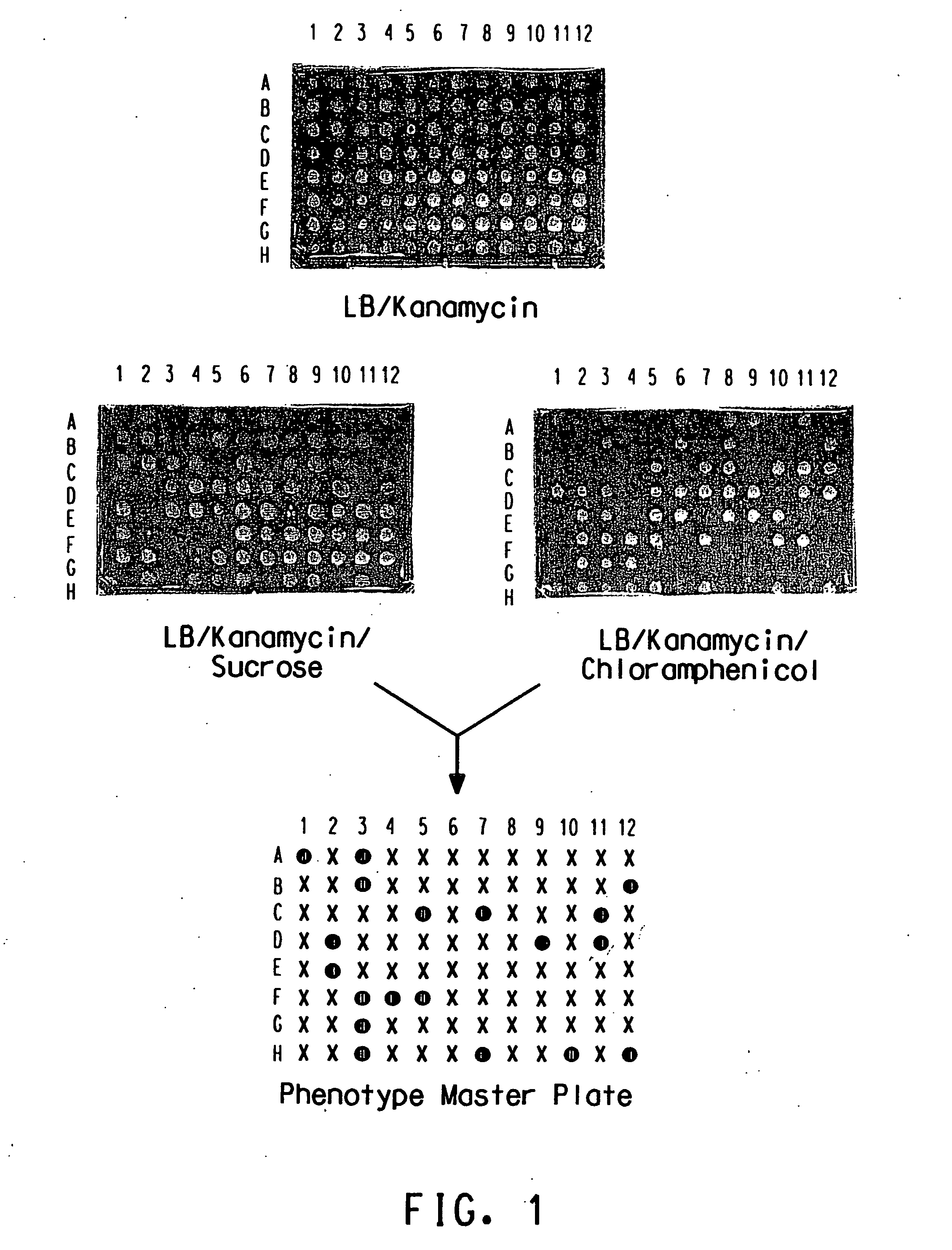
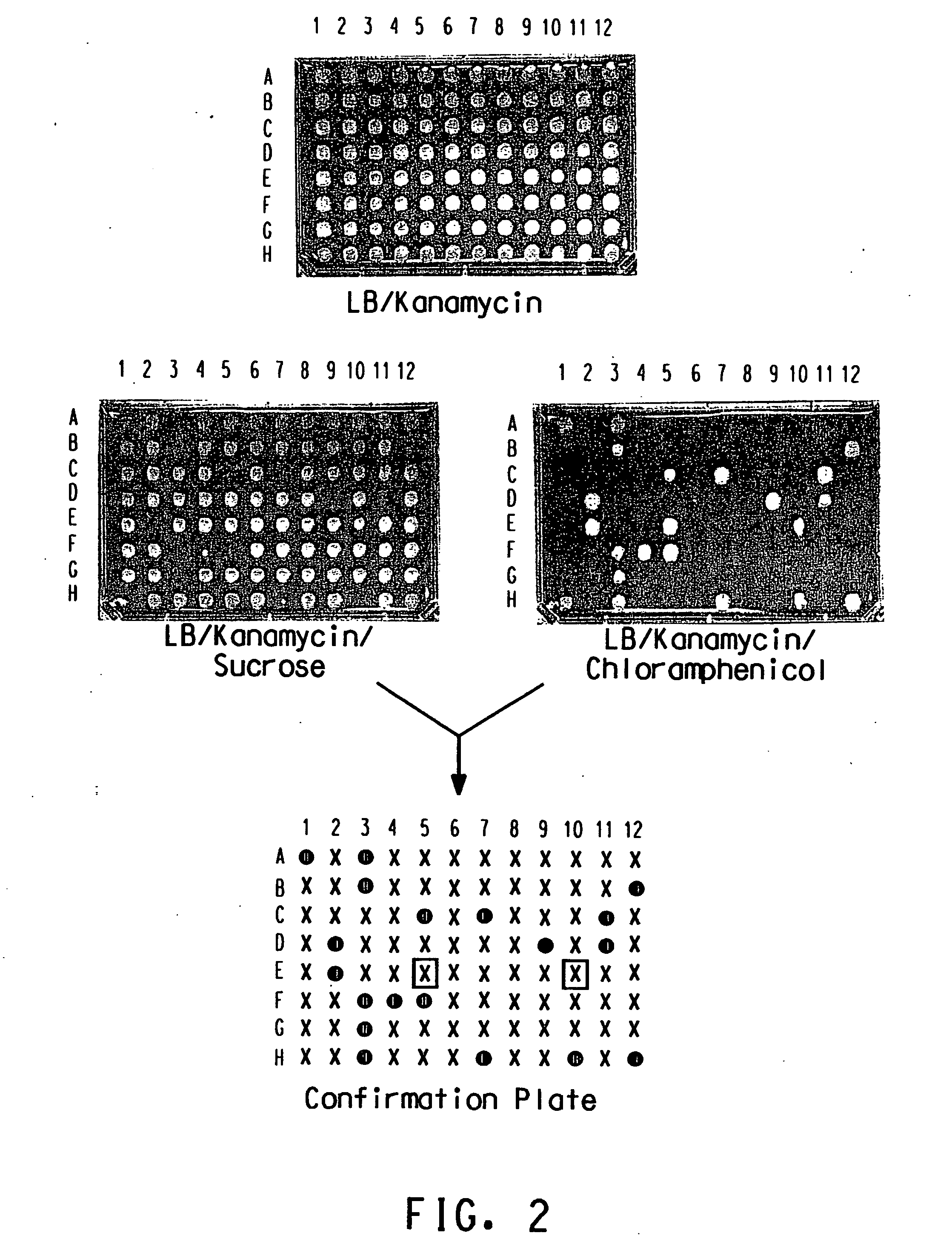
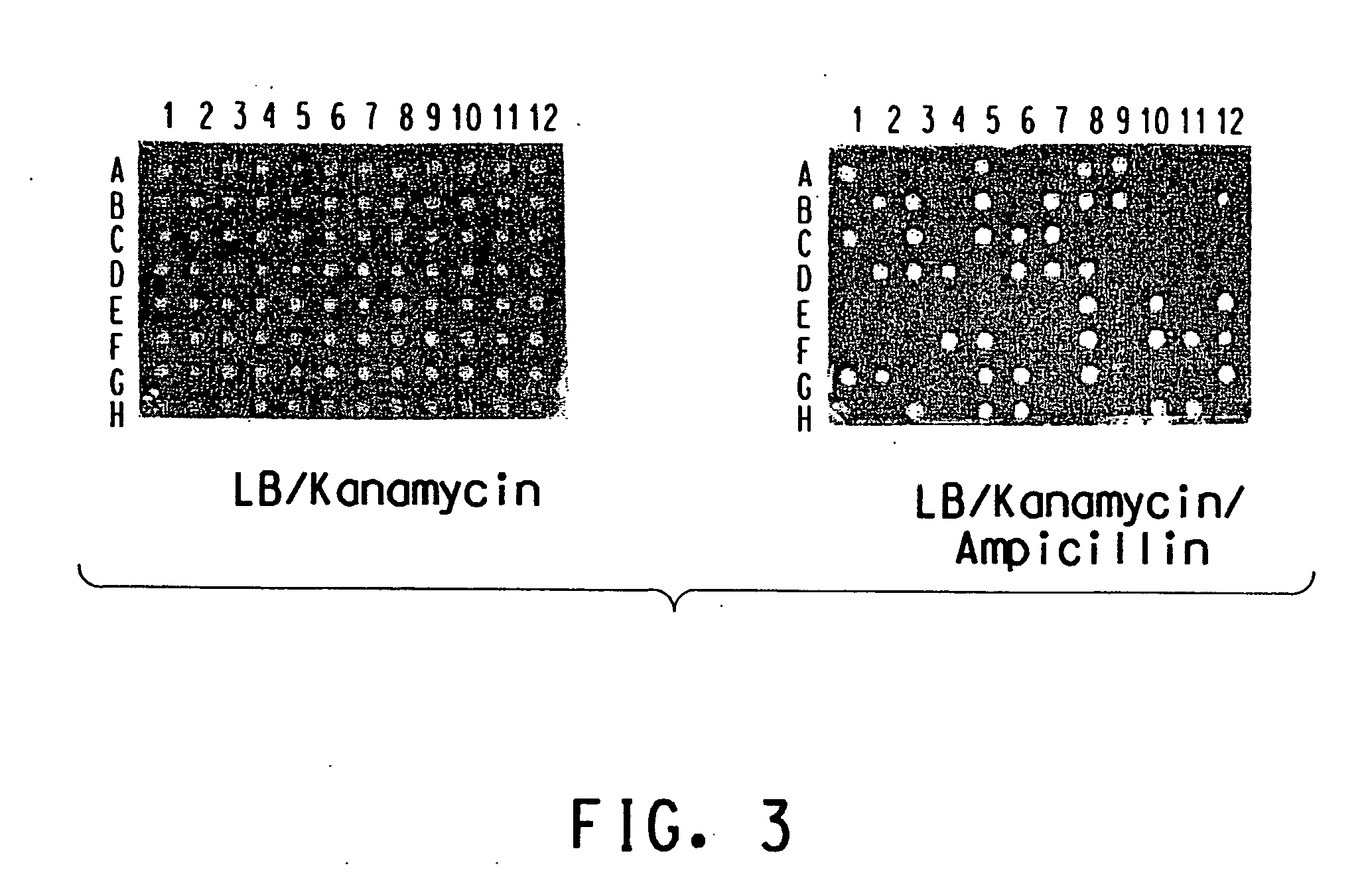
Method for determination of gene function
a gene function and gene technology, applied in the field of molecular biology and microbiology, can solve the problems of limited knowledge of restriction sites, time-consuming and laborious, and relatively few htp methods to da
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0112] Construction Of Genomic Library In Chromosomal Intepration Vector Isolation Of Chromosomal DNA
[0113] A “seed” culture of E. coli strain W3110 was prepared by inoculating an isolated colony into 5 mL of LB broth. The culture was grown overnight with shaking at 37° C. The following day a 1:1000 dilution of the seed culture was made into fresh LB broth and the culture was grown to an OD600 equal to 0.7-0.8. The cells were pelleted and resuspended into 2.5 mL of 10 mM Tris-EDTA. A hundred microliter of lysozyme (5 mg / mL) was added to the cells. Following a 15-minute incubation at 37° C., 0.1- mL of proteinase K and 0.125 mL of sodium doceyl sulfate was added to the cell suspension. The cell lysate was incubated for an additional 50-minutes