Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "CD37" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Leukocyte antigen CD37 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD37 gene.
Immunoregulatory antibodies and uses thereof
InactiveUS20030103971A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCD37CD23
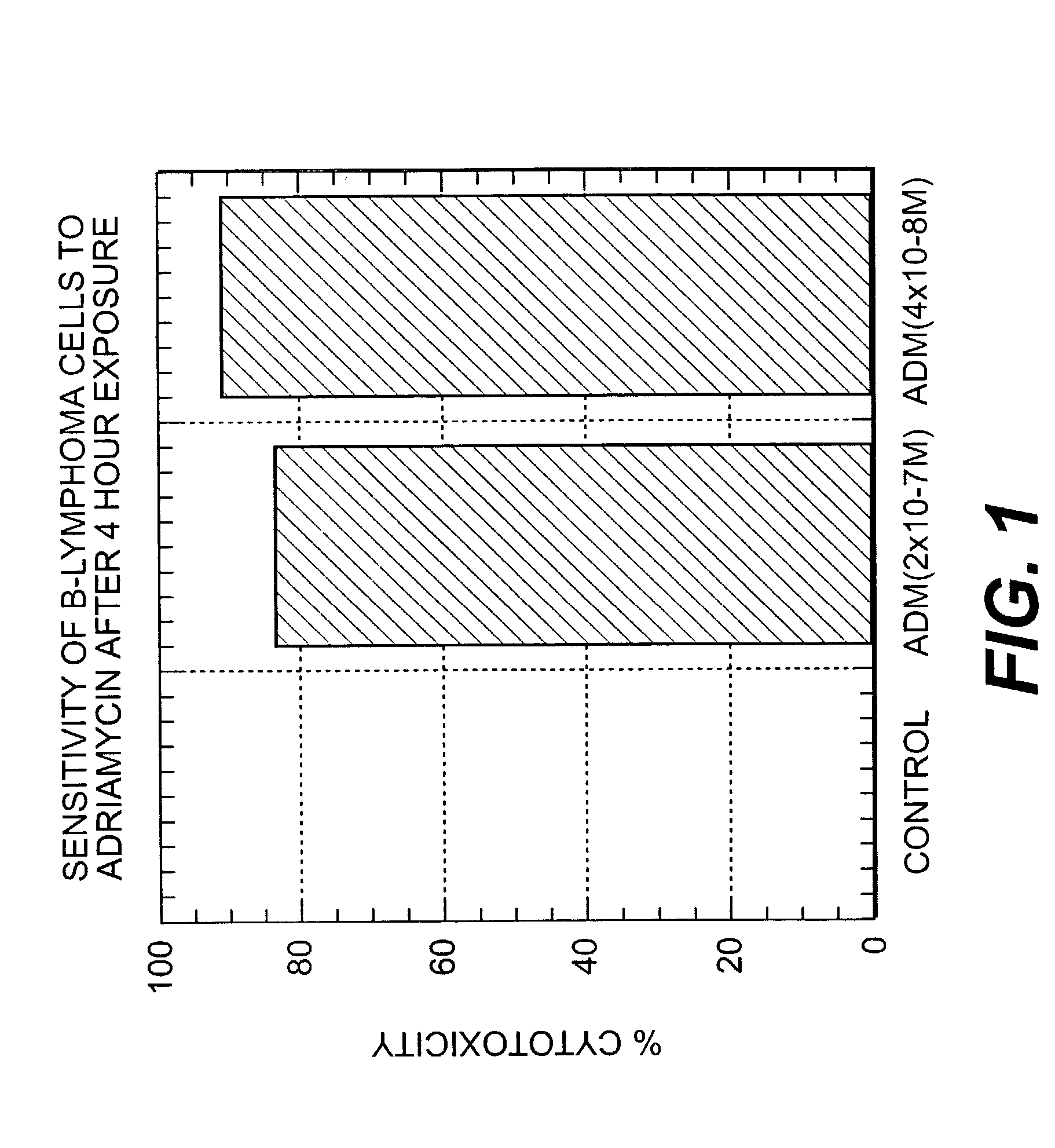
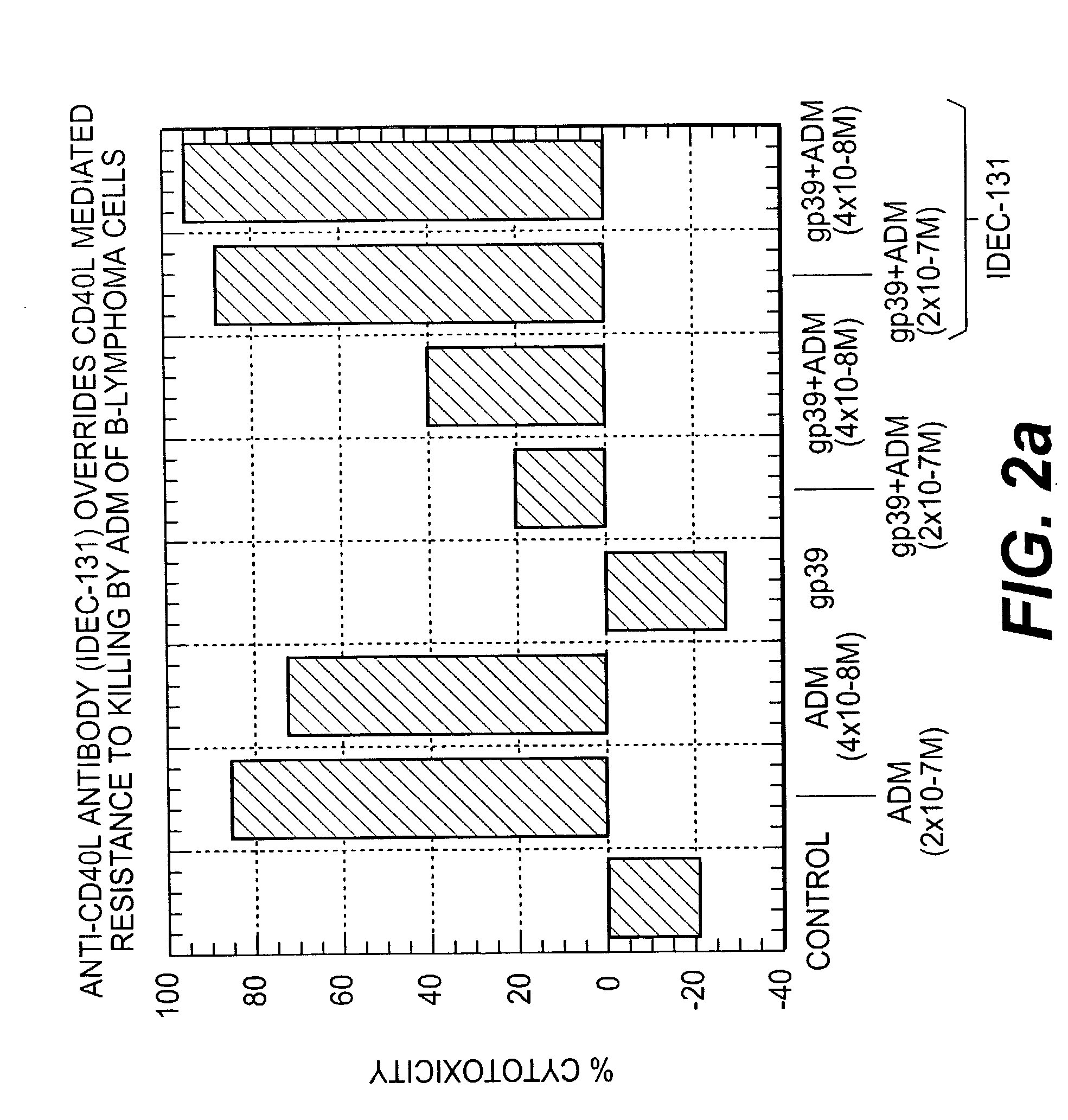
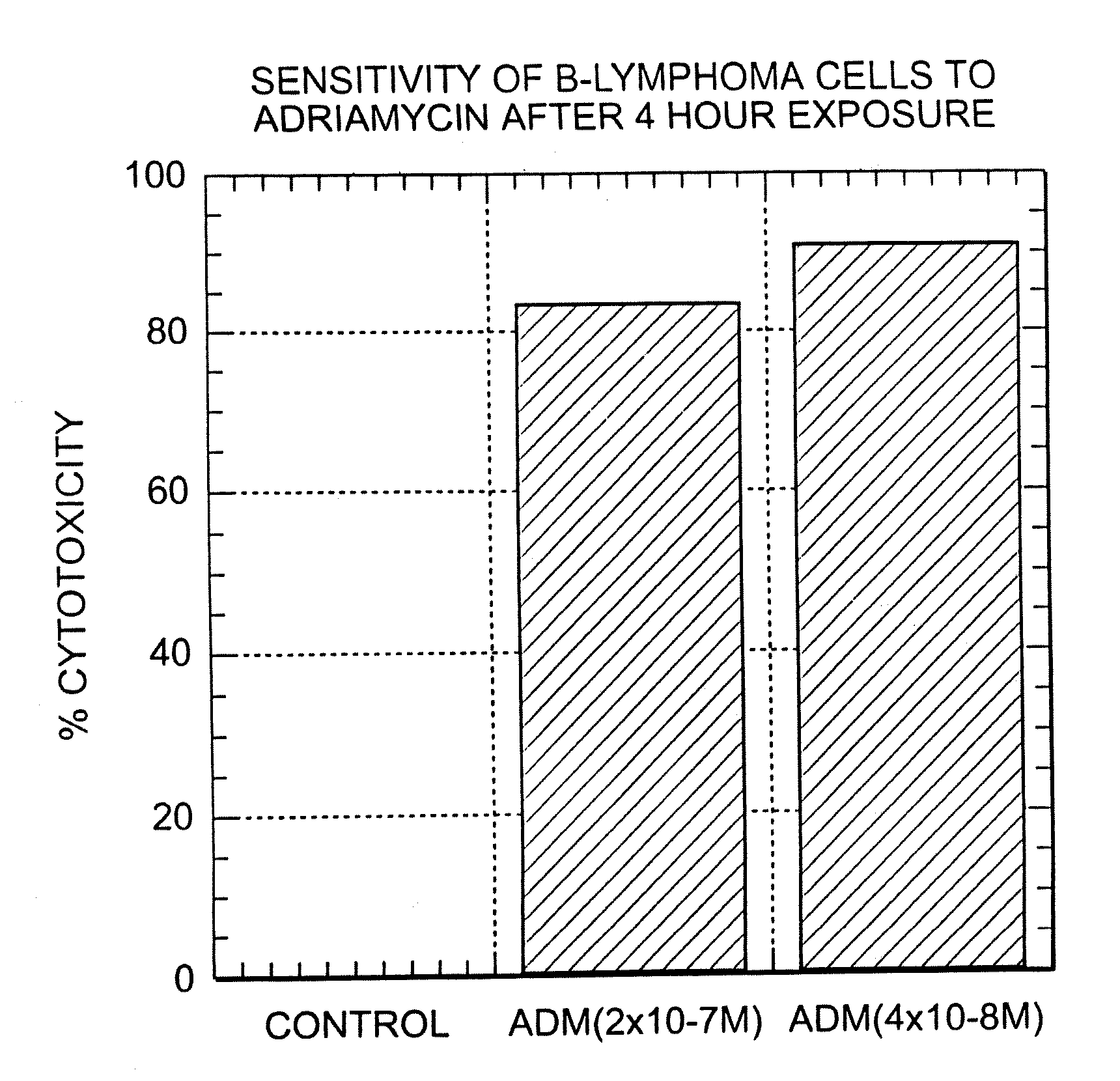
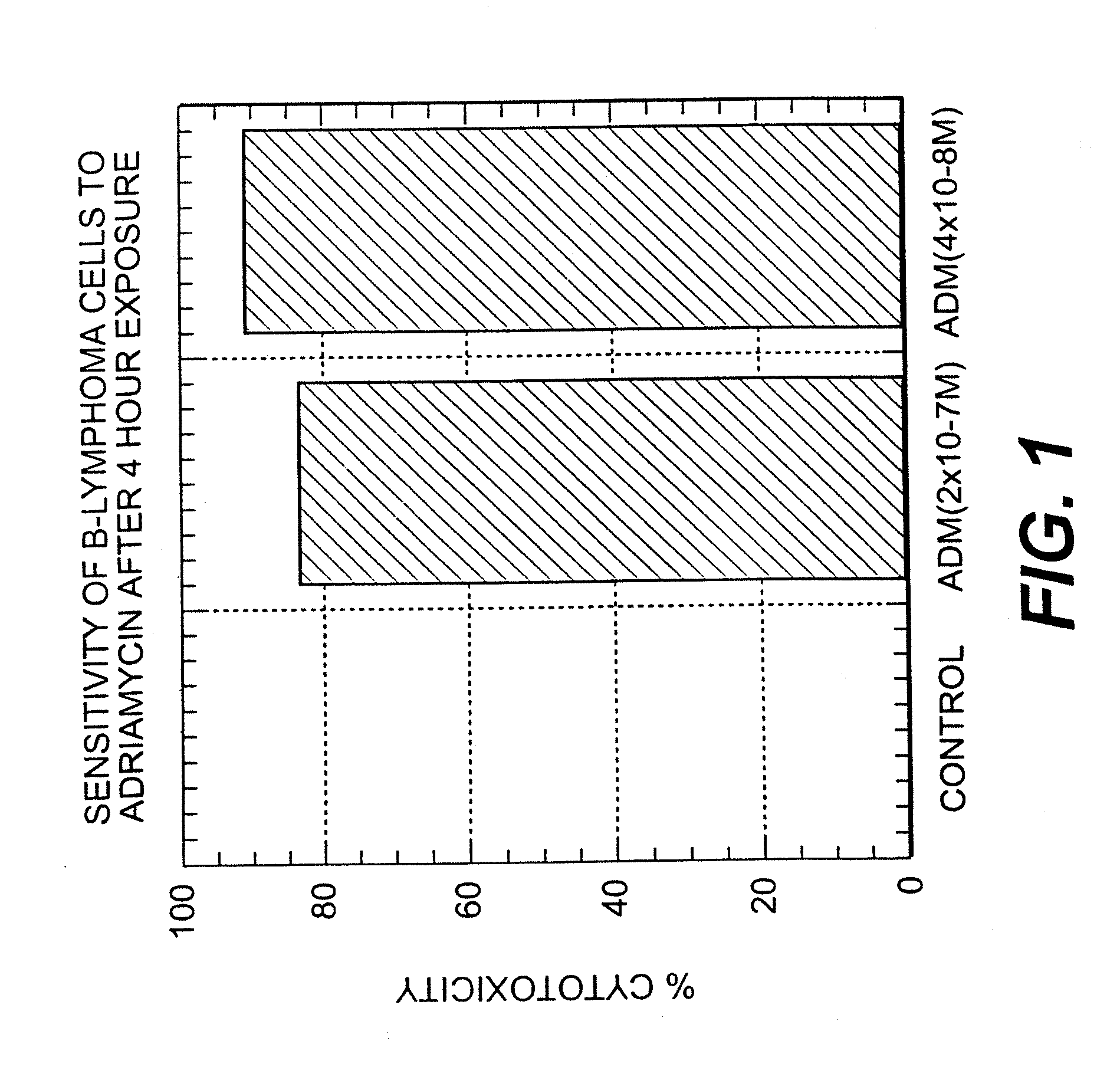
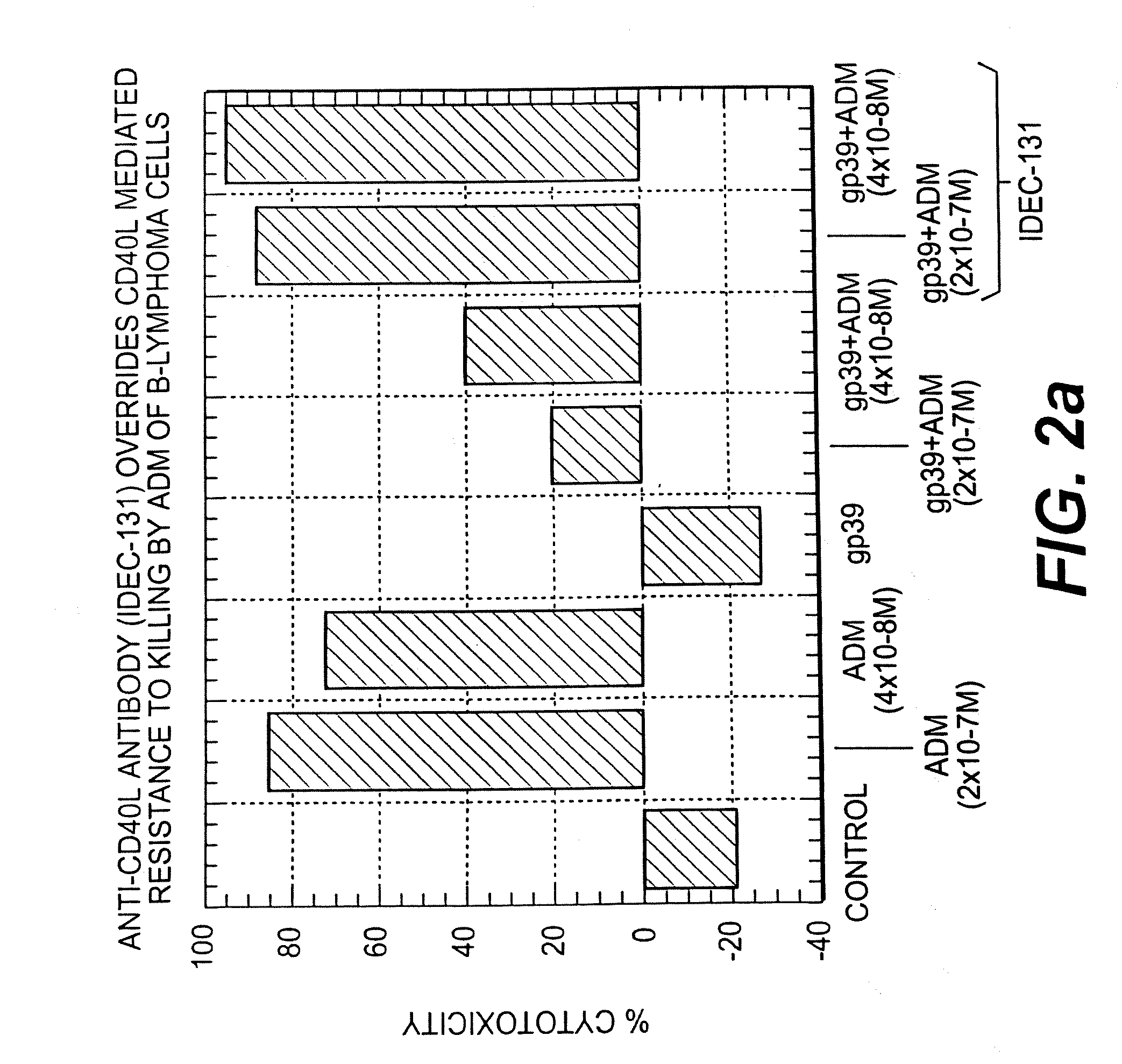
A combination antibody therapy for treating B cell malignancies using an immunoregulatory antibody, especially an anti-B7, anti-CD23, or anti-CD40L antibody and a B cell depleting antibody, especially anti-CD19, anti-CD20, anti-CD22 or anti-CD37 antibody is provided. Preferably, the combination therapy will comprise anti-B7 and anti-CD20 antibody administration.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
