Bidirectional transient voltage suppression device and preparation method thereof
A transient voltage suppression and device technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical solid-state devices, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as low clamping voltage and low breakdown voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
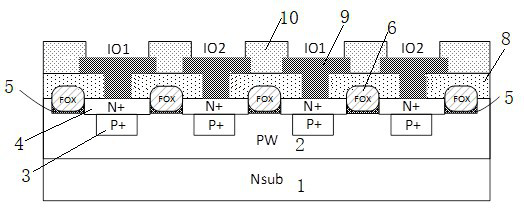
[0042] In a preferred embodiment of the present application, based on the above-mentioned problems existing in the prior art, a bidirectional transient voltage suppression device is now provided, such as Figure 1-11As shown, it includes: a substrate 1, the substrate 1 has a first conductivity type; a well region 2 is formed on the upper surface of the substrate 1, and the well region 2 has a second conductivity type; if the first conductivity type is N type , then the second conductivity type is P-type; if the first conductivity type is P-type, then the second conductivity type is N-type. In Embodiment 1, the first conductivity type is N-type, and the second conductivity type is P-type as an example. , that is, the substrate 1 is an N-type silicon chip N sub, and the well region 2 is a P-type PW; a first predetermined region is located in the well region 2, and the first predetermined region includes a plurality of first predetermined regions having a second conductivity type ...
Embodiment 2
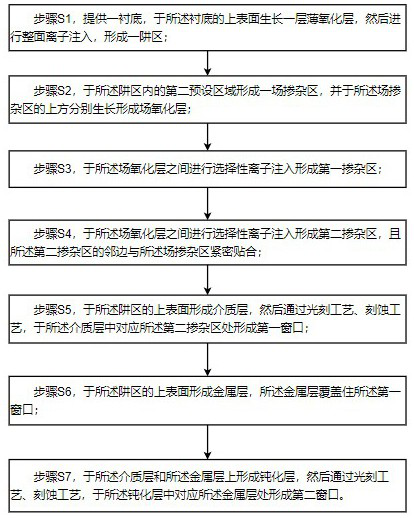
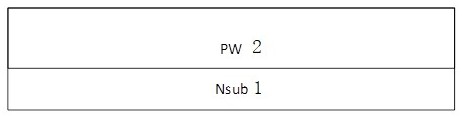
[0051] The present invention also provides a method for preparing a bidirectional transient voltage suppression device, which is used to prepare a bidirectional transient voltage suppression device as described above, such as figure 2 As shown, the following steps are also included: step S1, such as image 3 As shown, a substrate 1 (Nsub) is provided, a thin oxide layer is grown on the upper surface of the substrate 1 (Nsub), and then ion implantation is performed on the entire surface, and then a thermal process is carried out to form a well region 2 (PW) ; Preferably, the substrate 1 (Nsub) is N-type lightly doped, and the resistivity of the substrate 1 (Nsub) is 10~50Ω*cm; the growth thickness of the thin oxide layer is 200~500Å.
[0052] As a preferred implementation, in step S1, the ion implantation element in the well region 2 (PW) is boron or boron difluoride, the implantation energy is 60~100KeV, and the implantation dose is 2E12~1E13c , the implantation angle is 7 ...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Such as Figure 11 As shown, this embodiment is similar to Embodiment 2, the difference is that the doping type is changed, that is, the substrate 1 is changed from Nsub to Psub, the well region 2 is changed from PW to NW, and the first doped region 3 is changed from P+ to N+ , the second doped region 4 is changed from N+ to P+, and the field oxide layer 6 is changed from PF to NF. The other structures are the same as those in Embodiment 2, the manufacturing process is also the same, and the functions realized by the device remain unchanged.
[0073] The beneficial effect of the technical solution of the present invention is that the device prepared in the present invention has the characteristics of low breakdown voltage and larger negative resistance characteristics, so it has lower clamping voltage, and thus has ultra-low trigger voltage and ultra-low clamping voltage. The characteristics of the bit voltage, the ability to protect the subsequent circuit is stronger. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com