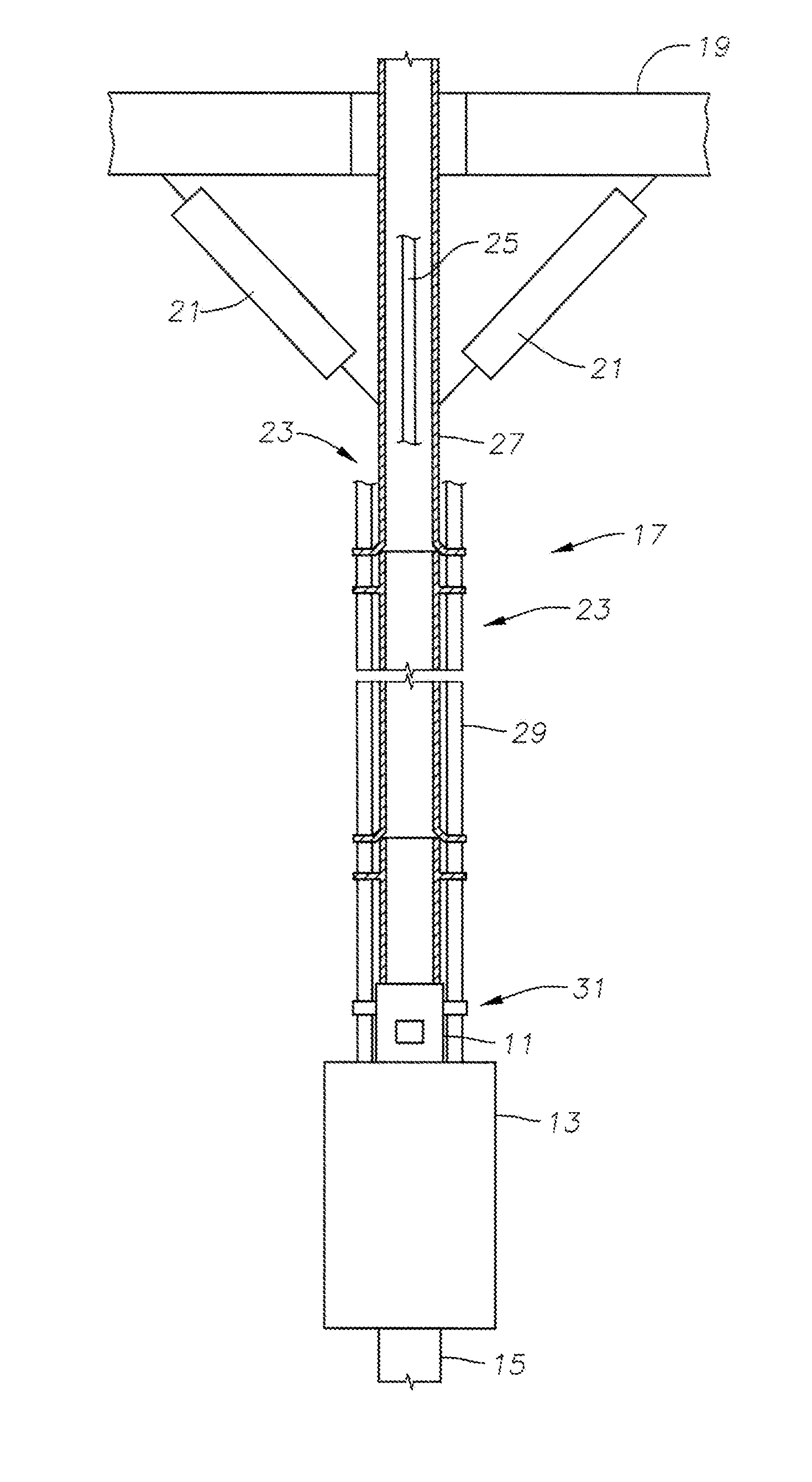
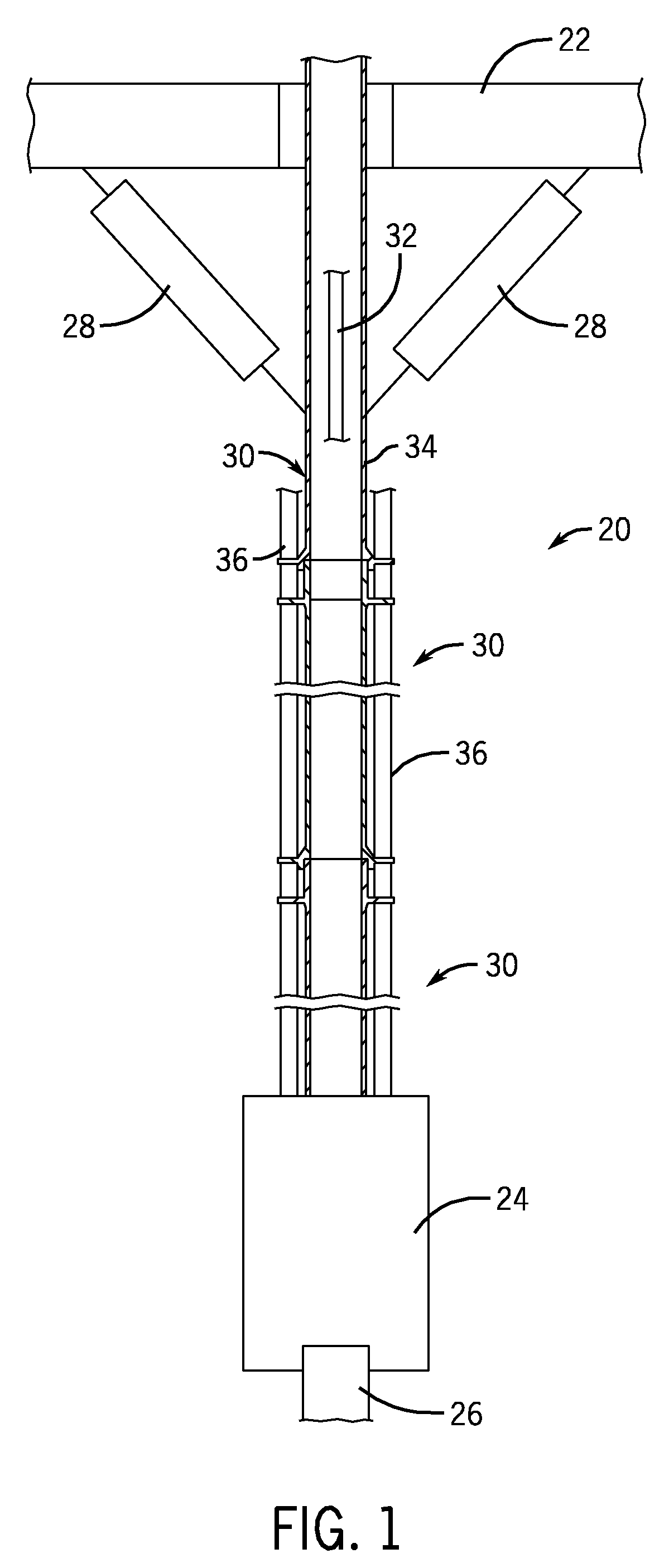
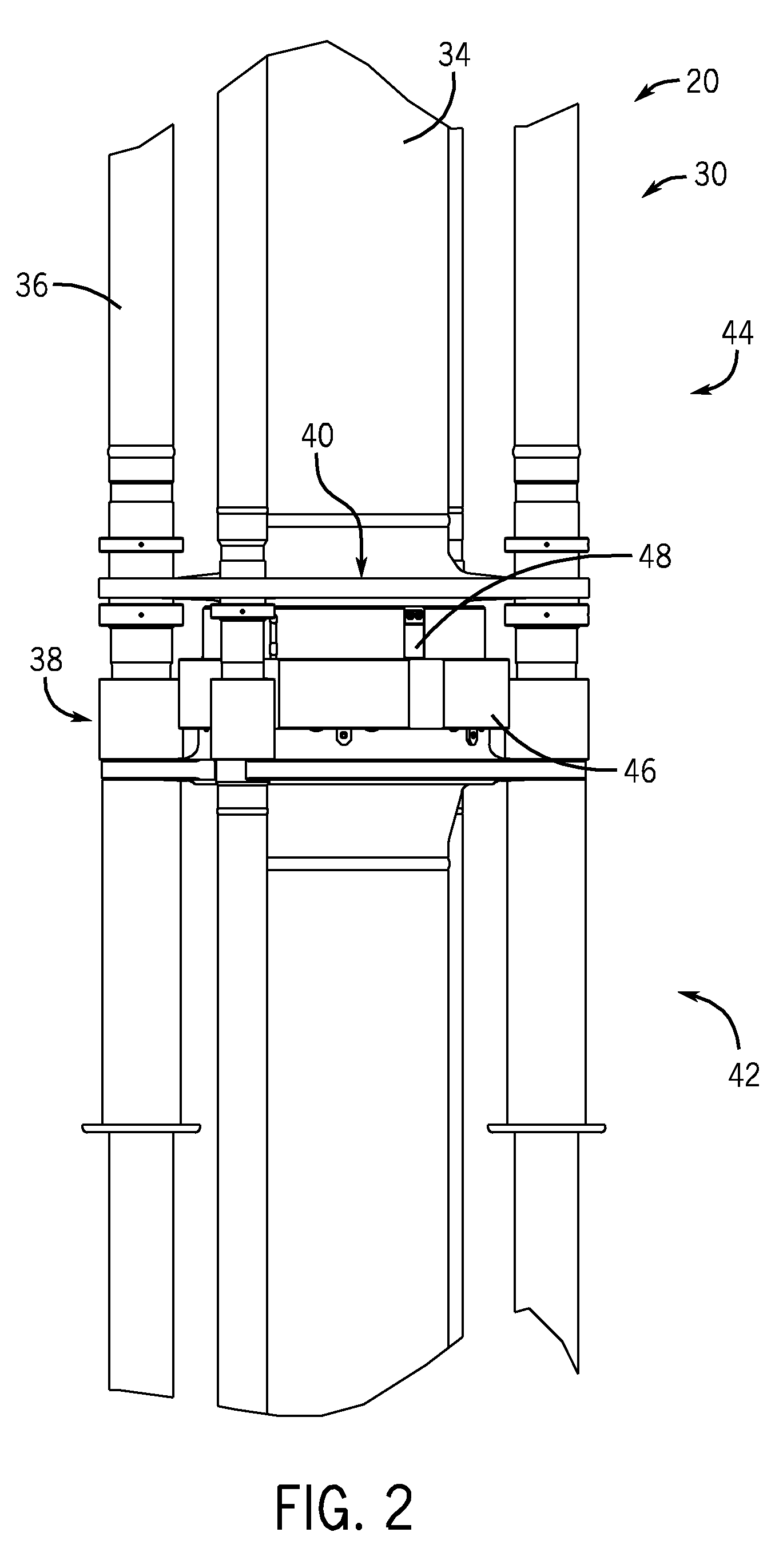
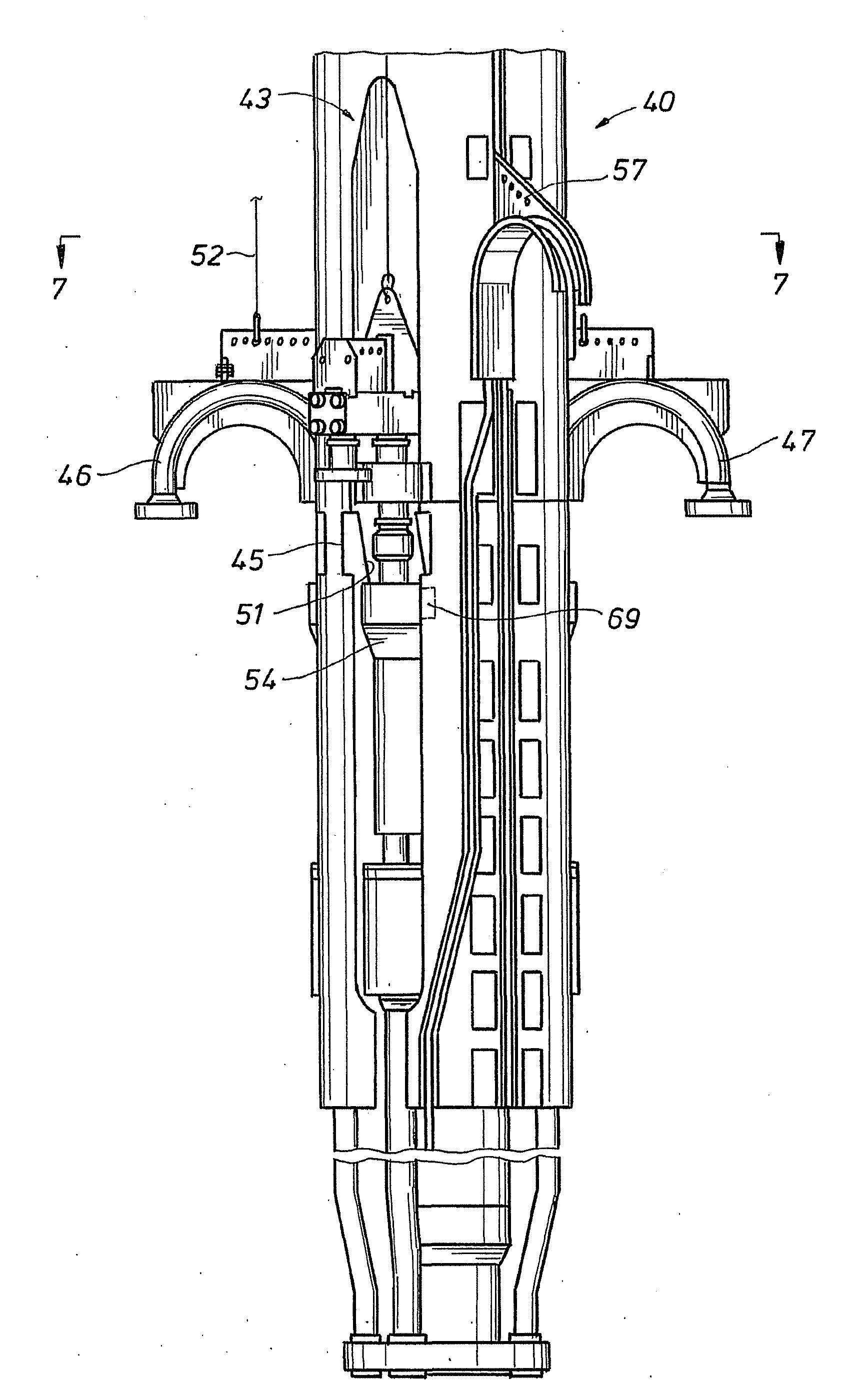
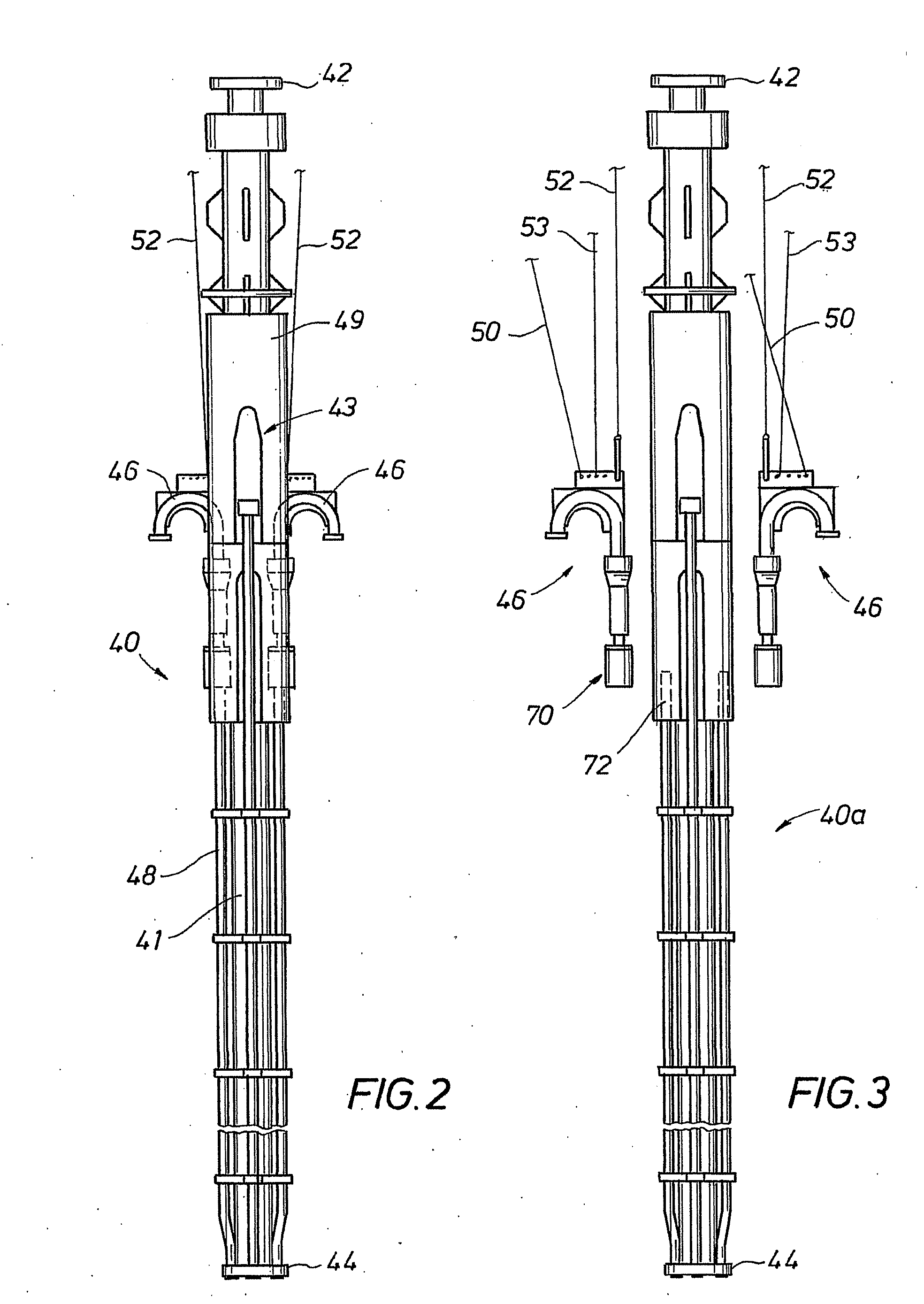
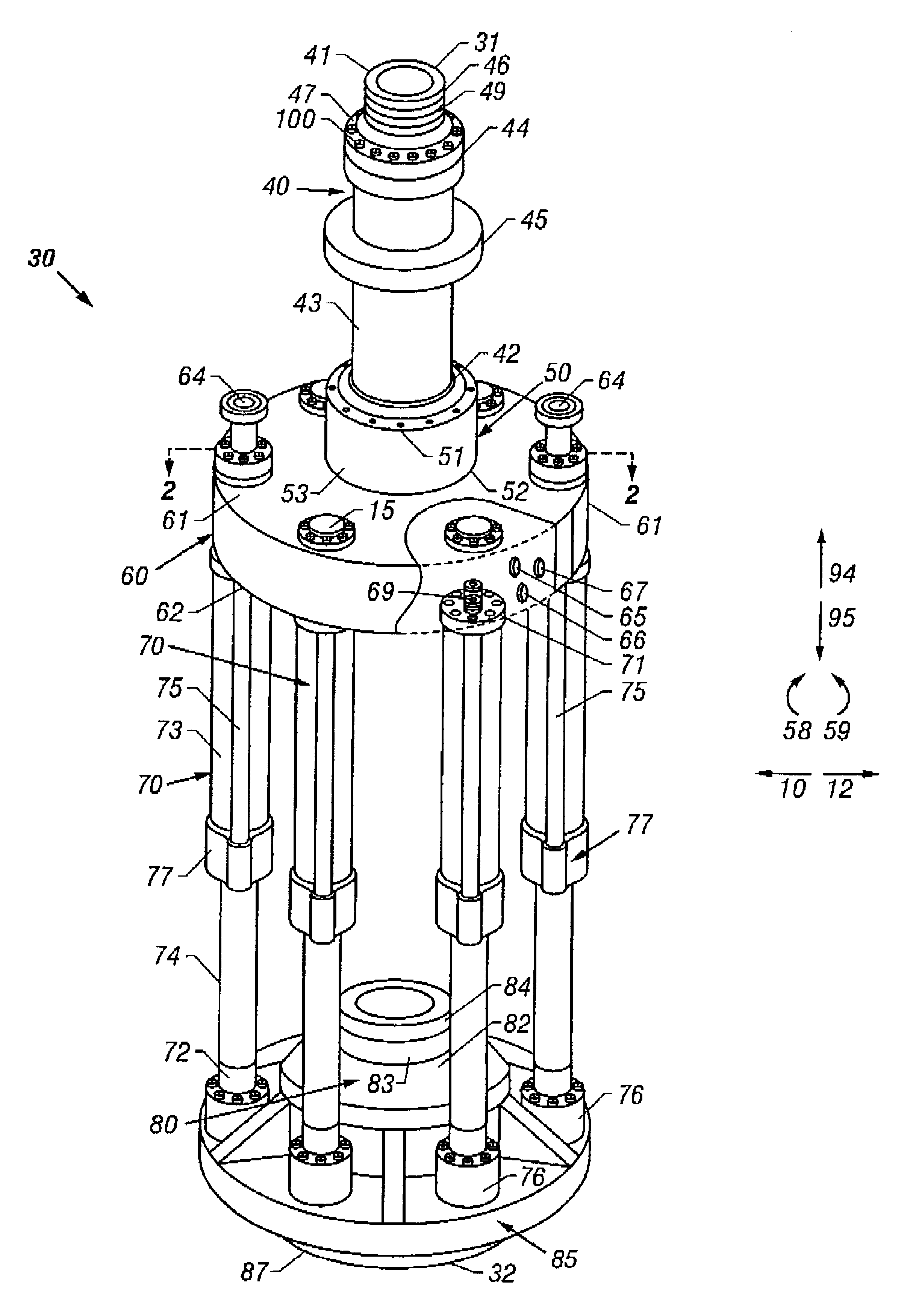
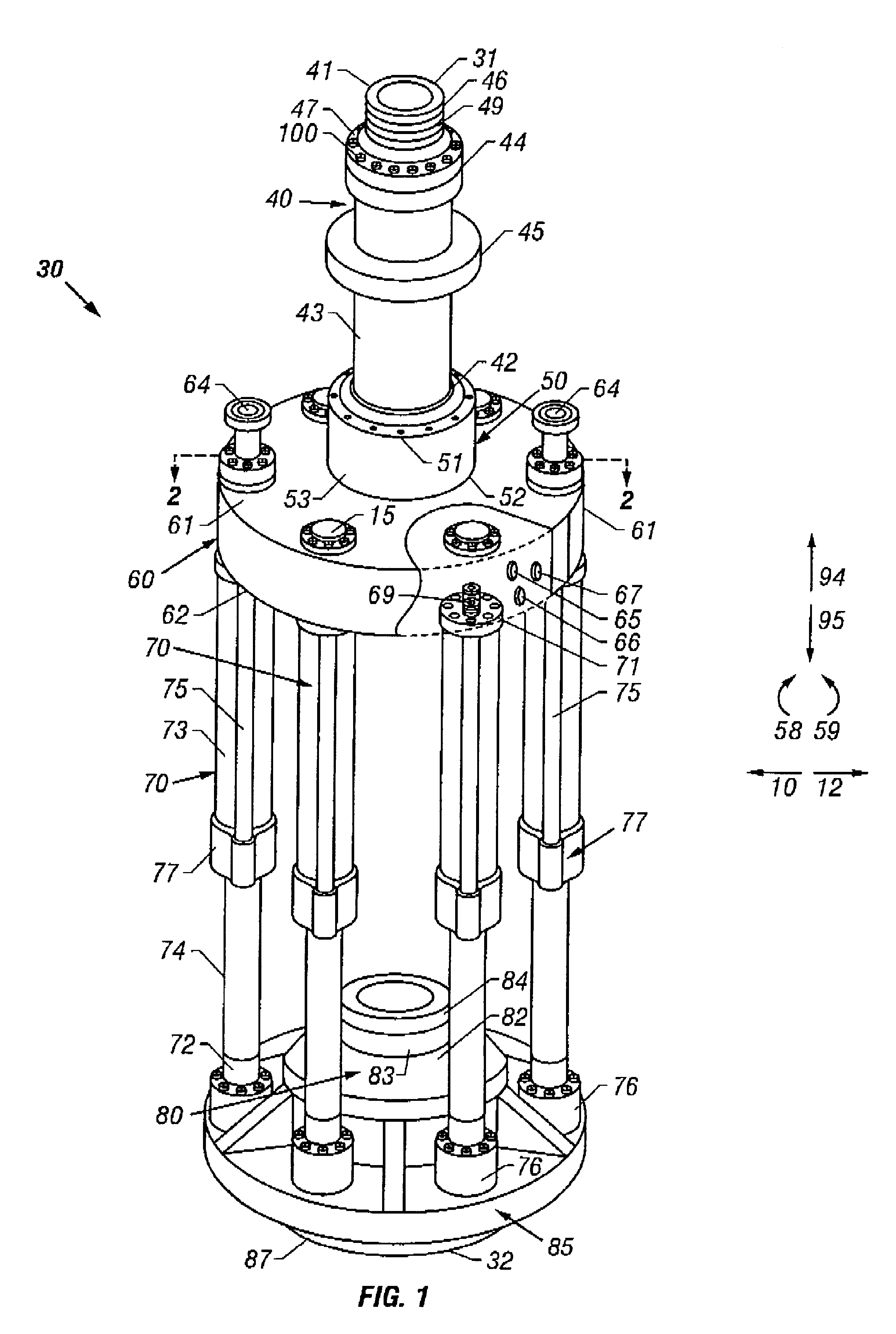
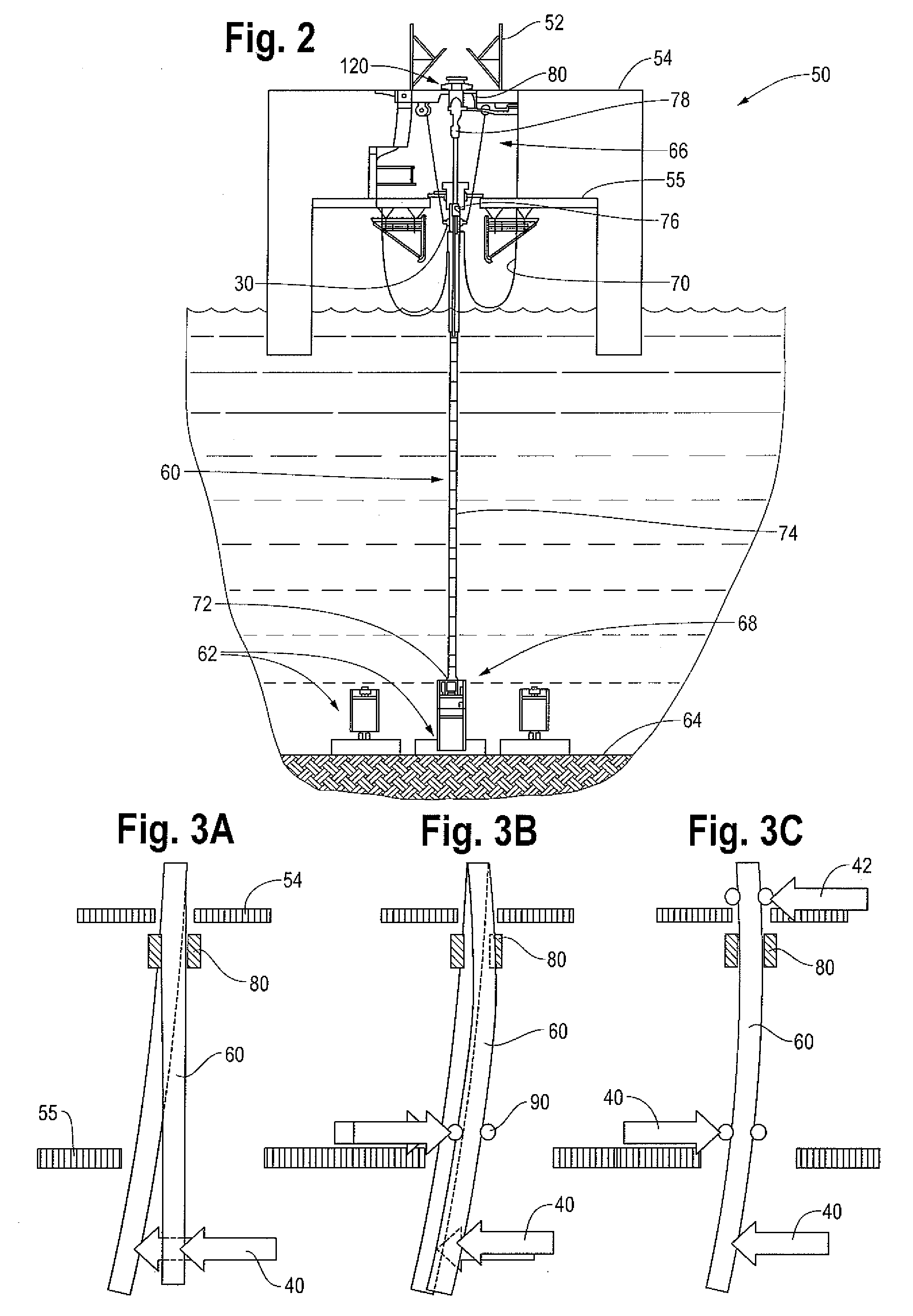
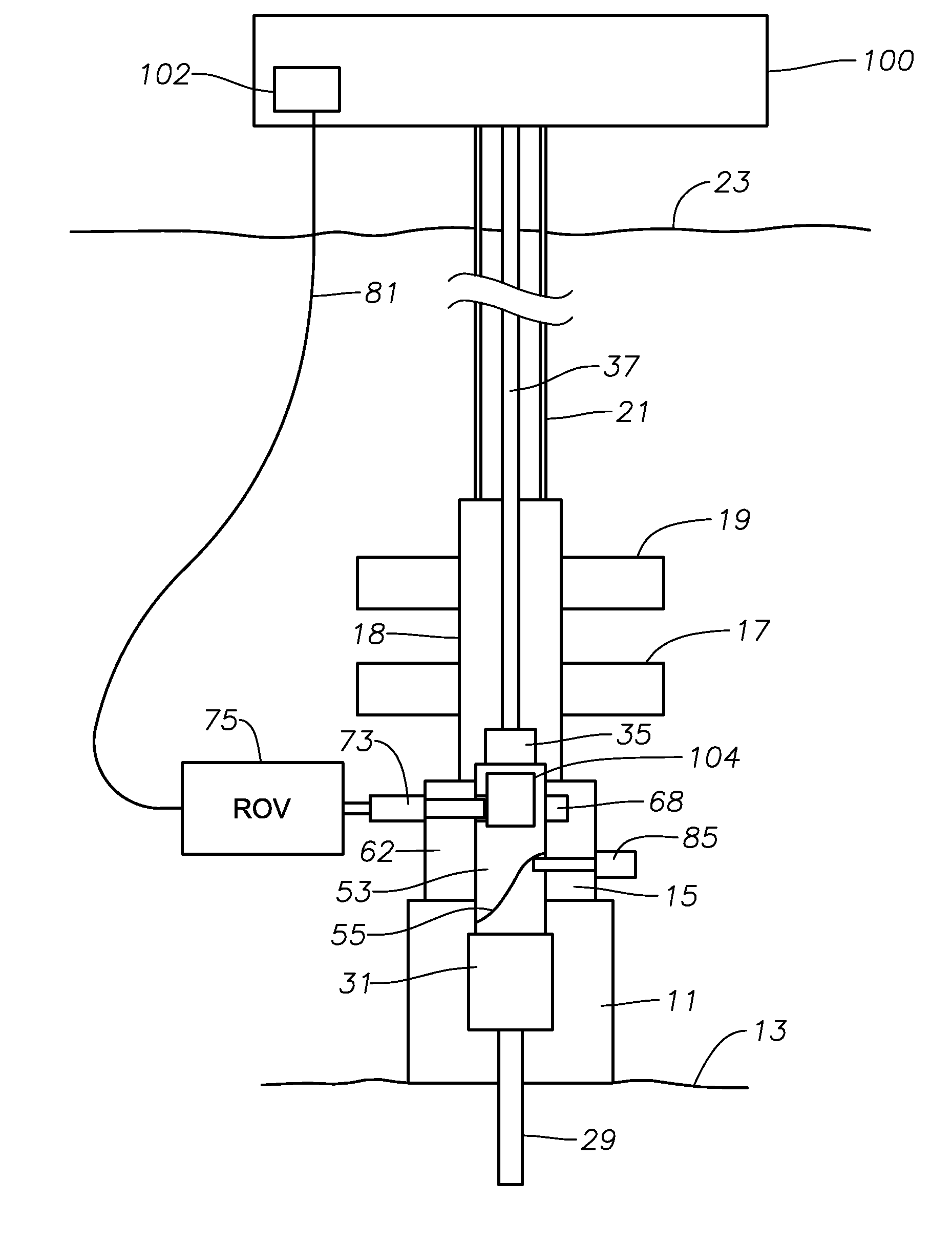
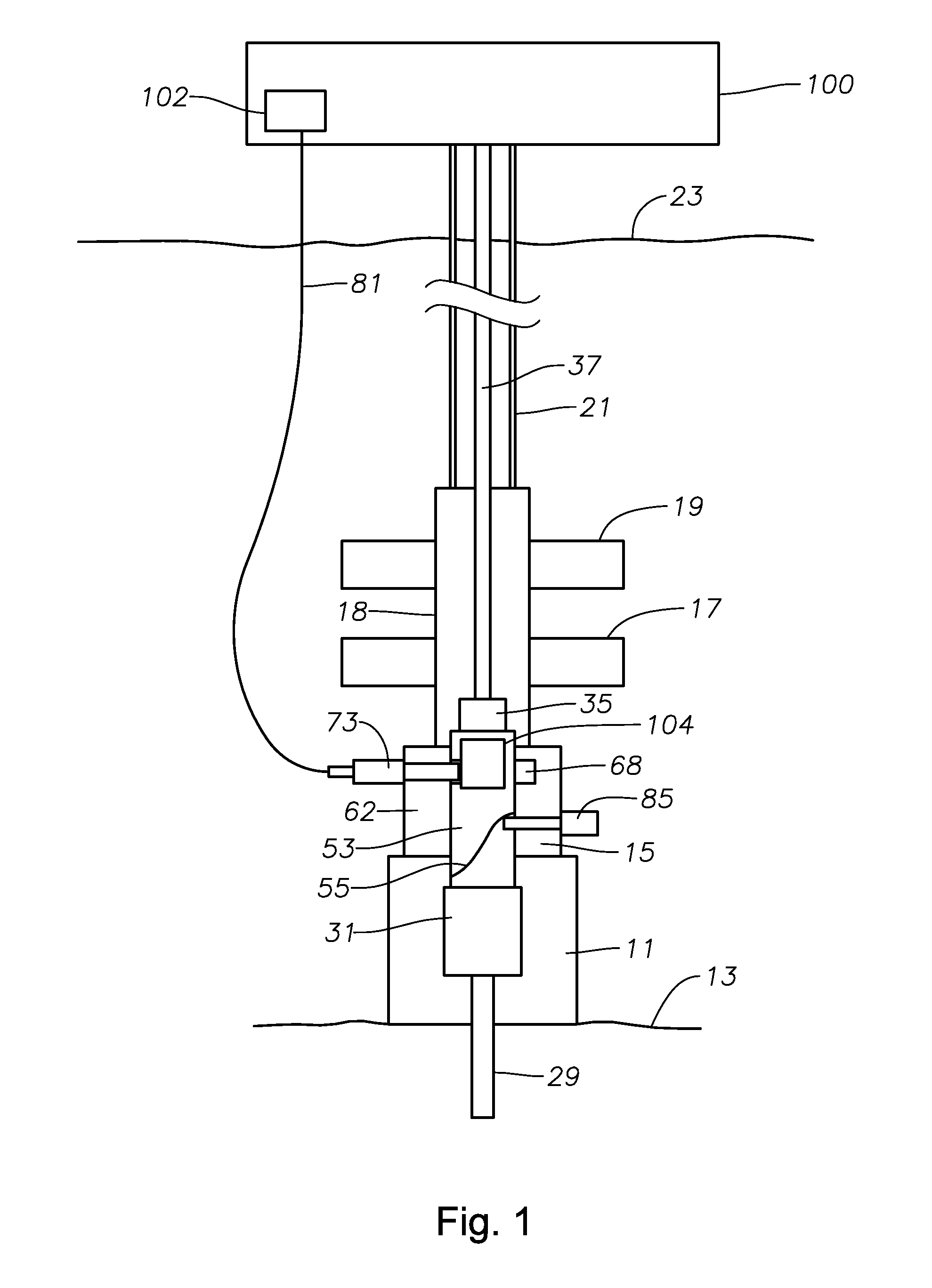
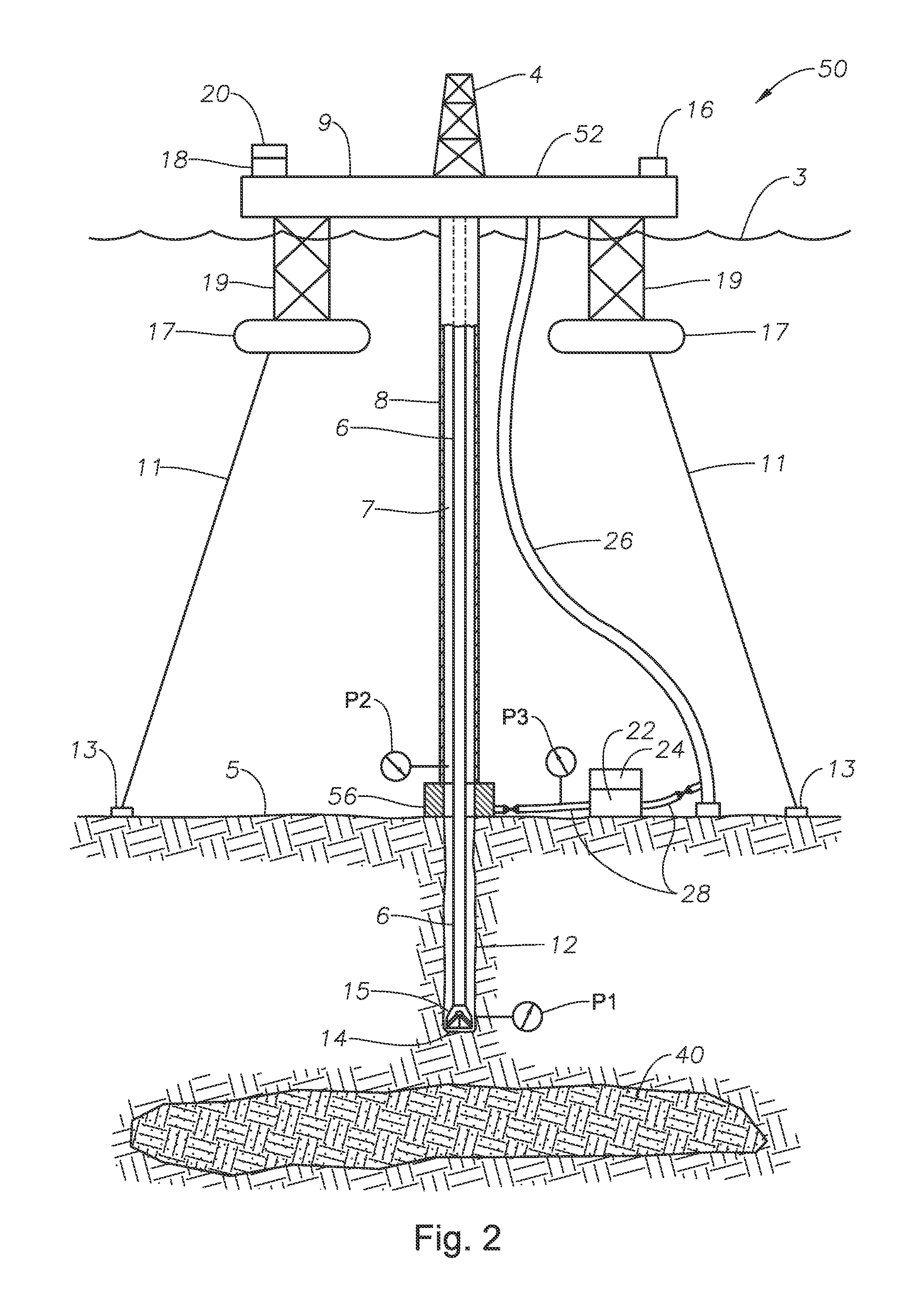
Co-linear tensioner and methods for assembling production and drilling risers using same
A tensioner for providing a conduit, e.g., drilling and production riser strings, from a floating vessel