B-cell reduction using CD37-specific and CD20-specific binding molecules
ActiveUS20070059306A1Increase profitPermit absorptionSenses disorderNervous disorderCD20Cell activity
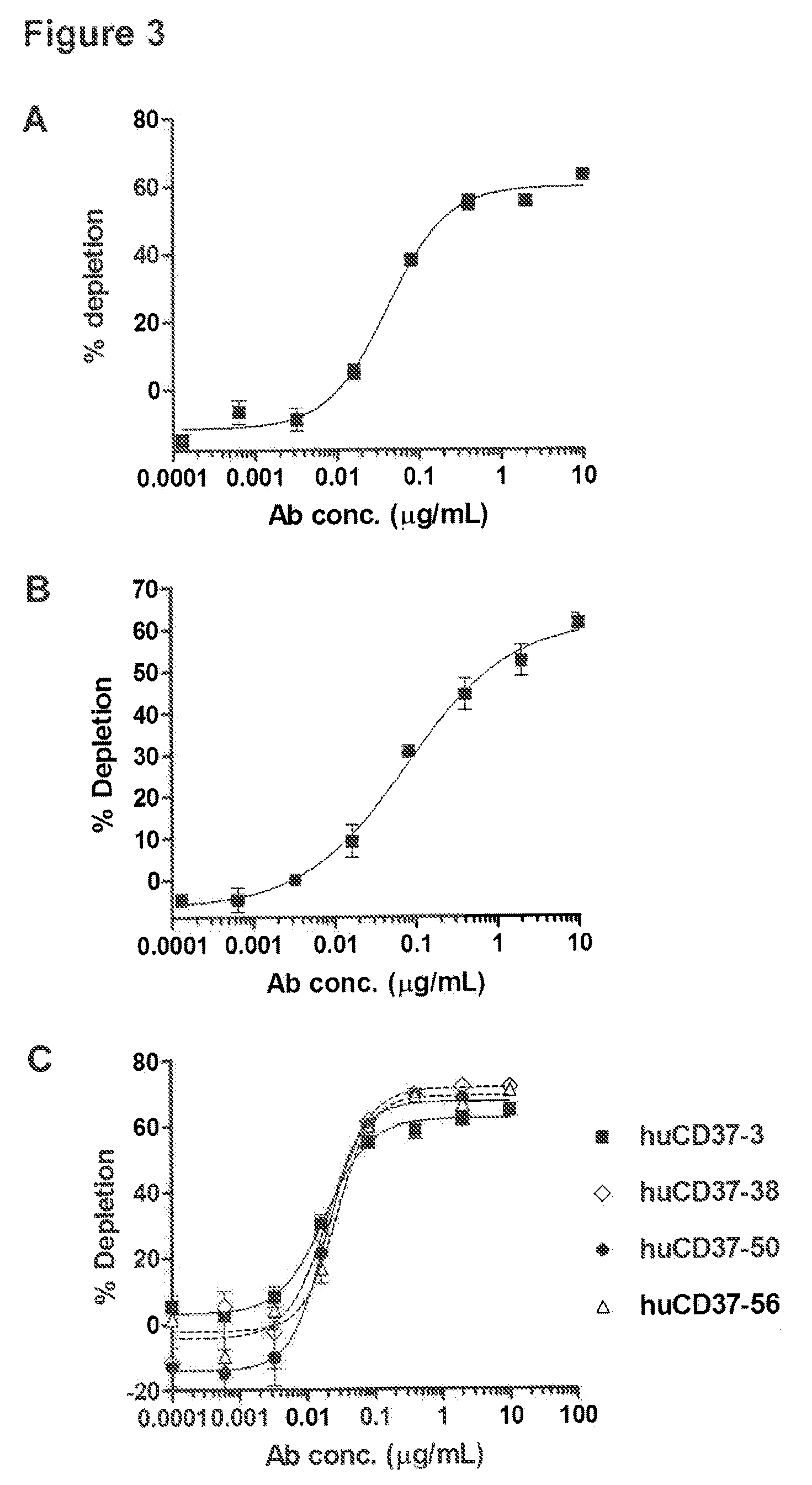
The present invention generally provides methods for B-cell reduction in an individual using CD37-specific binding molecules. In particular, the invention provides methods for B-cell reduction using CD37-specific binding molecules alone, or a combination of CD37-specific binding molecules and CD20-specific binding molecules, in some instances a synergistic combination. The invention further provides materials and methods for treatment of diseases involving aberrant B-cell activity. In addition, the invention provides humanized CD37-specific binding molecules.
