Developable film for implanting medical device and preparation method of developable film
A technology for implanting medical devices and medicine, applied in pharmaceutical formulations, applications, medical science, etc., can solve the problem that the film cannot be detected by X-ray, and achieve the effect of good application prospects, environmental friendliness, and good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
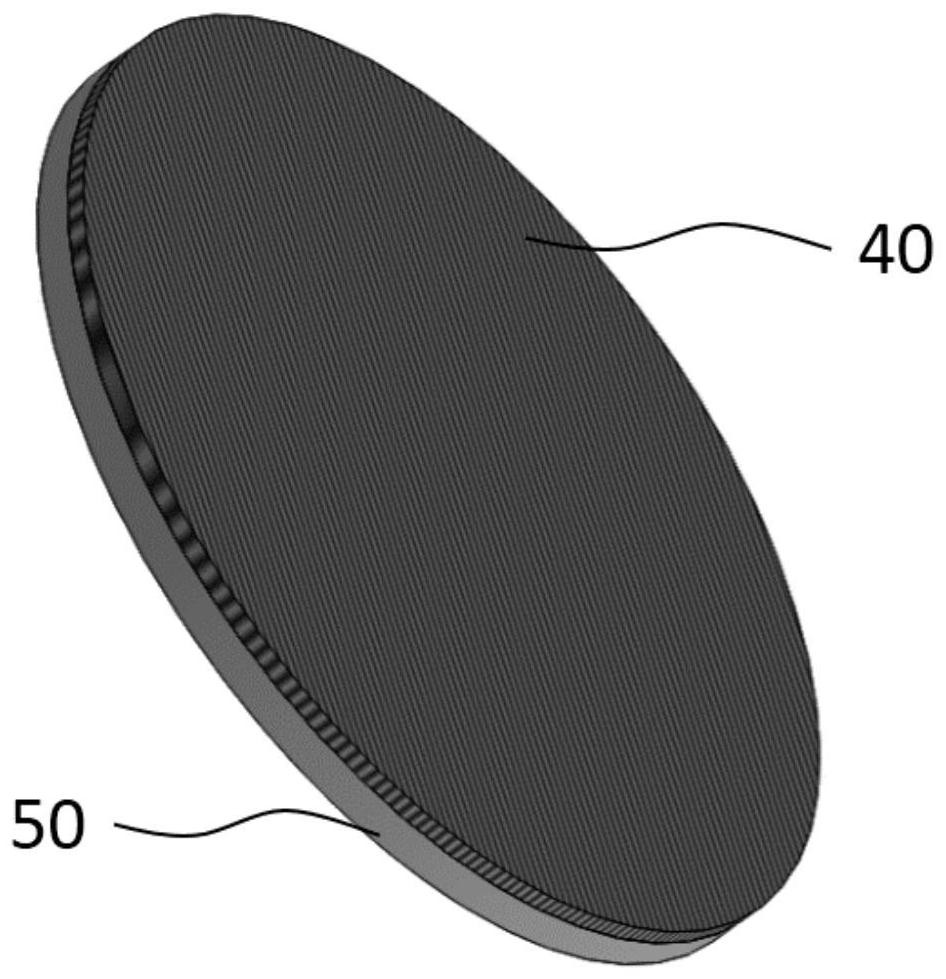
[0056] Make a solution of an appropriate amount of iodophor (containing 0.01g of iodine) and degradable polymer polylactic acid. The mass ratio of iodine in iodophor to polylactic acid is 20:100. (1g) evenly spray the prepared solution on one side of the surface. By drying, the povidone iodine is fixed on the film substrate of the degradable occluder by the degradable polylactic acid to obtain a film with a degradable occluder that can be developed or seen under X-ray irradiation. Since both the degradable polymer polylactic acid and the substrate of the degradable occluder membrane are polymer materials, the degradable polymer polylactic acid can increase the combination of iodophor and the membrane substrate of the degradable occluder Force, so that the development component iodophor is stably placed on the membrane substrate of the degradable occluder. Such as figure 1 As shown, in this solution, one side surface of the film substrate 50 of the degradable occluder is coat...
