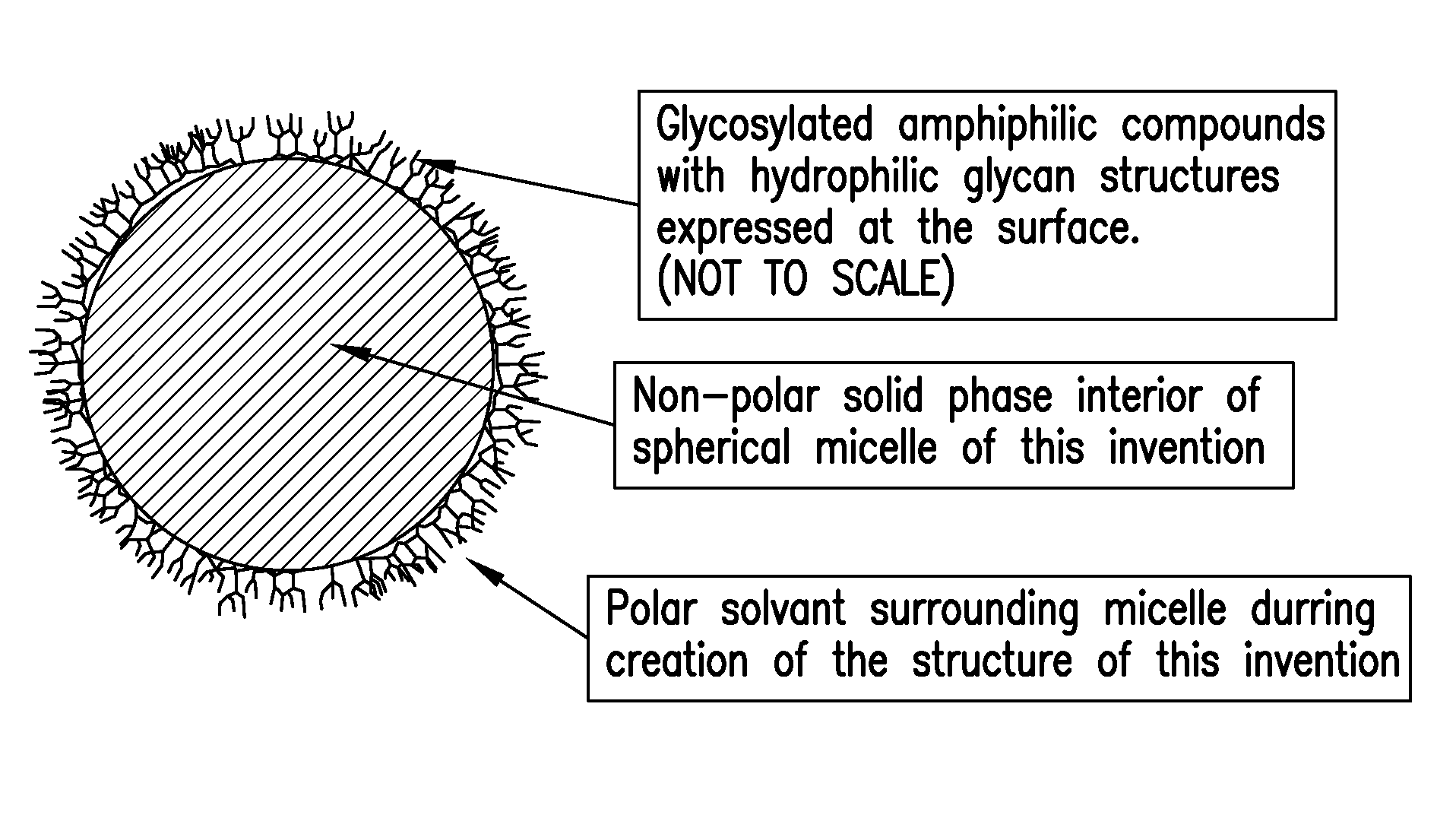
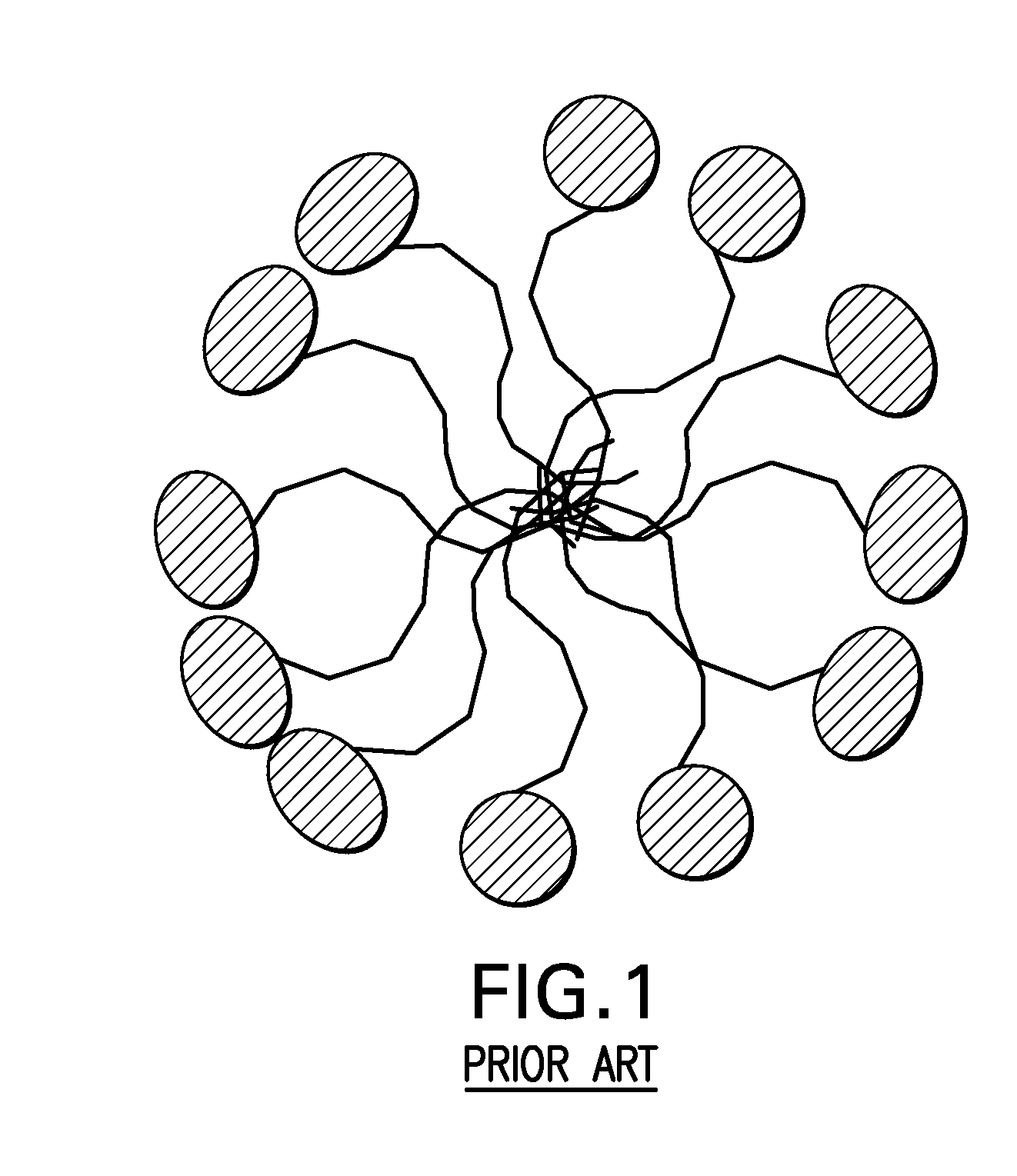
Biomimetic particles and films for pathogen capture and other uses
a biomimetic particle and film technology, applied in the field of glycosylated molecule identification and immobilization, can solve the problems of limited ability of the technique to capture unexpected, rapidly evolving or engineered pathogens, uncharacterized options, and inability to mount an adequate defense, so as to enhance the biocompatibility of the medical device and prevent the immune response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
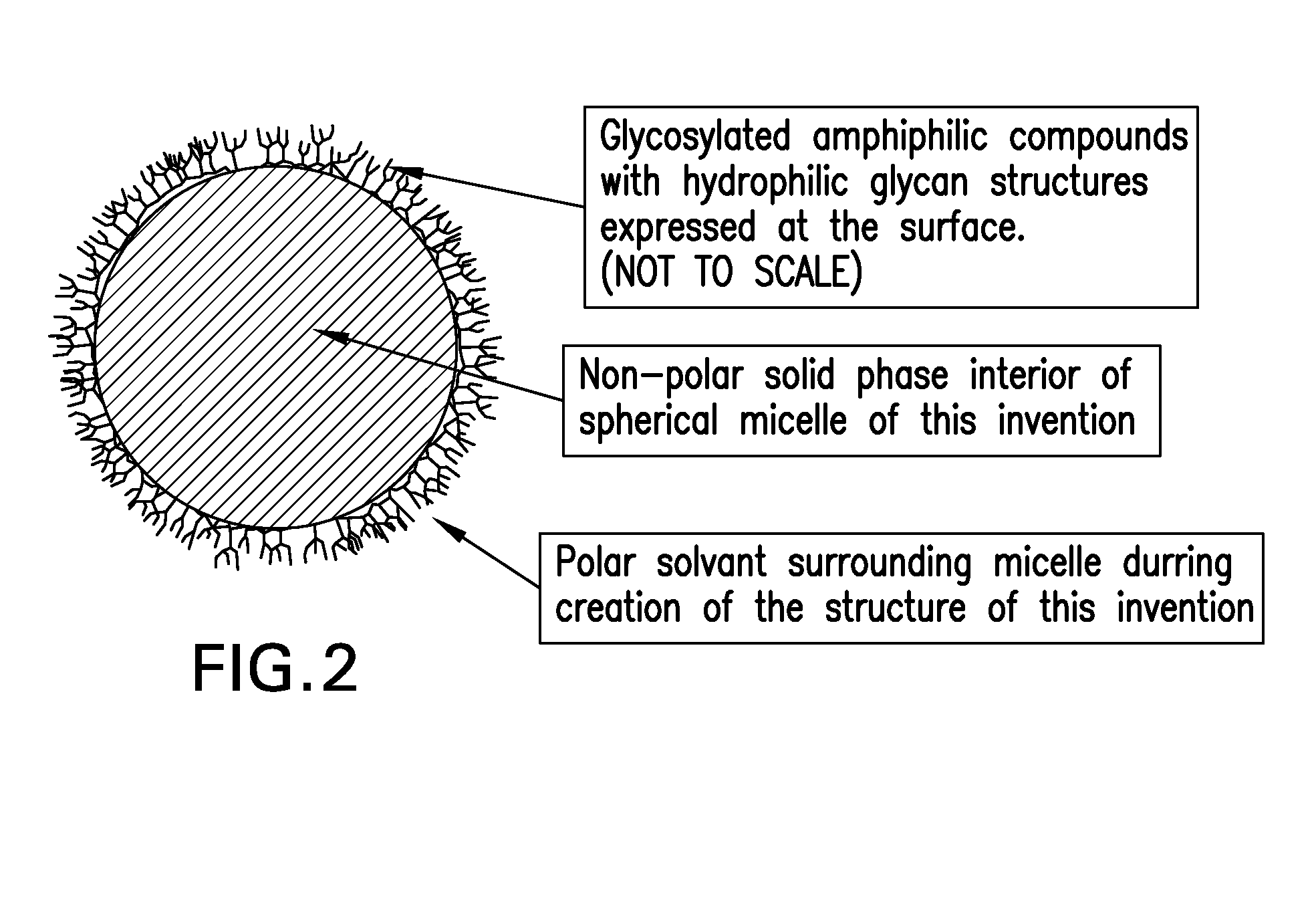
Image
Examples
example 1
[0337]Porcine small intestine was treated in a tissue disruptor and then sonicated to release the membrane bound glycosylated compound. The resultant solution was sterile filtered. The glycoprotein rich filtrate was heated along with food grade paraffin wax to 60 degrees Celsius. The resulting mixture was agitated and then pumped through a zone excited by sonication. The mixture was then sprayed through a small orifice into a continuous stream of cold water. The resulting particles in