Owner:APTEVO RES & DEV LLC
Camptothecin Conjugates of Anti-CD22 Antibodies for Treatment of B Cell Diseases
ActiveUS20110305631A1Increase the number ofNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCD20Autoimmune condition
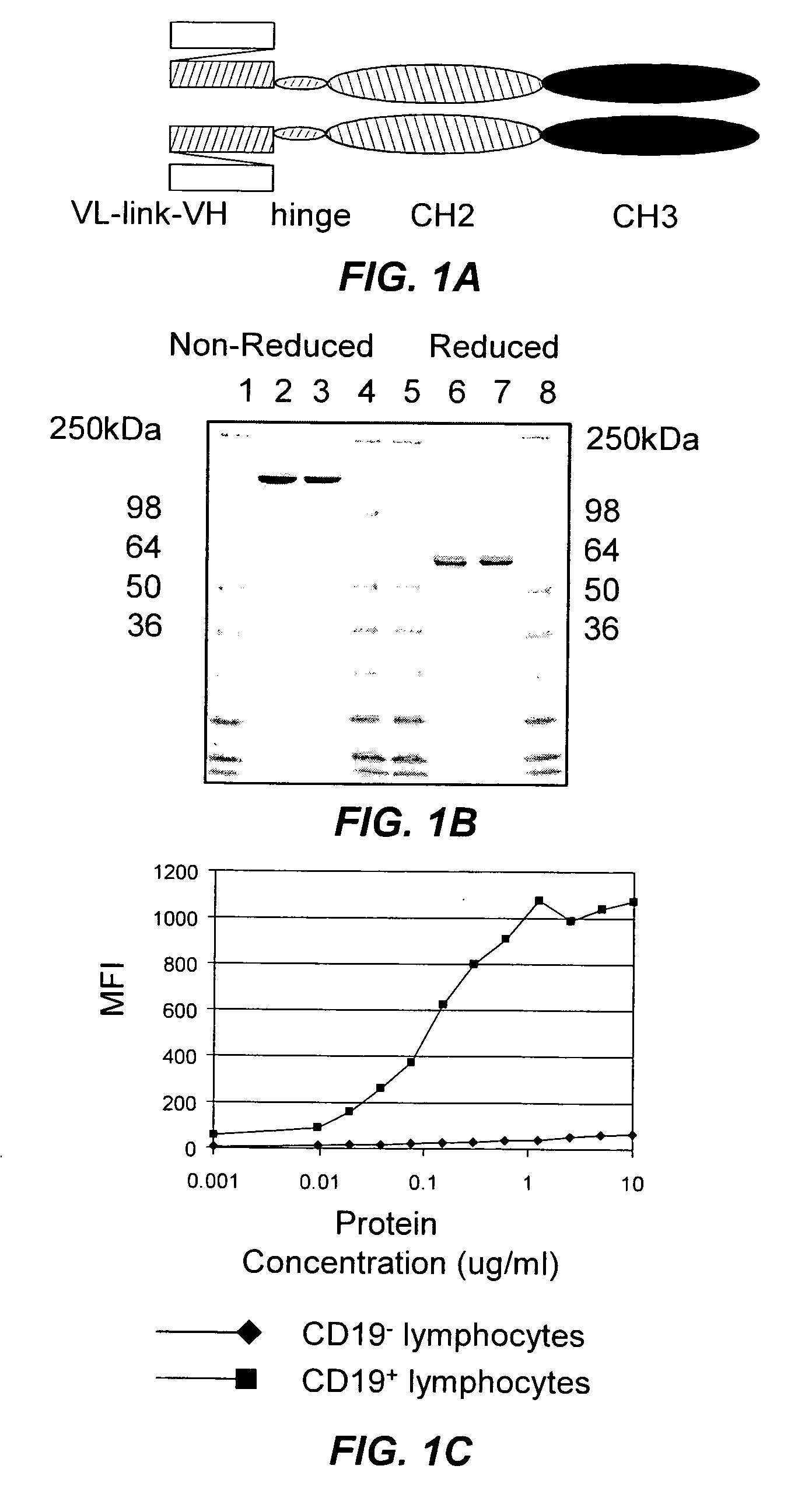
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods of use comprising combinations of anti-CD22 antibodies with a therapeutic agent. The therapeutic agent may be attached to the anti-CD22 antibody or may be separately administered, either before, simultaneously with or after the anti-CD22 antibody. In preferred embodiments, the therapeutic agent is an antibody or fragment thereof that binds to an antigen different from CD22, such as CD19, CD20, CD21, CD22, CD23, CD37, CD40, CD40L, CD52, CD80 and HLA-DR. However, the therapeutic agent may an immunomodulator, a cytokine, a toxin or other therapeutic agent known in the art. More preferably, the anti-CD22 antibody is part of a DNL complex, such as a hexavalent DNL complex. Most preferably, combination therapy with the anti-CD22 antibody or fragment and the therapeutic agent is more effective than the antibody alone, the therapeutic agent alone, or the combination of anti-CD22 antibody and therapeutic agent that are not conjugated to each other. Administration of the anti-CD22 antibody and therapeutic agent induces apoptosis and cell death of target cells in diseases such as B-cell lymphomas or leukemias, autoimmune disease or immune dysfunction disease.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
B-cell reduction using cd37-specific and cd20-specific binding molecules
The present invention generally provides methods for B-cell reduction in an individual using CD37-specific binding molecules. In particular, the invention provides methods for B-cell reduction using CD37-specific binding molecules alone, or a combination of CD37-specific binding molecules and CD20-specific binding molecules, in some instances a synergistic combination. The invention further provides materials and methods for treatment of diseases involving aberrant B-cell activity. In addition, the invention provides humanized CD37-specific binding molecules.
Owner:EMERGENT PRODUCTS DEVELOPMENT SEATTLE LLC
Treatment of B cell malignancies using combination of B cell depleting antibody and immune modulating antibody related applications
InactiveUS20050123540A1Radioactive preparation carriersImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCD37Combination therapy
A combination antibody therapy for treating B cell malignancies using an immunoregulatory antibody, especially an anti-B7, anti-CD23, or anti-CD40L antibody and a B cell depleting antibody, especially anti-CD19, anti-CD20, anti-CD22 or anti-CD37 antibody is provided. Preferably, the combination therapy will comprise anti-B7 and anti-CD20 antibody administration.
Owner:IDEC PHARM CORP +1
Immunoregulatory Antibodies and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20070009519A1Convenient treatmentIn-vivo radioactive preparationsPharmaceutical containersCD37Combination therapy
A combination antibody therapy for treating B cell malignancies using an immunoregulatory antibody, especially an anti-B7, anti-CD23, or anti-CD40L antibody and a B cell depleting antibody, especially anti-CD19, anti-CD20, anti-CD22 or anti-CD37 antibody is provided. Preferably, the combination therapy will comprise anti-B7 and anti-CD20 antibody administration.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
B-Cell Reduction Using CD37-Specific and CD20-Specific Binding Molecules
The present invention generally provides methods for B-cell reduction in an individual using CD37-specific binding molecules. In particular, the invention provides methods for B-cell reduction using CD37-specific binding molecules alone, or a combination of CD37-specific binding molecules and CD20-specific binding molecules, in some instances a synergistic combination. The invention further provides materials and methods for treatment of diseases involving aberrant B-cell activity. In addition, the invention provides humanized CD37-specific binding molecules.
Owner:TRUBION PHARM INC
Cd37 immunotherapeutic combination therapies and uses thereof
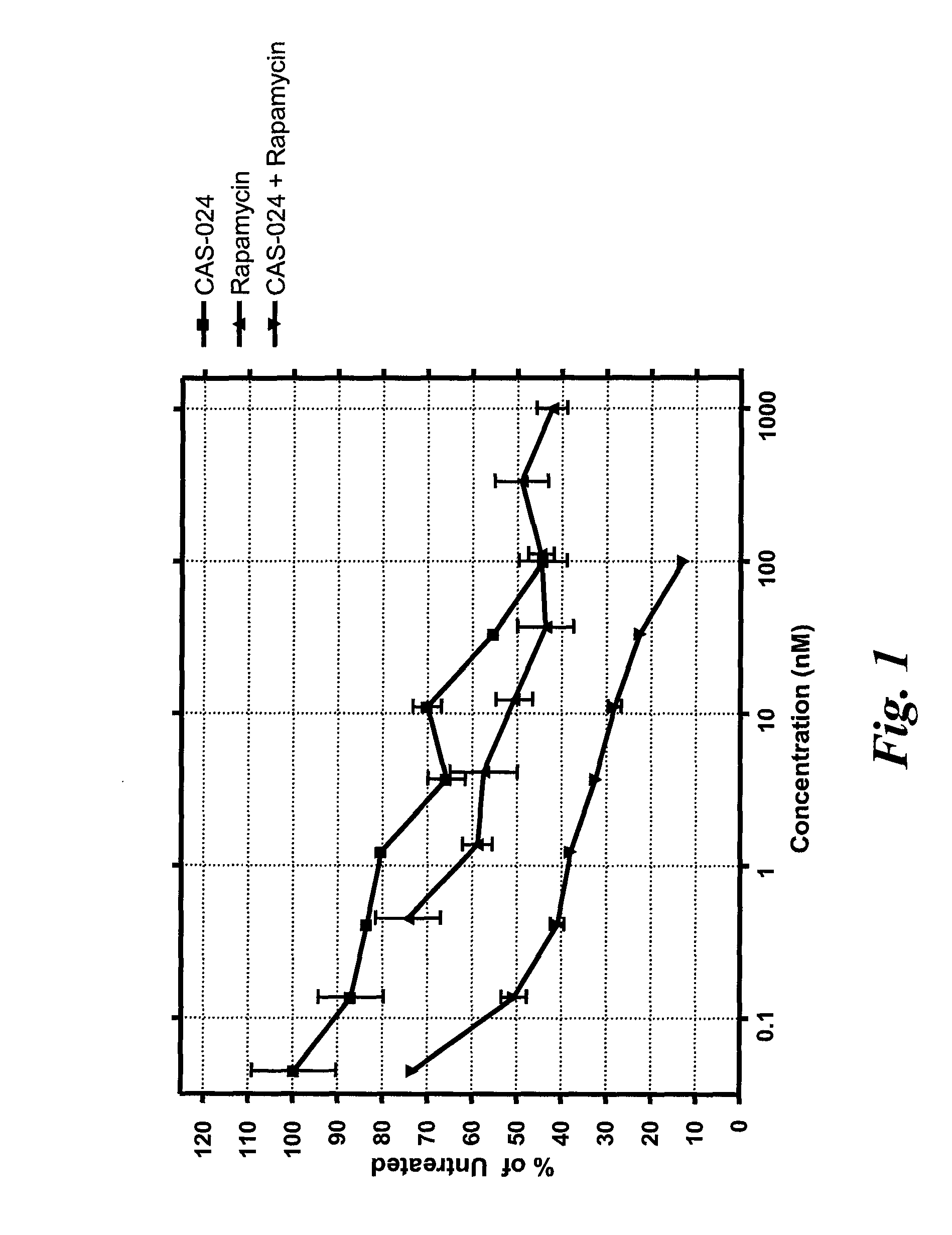
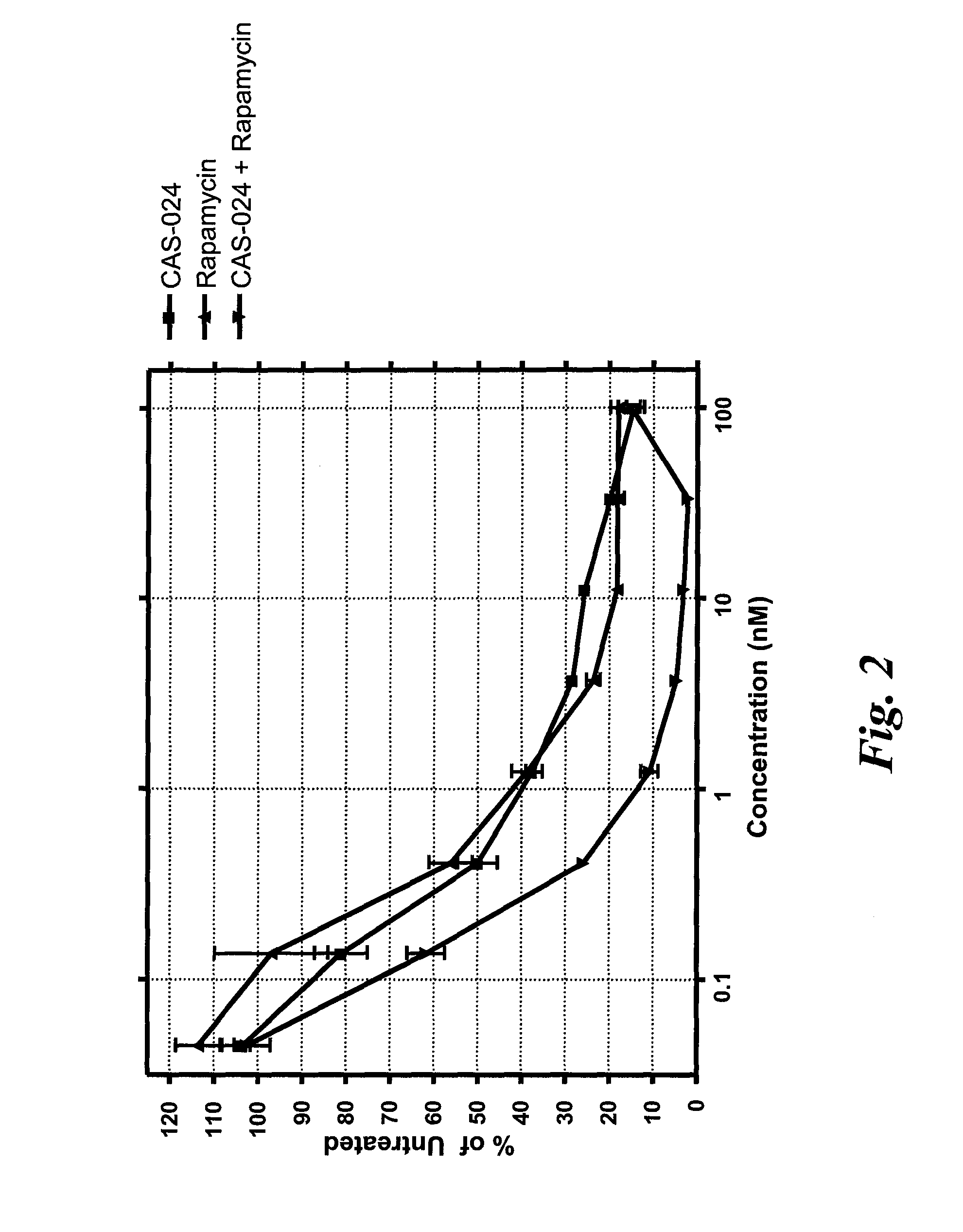
The present disclosure provides methods for using CD37-specific binding molecules (such as a CD37-specific SMIP or antibody) in combination with mTOR inhibitors (such as rapamycin and derivatives or analogues thereof) or phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors (such as p110δ-specific inhibitors or the like), which can be done concurrently or sequentially, to treat or prevent a B-cell related hyperproliferative disease, such as a lymphoma, carcinoma, myeloma, or the like.
