Compositions and methods for targeted inactivation of HIV cell surface receptors
a technology of cell surface receptors and compositions, applied in the direction of antibacterial agents, peptide/protein ingredients, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of complex delivery systems, limited frequency of homologous integration, toxicity, efficacy and drug resistance, etc., to reduce the viral load of an individual already, and prevent infection of an individual
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Binding of a Peptide Nucleic Acid to a Fragment of the CCR5 Gene and Design of Donor Oligonuclotides
[0129]A bis-PNA was designed to bind to CCR5 with high affinity and specificity. The PNA is represented by the following sequence: JTJTIITTJT-e-e-e-TCTICTTCTC-Lys-Lys-Lys, where J=pseudoisocytosine and e=flexible linker (SEQ ID NO:7). In vitro binding was evaluated using a gel-shift assay which confirmed that the molecule binds to the target site at μM concentrations. Three single-stranded 60mer donor oligonucleotides were designed and synthesized. All donors were completely homologous to the template strand (antisense) of the CCR5 gene, except for the 6 center bases which contain a stop codon. The donors were designed to place this stop codon near the Δ32 mutation site to mimic this mutation which has been shown to inactivate CCR5 by truncation and mislocalization of the protein. One donor (983) was designed to introduce a 6 bp DdeI restriction site (which also contains an inframe st...
example 2
Mutation of the CCR5 Gene in THP-1 Human Leukemia Cells Using PNAs and Donor Oligonucleotides
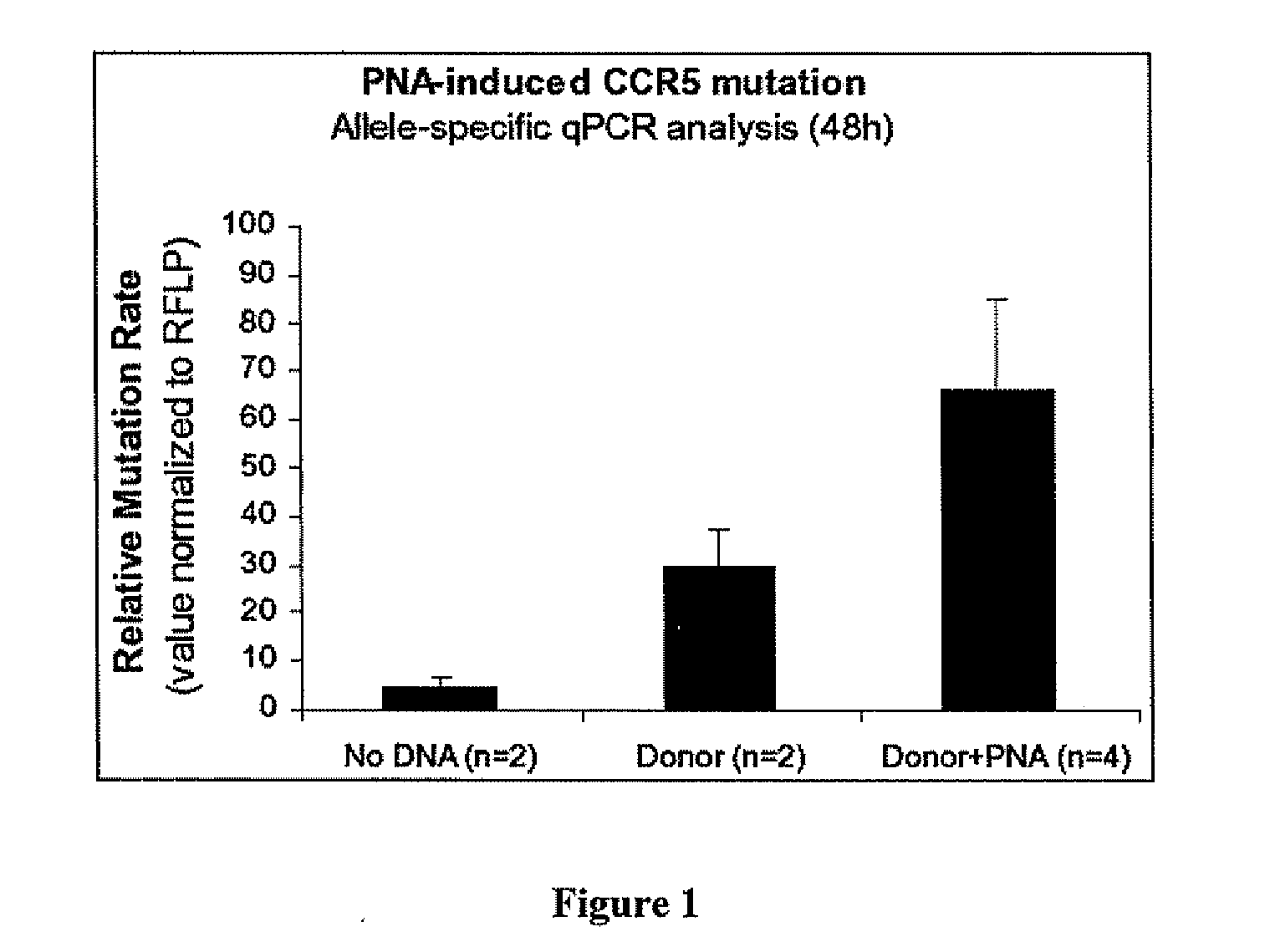
[0130]ASPCR primers were designed for specific amplification of the mutant CCR5 sequence. Allele-specific forward primers were designed containing the specific 6 bp mutant sequence at its 3′ end. When paired with the gene-specific reverse primer, the allele-specific primer will preferentially amplify the mutant CCR5 gene. To determine ASPCR conditions, gradients were run with plasmid controls to determine the optimal Tm for specific amplification of the mutant sequence. Combinations of donor molecules and bis-PNA were then transfected into THP-1 cells to test for homologous recombination, and the genomic DNA from these cells was analyzed by ASPCR.
[0131]THP-1 cells were transfected with either nothing, 5 μg of 983 donor, or 5 μg of 983 donor with 2 μM PNA. 48 hours after transfection an aliquot of approximately one million cells were taken and genomic DNA was isolated. Allele-specific PCR was...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Stability | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com