at 37° C. The cell lysate was extracted twice with equal volumes of phenol, twice with a 1:1 ratio of phenol / chloroform, and twice with equals of chloroform. {fraction (1 / 10)} volume of a 3M sodium acetate solution and 2× volume of 100% ethano...
example 2
In vitro Transiposition
[0116] In vitro Transposition Reactions Using A Tn5-Based Transposition System
[0117] The E. coli W3110 DNA fragments were randomly mutagenized using the EZ::TN™ Insertion Kit (Epicentre Technologies, Madison, Wis.). The transposon donor DNA used in the transposition reactions was the EZ::TN™ Transposon (a linear DNA fragment), which carries the gene that confers resistance to Kanamycin between the ends of the transposable element. Per Epicentre's instructions, 0.2 μg of the target DNA (E. coli W3110 DNA fragments) was incubated with molar equivalents of the EZ::TN™ Transposon and 1U of the EZ::TN™ transposase. The reaction mixture was incubated for 2 hours at 37° C. The transposition reaction was stopped by adding 1 μL of the 10× Stop Solution and incubating the mixture for 10 minutes at 70° C.
[0118] In vitro Transposition Reactions Using A Tn7-Based Transposon System
[0119] The E. coli W3110 DNA fragments were randomly mutagenized using the GPS™-1 Genome P...
example 3
DNA Library Construction
[0120] Preparation of the Tn5-Based Mutant DNA Library
[0121] Sau3A digested W3110 DNA fragments (50 ng) containing the EZ::TN (Tn5-based) insertions (Kanamycin-resistant) were ligated into the dephosphorylated BamHI of pTSCSE7 (50 ng). The plasmid pTSCSE7 is a derivative of temperature sensitive vector pTSC29 and contains a gene that confers resistance to Chloroamphenicol (G. J. Phillips Plasmid (1999) 41, 78-81). pTSCSE7 also contain the npr-sacB gene from pBE83, which confers sensitivity to sucrose (V. Nagarajan, H. Albertson, M. Chen and J. Ribbe Gene (1992) 114, 121-126). The ligation reactions were done according to manufacturing specifications (New England Biolabs, Beverly, Mass.) and were incubated overnight at 16° C.
[0122] Any temperature-sensitive replicon can be used in the preparation of the mutant DNA library. The vector of choice must contain a selectable marker that is different from selectable marker that is present between transposon ends....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electrical resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com