Manufacturing method of optical fiber optical fluid channel
A fabrication method and fluid channel technology, which are applied in the directions of cladding optical fibers, optical waveguides, and structures/shapes of active media, can solve the problems of unavailability, complex technology, and high viscosity of paraffin oil, and achieve simple, easy-to-implement, low-cost effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] The structure of the present invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings and through embodiments. It should be noted that this embodiment is descriptive, not restrictive.
[0040] A method of fabricating a fiber optic fluid channel, see Figure 1-10 , including the following steps:
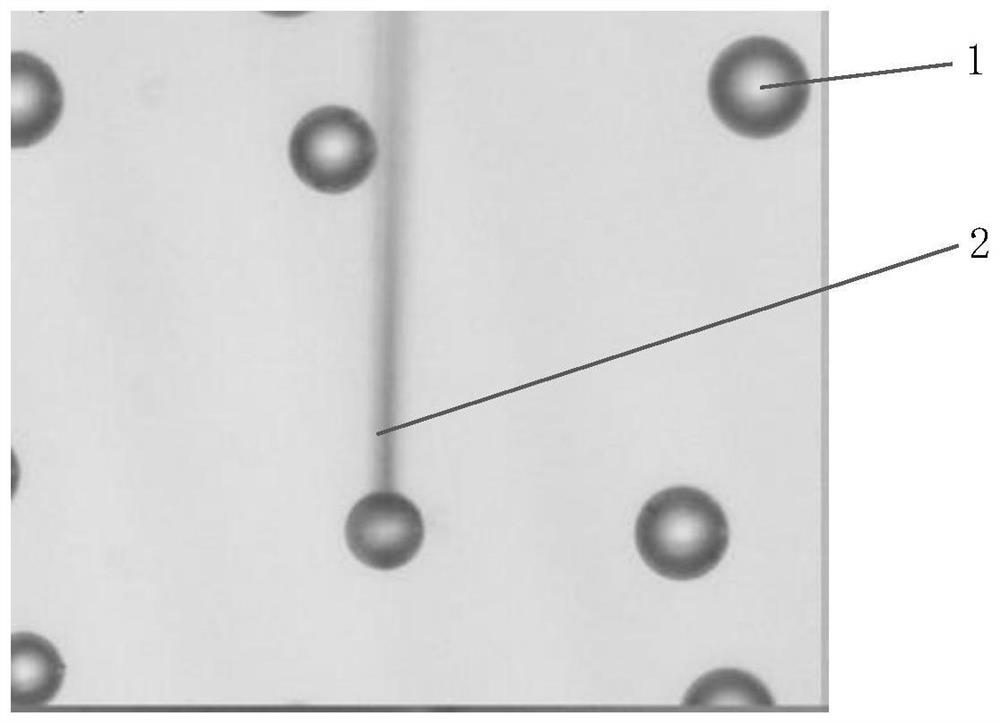