at the surface of the ocean to the blowout preventer stack, production tree, or other assembly which is connected to the wellhead at the sea floor. The tensioner compensates for vessel motion induced by wave action and heave and maintains a variable tension to the riser string alleviating the potential for compression and thus buckling or failure of the riser string. The tensioner of the present invention preferably includes at least one mandrel having at least one hang-off donut; at least one upper flexjoint swivel assembly, at least one radially ported manifold, and at least one tensioning cylinder co-linearly combined in a single unit. Methods for assembling risers are also disclosed.
Owner:CONTROL FLOW
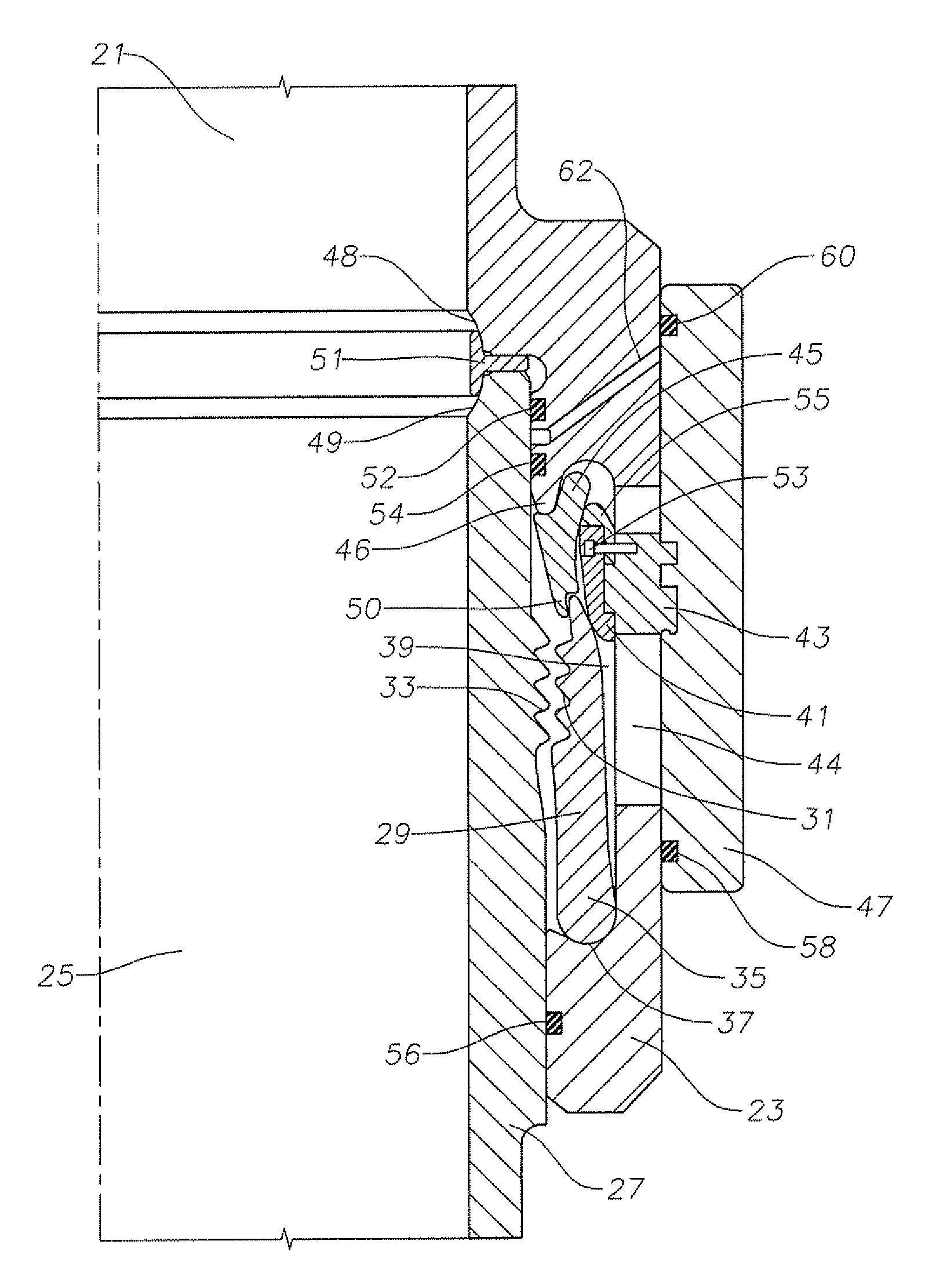
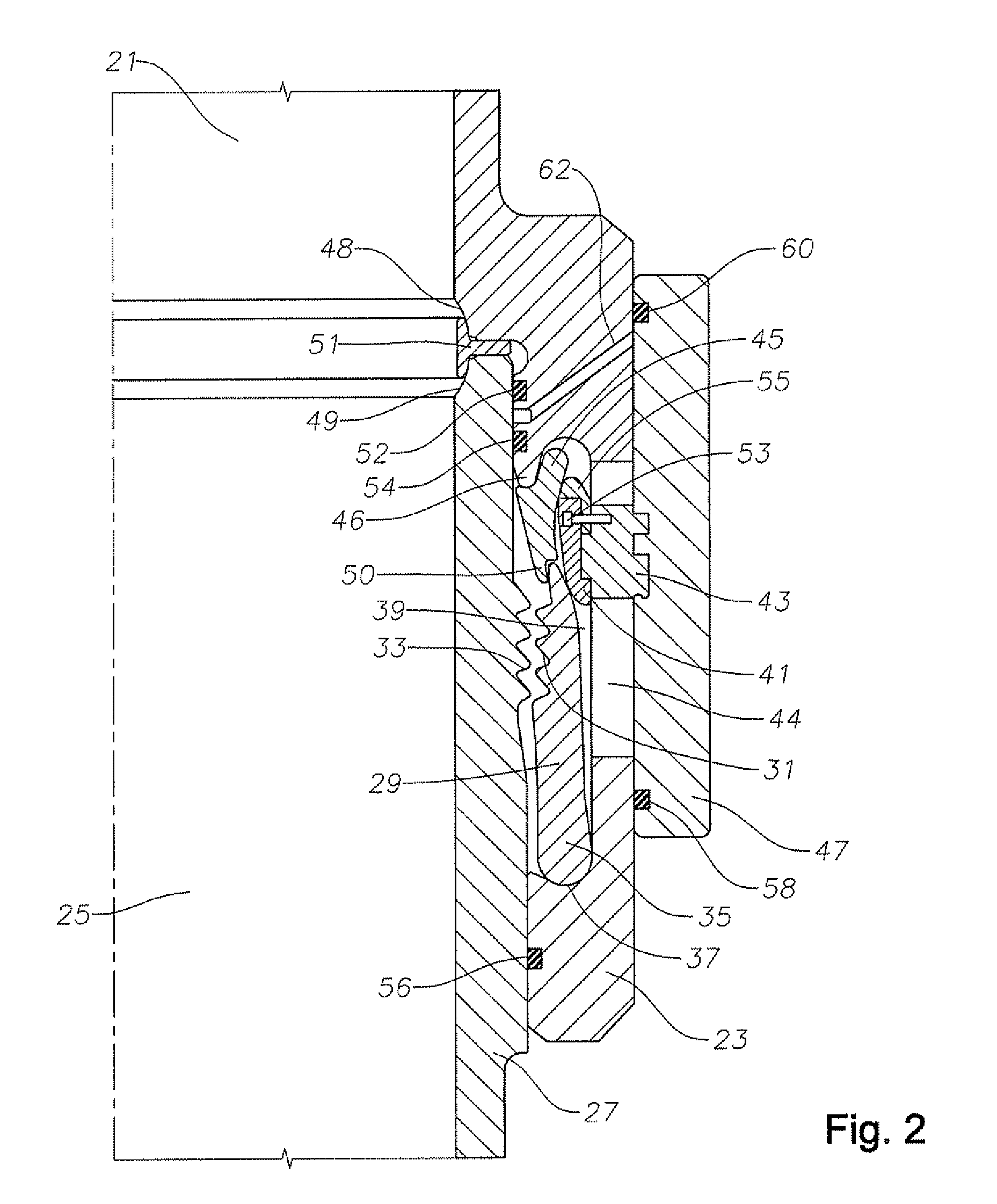
Underbalanced marine drilling riser
A riser assembly for offshore drilling has an inner conduit suspended within an outer riser. A seal assembly seals an annular space between the inner conduit and the riser at the lower end of the inner conduit. The seal assembly has a pressure area that is independent of the inner conduit, so that any forces acting on the assembly due to pressure in the annulus below the seal assembly pass through the assembly to the riser and not to the inner conduit.
