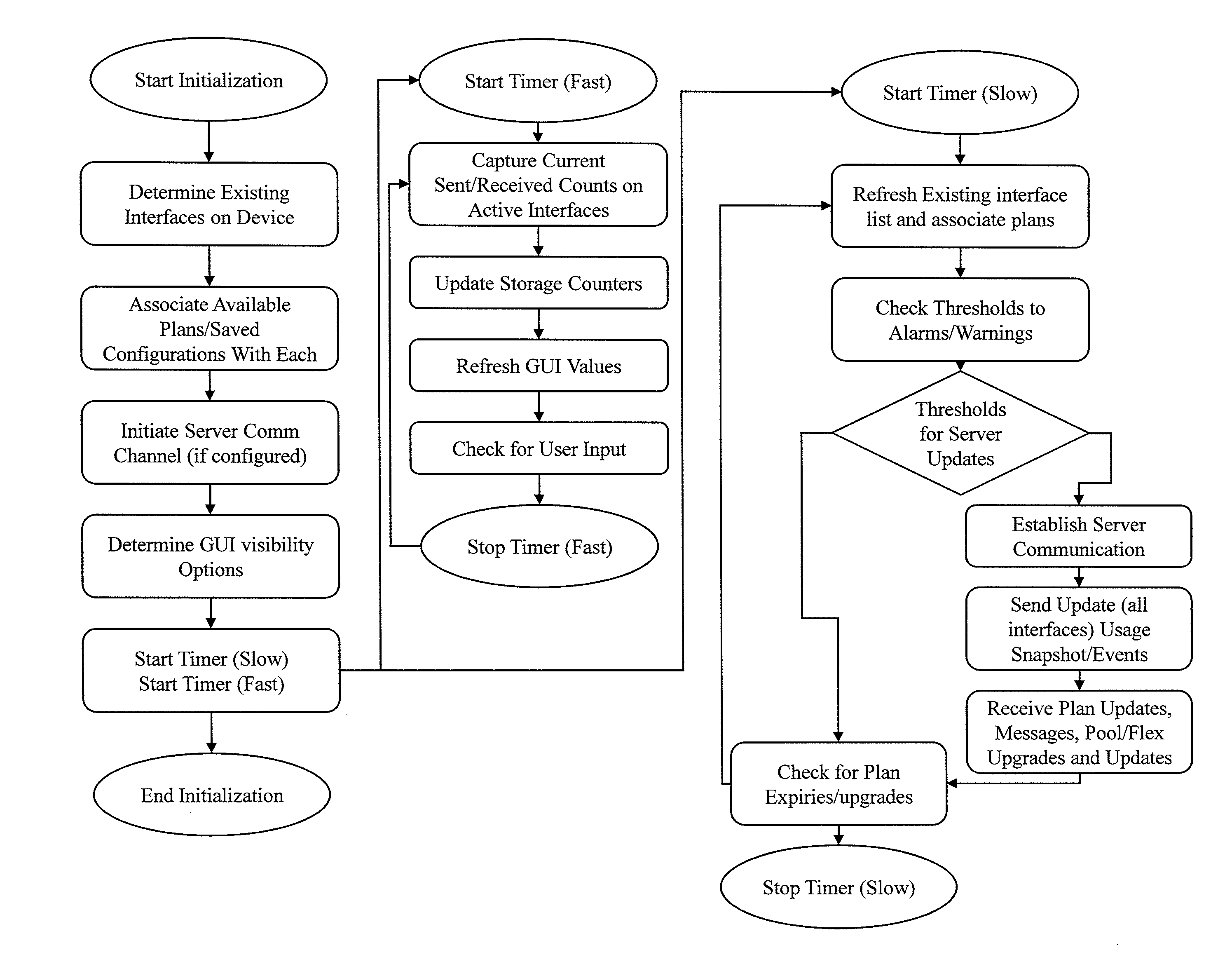
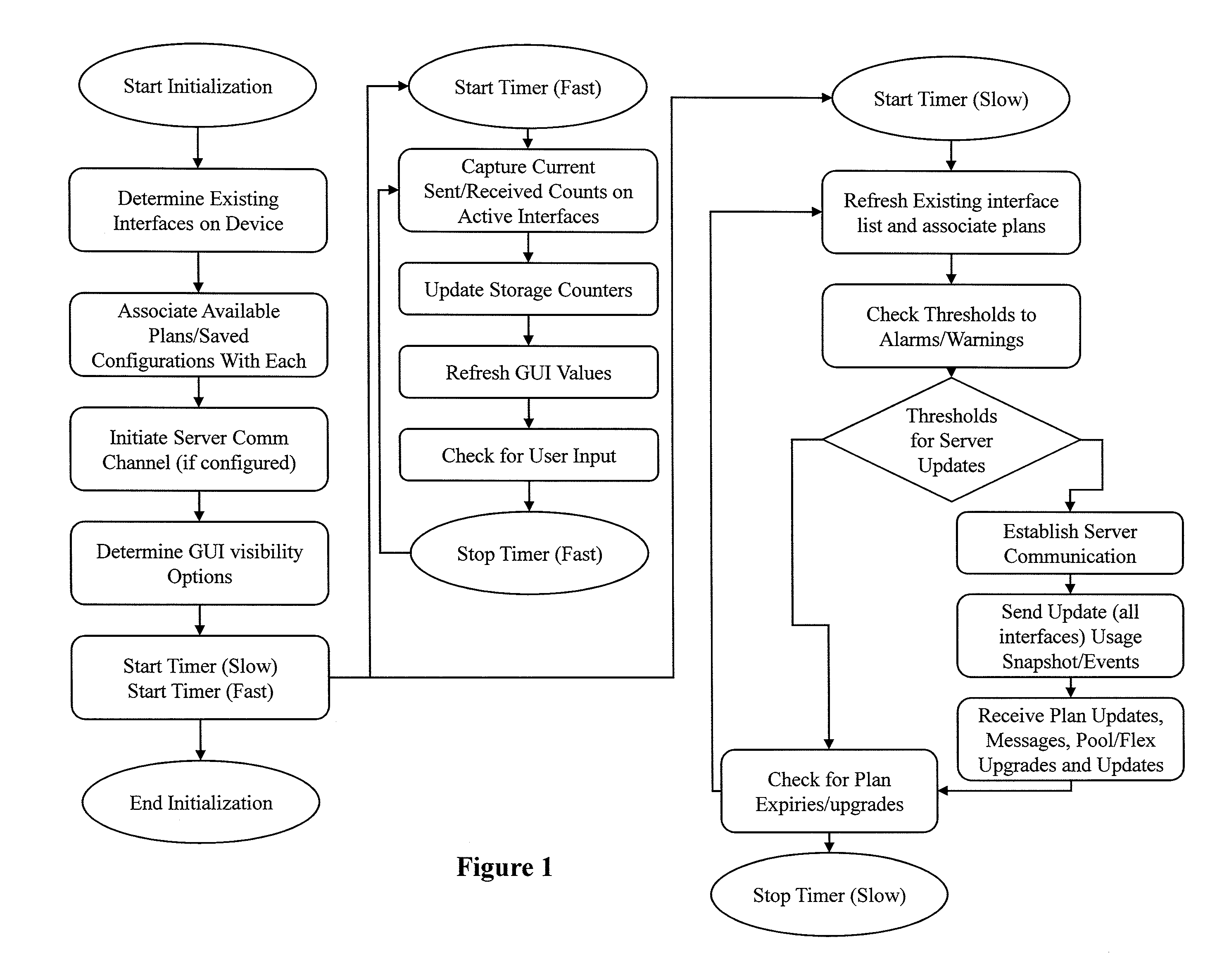
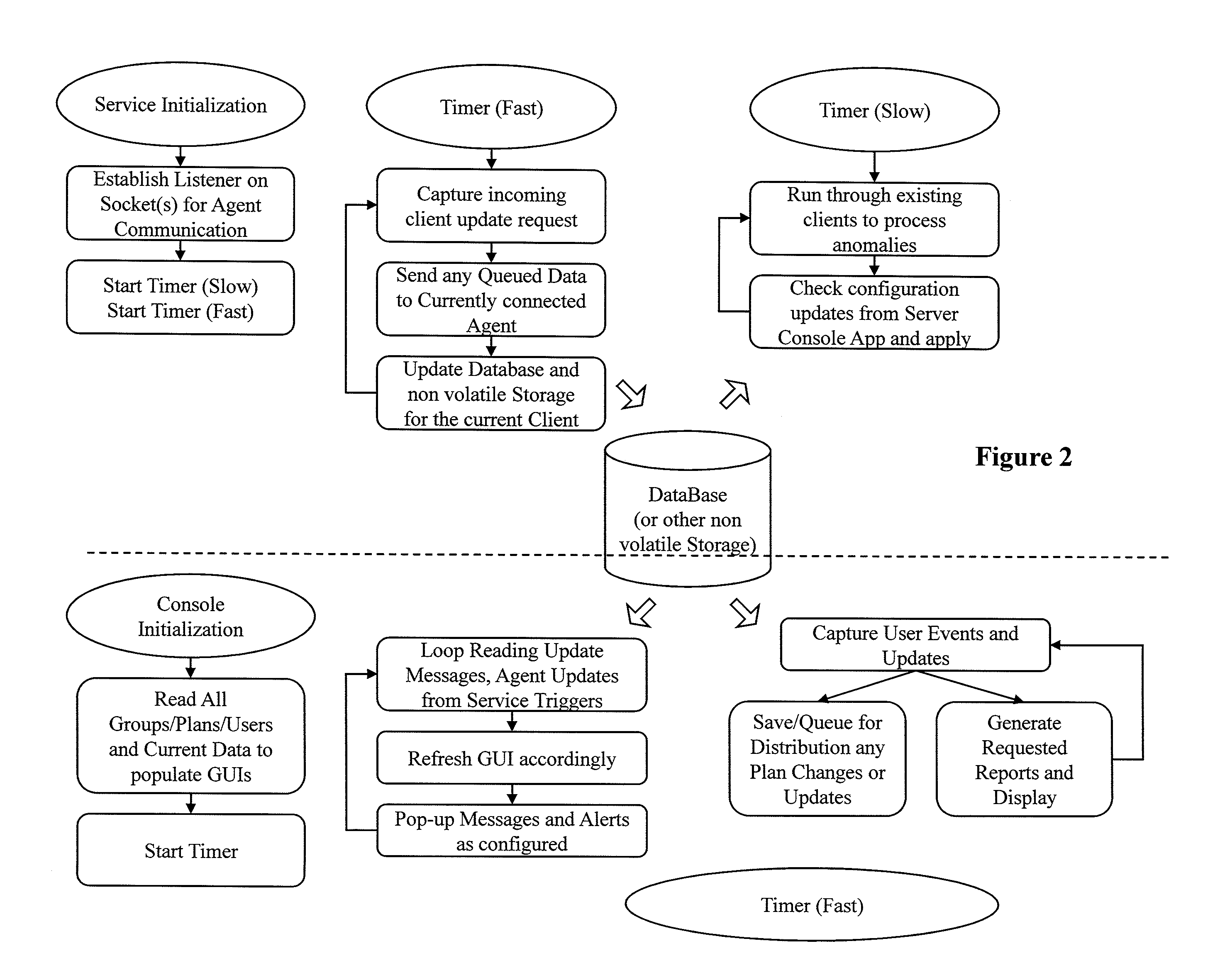
Determining Usage Predictions and Detecting Anomalous User Activity Through Traffic Patterns
a traffic pattern and usage prediction technology, applied in data switching details, transmission systems, transmission, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the normal operation of the average user, the difficulty of the average user to assess their data usage needs or history, and the overage charge for all consumption. , to achieve the effect of eliminating cost and security issues, avoiding false reports, and increasing accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0094]After a 31 day plan period with an initial