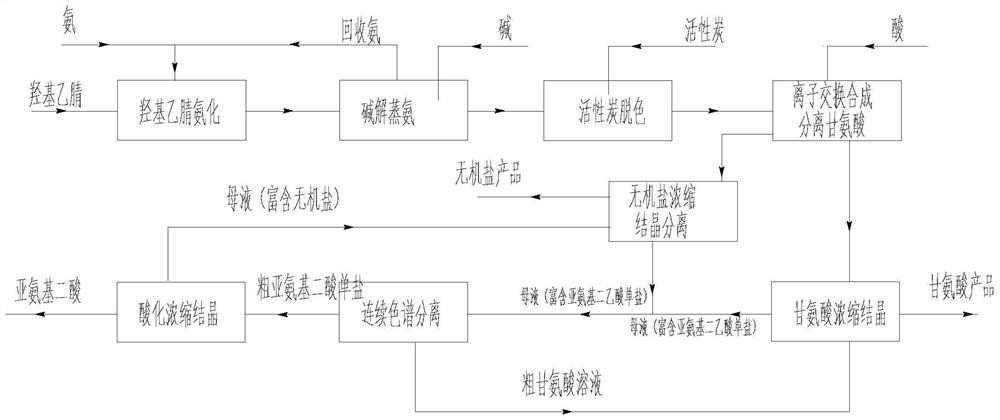
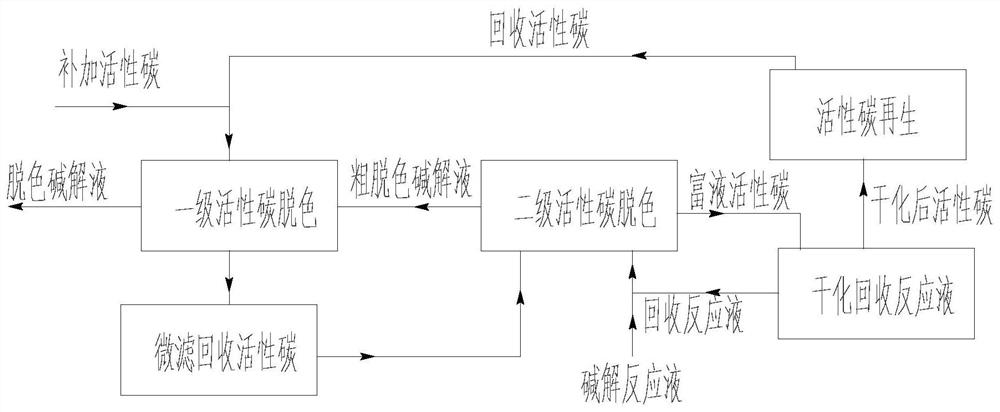
Production process of glycine
A production process, glycine technology, applied in the chemical industry, can solve the problems of increased side reactions, increased energy consumption, high energy consumption of electrodialysis, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing the probability of occurrence, reducing the probability of generation, and improving the efficiency of ammonia removal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0117] Raw materials: hydroxyacetonitrile (concentration 42%) 5.43Kg / h, ammonia water (23%) 11.83Kg / h
[0118] Technology: adopt continuous steps of the present invention, the process parameter of each step is as follows:
[0119]1) Ammonification: premixed + three-stage tubular reactor in series, reaction pressure 0.5MPa, first-stage reaction temperature 30°C, residence time 1min, second-stage reaction temperature 45°C, residence time 3min, third-stage reaction temperature 60°C, The residence time is 2 minutes;
[0120] 2) Alkaline hydrolysis ammonia distillation: add alkali to react rectification and distill ammonia, add alkali molar ratio 1.1 (NaOH): 1 (hydroxyacetonitrile), tower bottom temperature 80°C, tower top temperature and pressure 0.01MPa, residence time 2 hours, discharge The control value of free ammonia content in the reaction solution is not more than 100ppm;
[0121] 3) Decolorization: Two-stage decolorization, the addition ratio of activated carbon is 1%, t...
Embodiment 2
[0130] Raw material: raw material flow rate is identical with embodiment 1.
[0131] Process: Except that the temperature of the activated carbon decolorization reaction is 85° C., other process conditions are the same as in Example 1.
[0132] Experimental results: Glycine was obtained at 2.76Kg / h (100%), the yield of glycine was 91.5%, and the crystals of glycine particle size in the range of 0.18mm to 0.42mm were about 72%. Iminodiacetic acid 154g / h (100%), glycine+iminodiacetic acid total yield 97.5%.
Embodiment 3
[0134] Raw material: raw material flow rate is identical with embodiment 1.
[0135] Technology: except that alkali hydrolysis temperature is 85 ℃, other technology is all identical with embodiment 1.
[0136] Experimental results: Glycine was obtained at 2.72Kg / h (100%), the yield of glycine was 90.5%, and the crystals with glycine particle size in the range of 0.18mm to 0.42mm were about 71%. Iminodiacetic acid 150g / h (100%), glycine+iminodiacetic acid total yield 96.2%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com