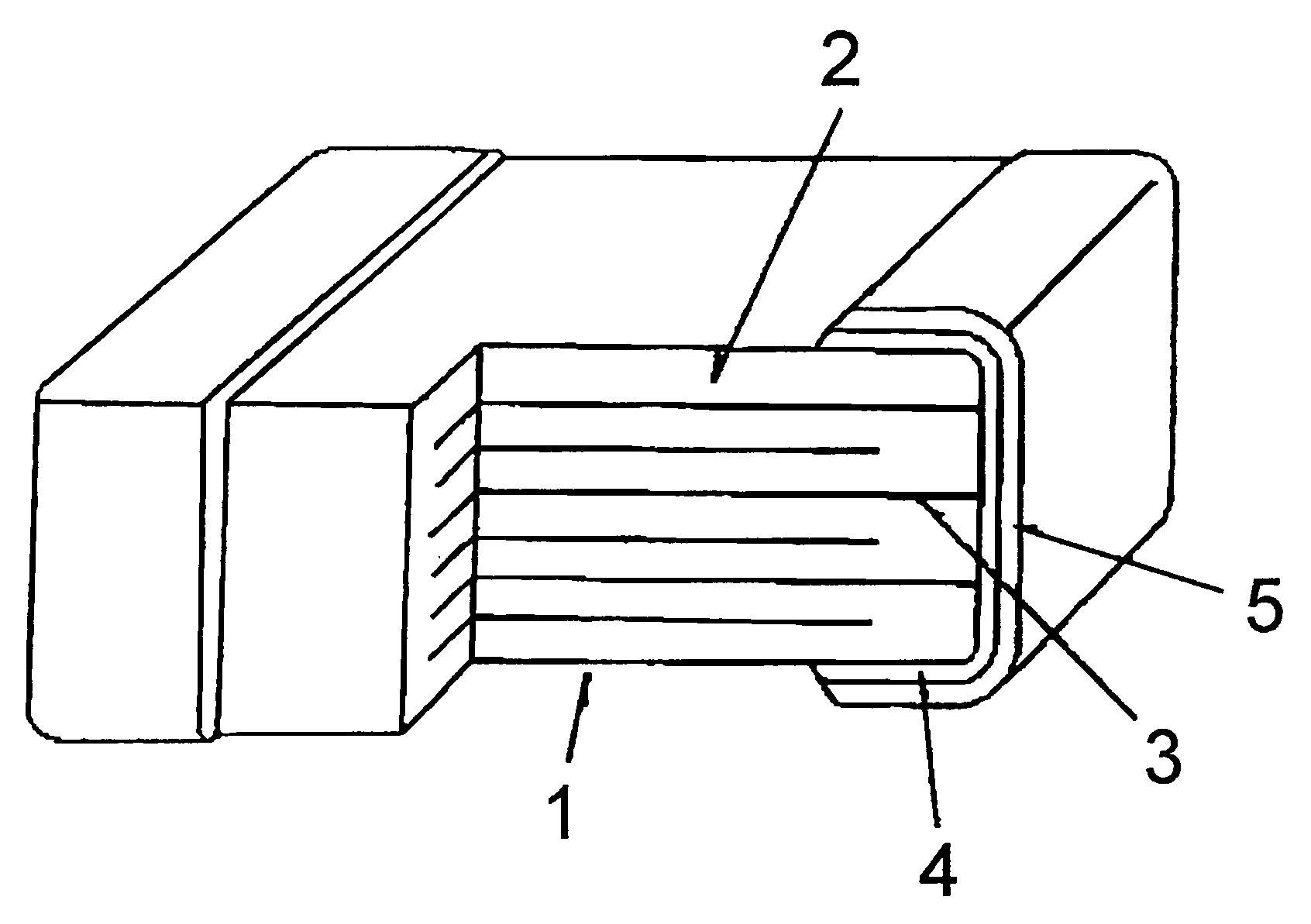
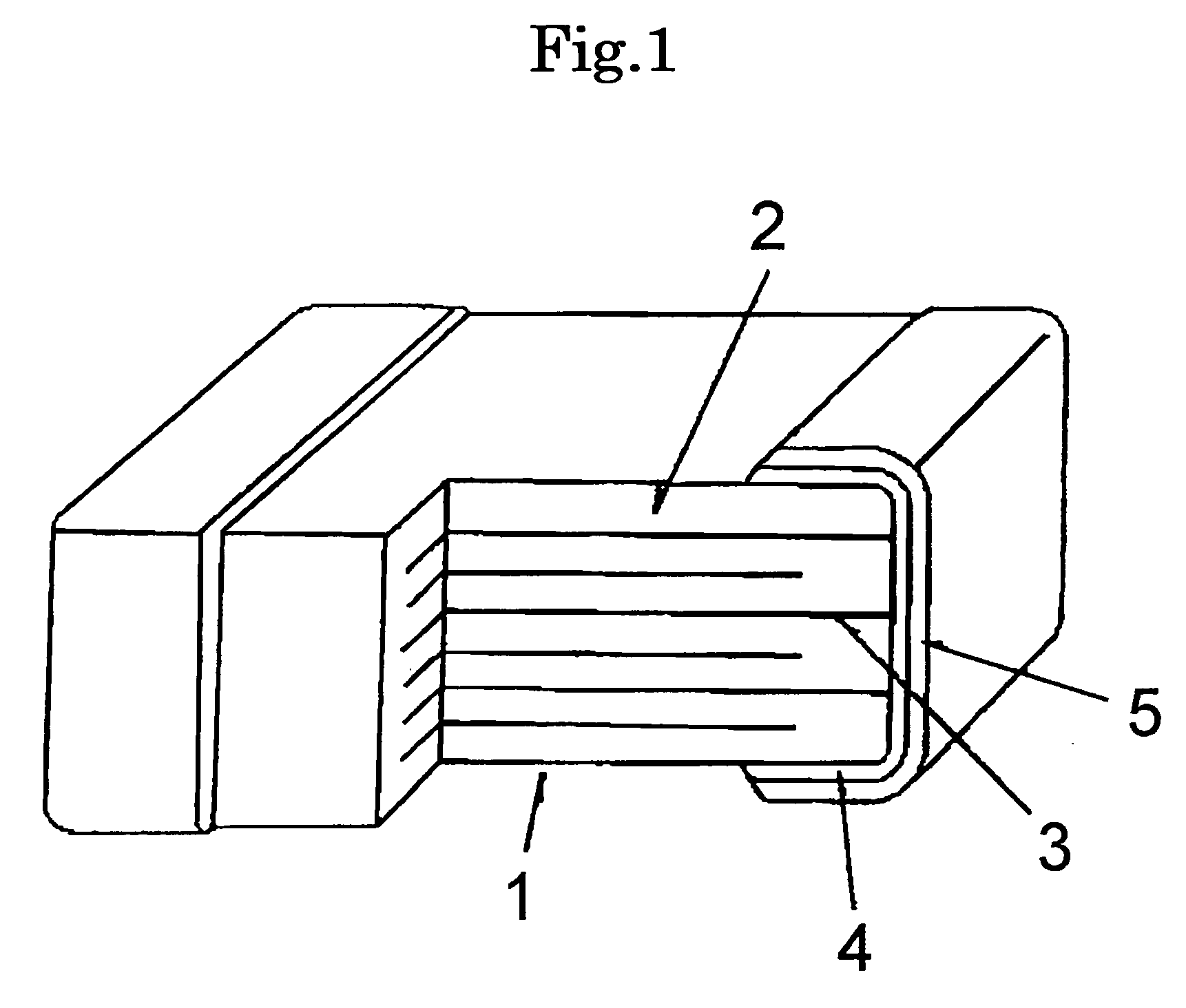
Electronic part with external electrode
a technology of electronic parts and electrodes, applied in the direction of non-metal conductors, conductors, fixed capacitor details, etc., can solve the problems of poor plating adhesion, cracks, and reliability of capacitor performance, and achieve excellent bonding properties and high melting points
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Thermosetting Electrode
[0044] A thermosetting conductive paste (C) as shown in Table 1 was applied, dried, cured and plated under conditions in Comparative Example 2 so as to obtain a chip multilayer capacitor.
[Measurement]
[0045] Each chip multilayer capacitor element obtained in the above was put on a Pb-free solder paste which had been printed on a copper-clad electrode of a glass-epoxy substrate. The capacitor element was solder-jointed with the substrate electrode at a temperature at which the solder paste was sufficiently fused, for example, at a temperature of 250 to 260° C. so as to be used as a test sample for the electric properties and the bonding strength. The initial electric properties (electric capacitance, tanδ) of the sample were determined by means of a 4278A manufactured by Agilent, and the bonding strength (shear strength) of the capacitor element to the substrate electrode was determined by means of a bonding strength-testing machine manufacture...
examples 1a to 1d
[0048] In order to examine a case wherein each content of conductive particles having a high melting point and metal powder having a melting point of 300° C. or less in a thermosetting conductive paste is modified, a thermosetting conductive paste in a manner similar to the one described above