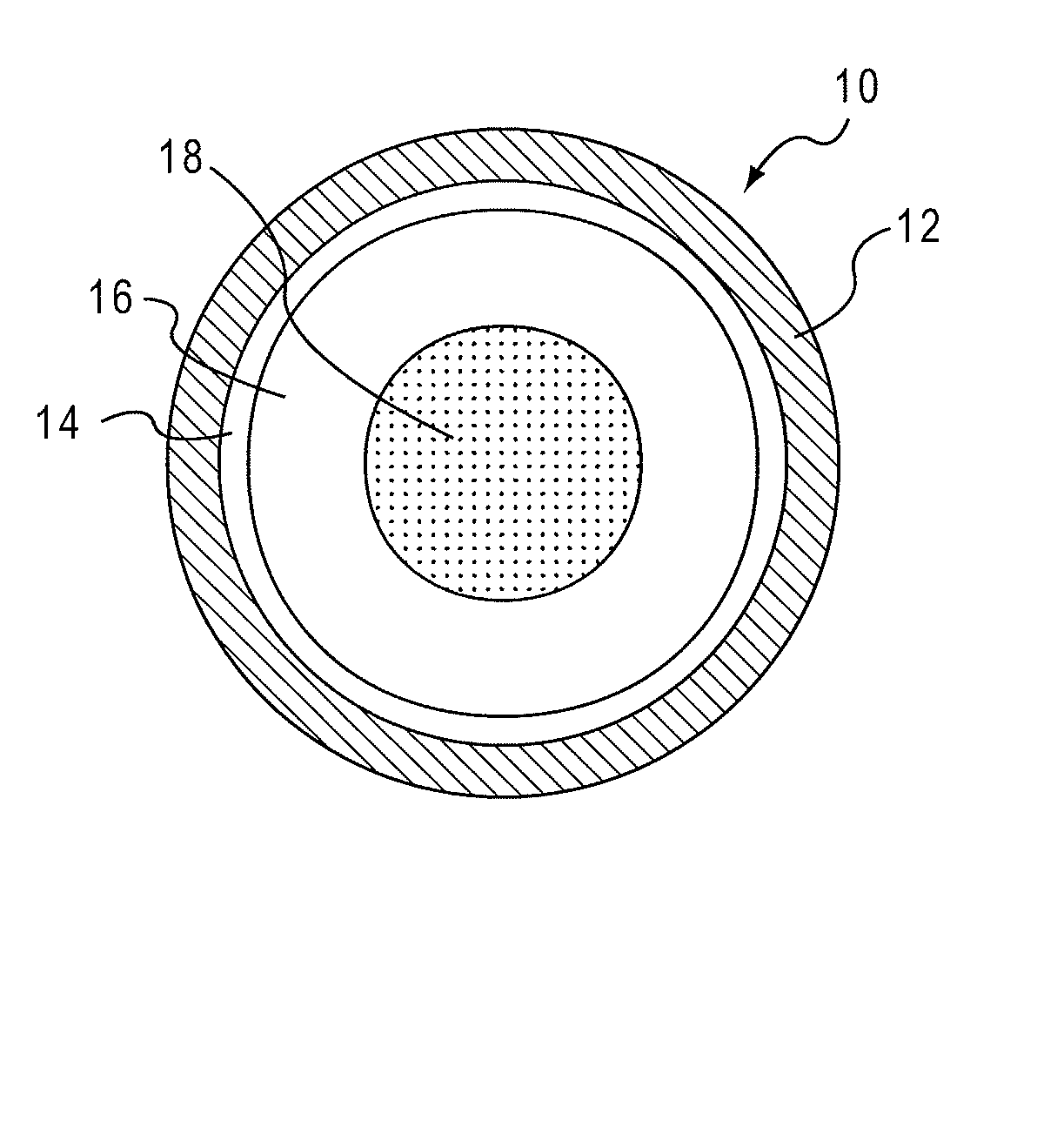
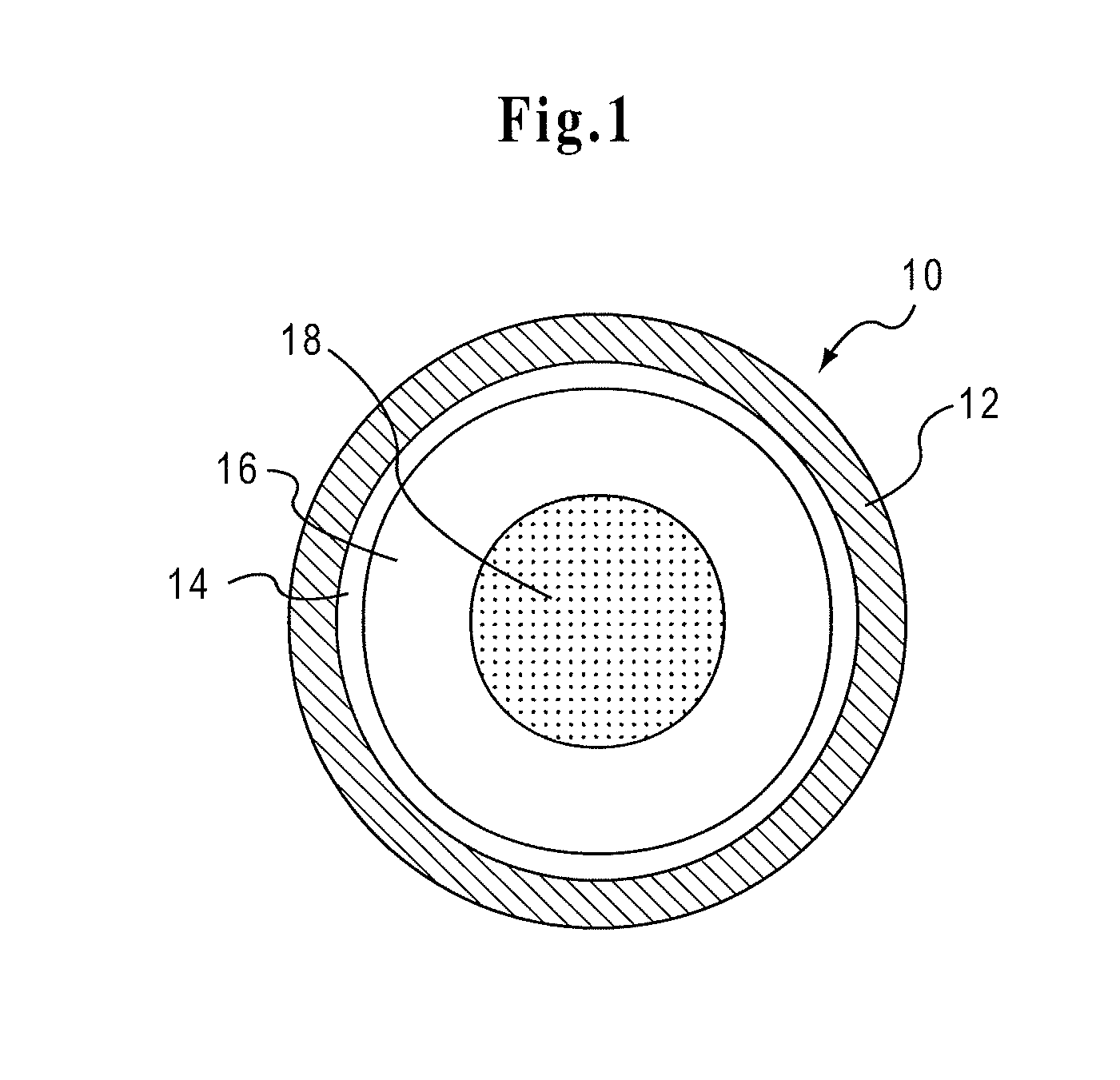
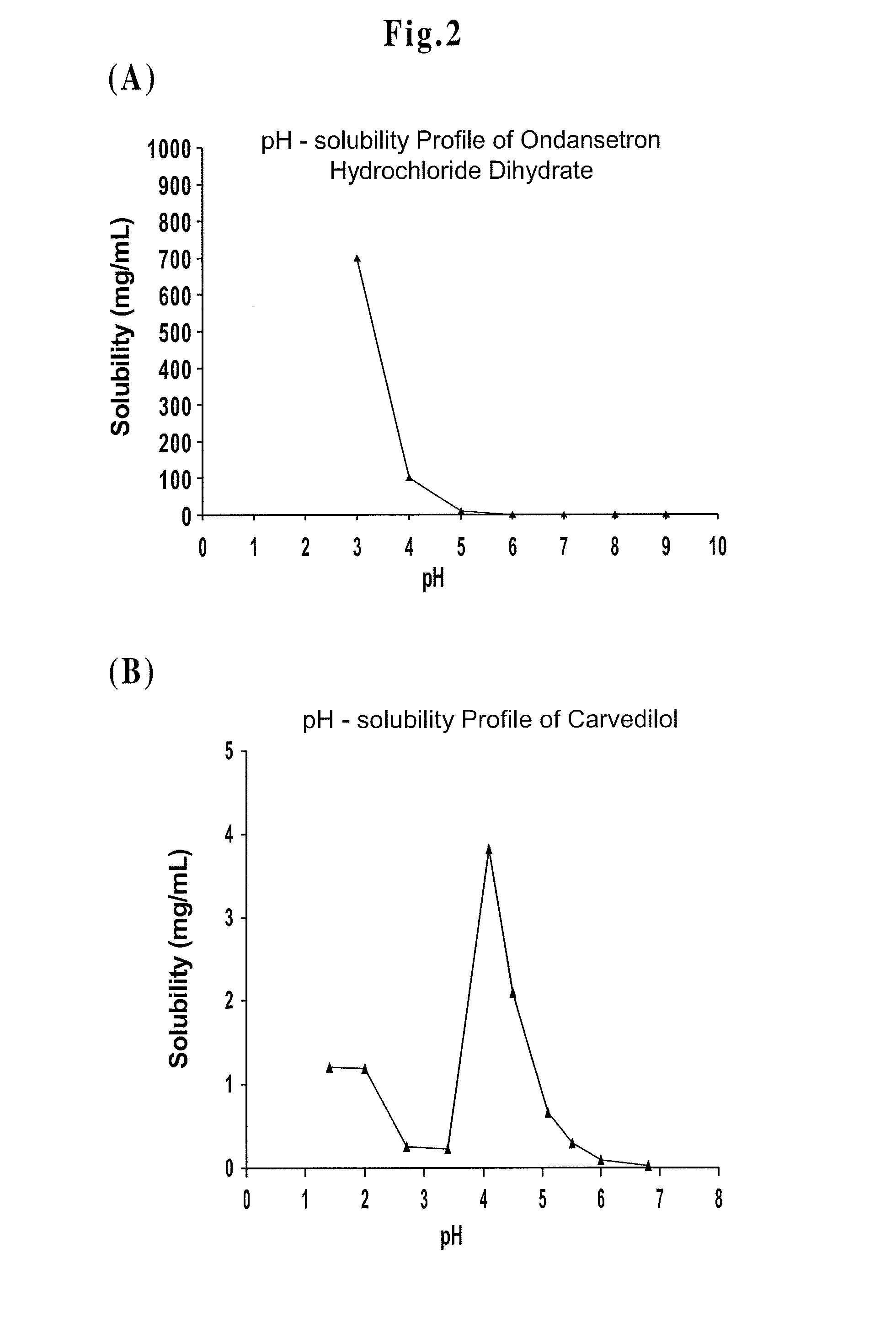
Drug Delivery Systems Comprising Solid Solutions of Weakly Basic Drugs
a weakly basic, solid solution technology, applied in the direction of drug compositions, biocide, cardiovascular disorders, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to achieve drug release at constant rates, difficult to develop oral pharmaceutical dosage forms which deliver, and inability to meet the needs of patients,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0088] Turbidity Measurements
[0089] A concentrated solution (3 mL) of lercanidipine hydrochloride in acetone (0.5 mg / ml) was added to 200 mL of a buffer solution (pH 6.0) containing Kollidon VA 64, Methocel E5 (hypromellose), polyethylene glycol (PEG 6000), cyclodextrin or Kollidon 14 PF (polyvinyl pyrrolidone) at the ratio of 1:2 by weight with respect to the polymer. It is evident from FIG. 3A that the drug solutions showed improved stability thus strongly reducing the risk of crystallization of the conjugated base of lercanidipine HCl.
[0090] Intrinsic Dissolution Rate Measurements
