RF coil for use in magnetic resonance imaging in integrated spect and mr imaging
a magnetic resonance imaging and integrated spect technology, applied in the field of magnetic resonance imaging methodologies, can solve the problems of inability to perform temporal coregistration in the time domain of combined dynamic studies using both imaging techniques simultaneously, inability to use conventional motors in high magnetic fields used in magnetic resonance imaging (mri), and inability to accurately perform other less rigid body parts. , to achieve the effect of improving image accuracy, optimizing wiener filtering, and improving image accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
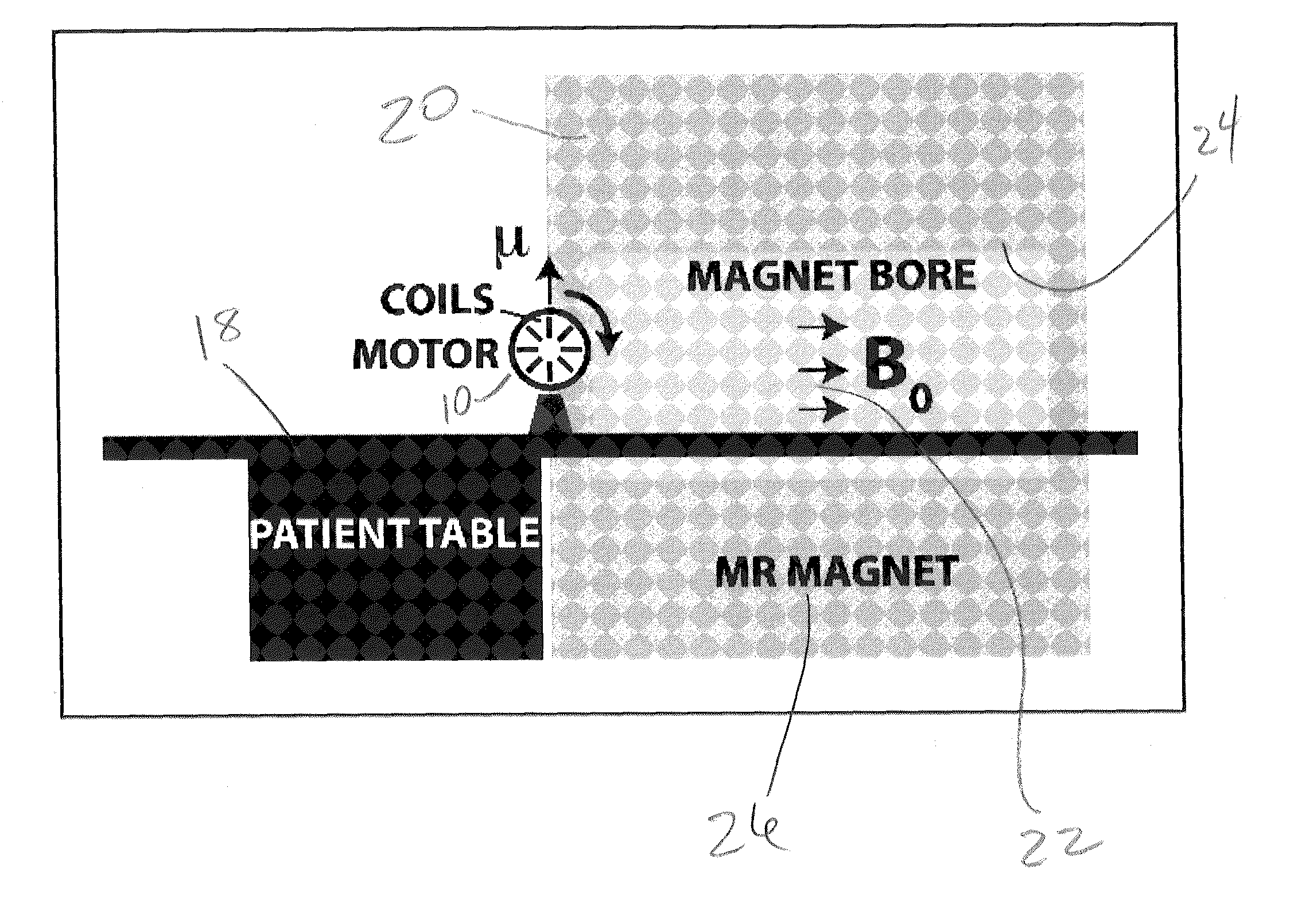
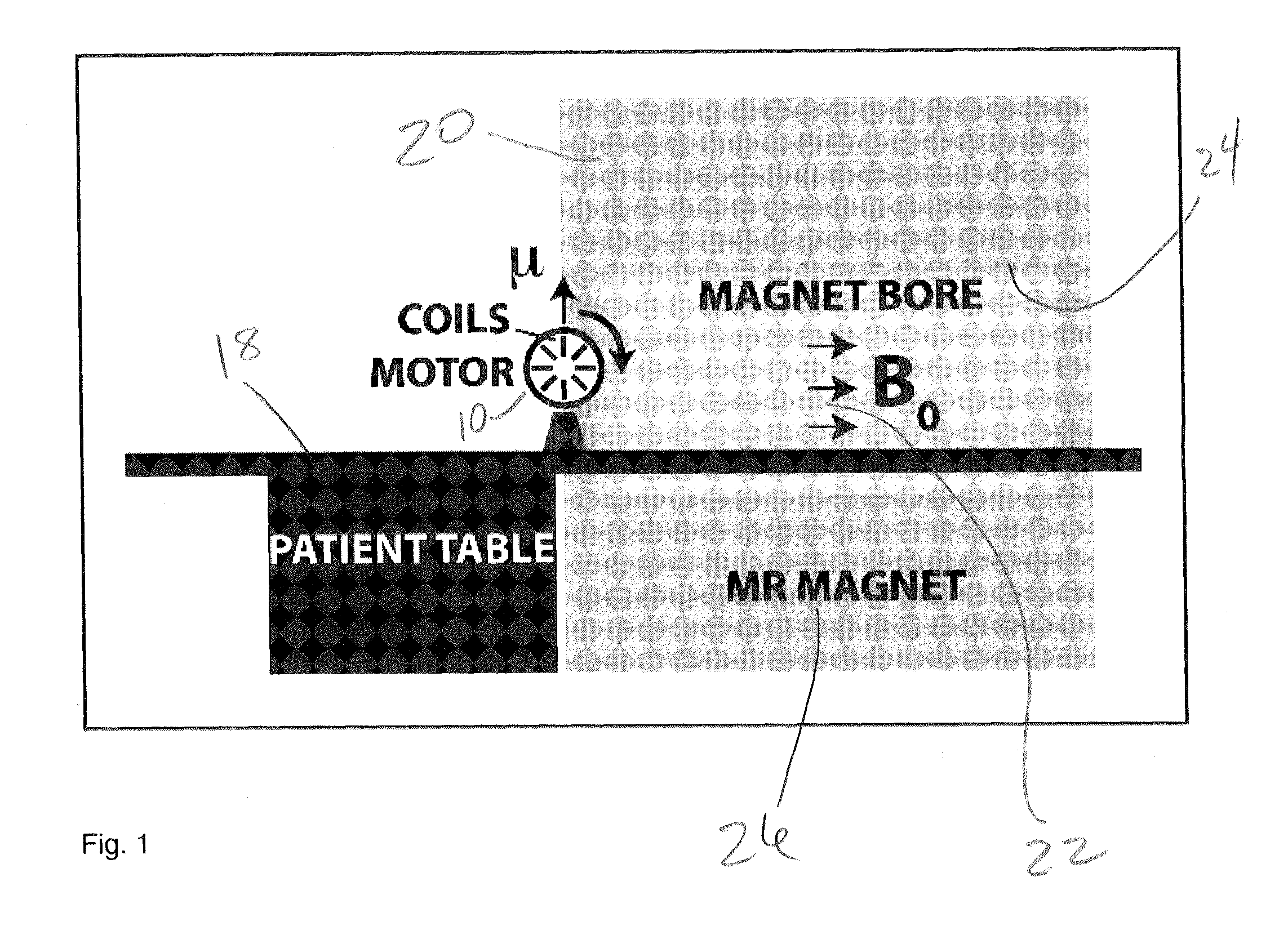
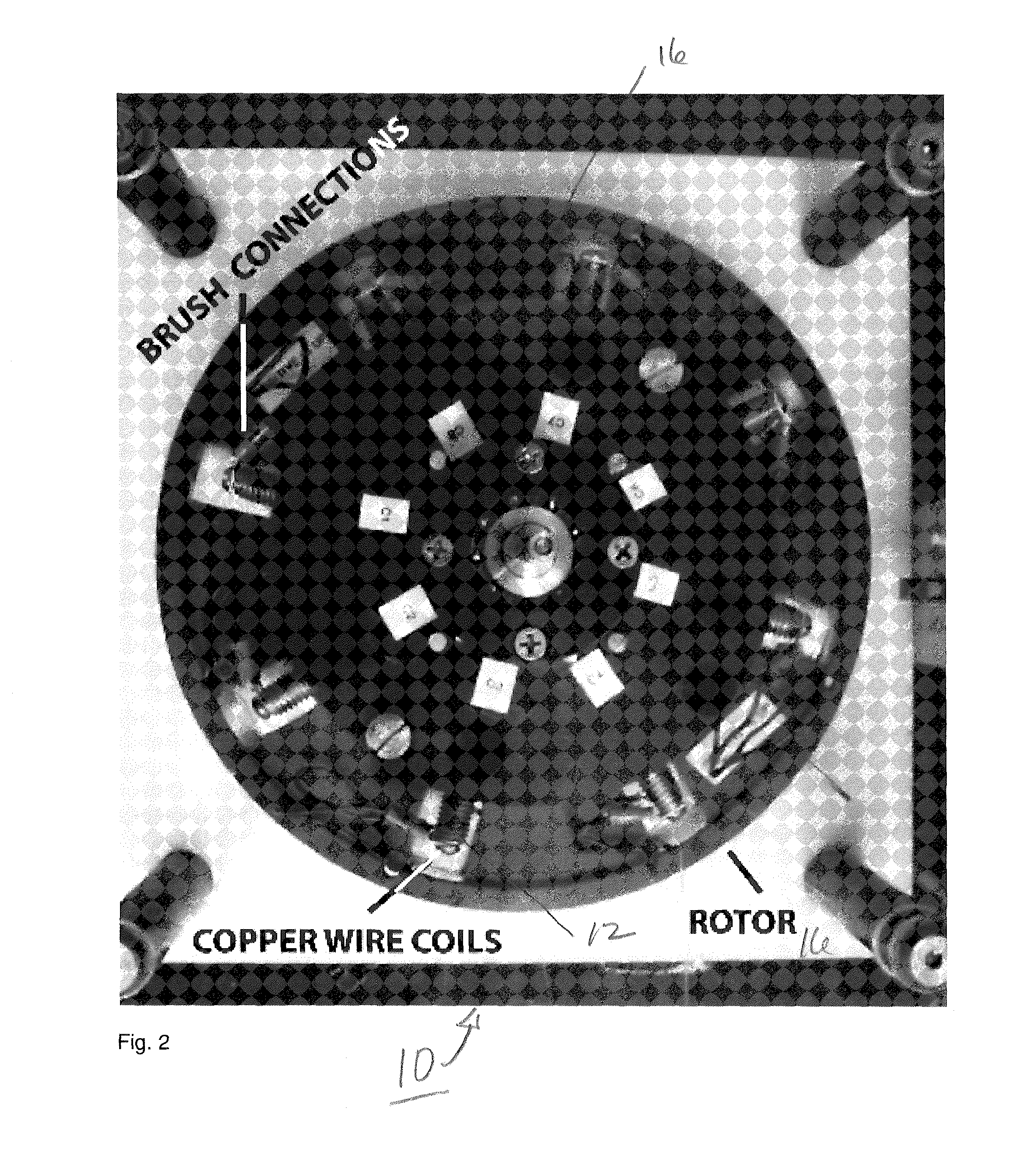
[0038]An illustration of a prototype motor 10 and the experimental set-up is shown diagrammatically in FIG. 1. The motor assembly 10 is constructed with MR compatible plastic material and screws and bolts made out of brass. The motor assembly 10 shown in the photograph of FIG. 2 includes eight MR compatible copper coils 12 wound onto a plastic bobbin (not shown) placed radially within the rotor body 16 and separated by 45 degrees from each other as shown in FIG. 2. The outer diameter of the main rotor body 16 is 20.3 cm. Directional rotary motion is achieved by passing electric current through opposing coils 12 by means of a pair of dedicated brushes (not shown) under computer control and hence creating a torque due to the interaction of the magnetic field induced in coils 12 carrying current with the magnetic field of the MR system as shown in FIG. 1.
[0039]As well known from basic electromagnetics the torque is linearly related to the local magnetic field of the MR system and the c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com