Electrochemical fingerprint identification method for edible oil
A fingerprint, oil electrochemical technology, applied in the field of edible oil electrochemical fingerprint identification, can solve the problems of slow detection speed and large detection error.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
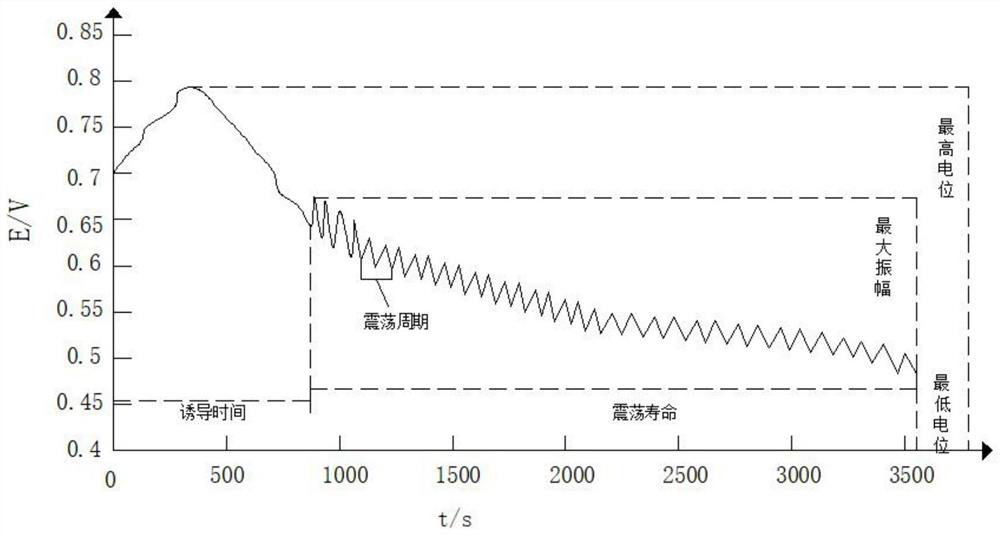
[0041] An edible oil electrochemical fingerprint identification method, comprising the following steps:
[0042] (1) Use 5 batches of sesame oil of the same origin and the same brand as standard samples, and store them in an incubator. The temperature of the incubator is set at 25°C;
[0043] (2) Mix 0.5ml of sesame oil, 40mL of H 2 SO 4 Solution, 20mL malonic acid solution and 1.8mL sodium bromide solution are placed in the reaction tank, then add nonionic surfactant to the mixed solution, the nonionic surfactant is polyethylene glycol glucoside, and the nonionic surface active The addition of agent is 1.3% of the total mass of the mixed solution, and then cover the reaction tank cover with thermometer, injection hole and electrode;
[0044] (3) Then turn on the computer, millivoltmeter and magnetic stirrer connected to the data acquisition device, and start timing;
[0045](4) Turn on the super thermostat and adjust the temperature in the reaction tank to reach 35.0°C, co...
Embodiment 2
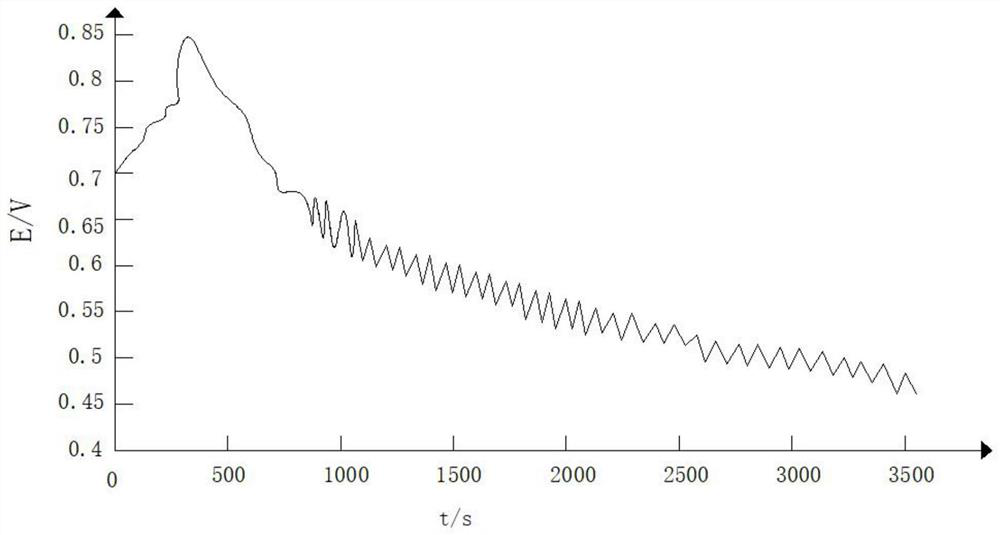
[0062] An edible oil electrochemical fingerprint identification method, comprising the following steps:
[0063] (1) 6 batches of soybean oil of the same origin and the same brand were used as standard samples and stored in an incubator. The temperature of the incubator was set at 26°C;
