Diamond cutting tool based on rare earth modified iron-based binding agent and preparation method of diamond cutting tool
An iron-based binder and rare earth modification technology, which is applied to other manufacturing equipment/tools, engine components, turbines, etc., can solve the problems of poor wettability of diamonds, improve the encasement strength, reduce thermal damage, and increase wear resistance sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] (1) Mix 30-40 mesh synthetic diamonds with a metal bond at a volume ratio of 1:5 to obtain a mixed powder. The metal bond includes 94.5% of Fe70Cu30 pre-alloyed powder, 5.0% of Ni50Cr50 pre-alloyed powder, and 0.5% of praseodymium (mass Fraction);
[0026] (2) After putting the mixed powder into a graphite mold, carry out hot-press sintering, the sintering temperature is 960°C, the sintering pressure is 13MPa, and the heat preservation is 3 minutes to obtain the diamond cutting unit;
[0027] (3) The diamond cutting unit is fixed on the steel body of the saw blade by brazing to make a diamond saw blade.
[0028] The holding force coefficient of the diamond cutting unit carcass obtained in Example 1 is 0.538, and the diamond impact strength is 0.889.
Embodiment 2
[0030] (1) Mix 40-50 mesh synthetic diamonds with metal bonding agent at a volume ratio of 1:4 to obtain a mixed powder. The metal bonding agent includes 89.2% of Fe70Cu30 pre-alloyed powder, 10.0% of Ni50Cr50 pre-alloyed powder, and 0.8% of praseodymium (mass fraction );
[0031] (2) After putting the mixed powder into a graphite mold, carry out hot-press sintering, the sintering temperature is 1000° C., the sintering pressure is 15 MPa, and the heat preservation is 5 minutes to obtain the diamond cutting unit;
[0032] (3) The diamond cutting unit is fixed on the steel body of the drill bit by welding to make a diamond drill bit.
[0033] The diamond holding force coefficient of the cutting tooth matrix obtained in Example 2 is 0.539, and the diamond impact strength is 0.875.
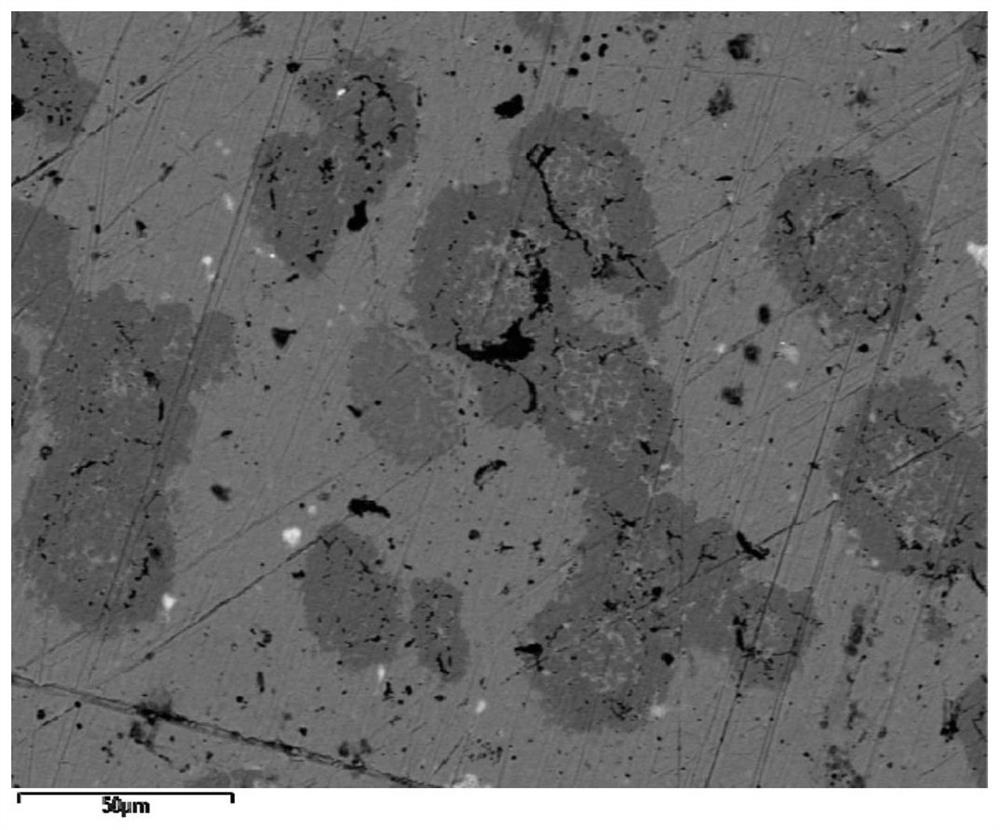
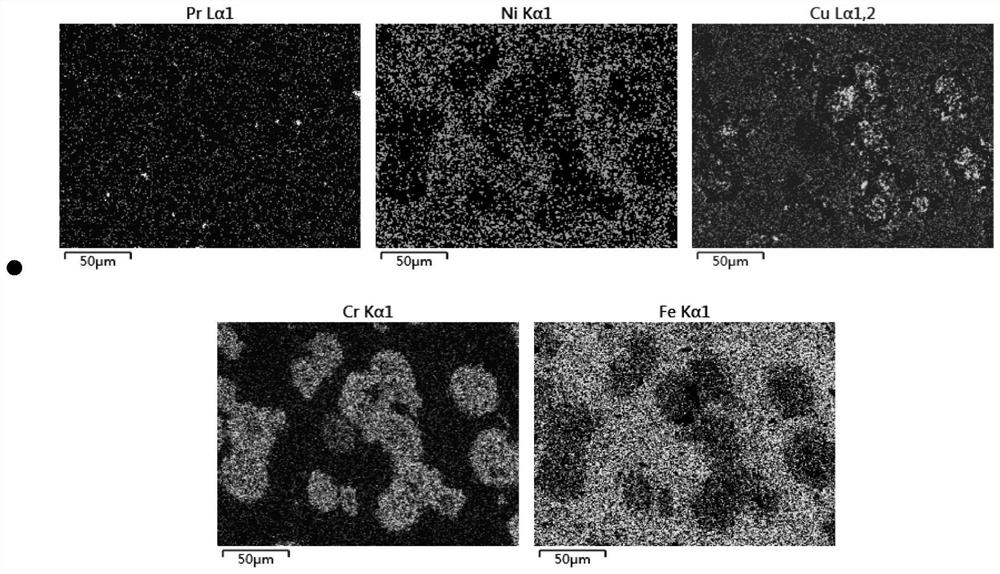
[0034] Such as figure 1 with figure 2 , from the energy spectrum of the cutting unit carcass surface, it can be seen that Pr can promote the formation of solid solution between Cu and Cr, and impr...
Embodiment 3
[0036] (1) Mix 50-60 mesh synthetic diamonds with a metal bond at a volume ratio of 3:10 to obtain a mixed powder. The metal bond includes 84.0% of Fe70Cu30 pre-alloyed powder, 15.0% of Ni50Cr50 pre-alloyed powder, and 1.0% of praseodymium (mass fraction );
[0037] (2) After putting the mixed powder into a graphite mold, carry out hot-press sintering, the sintering temperature is 1100°C, the sintering pressure is 18MPa, and the heat preservation is 6 minutes to obtain the diamond cutting unit;
[0038] (3) The diamond cutting unit is directly hot-pressed and sintered on the steel body of the drill bit to make a diamond drill bit.
[0039] The diamond holding force coefficient of the cutting tooth carcass obtained in Example 3 is 0.577, and the diamond impact strength is 0.867.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com