Somatic cell nuclear transplantation method and application thereof
A technology of somatic cells and embryonic stem cells, applied in botany equipment and methods, applications, embryonic cells, etc., can solve the problems of cloning mammalian defects that have little effect and exceed the ability of reprogramming, and achieve the effect of improving cloning efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0240] 11. RNA-Seq library preparation and data analysis
[0241] Mince the placenta and digest it with 0.25% trypsin at 37°C. During the digestion process, blow and suck several times with the tip of a pipette to make the digestion more comprehensive, and stop the digestion after 10-15 minutes. GFP-positive placental cells were sorted by flow cytometry and analyzed by RNA sequencing after collection.
[0242] For transcriptome analysis in mice, brain tissues from WT mice, Δ4-NT-3KO and native mice were collected for RNA-Seq. Total RNA was extracted from fetuses using TRIzol, followed by reverse transcription-polymerase reactions with 1 μg of purified RNA each time.
[0243] RNA-seq library construction and data analysis: 2 rounds of PolyA-tailed RNA purification were performed for each sample. 150bp paired-end sequencing was performed with an Illumina HiSeq4000 sequencer. RNA-seq data were analyzed with HISAT2 (version 2.1.0) and Cufflinks (version 2.2.1). Data statistics...
Embodiment 1
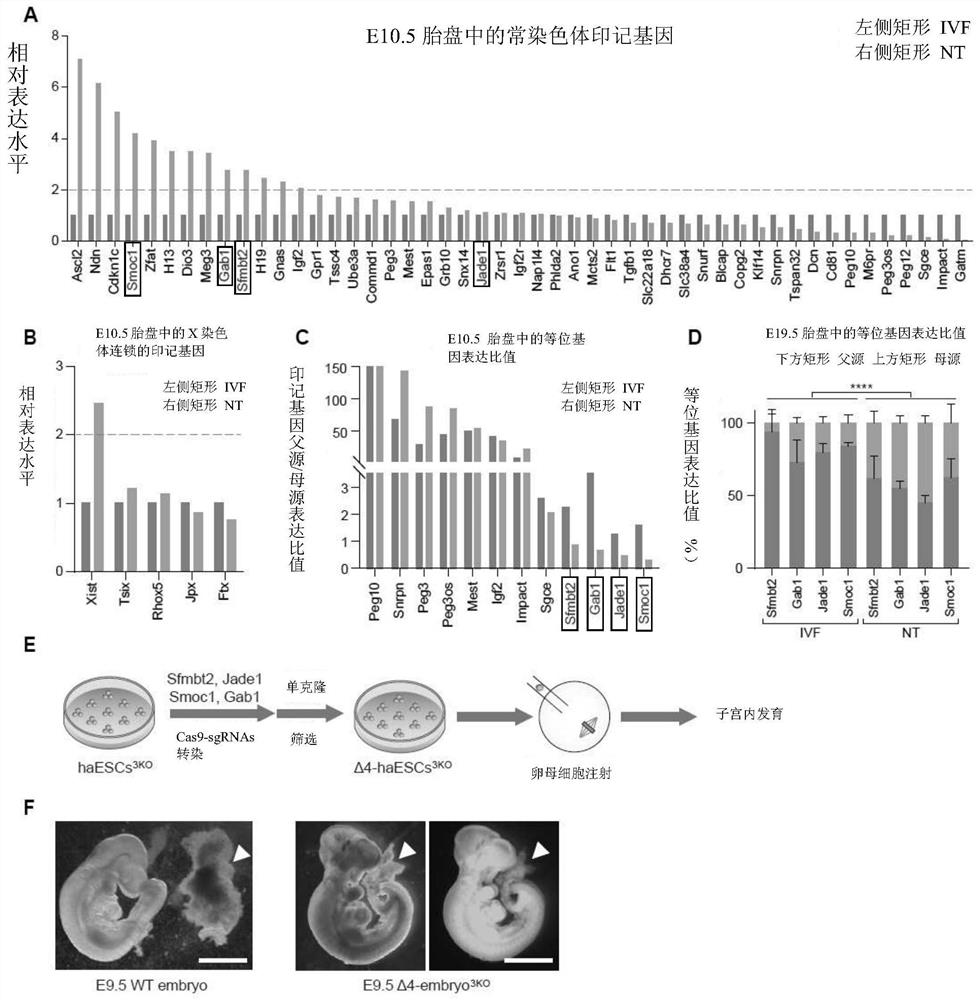
[0254] Example 1 Abnormal biallelic expression of H3K27me3 imprinted gene in E19.5 clone placenta
[0255] In order to study the specific expression of the H3K27me3 imprinted gene, the offspring of two inbred strains of mice were used as the research object in the present invention.
