Process for extracting lead from zinc-lead dust
A dust, zinc-lead technology, applied in the process of zinc-lead dust lead extraction, can solve the problems of difficult separation of zinc and lead, waste of lead resources, difficult leaching, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
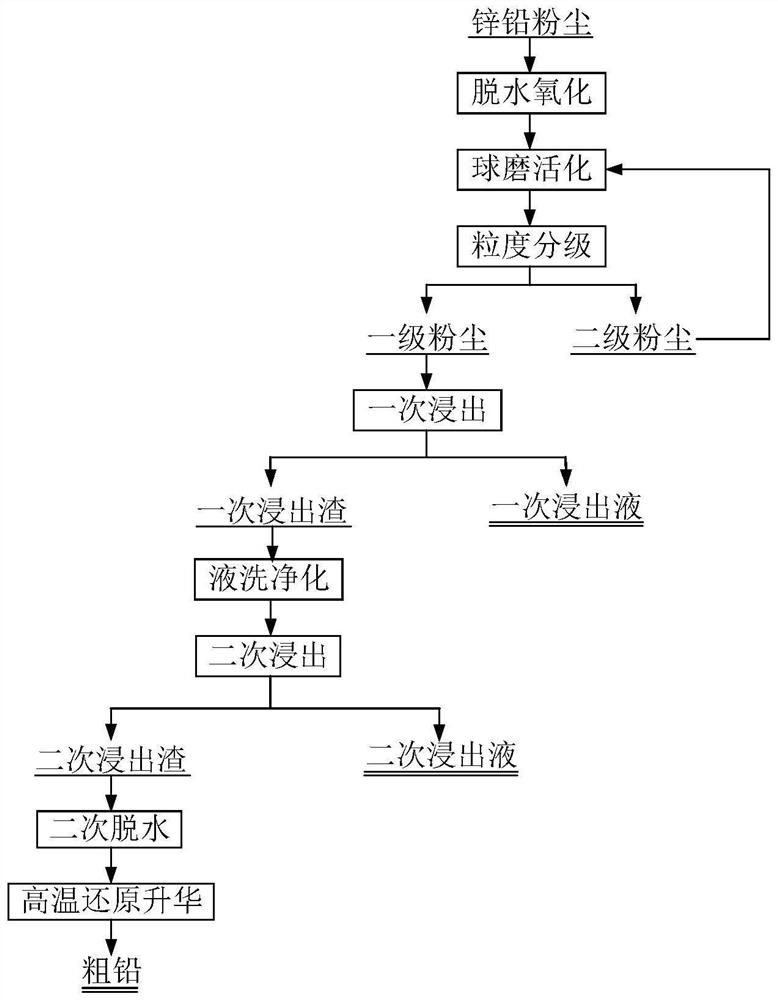
[0041] A kind of technology that zinc-lead dust extracts lead, refer to figure 1 , including the following steps:
[0042] S1, dehydration oxidation, includes the following steps:
[0043] S11, carried out at 110°C in the low-temperature stage, with a vacuum degree of 0.08MPa, and directly raised to the high-temperature stage after 120 minutes of treatment;
[0044] S12, the high-temperature stage is carried out at 490°C, and oxygen is introduced to react for 20 minutes;
[0045] S2, ball milling activation, comprises the following steps:
[0046] S21, crush the dehydrated and oxidized dust in the crusher until the particle size is uniform, then use agate balls for high-strength grinding and activation in the planetary ball mill, the ratio of material to ball is 1:1, and the speed is 350r·min -1 , ball milled for 8 hours to obtain the first-grade dust with a particle size of less than 200 mesh and the second-grade dust with a particle size larger than 200 mesh;
[0047] S2...
Embodiment 2
[0057] A process for extracting lead from zinc-lead dust, comprising the following steps:
[0058] S1, dehydration oxidation, includes the following steps:
[0059] S11, the low temperature stage is carried out at 115°C, the vacuum degree is 0.075MPa, and the temperature is directly raised to the high temperature stage after 90 minutes of treatment;
[0060] S12, the high-temperature stage is carried out at 500 ° C, and carbon dioxide is introduced, and the reaction is carried out for 25 minutes;
[0061] S2, ball milling activation, comprises the following steps:
[0062] S21, crush the dehydrated and oxidized dust in a crusher until the particle size is uniform, then use agate balls in a planetary ball mill for high-strength grinding and activation, the ratio of material to ball is 1:2, and the speed is 450r min -1 , ball milling for 6h;
[0063] S22, mixing the secondary dust and the primary dust with a mass ratio of 1:5, and performing ball milling activation again;
...
Embodiment 3
[0073] A process for extracting lead from zinc-lead dust, comprising the following steps:
[0074] S1, dehydration oxidation, includes the following steps:
[0075] S11, the low temperature stage is carried out at 120°C, the vacuum degree is 0.065MPa, and the temperature is directly raised to the high temperature stage after 60 minutes of treatment;
[0076] S12, the high temperature stage is carried out at 510°C, carbon dioxide and oxygen are introduced, the gas volume ratio is 1:1, and the reaction is 30 minutes;
[0077] S2, ball milling activation, comprises the following steps:
[0078] S21, crush the dehydrated and oxidized dust in a crusher until the particle size is uniform, then use agate balls in a planetary ball mill for high-strength grinding and activation, the ratio of material to ball is 1:3, and the speed is 550r·min -1 , ball milling for 4h;
[0079] S22, mixing the secondary dust and the primary dust with a mass ratio of 1:4, and performing ball milling ac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com