Anti cd37 antibodies
a technology of anti-cd37 and antibody molecules, applied in the field of immunotherapies, to achieve the effect of exquisite antigen specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
Chimeric mAb A0 Specifically Recognizes the CD37 Antigen
[0186]The specificity of MAb A0 for cellular CD37 is tested in a FACS competition assay on Ramos Burkitt lymphoma cells (ATCC #CRL-1596). Cells are grown in tissue culture flasks (175 cm2) using RPMI-1640+ GlutaMAX supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, 12.5 mM HEPES, 1 mM sodium pyruvat, 1% MEM non-essential amino acids as culture medium. Cells are cultivated with an initial density of 3×105 cells / ml at 37° C. and 5% CO2 in a humidified atmosphere for three days. The cultures are maintained at a cell concentration between 3×105 and 1.8×106 / ml by sub-cultivation in a ratio of 1:6 with fresh culture medium 2-3 times a week. For FACS competition analysis, the CD37-specific mAb HH1 (Santa Cruz) directly labeled with phycoerythrin (PE) is used at a concentration of 1 μg / ml. The antibody is preincubated with the unlabelled competitor antibody A0 for 10 min at 4° C. at the indicated molar ratio. Thereafter, 1×105 ...
example 3
Binding of Humanized Versions of mAb A0 to Cellular CD37 Antigen
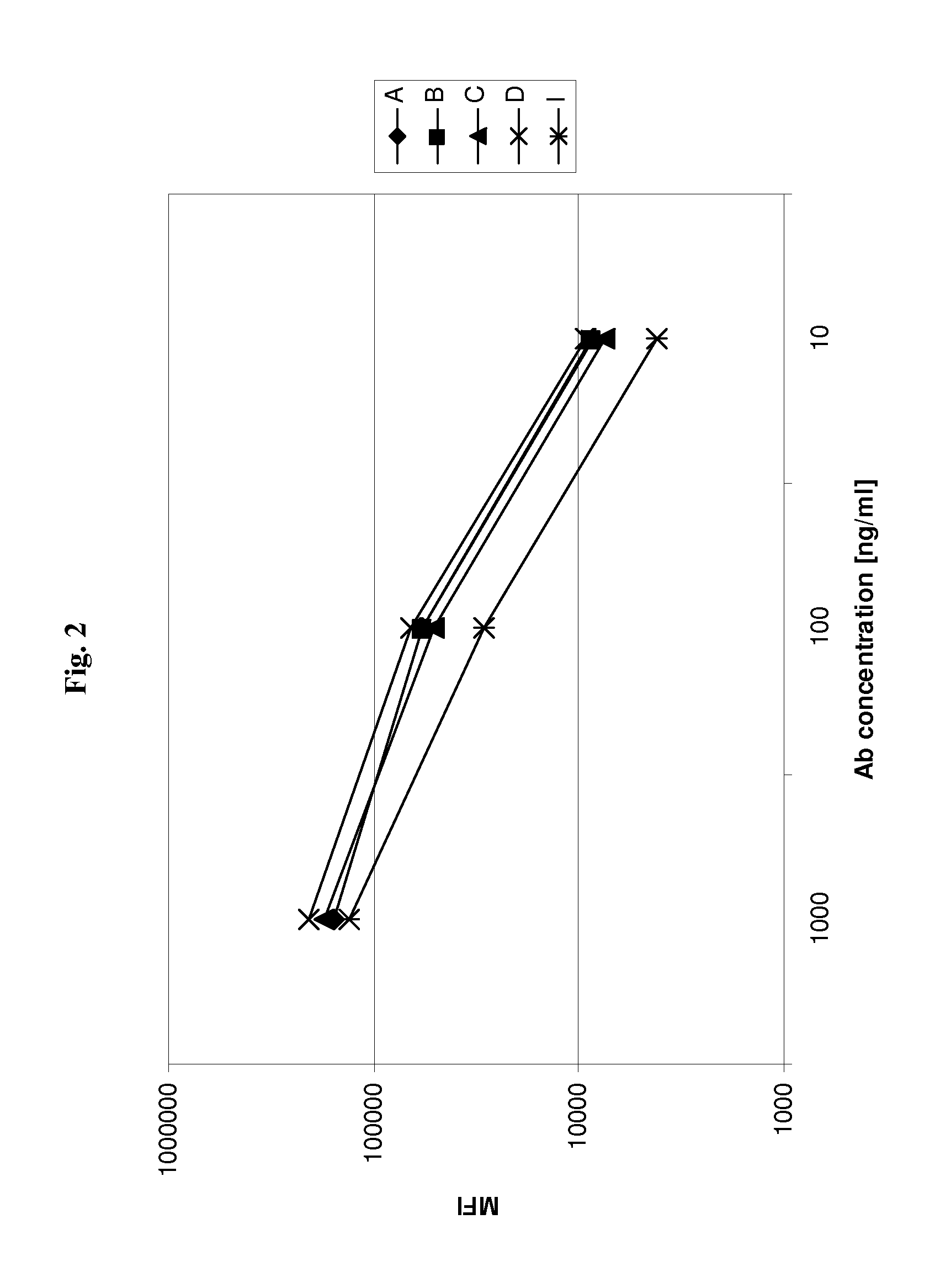
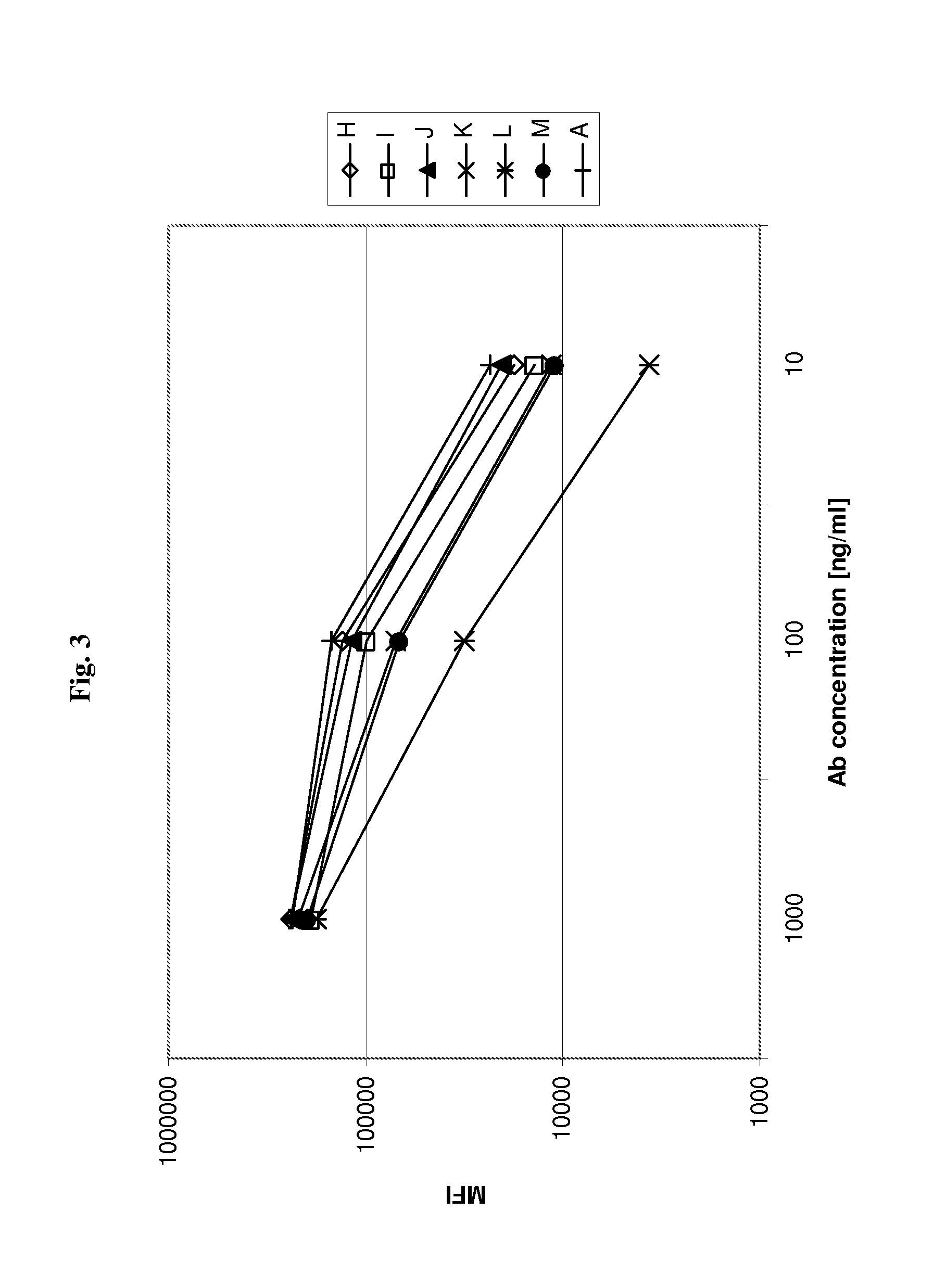