[0256] experimental method:
[0257] The female parent is a female mouse of the C57BL / 6-Tg(CAG-EGFP)1Osb / J strain, and the male parent is a male mouse of the PWK / PhJ strain. Somatic cell nuclear transfer was performed using granulosa cells from hybridized F1 mice, and the specific steps were as described in Experimental Method 7 above (that is, the part of somatic cell nuclear transfer and embryo culture). At the same time, C57 (GFP+) and PWK sperm and oocytes were used as controls for in vitro fertilization. These imprinted genes were not detected after E9.5. The inventors therefore analyzed E10.5 SCNT and IVF embryos. Fetal-derived placental cells with green fluorescence are isolated by flo...
Embodiment 2
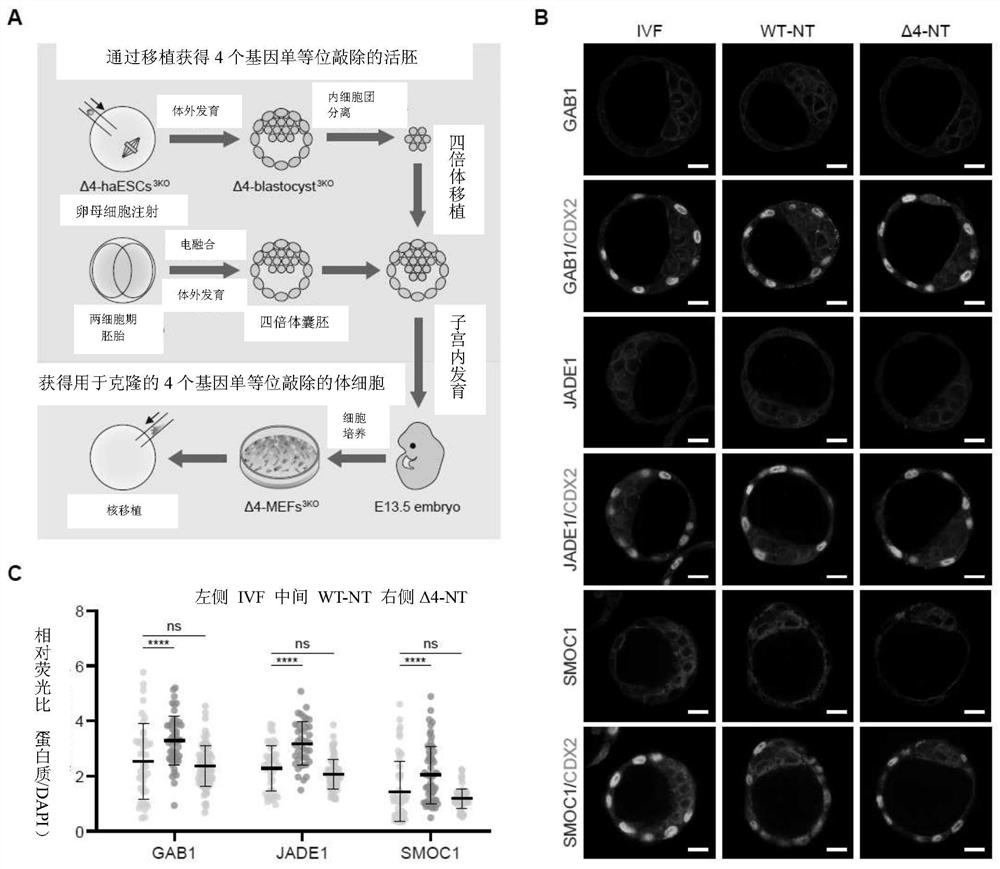
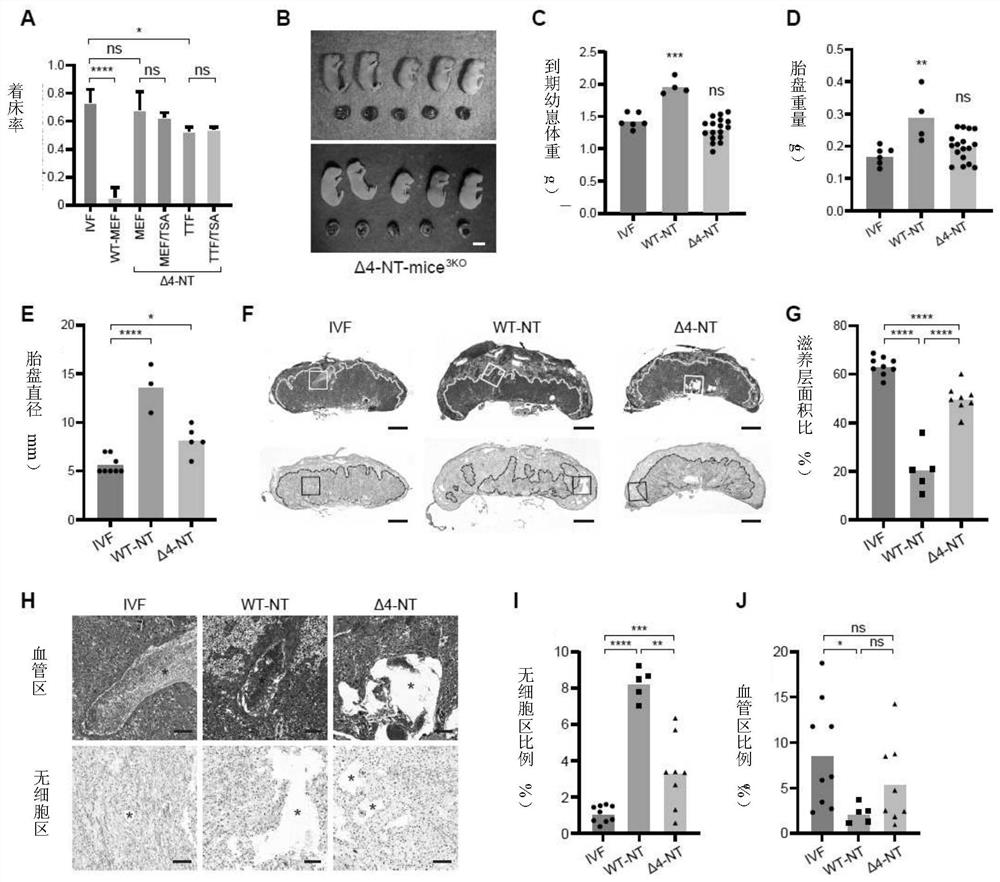
[0267] Example 2 Monoallelic knockout of four H3K27me3 imprinted genes can significantly improve cloning efficiency
[0268] experimental method:
[0269] The invention discloses a method for improving the cloning efficiency of mice, a cell line and a model mouse which can be used for improving the cloning efficiency. The specific steps are:
[0270] 1. Obtain oocytes. Select female mice of appropriate age, inject pregnant horse serotonin (PMSG), and inject human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) within 13-17 hours after injection. The egg retrieval operation was performed 13-15 hours after the injection of HCG. The collected oocytes were washed with Hepes-CZB, then cultured in M16 (Sigma) medium, and placed in a 37°C, 5% CO2 incubator for further use. Granulosa cells were removed by digestion with hyaluronidase, and oocytes were temporarily stored in CZB medium containing 3 mg / mL BSA prior to micromanipulation.
[0271] 2. Obtain haploid embryonic stem cells in which Sfmbt2, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com