Continuous casting tundish direct current plasma arc heating control method
A plasma arc and continuous casting tundish technology, applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, casting equipment, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve the problems such as the control method of tundish heating process is not given
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
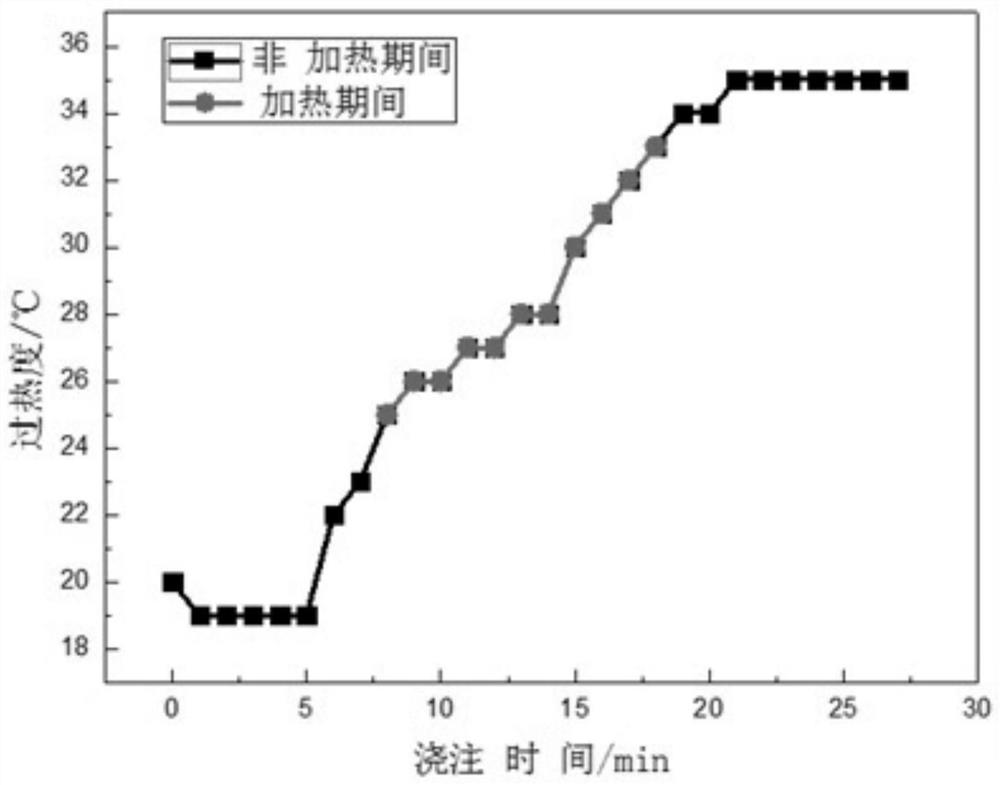
[0024] A factory smelts low-carbon steel. The process flow is: converter smelting→LF refining→RH refining→continuous casting production. The liquidus temperature is 1531°C and the target superheat is 30°C. A DC plasma heating device is used for double-strand Slab continuous casting: three electrodes, one positive electrode and placed in the pouring hole of the tundish, two negative electrodes and placed near the upstream of the outlet of the tundish, specifically for the steel in the tundish The steps of liquid heating for temperature compensation (that is, the control method of heating the molten steel in the tundish by DC plasma arc) are as follows:
[0025] 1. Opening stage
[0026] 1) When the liquid steel level in the tundish reaches 200-300mm, and when the temperature of the molten steel in the tundish is lower than the set temperature range, lower the electrode to a point 50-100mm above the liquid steel level, turn on the power supply and output direct current to the el...
Embodiment 2
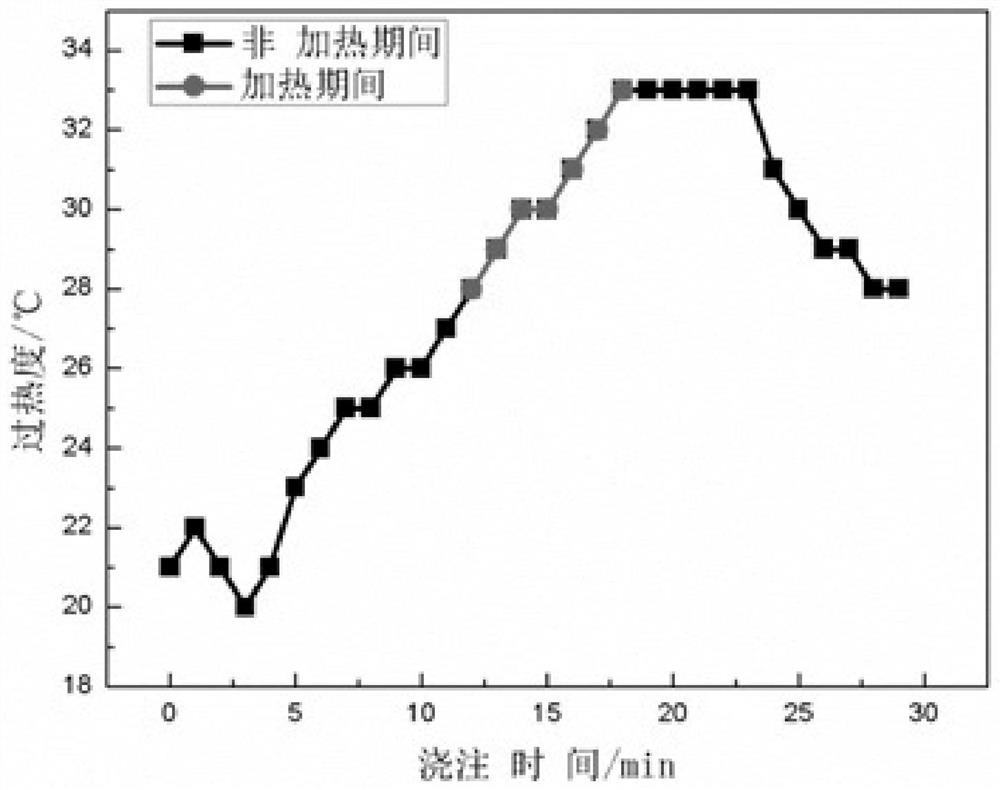
[0038]A factory smelts low-carbon steel. The process flow is: converter smelting→LF refining→RH refining→continuous casting production. The liquidus temperature is 1529°C and the target superheat is 30°C. Specifically, the steps of performing temperature compensation on the heating of molten steel in the tundish are the same as those in Embodiment 1. The difference is: turn on the plasma heating for 11 minutes, set the left and right power to 550kw, and raise the temperature by 8°C. The change of its superheat is as follows figure 2 As shown, it can be seen that during the heating process, the superheat of molten steel can be controlled within ±5°C, and in the later stage of heating, the superheat can be kept within the target value of ±5°C, realizing the precise control of the superheat of the tundish.
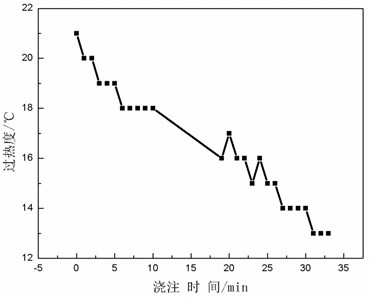
[0039] In contrast to this example: when the tundish is not heated and compensated for temperature during the pouring process, its superheat changes as image 3 shown. It...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com