Owner:VETCO GRAY LLC
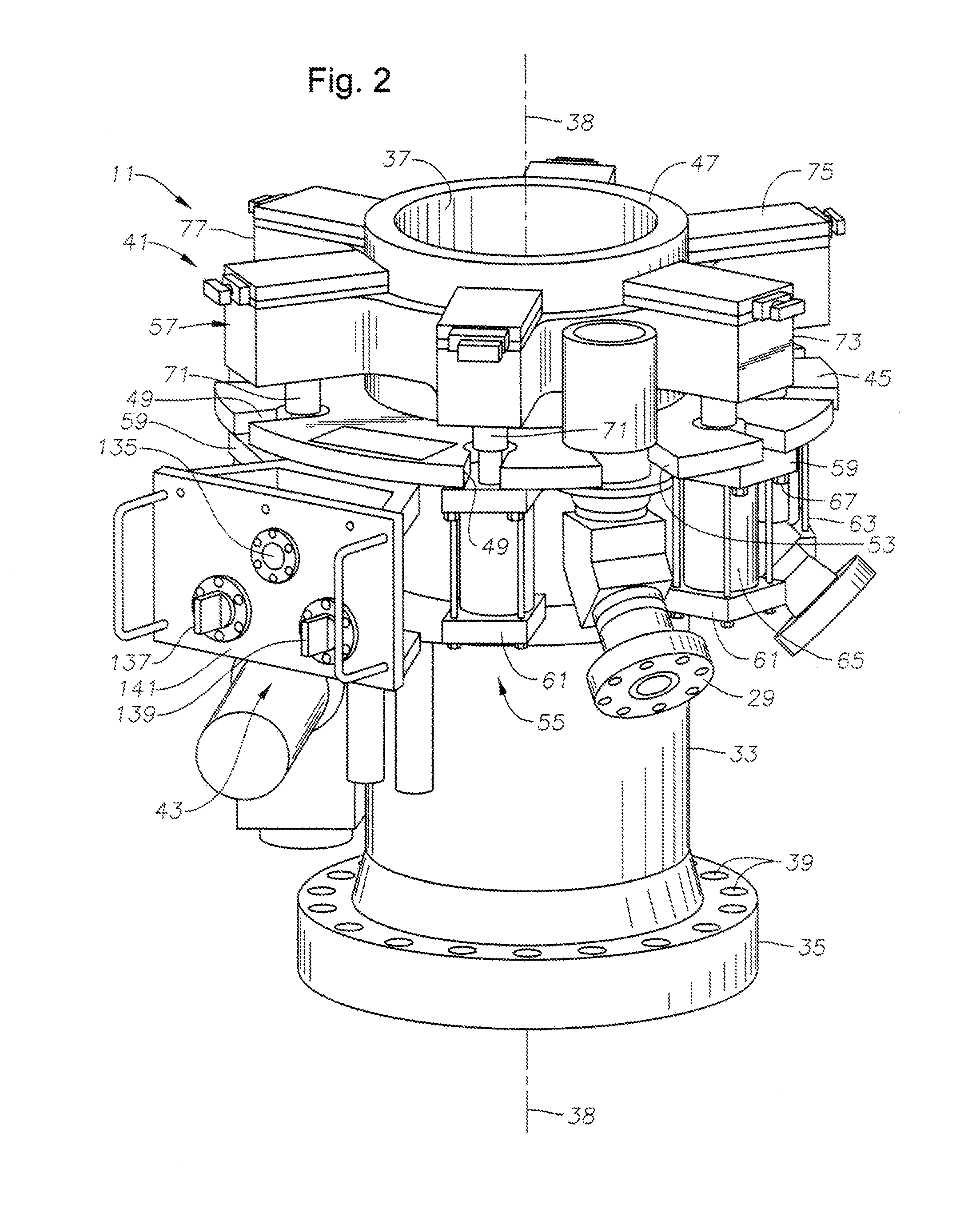
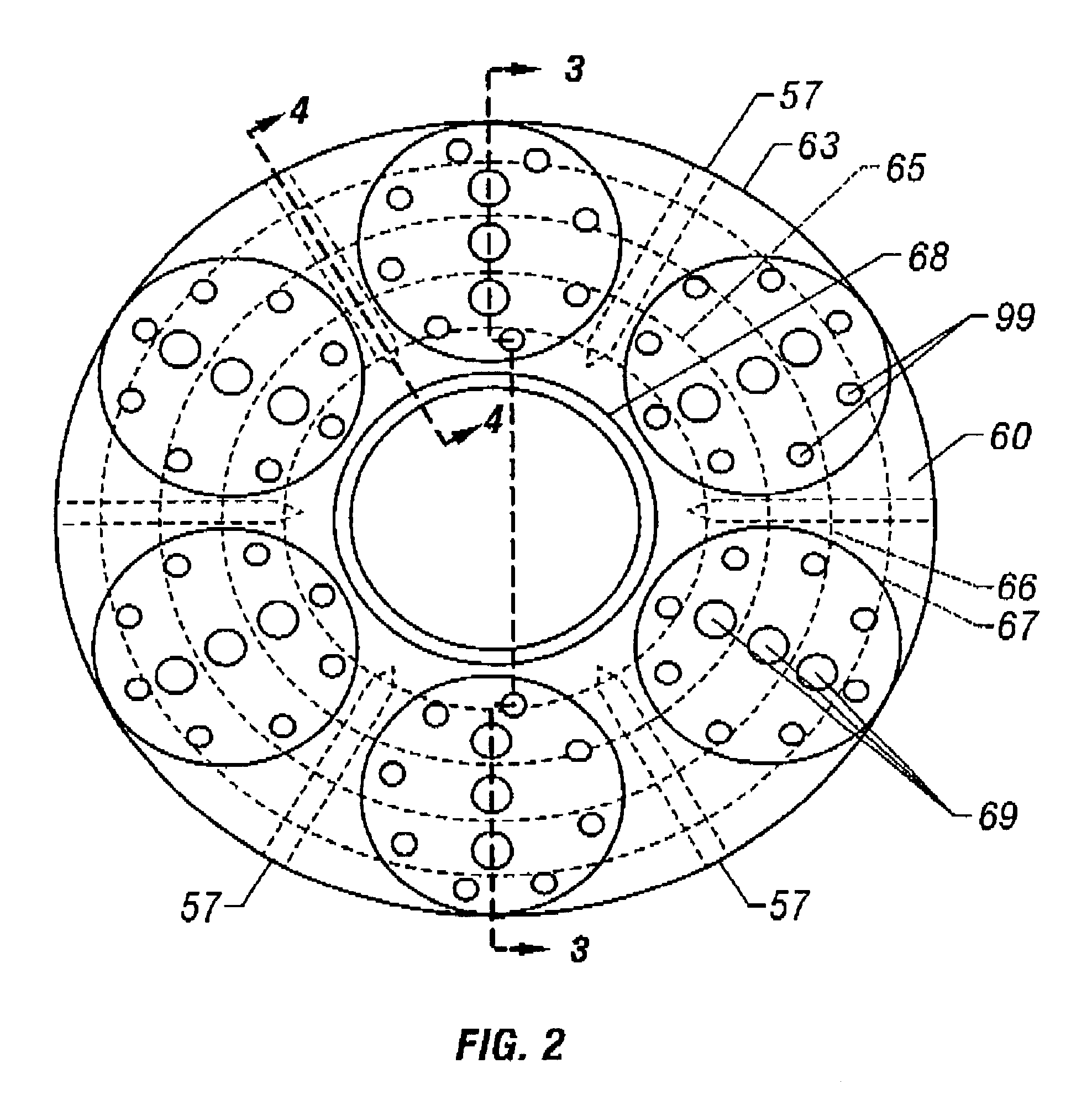
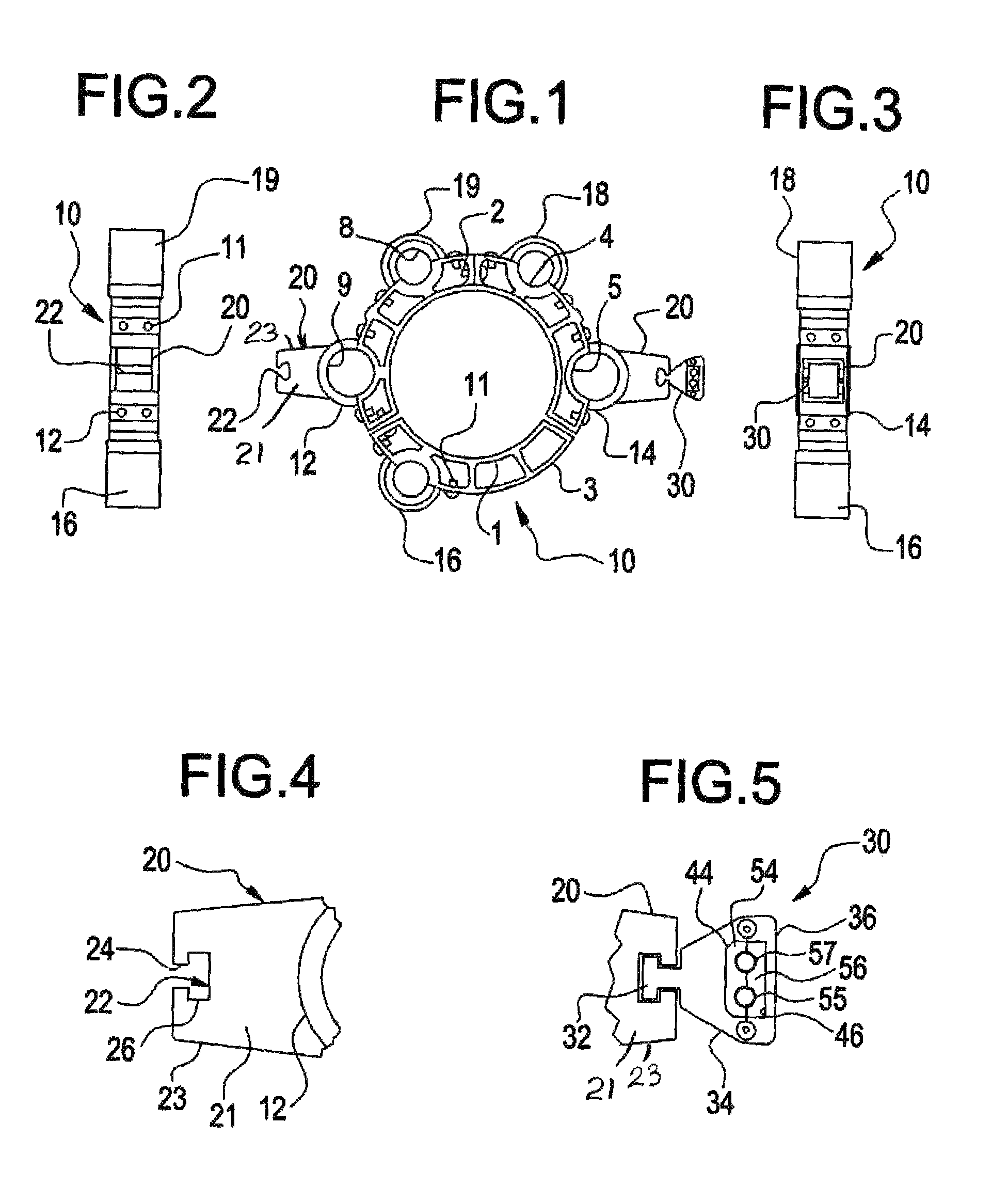
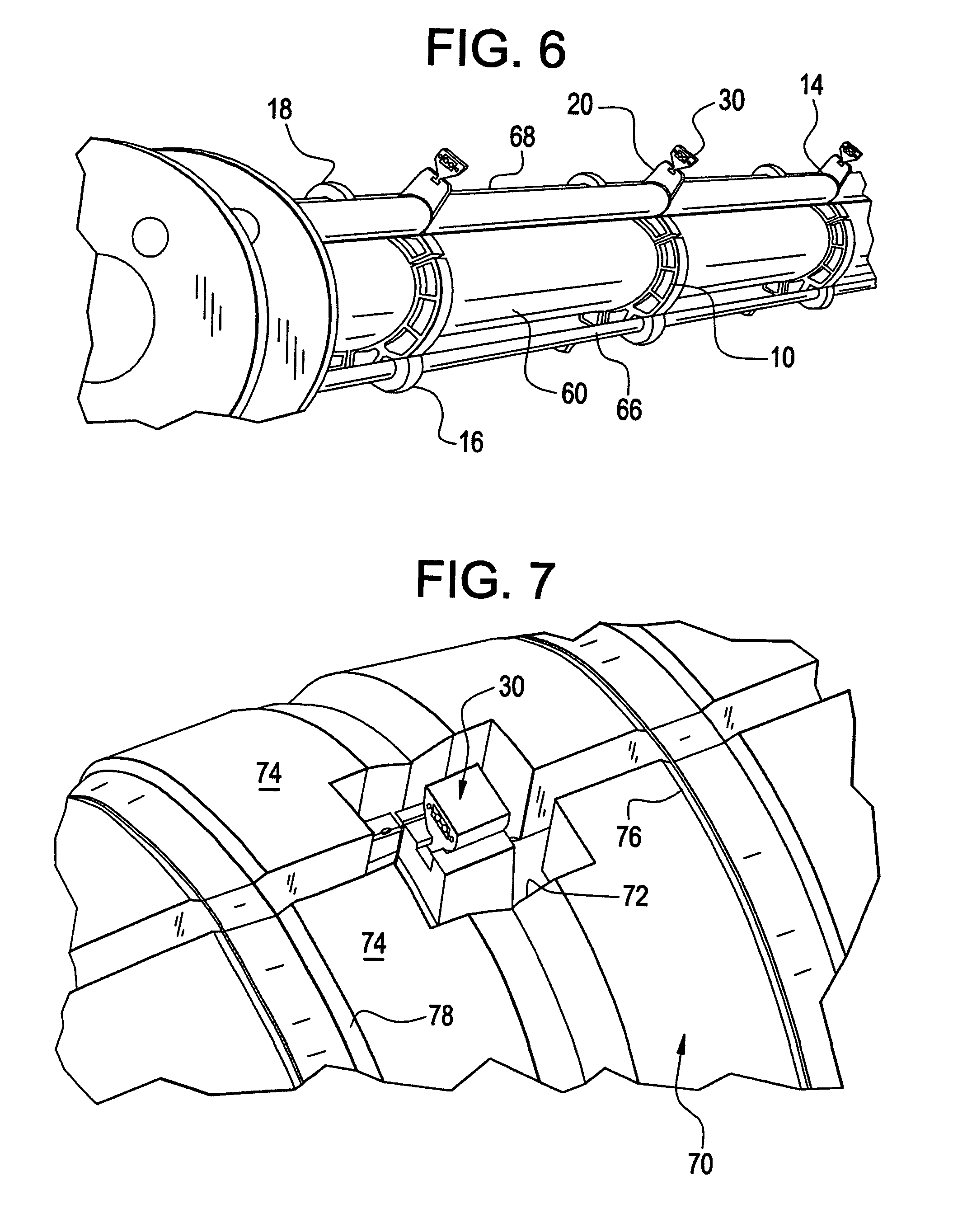
Riser Centralizer System (RCS)
ActiveUS20100147528A1Avoid damageReducing to facilityDrilling rodsFluid removalDrilling riserPetroleum engineering
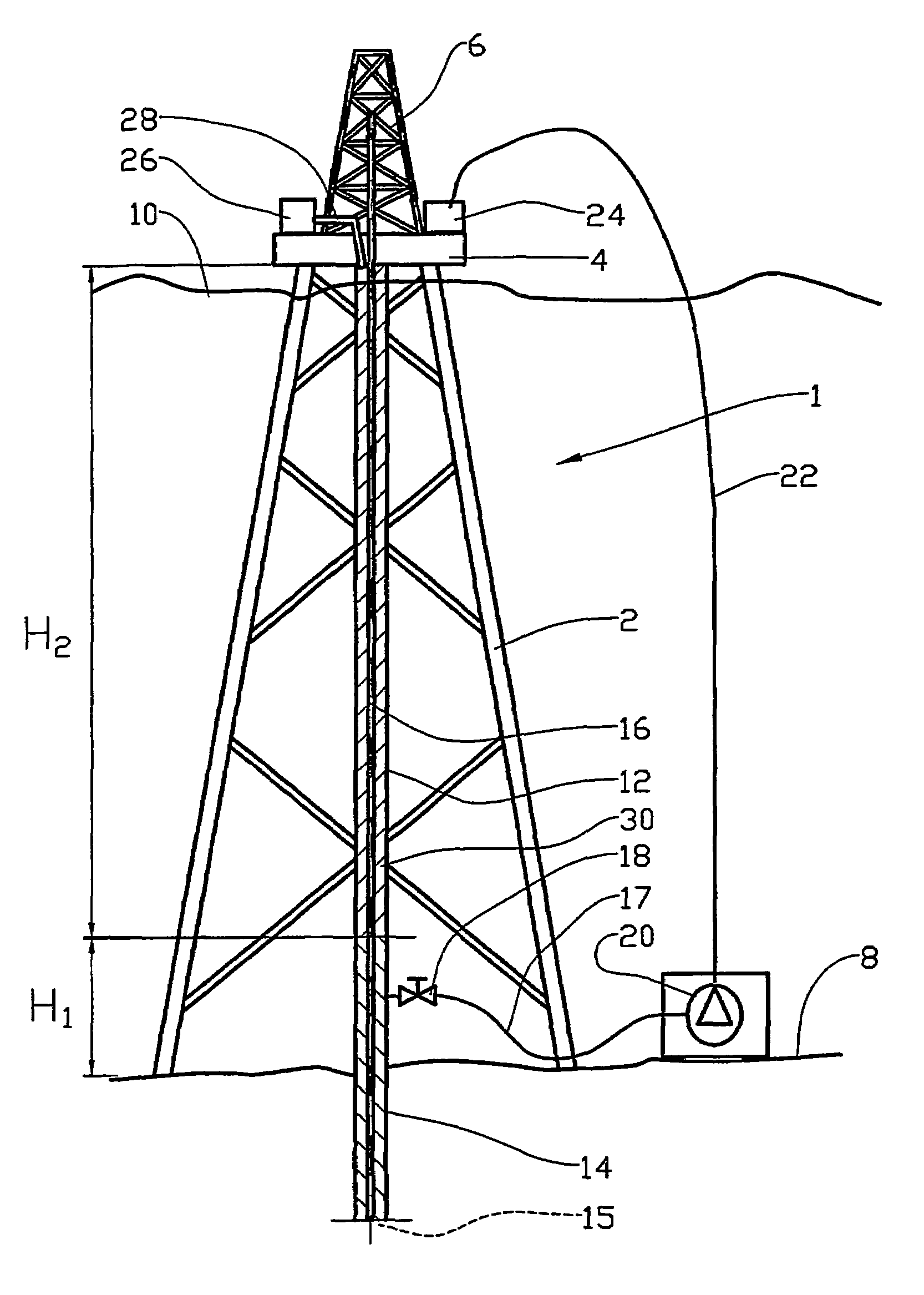
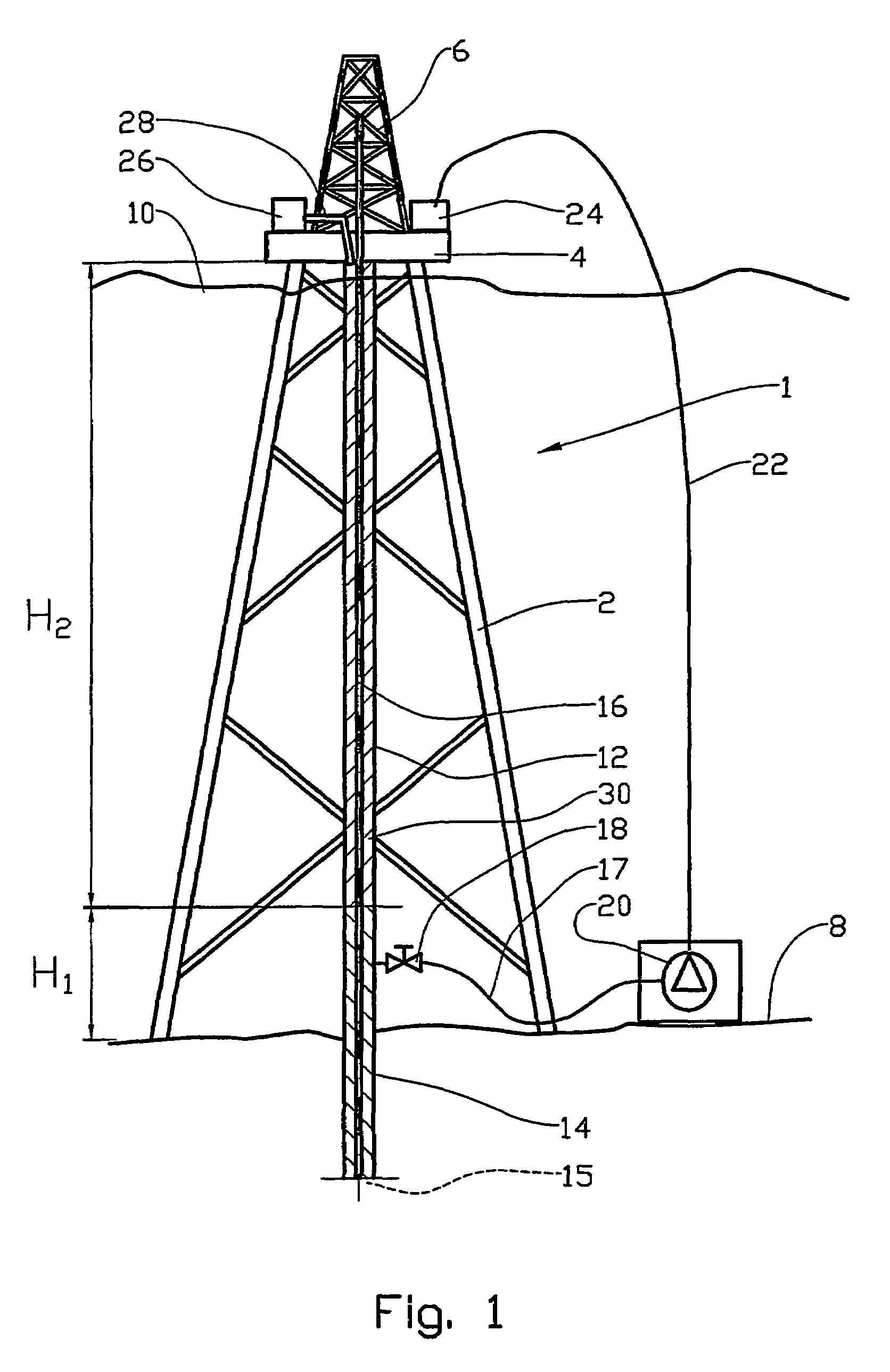
In an offshore drilling facility, apparatus is disclosed comprising: a drilling floor centralizer for receiving the upper end of a string of drilling riser sections; a moonpool centralizer for receiving another portion of the drilling riser; and at least one roto-track, removably and rotationally carried by at least one of the pin end of one drilling riser section and the box end of the adjacent drilling riser section, for extending the outer diameter of each of the adjacent ends to the outer diameter of the adjacent drilling risers sections intermediate the ends of the drilling riser sections.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
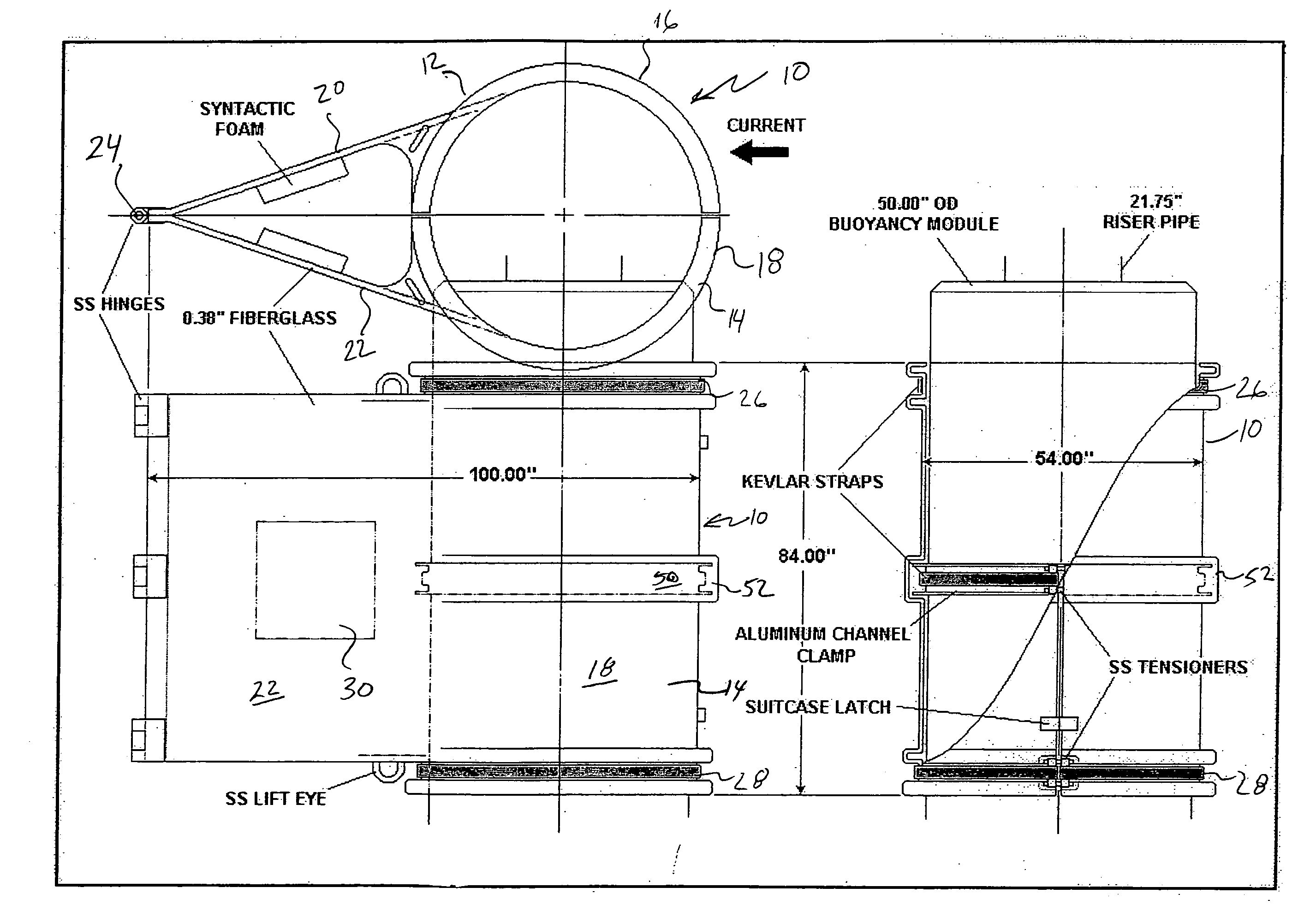
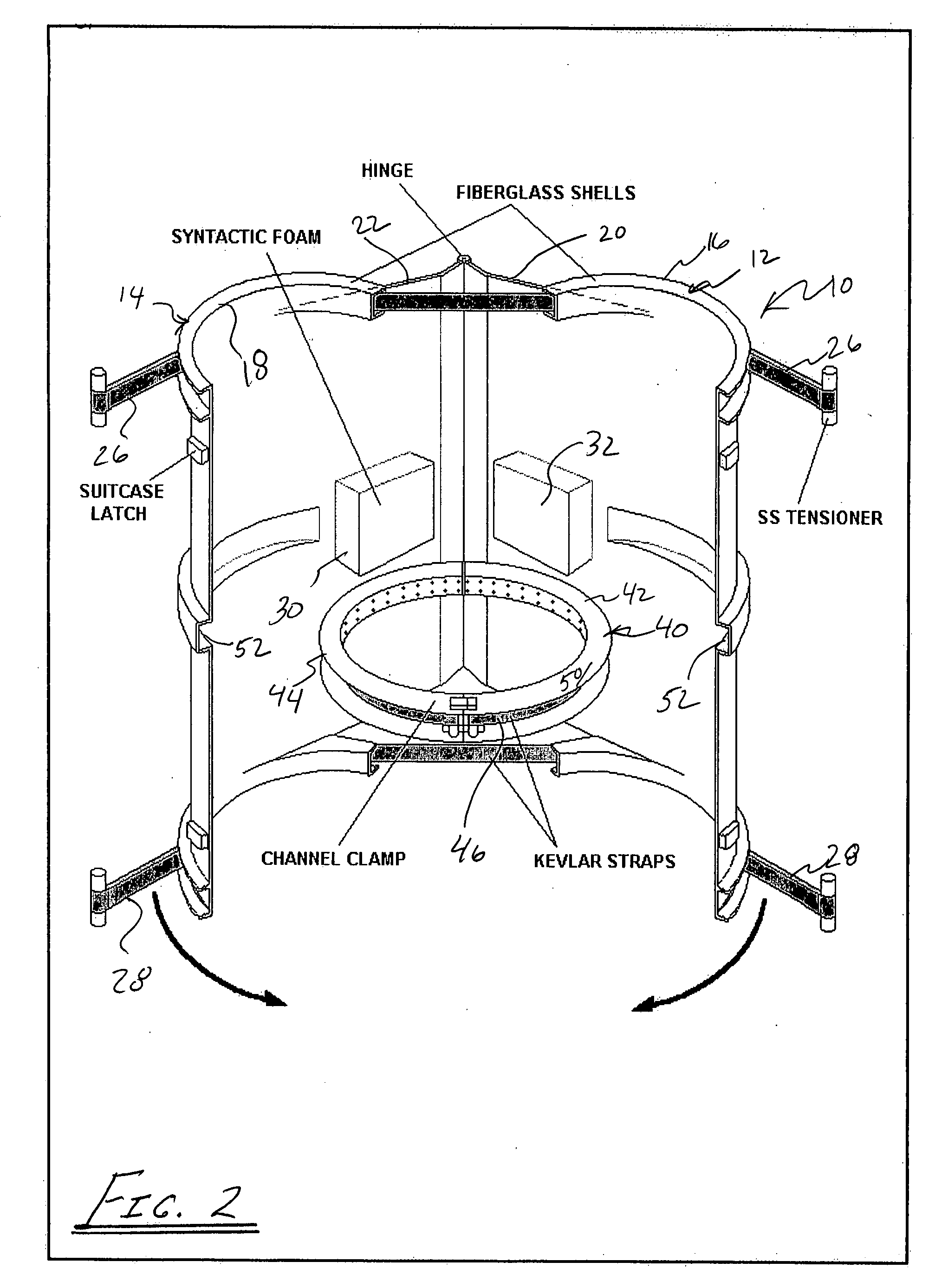
Fairing for marine drilling risers
InactiveUS20080025800A1Prevent movementArtificial islandsPipe laying and repairFree rotationEngineering
A fairing includes two half-shells of fiber reinforced plastic or fiberglass. The shell halves are shaped to close around the buoyancy modules (e.g., cylindrical syntactic foam buoyancy modules) commonly used on deep-water risers, but with an extended trailing edge. The fairing includes a tail that streamlines the riser and reduces / prevents formation of the vortex, which causes drag and vibration. Hinges at the tail join the halves and enable them to be opened for assembly around the riser pipe as it is being run into the water. The fairing may be fastened together by bolted stainless steel tensioners that tightly draw together straps of high strength aramid fiber, such as KEVLAR®. The fairing is positioned on the riser such that the fairing is free to swivel and rotate into the current, while integral buoyancy blocks support the tail. To prevent movement up or down the riser string, the fairing is held in place by a channel clamp gripping the outside diameter of the syntactic foam buoyancy module.
Owner:CUMING CORP
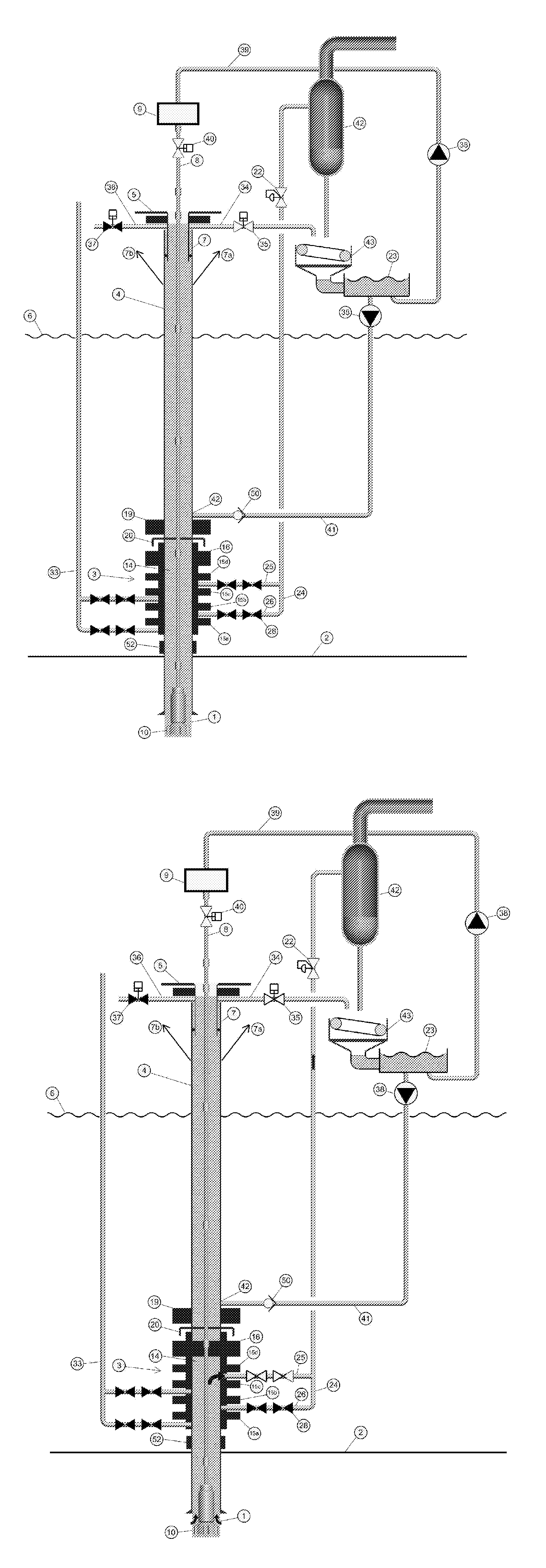