Embodiment 2
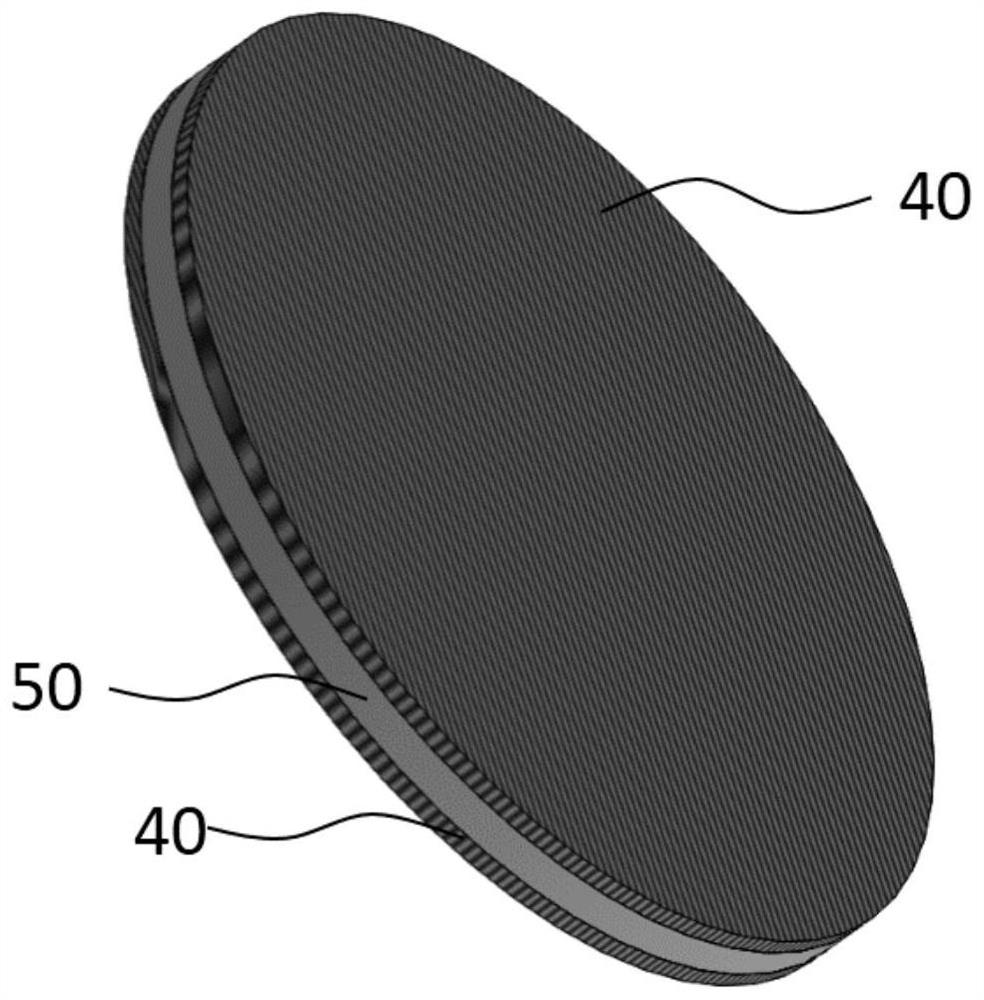
[0058] On the surface of the polydioxanone film substrate (1g) of the degradable occluder, dip-coat iopamidol (containing iodine 0.2g) evenly, by irradiating ultraviolet light for 5 minutes, iopamidol is fixed on On the surface of the membrane of the degradable occluder, a membrane with a degradable occluder that can be visualized or visualized under X-ray irradiation is obtained. Since the ultraviolet rays can increase the binding force between the iopamidol and the membrane of the degradable occluder, the imaging component iopamidol is stably placed on the membrane of the degradable occluder. Such as figure 2 As shown, it is also possible to double-coat the development layer 40 on both sides of the film substrate 50 of the degradable occluder, and the development effect is as follows: Figure 6 shown. In an alternative embodiment, in this solution, one side surface of the film substrate 50 of the degradable occluder is coated with the developing layer 40 on one side. In ...
