Method for identifying adulterated honey
A technology of honey and external standard method, applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve the problems of large amount of organic reagents, narrow application range, cumbersome processing, etc., and achieve the effects of good applicability, good repeatability, and accurate detection results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
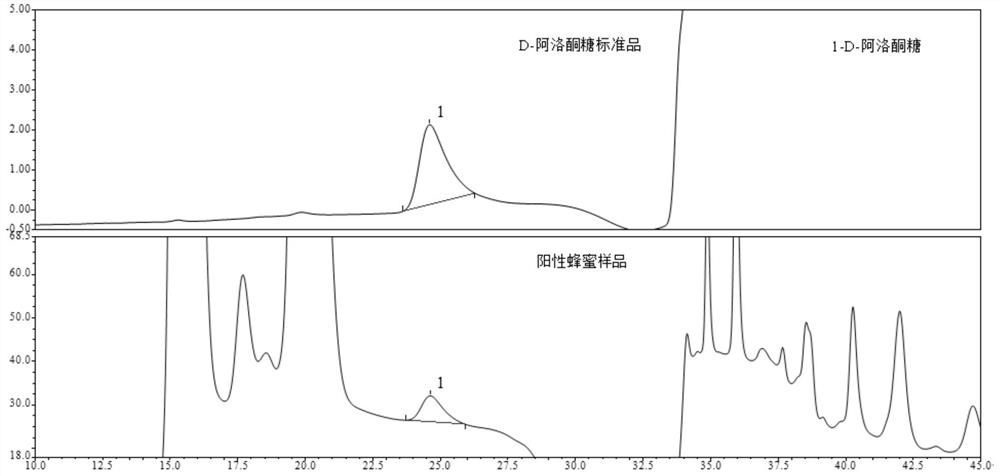
[0048] Example 1. Determination of D-psicose content in collected honey and syrup samples
[0049] Step 1. Sample collection
[0050] A total of 50 samples of different honey species were directly collected from the beekeepers, including 10 honey from flowers, 10 honey from rapeseed, 10 honey from Vitex twigs, 10 honey from linden tree, and 10 honey from acacia honey. 6 syrup samples were purchased from the Internet or supermarkets, including 4 fructose syrup and 2 corn syrup.
[0051] Step 2, sample pretreatment,
[0052] Weigh 1g of uniform honey or syrup sample (accurate to 0.001g) into a beaker, add an appropriate amount of deionized water to dissolve and mix, transfer to a 100mL volumetric flask, dilute with deionized water, and mix well; accurately pipette the solution for 0.5 mL in a 10mL volumetric flask, make up to volume with deionized water, and mix well. This solution was tested through a 0.22 μm filter membrane.
[0053] Step 3, standard working solution confi...
Embodiment 2
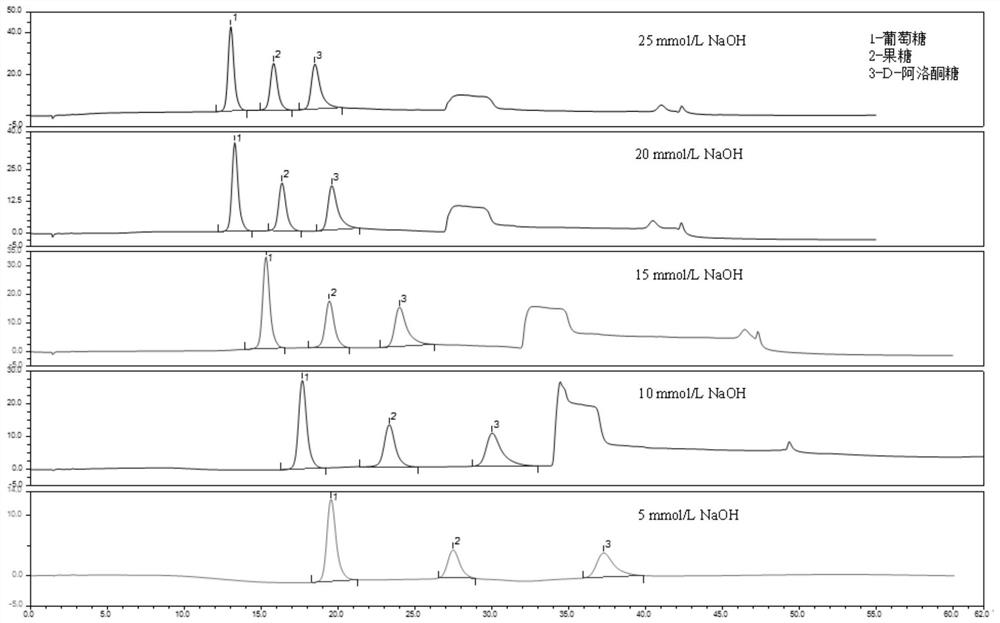
[0072] Embodiment 2, the influence of different eluent NaOH concentration on carbohydrate chromatogram
[0073] Configure 5 mg / L glucose, fructose, allulose mixed standard solution, and elute it with 25, 20, 15, 10, 5 mmol / L NaOH solution respectively, and investigate the separation degree and peak shape of different NaOH concentrations on chromatographic peaks affect, as a result figure 1 shown.
