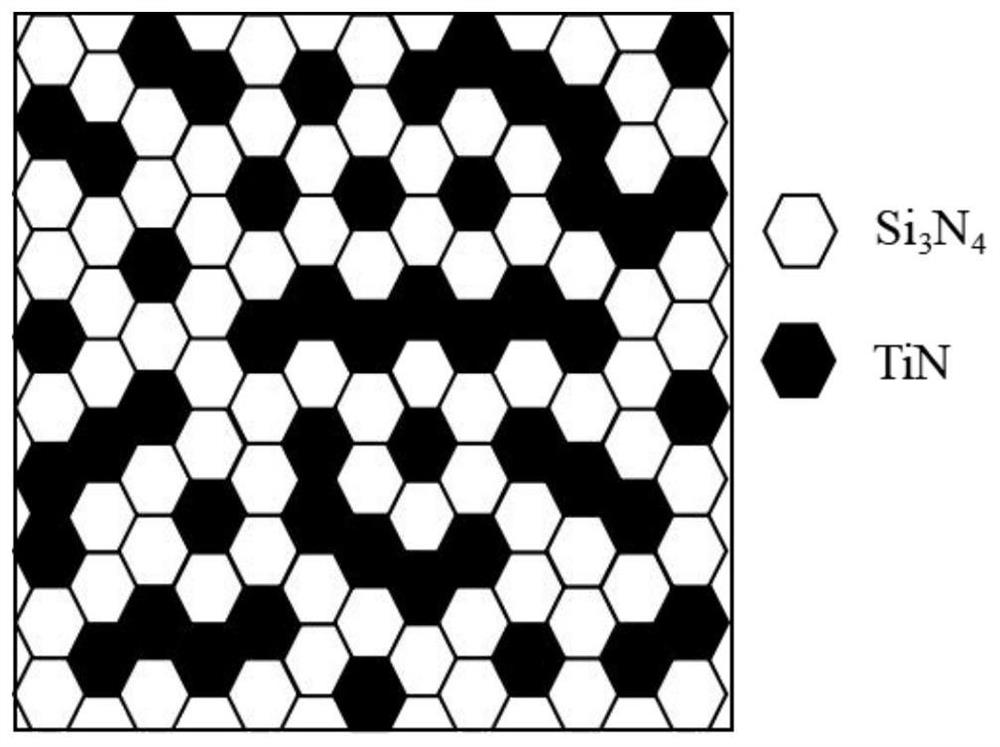
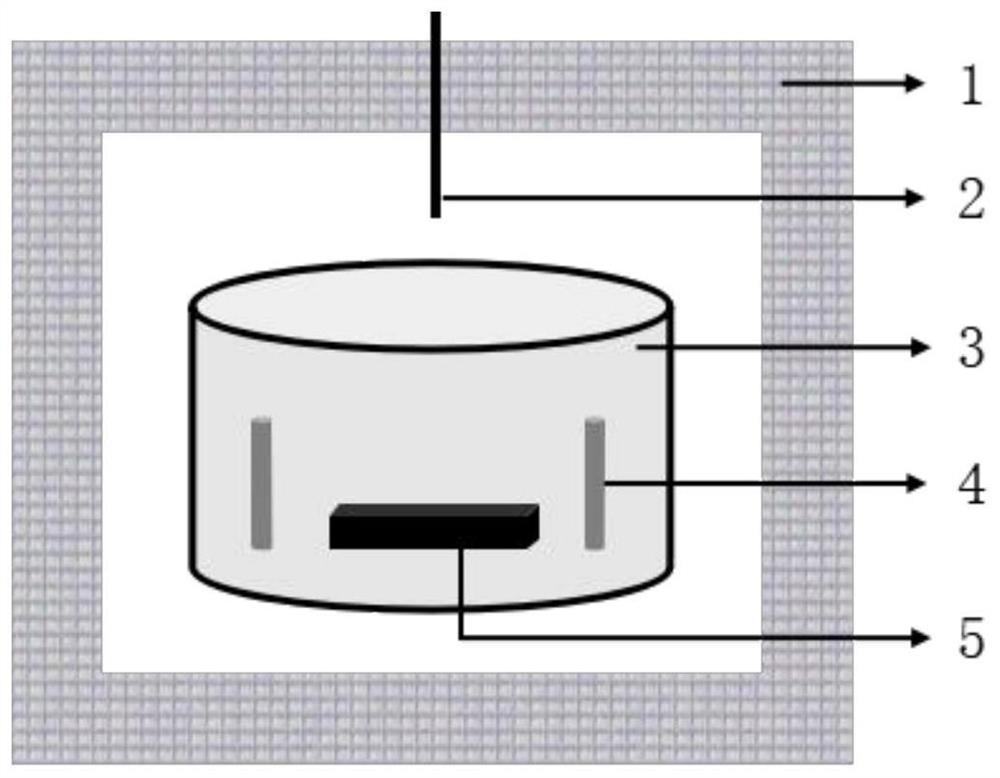
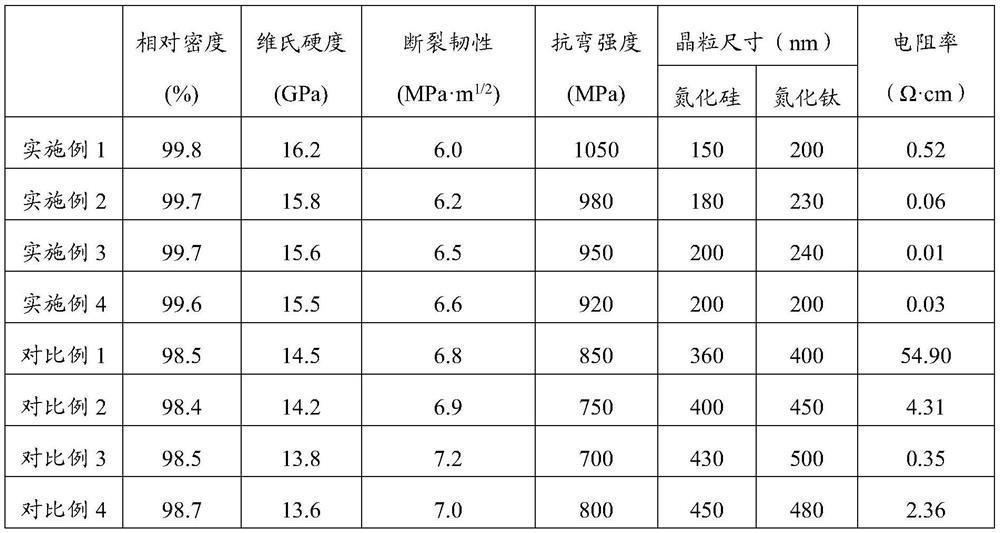
Preparation method of silicon nitride-based multiphase conductive ceramic
A technology based on conductive ceramics and silicon nitride, which is applied in the field of conductive ceramics, can solve the problems of hindering the sintering densification of silicon nitride, the decrease of mechanical properties such as hardness and strength of silicon nitride ceramics, and achieve the purpose of inhibiting the growth of grains and mechanical properties. Effects of improving performance and suppressing grain boundary migration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0023] The invention provides a method for preparing silicon nitride-based multiphase conductive ceramics, comprising the following steps:
[0024] (1) Mixing silicon nitride, a conductive phase and a sintering aid and then molding to obtain a green body; the sintering aid includes rare earth oxides and metal oxides, and the metal oxides include aluminum oxide or magnesium oxide;
[0025] (2) Sequentially performing high-temperature microwave sintering and low-temperature microwave sintering on the green body obtained in the step (1) to obtain silicon nitride-based multiphase conductive ceramics.
[0026] In the invention, silicon nitride, conductive phase and sintering auxiliary agent are mixed and then molded to obtain a green body.
[0027] In the present invention, the mass content of silicon nitride in the green body is preferably 40-60%, more preferably 45-55%. In the present invention, the β-Si in the silicon nitride 3 N 4 The mass content of is preferably ≥ 85%, mor...
Embodiment 1
[0048] raw material:
[0049] Silicon nitride (β-Si 3 N 4 The mass content of ≥95%, the average particle size D50 is 0.5μm): 53%,
[0050] Titanium nitride (purity ≥ 99%, average particle size D50 is 0.1μm): 35%,
