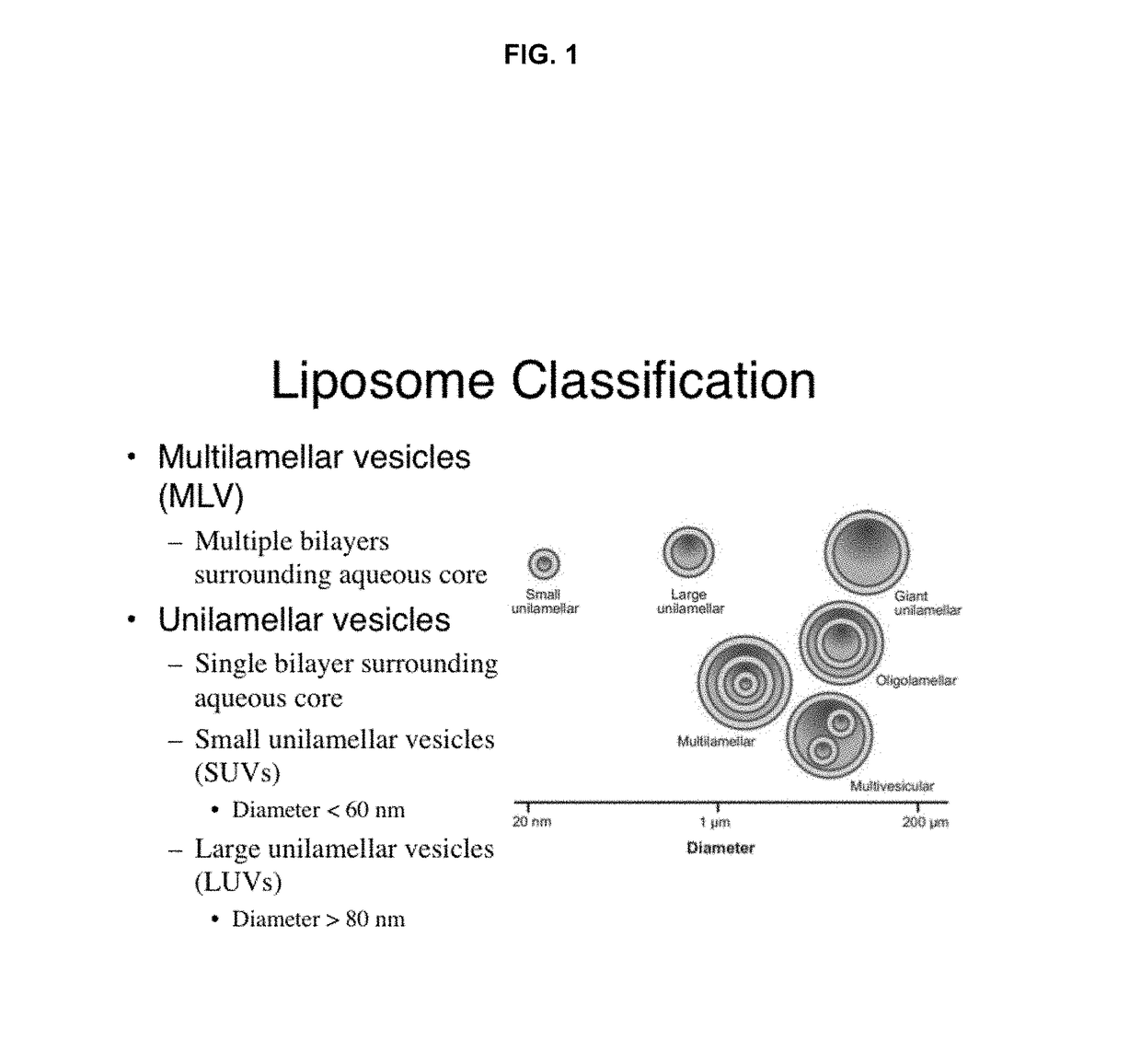
Remote loading of sparingly water-soluble drugs into liposomes
a technology of liposomes and water-soluble drugs, applied in the field of pharmaceutical compositions, can solve the problems of large loss of active compounds, and achieve the effect of high functional compound-lipid ratio and cost efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
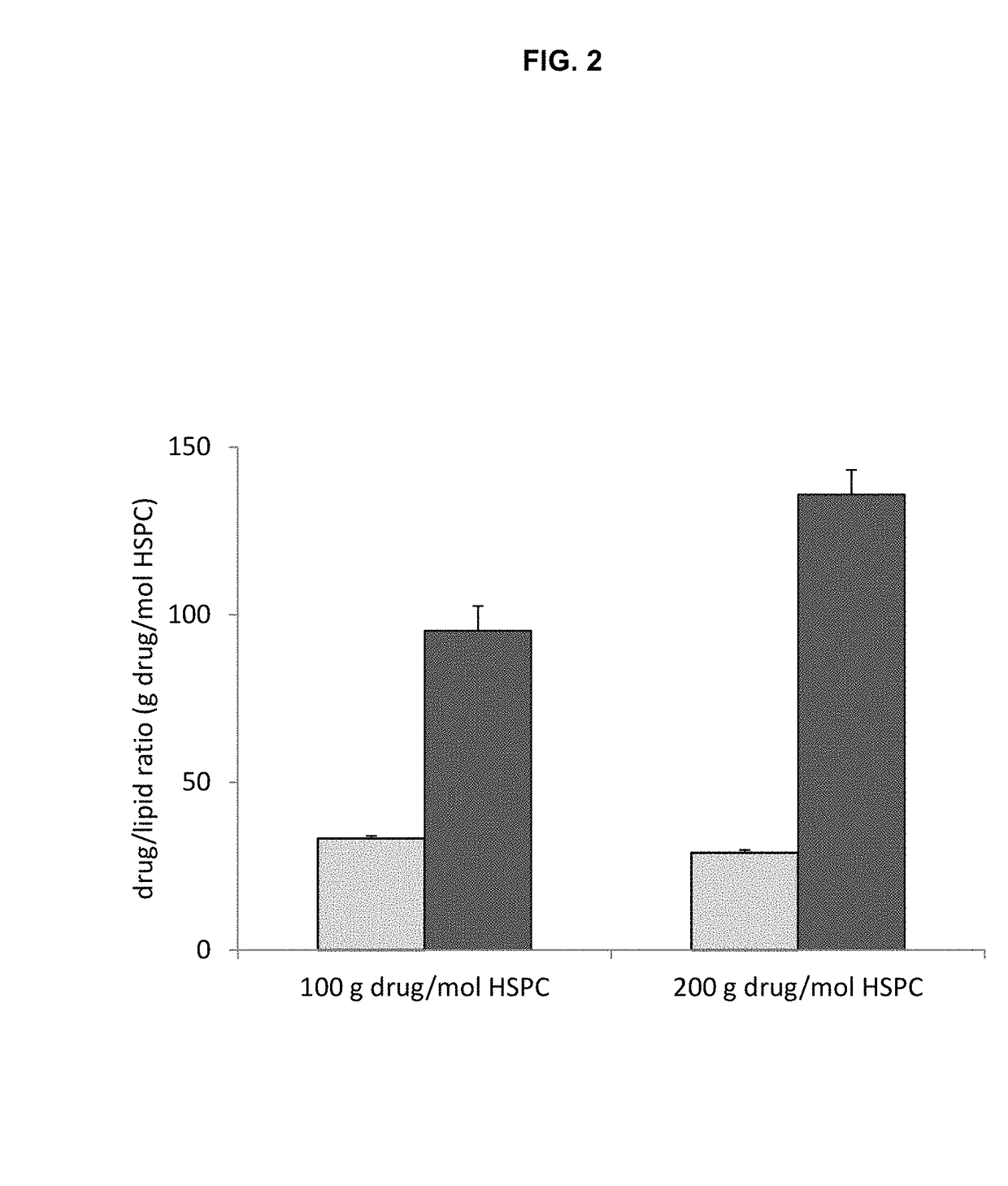
Carfilzomib Liposome Entrapment by Remote Loading
Materials and Method
[0120]Ammonium sulfate solution was prepared by dissolving ammonium sulfate solid to a final concentration of 250 mM (500 mequivilents of anion / L) no pH adjustment was made to yield a final pH of 5.6. Sodium sulfate solution (250 mM) was prepared by adding 0.35 g sodium sulfate to 10 mL deionized water.
[0121]The liposomes were formed by extrusion. Lipids were dissolved in ethanol at a concentration of 500 mM HSPC (591 mg / mL total lipid) at 65° C. and the 9 volumes of the trapping agent solution heated to 65° C. was added to the ethanol / lipid solution also at 65° C. The mixture was vortexed and transferred to a 10 mL thermostatically controlled (65° C.) Lipex Extruder. The liposomes were formed by extruding 10 times through polycarbonate membranes having 0.1 um pores. After extrusion the liposomes were cooled on ice. The transmembrane electrochemical gradient was formed by purification of the liposomes by dialysis i...
