Acid-resistant and high-temperature-resistant staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage as well as composition, kit and application thereof
A staphylococcus, golden yellow technology, applied in the field of bacteriophage, can solve problems such as poor bactericidal effect, and achieve the effect of strong acid resistance, good high temperature resistance, and no side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
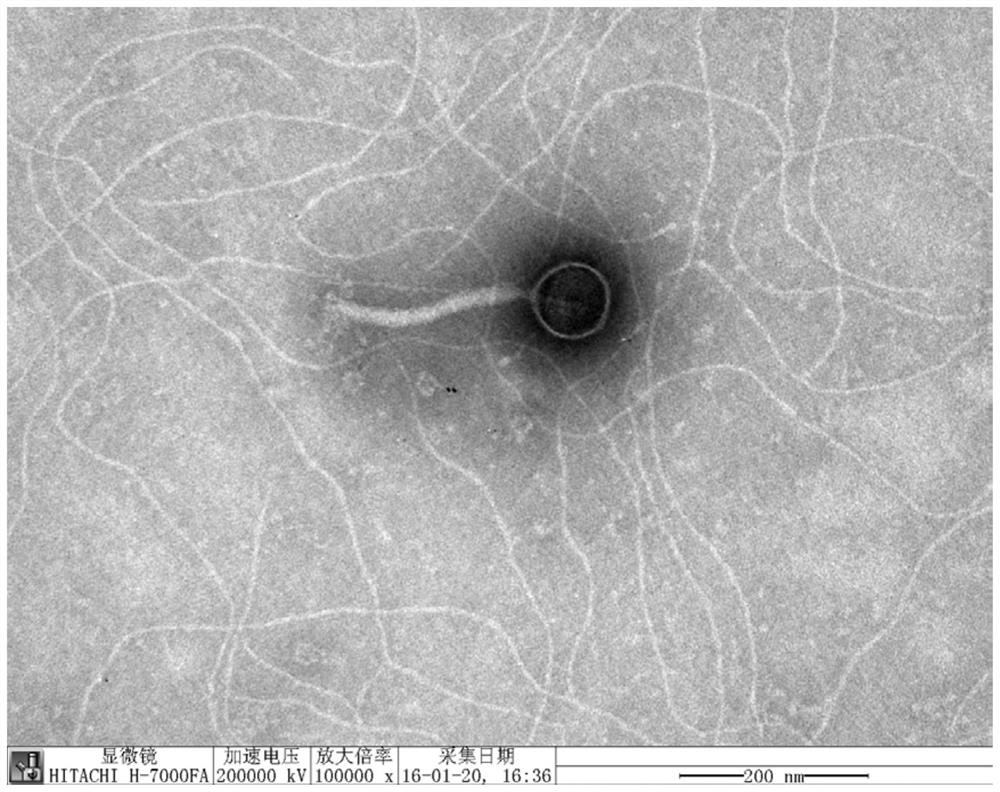
[0042] Example 1 Screening and Purification of Phage
[0043] (1) Sample collection and processing
[0044] The sample in the present invention is obtained from the water body near the Zhongcai Logistics Market in Jiangning District, Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province.
[0045] (2) Enrichment of phages targeting the target Staphylococcus aureus in the sample Mix the above filtrate with 2 times LB liquid medium at a ratio of 1:1, inoculate 100 μL of the target Staphylococcus aureus strain, and enrich overnight.
[0046] (3) Phage screening
[0047] Centrifuge the above-mentioned enrichment solution to get the supernatant to pass through a 0.22μm membrane, mix 1mL with 5mL LB semi-solid medium containing the target Staphylococcus aureus, pour it on a petri dish containing LB solid medium, and wait until the semi-solid medium After the medium solidified, culture overnight at 37°C, observe whether there are plaques the next day, and record the experimental results.
[0048] (4) Pha...
Embodiment 2
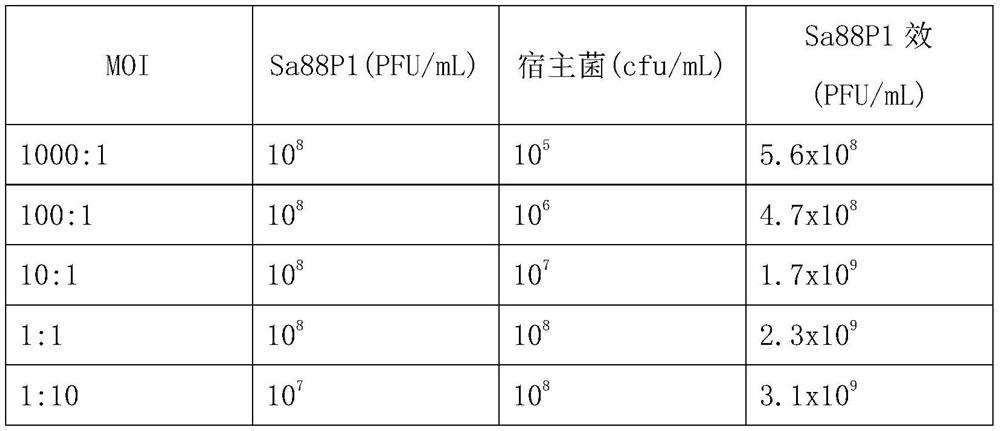
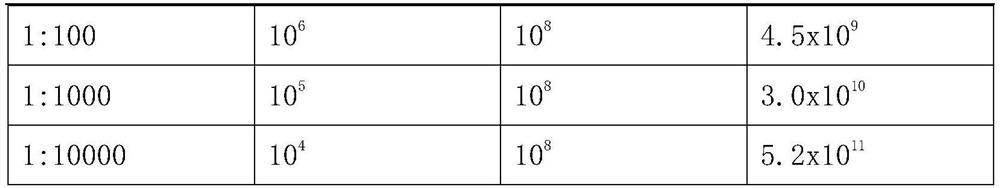
[0052] Example 2 Determination of the optimal multiplicity of infection (MOI) of Staphylococcus aureus phage Sa88P1 (Staphylococcus aureus phageSa88P1) to Staphylococcus aureus Pick a single colony of Staphylococcus aureus and inoculate it into a test tube filled with 3 mL of LB culture solution, 37 Cultivate with shaking at 150 rpm for 12 hours to obtain a suspension of the host bacteria. The bacterial suspension was transferred to 10 mL LB culture medium at a ratio of 1:100, and cultured at 37°C with shaking at 150 rpm to the pre-logarithmic phase. Add the pure culture solution of Staphylococcus aureus phage SA88P1 (prepared by Example 1) and host bacteria (MOI=number of phages / number of bacteria) according to the multiplicity of infection ratio, and add LB liquid medium to make the total volume of each tube the same. Shake overnight at 150 rpm in a shaker at 37°C. After the culture was completed, centrifuge at 5000 g for 10 min and collect the supernatant to measure the ph...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3 Deletion detection test of virulence genes or adverse genes of Staphylococcus aureus phage Sa88P1 In this example, 103 virulence genes identified as originating from lysogenic phages in pathogenic bacteria were selected as shown in Table 2. The complete genome of staphylococcal phage Sa88P1 was analyzed by bioinformatics to determine whether it contained the following virulence genes. The results show that Staphylococcus aureus phage Sa88P1 does not contain the following virulence genes or adverse genes, so it cannot encode proteins that may cause potential health risks. Therefore, Staphylococcus aureus phage Sa88P1 will not affect the health of humans or animals.
[0058] Table 2 The main known virulence genes of lysogenic phages in pathogenic bacteria
[0059]
[0060]
[0061]
[0062]
[0063]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com