was prepared with a composition as shown in the following Table 3. The total content of the conductive particles having a high melting point and the metal powder having a melting point of 300° C. or less in the thermosetting conductive paste was 60 to 98% by weight relative to the total weight of the conductive particles having a high melting point, the metal powder having a melting point of 300° C. or less and a resin(s). Furthermore, a capacitor sample was prepared with each of the prepared pastes in a manner similar to the one described in Example 1 so as to determine the electric properties and the bonding strength.
[0049] The capacitor obtained in each of Examples 1a to 1d was excellent i...
examples 1e to 1g
[0050] In order to examine a case wherein the content of metal powder having a melting point of 300° C. or less in a thermosetting conductive paste is modified, a thermosetting conductive paste was prepared with a composition as shown in the following Table 4 in a manner similar to the one described above. The content of the metal powder having a melting point of 300° C. or less in the paste was 1 to 25% by weight relative to the total weight of the conductive particles having a high melting point and the metal powder having a melting point of 300° C. or less. Furthermore, a capacitor sample was prepared with each of the prepared pastes in a manner similar to the one described in Example 1 so as to determine the electric properties and the bonding strength.
[0051] The capacitor obtained in each of Examples 1e to 1 g was excellent in electric properties and bonding strength just like the one described in Example 1. In particular, when the content (i.e. Ratio of Tin Powder to Total Me...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com