the 50 nm to 1000 nm diameter size range were concentrated and washed. The particles were then added to an LB broth solution with active Salmonella Montevideo present and rotated for 20 minutes at 37 degrees Celsius. The particles were removed from the LB broth solution and then rinsed. One sample was stained and observed under a microscope. Salmonella were observed bound to the surface of the particles. A second sample was processed for PCR analysis techniques known to those skilled in the art. The wa...
example 2
[0339]Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) in solution was heated to 55 degrees Celsius. Food grade paraffin wax, also at 55 degrees was added to the solution. The resulting mixture was agitated at high shear using a food processor and then rapidly quenched in a volume of 25 degree Celsius water. The resultant micelle-like particles in the range of 500 nm to 5000 nm were allowed to rise to the surface and then collected. The particles were then rediluted and separated by rise time in the fluid over three successive dilutions to yield relative size separations. Samples of the various size fractions were successfully demonstrated as agglutination assay in trials on a mutant Escherichia Coli strain which is always fimbirated.
example 3
[0340]Shaw, et. al., 32 demonstrated that Tir can be translocated into red blood cell (RBC) membranes, and that the resulting transmembrane molecules (described by Race, et. al.33) which are expressed can result in Tir-intimin binding of other serotypes than those initially secreting the Tir. Accordingly, red blood cells are exposed to Tir producing bacteria per the procedures used by Shaw, et. al. (E. coli strain CVD206 was used in that case, but the technique is applicable to other strains as well). The resulting sample of infected red blood cells is then subjected to cell rupture techniques which both destroy the bacteria as well as liberate the transmembrane molecules of Tir, which according to Shaw are in the 78 kDa size range. In this example, the transmembrane Tir, with expressed intimin receptors is immobilized directly into a solid substrate based on amphiphilic properties, along with the other transmembrane glycoproteins of RBC using self-aligning film techniques. It is al...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com