[0051] Alumina (purity ≥ 99%, average particle size D50 is 0.5μm): 3%,
[0052] Yttrium oxide (purity ≥ 99%, average particle size D50 is 0.2μm): 6%,
[0053] Silicon carbide (purity ≥ 98.5%, average particle size D50 of 0.5 μm): 3%.
[0054] After the above raw materials are mixed evenly, dry pressing is performed first, the size of the obtained product is 45×45×8mm, the pressure of dry pressing is 20MPa, and then cold isostatic pressing is performed, and the pressure of cold isostatic pressing is 300MPa, and the obtained body. Put the above green body into the furnace cavity of the microwave sintering furnace, evacuate until the vacuum degree in the furnace is less than 100Pa, and then pass nitrogen gas to make the pressure in the furnace reach 0.1MPa. After...
Embodiment 2
[0056] raw material:
[0057] Silicon nitride (β-Si 3 N 4 The mass content of ≥95%, the average particle size D50 is 0.5μm): 50%,
[0058] Titanium nitride (purity ≥ 99%, average particle size D50 is 0.1μm): 40%,
[0059] Alumina (purity ≥ 99%, average particle size D50 is 0.5μm): 3%,
[0060] Yttrium oxide (purity ≥ 99%, average particle size D50 is 0.2μm): 5%,
[0061] Silicon carbide (purity ≥ 98.5%, average particle size D50 of 0.5 μm): 2%.
[0062] After the above raw materials are mixed evenly, dry pressing is performed first, the size of the obtained product is 45×45×8mm, the pressure of dry pressing is 20MPa, and then cold isostatic pressing is performed, and the pressure of cold isostatic pressing is 300MPa, and the obtained body. Put the above green body into the furnace cavity of the microwave sintering furnace, evacuate until the vacuum degree in the furnace is less than 100Pa, and then pass nitrogen gas to make the pressure in the furnace reach 0.1MPa. After...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Vickers hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com