[0064] (2) 0.6ml soybean oil, 50mL H 2 SO 4 Solution, 20mL malonic acid solution and 2.2mL sodium bromide solution are placed in the reaction tank, then add non-ionic surfactant to the mixed solution, the non-ionic surfactant is polyethylene glycol glucoside, and the non-ionic surface active The addition of agent is 1.6% of the total mass of the mixed solution, and then cover the reaction tank lid with thermometer, injection hole and electrode;
[0065] (3) Then turn on the computer, millivoltmeter and magnetic stirrer connected to the data acquisition device, and start timing;
[0066] (4) Turn on the super thermostat and adjust the temperature in the reaction tank to 38°C, control the ma...
Embodiment 3
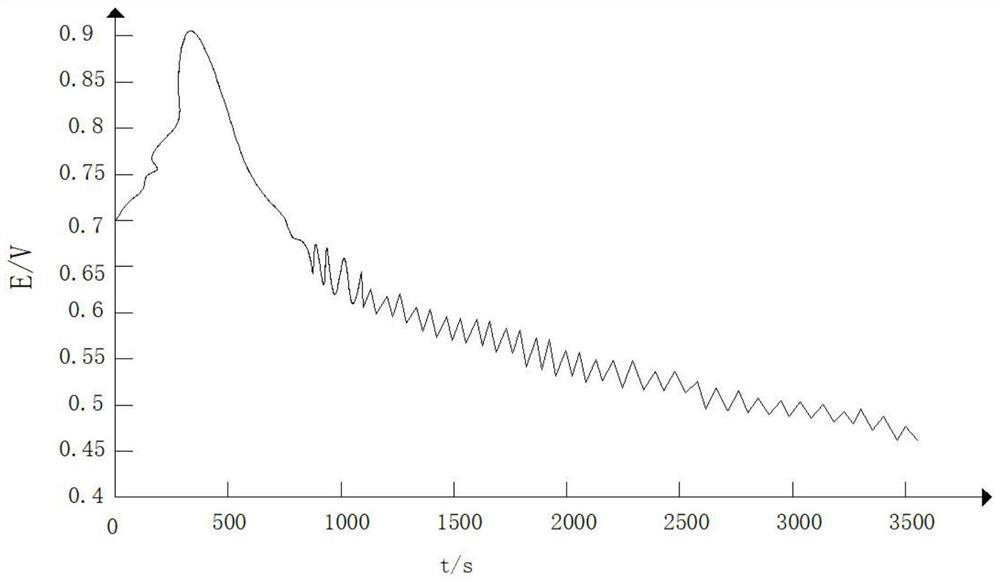
[0083] An edible oil electrochemical fingerprint identification method, comprising the following steps:
[0084] (1) Use 4-8 batches of peanut oil of the same origin and brand as standard samples, and store them in an incubator with the temperature of the incubator set at 28°C;
[0085] (2) Mix 0.8ml peanut oil, 50mL H 2 SO 4 Solution, 20mL malonic acid solution and 2.5mL sodium bromide solution are placed in the reaction tank, then add nonionic surfactant to the mixed solution, the nonionic surfactant is selected from xylitol glucoside, and the nonionic surface active The addition of agent is 1.8% of the total mass of the mixed solution, and then cover the reaction tank lid with thermometer, injection hole and electrode;
[0086] (3) Then turn on the computer, millivoltmeter and magnetic stirrer connected to the data acquisition device, and start timing;
[0087] (4) Turn on the super thermostat and adjust the temperature in the reaction tank to 40°C, control the magnetic ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com