Owner:EMERGENT PRODUCTS DEVELOPMENT SEATTLE LLC
Anti cd37 antibodies
InactiveUS20100189722A1Lower levelImprove the level ofAntipyreticAnalgesicsDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
CD37-Binding Molecules and Immunoconjugates Thereof
Novel anti-cancer agents, including, but not limited to, antibodies and immunoconjugates, that bind to CD37 are provided. Methods of using the agents, antibodies, or immunoconjugates, such as methods of inhibiting tumor growth are further provided.
Owner:DEBIOPHARM INTERNATIONAL SA
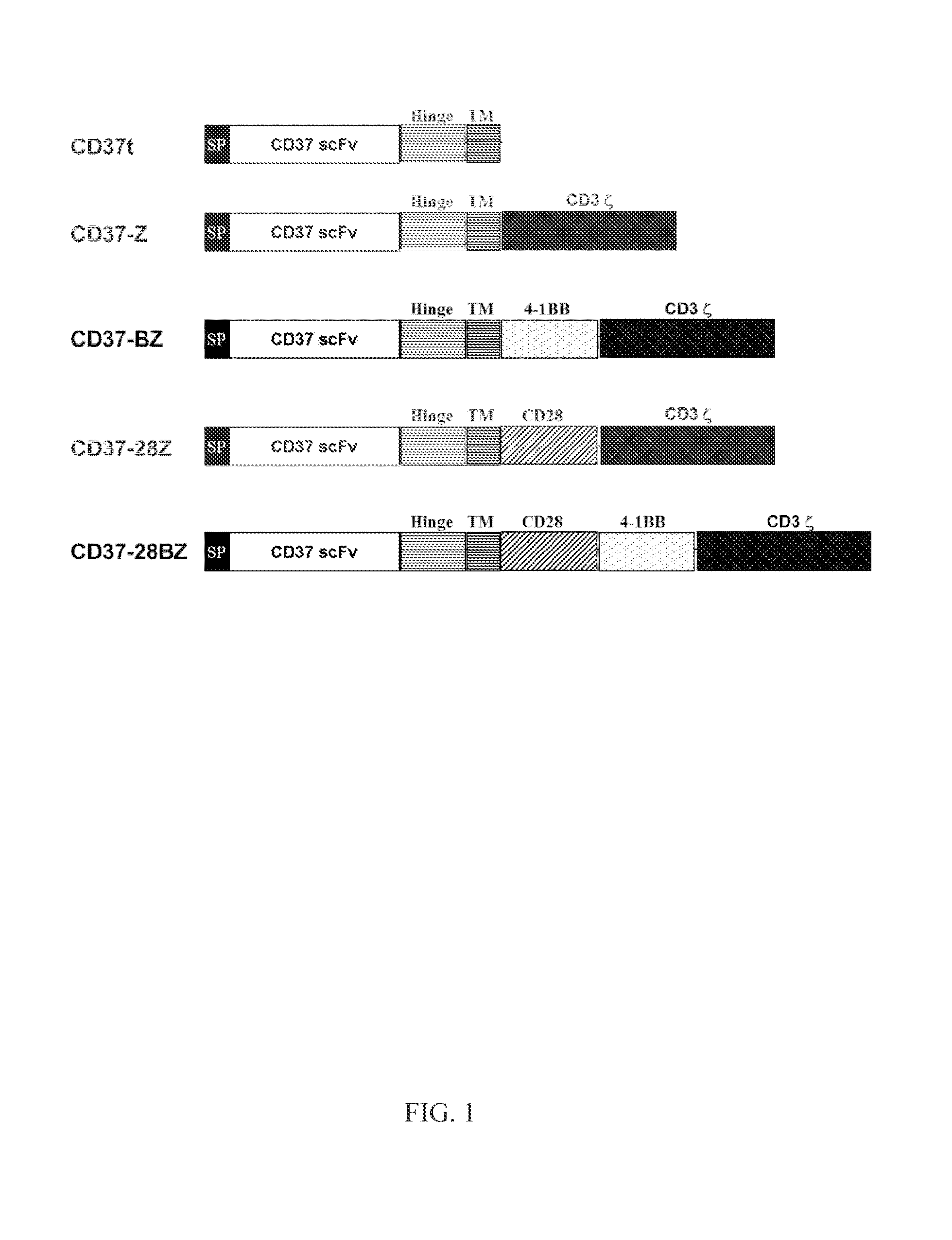
Chimeric antigen receptors and immune cells targeting b cell malignancies
The disclosure describes genetically engineered CD37 specific redirected immune effector cells expressing a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) protein comprising an antigen binding domain derived from an antibody, a single chain antibody or portion thereof that binds CD37; a hinge region; a transmembrane domain and an intracellular signaling domain derived from human CD3ζ or FcRγ; and optionally one or more co-stimulatory intracellular signaling domains The invention includes nucleic acids, vectors and immune effector cells associated with the production of the CAR protein, as well as methods of treating B cell malignancies in humans by cellular immunotherapy.
Owner:BLUEBIRD BIO INC
CD37-Binding Molecules and Immunoconjugates Thereof
ActiveUS20110256153A1Inhibit tumor growthTreat cancerMicroorganismsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAnticarcinogenCD37
Novel anti-cancer agents, including, but not limited to, antibodies and immunoconjugates, that bind to CD37 are provided. Methods of using the agents, antibodies, or immunoconjugates, such as methods of inhibiting tumor growth are further provided.
Owner:DEBIOPHARM INTERNATIONAL SA
Immunoregulatory antibodies and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080227198A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCD37CD23
A combination antibody therapy for treating B cell malignancies using an immunoregulatory antibody, especially an anti-B7, anti-CD23, or anti-CD40L antibody and a B cell depleting antibody, especially anti-CD19, anti-CD20, anti-CD22 or anti-CD37 antibody is provided. Preferably, the combination therapy will comprise anti-B7 and anti-CD20 antibody administration.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Immunoregulatory antibodies and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080226626A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCD37CD23
A combination antibody therapy for treating B cell malignancies using an immunoregulatory antibody, especially an anti-B7, anti-CD23, or anti-CD40L antibody and a B cell depleting antibody, especially anti-CD19, anti-CD20, anti-CD22 or anti-CD37 antibody is provided. Preferably, the combination therapy will comprise anti-B7 and anti-CD20 antibody administration.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
CD37-Binding Molecules and Immunoconjugates Thereof
Owner:DEBIOPHARM INTERNATIONAL SA
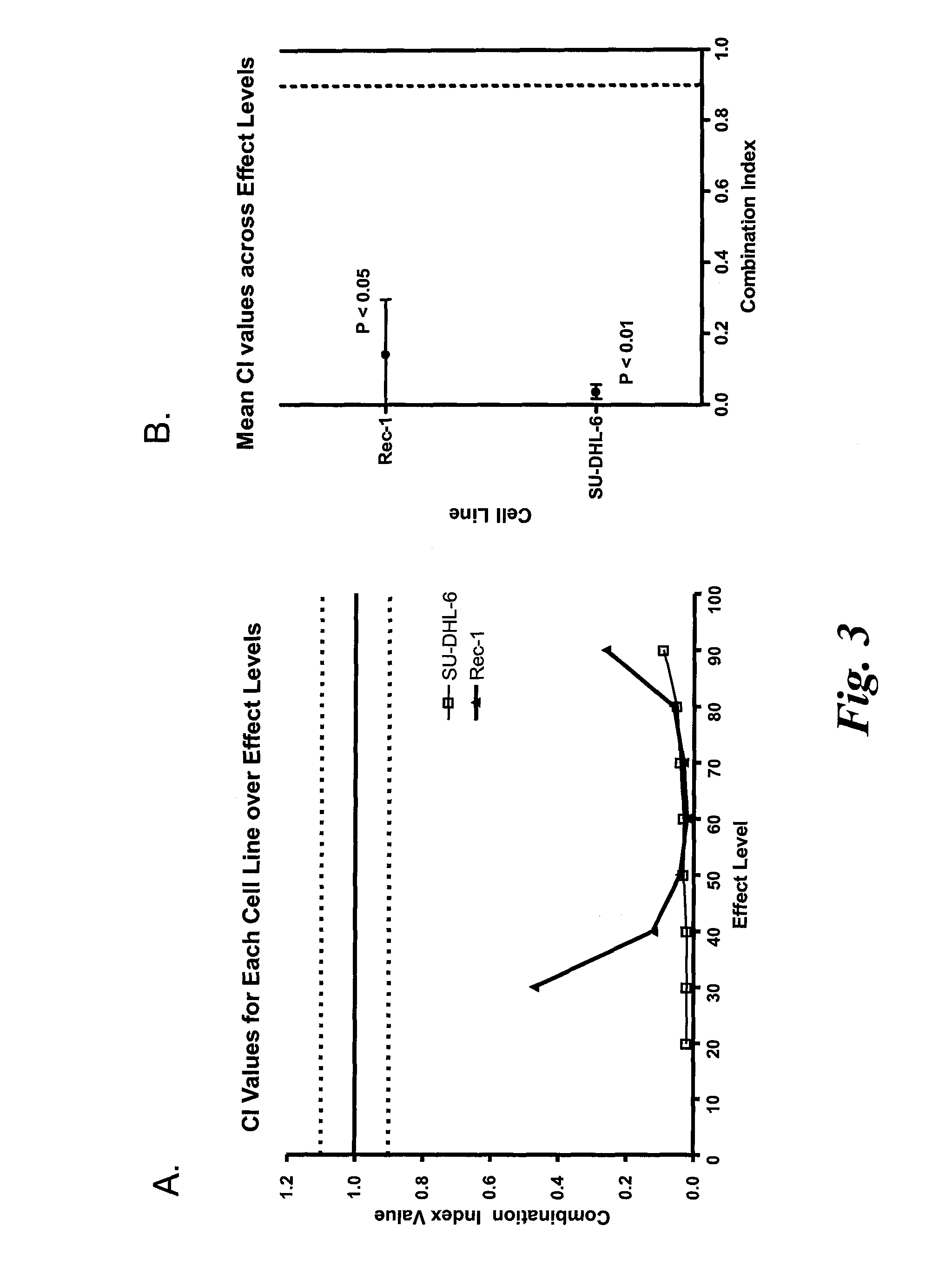
Combination of CD37 antibodies with ICE
