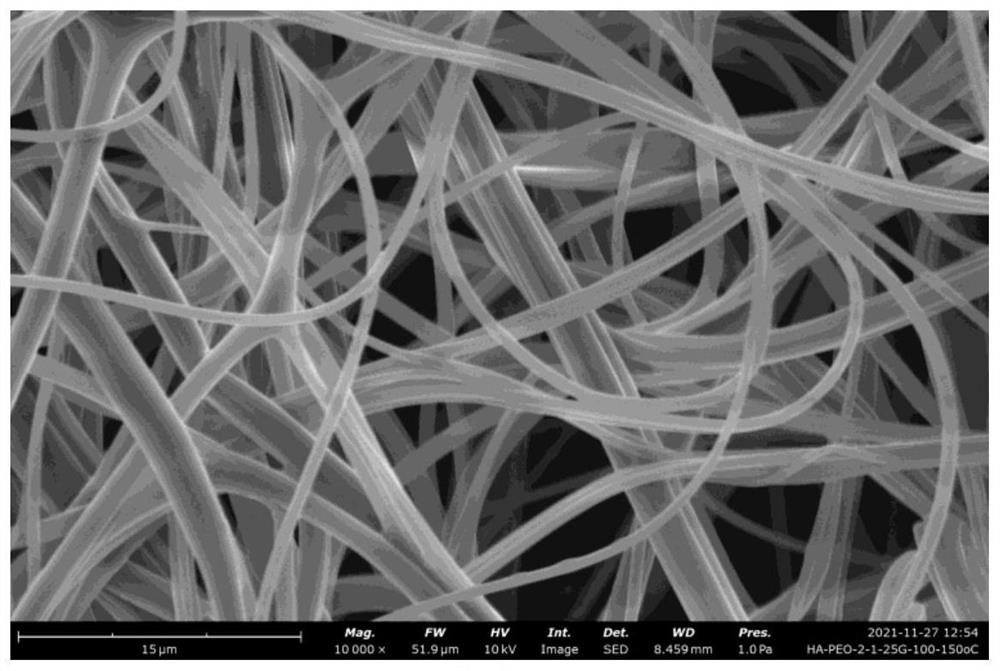
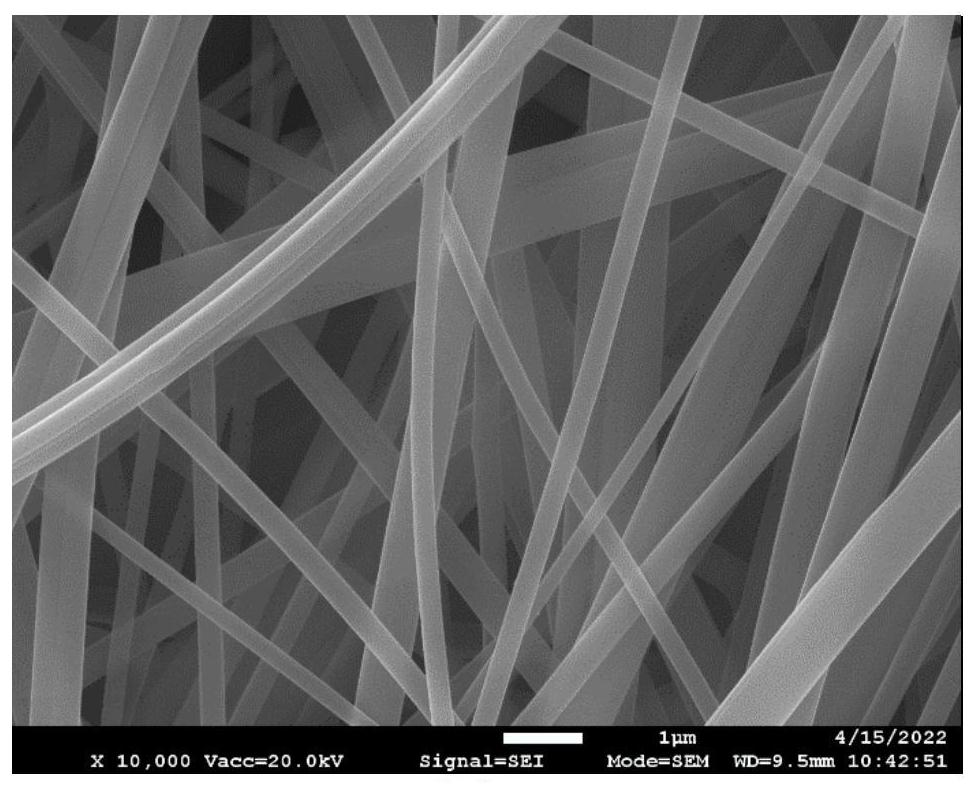
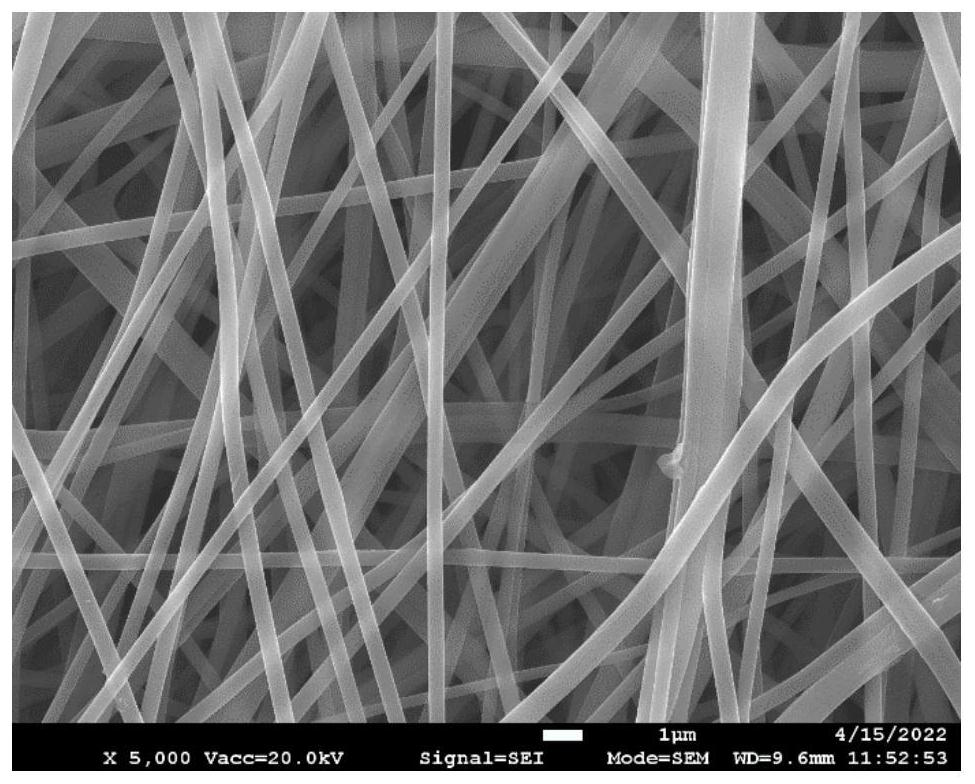
Submicron heterocyclic aramid fiber and preparation method thereof
A technology for spinning heterocyclic aramid fibers and heterocyclic aramid fibers, which is applied in the directions of fiber treatment, spinning solution preparation, fiber chemical characteristics, etc., can solve the problems of high hardness and large size of heterocyclic aramid fibers, and achieve excellent flexibility. performance, low equipment requirements, and the effect of reducing surface tension
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0036] Preparation method of heterocyclic aramid fiber spinning solution
[0037] The embodiment of the first aspect of the present application provides a preparation method of a submicron heterocyclic aramid fiber, comprising:
[0038] S10. The step of preparing a polymer includes performing solution polymerization of a diamine monomer and a diacid chloride in a mixed solution of an organic solvent and an inorganic compound to obtain a polymer; wherein the diamine monomer includes a first diamine monomer and a second diamine monomer, the first diamine monomer is a heterocyclic diamine, the second diamine monomer is an aromatic ring diamine, and the molar concentration of the diamine monomer is 0.05-0.5 mol / L;
[0039] S20. The step of preparing a spinning solution for heterocyclic aramid fiber, comprising dissolving the polymer in a spinning solvent containing a viscosity modifier to obtain a spinning solution for heterocyclic aramid fiber, wherein the heterocyclic aramid f...
Embodiment 1
[0100] Under nitrogen protection, the dewatered N,N-dimethylacetamide was mixed with lithium chloride, stirred to dissolve the lithium chloride, and cooled to 10°C in a cold water bath to obtain a mixed solution, wherein N,N- The weight ratio of dimethylacetamide to lithium chloride was 50:1.75.
