Highly heat-resistant resin composite including chemically modified, fine cellulose fibers
A chemical modification, microfiber technology, applied in the direction of synthetic cellulose fibers, post-treatment modification of cellulose pulp, paper, etc., can solve the problems of mechanical properties, insufficient dimensional stability, high specific gravity of resin composition, and weight of resin moldings. increase, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
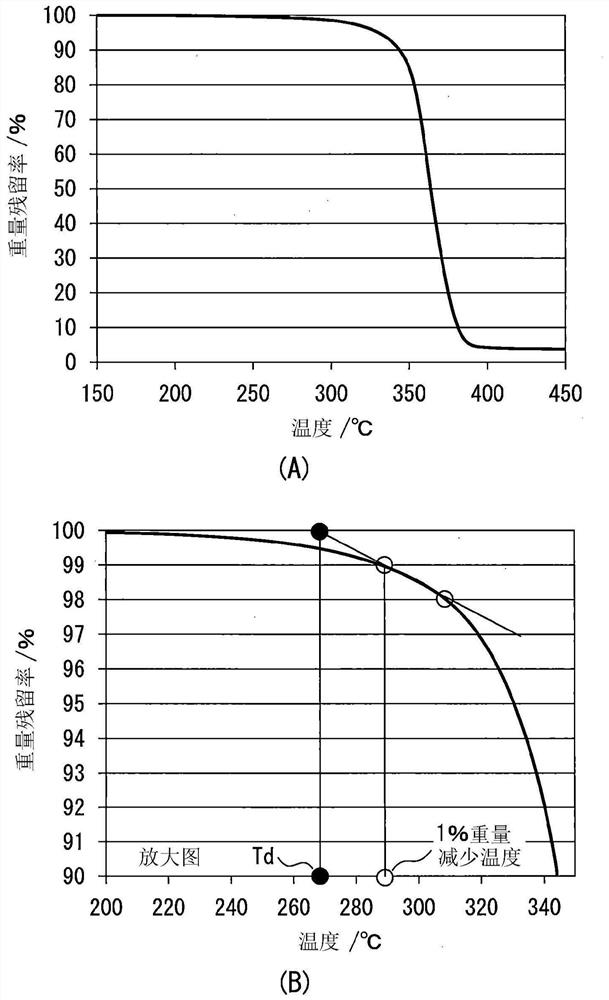
[0092] The 1st embodiment which is one form of this invention provides a kind of resin composite which contains thermal decomposition initiation temperature (T D ) is a chemically modified cellulose fine fiber having a temperature of 270° C. or higher and a number average fiber diameter of 10 nm or more and less than 1 μm. In one aspect, the resin composite contains 0.5 to 40% by mass of chemically modified cellulose fine fibers. In one embodiment, the crystallinity of the chemically modified cellulose fine fibers is 60% or more.
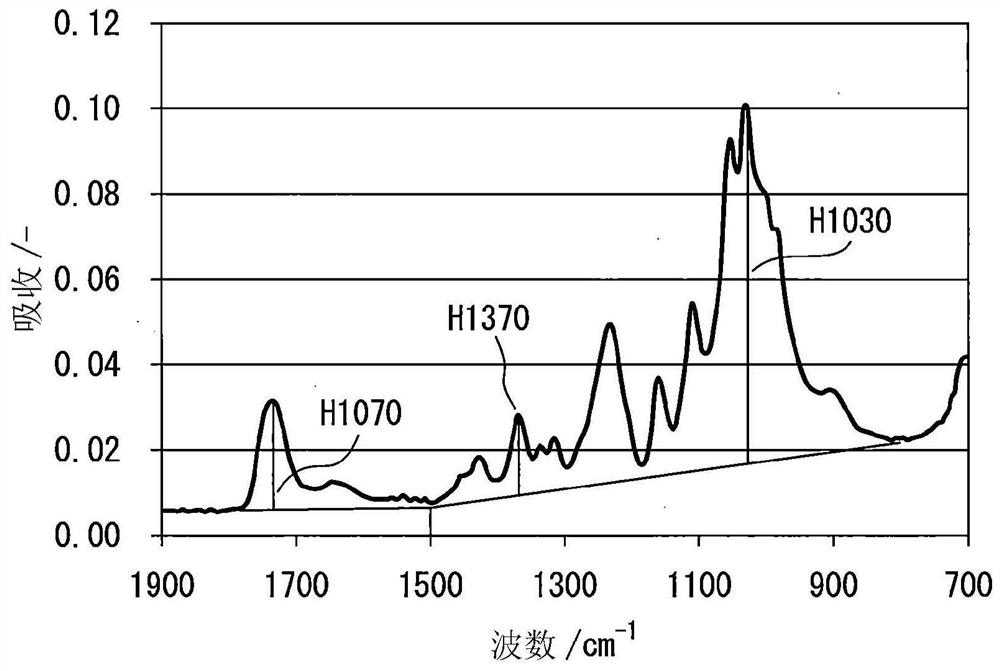
[0093] "Chemically modified cellulose fine fibers" (may also be referred to as "chemically modified fine fibers" in the present invention) refer to cellulose fine fibers in which at least a part of the hydroxyl groups in the cellulose skeleton has been modified. In a typical embodiment, the entire cellulose is not chemically modified, and the chemically modified fine fibers maintain the crystal structure of the cellulose fine fibers before chemical...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0271] A second embodiment that is one aspect of the present invention provides a chemically modified polycarbonate compound having a weight average molecular weight (Mw) of 100,000 or more and a ratio (Mw / Mn) of the weight average molecular weight (Mw) to the number average molecular weight (Mn) of 6 or less. Cellulose microfibers. As described above about the first embodiment, since the ends of the cellulose molecules are the starting points of thermal decomposition, by increasing the weight average molecular weight and narrowing the width of the molecular weight distribution, cellulose with high heat resistance can be obtained. A fine fiber and a resin composite of the cellulose fine fiber and a resin.
[0272] In one aspect, the chemically modified fine fibers of the second embodiment have an alkali-soluble component content of 12% by mass or less.
[0273] In one aspect, the chemically modified fine fiber of the second embodiment has a thermal decomposition initiation te...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0280]A third embodiment that is one aspect of the present invention provides a resin composite comprising 0.5 to 40% by mass of chemically modified cellulose fine fibers and a resin, wherein the chemically modified fibers The DS unevenness ratio (DSs / DSt) of the plain fine fiber is 1.1 or more, and the variation coefficient (CV) of the DS unevenness ratio (DSs / DSt) is 50% or less. The DS unevenness ratio (DSs / DSt) is the fiber surface layer The ratio of the degree of modification (DSs) to the degree of modification (DSt) of the fiber as a whole.
[0281] The third embodiment also provides a method for producing a resin composite comprising 0.5 to 40% by mass of chemically modified cellulose fine fibers and a resin, which includes the following steps:
[0282] The fiber opening step is to open the cellulose raw material in a dispersion liquid containing the cellulose raw material and an aprotic solvent and substantially not containing ionic liquid and sulfuric acid to obtain c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Intrinsic viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com