Multi-vector stress dispersion interlocking configuration oral implant
A technology for oral implants and stress dispersion, which is applied in the fields of dental implants, medical science, and dentistry, and can solve problems such as bone resorption and stress shielding that cannot be completely avoided
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: Submerged dental implant
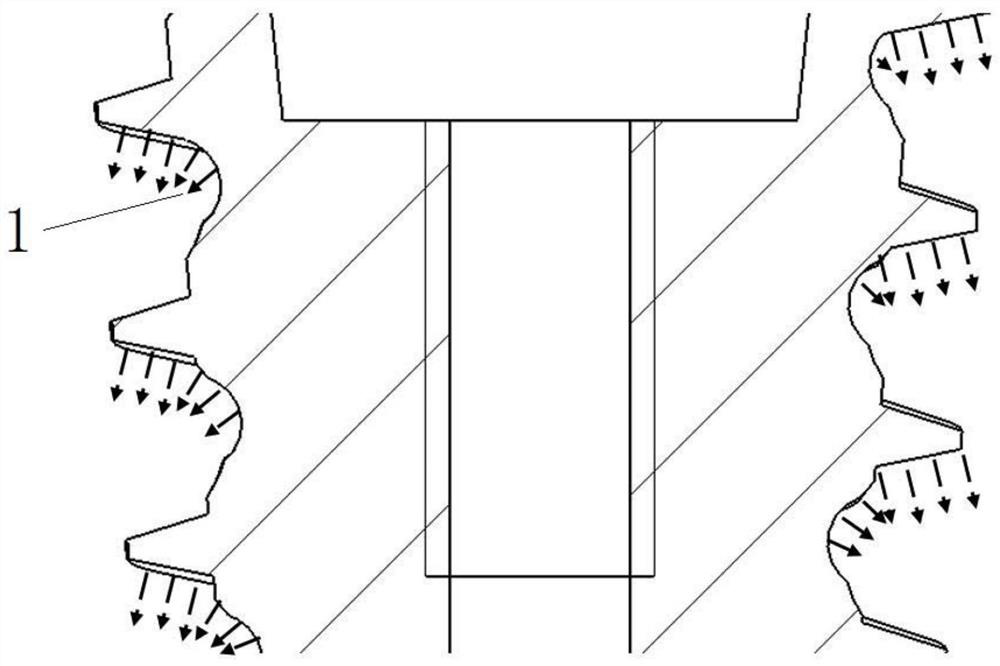
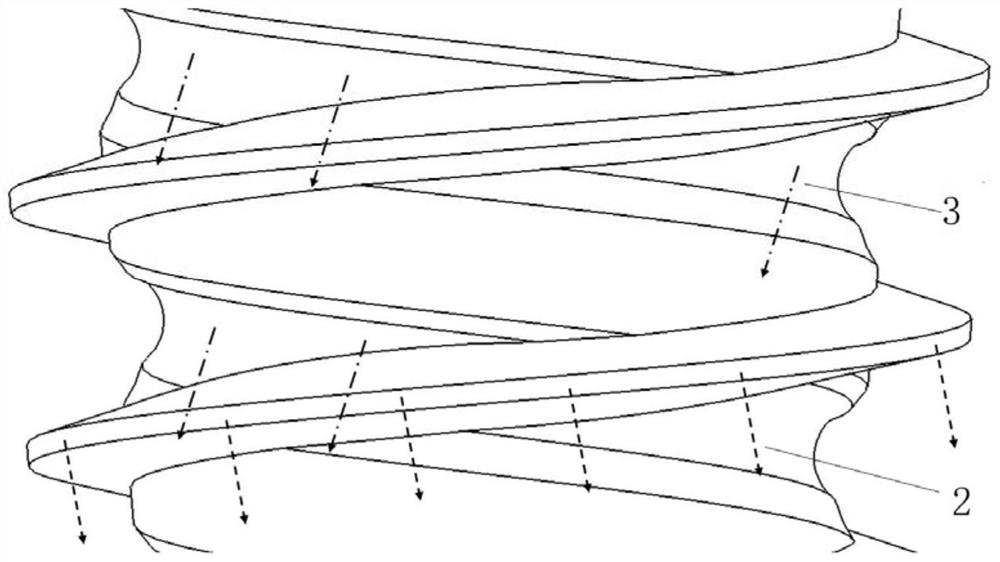
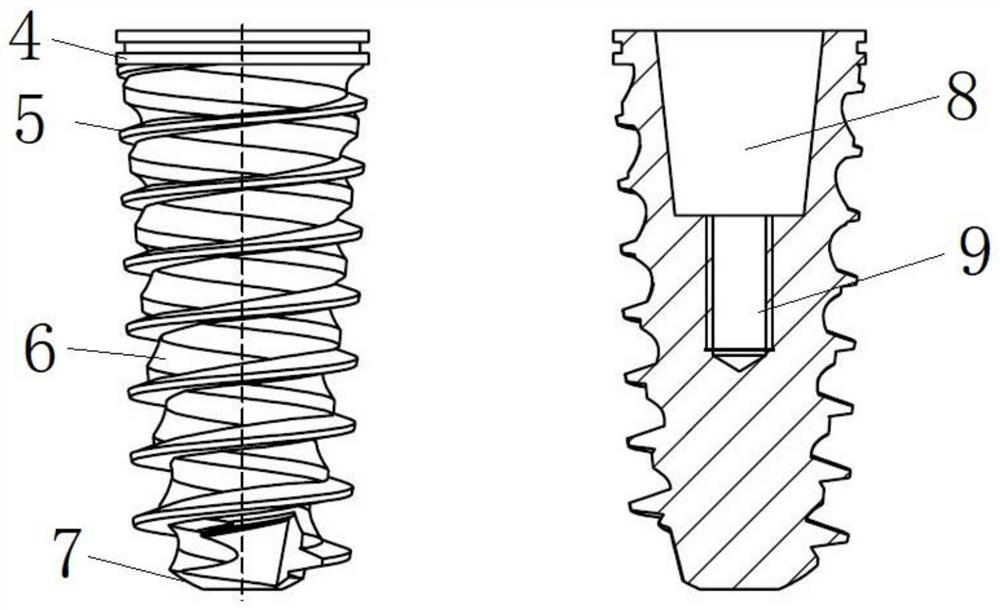
[0035] The invention provides a design scheme of the geometric shape of the cone thread, the cone cylinder surface and the alveolar crest module of the dental implant, so as to achieve the best initial stability and secondary stability. At the same time, a manufacturing process based on laser fusion 3D printing is provided to manufacture this implant with a complex curved surface. The dental implant of the present invention includes the multi-vector stress dispersion configuration embedded implant, that is, a self-tapping implant with a reverse spiral concave surface, and an embedded implant with a dense thread short alveolar crest module. Dental implants to adapt to bone tissue level implant operation. Implant body comprises the alveolar crest module 4 of upper end (as image 3 ) and cone 5 (such as image 3 ); the upper end of the cone 5 is connected to the lower end of the alveolar crest; the diameter of the lower base of the ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2: non-submerged dental implant