InactiveUS8992915B2High degreeGood benefitOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
The present invention relates to immunotherapies that are based on depletion of CD37-positive cells such as B-cells. The present invention provides methods for reduction of CD37-positive cells such as B-cells in an individual / patient using a combination of CD37 antibody / antibodies and ICE. The combination of CD37 antibodies and ICE is shown to have improved anti-tumor efficacy compared to single agent treatment. The application further provides materials and methods for treatment of diseases involving aberrant B-cell activity.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
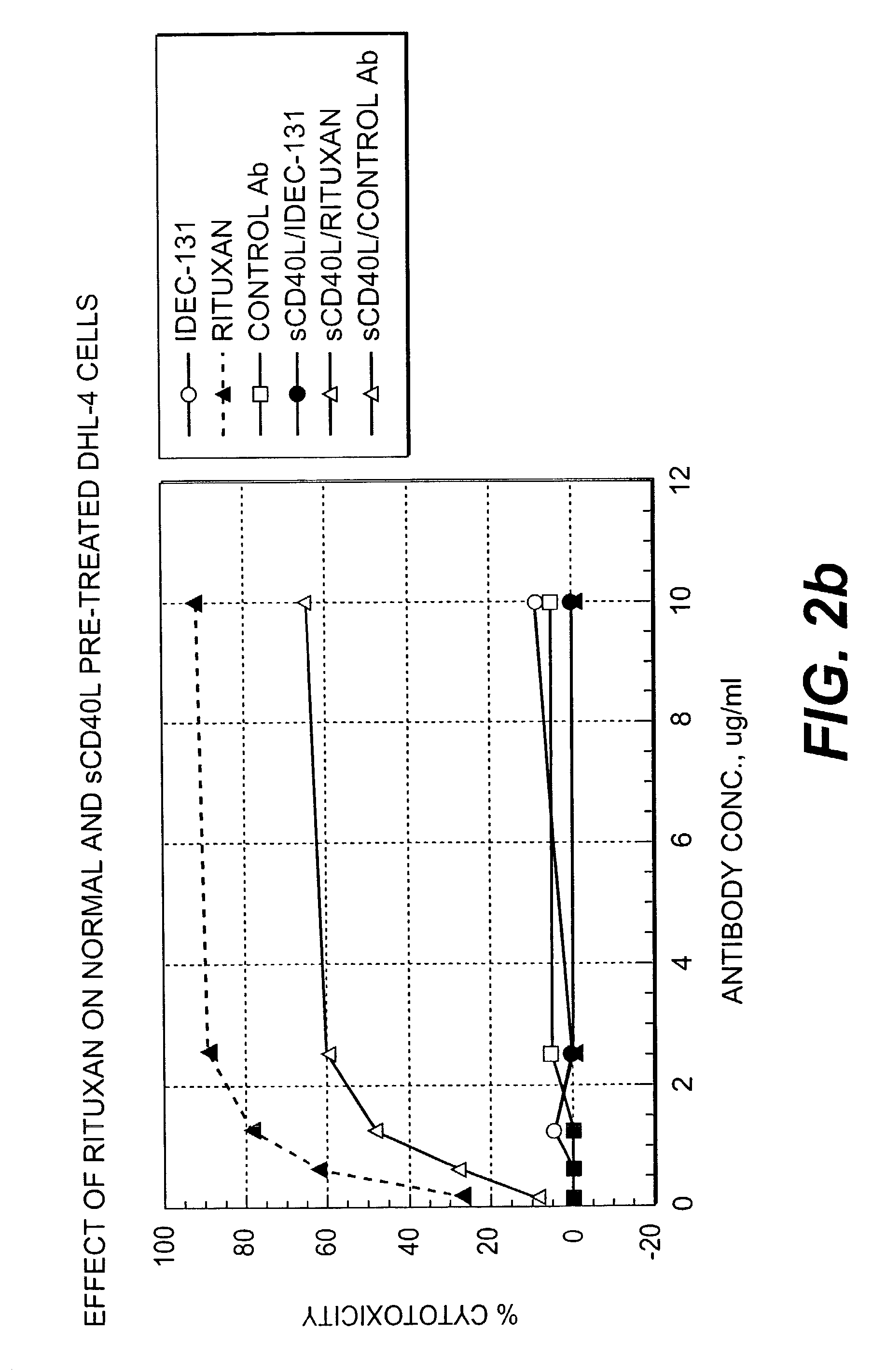
Combination of cd37 antibodies with rituximab
InactiveUS20130309224A1Improve stabilityEasy to manageOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseCD20
The present invention relates to immunotherapies that are based on depletion of CD37-positive cells such as B-cells. The present invention provides methods for reduction of CD37-positive cells such as B-cells in an individual / patient using a combination of CD37 antibody / antibodies and bendamustine. The combination of CD37 antibodies, CD20 antibodies and bendamustine is shown to have a synergistic effect. The application further provides materials and methods for treatment of diseases involving aberrant B-cell activity.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Combination of cd37 antibodies with bendamustine
InactiveUS20130287797A1Improve stabilityEasy to manageOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseCD37
The present invention relates to immunotherapies that are based on depletion of CD37-positive cells such as B-cells. The present invention provides methods for reduction of CD37-positive cells such as B-cells in an individual / patient using a combination of CD37 antibody / antibodies and bendamustine. The combination of CD37 antibodies and bendamustine is shown to have a synergistic effect. The application further provides materials and methods for treatment of diseases involving aberrant B-cell activity.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
CD37-binding molecules and immunoconjugates thereof
Owner:DEBIOPHARM INTERNATIONAL SA
Anti cd37 antibodies
InactiveUS20110165153A1Lower levelImprove the level ofAntipyreticMicroorganismsDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
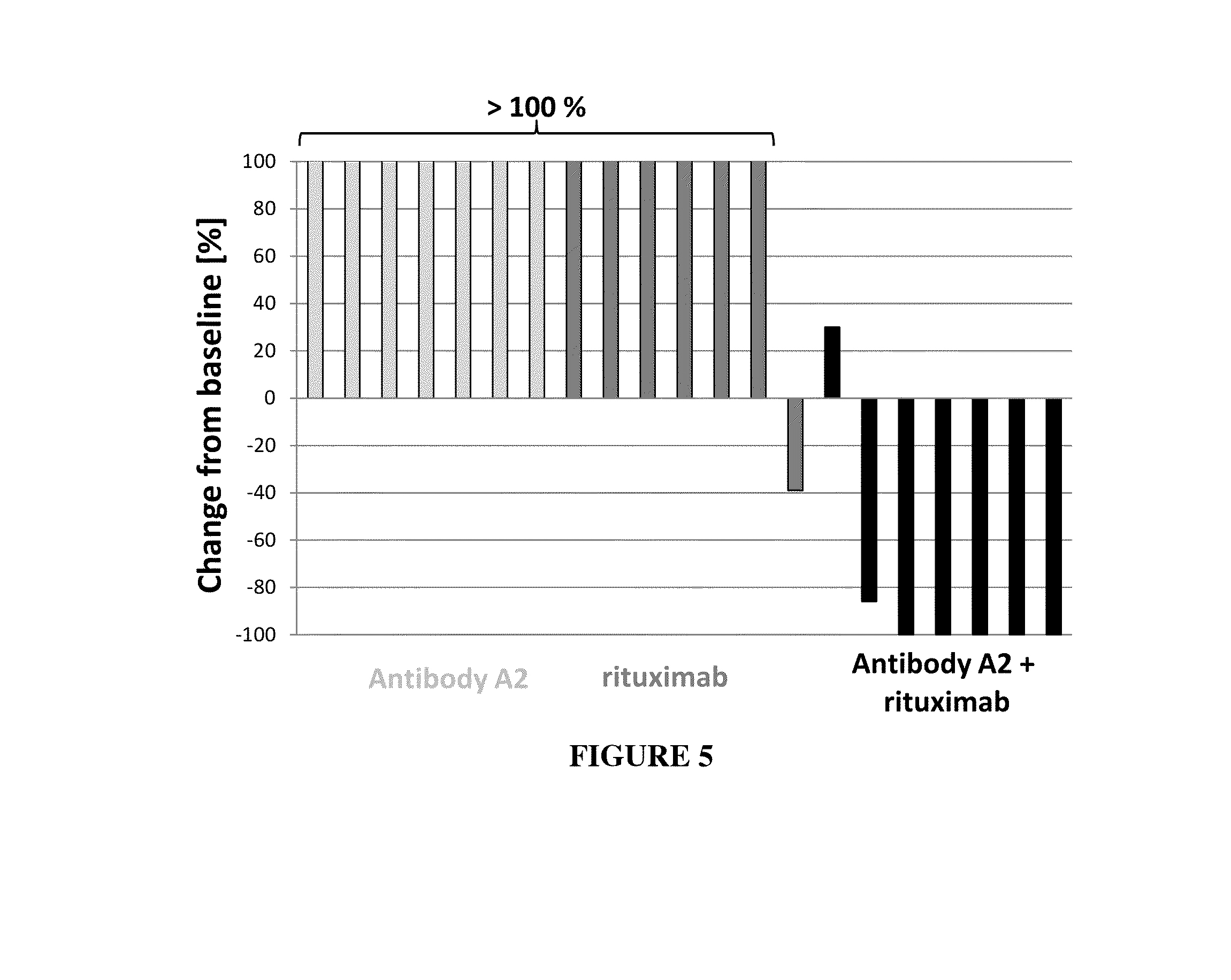
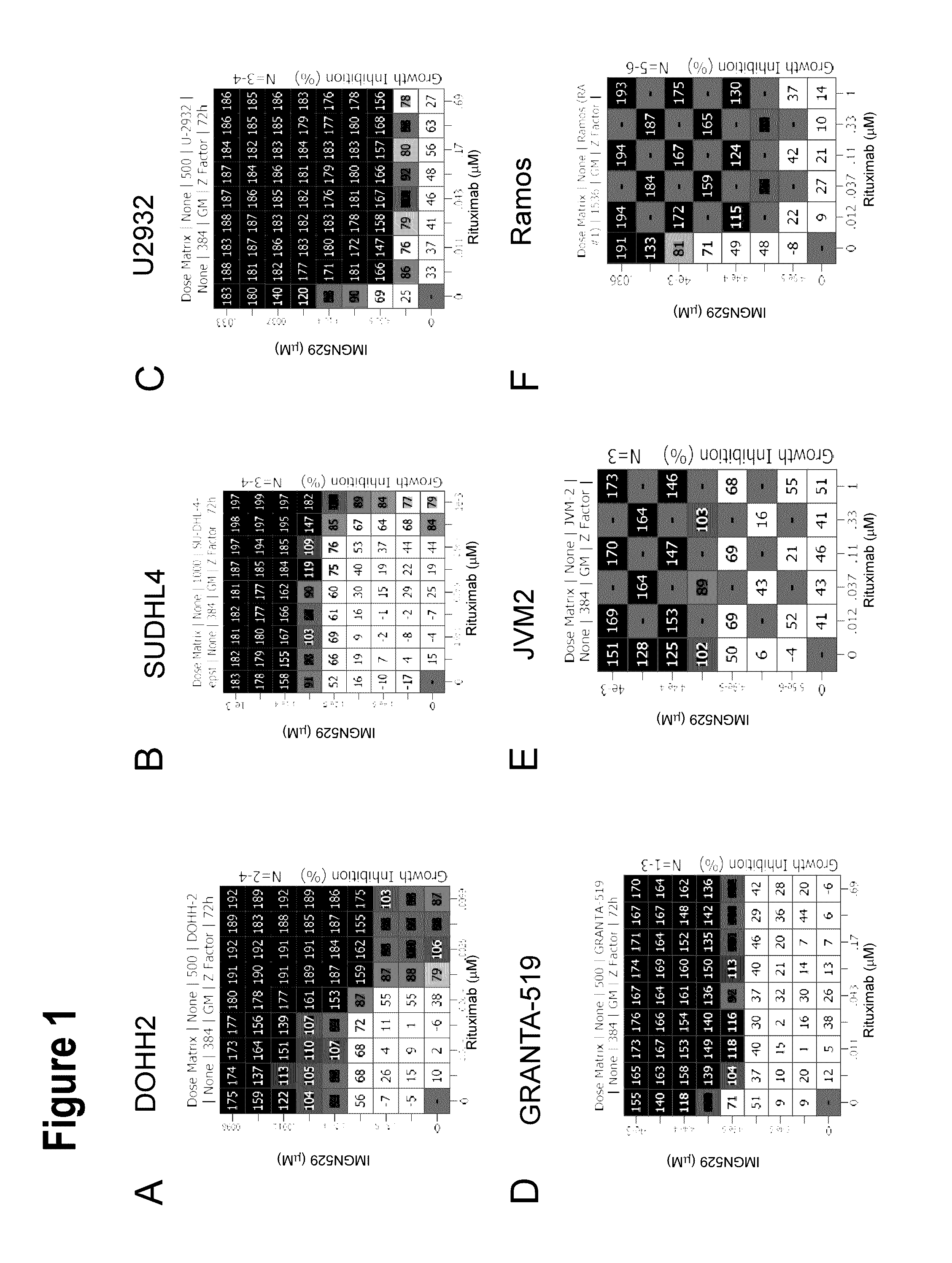
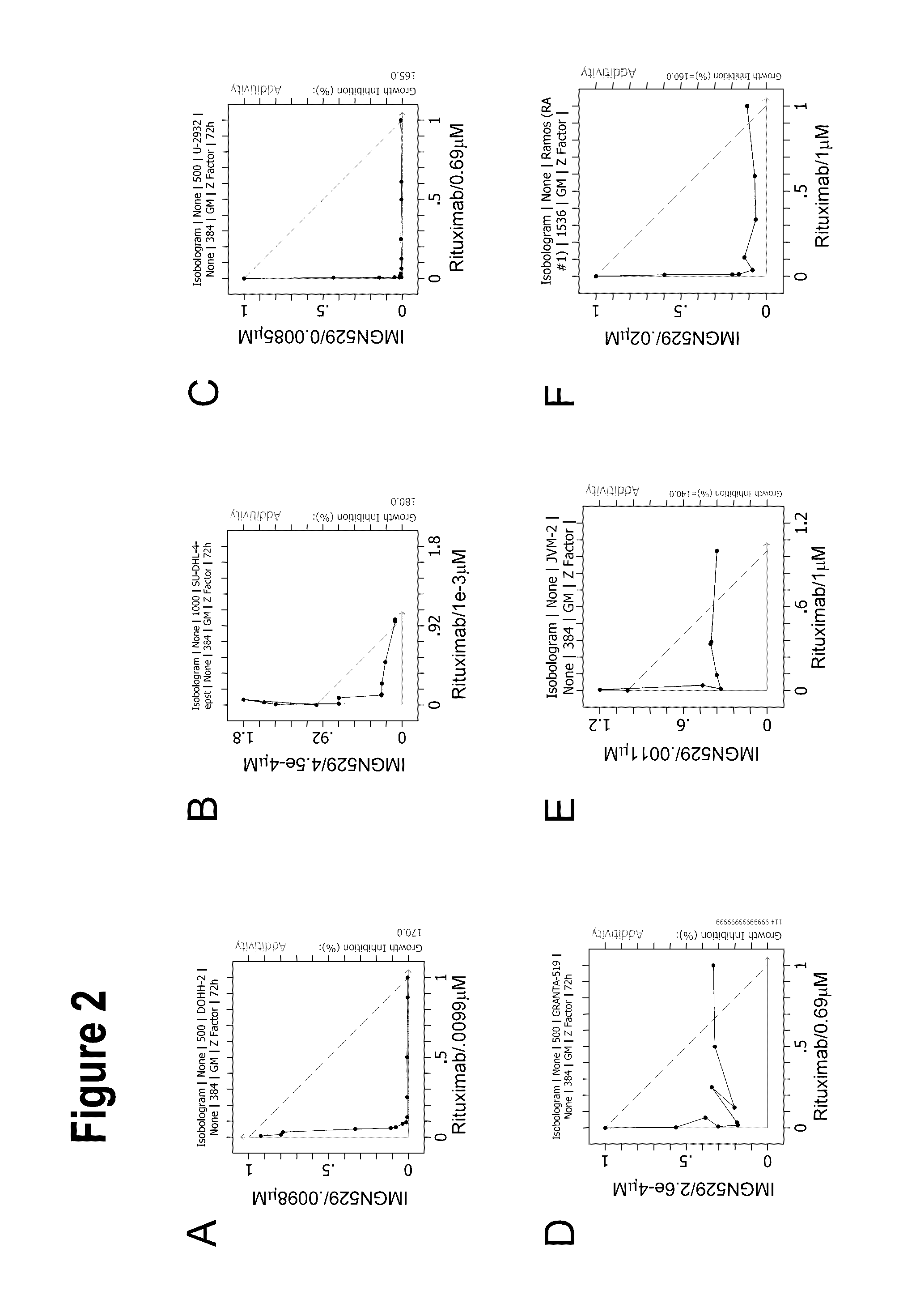
Anti-cd37 immunoconjugate and Anti-cd20 antibody combinations
InactiveUS20170000900A1Efficacy and synergy and reduction in toxicityImprove efficacyPharmaceutical delivery mechanismImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCD20Antiendomysial antibodies
Methods of administering immunoconjugates that bind to CD37 (e.g., IMGN529) in combination with antibodies that bind to CD20 are provided. The methods comprise administering an anti-CD37 immunoconjugate (e.g., IMGN529) and an anti-CD20 antibody to a person in need thereof, for example, a cancer patient.
