High k gate stack on III-V compound semiconductors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
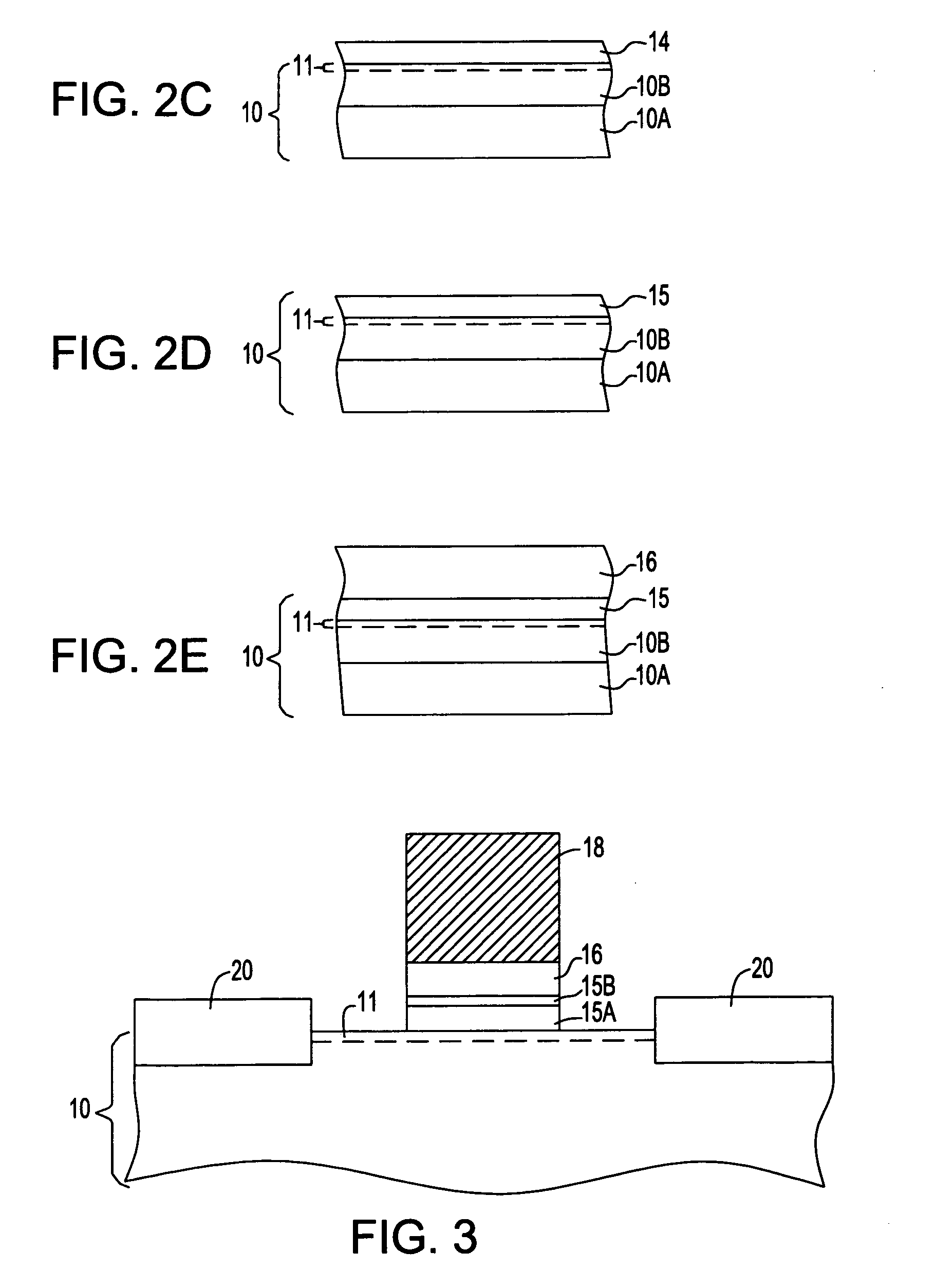
[0081] In this example, a MOSCAP was prepared utilizing a semiconductor structure in accordance with the present invention. The inventive structure included, from bottom to top, an atomic-H passivated GaAs substrate, an amorphous Si layer, SiOx and HfO2. The structure was formed utilizing the inventive processing details described above. After formation, a gate electrode was formed thereon and the structure was annealed at 700° C., 1 min., in nitrogen.
[0082]FIG. 4A shows the CV curves of such a MOSCAP at 1 kHz, 10 kHz, 100 kHz and 1 MHz. Specifically, the CV curves have very low frequency dispersion, which is indicative of low interface state density. FIG. 4B shows the Dit extracted as a function of gate voltage of the same MOSCAP as in FIG. 4A using the frequency-dependent method well known in the art. The results show a minimum Dit value of 6×1011 cm−2 / eV, which is over an order of magnitude lower than typically obtained on MOSCAPs with HfO2 directly on an unpassivated GaAs.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com