Method for preparing ferro-titantium, steel and ferrovanadium from vanadium-titantium iron headings
A technology for vanadium-titanium-iron concentrate and ferro-titanium, which is applied in the metallurgical field, can solve the problems of difficult disposal of pollutants, long process, large consumption of refractory materials, etc., and achieves uncontrolled production scale, low energy consumption, and low environmental pollution. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
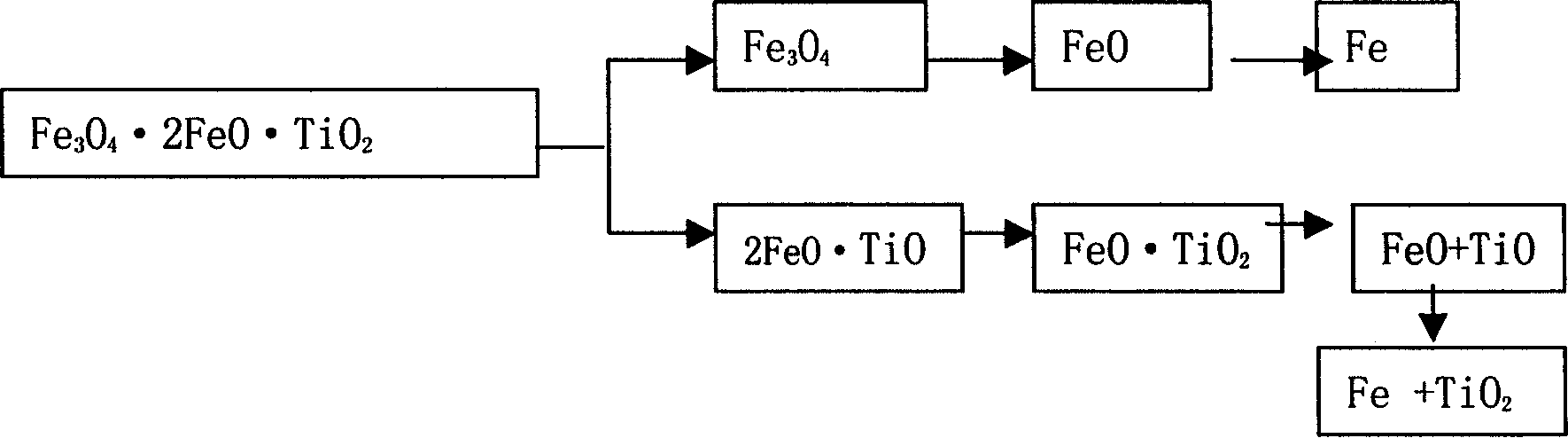
[0050] Embodiment 1, single slag method for extracting vanadium
[0051] 1. Mix 94% vanadium-titanium-iron ore concentrate (weight percentage, the same below), 3% sodium carbonate and 3% syrup evenly, pelletize with a pelletizer, and dry in a drying kiln to form ore pellets.
[0052] 2. Mix materials according to the ratio of 75% of ore balls and 25% of coke powder, put them into refractory tanks, and put the refractory tanks on tunnel kiln cars for reduction.
[0053] 3. After the reduction is completed, the kiln is forced to cool by blowing air and then exit the kiln.
[0054] 4. When the carbon content of the pellets is less than 0.6%, the melting requires carbon distribution. The carbon distribution is 5% of the weight of the pellets, and it enters the electric furnace through the feeding system. When the total iron in the slag is less than 3%, put the slag into the slag vat, and then discharge half of the molten steel.
Embodiment 2
[0062] Embodiment 2, single slag method for extracting vanadium
[0063] 1. Mix 91% vanadium-titanium-iron ore concentrate (percentage by weight, the same below), 5% potassium carbonate and 4% syrup evenly, pelletize with a pelletizer, and dry in a drying kiln to form ore pellets.
[0064] 2. Mix materials according to the ratio of 73% of ore balls and 27% of coke powder, put them into a refractory tank, and put the refractory tank on a tunnel kiln car for reduction.
[0065] 3. After the reduction is completed, the kiln is forced to cool by blowing air and then exit the kiln.
[0066] 4. When the carbon content of the pellets is less than 0.6%, the melting requires carbon distribution. The carbon distribution is 6% of the weight of the pellets, and it enters the electric furnace through the feeding system. When the total iron in the slag is less than 3%, put the slag into the slag vat, and then discharge half of the molten steel.
[0067] 5. Add lime and iron scale to the t...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Embodiment 3: Double slag method for extracting vanadium
[0075] 1. Mix the organic matter extracted from 89% vanadium-titanium ferrite concentrate, 6% sodium chloride and 5% humic coal evenly, make pellets with a pelletizer, and dry them in a drying kiln to form ore pellets.
[0076] 2. Mix materials according to the ratio of 70% ore balls and 30% coke powder, put them into refractory tanks, and put the refractory tanks on tunnel kiln cars for reduction.
[0077] 3. After the reduction is completed, it is forced to cool by blowing air and then exits the kiln.
[0078] 4. When the carbon content of the metallized ball is less than 0.6%, the carbon is melted and distributed, and the carbon content is 8% of the weight of the pellet, and it enters the electric furnace through the feeding system. When the total iron in the slag is less than 3%, put the slag into the slag vat, and then discharge half of the molten steel.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com