Owner:DEBIOPHARM INTERNATIONAL SA
Antibody drug conjugates (ADC) that bind to CD37 proteins
Antibody drug conjugates (ADC's) that bind to CD37 protein and variants thereof are described herein. CD37 exhibits a distinct and limited expression pattern in normal adult tissue(s), and is aberrantly expressed in the cancers listed in Table I. Consequently, the ADC's of the invention in some embodiments provide a therapeutic composition for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:AGENSYS
Anti cd37 antibodies
InactiveUS20140004110A1Lower levelImprove the level ofAntipyreticAnalgesicsDiseaseAutoimmune responses
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
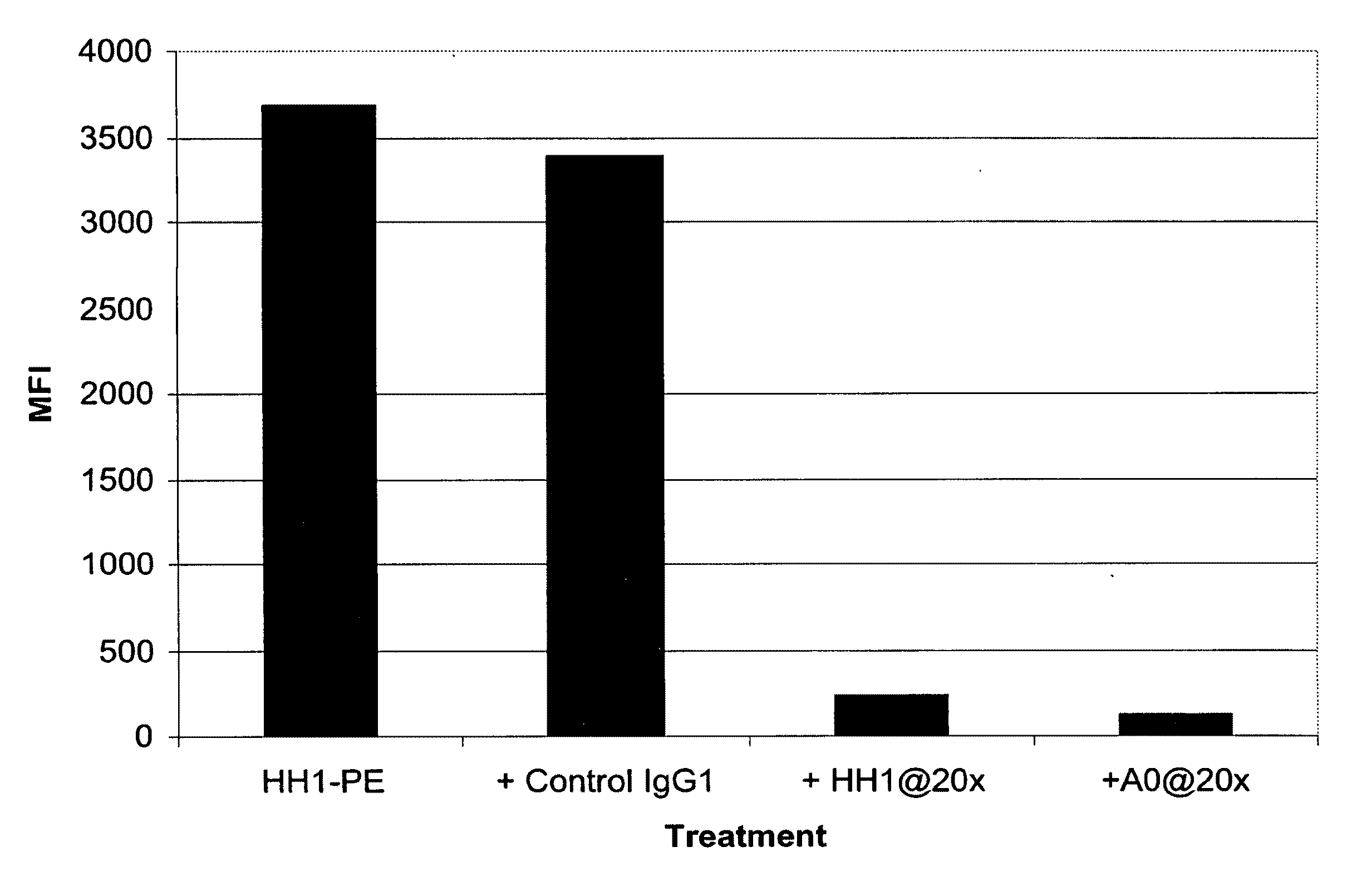
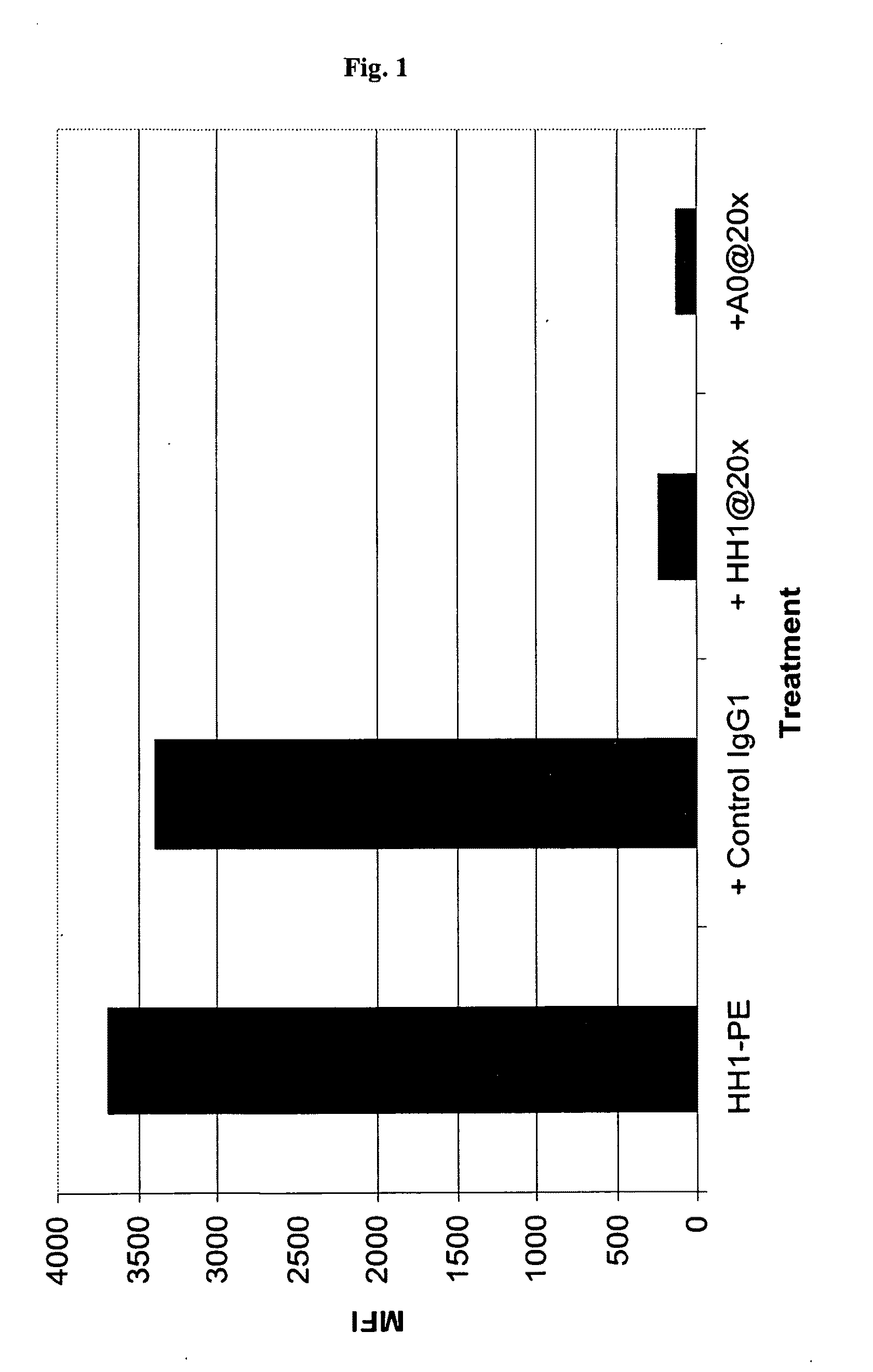
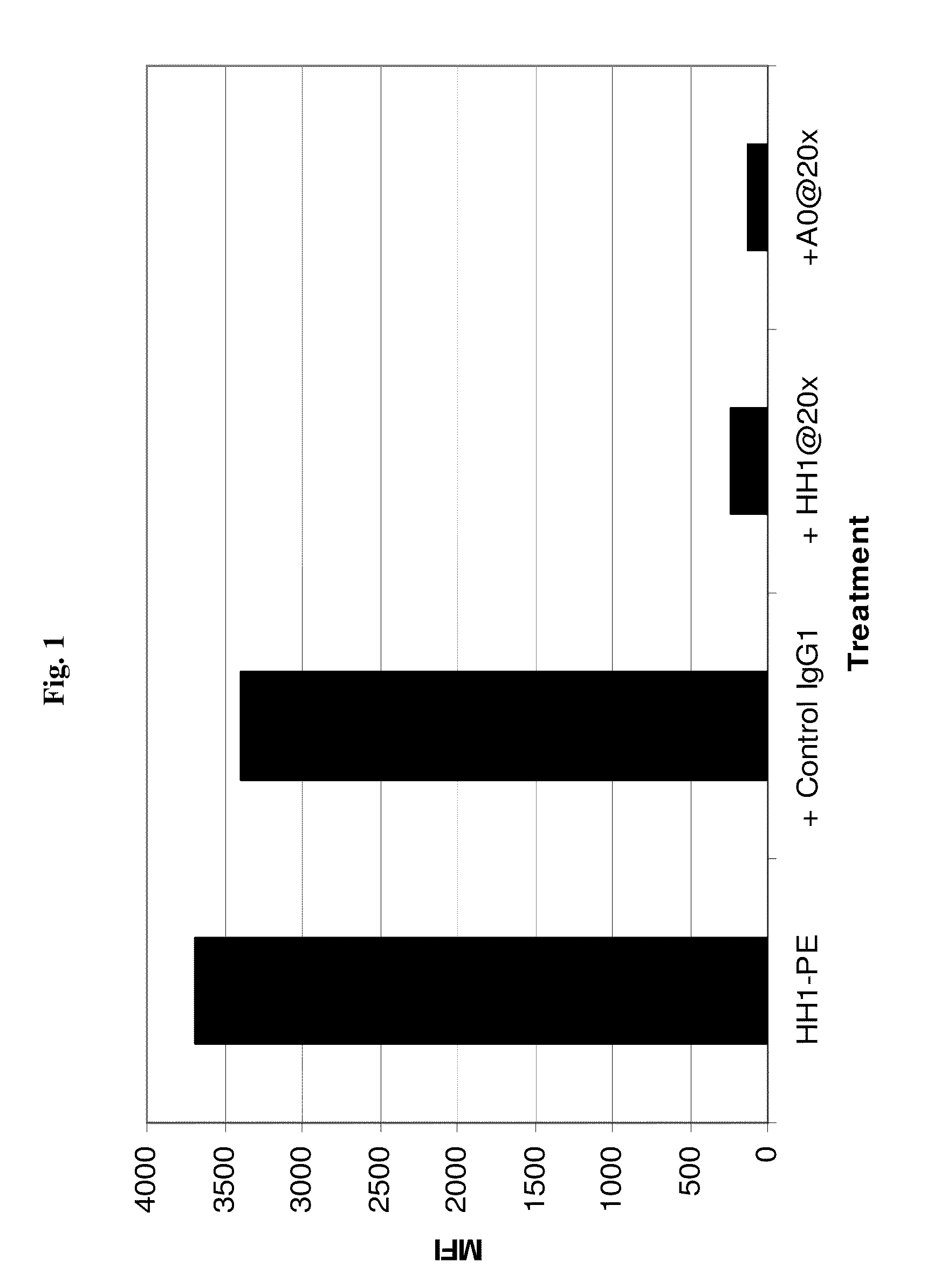
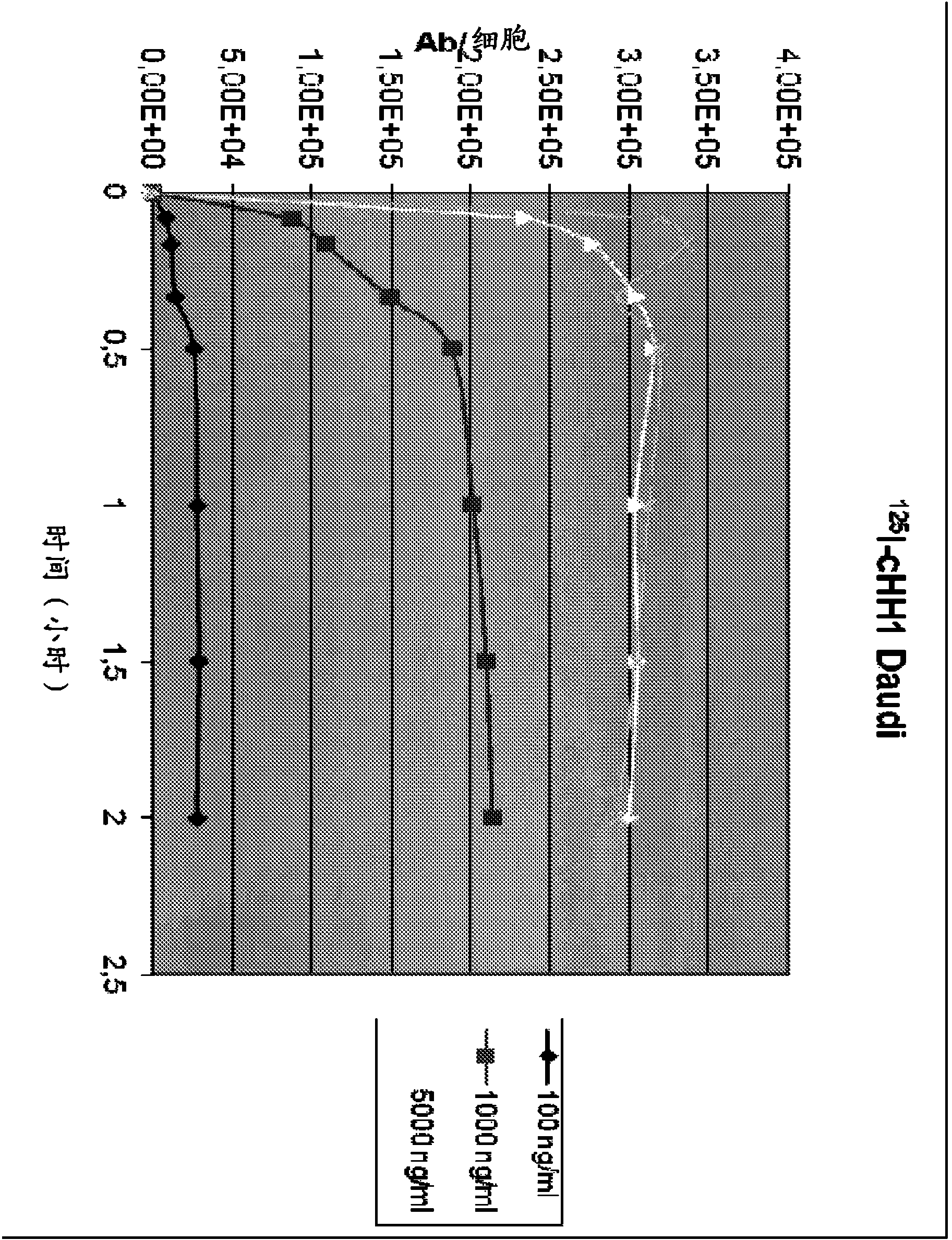
Chimeric therapeutic anti-CD37 antibodie HH1
InactiveCN104114192ARadioactive preparation carriersImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCD37Radioimmunoconjugate
The present invention relates to chimieric or humanized antibodies derived from the mouse monoclonal antibody HH1. The applications of the present invention include therapeutic applications in which pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies of the present invention or radioimmunoconjugates hereof are used for treating B-cell malignancies.
Owner:NORDIC NANOVECTOR
Anti-cd37 immunoconjugate and Anti-cd20 antibody combinations
ActiveUS20190183788A1Improve efficacySynergistic efficacy against tumorsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCD20Antiendomysial antibodies
Methods of administering immunoconjugates that bind to CD37 (e.g., IMGN529) in combination with antibodies that bind to CD20 are provided. The methods comprise administering an anti-CD37 immunoconjugate (e.g., IMGN529) and an anti-CD20 antibody to a person in need thereof, for example, a cancer patient.
Owner:DEBIOPHARM INTERNATIONAL SA
Combination of cd37 antibodies with ice
InactiveUS20130309225A1Improve stabilityEasy to manageOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseCD37