[0101] P-phenylenediamine and 2-(4-aminophenyl)-5-aminobenzimidazole are added to the mixed solution, and the molar concentration of the diamine monomer in the mixed solution is 0.15mol / L, wherein p-phenylenediamine and The molar ratio of 2-(4-aminophenyl)-5-aminobenzimidazole was 1:2. After the diamine monomer was dissolved, it was cooled to 0°C, and then terephthaloyl chloride was added. The molar ratio of the structural unit of the diacid chloride and the structural unit of the diamine was 1.01:1, and the polymerization reaction was carried out with high-speed stirring, and the stirring speed was 500rpm. , the reaction time was 45 min, and the polymer was obtained.
[0102] N,N-...
Embodiment 2
[0105] Under nitrogen protection, the dewatered N,N-dimethylformamide was mixed with calcium chloride, stirred to dissolve calcium chloride, and cooled to 10°C in a cold water bath to obtain a mixed solution, wherein N,N- The weight ratio of dimethylformamide to calcium chloride was 50:3.
[0106] 5-chloro-p-phenylenediamine and 2-(4-aminophenyl)-5-aminobenzimidazole are added to the mixed solution, and the molar concentration of the diamine monomer in the mixed solution is 0.3 mol / L, wherein 5 - The molar ratio of chloro-p-phenylenediamine and 2-(4-aminophenyl)-5-aminobenzimidazole is 1:2. After the diamine monomer is dissolved, it is cooled to 0 °C, and then terephthaloyl chloride is added. The molar ratio of the structural unit of diacid chloride and the structural unit of diamine is 1:1, and the polymerization reaction is carried out with high-speed stirring, and the stirring speed is 1000rpm. , the reaction time is 30min, and the polymer is obtained.
[0107] N,N-dimeth...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com