Heat treatment process for casting precipitation strengthened nickel-based superalloy
A nickel-based superalloy and precipitation strengthening technology, which is applied in the field of heat treatment process of casting precipitation-strengthened nickel-based superalloy, can solve the problems of hard alloy performance, coarsening and growth, etc., and achieve the effect of improving mechanical properties and improving uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
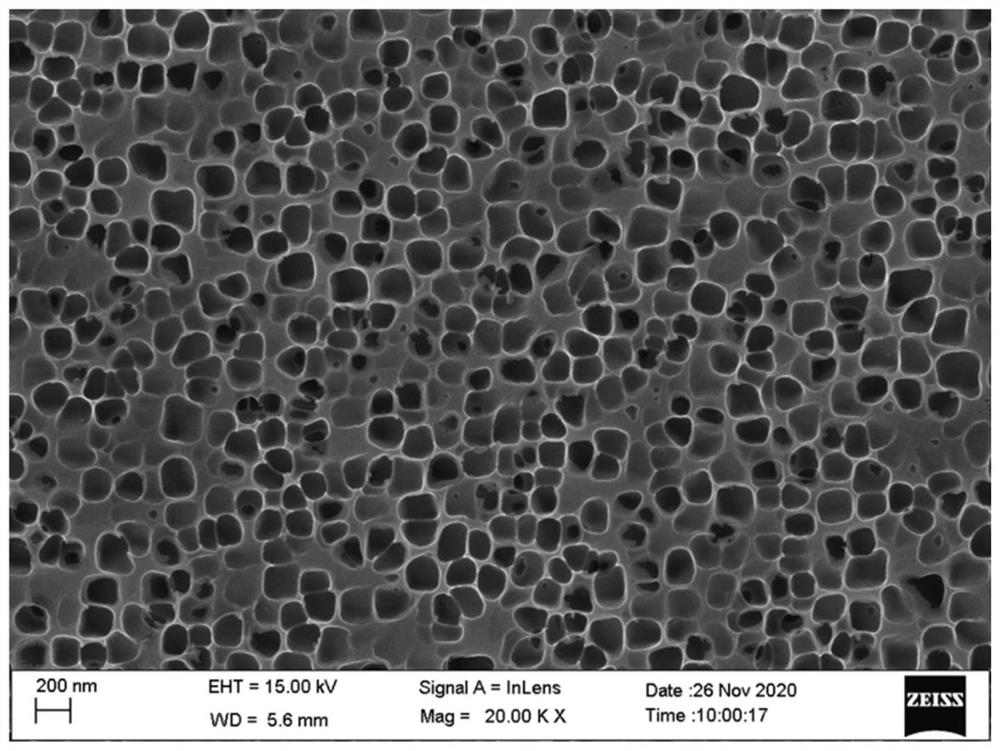
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
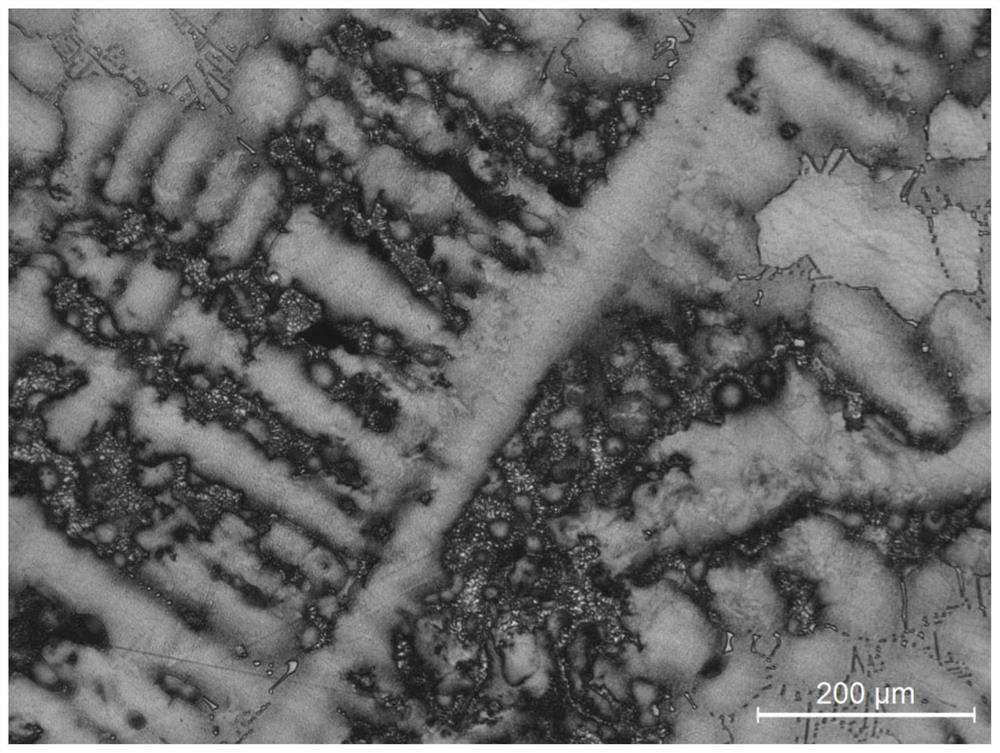
[0041] The master alloy of the cast precipitation-strengthened nickel-based superalloy is put into a vacuum induction furnace for melting to obtain a master alloy ingot, and then the alloy test rod is drawn in the vacuum melting furnace, and the drawing speed of the test rod is 5mm / min. The microstructure of the as-cast alloy is as follows: figure 1 shown. Subsequently, the alloy is heat treated, and the specific heat treatment process is as follows:
[0042] 1) Solution treatment: send the alloy test rod into the vacuum heat treatment furnace and raise the temperature to 1210°C with the furnace at a rate of 6.7°C / min, keep it for 8h, then raise the temperature to 1228°C for 2h, keep it for 20h, and then pass through the air cooling zone to room temperature.