configuration of Tmino=8 am, and N=5 (to take the 5 earliest periods), the system captures the earliest activity periods as (7:01, 7:10, 7:11, 7:13, 7:15) giving variance values from the Tmino value of (−59, −50, −49, −47, −45 minutes respectively, and an average variance of −50 minutes. In this case: The Tmin value for the next plan period will be 7:10 instead of 8:00 am (in this example, each of the ‘out of range, or before 8 am events will trigger an anomaly)
example 2
[0095]After a 30 day plan period with an initial configuration of Tmin0=9 am, and N=30 the system reads starting times between 9:00 and 9:30 every day with an average (of the 30 readings) being +15 Minutes Variance. The Tmin value for the next plan period will start at 9:15. (in this example, since each of the Tmin1 . . . 30 events are after the Tmino setting of 9:00, there will NOT be any anomalies triggered.
[0096]Note a separate method for weekend (Sat / Sun work is performed) where by abnormal weekend work does not skew working times during the week.
[0097]Further, the Min / Max algorithm can also be used for both startMin and StartMax and StopMin / StopMax values as a variant. In this case, starting work either before startMin or after startMax will be considered an anomaly and the times will adjust using the same learning algorithm.
Tmin=Tmino+ / −Max(1,{Avg(Tmin1 . . . TminN)})
Tmax=Tmaxo+ / −Max(1,{Avg(Tmax1 . . . TmaxN)})
[0098]Further learning of repetitive atypical events is achieved th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com