[0187]Humanized versions of A0 are tested for their binding to cellular CD37 antigen by FACS analysis. Antibodies are added to Ramos cells at the indicated concentrations and allowed for binding for 30 min at 4° C. Thereafter, bound antibody is detected with PE-labelled goat-anti-human IgG antibody (Sigma), cells are washed twice with PBS, and thereafter cells are resuspended in FACS buffer and analyzed by FACS on a BD FACS Canto. Examples are shown in FIGS. 2 and 3 (antibodies A, B, C, D, I or A, H, I, J, K, L and M, respectively; see Table 1). Several of the humanized versions of A0 show similar binding to Ramos cells as the parental antibody A0, indicating that humanization does not reduce binding to cellular CD37 antigen.
example 4
FACS Scatchard Analysis of Humanized Versions of Chimeric mAb A0
[0188]The affinity of humanized versions of antibody A0 (designated B, C, D, H, I and K; see Table 1) to cellular CD37 antigen is determined by FACS scatchard analysis as described elsewhere (Brockhoff et al., 1994). Briefly, antibody dilutions are prepared in a 96 well plate starting with 100-400 nM in the first well (80 μA), followed by 11 dilution steps (1:2, 40+40 μl). 50 μl of mAb dilutions are added to FACS tubes, 150 μl cells (0.8×106 / ml=1.2×105 cells / tube) are added to each FACS tube. Cells are gently mixed and incubated for 1 h on ice. Thereafter 50 μl FITC conjugated secondary antibody (conc. 15 μg / ml; mouse mAb anti-hu IgG all subclasses, Zymed 05-4211) is added, mixed, and incubated for 30 min on ice. 4 ml PBS ph7.2 containing 0.02% acid are added thereafter, cells are pelleted and resuspended in 300 μl PBS pH 7.2 and subjected to FACS analysis using a BD FACS Canto. All experimental steps are performed on w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com