example 2
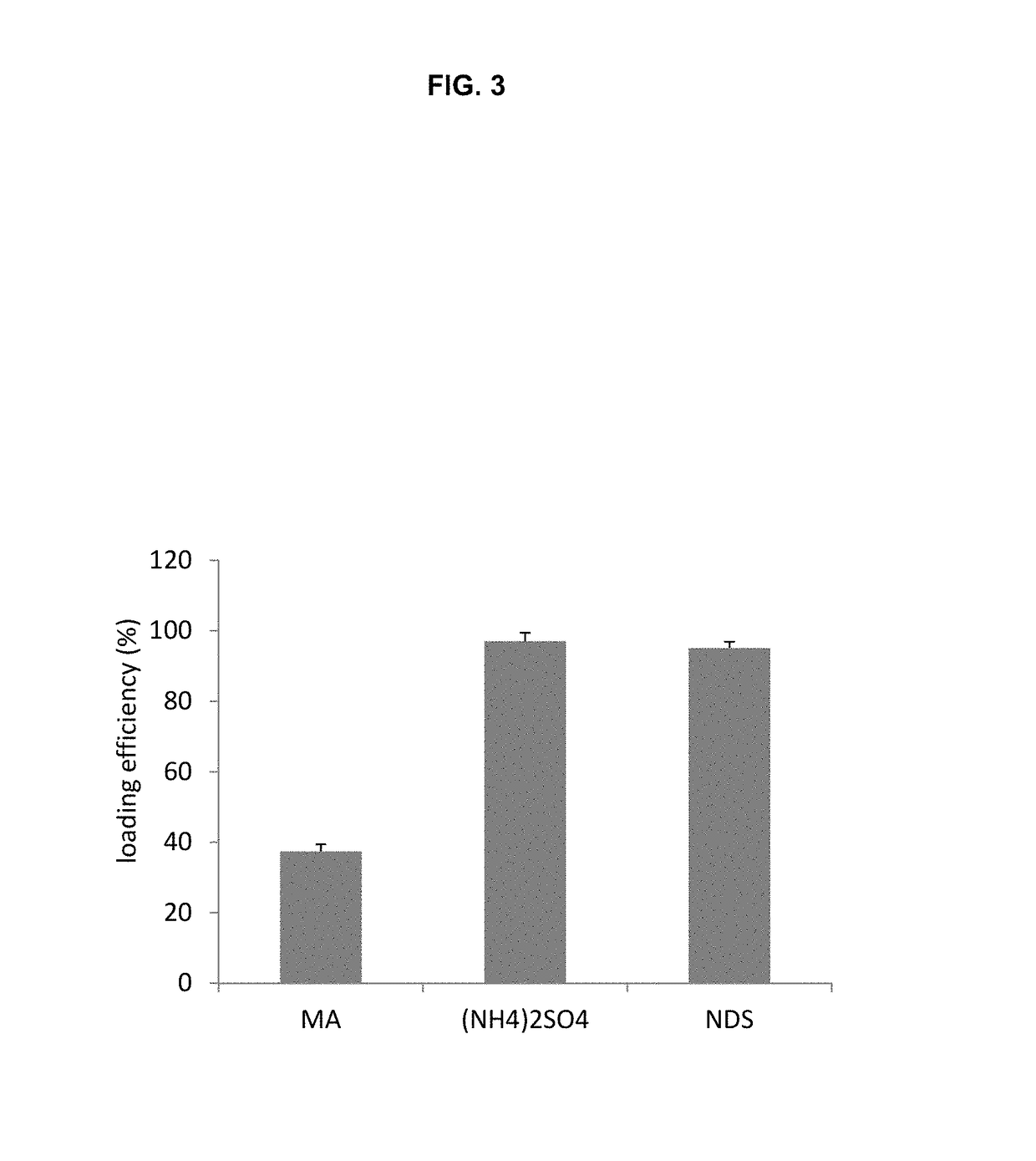
Comparison of Liposome Trapping Agents
Introduction
[0126]Liposomes to be used for remote loading are formed in an ionic solution that is intended to complex the loaded drug as a salt. Trapping agents can form complexes with loaded drugs and the stability of this complex is one factor that dictates liposome drug loading ability, stability and drug release rates. Comparison of different liposome trapping agents was made by evaluating the efficiency of carfilzomib loading.
Methods
[0127]Three liposome formulations were used, all at a molar ratio 3 HSPC / 2 Chol / 0.15 PEG-DSPE each with a different trapping agent: 1. mellitic acid; 2. ammonium sulfate; and 3. napthelene disulfononic acid.
[0128]Mellitic acid (MA) was dissolved in water and titrated with diethylamine to a final pH of 5.5 and concentration of 83 mM (500 mequivilents of anion / L). Ammonium sulfate was prepared by dissolving ammonium sulfate solid to a final concentration of 250 mM (500 mequivilents of anion / L) no pH adjustment was...
example 3
Comparison of Method for Introducing Drug
Method
[0134]A comparison of the method used for addition of the drug to the liposomes during the loading procedure. The loading procedure was the same as described above in Example 1 with the exception of the drug being added to the liposome loading solution as a solid powder, followed by the addition of DMSO to a final concentration of 2% (vol / vol), as a 10 mg / mL DMSO solution quickly and as 10 mg / mL DMSO solution slowly (both at a final DMSO content of 2% (vol / vol).
Results
[0135]The efficiency of carfilzomib remote loading into liposomes at 100 g drug / mol of HSPC lipid for the drug which was first added as the solid powder was 3.88%±0.053% and 3.47%±0.030% when heated to 65° C. for 30 and 120 min respectively. The efficiency of loading the drug from initial stock solutions of 10 mg / mL DMSO solution was 97.0%±2.38% when the drug / DMSO was added quickly and 96.3%±1.09% when the drug / DMSO was added in 5 increments over 1 min to a liposome soluti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com