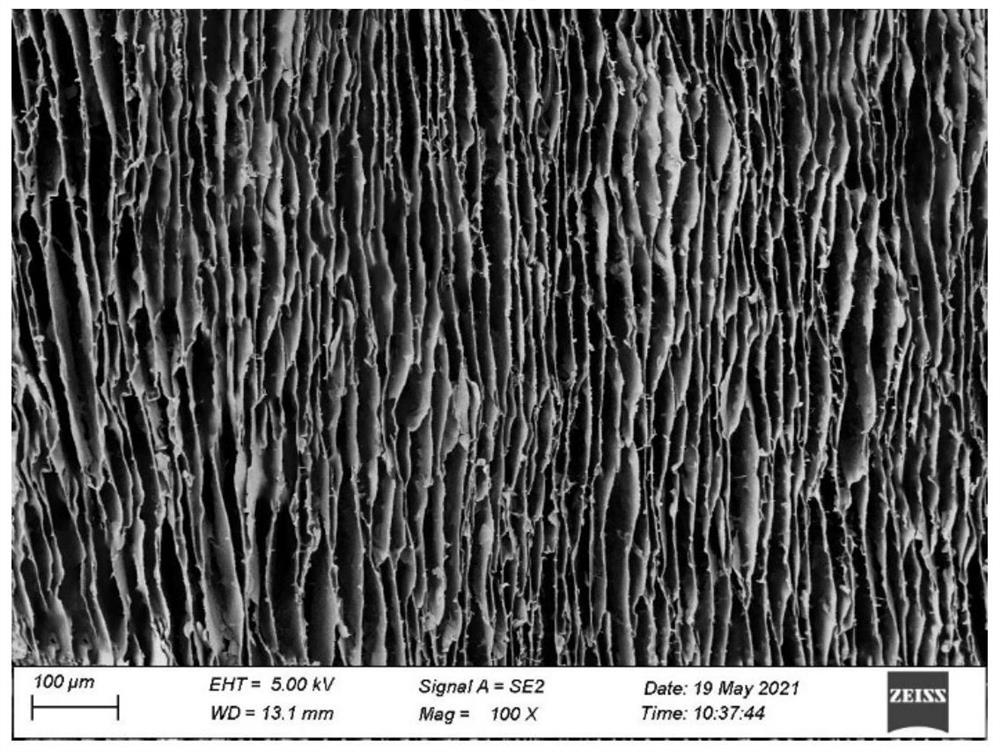
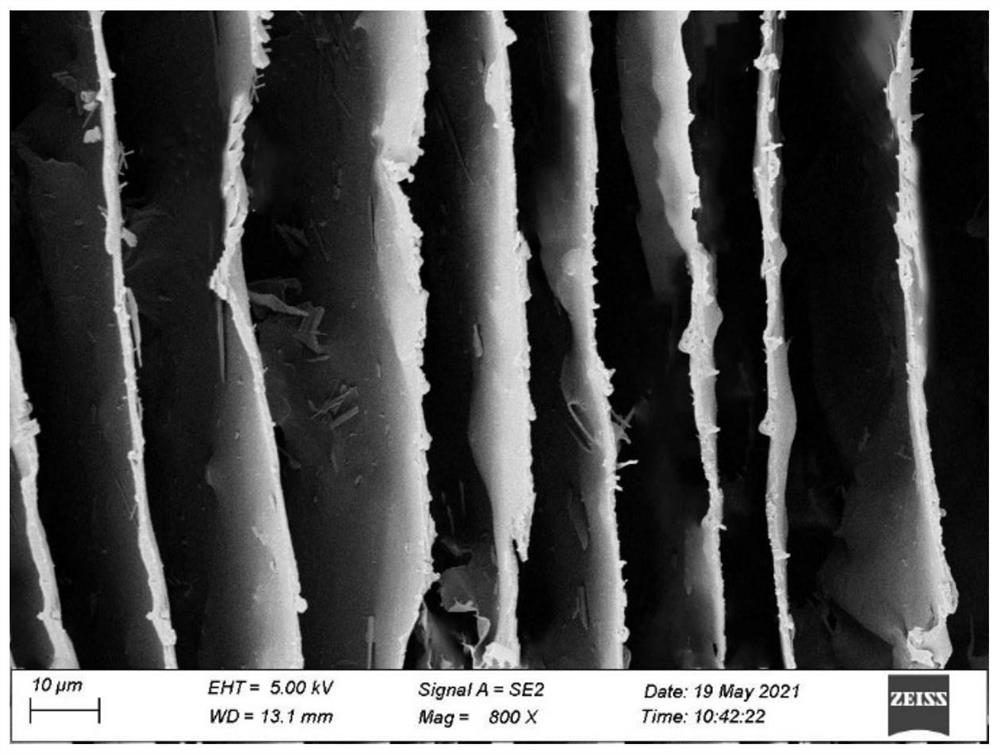
Ordered lamellar polyamidoxime-based graphene oxide composite material for extracting uranium from seawater and preparation method thereof
A technology of polyamidoxime and composite materials, applied in chemical instruments and methods, alkali metal compounds, alkali metal oxides/hydroxides, etc., can solve the problem of limited uranium extraction effect, slow adsorption rate of uranyl ions, and poor adsorption rate. Slow and other problems, to achieve ultra-high hydrophilicity and water permeability, good uranium adsorption performance, the effect of simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Embodiment 1: A method for preparing an ordered lamellar polyamidoxime-based graphene oxide composite material for extracting uranium from seawater, comprising the following steps:
[0022] S101: Preparation of amidoxime-based polyacrylonitrile powder
[0023] Add 5.5g of hydroxylamine hydrochloride to a flask containing 60mL of N-N dimethylformamide, heat to 45°C, stir magnetically until completely dissolved, then add 3.8g of sodium bicarbonate and 1g of sodium hydroxide, stir for at least 3h, then add 4.2 g polyacrylonitrile powder, fully dissolved, heated to 65°C for 24 hours, then added 1.9g sodium bicarbonate and 0.5g sodium hydroxide to react for 12 hours, cooled and centrifuged at 10000rpm / min to obtain amidoximated polyacrylonitrile solution , the solution was dropped into deionized water to obtain a white precipitate, and finally vacuum-dried at 60° C. to obtain amidoximated polyacrylonitrile powder.
[0024] S102: Preparation of amidoxime-based polyacrylonitr...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment two: the difference between embodiment two and embodiment one is that the mass ratios of graphene oxide and polyamidoxime used in step S103 are respectively 25:75, 20:80, 15:85, 10:90, 5: 95 and 0:100, uranium adsorption test was carried out at room temperature (25°C), 1L, 8ppm uranium spiked simulated seawater (pH=8).