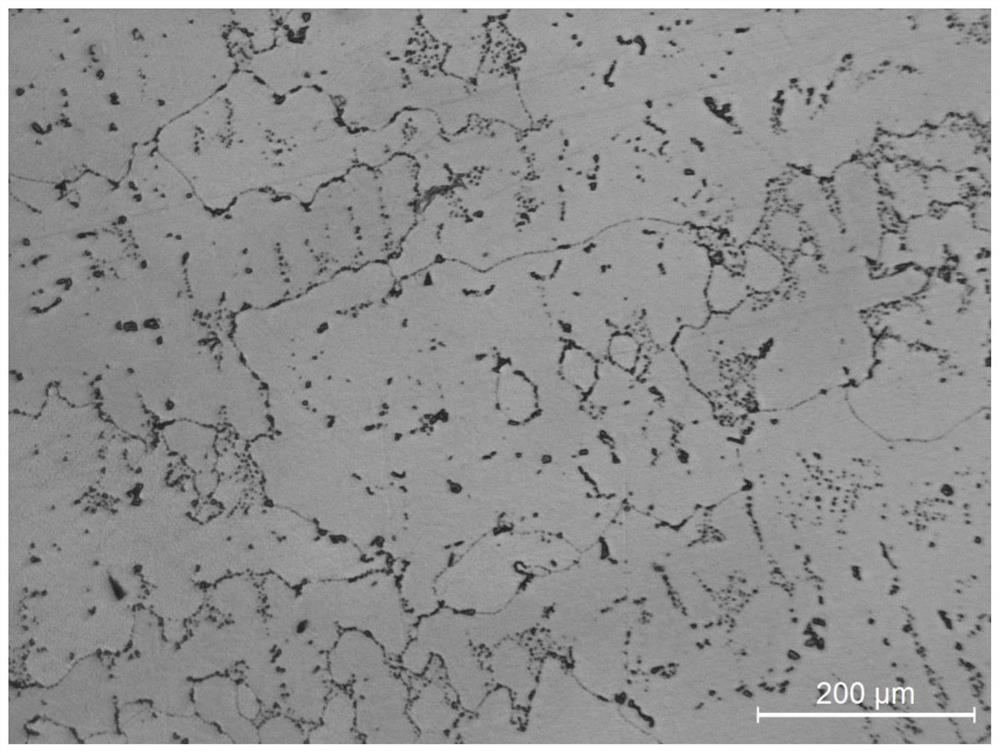
[0043] The low magnification image of the microstructure of the alloy after solution treatment is as follows: figure 2 shown. from figure 2 It can be seen that the γ / γ′ eutectic structure is completely eliminated...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The master alloy ingot was obtained by melting in a vacuum induction furnace, and then the alloy test bar was drawn in the vacuum melting furnace. The drawing rate of the test bar was 5mm / min. figure 1 shown.
[0050] 1) Solution treatment: Put the alloy test rod into the vacuum heat treatment furnace and raise the temperature to 1215°C with the furnace at a rate of 6.8°C / min, keep it for 6h, then raise the temperature to 1225°C for 2h, keep it for 20h, and then pass through the air cooling zone to room temperature.
[0051] The low-magnification image of the microstructure of the alloy after solution treatment is as follows Image 6 shown. from Image 6 It can be seen that the γ / γ′ eutectic structure is completely eliminated, and the dendrite segregation and component segregation are basically completely eliminated.
[0052] 2) Stabilization heat treatment: Send the sample after solid solution treatment and cold zone into a vacuum heat treatment furnace and heat i...
Embodiment 3
[0060] The master alloy ingot was obtained by melting in a vacuum induction furnace, and then the alloy test bar was drawn in the vacuum melting furnace. The drawing rate of the test bar was 4 mm / min. The microstructure of the cast alloy was as follows figure 1 shown.
[0061] 1) Solution treatment: Put the alloy test rod into the vacuum heat treatment furnace and raise the temperature to 1205°C with the furnace at a rate of 6°C / min, keep it for 7h, then raise the temperature to 1220°C for 2h, keep it for 10h, and then pass through the air cooling zone to room temperature.
[0062] 2) Stabilization heat treatment: Send the sample after solid solution treatment and cold zone into a vacuum heat treatment furnace and heat it up to 1075°C at a rate of 15°C / min, keep it for 2 hours, and then pass through the air cooling zone to room temperature.
[0063] 3) Aging treatment: Send the alloy test rod after solid solution and stabilization heat treatment into a vacuum heat treatment ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com