The present invention relates to immunotherapies that are based on depletion of CD37-positive cells such as B-cells. The present invention provides methods for reduction of CD37-positive cells such as B-cells in an individual / patient using a combination of CD37 antibody / antibodies and ICE. The combination of CD37 antibodies and ICE is shown to have improved anti-tumor efficacy compared to single agent treatment. The application further provides materials and methods for treatment of diseases involving aberrant B-cell activity.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Anti-cd37 antibodies and Anti-cd20 antibodies, compositions and methods of use thereof
PendingUS20210371539A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCD20Disease
The present invention relates to anti-CD37antibodies having an Fc-Fc interaction enhancing substitution in the Fc-region of a human IgG, for use as a medicament in combination with anti-CD20 antibodies having an Fc-Fc interaction enhancing substitution in the Fc-region of a human IgG. The invention also relates to a novel composition of anti-CD37 antibodies having an Fc-Fc 5 interaction enhancing substitution and anti-CD20 antibodies having an Fc-Fc interaction enhancing substitution. In particular, the invention relates to compositions wherein the anti-CD37 antibody binds human CD37 and the anti-CD20 antibody binds human CD20. The invention also relates to compositions where the composition is a pharmaceutical composition and the use of such compositions in treatment of cancer and other diseases.
Owner:GENMAB HLDG BV
Kit for rapid detection of common mutant genes of thalassemia
The invention discloses a kit for rapid detection of common mutant genes of thalassemia. The kit includes primers designed specific to --<SEA>, --<THAI>, -alpha<2.4>, -alpha<21.9>, HPFH-SEA, DBT, -alpha<4.2>, -alpha<3.7>, alpha<CS>alpha, alpha<QS>alpha, alpha<Westmead>alpha, Hb Q-Thailand, beta<-90>, beta<-29>, beta<-28>, beta<Cap+40-43>, beta<Int M>, beta<Int CD>, beta<CD14-15>, beta<CD17>, beta<CD26>, beta<27 / 28>, beta<IVS-I-1>, beta<IVS-I-5>, beta<CD37>, beta<CD41-42>, beta<CD43>, beta<CD71-72>, beta<CD95>, and beta<IVS-II-654> and gender detection primers, and the primers are subpackaged in 2 tubes. The kit provided by the invention can rapidly and accurately detect the common mutant genes of thalassemia.