[0074] The experiment found that: the retention time of glucose and al-D-glutose is far apart, which has no effect on the determination; the retention time of fructose and D-glutose is relatively close, and the separation degree of the two decreases with the decrease of NaOH concentration. Upward trend. In addition, with the decrease of NaOH concentration, the retention time of D-psicose peak lengthened and the response value decreased.
[0075] Considering the resolution, response value, analysis time and other factors comprehensively, the preferred concentration of NaOH in the ...
Embodiment 3
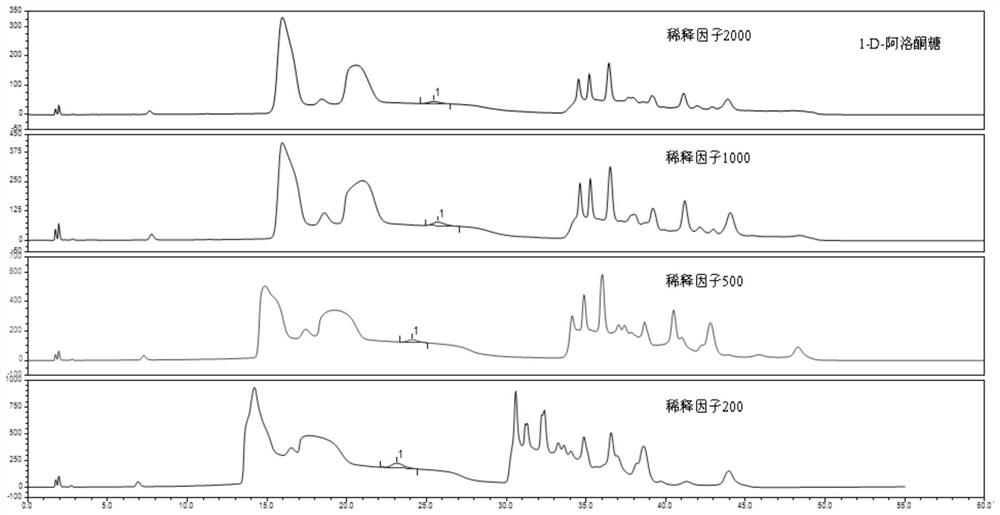
[0076] Embodiment 3, the impact of different dilution factors on the sugar chromatogram in the sample
[0077] Select a representative positive honey sample (where the D-psicose content is 2300mg / kg), use 15mmol / L NaOH as the eluent, and test the honey samples with dilution factors of 200, 500, 1000, and 2000 respectively, and investigate Investigate the influence of different NaOH concentrations on the resolution and peak shape of chromatographic peaks, the results are as follows figure 2 As shown, the definition of the dilution factor is: when every 1 gram of honey sample is diluted with 200ml water, the dilution factor is 200; when every 1 gram of honey sample is diluted with 500ml water, the dilution factor is 500, and every 1 gram of honey sample is diluted with When 2000ml of water is diluted, the dilution factor is 2000, and so on.
[0078] The experiment found that: with the increase of the dilution factor, the resolution increased, but the detection limit of the act...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com