Systems and methods for circulating out a well bore influx in a dual gradient environment
Methods and systems for drilling subsea wells bores with dual-gradient mud systems include drilling the subsea well bore while employing a subsea pumping system, a subsea choke manifold and one or more mud return risers to implement the dual gradient mud system. When a well bore influx is detected, the well bore is shut in, and components determine if pressure control may be used to circulate the influx out of the well bore, the size of the influx, and how much the mud system weight will need to be reduced to match the dual gradient hydrostatic head before the influx reaches the subsea pump take point. The subsea pumping system, subsea choke manifold, and mud risers are isolated while the influx is circulated up one or more fluid passages in the drilling riser package using the surface pump, through the wellhead, and out the surface choke manifold.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Cantilevered multi purpose tower and method for installing drilling equipment
A drilling rig having a deck capable of being used offshore and a method for commissioning a well using the drilling rig and a method for decommissioning a well using the drilling rig, wherein the drilling rig comprises: a cantilever which is mounted so as to be moveable in a first direction and a second direction; a Multi Purpose Tower mounted on the cantilever; a supporting cart disposed between the cantilever and the deck which in turn is movably fixed on the deck of the drilling rig; at least two friction reducing devices attached to the supporting cart; and wherein the cantilever can slide relative to the drilling platform.
Owner:ITREC BV
Drilling riser buoyancy modules
InactiveUS7628665B1Improve manufacturabilityImprove performanceArtificial islandsDrilling rodsFiberContact pad
Buoyancy modules for subsea riser pipes are made of syntactic foam solid cores covered with tough high density polyethylene shells. Inner surfaces have partial semi-cylindrical surfaces to fit the riser pipes. Internal radial grooves hold flexible contact pads. Recesses in the inner surfaces hold auxiliary lines. Flat surfaces between the inner and outer semi-cylindrical surfaces have complementary longitudinally extending semi-cylindrical grooves to position choke and kill lines. Grooves in the outer semi-cylindrical surfaces hold composite