[0038] The dental implant of the present invention includes the multi-vector stress dispersion configuration embedded implant, that is, a self-tapping implant with a reverse spiral concave surface, and a non-embedded long alveolar crest module with a smooth outer wall. Recessed dental implants are suitable for soft tissue level implant operations. Implant body comprises the alveolar crest module 4 of upper end (as Figure 5 ) and cone 5 (such as Figure 5 ); the upper end of the cone 5 is connected to the lower end of the alveolar crest 4; the diameter of the lower base of the cone 5 is smaller than the diameter of the upper base; the outer surface of the cone 5 has a clockwise spiral (looking down from the upper end) convex thread ; The outer surface of the cone has a counterclockwise spiral concave surface 6 . In the dental implant of the present invention, the length of the tapered portion 5 is about 9.2±0.02mm. The le...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Apply laser fusion 3D printing technology to manufacture the molding and manufacturing of the above-mentioned dental implants, the specific steps are as follows:
[0044] Use 3D-CAD software (such as but not limited to Solidworks, CATIA, Within Medical, etc.) to design the 3D shape of the dental implant through computer-aided design technology, including the upper alveolar ridge module and the lower end cone. The function of the catenary torus is compiled on the reference surface of the implant cone cylinder wall, and the concave structure of the curved surface is excised on the vertebral body along this predefined helix.
[0045] After saving the 3D simulation file in STL format, use Magics to modify the shape, check the unclosed surface and the arm structure with too large projected area. Slice the 3D model layer by layer, add support and other data and other preprocessing, and obtain the cross-sectional information of each layer;
[0046] The sliced multiple 3D mo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com