Owner:亚能生物技术(深圳)有限公司
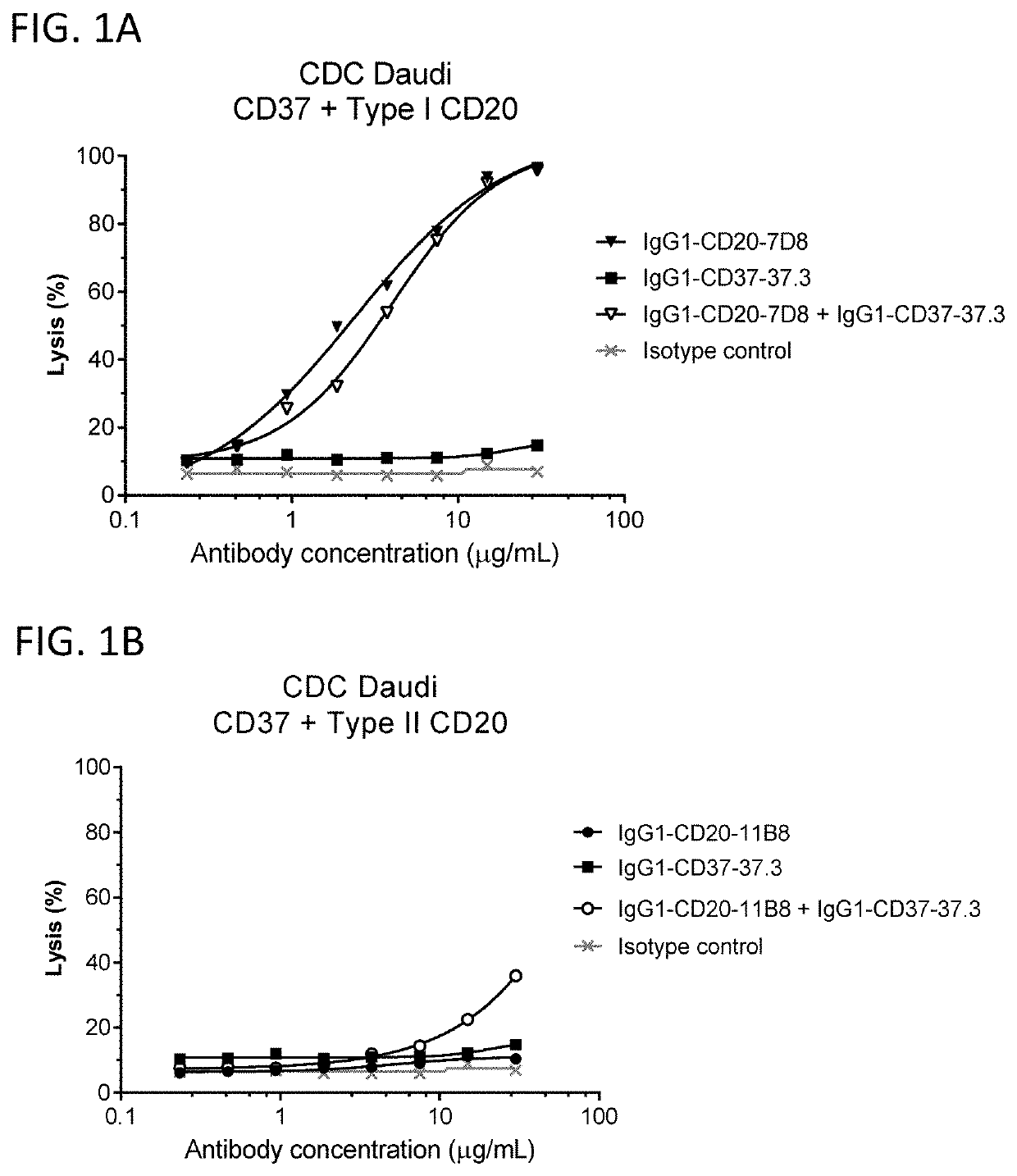
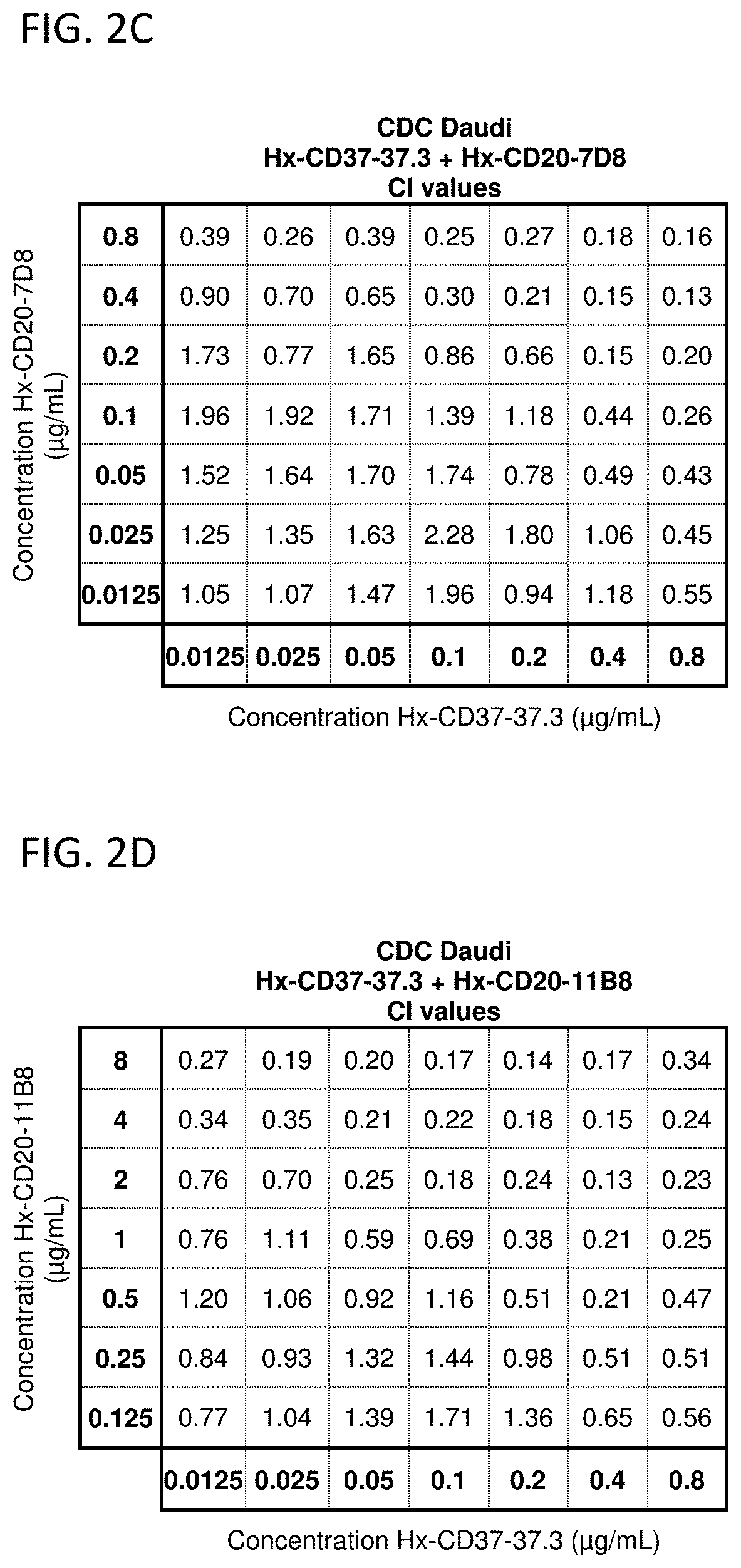
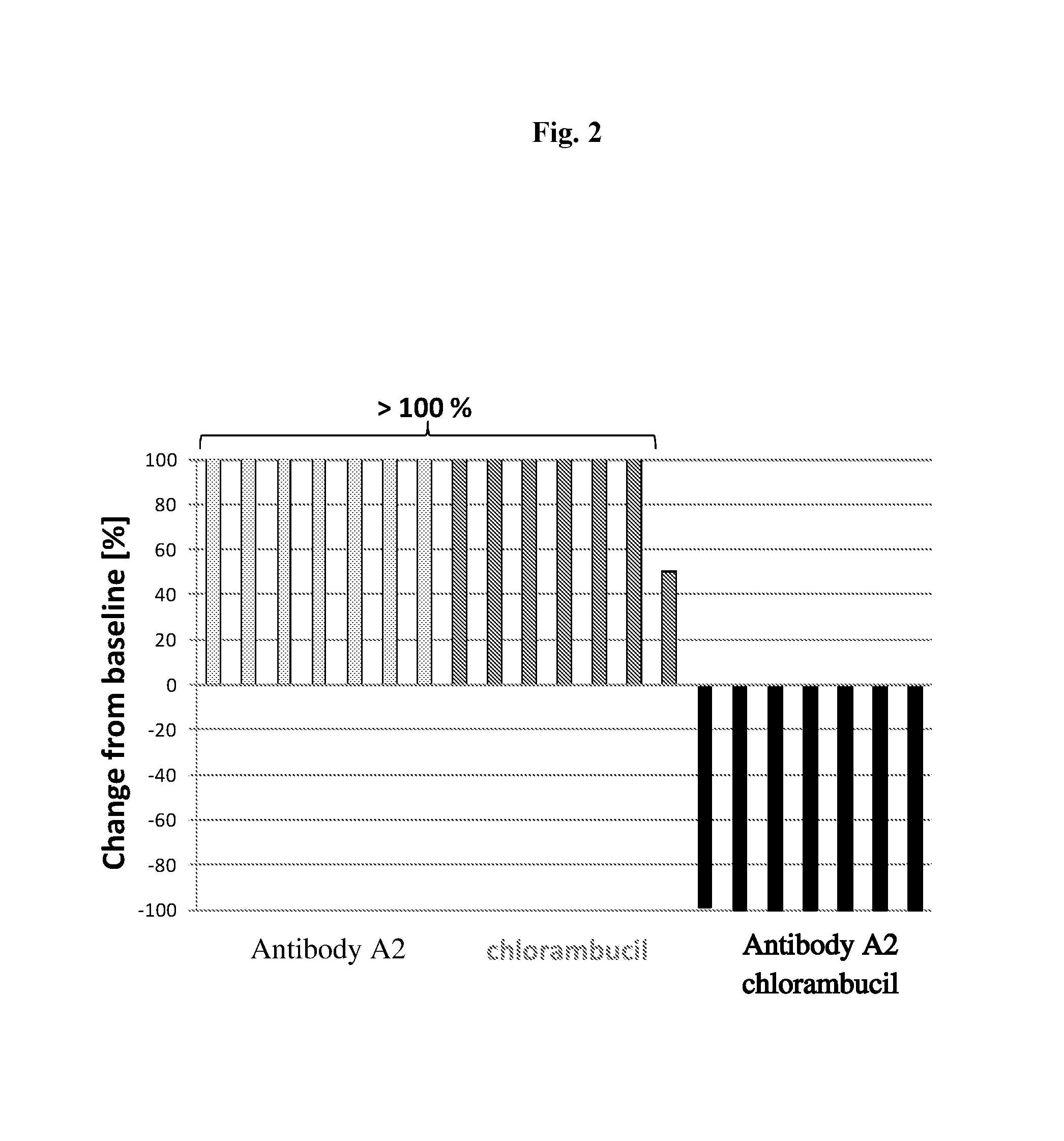
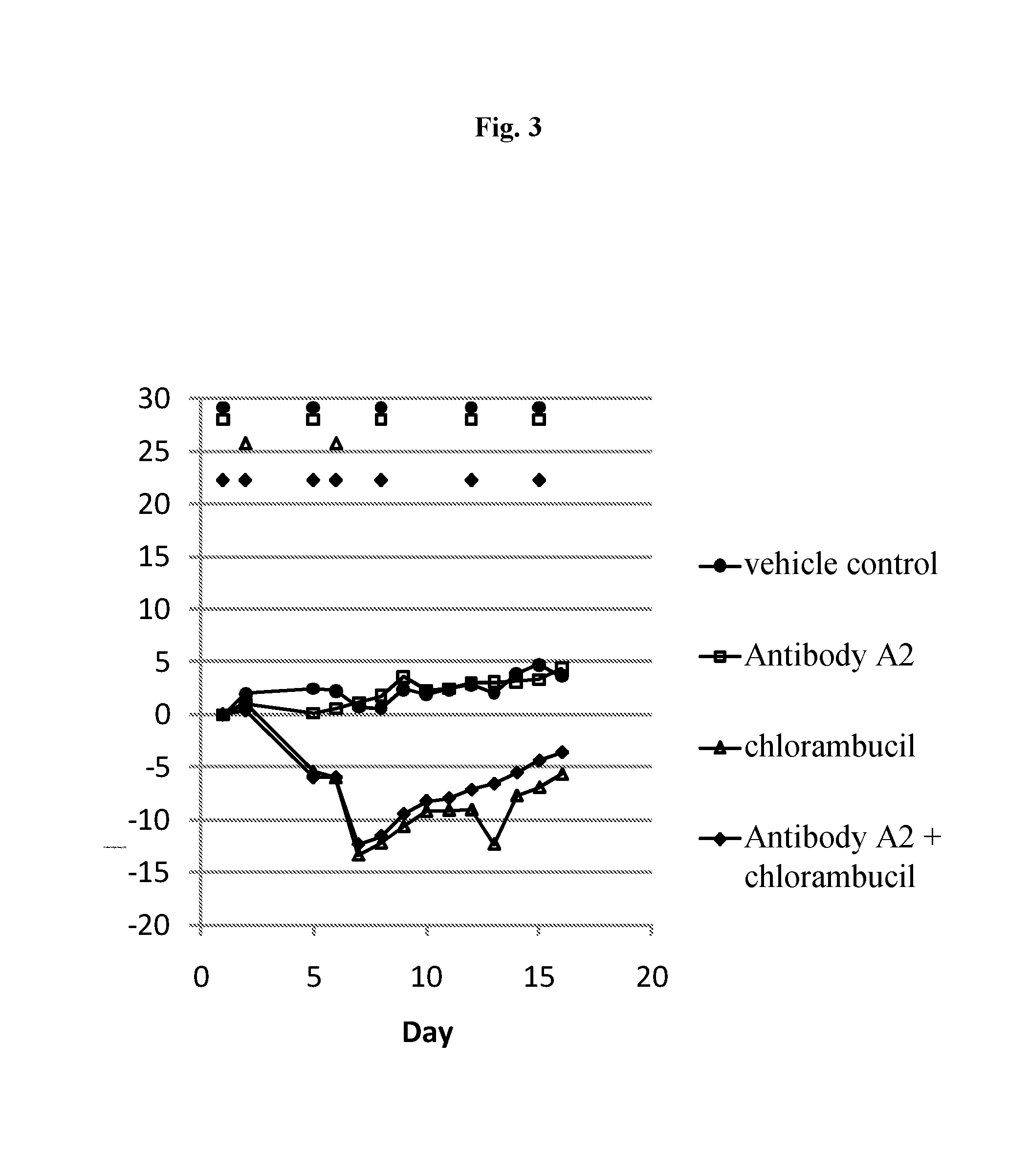
Combination of cd37 antibodies with chlorambucil
InactiveUS20160106837A1Improve stabilityEasy to manageOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseCD37
The present invention relates to immunotherapies that are based on depletion of CD37-positive cells such as B-cells. The present invention provides methods for reduction of CD37-positive cells such as B-cells in an individual / patient using a combination of CD37 antibody / antibodies and chlorambucil. The combination of CD37 antibodies and chlorambucilis shown to have a synergistic effect. The application further provides materials and methods for treatment of diseases involving aberrant B-cell activity.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Antibody drug conjugates (ADC) that bind to cd37 proteins
Antibody drug conjugates (ADC's) that bind to CD37 protein and variants thereof are described herein. CD37 exhibits a distinct and limited expression pattern in normal adult tissue(s), and is aberrantly expressed in the cancers listed in Table I. Consequently, the ADC's of the invention in some embodiments provide a therapeutic composition for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:AGENSYS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com