fiber tensioning straps directly outward from the flexible contact pads. Flat areas of the grooves hold tensioning hardware. Tensioning the straps grips the riser pipe with the pads and grips the choke and kill lines in the semi-circular grooves. Cavities in the ends allow the buoyancy module halves to be assembled on the riser pipe around clamps which hold the accompanying lines.
Owner:CUMING CORP
Collapsible substructure for a mobile drilling rig
Owner:NAT OILWELL VARCO LP
Through riser installation of tree block
Owner:VETCO GRAY
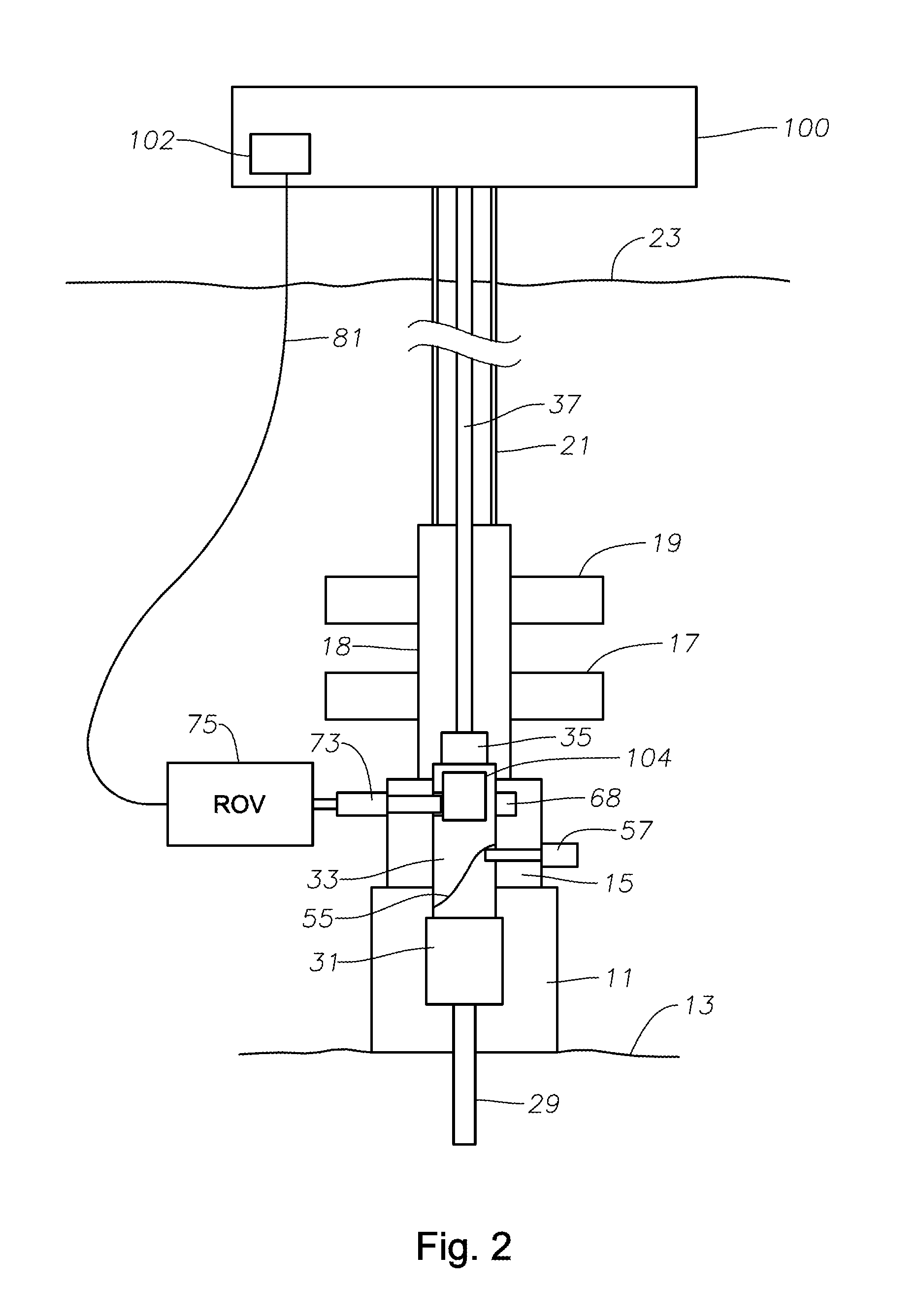
System and Method for Inductive Signal and Power Transfer from ROV to In Riser Tools
A subsea wellhead assembly having a completion landing string inside a drilling riser is described herein and comprises a power source for generating an alternating electrical current; a connector for connecting the power source to a receptacle in the subsea well assembly; a first inductor electrically connected to the power source through the connector; a subsea control module delivering power and control signals to the subsea well assembly; and a second inductor spaced from the first inductor, and located in the subsea control module, the second inductor positioned so that an EMF is produced on the second inductor when the alternating electrical current is passed through the first inductor to thereby generate an alternating current signal on the second inductor.
Owner:VETCO GRAY
Rapid Makeup Drilling Riser
ActiveUS20070267197A1Reduce the overall diameterMove upwardSleeve/socket jointsDrilling rodsWell drillingEngineering
A connector for connecting sections of drilling riser pipe wherein a first riser contains a pin assembly with an external first grooved profile and a second riser contains a housing assembly. An internal split pivoting latch segment assembly carried by the housing assembly contains a second grooved profile adapted to mate to the first grooved profile and a split actuation ring movably carried by the housing assembly forces the second grooved profile of the latch segment assembly into engagement with the first grooved profile of the pin assembly. A plurality of retraction links engage an upper edge of the latch segment assembly to disengage the second grooved profile of the latch segment assembly from the first grooved profile of the pin assembly if the risers are to be disconnected.
