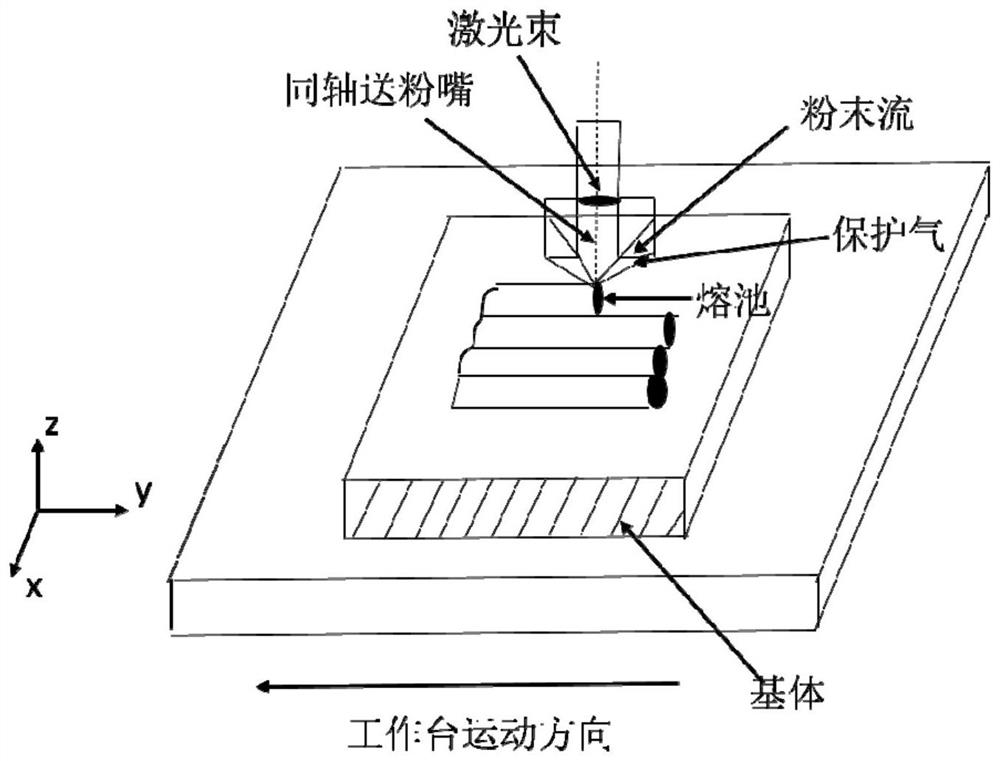
Preparation method of laser cladding in-situ synthesis ceramic phase reinforced copper-based cladding layer
A technology of laser cladding and in-situ synthesis, which is applied in the coating, metal material coating process, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient hardness and wear resistance, poor bonding of the interface between the substrate and the cladding layer, etc. Achieve the effect of simple production equipment and process, easy automation and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] The laser power is 2000W, Mo and SiC are proportioned according to the following reaction:
[0036] 5Mo+2SiC=MoSi 2 +2Mo 2 C;
[0037] That is, Mo accounts for 85.67wt.% (34 grams), and SiC accounts for 14.33 wt.% (6 grams);
[0038] Among them, the sum of the content of Mo and SiC accounts for 20 wt.% (40 grams) of the total cladding powder mass;
[0039] Ni powder accounts for 35 wt.% (70 grams), Cu powder accounts for 45 wt.% (90 grams);
[0040] S1. Substrate pretreatment
[0041] The working surface of the pure copper substrate is polished with sandpaper, degreased, derusted, and cleaned to finally obtain a clean surface, and then blackened, that is, a layer of carbon ink is evenly painted on the working surface of the pure copper substrate;
[0042] S2. Preparation of cladding powder
[0043] According to the molar ratio of the reaction, it is converted into a mass ratio, weighed, and proportioned. The cladding powder includes 90 grams of commercially availa...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The laser power is 2400W, Mo and SiC are proportioned according to the following reaction:
[0054] 5Mo+2SiC=MoSi 2 +2Mo 2 C;
[0055] That is, Mo accounts for 85.67wt.% (34 grams), and SiC accounts for 14.33 wt.% (6 grams);
[0056] Among them, the sum of the content of Mo and SiC accounts for 20 wt.% (40 grams) of the total cladding powder mass;
[0057] Ni powder accounts for 35 wt.% (70 grams), Cu powder accounts for 45 wt.% (90 grams);
[0058] S1. Substrate pretreatment
[0059] The working surface of the pure copper substrate is polished with sandpaper, degreased, derusted, and cleaned to finally obtain a clean surface, and then blackened, that is, a layer of carbon ink is evenly applied to the working surface of the pure copper substrate;
[0060] S2. Preparation of cladding powder
[0061] According to the molar ratio of the reaction, it is converted into a mass ratio, weighed, and proportioned. The cladding powder has 90 grams of commercially available C...
Embodiment 3
[0067] The laser power is 2000W, Mo and SiC are proportioned according to the following reaction:
[0068] 5Mo+2SiC=MoSi 2 +2Mo 2 C;
[0069] That is, Mo accounts for 85.67wt.% (17 grams), and SiC accounts for 14.33 wt.% (3 grams);
[0070] Among them, the sum of the content of Mo and SiC accounts for 10 wt.% (20 grams) of the total cladding powder mass;
[0071] Ni powder accounts for 30 wt.% (60 grams), Cu powder accounts for 60 wt.% (120 grams);
[0072] S1. Substrate pretreatment
[0073] The working surface of the pure copper substrate is polished with sandpaper, degreased, derusted, and cleaned to finally obtain a clean surface, and then blackened, that is, a layer of carbon ink is evenly applied to the working surface of the pure copper substrate;
[0074] S2. Preparation of cladding powder
[0075] According to the molar ratio of the reaction, it is converted into a mass ratio, weighed, and proportioned. The cladding powder includes 120 grams of commercially avai...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com