[0091] Intrinsic dissolution rates were determined for two different polymorphs of lercanidipine hydrochloride as well as amorphous materials (e.g., amorphous drug and 1:2 solid solutions of lercanidipine hydrochloride with Methocel E5 and Kollidon VA 64). The data are shown in FIG. 4. While the crystalline polymorphs exhibit poor dissolution rates as well as extent of dissolution, the solid solutions...
example 2
[0094] Turbidity Measurements
[0095] A concentrated solution (3 mL) of Nifedipine in acetone (0.5 mg / mL) was added to 200 mL of a buffer solution (pH 6.0) containing Kollidon VA 64, Methocel E5 (hypromellose), polyethylene glycol (PEG 6000), cyclodextrin or Kollidon 14 PF (polyvinyl pyrrolidone) at a nifedipine / polymer ratio of 1:2 by weight. The transmittance of the nifedipine / polymer solutions was monitored over time as shown in FIG. 3B. The more stable solutions exhibited a slower decline in transmittance over time, due to slower crystallization of nifedipine from solution. Methocel E5, Kollidon VA 64, and Kollidon 14 PF exhibited greater stabilization.
[0096] Powder X-Ray Diffraction
[0097] Two co-precipitates of nifedipine and Methocel E5 (hypromellose) were prepared at a nifedipine / Methocel ratio of 1:1 and 1:2 by dissolving the nifedipine and Methocel in a mixture of dichloromethane-methanol (1:1, v / v), then drying the solutions to a residual solvent level of less than 1% (w / ...
example 3
[0098] 3A—Nifedipine IR Beads (Nominal Nifedipine Loading: 10%)
[0099] Kollidon VA 64 (800 g) was slowly added to a 72.5 / 22.5 / 5 mixture of 95% ethanol / acetone / water (4930 g / 1530 g / 340 g) while vigorous stirring until dissolved, and then nifedipine (400 g) was slowly until dissolved. A Glatt GPCG 3 equipped with a 7″ bottom spray / 8″ column height Wurster insert, 20 mm partition gap, air-distribution plate B (250 μm screen), 1.0 mm nozzle port, atomization air pressure of 1.5 bar, and 3.2 mm inner diameter tubing, was charged with 2584 g of 25-30 mesh Sugar Spheres. About 40 g of talc was homogenized into the nifedipine / polymer solution to minimize static build-up. The nifedipine solution, at a solids content of 15% by weight, was sprayed onto the sugar spheres at a spray rate of 8-17 g / min and outlet flap at ˜60-80% (air velocity: ˜85-115 m3 / hr) while maintaining the product temperature at about 36-40° C. The resulting nifedipine-layered beads (batch size: 3724 g) were dried in the G...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com