Owner:VETCO GRAY
Marine drilling riser connector with removable shear elements
Owner:DIAMOND OFFSHORE DRILLING
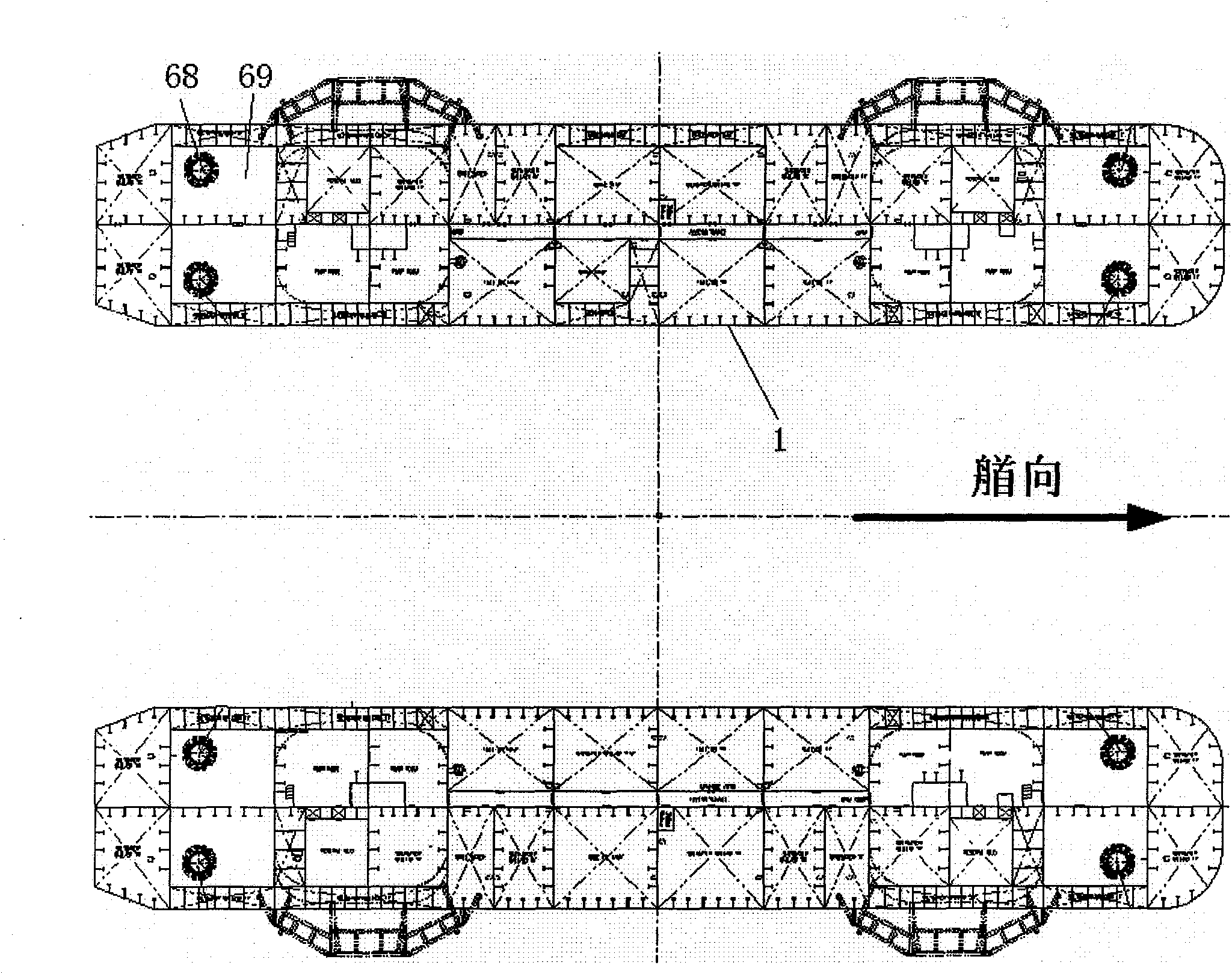
Deepwater semi-submerged drilling platform
ActiveCN101954959ASmall footprintConvenient pre-connection workFloating buildingsEngineeringDrilling riser
The invention relates to a deepwater semi-submerged drilling platform, which comprises floating tanks, an upright post, a transverse supporting rod and a main deck, wherein a drilling block is arranged above a moon pool in the middle of the main deck; and a derrick is arranged on the drilling block. The deepwater semi-submerged drilling platform is characterized in that: a half derrick space for pre-connecting a drilling tool is reserved on one side of the derrick; a water isolating pipe, a drilling stem, a blowout preventer and a production tree are arranged on the main deck around the moon pool respectively; and an anchor moored positioning and dynamic positioning combined position system which consists of front and back four groups of anchor gears distributed on the left and right sides of the main deck is adopted, each group of anchor gears are provided with 3 anchor chains, a dynamic positioning system consists of 8 dynamic thrusters capable of rotating 360 degrees at the front and back four corners of the bottom of the two floating tanks. In the deepwater semi-submerged drilling platform, the maximum operation water depth is up to 3,000 meters, the maximum drilling depth is up to 12,000 meters, and the maximum variable load is up to 9,000 tons. The deepwater semi-submerged drilling platform can operate in the South China Sea, Southeast Asian sea area and West Africa sea area with severe sea conditions efficiently and safely.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Systems and methods for circulating out a well bore influx in a dual gradient environment
Methods and systems for drilling subsea wells bores with dual-gradient mud systems include drilling the subsea well bore while employing a subsea pumping system, a subsea choke manifold and one or more mud return risers to implement the dual gradient mud system. When a well bore influx is detected, the well bore is shut in, and components determine if pressure control may be used to circulate the influx out of the well bore, the size of the influx, and how much the mud system weight will need to be reduced to match the dual gradient hydrostatic head before the influx reaches the subsea pump take point. The subsea pumping system, subsea choke manifold, and mud risers are isolated while the influx is circulated up one or more fluid passages in the drilling riser package using the surface pump, through the wellhead, and out the surface choke manifold.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Drilling riser auxiliary clamp with integral mux clamp
Segments of open framework auxiliary clamps are fastened together around a drilling riser. The clamps have depressions which mate with recesses in caps to hold auxiliary lines. Larger depressions and recesses hold choke and kill lines. The caps of the choke and kill clamps are extended radially through openings in buoyancy covers as mux clamp mounts. Extensions on mux clamps engage slots in the mux clamp mounts. Opposing channels in the mux clamps and covers hold inserts, with grooves in which multiplex lines are mounted.
Owner:CUMING CORP
System and method for inductive signal and power transfer from ROV to in riser tools
A subsea wellhead assembly having a completion landing string inside a drilling riser is described herein and comprises a power source for generating an alternating electrical current; a connector for connecting the power source to a receptacle in the subsea well assembly; a first inductor electrically connected to the power source through the connector; a subsea control module delivering power and control signals to the subsea well assembly; and a second inductor spaced from the first inductor, and located in the subsea control module, the second inductor positioned so that an EMF is produced on the second inductor when the alternating electrical current is passed through the first inductor to thereby generate an alternating current signal on the second inductor.
Owner:VETCO GRAY
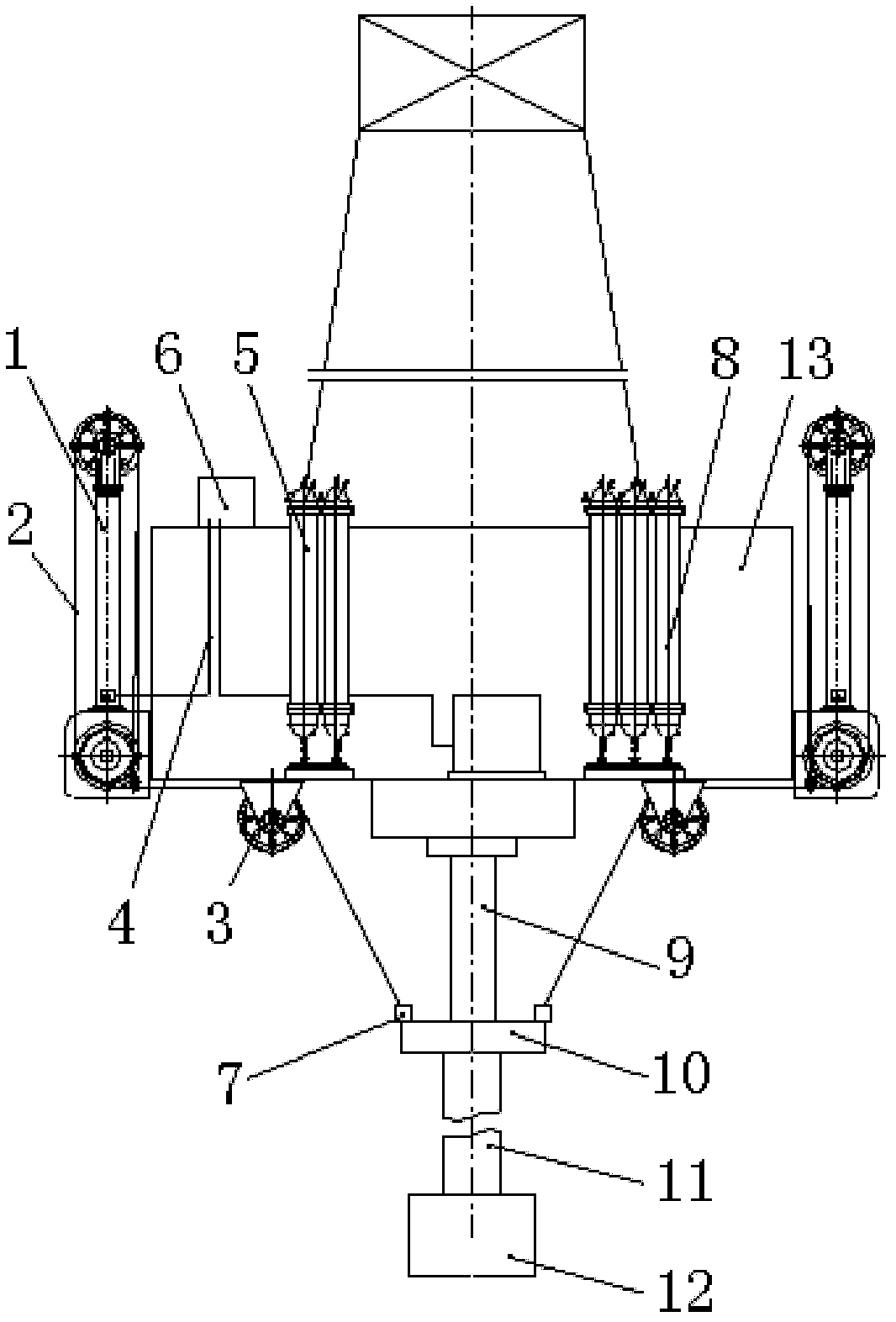
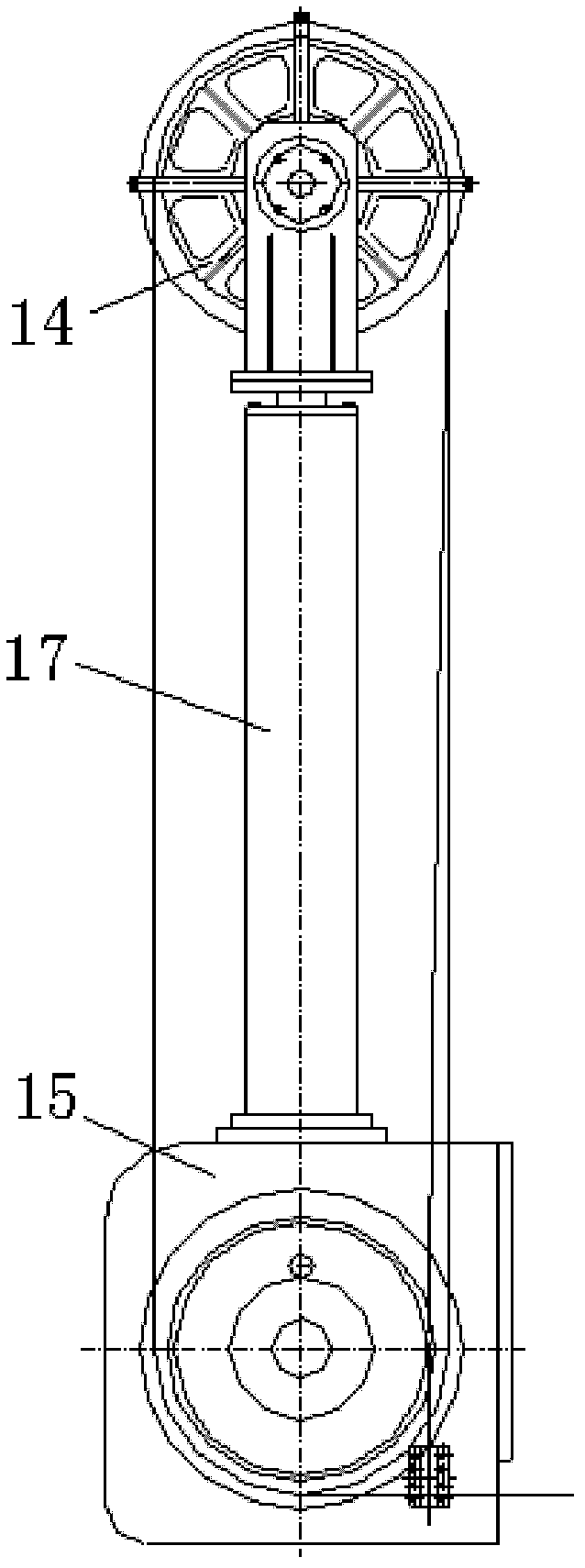
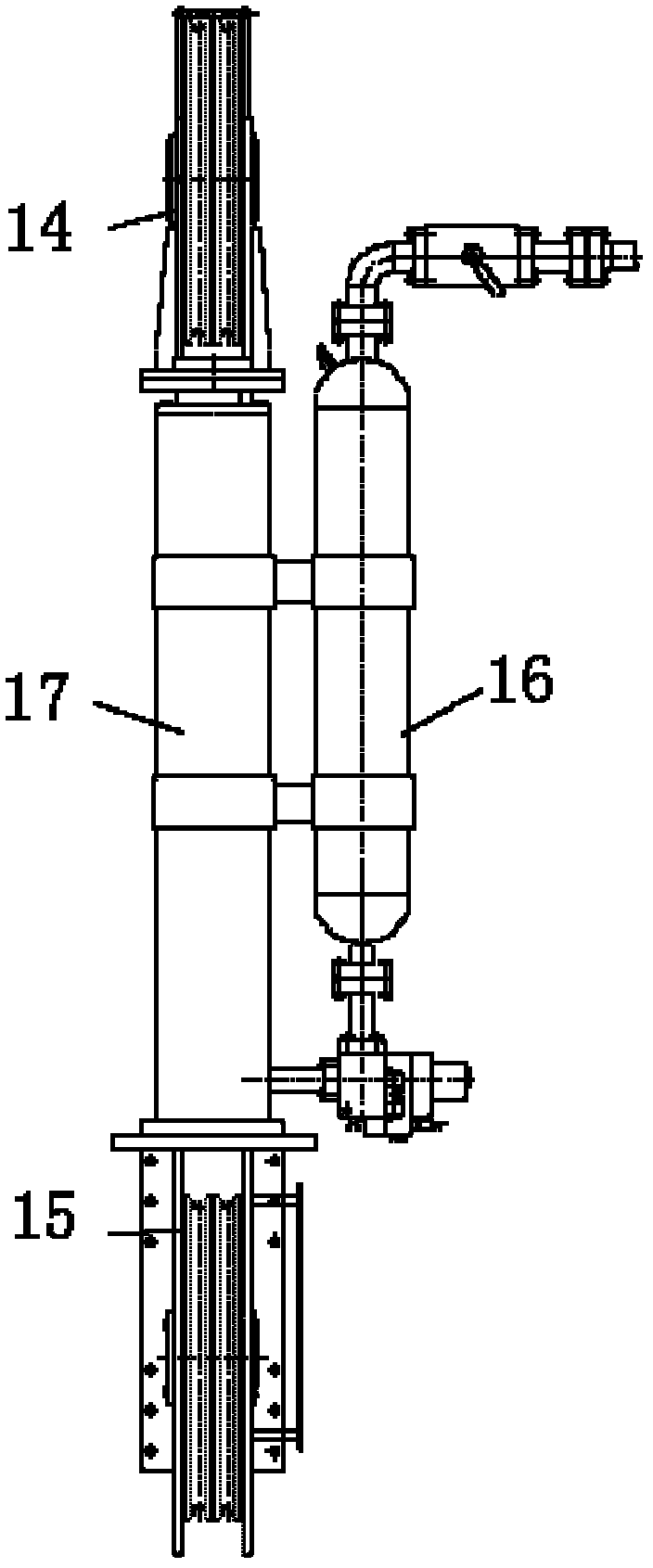
Marine drilling riser tensioning system
InactiveCN102330541ACompensation for heave motionSimple structureDrilling rodsDrilling casingsBlock and tackleEngineering
The invention discloses a marine drilling riser tensioning system which comprises a plurality of tensioner assemblies respectively arranged around a floating type drilling platform, wherein each tensioner assembly comprises a tensioning cylinder and an energy storage device, wherein the upper end and the lower end of the tensioning cylinder are respectively provided with an upper tackle block and a lower tackle block, the distance between the upper tackle block and the lower tackle block is changed with the flexibility of a piston; a lower cavity of the energy storage device is filled with a high-pressure liquid, an upper cavity of the energy storage device is filled with a high-pressure gas, the lower cavity of the energy storage device is communicated with a piston cavity of the tensioning cylinder, the upper cavity of the energy storage device is communicated with a high-pressure air system; and a steel rope sequentially bypasses through the upper tackle block and the lower tackle block and is connected with a connection device after guided by a guide pulley, and the connection device is connected with a tensioning ring hung on a riser system. The marine drilling riser tensioning system has the advantages of simple structure, convenience for control, reliability in control, low manufacture cost and large bearing capacity.