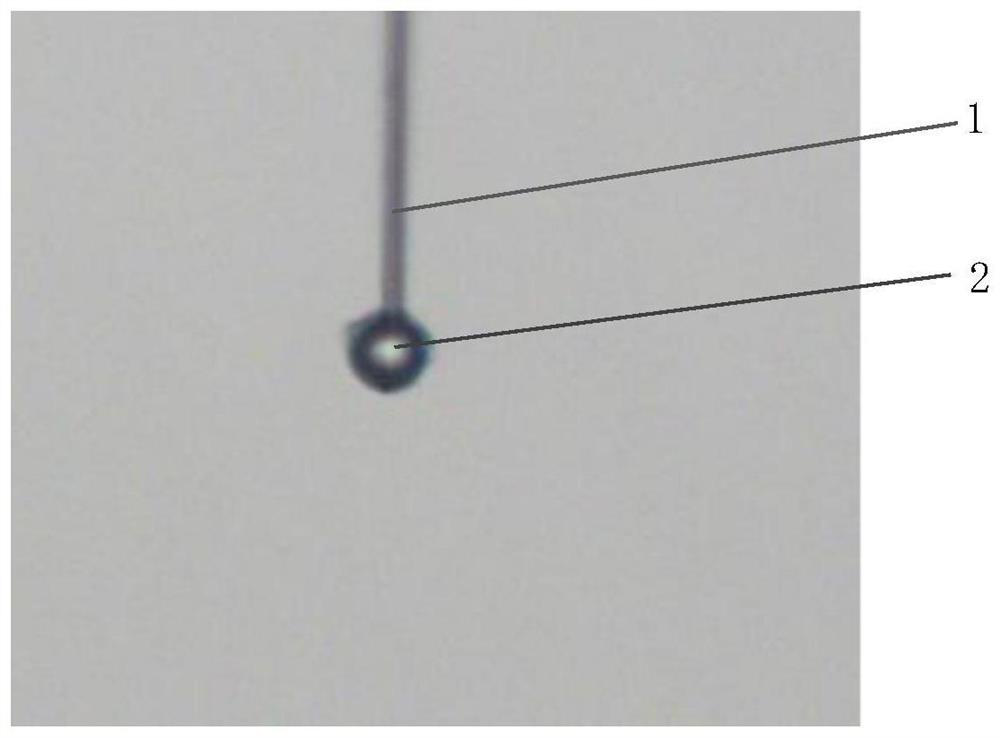
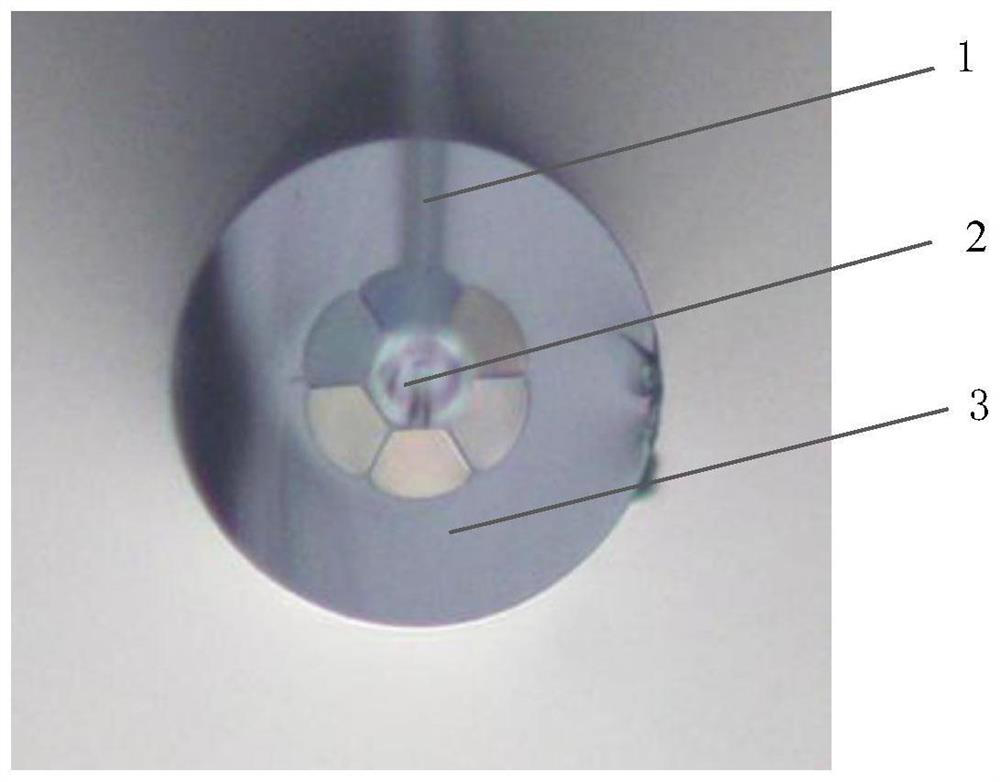
[0041] Step 1. Treat one end of the optical fiber with a selective filling method based on polystyrene microspheres and paraffin oil. First, take a microstructured optical fiber of appropriate length, remove the coating layer from both ends and cut the end face to be flat, and place it vertically under the microscope for use. At the same time, polystyrene microspheres 1 were sprinkled on the glass slide and placed on the microscope stage. After that, the polystyrene microspheres are operated by using the taper-drawing capillary probe 2 as a tool. The taper-drawing capillary probe can be drawn by the fiber-optic fusion taper-drawing machine, and t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com