Embodiment 3
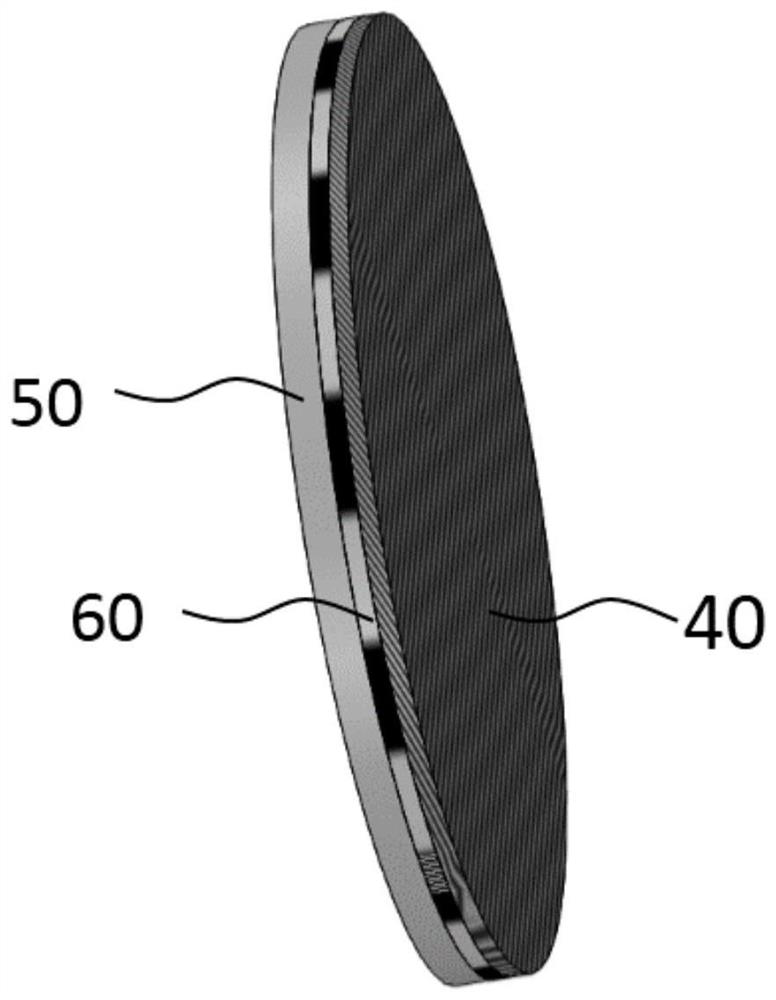
[0060] Such as image 3 As shown, on one side surface of the polycaprolactone film substrate 50 of the degradable occluder, evenly roll-coat an adhesive, such as ultraviolet sensitive glue, to form an adhesive layer 60, and then roll-coat 0.3g iodine on the degradable occluder One side surface of the film substrate (1g) of the occluder has an adhesive, and the iodine is fixed on the film substrate 50 of the degradable occluder by the adhesive, and forms a developing layer 40 to obtain The film of the degradable occluder that can be developed or visible under the film, the developing effect is as follows Figure 7 shown. Since the adhesive can increase the combination of iodine and the film substrate of the degradable occluder, the iodine, the developing component, is stably placed on the film substrate of the degradable occluder.
[0061] In this embodiment, the surface of the film base material of the degradable occluder is coated on one side. surface coating, such as Fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com