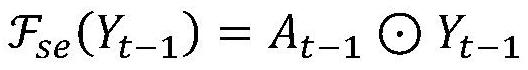Low-signal-to-noise-ratio speech enhancement method based on information distillation and aggregation
A low signal-to-noise ratio, speech enhancement technology, applied in speech analysis, speech recognition, biological neural network model, etc., can solve the problem of noise semantic difference, and achieve the effect of high stability, good feature processing ability and excellent performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
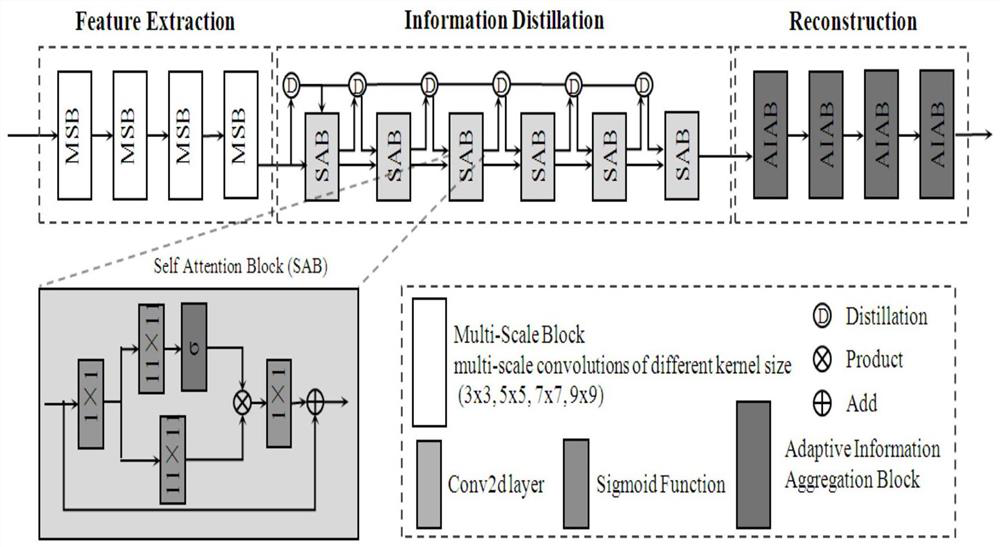
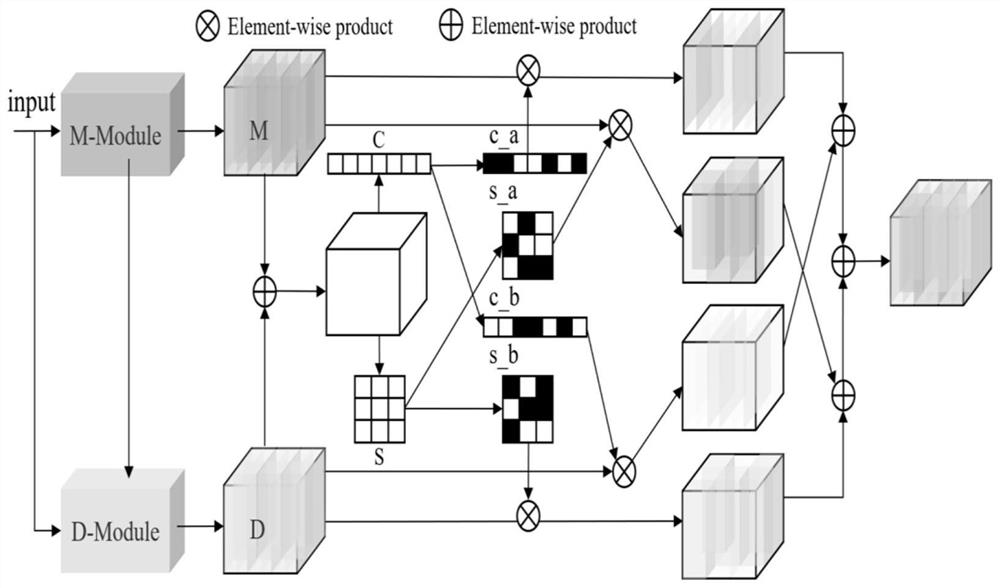
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] In the time domain, a noise signal x(n) can be expressed as:
[0025] x(n)=s(n)+d(n)
[0026] Among them, n is the index of the time frame, s(n) represents the original signal, and d(n) represents the noise signal. It is worth noting that the dimension of the time frame in each sample is not fixed due to the different duration of the input speech. Given a real-valued vector x of size N in the time domain, transform x(n) into the time-frequency domain by the short-time Fourier transform STFT:
[0027]
[0028] in is the complex conjugate of z, α is the time-shift step size, g is an analysis window (usually using Hanning window or Hamming window), l is the length of the original wave, and N is the number of frequency points. In the definition of STFT, the number of time frames is t=l / α. Therefore, the output of STFT is a two-dimensional matrix of size T×F. The input is a noisy magnitude spectrum, and after processing, an enhanced magnitude spectrum is obtained....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com