[0034] Table 1 Effect of different polyamidoxime concentrations on the properties of polyamidoxime graphene oxide composites
[0035]
[0036]It can be seen from Table 1 that with the increase of polyamidoxime concentration, the uranyl ion adsorption capacity of the prepared ordered lamellar polyamidoxime graphene oxide composite material first gradually increased and then decreased, and at 85% When the mass ratio of polyamide oxime is 75%, the uranium adsorption capacity of the material is significantly lower than that of 85%, the main reason is that the structure gradually changes from disorder to order, and the order structure is optima...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Embodiments three to four: The difference between embodiment three and embodiment one is that in step (3), the molds are respectively immersed in liquid nitrogen for freezing, and at room temperature (25° C.), 1 L, 8 ppm uranium spiked simulated seawater (pH =8) for uranium adsorption test. The difference between Example 3 and Example 1 is that it was directly frozen at -60°C for 24 hours and formed without undergoing rapid freezing in a liquid nitrogen environment.
[0038] Table 2 Effects of different freezing conditions on the properties of polyamide oxime graphene oxide composites
[0039]
[0040] It can be seen from Table 2 that different freezing methods will directly affect the forming structure of the material, and the uranium adsorption effect of the ordered lamellar structure is better than that of the disordered structure, because the specific surface area and adsorption property of the ordered structure are better. in a disordered structure.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com