Owner:BAOJI PETROLEUM MASCH CO LTD
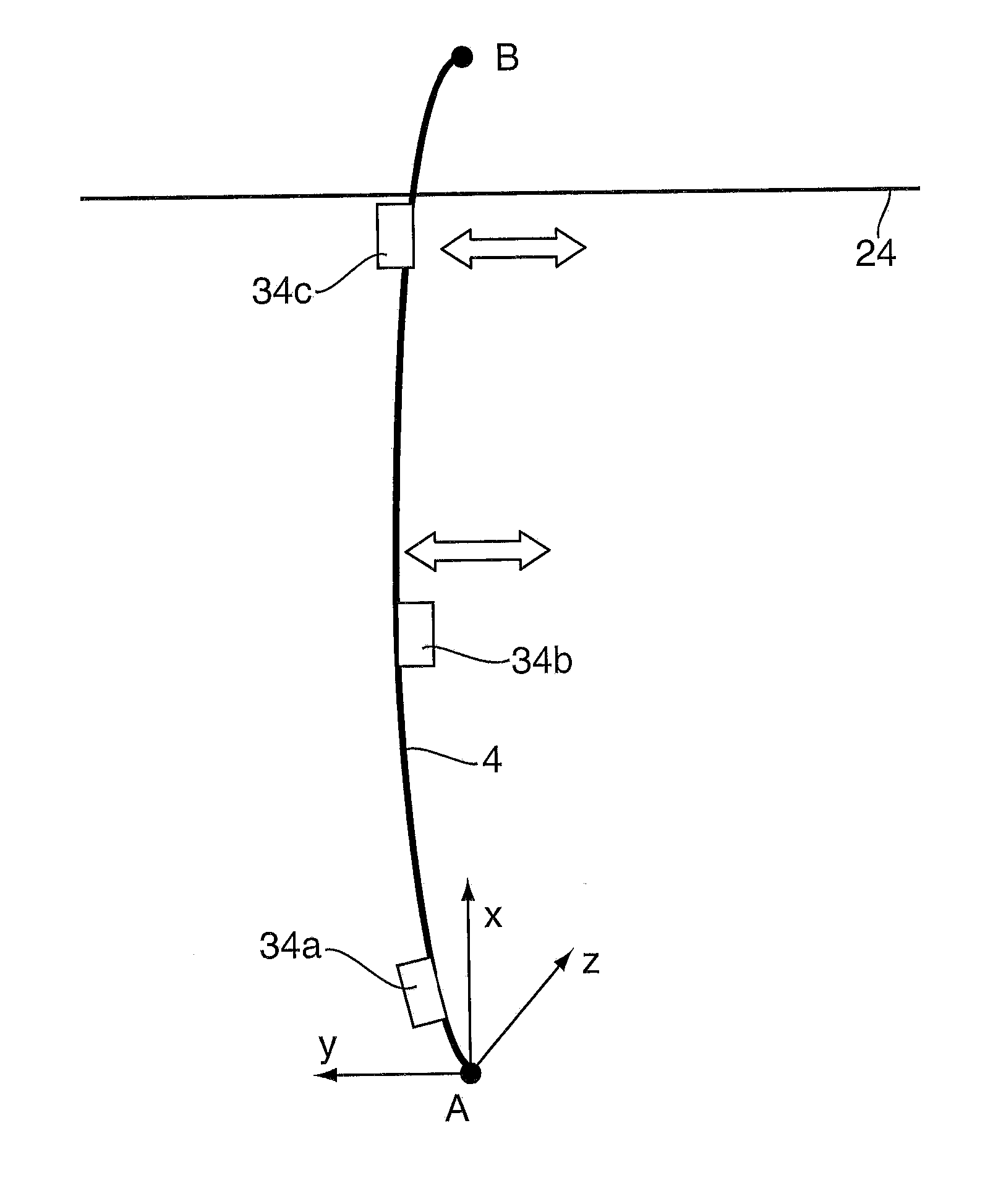
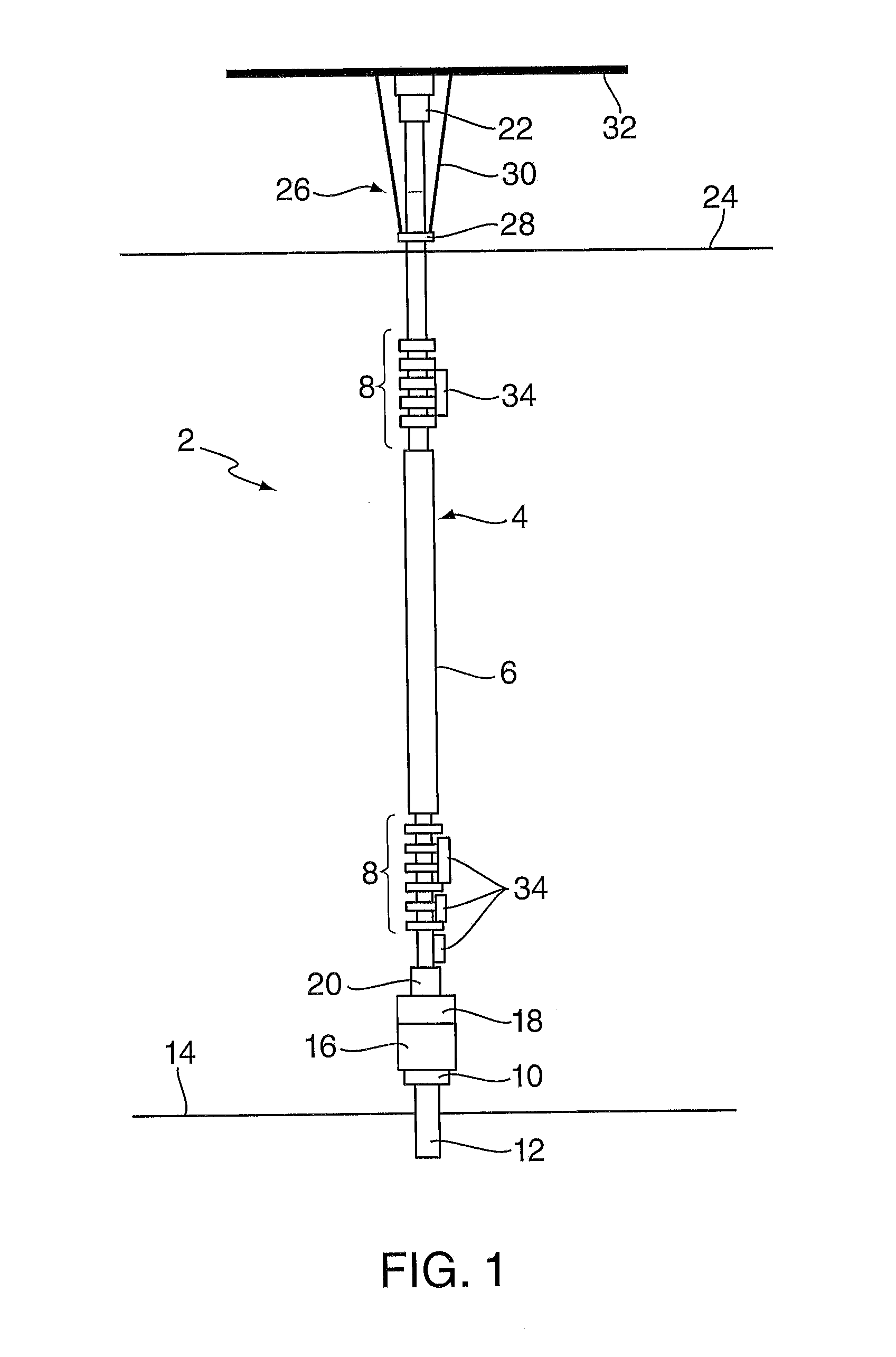
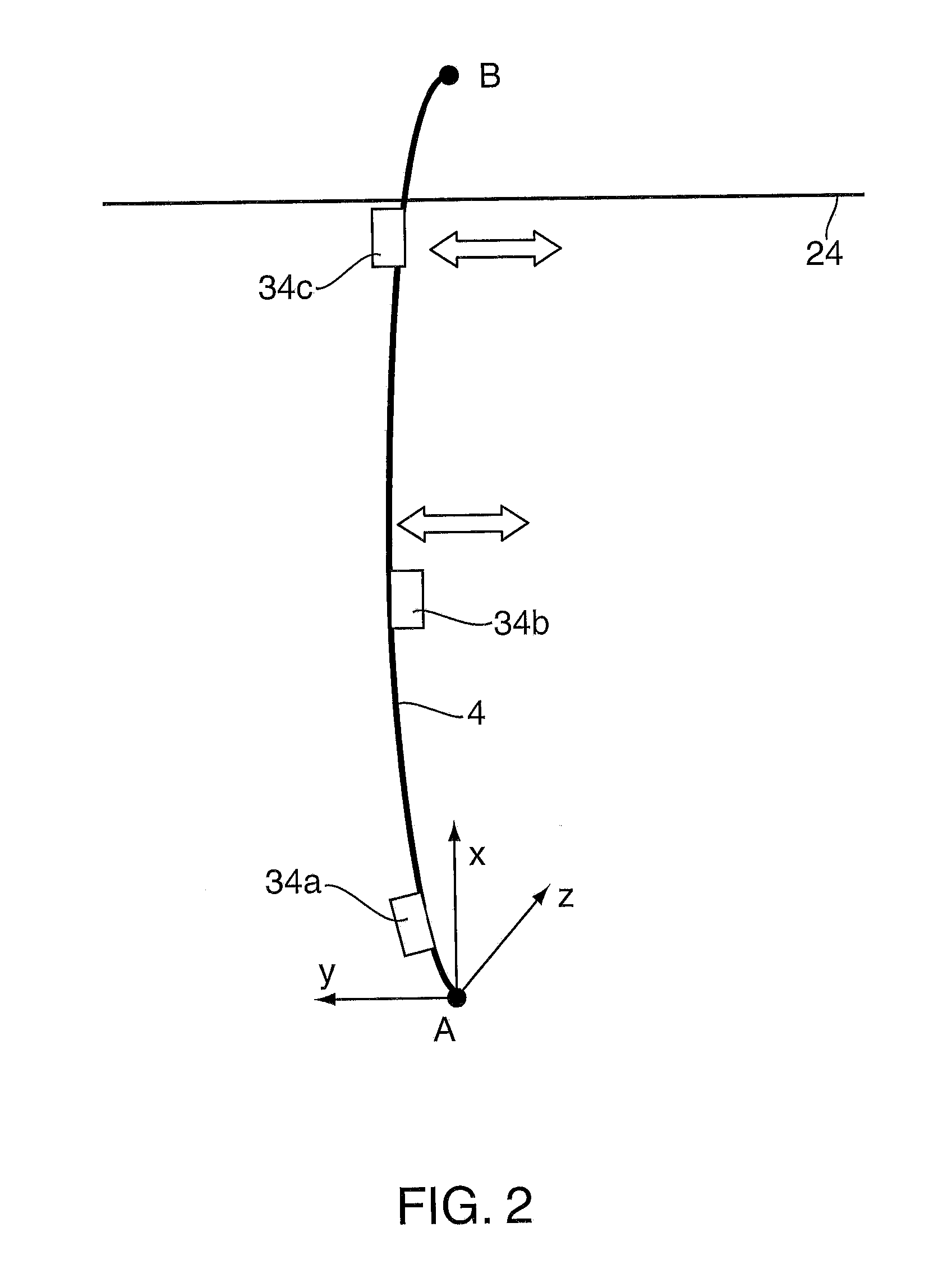
Riser Fatigue Monitoring
ActiveUS20150176237A1Effective installationReduce distractionsPlug gaugesDrilling rodsCatenaryDrilling riser
A system and method is provided for determining curvature for subsea riser system, including but not limited to drilling risers, steel catenary risers, lazy-wave catenary risers and riser jumpers, comprising the steps of: periodically measuring acceleration in a first lateral direction at said vertical position to obtain a first acceleration timetrace processing said first acceleration timetrace to obtain a first acceleration spectra; applying a transfer function to said first acceleration spectra to obtain a first curvature spectra; and processing said first curvature spectra to obtain a first curvature timetrace. Preferably the transfer function is determined by a method comprising the step of modelling the riser as a Tensioned Timoshenko Beam.The curvature may be used to determine stress and fatigue damage in a structure from motions measured at a single location or a combination of motions measured at a single location with or without tension measurement. The method can be used to determine curvature and hence stress and fatigue damage from any source of excitation, for example the excitation at the tension ring by the top tensioner system, and the vortex induced vibration locked in at any water depth.
Owner:BP EXPLORATION & PRODION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com